Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
160 viewsDiscrimination in The Workplace Research LL
Discrimination in The Workplace Research LL
Uploaded by
Hardik ShettyWorkplace discrimination occurs when employees or job applicants are treated unfavorably due to characteristics like age, disability, race, sex, and religion. It is illegal under federal law to discriminate in hiring practices or in the workplace based on protected traits. Discrimination can take various forms such as unequal pay, denial of benefits or promotions, or harassment. Employees who experience discrimination have legal recourse by filing complaints with enforcement agencies. Employers must ensure their practices do not discriminate or allow for a hostile work environment to support a fair and productive workplace.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Talent Management Employer QuestionnaireDocument6 pagesTalent Management Employer Questionnairekamdica57% (14)
- Detroit Pistons and Rob Murphy LawsuitDocument38 pagesDetroit Pistons and Rob Murphy LawsuitWXYZ-TV Channel 7 DetroitNo ratings yet
- Dave Armstrong CaseDocument1 pageDave Armstrong CasegaryhamsterNo ratings yet
- ACAS - Bullying and Harassment at Work (Guide For Employees)Document12 pagesACAS - Bullying and Harassment at Work (Guide For Employees)qbl777No ratings yet
- Employment Discrimination Law Outline 2018Document8 pagesEmployment Discrimination Law Outline 2018Catlin PegelowNo ratings yet
- EEOC On Race and ColorDocument57 pagesEEOC On Race and ColorYuriNo ratings yet
- Employment Discrimination Outline - Fall 2011 PublicDocument46 pagesEmployment Discrimination Outline - Fall 2011 PublicAmaka Obiesie100% (2)
- 4 Equal Employment OpportunityDocument43 pages4 Equal Employment OpportunityApril Angel Mateo MaribbayNo ratings yet
- Types of DiscriminationDocument2 pagesTypes of DiscriminationAbegail MoratalNo ratings yet
- Employment Discrimination 2012Document44 pagesEmployment Discrimination 2012Mal Durham-BowmansNo ratings yet
- Workplace Harassment and DiscriminationDocument7 pagesWorkplace Harassment and Discriminationjoshua nyangaresiNo ratings yet
- Common Ethical Issues in The WorkplaceDocument5 pagesCommon Ethical Issues in The WorkplacePXQ DIGITALSNo ratings yet
- GPGB Disability DiscriminationDocument6 pagesGPGB Disability DiscriminationKNo ratings yet
- EeocDocument10 pagesEeocChris Jackson'sNo ratings yet
- Employment DiscriminationDocument28 pagesEmployment DiscriminationFawwaz AnwerNo ratings yet
- Bullying Harassment and Stress in The Workplace A European PerspectiveDocument21 pagesBullying Harassment and Stress in The Workplace A European Perspectivetanbraga09No ratings yet
- Your Guide To Preventing and Identifying Harassment in The WorkplaceDocument5 pagesYour Guide To Preventing and Identifying Harassment in The WorkplaceShah Danish AhmedNo ratings yet
- Discrimination LawDocument9 pagesDiscrimination Lawduende8606No ratings yet
- Anti-Discrimination Law and EmploymentDocument4 pagesAnti-Discrimination Law and EmploymentDiane OlivasNo ratings yet
- DOJ EEOC ComplaintDocument21 pagesDOJ EEOC ComplaintSusan SvrlugaNo ratings yet
- Workplace HarassmentDocument31 pagesWorkplace HarassmentDien NursalNo ratings yet
- The Law: Equal Employment Opportunity IsDocument9 pagesThe Law: Equal Employment Opportunity IsStarmelAllahNo ratings yet
- Anti Discrimination PolicyDocument4 pagesAnti Discrimination PolicyAditya Kedia100% (1)
- EEO Complaint Process BrochureDocument2 pagesEEO Complaint Process BrochureKyle Fernando Foster-ElNo ratings yet
- Texas House Committee Revises Sexual Harassment PolicyDocument5 pagesTexas House Committee Revises Sexual Harassment PolicyAnonymous Pb39klJNo ratings yet
- The Ethics of Job DiscriminationDocument17 pagesThe Ethics of Job DiscriminationTania cruzNo ratings yet
- Hostile Work EnvironmentDocument6 pagesHostile Work EnvironmentScoutMaster DougNo ratings yet
- Employment Law-Final OutlineDocument18 pagesEmployment Law-Final OutlineflyygeminiNo ratings yet
- Of Workplace Harassment: C 1 Overview of The LawDocument65 pagesOf Workplace Harassment: C 1 Overview of The LawMack KnifeNo ratings yet
- Employment Law Outline: Download NowDocument36 pagesEmployment Law Outline: Download NowseabreezeNo ratings yet
- Outline Constitutional Law1Document33 pagesOutline Constitutional Law1Jake HuynhNo ratings yet
- Empd I ScrimDocument46 pagesEmpd I ScrimstillaireNo ratings yet
- Business Ethics and Job DiscriminationDocument22 pagesBusiness Ethics and Job Discriminationhanishdhillon100% (5)
- Sexual Harassment in The Workplace !Document16 pagesSexual Harassment in The Workplace !Hajar MkounNo ratings yet
- Employment Case Map (Formatted)Document24 pagesEmployment Case Map (Formatted)avaasiaNo ratings yet
- Employment Discrimination: Pretext, Implicit Bias, and The Beast of BurdensDocument27 pagesEmployment Discrimination: Pretext, Implicit Bias, and The Beast of BurdensNew England Law Review100% (1)
- Eeo Storyboard 3Document93 pagesEeo Storyboard 3api-482724270No ratings yet
- C4C Upload: EEOC Decision Finding Discrimination (Katrina Webster V Dept. of NavyDocument15 pagesC4C Upload: EEOC Decision Finding Discrimination (Katrina Webster V Dept. of NavyC4C100% (1)
- Workplace - Ethics in HRMDocument7 pagesWorkplace - Ethics in HRMDr. Meghdoot GhoshNo ratings yet
- Investigative DispositionDocument6 pagesInvestigative DispositionThe Standard-TimesNo ratings yet
- 22-088 EEOC KnowYourRightsDocument2 pages22-088 EEOC KnowYourRightsBelal AhmedNo ratings yet
- 323 - Direct and Indirect Discrimination - Explanation and ExamplesDocument2 pages323 - Direct and Indirect Discrimination - Explanation and ExamplesKhvichaKopinadzeNo ratings yet
- Complaint: Employment Sexual Harassment Discrimination Against Omnicom & DDB NYDocument38 pagesComplaint: Employment Sexual Harassment Discrimination Against Omnicom & DDB NYscl1116953No ratings yet
- HRM/510 Week 11 Final Exam QuizDocument95 pagesHRM/510 Week 11 Final Exam QuizgoodNo ratings yet
- Age Discrimination in Employment ThesisDocument4 pagesAge Discrimination in Employment Thesisafkofvidg100% (2)
- Employee RightsDocument2 pagesEmployee RightsJustine ManueleNo ratings yet
- Unethical PracticesDocument9 pagesUnethical PracticesZahra IjazNo ratings yet
- Utech, Faculty of Law Discrimination Law: Sexual HarassmentDocument12 pagesUtech, Faculty of Law Discrimination Law: Sexual HarassmentPersephone WestNo ratings yet
- 1 PF Complaint-AldridgeDocument16 pages1 PF Complaint-AldridgeCory DewayneNo ratings yet
- EEOC Dismissal and Notice of RightsDocument2 pagesEEOC Dismissal and Notice of RightsGregory YoungNo ratings yet
- How To Develop A Diversity and Inclusion InitiativeDocument2 pagesHow To Develop A Diversity and Inclusion InitiativeRayno MareeNo ratings yet
- I C J J: Nterbranch Ommission Uvenile UsticeDocument25 pagesI C J J: Nterbranch Ommission Uvenile UsticeCalifornia Judicial Branch News Service - Investigative Reporting Source Material & Story IdeasNo ratings yet
- Aleciah Jackson vs. City of Dallas LawsuitDocument7 pagesAleciah Jackson vs. City of Dallas LawsuitAnonymous ovJgHANo ratings yet
- What Is The Difference Between Recruitment and Talent Acquisition by Hemant KumaarrDocument4 pagesWhat Is The Difference Between Recruitment and Talent Acquisition by Hemant KumaarrSujan DeyNo ratings yet
- Workers' Compensation and Injury Duration: Evidence From A Natural ExperimentDocument20 pagesWorkers' Compensation and Injury Duration: Evidence From A Natural Experimentmarcel0555777No ratings yet
- Express Implied Terms and Post Termination RestraintsDocument3 pagesExpress Implied Terms and Post Termination Restraintsnahian ayman shababNo ratings yet
- 11th Ward Aldermanic Candidate ResumesDocument61 pages11th Ward Aldermanic Candidate ResumesjrNo ratings yet
- Ethical RelativismDocument11 pagesEthical RelativismKarelle MalasagaNo ratings yet
- Equal Employment Opportunity EEO and Anti Discrimination PolicyDocument8 pagesEqual Employment Opportunity EEO and Anti Discrimination PolicyBala Krishnan100% (1)
- Manual on the Character and Fitness Process for Application to the Michigan State Bar: Law and PracticeFrom EverandManual on the Character and Fitness Process for Application to the Michigan State Bar: Law and PracticeNo ratings yet
- Gender Differences in The WorkplaceDocument3 pagesGender Differences in The WorkplaceHardik ShettyNo ratings yet
- Discrimination at Work Place Labour LawDocument10 pagesDiscrimination at Work Place Labour LawHardik ShettyNo ratings yet
- Central Door Steel Corporation Case StudyDocument5 pagesCentral Door Steel Corporation Case StudyHardik ShettyNo ratings yet
- Project Report On Anand RathiDocument10 pagesProject Report On Anand RathiHardik ShettyNo ratings yet
- The Code On WagesDocument48 pagesThe Code On WagesHardik ShettyNo ratings yet
- The Industrial Relations Code, 2020Document27 pagesThe Industrial Relations Code, 2020Hardik ShettyNo ratings yet
- Project Report On Tata IPL ResearchDocument12 pagesProject Report On Tata IPL ResearchHardik ShettyNo ratings yet
- Research - On - IPL 2022 Dy PatilDocument10 pagesResearch - On - IPL 2022 Dy PatilHardik ShettyNo ratings yet
- Research On IPLDocument12 pagesResearch On IPLHardik ShettyNo ratings yet
- Project Report On Tata IPL (Bane or Boon)Document12 pagesProject Report On Tata IPL (Bane or Boon)Hardik ShettyNo ratings yet
- Cia 2 EcbmDocument9 pagesCia 2 Ecbmchakradhar pmNo ratings yet
- Labour Law Questions Asked in EPFO by Anuj GargDocument78 pagesLabour Law Questions Asked in EPFO by Anuj GargArpit ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Establishing A Pay StructureDocument28 pagesEstablishing A Pay StructureHelena MontgomeryNo ratings yet
- Job DeskDocument2 pagesJob DesksimatelexrecruitsmbNo ratings yet
- A&P Salary Adjustment TemplateDocument2 pagesA&P Salary Adjustment TemplateSachin SaxenaNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Technologies and Workload On Employees in Call CentersDocument11 pagesThe Impact of Technologies and Workload On Employees in Call CentersNameerahNo ratings yet
- Capt. Sandeep Goswami: Contact: 9836666066/9831147783 E-MailDocument3 pagesCapt. Sandeep Goswami: Contact: 9836666066/9831147783 E-MailHRD CORP CONSULTANCYNo ratings yet
- VOCAB LIST EmploymentDocument3 pagesVOCAB LIST EmploymentAdriana SalazarNo ratings yet
- Employee Development and Talent ManagementDocument12 pagesEmployee Development and Talent ManagementAnkita Dey GroverNo ratings yet
- PERENCANAAN SDM (4 & 5) Human Resource PlanningDocument28 pagesPERENCANAAN SDM (4 & 5) Human Resource PlanningTimoteus AnggadianNo ratings yet
- 04 - Worksheet - 1-Activity in BusmathDocument2 pages04 - Worksheet - 1-Activity in BusmathJemimah VillanocheNo ratings yet
- Inland Empire Amazon Workers United 2023 SurveyDocument5 pagesInland Empire Amazon Workers United 2023 SurveyThe Press-Enterprise / pressenterprise.comNo ratings yet
- Appraising and Rewarding Performance Part 2 PDFDocument33 pagesAppraising and Rewarding Performance Part 2 PDFAnnaliza LacasaNo ratings yet
- Career Planning CaseDocument2 pagesCareer Planning CaseABDUL BASIT KHANNo ratings yet
- Short-Term Incentives Around The World: SampleDocument44 pagesShort-Term Incentives Around The World: Sampleammarmughal348No ratings yet
- Agricultural Truck Driver: U.S. Department of Labor A. Job Offer InformationDocument21 pagesAgricultural Truck Driver: U.S. Department of Labor A. Job Offer InformationEdro RibeiroNo ratings yet
- SL No. Name of Acts & Rules Name and Description of Forms Remarks Shop and Establishment Act and Rules 2004Document3 pagesSL No. Name of Acts & Rules Name and Description of Forms Remarks Shop and Establishment Act and Rules 2004Soumya Ranjan Nayak100% (1)
- Pelayanan Home Care Di EropaDocument4 pagesPelayanan Home Care Di EropaSandra RNo ratings yet
- Muhammad - Ahmad - 00720183 - IG - 2023 04 26 08 41 23Document2 pagesMuhammad - Ahmad - 00720183 - IG - 2023 04 26 08 41 23Muhammad AhmadNo ratings yet
- Staffing: Recruitment and SelectionDocument19 pagesStaffing: Recruitment and SelectionMylene SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Edwin Flippo Defines-Human Resource Management As "Planning, Organizing, DirectingDocument5 pagesEdwin Flippo Defines-Human Resource Management As "Planning, Organizing, DirectingMaaz Ahmad KhanNo ratings yet
- Hazard Communication: OSHA Office of Training and Educ AtionDocument17 pagesHazard Communication: OSHA Office of Training and Educ AtionJames PaddisonNo ratings yet
- Database On Labour & Employment Statistics of West Bengal - 2014Document231 pagesDatabase On Labour & Employment Statistics of West Bengal - 2014NIKHIL KUMAR AGRAWALNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 Employee Safety and HealthDocument13 pagesChapter 16 Employee Safety and HealthAmmarNo ratings yet
- Sweatshop Saipan Abortion Class Action Settlement Irbid JordanDocument1 pageSweatshop Saipan Abortion Class Action Settlement Irbid JordanKristina KolodeevaNo ratings yet
- Managing Human Resources in Entrepreneurial FirmsDocument44 pagesManaging Human Resources in Entrepreneurial FirmsKhalid Jama HusseinNo ratings yet
- San Miguel Foods, Inc. v. San Miguel Corp. Supervisors and Exempt UnionDocument10 pagesSan Miguel Foods, Inc. v. San Miguel Corp. Supervisors and Exempt Union149890No ratings yet
- Immunities of Trade Unions AssignmentDocument14 pagesImmunities of Trade Unions AssignmentKumar AnkitNo ratings yet
Discrimination in The Workplace Research LL
Discrimination in The Workplace Research LL
Uploaded by
Hardik Shetty0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
160 views5 pagesWorkplace discrimination occurs when employees or job applicants are treated unfavorably due to characteristics like age, disability, race, sex, and religion. It is illegal under federal law to discriminate in hiring practices or in the workplace based on protected traits. Discrimination can take various forms such as unequal pay, denial of benefits or promotions, or harassment. Employees who experience discrimination have legal recourse by filing complaints with enforcement agencies. Employers must ensure their practices do not discriminate or allow for a hostile work environment to support a fair and productive workplace.
Original Description:
Original Title
Discrimination in the Workplace Research LL
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentWorkplace discrimination occurs when employees or job applicants are treated unfavorably due to characteristics like age, disability, race, sex, and religion. It is illegal under federal law to discriminate in hiring practices or in the workplace based on protected traits. Discrimination can take various forms such as unequal pay, denial of benefits or promotions, or harassment. Employees who experience discrimination have legal recourse by filing complaints with enforcement agencies. Employers must ensure their practices do not discriminate or allow for a hostile work environment to support a fair and productive workplace.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
160 views5 pagesDiscrimination in The Workplace Research LL
Discrimination in The Workplace Research LL
Uploaded by
Hardik ShettyWorkplace discrimination occurs when employees or job applicants are treated unfavorably due to characteristics like age, disability, race, sex, and religion. It is illegal under federal law to discriminate in hiring practices or in the workplace based on protected traits. Discrimination can take various forms such as unequal pay, denial of benefits or promotions, or harassment. Employees who experience discrimination have legal recourse by filing complaints with enforcement agencies. Employers must ensure their practices do not discriminate or allow for a hostile work environment to support a fair and productive workplace.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 5
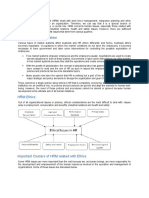
What is workplace discrimination, and what constitutes discrimination against
employees or job applicants? Employment discrimination happens when an
employee or job candidate is treated unfavorably because of age, disability,
genetic information, national origin, pregnancy, race or skin color, religion, or
sex. In addition, federal laws against discrimination protect workers from
retaliation for “asserting their rights to be free from employment discrimination.”
It is illegal to discriminate based on these protected characteristics when hiring or
in the workplace.
What Is Workplace Discrimination?
Title VII of the Civil Rights Act of 1964 makes it unlawful to discriminate in hiring,
discharge, promotion, referral, and other facets of employment, on the basis of
color, race, religion, sex, or national origin. This is enforced by the Equal
Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC).
In addition, the U.S. Supreme Court has ruled that Civil Rights Act provision
banning discrimination in the workplace protects LGBTQ employees from being
fired because of their sexual orientation.
Federal contractors and subcontractors must take affirmative action to guarantee
equal employment opportunity without regard to race, color, religion, sex, sexual
orientation, gender identity, or national origin. Executive Order 11246 is
enforceby the Office of Federal Contract Compliance Programs (OFCCP).
Discrimination vs. Harassment
What's the difference between discrimination and harassment? Harassment is a
form of discrimination. As with discrimination, there are different types of
harassment, including unwelcome behavior by a co-worker, manager, client, or
anyone else in the workplace, that is based on race, color, religion, sex (including
pregnancy), nationality, age (40 or older), disability, or genetic information.
Different Types of Workplace Discrimination
Workplace discrimination occurs when an individual is discriminated against due
to any number of factors. In addition to the reasons listed above, employees and
job applicants can also be discriminated against because of their relationship to
another person. For example, an employer is legally prohibited from refusing to
hire a job candidate because their spouse is disabled and they fear that the
candidate’s caregiving responsibilities may interfere with their work. This would
be discrimination under the ADA, even though the candidate is not the disabled
party. Review this list of the different types of employment discrimination,
examples of workplace discrimination, and tips for handling workplace
discrimination issues.
Age
Gender
Race
Ethnicity
Skin Color
National Origin
Mental or Physical Disability
Genetic Information
Relationship to someone who may be discriminated against
Pregnancy or Parenthood
Examples of Employment Discrimination
Employment discrimination could occur in any number of situations, including:
Stating or suggesting preferred candidates in a job advertisement
Excluding potential employees during recruitment
Denying certain employees compensation or benefits
Paying equally-qualified employees in the same position different salaries
Discriminating when assigning disability leave, maternity leave, or
retirement options
Denying or disrupting the use of company facilities
Discrimination when issuing promotions or lay-offs
Discrimination Legislation and Issues
There are several types of workplace-based discrimination that have been
addressed by and are protected under federal legislation. These include:
Age Discrimination in the Workplace
Age discrimination is a practice specifically prohibited by law. With a few rare
exceptions, companies are forbidden from specifying an age preference in job
advertisements.
Employees must receive the same benefits regardless of age, the only exception
being when the cost of providing supplemental benefits to young workers is the
same as providing reduced benefits to older workers. Also, age discrimination in
apprenticeship programs or internship opportunities is illegal.
Disability Discrimination
The Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) of 1990 made it illegal to discriminate
against qualified job candidates or employees on the basis of disability. In
practical terms, this means that employers cannot refuse to hire disabled
candidates or penalize disabled workers purely for their disabilities. The
Rehabilitation Act of 1973 prohibits discrimination in federal employment on
much the same terms as the ADA.
Sex and Gender Discrimination in the Workplace
The Equal Pay Act of 1963 states that employers must give men and women equal
pay for equal work. Further, the act specifies that job content, not title,
“determines whether jobs are substantially equal.”
Title VII of the Civil Rights Act also prohibits discrimination on the basis of sex. In
short, it is illegal for employers to pay men and women different salaries based on
their sex or gender.
Pregnancy Discrimination in the Workplace
Pregnancy-based discrimination is illegal. Employers are required to handle
pregnancy in the same way that they would handle a temporary illness or other
non-permanent condition that would necessitate special consideration. Job
seekers have the same rights as employees, and both are protected by the
Pregnancy Discrimination Act (PDA) passed in 1978.
Race Discrimination in the Workplace
It is illegal to treat either a job applicant or an employee unfavorably because
they are of a certain race or because of personal characteristics associated with
race. Color discrimination, which is treating someone unfavorably because of skin
color complexion, is also illegal.
Religious Discrimination in the Workplace
It is illegal for employers to discriminate based on an individual's religious
customs. Businesses are required to make reasonable accommodation of an
employee's religious beliefs, as long as doing so doesn't have excessive negative
consequences for the employer.
What is a Hostile Work Environment?
A hostile work environment is created when harassment or discrimination
interferes with an employee’s work performance or creates a difficult or offensive
work environment for an employee or group of employees.
Unlawful Discrimination and Harassment
It's important to note that discriminatory practices can occur in any aspect of
employment. It is illegal for an employer to make assumptions based on race,
gender, or age-related stereotypes, and it's also unlawful for an employer to
assume that an employee may be incapable because he or she is disabled.
Additionally, companies are prohibited from withholding employment
opportunities from an employee because of his or her relationship with someone
of a certain race, religion, or ethnicity. Unlawful discrimination also includes
harassment based on legally protected personal traits, including (but not limited
to) race, gender, age, and religion.
Employment Discrimination Complaints
Under United States laws, companies are prohibited from subjecting employees
to unfair treatment or blatant discrimination based on these legally-protected
characteristics. Also, it is illegal for an employer to retaliate against a person who
has filed a complaint about discrimination or participated in a related
investigation.
Conclusion
Discrimination in the workplace is unethical and has negative effects on the
employee and the company both. The employee could face mental and emotional
stress and the employer could face a lawsuit, as well as a negative reputation.
Without workplace discrimination, both the employer and the employee could
have a positive work environment and experience together.
Suggestions
The average person will spend approximately 90,000 hours at work over a
lifetime. This is about one-third of our life, which means, besides home, the
workplace is where we spend the majority of our time.
For this reason, it is important that we feel safe, not mistreated or discriminated
against in the workplace. Companies have to learn how to prevent discrimination
in the workplace.
They can do this by taking a closer look at companies' practices or policies to
ensure employees' needs are taken into consideration, as otherwise, productivity,
performance, staff commitment, and morale can be affected.
Unfortunately, this issue is often overlooked or not spoken widely about, leaving
employers and employees in the dark when it comes to dealing with
discrimination. In several cases, this will also lead to employee turnovers due to a
lack of effective measures to stop the problem.
You might also like
- Talent Management Employer QuestionnaireDocument6 pagesTalent Management Employer Questionnairekamdica57% (14)
- Detroit Pistons and Rob Murphy LawsuitDocument38 pagesDetroit Pistons and Rob Murphy LawsuitWXYZ-TV Channel 7 DetroitNo ratings yet
- Dave Armstrong CaseDocument1 pageDave Armstrong CasegaryhamsterNo ratings yet
- ACAS - Bullying and Harassment at Work (Guide For Employees)Document12 pagesACAS - Bullying and Harassment at Work (Guide For Employees)qbl777No ratings yet
- Employment Discrimination Law Outline 2018Document8 pagesEmployment Discrimination Law Outline 2018Catlin PegelowNo ratings yet
- EEOC On Race and ColorDocument57 pagesEEOC On Race and ColorYuriNo ratings yet
- Employment Discrimination Outline - Fall 2011 PublicDocument46 pagesEmployment Discrimination Outline - Fall 2011 PublicAmaka Obiesie100% (2)
- 4 Equal Employment OpportunityDocument43 pages4 Equal Employment OpportunityApril Angel Mateo MaribbayNo ratings yet
- Types of DiscriminationDocument2 pagesTypes of DiscriminationAbegail MoratalNo ratings yet
- Employment Discrimination 2012Document44 pagesEmployment Discrimination 2012Mal Durham-BowmansNo ratings yet
- Workplace Harassment and DiscriminationDocument7 pagesWorkplace Harassment and Discriminationjoshua nyangaresiNo ratings yet
- Common Ethical Issues in The WorkplaceDocument5 pagesCommon Ethical Issues in The WorkplacePXQ DIGITALSNo ratings yet
- GPGB Disability DiscriminationDocument6 pagesGPGB Disability DiscriminationKNo ratings yet
- EeocDocument10 pagesEeocChris Jackson'sNo ratings yet
- Employment DiscriminationDocument28 pagesEmployment DiscriminationFawwaz AnwerNo ratings yet
- Bullying Harassment and Stress in The Workplace A European PerspectiveDocument21 pagesBullying Harassment and Stress in The Workplace A European Perspectivetanbraga09No ratings yet
- Your Guide To Preventing and Identifying Harassment in The WorkplaceDocument5 pagesYour Guide To Preventing and Identifying Harassment in The WorkplaceShah Danish AhmedNo ratings yet
- Discrimination LawDocument9 pagesDiscrimination Lawduende8606No ratings yet
- Anti-Discrimination Law and EmploymentDocument4 pagesAnti-Discrimination Law and EmploymentDiane OlivasNo ratings yet
- DOJ EEOC ComplaintDocument21 pagesDOJ EEOC ComplaintSusan SvrlugaNo ratings yet
- Workplace HarassmentDocument31 pagesWorkplace HarassmentDien NursalNo ratings yet
- The Law: Equal Employment Opportunity IsDocument9 pagesThe Law: Equal Employment Opportunity IsStarmelAllahNo ratings yet
- Anti Discrimination PolicyDocument4 pagesAnti Discrimination PolicyAditya Kedia100% (1)
- EEO Complaint Process BrochureDocument2 pagesEEO Complaint Process BrochureKyle Fernando Foster-ElNo ratings yet
- Texas House Committee Revises Sexual Harassment PolicyDocument5 pagesTexas House Committee Revises Sexual Harassment PolicyAnonymous Pb39klJNo ratings yet
- The Ethics of Job DiscriminationDocument17 pagesThe Ethics of Job DiscriminationTania cruzNo ratings yet
- Hostile Work EnvironmentDocument6 pagesHostile Work EnvironmentScoutMaster DougNo ratings yet
- Employment Law-Final OutlineDocument18 pagesEmployment Law-Final OutlineflyygeminiNo ratings yet
- Of Workplace Harassment: C 1 Overview of The LawDocument65 pagesOf Workplace Harassment: C 1 Overview of The LawMack KnifeNo ratings yet
- Employment Law Outline: Download NowDocument36 pagesEmployment Law Outline: Download NowseabreezeNo ratings yet
- Outline Constitutional Law1Document33 pagesOutline Constitutional Law1Jake HuynhNo ratings yet
- Empd I ScrimDocument46 pagesEmpd I ScrimstillaireNo ratings yet
- Business Ethics and Job DiscriminationDocument22 pagesBusiness Ethics and Job Discriminationhanishdhillon100% (5)
- Sexual Harassment in The Workplace !Document16 pagesSexual Harassment in The Workplace !Hajar MkounNo ratings yet
- Employment Case Map (Formatted)Document24 pagesEmployment Case Map (Formatted)avaasiaNo ratings yet
- Employment Discrimination: Pretext, Implicit Bias, and The Beast of BurdensDocument27 pagesEmployment Discrimination: Pretext, Implicit Bias, and The Beast of BurdensNew England Law Review100% (1)
- Eeo Storyboard 3Document93 pagesEeo Storyboard 3api-482724270No ratings yet
- C4C Upload: EEOC Decision Finding Discrimination (Katrina Webster V Dept. of NavyDocument15 pagesC4C Upload: EEOC Decision Finding Discrimination (Katrina Webster V Dept. of NavyC4C100% (1)
- Workplace - Ethics in HRMDocument7 pagesWorkplace - Ethics in HRMDr. Meghdoot GhoshNo ratings yet
- Investigative DispositionDocument6 pagesInvestigative DispositionThe Standard-TimesNo ratings yet
- 22-088 EEOC KnowYourRightsDocument2 pages22-088 EEOC KnowYourRightsBelal AhmedNo ratings yet
- 323 - Direct and Indirect Discrimination - Explanation and ExamplesDocument2 pages323 - Direct and Indirect Discrimination - Explanation and ExamplesKhvichaKopinadzeNo ratings yet
- Complaint: Employment Sexual Harassment Discrimination Against Omnicom & DDB NYDocument38 pagesComplaint: Employment Sexual Harassment Discrimination Against Omnicom & DDB NYscl1116953No ratings yet
- HRM/510 Week 11 Final Exam QuizDocument95 pagesHRM/510 Week 11 Final Exam QuizgoodNo ratings yet
- Age Discrimination in Employment ThesisDocument4 pagesAge Discrimination in Employment Thesisafkofvidg100% (2)
- Employee RightsDocument2 pagesEmployee RightsJustine ManueleNo ratings yet
- Unethical PracticesDocument9 pagesUnethical PracticesZahra IjazNo ratings yet
- Utech, Faculty of Law Discrimination Law: Sexual HarassmentDocument12 pagesUtech, Faculty of Law Discrimination Law: Sexual HarassmentPersephone WestNo ratings yet
- 1 PF Complaint-AldridgeDocument16 pages1 PF Complaint-AldridgeCory DewayneNo ratings yet
- EEOC Dismissal and Notice of RightsDocument2 pagesEEOC Dismissal and Notice of RightsGregory YoungNo ratings yet
- How To Develop A Diversity and Inclusion InitiativeDocument2 pagesHow To Develop A Diversity and Inclusion InitiativeRayno MareeNo ratings yet
- I C J J: Nterbranch Ommission Uvenile UsticeDocument25 pagesI C J J: Nterbranch Ommission Uvenile UsticeCalifornia Judicial Branch News Service - Investigative Reporting Source Material & Story IdeasNo ratings yet
- Aleciah Jackson vs. City of Dallas LawsuitDocument7 pagesAleciah Jackson vs. City of Dallas LawsuitAnonymous ovJgHANo ratings yet
- What Is The Difference Between Recruitment and Talent Acquisition by Hemant KumaarrDocument4 pagesWhat Is The Difference Between Recruitment and Talent Acquisition by Hemant KumaarrSujan DeyNo ratings yet
- Workers' Compensation and Injury Duration: Evidence From A Natural ExperimentDocument20 pagesWorkers' Compensation and Injury Duration: Evidence From A Natural Experimentmarcel0555777No ratings yet
- Express Implied Terms and Post Termination RestraintsDocument3 pagesExpress Implied Terms and Post Termination Restraintsnahian ayman shababNo ratings yet
- 11th Ward Aldermanic Candidate ResumesDocument61 pages11th Ward Aldermanic Candidate ResumesjrNo ratings yet
- Ethical RelativismDocument11 pagesEthical RelativismKarelle MalasagaNo ratings yet
- Equal Employment Opportunity EEO and Anti Discrimination PolicyDocument8 pagesEqual Employment Opportunity EEO and Anti Discrimination PolicyBala Krishnan100% (1)
- Manual on the Character and Fitness Process for Application to the Michigan State Bar: Law and PracticeFrom EverandManual on the Character and Fitness Process for Application to the Michigan State Bar: Law and PracticeNo ratings yet
- Gender Differences in The WorkplaceDocument3 pagesGender Differences in The WorkplaceHardik ShettyNo ratings yet
- Discrimination at Work Place Labour LawDocument10 pagesDiscrimination at Work Place Labour LawHardik ShettyNo ratings yet
- Central Door Steel Corporation Case StudyDocument5 pagesCentral Door Steel Corporation Case StudyHardik ShettyNo ratings yet
- Project Report On Anand RathiDocument10 pagesProject Report On Anand RathiHardik ShettyNo ratings yet
- The Code On WagesDocument48 pagesThe Code On WagesHardik ShettyNo ratings yet
- The Industrial Relations Code, 2020Document27 pagesThe Industrial Relations Code, 2020Hardik ShettyNo ratings yet
- Project Report On Tata IPL ResearchDocument12 pagesProject Report On Tata IPL ResearchHardik ShettyNo ratings yet
- Research - On - IPL 2022 Dy PatilDocument10 pagesResearch - On - IPL 2022 Dy PatilHardik ShettyNo ratings yet
- Research On IPLDocument12 pagesResearch On IPLHardik ShettyNo ratings yet
- Project Report On Tata IPL (Bane or Boon)Document12 pagesProject Report On Tata IPL (Bane or Boon)Hardik ShettyNo ratings yet
- Cia 2 EcbmDocument9 pagesCia 2 Ecbmchakradhar pmNo ratings yet
- Labour Law Questions Asked in EPFO by Anuj GargDocument78 pagesLabour Law Questions Asked in EPFO by Anuj GargArpit ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Establishing A Pay StructureDocument28 pagesEstablishing A Pay StructureHelena MontgomeryNo ratings yet
- Job DeskDocument2 pagesJob DesksimatelexrecruitsmbNo ratings yet
- A&P Salary Adjustment TemplateDocument2 pagesA&P Salary Adjustment TemplateSachin SaxenaNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Technologies and Workload On Employees in Call CentersDocument11 pagesThe Impact of Technologies and Workload On Employees in Call CentersNameerahNo ratings yet
- Capt. Sandeep Goswami: Contact: 9836666066/9831147783 E-MailDocument3 pagesCapt. Sandeep Goswami: Contact: 9836666066/9831147783 E-MailHRD CORP CONSULTANCYNo ratings yet
- VOCAB LIST EmploymentDocument3 pagesVOCAB LIST EmploymentAdriana SalazarNo ratings yet
- Employee Development and Talent ManagementDocument12 pagesEmployee Development and Talent ManagementAnkita Dey GroverNo ratings yet
- PERENCANAAN SDM (4 & 5) Human Resource PlanningDocument28 pagesPERENCANAAN SDM (4 & 5) Human Resource PlanningTimoteus AnggadianNo ratings yet
- 04 - Worksheet - 1-Activity in BusmathDocument2 pages04 - Worksheet - 1-Activity in BusmathJemimah VillanocheNo ratings yet
- Inland Empire Amazon Workers United 2023 SurveyDocument5 pagesInland Empire Amazon Workers United 2023 SurveyThe Press-Enterprise / pressenterprise.comNo ratings yet
- Appraising and Rewarding Performance Part 2 PDFDocument33 pagesAppraising and Rewarding Performance Part 2 PDFAnnaliza LacasaNo ratings yet
- Career Planning CaseDocument2 pagesCareer Planning CaseABDUL BASIT KHANNo ratings yet
- Short-Term Incentives Around The World: SampleDocument44 pagesShort-Term Incentives Around The World: Sampleammarmughal348No ratings yet
- Agricultural Truck Driver: U.S. Department of Labor A. Job Offer InformationDocument21 pagesAgricultural Truck Driver: U.S. Department of Labor A. Job Offer InformationEdro RibeiroNo ratings yet
- SL No. Name of Acts & Rules Name and Description of Forms Remarks Shop and Establishment Act and Rules 2004Document3 pagesSL No. Name of Acts & Rules Name and Description of Forms Remarks Shop and Establishment Act and Rules 2004Soumya Ranjan Nayak100% (1)
- Pelayanan Home Care Di EropaDocument4 pagesPelayanan Home Care Di EropaSandra RNo ratings yet
- Muhammad - Ahmad - 00720183 - IG - 2023 04 26 08 41 23Document2 pagesMuhammad - Ahmad - 00720183 - IG - 2023 04 26 08 41 23Muhammad AhmadNo ratings yet
- Staffing: Recruitment and SelectionDocument19 pagesStaffing: Recruitment and SelectionMylene SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Edwin Flippo Defines-Human Resource Management As "Planning, Organizing, DirectingDocument5 pagesEdwin Flippo Defines-Human Resource Management As "Planning, Organizing, DirectingMaaz Ahmad KhanNo ratings yet
- Hazard Communication: OSHA Office of Training and Educ AtionDocument17 pagesHazard Communication: OSHA Office of Training and Educ AtionJames PaddisonNo ratings yet
- Database On Labour & Employment Statistics of West Bengal - 2014Document231 pagesDatabase On Labour & Employment Statistics of West Bengal - 2014NIKHIL KUMAR AGRAWALNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 Employee Safety and HealthDocument13 pagesChapter 16 Employee Safety and HealthAmmarNo ratings yet
- Sweatshop Saipan Abortion Class Action Settlement Irbid JordanDocument1 pageSweatshop Saipan Abortion Class Action Settlement Irbid JordanKristina KolodeevaNo ratings yet
- Managing Human Resources in Entrepreneurial FirmsDocument44 pagesManaging Human Resources in Entrepreneurial FirmsKhalid Jama HusseinNo ratings yet
- San Miguel Foods, Inc. v. San Miguel Corp. Supervisors and Exempt UnionDocument10 pagesSan Miguel Foods, Inc. v. San Miguel Corp. Supervisors and Exempt Union149890No ratings yet
- Immunities of Trade Unions AssignmentDocument14 pagesImmunities of Trade Unions AssignmentKumar AnkitNo ratings yet