Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 viewsNeuro Part 1 Notes
Neuro Part 1 Notes
Uploaded by
Marc JasminThe document discusses the autonomic nervous system, which has two divisions:
1. The sympathetic division is responsible for the fight or flight response through effects like increased heart rate and adrenaline release.
2. The parasympathetic division is responsible for rest and digest functions like decreased heart rate, increased digestive activity, and conserving energy.
It provides examples of how the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions have opposing effects on many organs like increasing versus decreasing heart rate respectively.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Adir SampleDocument4 pagesAdir SampleTerapie Aba67% (3)
- Fdar Samples PresentationDocument29 pagesFdar Samples PresentationAnnette Aquino Guevarra100% (2)
- Mayo Clinic CaseDocument2 pagesMayo Clinic CaseShinchan Nohara50% (2)
- TOF-WatchSXUsermanual Avalon MedicalDocument90 pagesTOF-WatchSXUsermanual Avalon MedicalestrellanaNo ratings yet
- OSHA 2013 AnswersDocument3 pagesOSHA 2013 Answerslacurva67% (3)
- Nutshell NeuroDocument15 pagesNutshell NeuroAdeel abbas rajaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 - Nervous SystemDocument7 pagesChapter 9 - Nervous SystemElla LagramaNo ratings yet
- Society of Metaphysicians - The Structure of AllDocument30 pagesSociety of Metaphysicians - The Structure of Alldiddi21No ratings yet
- Photosynthesis Questions and AnswerDocument20 pagesPhotosynthesis Questions and Answerkumara guruparanNo ratings yet
- Linkage IsomersDocument61 pagesLinkage IsomersMonica NC67% (3)
- Practical 2 RDTDocument20 pagesPractical 2 RDTDoraemon CuteNo ratings yet
- Amputation Lower ExtremityDocument5 pagesAmputation Lower ExtremityJulia SalvioNo ratings yet
- Myasthenia GravisDocument2 pagesMyasthenia GravisJulia SalvioNo ratings yet
- Crystalline Solid-State Ion-Selective ElectrodesDocument13 pagesCrystalline Solid-State Ion-Selective ElectrodesNaeem MalikNo ratings yet
- Slide 2-Site ClearanceDocument18 pagesSlide 2-Site ClearanceZahin IsmailNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document17 pagesAssignment 1ShammimBegumNo ratings yet
- Man Dan Yang Acupuncture - The 12 Miraculous PointsDocument5 pagesMan Dan Yang Acupuncture - The 12 Miraculous PointsAnonymous ofwFwNtMNo ratings yet
- Kinesiology: Chapter 1: Kinematics Joint MovementsDocument4 pagesKinesiology: Chapter 1: Kinematics Joint MovementsCrescent LazoNo ratings yet
- Viknesh TA19154 Peaucellier ReportDocument9 pagesViknesh TA19154 Peaucellier Reportkameene0% (1)
- Bio621 MindmapDocument3 pagesBio621 MindmapMizahNo ratings yet
- A Long and Healthy LifeDocument4 pagesA Long and Healthy LifeRoxi PascaNo ratings yet
- Brunei Brief DescriptionDocument40 pagesBrunei Brief DescriptionlerujNo ratings yet
- Cosmtic Diploma SyllabusDocument11 pagesCosmtic Diploma SyllabusPrakash VerekarNo ratings yet
- Neuro 1.27.22Document19 pagesNeuro 1.27.22Vhince PiscoNo ratings yet
- Autonomic Nervous System - Part 1Document8 pagesAutonomic Nervous System - Part 1karageeNo ratings yet
- Nervous Sytem 1Document11 pagesNervous Sytem 1Elaine Victoria ElizanNo ratings yet
- 3 QTR Notes - Biology: Functions of The Nervous System Nervous System Histology Neurons Nerve CellsDocument4 pages3 QTR Notes - Biology: Functions of The Nervous System Nervous System Histology Neurons Nerve CellsHazel Kristy CatagueNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Neurologic Function Notes - AnatomyDocument1 pageAssessment of Neurologic Function Notes - AnatomyMichelle Dona MirallesNo ratings yet
- Biological Foundations of Behavior General Psychology IntroductionDocument5 pagesBiological Foundations of Behavior General Psychology IntroductionmlpdmarasiganNo ratings yet
- 3aDasar-Dasar Neuroanatomi (2016)Document157 pages3aDasar-Dasar Neuroanatomi (2016)Magfira Al HabsyiNo ratings yet
- Cranial NervesDocument14 pagesCranial NervesAdrija ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Points To Remember: Neural Control and CoordinationDocument107 pagesPoints To Remember: Neural Control and CoordinationRagheNo ratings yet
- Biology F4 Review Summary NoteDocument117 pagesBiology F4 Review Summary NoteSocdal AbdiNo ratings yet
- Mindmap Bio621 Chapter1Document3 pagesMindmap Bio621 Chapter1MizahNo ratings yet
- Proprioceptive Sensory SystemsDocument9 pagesProprioceptive Sensory SystemsRex HuangNo ratings yet
- Unit 10 The Nervous SystemDocument80 pagesUnit 10 The Nervous SystemPavithra BCNo ratings yet
- Reviewer 3Document2 pagesReviewer 3blessiejamNo ratings yet
- Neuro HandoutDocument13 pagesNeuro HandoutFatima Shaira PulahongNo ratings yet
- Biology NotesDocument102 pagesBiology Notesajabgul123493No ratings yet
- Development of Nerve Tissue 161 Neurons 163 Central Nervous System 175Document32 pagesDevelopment of Nerve Tissue 161 Neurons 163 Central Nervous System 175Law LightNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Neuroanatomy (2016)Document14 pagesIntroduction of Neuroanatomy (2016)bima sarewoNo ratings yet
- REVIEWER Neurological SystemDocument5 pagesREVIEWER Neurological SystemKeren GaciasNo ratings yet
- Neuroanatomy: Muh - Iqbal Basri Anatomy Department Hasanuddin UniversityDocument19 pagesNeuroanatomy: Muh - Iqbal Basri Anatomy Department Hasanuddin UniversitySuardimanAchoNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument11 pagesNervous Systemmohd nazmieNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 ANAPHY Nervous SystemDocument5 pagesChapter 8 ANAPHY Nervous Systemrobh0026No ratings yet
- Nervous System EQs PPT SlidesDocument15 pagesNervous System EQs PPT SlidesJatin yadavNo ratings yet
- NEUROGLIAL ("White Matter") AstrocytesDocument12 pagesNEUROGLIAL ("White Matter") AstrocytesGabrielle MagdaraogNo ratings yet
- Nervous System: Nissl Bodies-Sites of Protein Synthesis in NeuronsDocument16 pagesNervous System: Nissl Bodies-Sites of Protein Synthesis in NeuronsZella ViaNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument49 pagesNervous SystemJulie Ann SaquilayanNo ratings yet
- 03 Nervous System BDocument41 pages03 Nervous System BBalew KassieNo ratings yet
- Chapter-7-Control and CoordinationDocument9 pagesChapter-7-Control and Coordinationapi-400692183No ratings yet
- AnaPhy Lab Nervous NotesDocument7 pagesAnaPhy Lab Nervous NotesDING ANG BATONo ratings yet
- ANAPHY SpinalCord PeripheralNervousSystemDocument7 pagesANAPHY SpinalCord PeripheralNervousSystemAysha AishaNo ratings yet
- Central - Peripheral Nervous SystemDocument82 pagesCentral - Peripheral Nervous System52-nur Fadiyyah FNo ratings yet
- NCM 103 Case Analysis 1 (Ms. Perez)Document7 pagesNCM 103 Case Analysis 1 (Ms. Perez)Josefina Isabel GullasNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument4 pagesNervous SystemEds SyNo ratings yet
- Introduction To AnsDocument12 pagesIntroduction To AnsSusmita BeheraNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Neuroanatomy: Muhammad Iqbal BasriDocument14 pagesIntroduction of Neuroanatomy: Muhammad Iqbal BasriUgaNo ratings yet
- Pharma 2Document12 pagesPharma 2MARIEMIL FOLLOSONo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument2 pagesNervous SystemShanel Aubrey AglibutNo ratings yet
- Sheniblog-10 Biology (Eng Med) Revision Notes by Rasheed OdakkalDocument14 pagesSheniblog-10 Biology (Eng Med) Revision Notes by Rasheed OdakkalhadiyxxNo ratings yet
- Organization of The Nervous SystemDocument11 pagesOrganization of The Nervous SystemEllaiza Astaca-anNo ratings yet
- Peripheral Nervous SystemDocument58 pagesPeripheral Nervous Systemapi-26762768100% (4)
- Control and Coordination: Chapter - 7Document9 pagesControl and Coordination: Chapter - 7milind dhamaniya100% (1)
- Nervous_System_Notes.docxDocument9 pagesNervous_System_Notes.docxLeah Rose FelixNo ratings yet
- FlipCutter A Pin That Changes Arthroscopic Tunnel Drilling Forever...Document12 pagesFlipCutter A Pin That Changes Arthroscopic Tunnel Drilling Forever...andrelbportoNo ratings yet
- Cat Dissection Lab Experience ReflectionDocument12 pagesCat Dissection Lab Experience Reflectionapi-243202220No ratings yet
- Poc Pamphlet4Document2 pagesPoc Pamphlet4api-278308431No ratings yet
- Stay-Safe CAPD Procedure Card-100290-01Document2 pagesStay-Safe CAPD Procedure Card-100290-01Bhanu KumarNo ratings yet
- A Guide To Working Safely With SilicaDocument21 pagesA Guide To Working Safely With SilicaNAC Supply, Inc.No ratings yet
- Antihyperlipidemic Agents: Phar406 Pharmaceutical Chemistry Iv Emu-Spring TermDocument55 pagesAntihyperlipidemic Agents: Phar406 Pharmaceutical Chemistry Iv Emu-Spring TermN. IndupriyaNo ratings yet
- Formularium Obat PuskesmasDocument6 pagesFormularium Obat PuskesmasWildan Wisnu WardayaNo ratings yet
- NP2 RationaleDocument19 pagesNP2 RationaleElizabella Henrietta TanaquilNo ratings yet
- Business Plan Ipsen2005-2008Document21 pagesBusiness Plan Ipsen2005-2008jglaguadoNo ratings yet
- Injury Prevention 101 - 3 Ways To Prevent A Knee InjuryDocument8 pagesInjury Prevention 101 - 3 Ways To Prevent A Knee InjuryAliNo ratings yet
- Arfa 1Document3 pagesArfa 1bryan leguiabNo ratings yet
- Lexis Gillette-Corsi Annotated BibDocument8 pagesLexis Gillette-Corsi Annotated Bibapi-273261825No ratings yet
- Amoeba 2Document3 pagesAmoeba 2Anglophile123No ratings yet
- The Compliance Following Medical AdviceDocument37 pagesThe Compliance Following Medical AdviceAamna HaneefNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument8 pagesNCPchiki08No ratings yet
- Endocrine System Quiz 1Document6 pagesEndocrine System Quiz 1hamid50% (2)
- New India Mediclaim Policy ProspectusDocument15 pagesNew India Mediclaim Policy ProspectusAazam AdtechiesNo ratings yet
- 2016 Goods Awarded ContractsDocument26 pages2016 Goods Awarded ContractsMANOJNo ratings yet
- Sleep Hygiene: "Sleep Is The Key To Health, Performance, Safety, and Quality of Life"Document8 pagesSleep Hygiene: "Sleep Is The Key To Health, Performance, Safety, and Quality of Life"Child and Family InstituteNo ratings yet
- Reproductive Endocrinology For Gynaecologist SDocument356 pagesReproductive Endocrinology For Gynaecologist SFebey Arie Mulya100% (1)
- Analisa Sintesa MaternitasDocument29 pagesAnalisa Sintesa MaternitasRia Aryanti Putri IINo ratings yet
- Brain Rejuvenation BookDocument71 pagesBrain Rejuvenation Bookfr37375100% (4)
- Physically FitDocument5 pagesPhysically FitGary Mena ArbadoNo ratings yet
- Tracy EnfingerDocument4 pagesTracy Enfingerapi-364917278No ratings yet
Neuro Part 1 Notes
Neuro Part 1 Notes
Uploaded by
Marc Jasmin0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views3 pagesThe document discusses the autonomic nervous system, which has two divisions:
1. The sympathetic division is responsible for the fight or flight response through effects like increased heart rate and adrenaline release.
2. The parasympathetic division is responsible for rest and digest functions like decreased heart rate, increased digestive activity, and conserving energy.
It provides examples of how the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions have opposing effects on many organs like increasing versus decreasing heart rate respectively.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses the autonomic nervous system, which has two divisions:
1. The sympathetic division is responsible for the fight or flight response through effects like increased heart rate and adrenaline release.
2. The parasympathetic division is responsible for rest and digest functions like decreased heart rate, increased digestive activity, and conserving energy.
It provides examples of how the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions have opposing effects on many organs like increasing versus decreasing heart rate respectively.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
20 views3 pagesNeuro Part 1 Notes
Neuro Part 1 Notes
Uploaded by
Marc JasminThe document discusses the autonomic nervous system, which has two divisions:
1. The sympathetic division is responsible for the fight or flight response through effects like increased heart rate and adrenaline release.
2. The parasympathetic division is responsible for rest and digest functions like decreased heart rate, increased digestive activity, and conserving energy.
It provides examples of how the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions have opposing effects on many organs like increasing versus decreasing heart rate respectively.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
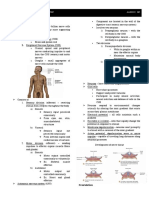
Neuro Part 1/5 Automatic Nervous System
Nervous System Sympathetic Parasympathetic
Thoracolumbar Craniosacral
1. Central Nervous System – upper motor Division Division
neuron lesion T1 to L3 (Cranial Nerves
a. Brain STRESS and Sacral Roots)
b. Spinal cord (SCI) PAHINGA
2. Peripheral Nervous System – lower motor Fight and Flight CN – 1973 (10
neuron lesion Response – face and 9)
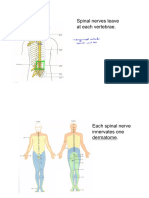
a. Spinal Nerves – 31 pairs of Spinal or run from the Cranial Nerve
Nerves situation used Nuclei
b. Cranial Nerves – 12 pairs of cranial during CN10 – Dorsal
nerves emergency Motor
c. Plexuses – situations. Nucleus/Dorsal
Excitement and Vagal Nucleus –
d. Ganglia – singular: ganglion. Collection
Exercise innervates heart,
of nerve cell bodies outside of the CNS.
Increase in Heart lungs, and GIT.
*basal nuclei
rate (tachycardia) Longest Cranial
*Dorsal Root Ganglion Nerve
Adrenaline Rush
* Peripheral Nervous Injury – common in (Adrenergic CN9 – Inferior
Response) → Salivatory Nucleus
brachial plexus (upper ext. nerves)
Epinephrine/Nor CN7 - Superior
Two Functional Subdivisions of the Peripheral epinephrine Salivatory Nucleus
Nervous System Glands for Saliva
Parotid
1. Autonomic Nervous System (largest) #9
- Regulated by the hypothalamus → Sublingual
homeostasis – under
- 2-neuron hook up – two neurons the tongue
will hook up before going to the Submandib
organ ular –
- Innervate visceral and glands → under the
involuntary structures (automatic mandible
structures) CN3 - Edinger
Westphal Nucleus
Example: heart, GIT
PERRLA – Pupils
Glands: sweat and salivary glands
equally rounded
a. Sympathetic reactive to light
b. Parasympathetic and
2. Somatic Nervous System accommodation
Skeletal Muscles → efferent, SR – S2 to S4 →
voluntary, striated. Nerve Supply of
Skin Urinary Bladder
Joints Rest and
Digest
Conservation
of Energy
*Dyspepsia/
Indigestion
Cholinergic →
Acetylcholine
Two-neuron hook Two-neuron
up (pre, ganglion, hook up (pre,
post-ganglion) ganglion, post-
Distance: shorter ganglion)
pre-ganglionic Distance:
the longer the longer pr-
distance to the ganglionic the
organ nearer to the
Diffused organ
Response Localized
Neurotransmitter Response
Agent from: Neurotransmi
pre-ganglionic: tter Agent:
- Acetylcho Pre-ganglionic –
line Acetylcholine
Post-ganglionic: Post-ganglionic –
Norepinephrine acetylcholine
Organ S P
Parotitis (Mumps) – inflammation of the Heart ↑ HR ↓ HR (CN10)
Parotid Gland Co
Stroke Volume (SU)
Test of Accommodation (3Cs) Force
1. Convergence of the eyes (Medial Rectal GIT ↓ Peristalsis ↑ Peristalsis
Muscles) Constipation Gastric Motility
2. Constriction of the Pupil Digestion
3. Curvature of the lens increase Gastric Juice
(convexity) Increase
Pancreatic Ax
Generalization (Guyton) Salivation (CN7/9)
1. All pre-ganglionic terminals: cholinergic BP ↑ due to ↓
2. All post-ganglionic parasympathetic peripheral
terminals: cholinergic vasoconstriction
Muscles in
3. Almost all of post-ganglionic
vasodilation
sympathetic: adrenergic
Coronary Artery
exceptions: sweat glands and piloerector dilation and
muscles (cholinergic/acetylcholine) muscles dilation
Bronchodilation Bronchoconstriction
(Bronchospasm)
Pupils
Demand increases blood flow = vasoconstriction
Example: exercise, LE vasodilate increase in
demand of blood due to activity
Coronary artery = sympathetic = increase in
pumping = vasodilation?
Example = asthmatic patient given
bronchodilators. Sympathomimetic
Betablockers = names with +olol sympatholytic
36:15
You might also like
- Adir SampleDocument4 pagesAdir SampleTerapie Aba67% (3)
- Fdar Samples PresentationDocument29 pagesFdar Samples PresentationAnnette Aquino Guevarra100% (2)
- Mayo Clinic CaseDocument2 pagesMayo Clinic CaseShinchan Nohara50% (2)
- TOF-WatchSXUsermanual Avalon MedicalDocument90 pagesTOF-WatchSXUsermanual Avalon MedicalestrellanaNo ratings yet
- OSHA 2013 AnswersDocument3 pagesOSHA 2013 Answerslacurva67% (3)
- Nutshell NeuroDocument15 pagesNutshell NeuroAdeel abbas rajaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 - Nervous SystemDocument7 pagesChapter 9 - Nervous SystemElla LagramaNo ratings yet
- Society of Metaphysicians - The Structure of AllDocument30 pagesSociety of Metaphysicians - The Structure of Alldiddi21No ratings yet
- Photosynthesis Questions and AnswerDocument20 pagesPhotosynthesis Questions and Answerkumara guruparanNo ratings yet
- Linkage IsomersDocument61 pagesLinkage IsomersMonica NC67% (3)
- Practical 2 RDTDocument20 pagesPractical 2 RDTDoraemon CuteNo ratings yet
- Amputation Lower ExtremityDocument5 pagesAmputation Lower ExtremityJulia SalvioNo ratings yet
- Myasthenia GravisDocument2 pagesMyasthenia GravisJulia SalvioNo ratings yet
- Crystalline Solid-State Ion-Selective ElectrodesDocument13 pagesCrystalline Solid-State Ion-Selective ElectrodesNaeem MalikNo ratings yet
- Slide 2-Site ClearanceDocument18 pagesSlide 2-Site ClearanceZahin IsmailNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document17 pagesAssignment 1ShammimBegumNo ratings yet
- Man Dan Yang Acupuncture - The 12 Miraculous PointsDocument5 pagesMan Dan Yang Acupuncture - The 12 Miraculous PointsAnonymous ofwFwNtMNo ratings yet
- Kinesiology: Chapter 1: Kinematics Joint MovementsDocument4 pagesKinesiology: Chapter 1: Kinematics Joint MovementsCrescent LazoNo ratings yet
- Viknesh TA19154 Peaucellier ReportDocument9 pagesViknesh TA19154 Peaucellier Reportkameene0% (1)
- Bio621 MindmapDocument3 pagesBio621 MindmapMizahNo ratings yet
- A Long and Healthy LifeDocument4 pagesA Long and Healthy LifeRoxi PascaNo ratings yet
- Brunei Brief DescriptionDocument40 pagesBrunei Brief DescriptionlerujNo ratings yet
- Cosmtic Diploma SyllabusDocument11 pagesCosmtic Diploma SyllabusPrakash VerekarNo ratings yet
- Neuro 1.27.22Document19 pagesNeuro 1.27.22Vhince PiscoNo ratings yet
- Autonomic Nervous System - Part 1Document8 pagesAutonomic Nervous System - Part 1karageeNo ratings yet
- Nervous Sytem 1Document11 pagesNervous Sytem 1Elaine Victoria ElizanNo ratings yet
- 3 QTR Notes - Biology: Functions of The Nervous System Nervous System Histology Neurons Nerve CellsDocument4 pages3 QTR Notes - Biology: Functions of The Nervous System Nervous System Histology Neurons Nerve CellsHazel Kristy CatagueNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Neurologic Function Notes - AnatomyDocument1 pageAssessment of Neurologic Function Notes - AnatomyMichelle Dona MirallesNo ratings yet
- Biological Foundations of Behavior General Psychology IntroductionDocument5 pagesBiological Foundations of Behavior General Psychology IntroductionmlpdmarasiganNo ratings yet
- 3aDasar-Dasar Neuroanatomi (2016)Document157 pages3aDasar-Dasar Neuroanatomi (2016)Magfira Al HabsyiNo ratings yet
- Cranial NervesDocument14 pagesCranial NervesAdrija ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- Points To Remember: Neural Control and CoordinationDocument107 pagesPoints To Remember: Neural Control and CoordinationRagheNo ratings yet
- Biology F4 Review Summary NoteDocument117 pagesBiology F4 Review Summary NoteSocdal AbdiNo ratings yet
- Mindmap Bio621 Chapter1Document3 pagesMindmap Bio621 Chapter1MizahNo ratings yet
- Proprioceptive Sensory SystemsDocument9 pagesProprioceptive Sensory SystemsRex HuangNo ratings yet
- Unit 10 The Nervous SystemDocument80 pagesUnit 10 The Nervous SystemPavithra BCNo ratings yet
- Reviewer 3Document2 pagesReviewer 3blessiejamNo ratings yet
- Neuro HandoutDocument13 pagesNeuro HandoutFatima Shaira PulahongNo ratings yet
- Biology NotesDocument102 pagesBiology Notesajabgul123493No ratings yet
- Development of Nerve Tissue 161 Neurons 163 Central Nervous System 175Document32 pagesDevelopment of Nerve Tissue 161 Neurons 163 Central Nervous System 175Law LightNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Neuroanatomy (2016)Document14 pagesIntroduction of Neuroanatomy (2016)bima sarewoNo ratings yet
- REVIEWER Neurological SystemDocument5 pagesREVIEWER Neurological SystemKeren GaciasNo ratings yet
- Neuroanatomy: Muh - Iqbal Basri Anatomy Department Hasanuddin UniversityDocument19 pagesNeuroanatomy: Muh - Iqbal Basri Anatomy Department Hasanuddin UniversitySuardimanAchoNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument11 pagesNervous Systemmohd nazmieNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 ANAPHY Nervous SystemDocument5 pagesChapter 8 ANAPHY Nervous Systemrobh0026No ratings yet
- Nervous System EQs PPT SlidesDocument15 pagesNervous System EQs PPT SlidesJatin yadavNo ratings yet
- NEUROGLIAL ("White Matter") AstrocytesDocument12 pagesNEUROGLIAL ("White Matter") AstrocytesGabrielle MagdaraogNo ratings yet
- Nervous System: Nissl Bodies-Sites of Protein Synthesis in NeuronsDocument16 pagesNervous System: Nissl Bodies-Sites of Protein Synthesis in NeuronsZella ViaNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument49 pagesNervous SystemJulie Ann SaquilayanNo ratings yet
- 03 Nervous System BDocument41 pages03 Nervous System BBalew KassieNo ratings yet
- Chapter-7-Control and CoordinationDocument9 pagesChapter-7-Control and Coordinationapi-400692183No ratings yet
- AnaPhy Lab Nervous NotesDocument7 pagesAnaPhy Lab Nervous NotesDING ANG BATONo ratings yet
- ANAPHY SpinalCord PeripheralNervousSystemDocument7 pagesANAPHY SpinalCord PeripheralNervousSystemAysha AishaNo ratings yet
- Central - Peripheral Nervous SystemDocument82 pagesCentral - Peripheral Nervous System52-nur Fadiyyah FNo ratings yet
- NCM 103 Case Analysis 1 (Ms. Perez)Document7 pagesNCM 103 Case Analysis 1 (Ms. Perez)Josefina Isabel GullasNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument4 pagesNervous SystemEds SyNo ratings yet
- Introduction To AnsDocument12 pagesIntroduction To AnsSusmita BeheraNo ratings yet
- Introduction of Neuroanatomy: Muhammad Iqbal BasriDocument14 pagesIntroduction of Neuroanatomy: Muhammad Iqbal BasriUgaNo ratings yet
- Pharma 2Document12 pagesPharma 2MARIEMIL FOLLOSONo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument2 pagesNervous SystemShanel Aubrey AglibutNo ratings yet
- Sheniblog-10 Biology (Eng Med) Revision Notes by Rasheed OdakkalDocument14 pagesSheniblog-10 Biology (Eng Med) Revision Notes by Rasheed OdakkalhadiyxxNo ratings yet
- Organization of The Nervous SystemDocument11 pagesOrganization of The Nervous SystemEllaiza Astaca-anNo ratings yet
- Peripheral Nervous SystemDocument58 pagesPeripheral Nervous Systemapi-26762768100% (4)
- Control and Coordination: Chapter - 7Document9 pagesControl and Coordination: Chapter - 7milind dhamaniya100% (1)
- Nervous_System_Notes.docxDocument9 pagesNervous_System_Notes.docxLeah Rose FelixNo ratings yet
- FlipCutter A Pin That Changes Arthroscopic Tunnel Drilling Forever...Document12 pagesFlipCutter A Pin That Changes Arthroscopic Tunnel Drilling Forever...andrelbportoNo ratings yet
- Cat Dissection Lab Experience ReflectionDocument12 pagesCat Dissection Lab Experience Reflectionapi-243202220No ratings yet
- Poc Pamphlet4Document2 pagesPoc Pamphlet4api-278308431No ratings yet
- Stay-Safe CAPD Procedure Card-100290-01Document2 pagesStay-Safe CAPD Procedure Card-100290-01Bhanu KumarNo ratings yet
- A Guide To Working Safely With SilicaDocument21 pagesA Guide To Working Safely With SilicaNAC Supply, Inc.No ratings yet
- Antihyperlipidemic Agents: Phar406 Pharmaceutical Chemistry Iv Emu-Spring TermDocument55 pagesAntihyperlipidemic Agents: Phar406 Pharmaceutical Chemistry Iv Emu-Spring TermN. IndupriyaNo ratings yet
- Formularium Obat PuskesmasDocument6 pagesFormularium Obat PuskesmasWildan Wisnu WardayaNo ratings yet
- NP2 RationaleDocument19 pagesNP2 RationaleElizabella Henrietta TanaquilNo ratings yet
- Business Plan Ipsen2005-2008Document21 pagesBusiness Plan Ipsen2005-2008jglaguadoNo ratings yet
- Injury Prevention 101 - 3 Ways To Prevent A Knee InjuryDocument8 pagesInjury Prevention 101 - 3 Ways To Prevent A Knee InjuryAliNo ratings yet
- Arfa 1Document3 pagesArfa 1bryan leguiabNo ratings yet
- Lexis Gillette-Corsi Annotated BibDocument8 pagesLexis Gillette-Corsi Annotated Bibapi-273261825No ratings yet
- Amoeba 2Document3 pagesAmoeba 2Anglophile123No ratings yet
- The Compliance Following Medical AdviceDocument37 pagesThe Compliance Following Medical AdviceAamna HaneefNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument8 pagesNCPchiki08No ratings yet
- Endocrine System Quiz 1Document6 pagesEndocrine System Quiz 1hamid50% (2)
- New India Mediclaim Policy ProspectusDocument15 pagesNew India Mediclaim Policy ProspectusAazam AdtechiesNo ratings yet
- 2016 Goods Awarded ContractsDocument26 pages2016 Goods Awarded ContractsMANOJNo ratings yet
- Sleep Hygiene: "Sleep Is The Key To Health, Performance, Safety, and Quality of Life"Document8 pagesSleep Hygiene: "Sleep Is The Key To Health, Performance, Safety, and Quality of Life"Child and Family InstituteNo ratings yet
- Reproductive Endocrinology For Gynaecologist SDocument356 pagesReproductive Endocrinology For Gynaecologist SFebey Arie Mulya100% (1)
- Analisa Sintesa MaternitasDocument29 pagesAnalisa Sintesa MaternitasRia Aryanti Putri IINo ratings yet
- Brain Rejuvenation BookDocument71 pagesBrain Rejuvenation Bookfr37375100% (4)
- Physically FitDocument5 pagesPhysically FitGary Mena ArbadoNo ratings yet
- Tracy EnfingerDocument4 pagesTracy Enfingerapi-364917278No ratings yet