Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Answer - Biology - Student Book 1
Answer - Biology - Student Book 1
Uploaded by
Aly HassanCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- SlideDoc - Us-Diagnostic Natural Science 4 Primary Byme - Plants - TreesDocument2 pagesSlideDoc - Us-Diagnostic Natural Science 4 Primary Byme - Plants - TreesJuanA.RodriguezGonzalez100% (7)
- A MathematicalModelof The Hemoglobin-OxygenDissociationCurve of Human Blood and of The Partial Pressure As A Function or TemperatureDocument6 pagesA MathematicalModelof The Hemoglobin-OxygenDissociationCurve of Human Blood and of The Partial Pressure As A Function or TemperatureakbianchessiNo ratings yet
- 2210 ABO Worksheet-1Document3 pages2210 ABO Worksheet-1Lida LindstromNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Plan SCIENCE 4 WEEK 3Document24 pagesDaily Lesson Plan SCIENCE 4 WEEK 3Carol Gelbolingo100% (2)
- Compelet Biology Sec1 SB Answers (S.A.files ?)Document34 pagesCompelet Biology Sec1 SB Answers (S.A.files ?)Suha AlgharazNo ratings yet
- Activity 3.1 Factors Affecting EcosystemDocument2 pagesActivity 3.1 Factors Affecting EcosystemAT4-11 HUMSS 2 CEDRICK ILAONo ratings yet
- Sci Mod3 1Document11 pagesSci Mod3 1Pauline Jane FernandezNo ratings yet
- U2 Ans CoursebookDocument2 pagesU2 Ans CoursebookKshitij SoniNo ratings yet
- Science 4 LessonplanDocument4 pagesScience 4 LessonplanDanieta Salas PerezNo ratings yet
- All About PlantsDocument14 pagesAll About Plantsapi-234860390No ratings yet
- Ans Biology Work Book1Document26 pagesAns Biology Work Book1Aly HassanNo ratings yet
- Learning Area Grade Level Quarter Date: TLE-Agri Crop Nine ThreeDocument4 pagesLearning Area Grade Level Quarter Date: TLE-Agri Crop Nine ThreeÁthymosNo ratings yet
- STD - Iii Sub - Science CH - Plants in Our SurroundingsDocument3 pagesSTD - Iii Sub - Science CH - Plants in Our SurroundingsSudip GhoshNo ratings yet
- Science-6B-Week12-Adaptation of PlantsDocument3 pagesScience-6B-Week12-Adaptation of PlantsOlivia Maria ThomasNo ratings yet
- Answers Chapter 6Document44 pagesAnswers Chapter 6lunalabrijnNo ratings yet
- Plant PhysiologyDocument3 pagesPlant PhysiologyNica CordovaNo ratings yet
- Grades 2 and Up Plant RootsDocument17 pagesGrades 2 and Up Plant RootsAnubhav KashyapNo ratings yet
- Sci7 Unit B Unit ReviewDocument16 pagesSci7 Unit B Unit Reviewapi-242221534No ratings yet
- G3 - LSR - 2Y - 3.01 Plants and Trees GrowingDocument14 pagesG3 - LSR - 2Y - 3.01 Plants and Trees GrowingPhạm SửuNo ratings yet
- Getting To Know PlantsDocument29 pagesGetting To Know Plantsashutoshbombatkar2No ratings yet
- Science Unit 1Document14 pagesScience Unit 1SadakatMalihaNo ratings yet
- TLE-Agriculture and Fishery Arts: Quarter 3 Week 7-8 - Module 6Document11 pagesTLE-Agriculture and Fishery Arts: Quarter 3 Week 7-8 - Module 6Lara FloresNo ratings yet
- DoCN Housplant GuideDocument9 pagesDoCN Housplant GuideJunior ArreseNo ratings yet
- Cot Science 4 q2 w3Document54 pagesCot Science 4 q2 w3Frit ZieNo ratings yet
- First Book of Plant 00 Dick RichDocument98 pagesFirst Book of Plant 00 Dick RichjeubrasilNo ratings yet
- Lesson 27 Terrestrial PlantsDocument3 pagesLesson 27 Terrestrial PlantsMaricel Cebrero Santiago100% (4)
- Good Example Research PaperDocument9 pagesGood Example Research Paperapi-370973922No ratings yet
- Science - Other Ways of Classifying PlantsDocument7 pagesScience - Other Ways of Classifying PlantsRien Jing TianNo ratings yet
- G3 - LSR - 1G - 3.03 Where Plants and Animals LiveDocument14 pagesG3 - LSR - 1G - 3.03 Where Plants and Animals LiveNguyệt Ánh - Lucy TăngNo ratings yet
- Science Class With Miss RJDocument31 pagesScience Class With Miss RJOktaviana PusparaniNo ratings yet
- Lant Ingdom: Big PictureDocument2 pagesLant Ingdom: Big PicturehenryNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 WorksheetsDocument4 pagesUnit 5 WorksheetsenkarniNo ratings yet
- Science Chapter 6Document13 pagesScience Chapter 6GM EstradaNo ratings yet
- DLP - Aquatic and Terrestrial PlantsDocument7 pagesDLP - Aquatic and Terrestrial PlantsCLARKDOREAL CANTURIAS100% (2)
- Insight Link 6 - Answer Keys - WBDocument19 pagesInsight Link 6 - Answer Keys - WBElvie ColladoNo ratings yet
- CL 6 - SciDocument2 pagesCL 6 - SciK BhaiNo ratings yet
- Grade.4 ch.1, l.3Document26 pagesGrade.4 ch.1, l.3Hibara AliNo ratings yet
- Roots_of_Desert_Plants Sonoran DesertDocument2 pagesRoots_of_Desert_Plants Sonoran Desertanenyasha.guveyaNo ratings yet
- Plants Knowledge Organiser v1Document1 pagePlants Knowledge Organiser v1Catherine Dharshini LabrooyNo ratings yet
- TERM - 2 Notes & Work Book - Grade 8Document12 pagesTERM - 2 Notes & Work Book - Grade 8Hano MohdNo ratings yet
- Indian Educational School Bharatiya Vidya Bhavan, Kuwait Subject: Science Practice Worksheet Answer KeyDocument3 pagesIndian Educational School Bharatiya Vidya Bhavan, Kuwait Subject: Science Practice Worksheet Answer KeyRAJ STUDY WIZARDNo ratings yet
- How PlantsDocument3 pagesHow PlantsDanjenica Desoloc AsehanNo ratings yet
- Grade 3 Science - Plant - Parts of Leaves Different Types of Leaves - UNIT 1Document4 pagesGrade 3 Science - Plant - Parts of Leaves Different Types of Leaves - UNIT 1Surbhi BhatiaNo ratings yet
- AS - SSD - IV - EVS - Types of PlantsDocument4 pagesAS - SSD - IV - EVS - Types of PlantswasundesagarNo ratings yet
- PlantsDocument50 pagesPlantsMark JuliusNo ratings yet
- Basics of Indoor GardeningDocument9 pagesBasics of Indoor Gardeningمصطفى جاسمNo ratings yet
- Secondary-1 Bio Unit-1 Plants TextDocument9 pagesSecondary-1 Bio Unit-1 Plants TextMay Nyein ChanNo ratings yet
- Activity: Group Function Energy SourceDocument4 pagesActivity: Group Function Energy SourceKirstelle SarabilloNo ratings yet
- FRST 200 Seedling Lab ReportDocument13 pagesFRST 200 Seedling Lab ReportKaysha ReederNo ratings yet
- FOLLETO SCIENCE 2doDocument36 pagesFOLLETO SCIENCE 2doBodaq Decoracion De Interiores Papel TapizNo ratings yet
- Excerpt PDFDocument10 pagesExcerpt PDFerikNo ratings yet
- Science - 1 - WB AnsDocument12 pagesScience - 1 - WB AnsPaPa HeinNo ratings yet
- Answer Key For Class 8 J Biology J Transport in PlantsDocument3 pagesAnswer Key For Class 8 J Biology J Transport in Plantsgea1300015No ratings yet
- Q3 - Science - LessonDocument22 pagesQ3 - Science - LessonHF ManigbasNo ratings yet
- L2 Finals Plant Cell and Plant CharacteristicsDocument32 pagesL2 Finals Plant Cell and Plant CharacteristicsdonglmodestoNo ratings yet
- GK-I (Science) - Unit 7 Plants - p.48-54Document7 pagesGK-I (Science) - Unit 7 Plants - p.48-54عبیرہ کیانیNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Plants Organ SystemDocument32 pages1.2 Plants Organ SystemkitsujinnNo ratings yet
- Plant Needs and Growing Conditions: Give It ADocument30 pagesPlant Needs and Growing Conditions: Give It AAdyangNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in ScienceDocument6 pagesLesson Plan in Scienceesang quettNo ratings yet
- Looking After Plants: 1.1 Plants and Their PartsDocument10 pagesLooking After Plants: 1.1 Plants and Their PartsUbaid KhanNo ratings yet
- Week 6 Reproduction - Print Page 5-8Document8 pagesWeek 6 Reproduction - Print Page 5-8Hart OlpendaNo ratings yet
- Camp's Botany by the Numbers: A comprehensive study guide in outline form for advanced biology courses, including AP, IB, DE, and college courses.From EverandCamp's Botany by the Numbers: A comprehensive study guide in outline form for advanced biology courses, including AP, IB, DE, and college courses.No ratings yet
- Unit 3 WorksheetDocument13 pagesUnit 3 WorksheetAly HassanNo ratings yet
- Advanced Animations in Animate CCDocument10 pagesAdvanced Animations in Animate CCAly HassanNo ratings yet
- Grade-5 Chapter-7 Answer KeyDocument2 pagesGrade-5 Chapter-7 Answer KeyAly HassanNo ratings yet
- G 7 3.11 Tissues and OrganDocument3 pagesG 7 3.11 Tissues and OrganAly HassanNo ratings yet
- Ans Biology Work Book1Document26 pagesAns Biology Work Book1Aly HassanNo ratings yet
- 3.10 NervesDocument2 pages3.10 NervesAly HassanNo ratings yet
- WB Unit 1Document9 pagesWB Unit 1Aly HassanNo ratings yet
- Answer - Physics - Work Book 1Document21 pagesAnswer - Physics - Work Book 1Aly HassanNo ratings yet
- Capaian Kinerja Peserta RSDocument14 pagesCapaian Kinerja Peserta RSAyu AzrinaNo ratings yet
- Cerebral Circulation Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument5 pagesCerebral Circulation Anatomy and PhysiologyMayrjun Lo JacosalemNo ratings yet
- Who BCT Bts 01 3Document37 pagesWho BCT Bts 01 3Deo Tarigan SilangitNo ratings yet
- Survey Kompetitor Oktober 2021Document9 pagesSurvey Kompetitor Oktober 2021Velin AzzahraNo ratings yet
- Mock Test For Entrance ExamDocument19 pagesMock Test For Entrance ExamAeris Strong100% (1)
- Pada Wanita MenstruasiDocument7 pagesPada Wanita MenstruasiLab RS MMCNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument6 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyJulianne B. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- PBMC Isolation ProtocolDocument1 pagePBMC Isolation ProtocolKartik BhamidipatiNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: Biology 0610/22Document16 pagesCambridge IGCSE: Biology 0610/22Aisha YousifNo ratings yet
- 5 Patcharee Komvilaisak - Approaching To Pancytopenia 24112017Document43 pages5 Patcharee Komvilaisak - Approaching To Pancytopenia 24112017Satvik BansalNo ratings yet
- Discuss The Indications and Complications of Blood TransfusionDocument32 pagesDiscuss The Indications and Complications of Blood TransfusionYetunde Shakirat Amoo-Tella100% (1)
- Multifibren UDocument6 pagesMultifibren UJoseline Alejandra Bravo Bravo0% (1)
- Define Arteries, Veins and Capillaries. Explain The Differences Between ThemDocument5 pagesDefine Arteries, Veins and Capillaries. Explain The Differences Between Themzeenat gaziNo ratings yet
- SGBAU B.Pharm 1 SEM Human-Anatomy-n-Physiology-I 2018Document2 pagesSGBAU B.Pharm 1 SEM Human-Anatomy-n-Physiology-I 2018Abhay DeulkarNo ratings yet
- Effect of Tranexamic Acid On Blood Loss in Pediatric Cardiac Surgery: A Randomized TrialDocument8 pagesEffect of Tranexamic Acid On Blood Loss in Pediatric Cardiac Surgery: A Randomized TrialBetão AviãoNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Methods For Analyzing Monoclonal Proteins - UpToDateDocument50 pagesLaboratory Methods For Analyzing Monoclonal Proteins - UpToDatechali90No ratings yet
- PBSDocument72 pagesPBSKavi KaviNo ratings yet
- ABO Blood Typing: Forward Typing (Glass Slide Method)Document2 pagesABO Blood Typing: Forward Typing (Glass Slide Method)Marj MendezNo ratings yet
- MK Hematology-LeukemiasDocument35 pagesMK Hematology-LeukemiasMoses Jr KazevuNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Three Plant Extracts ActivityDocument106 pagesEvaluation of Three Plant Extracts ActivityDrmirfat AlkashifNo ratings yet
- International Health Olympiad Reference Book Juniors PDFDocument188 pagesInternational Health Olympiad Reference Book Juniors PDFRajesh KrishnanNo ratings yet
- No Risk ScoreDocument4 pagesNo Risk ScorehenrisaatjianNo ratings yet
- Citizen CharterDocument21 pagesCitizen CharterVedhanayagiNo ratings yet
- 1996 Biology Paper I Marking SchemeDocument13 pages1996 Biology Paper I Marking Schemetramysss80% (5)
- Evaluation of The Ruminant Complete Blood Dell CountDocument26 pagesEvaluation of The Ruminant Complete Blood Dell CountDirección Científica Laboratorio VitalabNo ratings yet
- LAS Science 4 MELC 1 Q2 Week1Document10 pagesLAS Science 4 MELC 1 Q2 Week1Jing Pelingon Carten86% (7)
- Blood Grouping Brochure 2013 - Priced PDFDocument8 pagesBlood Grouping Brochure 2013 - Priced PDFmwenyeweNo ratings yet
- Biology Paper 1Document32 pagesBiology Paper 1Cameron DaviesNo ratings yet
Answer - Biology - Student Book 1
Answer - Biology - Student Book 1
Uploaded by
Aly HassanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Answer - Biology - Student Book 1
Answer - Biology - Student Book 1
Uploaded by
Aly HassanCopyright:
Available Formats
Answers Student book
1 Plants 2a The leaf reduced the light meter reading from
100 to 50.
1.1 Leaves, stems, and roots b The leaf blocked or absorbed some of the light.
1 Roots spread out for two reasons: to hold the 3 Any two points from: Plants on Mars would receive
plant firmly and to absorb more water and less sunlight because Mars is further away from the
minerals from the soil. Sun than Earth is. This would make it harder for
2 Broad, thin leaves can absorb plenty of sunlight plants to get the energy they need to make their own
for making food. food. This means that plants probably wouldn’t
3 The tubes in the stem allow the plant to transport grow as well on Mars as on Earth.
food and water. 4a The average mass of leaves was the same (0.22 g).
4 Desert plants’ swollen stems allow them to store b The average width of leaves in dim light was
water, which keeps them alive until it rains again. twice as big as (accept bigger than) the average
1.2 Questions, evidence, and explanations width of leaves in bright light.
1 Van Helmont observed that the tree he planted c In dim light, leaves need to be wider to collect
gained 73 kg but the soil it was growing in only enough light energy.
lost a few grams. He thought that if the plant took 5a The trees planted close together (10 per m2) grew
food from the soil, the loss from the soil should 50 cm more than those planted far apart (1 per m2).
equal the plant’s gain in mass. b Trees planted close together grow taller because
2 Van Helmont thought that plants must be made of other plants are blocking their light. Growing taller
water, because they won’t grow without it. increases their chances of getting enough light.
3 Woodward’s results don’t support van Helmont’s 6a The plant with green leaves grew 12 cm in
explanation. Woodward’s plants grew more 1 month. The plant with white and green leaves
in water with soil than in pure water. If plants grew 6 cm in 1 month.
needed only water, both sets of plants would have b Food is required for growth so the plant with
grown by the same amount. green leaves made more food.
4 Plants take something they need for growth from c Kazim’s evidence does support his explanation.
the soil, in very small quantities. If leaves contain more of the green substance they
5 Malpighi thought that plants make food in their can absorb more light energy and make more food.
leaves and transport it to other parts of the plant. 7a The amount of radioactive sugar in the leaves
6 Malpighi did not have strong evidence. He should decreased and the amount in the tomato fruit
have repeated his experiment more than once increased.
and tested other plants. He did not have enough b Yes. Roots must take food from the leaves. They
evidence to show that the plant stopped growing cannot make their own food because they don’t
because it had no leaves. absorb light.
7 Trees are made of water, a gas from the air, and 8a The roots of the plants receiving 100 cm3 of
small amounts of material from the soil. Van water a day grew 20 cm but the roots of the plants
Helmont proved that most of the material trees receiving 500 cm3 grew only 10 cm. The roots of
are made from does not come from the soil – they the plants receiving less water grew twice as long
only take in water. Woodward showed that they do (accept longer).
take small amounts of material from soil. Malphigi b Longer roots help plants collect more water from
showed that seedlings cannot grow without leaves. deeper soil.
Hales found that they take in a gas from the air. 9a The total crop growth has decreased over 5 years
from 24 to 11 tonnes; it decreased more rapidly in
1.3 Review later years.
1a Plants take in light energy from the Sun. b The farmer could plant the same crop in a
b Any two differences, e.g. the leaves are different different field with fresh soil. All the other
shapes and different sizes. conditions that affect plant growth, such as light,
c Any two similarities, e.g. they are all thin, flat, amount of rain, and temperature, should be the
and green, have tubes (veins) running through same in both fields. If a bigger crop grows in the
them, or are attached to stems. new field, it would support the explanation.
Downloaded By Success Groups
HF92 © Oxford University Press 2013: this may be reproduced for class use solely for the purchaser’s institute
Checkpoint_Biology_TG_SB_Ans.indd 92 28/11/2013 16:03
2 Humans 6 The digestive system breaks down food into
smaller particles so that they can pass into the
2.1 The human skeleton bloodstream. Food particles that cannot be
1 Your skeleton protects vital organs such as the digested are excreted in faeces.
heart and lungs, helps to support your body, and
2.4 The circulatory system
allows you to move.
1 Harvey doubted Galen’s ideas because he
2 Your brain is protected by the solid bone in your
watched animals’ hearts beating and pumping
skull. Your heart and lungs are protected by your
out massive amounts of blood – it could never be
rib cage.
made that fast.
3 Knee and elbow joints are hinge joints.
2 Ibn al-Nafis’s discoveries were not known in
4 Hip and shoulder joints are ball-and-socket joints.
Europe when he made them because nobody
5 Knee joints are hinge joints which allow you to
translated his work.
bend and straighten your legs. Hip joints are ball-
3 Three types of blood vessel are arteries, veins
and-socket joints which allow you to swing your
and capillaries.
legs round in many directions.
4 Blood leaving the lungs returns to the heart,
6 The diagram should show two bones held together
which pumps it around the body. This supplies
by ligaments like the left-hand diagram at the
cells with oxygen. After travelling around the
bottom of page 14 in the Student book. Two
body, the blood returns to the other side of the
features should be labelled: synovial fluid inside the
heart. The heart sends it back to the lungs to pick
joint and cartilage covering the ends of the bones.
up oxygen, and the cycle repeats again.
7 a bone – hard, b cartilage – smooth,
5 Arteries carry blood away from your heart and
c ligaments – flexible.
veins carry it back to your heart.
2.2 Muscles and movement 6 If the heart stops beating, blood stops circulating.
1 Muscles are attached to bone. When they contract, The delivery of oxygen and nutrients stops so
they pull the bone. tissues cannot carry out respiration. They do not
2 Antagonistic muscles pull in opposite directions. get the energy they need to survive, so they die.
3 The muscle on the front of your arm (the biceps)
2.5 Studying the human body
feels firmer. To hold this position the biceps
1 Haematologist – they run tests on blood samples to
muscle must contract and the triceps muscle relax.
look for the changes different types of illness cause.
4 The muscle at the back of your leg (hamstrings)
2 Students should choose one from the following.
contracts to bend it. The muscle at the front of
Neuroscientist – they research brain diseases to
your leg (quadriceps) contracts to straighten it.
find the best treatments to aid their recovery.
5 The strong cord is a tendon. It attaches muscle
to bone so that the bone moves when the muscle Dietitian – they advise patients how to improve
contracts. their health and fitness by eating the right
6 Messages from your brain tell muscles when to combination of nutrients.
contract. These electrical messages are sent down 3 Students should choose two from the following.
nerves in your spinal cord to the smaller nerves Audiologist – they investigate hearing and
that carry the message to each muscle fibre. balance disorders in patients. They perform tests
to work out whether a patient has hearing loss and
2.3 Organ systems
can find out how severe their deafness is.
1 The nervous system controls how you respond to
your surroundings. Cardiologist – these are doctors who have
2 Messages are sent along nerves from taste buds in specialised in assessing, diagnosing, and treating
your tongue to your brain. Your brain processes the heart and circulatory problems.
information and decides how to react. Then your Dermatologist – these doctors are involved in
brain sends messages to the muscles in your mouth assessing and managing diseases involving the
to make you to spit out the fruit. skin, hair, and nails.
3 The digestive system takes in glucose (nutrients). Pathologist – these scientists study disease by
4 Oxygen is needed for respiration, which produces examining tissue samples under a microscope.
the energy your body needs. They also perform autopsies on people who have
5 As blood passes through your lungs, it exchanges died to find out what killed them.
carbon dioxide for oxygen. This is gas exchange.
© Oxford University Press 2013: this may be reproduced for class use solely for the purchaser’s institute 93
Checkpoint_Biology_TG_SB_Ans.indd 93 28/11/2013 16:03
2.6 Extending lives d A is the brain.
1 Not enough people opt to donate their organs for e The brain belongs to the nervous system.
transplantation. Only patients whose heart stops 5a As blood enters the lungs, it picks up more
working or whose brain is severely damaged are oxygen and gives up carbon dioxide. The carbon
suitable donors. People who require a transplant dioxide concentration in the blood drops by
are often very sick and cannot survive very long 10 units and the oxygen concentration increases
with their damaged organ. by 40 units.
2 A transplant patient’s body recognises the b Breathed out air contains more carbon dioxide
donated organ is not theirs. Their body would and less oxygen.
reject (destroy) the donated organ if they did not c After leaving the lungs, blood travels back to the
take drugs to stop this happening. heart. The heart pumps it around the body (to
3 Kidneys can be transplanted from living donors, every tissue) to deliver oxygen. Then it returns
as we each have two kidneys, but can survive to the heart and is pumped back to the lungs to
with one. Hearts can only come from deceased collect more oxygen.
donors, so it is harder to find enough hearts to d If patients cannot get enough oxygen, less
transplant. respiration takes place in their tissues, and they
4 Becoming a living donor is risky. release less energy.
5 Organs built from a person’s own tissues are not 6a Kevin is wrong.
rejected so the transplant patients don’t need b Respiration occurs in all your tissues. It is a
to take drugs and have less chance of suffering chemical reaction that releases energy from glucose
complications. using oxygen. Gas exchange occurs in the lungs
when oxygen from the air enters the blood and
2.7 Review
carbon dioxide passes from the blood to the air.
1a Karis: respiratory system; Amarjit: cardiovascular
7 The ends of her fingers did not get enough oxygen
system; Nadeen: nervous system; Ali: digestive
for respiration. Their tissues died because they
system; Simon: skeletal system.
lacked energy.
b Karis and Amarjit must be treated first. These
8a As an adult’s age increases, the recommended
patients are not getting enough oxygen to their
heart rate needed during exercise decreases.
tissues. Karis is struggling to breathe so won’t
b 92 beats per minute
be taking in enough air into her lungs. Amarjit
c Muscles require more energy during exercise
has no pulse, which means that his blood is not
(in order to contract more quickly and strongly).
circulating, so oxygen isn’t being delivered to
To release this extra energy, they need a greater
his cells. Without oxygen, these patients will die
supply of oxygen (and glucose). This is achieved
quickly because they cannot carry out respiration.
by increasing the heart rate so that blood is
2a The ball and socket joint on the left lets a
pumped around more quickly.
limb swing in every direction.The hinge joint
d Arteries carry blood away from the heart.
on the right lets a limb (arm or leg) bend and
e The heart is a double pump because one side
straighten.
pumps blood through the lungs and the other
b Students should include two from the following.
pumps blood around the rest of the body.
In both joints, the ends of bones are covered in
f Veins return blood to the heart.
cartilage to allow them to slide over each other
9a As age increases, the average reaction time also
smoothly.
increases. (There is a large jump in the reaction
Both joints contain synovial fluid to reduce friction. times between the 25–34 age group and the
Both joints use ligaments to hold the bones together. 35–44 age group.)
3a The leg bends at the knee.
b Muscle B (quadriceps) contracts. Muscle A b The driver’s eyes sense light reflected from the
(hamstrings) relaxes. scene of the accident. They send electrical messages
c Muscles can only pull on bones. They cannot to his brain. His brain interprets the messages and
push. So pairs of muscles pull your leg in decides how to respond. It sends messages down
opposite directions. the spinal cord and along smaller nerves to the
4a C muscle fibres in his leg to make his foot move and
b The heart belongs to the circulatory system. press down on the brake.
c The circulatory system circulates blood to every
part of the body (to supply the glucose and
oxygen needed for respiration).
94 © Oxford University Press 2013: this may be reproduced for class use solely for the purchaser’s institute
Checkpoint_Biology_TG_SB_Ans.indd 94 28/11/2013 16:03
10a The athlete’s blood glucose rises rapidly after 4 Bacteria are best seen using an electron
drinking a glucose drink (up to around 188 mg/dm3), microscope. They are very small but electron
then falls again. The athlete’s blood glucose microscopes allow us to magnify things up to
rises much more slowly after a meal (reaching 1 million times.
a maximum of 120 mg/dm3) and remains at 5 Viruses are not living things because they do
this level for about an hour, before it returns to not carry out the seven characteristics of living
baseline levels. things. They can only reproduce inside other
b The digestive system breaks food down into living things.
smaller particles and absorbs these into the blood.
3.3 Louis Pasteur
c The particles in the glucose drink are small enough
1 The process is called pasteurisation.
to be absorbed into the blood. The meal contains
2 Bacteria use sugar from milk for respiration and
larger particles that need to broken down in the
make lactic acid as a waste product. The lactic
digestive system before they can be absorbed.
acid causes milk to turn sour.
11a Bones support your body; protect vital organs
3 Pasteurised milk lasts longer because it contains
like your brain, heart, and lungs; and help you
fewer micro-organisms and these produce less
to move.
lactic acid.
b The 10–19 age group break bones in their feet
4 Warm, damp conditions are ideal for the growth
most often. The 60–69 age group break their hips
of micro-organisms. The leaves shrink because
most often.
micro-organisms are using nutrients from the
c The 10–19 age group break bones in their lower
leaves for respiration.
leg 4 times more often than the 60–69 age group.
5 Enough sugar and oxygen need to be added to the
fermenter to allow the yeast to respire.
3 Cells and organisms 3.4 Testing predictions
3.1 The characteristics of living things 1 The rotten meat ‘spontaneously generated’ the
1 M – movement; R – respiration (reproduction) maggots – they were created by the rotting meat.
S – sensitivity; G – growth; R – reproduction 2a Both pieces of meat would spontaneously
(respiration); E – excretion; N – nutrition. generate maggots as they rotted.
2 Plants make their own nutrients from water and b Pasteur would predict that only the meat in the
carbon dioxide using light energy. Animals get open jar would rot, as micro-organisms from
their nutrients by eating plants and other animals. the air were able to reach it and break it down.
3 Animals need to move around so that they can 3 If nutrients ran into the S-shaped tube, the
find enough food to eat. Plants make their own micro-organisms would be able to reach them.
food and so they do not need to move around. They could use the nutrients to respire and the
4 The seeds use nutrients stored inside them to liquid would turn cloudy.
respire. Respiration produces carbon dioxide 4 The crushed grapes would ferment. The yeast on
and releases energy. Some of the energy is the skin of the grapes would now be in contact
released as heat. with the grape juice and could ferment it. If the
5 Students’ answers need to show awareness of the juice was extracted from inside the grape, the
seven life processes and suggest ways to test for yeast on the grape skin would not be present so
them. For example: gently touch the flatworm no fermentation would occur.
to see if it moves and is sensitive to touch; make 5 You could stop a mixture of yeast, sugar, and
repeat observations/measurements to test whether water fermenting by boiling it to destroy the yeast.
it moves/grows/reproduces; look for evidence 6 A mixture of sugar and water turns cloudy if
of excretory products such as faeces and urine; micro-organisms grow in it.
keep it in a closed container and test whether it 3.5 Useful micro-organisms
removes oxygen from the air for respiration or 1 Yeasts are used to make bread soft and spongy.
adds carbon dioxide. 2 Lactobacillus bacteria are used to make yoghurt.
3.2 Microbes 3 The yeast increases the dough volume from
1 Bacteria, fungi, protozoa, algae. 10 cm3 to 69 cm3 (by 59 cm3).
2 Algae photosynthesise to make their own food, 4 Students should plot a line graph and join the
like plants do. points with a smooth curve.
3 Many protozoa resemble tiny animals because
they eat other micro-organisms. (Protozoa can
also take in nutrients from their surroundings.)
© Oxford University Press 2013: this may be reproduced for class use solely for the purchaser’s institute 95
Checkpoint_Biology_TG_SB_Ans.indd 95 28/11/2013 16:03
80 5 Evidence A: Sam; evidence B: Tomas;
evidence C: Maria.
dough volume (cm3) 60 6 40 °C
7 Sam’s method – it allows the volume of carbon
40 dioxide to be measured most accurately.
3.7 Harmful micro-organisms
20
1 Micro- Diseases caused How they get
0 organisms into the body
0 10 20 30 40 50 60 fungi ringworm, direct contact
temperature (°C) athlete’s foot
Between 10 and 30 oC, the dough volume protozoa malaria, sleeping from an insect
increases as the temperature rises. Between 30 sickness, bite (vector)
and 50 oC, the dough volume decreases as the leishmaniasis
temperature rises. bacteria typhoid, food consuming
5 The pH of milk drops from from 6 to 4.2 when it poisoning contaminated
is fermented for three days. food or drink
6 Many fungi and bacteria are involved in its
2 Two diseases caused by viruses are: colds/flu,
production, releasing a mixture of chemicals as
caught by breathing in virus particles; hepatitis C,
they ferment the cocoa. The length of time the
caught from contaminated needles.
microbes are left to ferment will affect how much
3 Ringworm: Avoid head to head contact, or sharing
of each chemical is produced and affect the taste
brushes and combs.
of the chocolate. If it is left too long, fungi can
Typhoid: Always wash your hands before eating.
ruin its flavour.
Only eat food that has been cooked thoroughly.
3.6 Planning investigations Only drink bottled water or water which has been
1 Finding the best conditions for the growth of boiled and then cooled.
each micro-organism allows scientists to obtain Malaria: Use mosquito repellent, take malaria
the maximum amount of product in a given time, prevention tablets, sleep under a mosquito net.
which makes the process more efficient.
Hepatitis C: Always use sterile needles when
2 One from: the mass of sugar (nutrients); the
injecting or taking blood. (Avoid having a tattoo
number of other yeast present; the pH.
or body piercing.)
3 Students should produce a diagram of
the student’s apparatus and describe the 3.8 Plant and animal cells
measurements needed. 1 Students should draw a simple animal cell
Tomas – test tubes of yeast/sugar solution covered diagram with the nucleus, cytoplasm, and cell
by balloons: measure the diameter of the balloon membrane labelled.
after a set time. 2 Students should label: A – chloroplast;
Sam – flask of yeast/sugar solution connected B – nucleus; C – vacuole; D – cytoplasm;
to a gas syringe: measure the volume of carbon E – cell membrane; F – cell wall.
dioxide produced after one hour. 3 Chloroplasts (chlorophyll).
Maria – test tubes of yeast/sugar solution: measure
the depth of the bubble layer after a set time.
Grace – flask of of yeast/sugar solution with a
delivery tube dipping into a test tube of water:
count how many bubbles escape in one minute.
Moses – flask of of yeast/sugar solution with
a delivery tube dipping into a test tube of
limewater: measure how long it takes for the
limewater to go cloudy.
4 All students need to control the mass of yeast,
mass (and type) of sugar, volume of water,
amount of stirring, and the apparatus used.
96 © Oxford University Press 2013: this may be reproduced for class use solely for the purchaser’s institute
Checkpoint_Biology_TG_SB_Ans.indd 96 28/11/2013 16:03
4, 5 Part of cell Function Plant, 2 It is hard to see individual cells because billions
animal, are packed together in the brain and each cell has
both? thousands of connections to other cells.
3 Light-detecting cells contain molecules that
nucleus contains genes, which both
change shape when light hits them. Sound-
control the cell
detecting cells contain hairs which vibrate when
cytoplasm where most of the cell’s both they detect a sound. Both changes make the
chemical reactions cells release chemicals which make nerves send
take place electrical messages to the brain.
cell controls what enters and both 4 Molecules in your light-detecting cells change
membrane leaves the cell shape as they detect light from the car these
chloroplast captures the light energy plant cells release chemicals nerve cells detect
used to make food the chemicals and send an electrical signal to
cell wall keeps the cell firm when plant your brain your brain interprets the signals
the vacuole pushes new electrical signals pass along nerve cells
against it to the muscles in your leg these nerve cells
vacuole helps to support the cell plant release chemicals your muscle cells detect the
by pushing against the chemicals and contract you jump out of the way.
cell wall 3.11 Tissues and organs
1 From smallest to largest: cell, tissue, organ,
6 If the plant is not watered, the cell vacuoles shrink
organ system.
and do not push against the cell wall. The cells
2 Tissues contain one type of cell. Organs contain
lose their firmness so the plant is unable to stand
more than one sort of tissue.
up straight.
3 Students should name one of the following.
3.9 Specialised cells Connective tissues; they hold other tissues together.
1 Students should draw each cell and explain why it Blood tissues; bring food(glucose) and oxygen.
is good at its job. 4a Tissues that make the heart beat – nervous tissue,
Red blood cell – small and round: small and muscle tissue.
flexible to squeeze through narrow blood b Tissues that give the inside of the heart its
vessels; no nucleus/packed full of haemoglobin required features – tough tendon tissue, smooth
to carry oxygen. lining tissue.
Muscle cell – long and thin: full of fibres that c Tissue that protects the heart muscle – fatty tissue.
allow them to contract (shorten) to pull on bones 5 Four tissues are visible in the root: xylem;
and cause movement. phloem; connective tissue; root hairs. The xylem
carries water and soluble minerals up from the
Fat cell – large and round: full of fat to act as a
roots. The phloem carries nutrients such as sugar.
food store; good insulator to keep you warm.
6 Muscle tissue with long thin cells that can
Bone cell – small with thin strands pointing in contract to cause movement.
every direction: produce fibres to attract minerals Bone tissue with cells that attract minerals to
and form bone. build a solid support.
Root hair cell – rectangular with one long, thin Nervous tissue with cells that carry electrical
extension: provide a large surface area to speed signals to allow the hand and arm to move or
the absorption of water and minerals. sense things they touch.
2 Students should draw each cell and describe Blood tissue to carry oxygen and nutrients to
where it would be found. other cells.
A – skin cell; covering the body.
Fat tissue to reduce heat loss from (insulate) the
B – nerve cell; in the nervous system. arm and protect other tissues from damage.
C – cilliated cell; in the lungs. Connective tissue to hold the other tissues together.
3.10 Nerves
1 Students should draw and label a long thin nerve
cell with end plates in contact with one or more
long thin muscle cells.
© Oxford University Press 2013: this may be reproduced for class use solely for the purchaser’s institute 97
Checkpoint_Biology_TG_SB_Ans.indd 97 28/11/2013 16:03
3.12 Review c The cell wall keeps the cells firm when their
1 Students’ answers need to show awareness of up vacuoles are filled with water.
to three of the seven life processes and suggest d The nucleus controls the activity of the cell.
ways to test for them. For example: gently touch 9a A influenza/flu/cold; B malaria; C food
it/make a sound/shine light on it to see if it is poisoning/typhoid.
sensitive and responds by moving; make repeat b A through the air in droplets from coughs/sneezes
observations/measurements to test whether it which can be breathed in.
grows/reproduces; look for evidence of excretory B by vectors/mosquitoes which transfer the
products in the water around it; keep it in a protozoa to new victims when they bite.
closed container and test whether it removes C by consuming food or drink contaminated by
oxygen from the water for respiration or adds bacteria from faeces.
carbon dioxide. 10a When the soil mineral content is low, there are
2a A bacterium. more root hair cells per mm and the average root
B virus particle. hair length is (400 mm) longer than in soil with
C fungus. high mineral content.
b A and C are living. b Root hair cells increase the surface area of the
3a Micro-organism (bacteria/fungus). roots; so plants can take up water and minerals
b Micro-organisms remove dead plants and animals more quickly.
and their wastes; this returns minerals in the 11a Organ because it contains several different tissues
organic waste to the soil/can be reused by plants. working together.
4a Bacteria obtain energy by converting the sugar in b Tissue because most of its cells are the same.
milk to lactic acid; which reduces the pH of the c Cell because it has a nucleus and cytoplasm.
milk/gives yoghurt its flavour. d Tissue because it contains more than one muscle
b Students’ answers need to include two from: cell/fibre.
number of bacteria added; volume of milk added;
type of milk. 4 Living things in their
c She can test the pH of the mixture. When the
yoghurt is ready, the pH should be 4.5. environment
d 32–34 °C 4.1 Habitats
5a The dough with the yeast added increased in 1 Kangaroo rats – desert; sloths – rainforest;
height from 12 mm to 42 mm (by 30 mm); the llamas – mountains.
dough without yeast did not change. 2 Students’ answers should name three animals,
b Yeast uses the sugar in the flour for respiration give a brief description of their habitats, and list
and produces carbon dioxide gas as a byproduct two or three adaptations that help each animal
of this reaction. (The bubbles of carbon dioxide survive in its habitat, e.g. antelopes; African
cause the dough to increase in volume.) savannah, which is grassland with widely spaced
c One from: add more yeast/sugar; warm trees; eyes near the sides of their head to spot
the mixture. predators; long, thin legs for speed; tan-coloured
6a Food is heated for long enough to kill most of the coats for camouflage.
micro-organisms present whilst preserving the
flavour. 4.2 Food chains
b It increases the time milk stays fresh. Fewer 1 Any one from: acacia tree giraffe lion;
micro-organisms are present so it takes longer for acacia tree/grass impala cheetah/leopard;
them convert the sugar in milk to lactic acid and grass zebra lion. The giraffe/impala/zebra
turn it sour. should be labelled herbivore. The lion/cheetah/
7a An open bottle would allow micro-organisms in leopard should be labelled carnivore.
from the air. These would use the sugars in fruit 2 Any one from: acacia tree giraffe lion;
juice for respiration and spoil it. acacia tree/grass impala cheetah/leopard;
b Carbon dioxide. grass zebra lion. The giraffe/impala/zebra
c Fermentation is faster at a higher temperature. should be labelled prey. The lion/cheetah/leopard
d After 8–10 days. should be labelled predator.
8a Chloroplasts carry out photosynthesis to make food 3 Any one from: acacia tree giraffe lion;
for the plant, which it respires to release energy. acacia tree/grass impala cheetah/leopard;
b The cell membrane controls what enters and grass zebra lion. The acacia tree/grass
leaves the cell. should be labelled producer. All the animals
should be labelled consumer.
98 © Oxford University Press 2013: this may be reproduced for class use solely for the purchaser’s institute
Checkpoint_Biology_TG_SB_Ans.indd 98 28/11/2013 16:03
4 The arrows represent the direction of energy flow 2 Negative: fridges and spray cans released CFCs
from producers to top predators. into the atmosphere which destroyed ozone/
5 A prey animal such as the impala uses some of caused a hole to appear in the ozone layer. Positive:
the energy it gets from the producers it eats to governments banned the use of CFCs in all products
build muscles and fat. When a predator such as a and over time the ozone layer should recover.
lion eats the prey, the energy passes to them. 3 Negative: burning fuels containing sulfur releases
6 The Sun provides the energy producers need an acidic gas that produces acid rain, which
to make their own food, so it also keeps damages trees and aquatic life. Positive: scientists
consumers alive. can now remove the sulfur from fuels before
7 The herbivores will have less food; their numbers they burn them and neutralise any acidic gases
could decrease if they starve, move away, or die released to prevent acid rain from forming.
faster than they reproduce. 4 Carbon dioxide acts like a greenhouse. It allows
8 The number of herbivores would increase, as they sunlight to enter and heat the ground but stops some
have fewer predators hunting them. The number of the heat from the ground escaping. If carbon
of plants would decrease, as the larger number of dioxide levels continue to rise, more heat will be
herbivores will eat more plants. trapped in the Earth’s atmosphere, causing the
9 Students should produce a valid Antarctic food temperature of the Earth to rise. This will damage
chain, e.g. phytoplankton krill fish penguin/ habitats and the organisms that inhabit them.
sea bird. 5 Any two from: cut down fewer trees/plant more
trees to take in more carbon dioxide; burn less
4.3 Feeding ourselves
fossil fuel to cut the release of carbon dioxide into
1 Food chains can be disrupted by habitat
the atmosphere.
destruction (which removes producers); pollution
6 Clouds reduce the amount of sunlight reaching
(which can kill plants or animals); invasive
the Earth, and mirrors reflect sunlight away from
species (which compete with the plants and
the Earth; less sunlight reaching the Earth means
animals in existing food chains).
there is less heat to be trapped by carbon dioxide.
2 We can get more food without damaging other
4.5 Preventing extinction
food chains by growing more food on the same
1 Extinction is caused by animals dying faster than
amount of land, e.g. by growing algae in tanks
they can reproduce due to: pollution of rivers;
to produce fuel and food for animals, so we have
killing by poachers; destruction of habitats to
more space to grow food crops; by building tall
clear land for farming or for building homes.
greenhouses that take up less land.
2 Wildlife sanctuaries protect endangered animals
3 Fertilisers increase crop growth by supplying
from poachers as the animals there are guarded.
minerals to plants, but they kill fish if too much
3 Students should describe a habitat, name a
runs into rivers. Herbicides kill weeds to stop
plant or animal under threat, and suggest how
them competing with crops for nutrients, but they
the organisms living there could be protected,
also destroy wild plants. Insecticides kill the pests
e.g. the rainforests of the southern Western
that eat crops, but they also kill beneficial insects
Ghats in India are being destroyed by humans
such as bees.
to provide space to grow crops and build
4 Students should give an example of an animal
homes. This endangers the Bengal tiger and
that has been affected by human activities,
the deer and antelope it feeds on. Bengal tigers
e.g. in India, mercury is released by burning
are also endangered due to poaching. These
coal in power plants. Rain carries the mercury
animals could be protected by building wildlife
into lakes, rivers, and the sea. Krill take in the
sanctuaries and protecting the animals from
mercury, which builds up inside them. Small
poachers. National parks could be set up in the
fish eat many krill and sharks eat many small
area to protect some of the remaining habitat.
fish. Sharks can accumulate enough mercury to
A captive breeding programme could be set up
poison them so their numbers have dropped.
to increase the number of Bengal tigers in zoos,
4.4 Changing the planet before releasing them back into the wild.
1 Our atmosphere lets us breathe, allows plants to 4 Breeding species in captivity allows the number
make food, shields us from harmful ultraviolet of individuals of that species to increase in a
radiation, and keeps the Earth at an ideal protected environment. These animals can be
temperature for life. Changing our atmosphere reintroduced into the wild once their numbers
could damage life on Earth. have increased enough.
© Oxford University Press 2013: this may be reproduced for class use solely for the purchaser’s institute 99
Checkpoint_Biology_TG_SB_Ans.indd 99 28/11/2013 16:03
4.6 Obtaining energy 4.8 Review
1 Non-renewable energy sources cannot be replaced 1a Any two from: the fennec fox has larger ears than
once they run out. Renewable sources of energy the arctic fox; the fennec fox is sand coloured
are constantly replaced. whilst the arctic fox is white; the fennec fox is
2 Non-renewable – coal, oil, gas. Renewable – any thinner than the arctic fox; the arctic fox has
three from: solar energy; biofuels; wind; moving thicker fur than the fennec fox.
water; geothermal energy. b The arctic fox has thicker fat to reduce heat loss.
3 Geothermal energy. c Any two from: the fennec fox would lose too
4a Solar energy/biofuels. much heat from its large ears; it would not be
b Solar energy. camouflaged/its predators would easily spot it;
c Geothermal energy. its fur/fat layer is too thin so it would lose too
d Moving water (hydroelectric power). much heat.
e Wind energy. 2a Any one from each category: carnivore – lizard/
hawk; herbivore – insect; producer – cactus;
4.7 Growing fuels
consumer– insect, lizard, hawk; predator – lizard,
1 Biodiesel comes from plant oils. Bioethanol
hawk; prey – insect, lizard.
comes from sugar cane.
b A rise in the number of foxes would cause the
2 Petrol releases carbon dioxide when it burns but
lizard population to reduce, as the foxes will
biofuels could be carbon neutral, which would
need more food. This means less food is available
reduce pollution; petrol is non-renewable because
for the hawk so it will raise fewer offspring
it is made from oil, but biofuels are renewable.
successfully.
3 Plants release carbon dioxide when they burn, but
c If all the lizards died, the insect population would
when crops are replanted, they take in the carbon
increase, as they would have fewer predators. The
dioxide that was released into the atmosphere. So
cactus population would then decrease as there
biofuels should not increase the amount of carbon
would be more insects to eat them.
dioxide in the atmosphere.
3 Any two from: they have long roots near the
4 Land is cleared to make space to grow biofuels/oil
surface with lots of root hair cells to increase their
palms by starting fires which release large quantities
surface area so they can take water quickly when it
of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere, and not
rains; their spines deter herbivores; having spines
enough oil palms are grown to take in all the carbon
instead of leaves cuts their surface area and reduces
dioxide that was released. It also takes more energy
water loss; they store water in their swollen stems.
to convert plant material into biofuels than it does to
4a Any two from: the population fell slowly between
convert oil to petrol and most of the energy needed
1900 and 1960 (from 320 000 to 275 000); the
for this is obtained by burning fossil fuels.
population fell rapidly between 1970 and 2010
5 Fungi make enzymes that can break down the
(to 10 000); since 2010 the population has fallen
plant cell walls. This allows more of a plant’s
more slowly.
biomass to be turned into sugar and fermented
b Between 1960 and 1980 their rainforest habitats
to make bioethanol.
were destroyed more rapidly to make room for
6 Students should give one advantage and one
crops/to provide timber.
disadvantage of each fuel.
c One from: people have become more aware of
Bioethanol advantages: cheaper to produce in
habitat destruction; the orang-utans’ habitats
warm countries; could be carbon neutral; could be
have been protected; they have been moved to
made from waste plant material.
sanctuaries.
Bioethanol disadvantages: uses fungal enzymes
which are expensive; yields are low if fungal
enzymes are not used.
Biodiesel advantages: algae grow quickly;
they could use up the carbon dioxide produced
by power stations to reduce pollution;
photobioreactors can be set up anywhere in the
world without taking up much space.
Biodiesel disdvantages: a lot of space is
required to grow the algae in water; algae could
be contaminated by other micro-organisms;
photobioreactors are expensive.
100 © Oxford University Press 2013: this may be reproduced for class use solely for the purchaser’s institute
Checkpoint_Biology_TG_SB_Ans.indd 100 28/11/2013 16:03
5a d Renewable energy sources do not release carbon
dioxide, or are carbon neutral. This means that
aphid numbers they won’t add carbon dioxide to the atmosphere.
Carbon dioxide causes global warming/reducing
the amount of carbon dioxide released decreases
global warming.
10a The more ozone there is in the atmosphere the less
harmful ultraviolet radiation reaches Antarctica;
the amount of ozone in the atmosphere fluctuates
but has shown an overall drop.
time
b The ozone layer absorbs ultraviolet radiation; so it
reduces the amount that reaches the Earth.
b 350
c Any one from: ultraviolet light can damage plants;
300
ultraviolet light can cause skin cancer in humans.
250
aphid numbers
200 5 Variation and classification
150
5.1 Variation
100
1 Any five visible differences, e.g. skin colour, hair
50 colour, height, body mass, eye colour.
0 2 Any five variables that can be tested, e.g.
1900 1920 1940 1960 1980 2000 2020
different ways of walking, voices, blood groups,
time
fingerprints, iris patterns.
Any two from: 3 Features that show discontinuous variation, such
A graph showing the ladybird population is as blood groups, can only take certain values.
always lower than the aphid population; the graph Those that show continuous variation, such as
has a similar shape to the aphid graph; the graph height, can take any value within a certain range.
peaks later. 4 Any three features that show continuous variation,
c One from: there was not enough wheat left so the e.g. height, body mass, foot length, arm or leg length.
aphids starved/stopped reproducing; ladybirds ate 5 On a frequency chart, the height of each bar
them faster than they could reproduce. shows the number of people in each category.
6a Timmy controlled the seed type, the volume of water 6 Everyone’s fingerprint has a unique pattern of lines
given each day and the amount of light they received. so fingerprints can be used to identify criminals.
b The plant receiving acid rain grew 5.5 cm less 7 Allow any choice as long as it is justified, e.g. an
than the plant given pure water, so acidic rain iris scanner would be best as iris patterns show
restricts plant growth; or acid rain causes leaves more variety than fingerprints; they take longer to
to turn brown and reduces photosynthesis/growth. scan than fingerprints but this could be done easily
7a The carbon dioxide concentration increased whilst sitting at a computer; scanning fingerprints
from 315 to 380 ppm (by 65 ppm) between may be difficult if the keyboard or fingers are dirty.
1960 and 2000. Or a fingerprint scanner would be best because they
b Increased burning of fossil fuels, releasing more are cheaper and most computers don’t need the
carbon dioxide; increased deforestation reducing very high security that iris scanners can provide.
the amount of carbon dioxide taken up by plants. 5.2 Causes of variation
8a The average temperatures in the Arctic and the rest 1 Any two from: hair colour; skin colour; eye colour.
of the world have increased from 1950 to 2000. The 2 Genes control cells and cells build your tissues
temperature has increased much more (by 1.25 oC) and organs, so genes influence your features.
in the Arctic than in the rest of the world (0.5 oC). 3 Any two from: eye colour; blood group;
b The ice will melt faster each year. earlobe shape.
c Polar bears cannot catch seals in open water, so as 4 Environmental variation.
the ice melts sooner, they will catch fewer seals. 5 The lower leaves receive less sunlight.
9a 86% 6 No – a bonsai tree is only small because it does not
b This figure will decrease in the future because get enough light, water, and minerals to grow bigger.
fossil fuels are running out, so we need to use The genes in its seeds could produce a full-sized tree
more renewable sources of energy. if the plant gets enough light, water, and minerals.
c Any four from: geothermal energy; moving water; 7 Genes and the environment both influence skill at
wind energy; solar energy; biofuels. football, health, and body mass.
© Oxford University Press 2013: this may be reproduced for class use solely for the purchaser’s institute 101
Checkpoint_Biology_TG_SB_Ans.indd 101 28/11/2013 16:03
5.3 Species 3 Students could choose any two animals from
1 Members of a species can breed with each other different vertebrate groups, e.g. a crocodile is
and produce offspring that are able to breed. a reptile because it has dry, scaly skin and lays
2 Members of a species do not always look similar, waterproof eggs on land. A pike is a fish because
e.g. there are many breeds of dog/cat that look it has gills and fins and lays its eggs in water.
very different from each other. 4 Students could choose any two land animals
3 Mules are not able to breed; they are infertile from different vertebrate groups, e.g. a panda
hybrids; the offspring of a horse and a donkey. is a mammal because it has fur, gives birth to
4 Breed the male and female wild cat together. Wait live young, produces milk to feed them, and is
until their offspring reach reproductive age and see warm blooded. An anaconda is a reptile because
if they are able to produce offspring of their own. it has dry, scaly skin, is cold blooded and lays
If they can, they are fertile. This means the male waterproof eggs on land.
and female wild cat came from the same species. 5 Mammals need more food than other vertebrate
5 We can’t be sure how many species there are groups because they are warm blooded.
because we haven’t found them all yet, and it is They need extra energy to keep their body
difficult to decide whether similar animals belong temperature constant.
to the same or different species. 6 Whale – unlike most mammals they have very
6 The first name Panthera is given as it is large little body hair.
cat that roars. The second name could be albus, Bat – unlike most mammals they can fly.
which is white in Latin. Snake – unlike most reptiles they do not have legs.
Penguin – unlike most birds they cannot fly.
5.4 Classification
1 73% 7 Olm – amphibian, but lives only in water and
2 There are far more invertebrate species (70%) has gills.
than vertebrate species (3%). Platypus – mammal, but lays eggs instead of
3 Vertebrates have a backbone; invertebrates do not. giving birth to live young.
4 Arthropods make up 60% of all the species on Caecilian – amphibian, but lives hidden in the
Earth. Most arthropods are insects and one-third ground instead of in water. They also give birth
of all insects are beetles. to live young, instead of laying eggs.
5 A spider: arachnid because it is an arthropod with Armadillo – mammal, but has a low body
eight legs. temperature.
B beetle: insect because it is an arthropod with 5.6 Classification of plants
six legs. 1 Students should draw simplified diagrams of each
C snail: mollusc because it has a single of the four types of plant shown on page 79 of the
muscular foot. Student book.
D worm: annelid because its body is divided 2 The diagrams should be labelled as follows:
into segents. moss – no roots/veins; fern – reproduces using
E millipede: myriapod because it is an arthropod spores; conifer – reproduces using seeds made in
with a long body divided into segments. cones; flowering plant – reproduces using seeds
F stick insect:insect because it is an arthropod made in flowers.
with six legs. 3 Plant A: fern – reproduces using spores.
G shrimp: crustacean because it is an arthropod Plant B: conifer – reproduces using seeds made
with with two pairs of antennae. in cones.
H crab: crustacean because it is an arthropod with
Plant C: moss – no roots/veins.
two pairs of antennae.
Plant D: flowering plant – reproduces using seeds
5.5 Vertebrates made in flowers.
1 a Dolphins – mammals.
4a Fern – grass and the flowering tree both produce
b Snakes – reptiles.
flowers.
c Sea turtles – reptiles.
b Flowering tree – plants in the other two groups do
d Sea horses – fish.
not produce flowers.
e Penguins – birds.
c Grass – moss and fern produce spores and grow
f Whales – mammals.
in damp, shady places.
g Komodo dragons – reptiles.
d Moss – conifers and ferns have roots and veins in
2 Typical mammalian features include being warm their stems to carry water and minerals up the plant.
blooded, giving birth to live young which are fed e Algae – ferns and flowering plants both have
on milk, having hair or fur. roots, stems, and leaves
102 © Oxford University Press 2013: this may be reproduced for class use solely for the purchaser’s institute
Checkpoint_Biology_TG_SB_Ans.indd 102 28/11/2013 16:03
5 Moss. 8a B (octopus), C (beetle).
6 The arrival of the gulls allowed flowering plants b They all have a backbone.
to grow as they deposited seeds from mainland c A (snake), D (turtle).
that had passed through their digestive systems. d Any two from: dry, scaly skin; lay eggs on land;
are cold blooded; breathe using lungs.
5.7 Review
9a Cow – mammal.
1a Green.
b Dolphin – mammal.
b Any feature than shows discontinuous variation,
c Penguin – bird.
e.g. blood group, gender, shoe size, hair colour.
d Frog – amphibian.
2a 38%
10a It has fur.
b Any two features that show discontinuous
b It lays eggs.
variation, e.g. height, body mass, foot length,
11 Mammals are covered with hair or fur, give birth
limb length.
to live young, and feed their young on milk.
3 60 12 Annelid because it has a segmented body.
13 Flies are insects because they have six legs.
50
Spiders have eight legs, so they are arachnids.
percentage of beetles
40 14a Invertebrate.
b Arthropod.
30 c Insect.
20 15 B (conifer).
16a Moss.
10 b Ferns.
c Conifers.
0
black dark pale
brown brown Stage 7 Review
Axes labelled. All points correctly plotted. 1a i D
4 50
ii F
iii C
40 iv E
percentage of beetles
b B (chloroplasts).
30 c A (nucleus), E (cell membrane), F (cytoplasm).
2a Bone.
20
b Any one from: attach to muscles to allow
10 movement; provide suport.
c Hinge joint.
0 d Muscles.
10–11 12–13 14–15 16–17 18–19
3a Hyacinth weevil nematode worm.
length (mm)
(Mark can only be awarded if all organisms are
Axes labelled. All points correctly plotted. in the right order and all arrows point in the
5a This indicates that the two bears are different direction of energy flow.)
species. b Water hyacinth.
b This indicates that the two bears come from c Weevil.
similar species. 4a They all have a backbone.
c Species have different names in different b Snake – reptile; frog – amphibian.
languages; all scientists need to use the same c Snake.
name so that they can share information about 5a The volume of acid given to each seedling.
each species. b Any one from: the number of times acid is added;
6 Scientists could breed a male and a female the concentration of the acid; the type/age of
cheetah from different parts of Africa. They could seedling; the amount of light the seedlings receive;
then attempt to breed their offspring to see if they the temperature; the soil the seedlings are planted in.
are fertile. If the offspring are fertile, the male and c Any one from: measure the height/mass; count
female cheetah came from the same species. the number of leaves; compare the colour of the
7a Hybrid. leaves after one week/a suitable time period.
b Zeedonks have a female donkey as their mother 6a B (root hair cell).
and a male zebra as their father. The offspring of b D (red blood cell).
different species are always infertile. c C (palisade/plant cell).
© Oxford University Press 2013: this may be reproduced for class use solely for the purchaser’s institute 103
Checkpoint_Biology_TG_SB_Ans.indd 103 28/11/2013 16:03
7a Petrol. 4 Small molecules of glucose are joined to form
b Bioethanol. giant starch molecules which can be stored in
c Any two from: geothermal energy; biodiesel; the leaves and broken down when the glucose
moving water; wind; solar. is needed.
8a The flower. 5 The Sun.
b This gives them better access to sunlight which
6 palisade cell – xylem tissue –
would be partially blocked out by lower branches. where most carries water up
c Water and minerals (magnesium, phosphate, photosynthesis from the roots
potassium, nitrate). takes place
9a B (triceps). spongy mesophyll –
phloem tissue –
b Muscles can only contract/can only pull in lets gases move
carries glucose
one direction. between the cells
down to the roots
10 Excretion; reproduction; growth. stoma – lets gases diffuse
11a Habitat. in and out of the leaf
b Variation.
c Adaptations. 6.2 Asking scientific questions
12a The pH decreased from 6 to 4.2 over the three days. 1 The question involves something you can change
b Bacteria (micro-organisms) converted the sugar in (the temperature of the water) and something
the milk to lactic acid. you can measure (the time it takes pondweed to
c The pH would have dropped at a faster rate. release 1 cm3 of oxygen).
13 Any two from the following. 2 Oxygen is produced during photosynthesis and
The number of bacteria per fingertip increases it can be can be collected/measured quickly and
between one minute and one hour after your easily using a measuring cylinder.
hands are washed. 3 Photosynthesis produces glucose. This is used
More bacteria are killed after washing with hand to create new biomass for growth. The faster
sanitiser than after washing with soap. photosynthesis occurs, the more glucose is made
and the more new biomass the plant produces.
It takes longer for the bacteria to increase in
4 Any two from: the temperature; carbon dioxide
number after washing your hands with hand
concentration; mineral supply.
sanitiser than after washing with soap.
5 Graphs make it easier to see trends or patterns in
the results.
6 Plants
6.3 Water and minerals
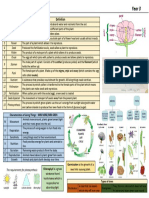
6.1 Why we need plants 1 A: xylem vessel cell – these cells are hollow to
1 Plants use photosynthesis to produce glucose allow water to travel up from the roots to the leaves.
which they use to build biomass; this feeds B: guard cell – these cells have specialised cell
animals so it provides all the food that we eat. walls. They push each other apart when turgid to
Photosynthesis is also our only source of oxygen open up the stoma between them and allow carbon
for respiration. dioxide to pass into the leaf. When the cells lose
2 Students should draw a simple outline of a leaf water and become flaccid, the stoma between them
with arrows entering it labelled light energy, closes and prevents water loss from the leaf.
carbon dioxide, and water, and arrows leaving it C: root hair cell – these cells give roots a large
labelled glucose and oxygen, e.g. surface area to take in water and minerals from
the soil.
light 2 More water leaves the bottom of the leaf because
energy this is where the stomata are.
oxygen 3 The water molecule is taken up by root hair
cells, enters xylem vessels, and travels up the
stem into a leaf. It evaporates and diffuses
carbon through air spaces in the leaf. If the guard cells
dioxide glucose are turgid, the stoma between them will be open.
The water will escape through a stoma on the
water bottom of the leaf.
4 Students should draw a flaccid plant cell like the
3 Plants use some of the glucose they make in
one shown on page 88 of the Student book. Cells
respiration to release energy. The rest is used
like this do not provide support so the leaves and
for the growth and repair which increases the
stem droop downwards and the plant wilts.
plant’s biomass.
104 © Oxford University Press 2013: this may be reproduced for class use solely for the purchaser’s institute
Checkpoint_Biology_TG_SB_Ans.indd 104 28/11/2013 16:03
5 Plant cells use minerals to build new cell 11a Water is leaving the underside of the leaf through
components. The minerals are taken in by root hair the stomata.
cells and travel through the plant in xylem vessels. b Transpiration.
12a The question includes a variable you can change
6.4 Review
by selecting places with different annual rainfalls
1a Climbing allows Convolvulus to collect more
to collect plants from. It also includes a variable
light for photosynthesis.
you can measure by counting the number of
b Cutting the stem prevents xylem vessels bringing
stomata these plants have.
water for support and to use in photosynthesis.
b Plants would have fewer stomata in places with
2a The pondweed uses carbon dioxide for
a lower average rainfall. Water is lost through
photosynthesis. Removing carbon dioxide from
stomata and if less water is available to the plant,
the solution turns the indicator purple.
it would be likely to minimise its water loss by
b In the dark, respiration adds carbon dioxide to
having fewer stomata.
the water.
3a As the light intensity increased, the amount of
dissolved oxygen increased. 7 Diet
b As the light intensity increased, the amount of
7.1 Food
dissolved carbon dioxide would decrease because
1 Nutrients provide materials for growth and repair;
more would be used for photosynthesis.
energy to keep your cells alive; and vital elements
4a Oxygen.
and compounds to maintain the chemical
b Apparatus B.
reactions in your cells.
c Any one from:increase the carbon dioxide
2 Fat and protein are need to build new cells.
concentration further; increase the light intensity;
3 Carbohydrates and fat provide energy.
increase the temperature of the water.
4 Vitamins help to maintain the chemical reactions
5a Plant a will lose more water because water is
in your cells
lost through stomata on the underside of the leaf.
Covering the top surface with oil will not reduce 5
water loss. part of a starch
b The pots are covered to prevent water evaporating molecule made by
from the soil so that water loss from the leaves joining glucose
molecules
can be compared fairly.
6a Stomata.
b Any one from: to allow the plant to take in carbon
dioxide for photosynthesis; to control water loss
from the plant. glycerol
c In wetter climates plants can use more stomata to
take in more carbon dioxide for photosynthesis
because they can replace all the water they lose fatty acid part of a protein
molecule made by
through the open stomata. a fat molecule
joining different
7a Palisade (leaf) cell. amino acids
b They can absorb more light for photosynthesis at
the top of the leaf. 6 Nutrient Foods that contain it
c Plants use starch grains to store glucose to use for
respiration when they cannot photosynthesise. carbohydrate wheat, rice, beans, potatoes, fruit,
d The number would decrease. The plant would use vegetables, chocolate, cakes
up the glucose stored in the starch grains because protein fish, eggs, nuts, beans, milk
it cannot photosynthesise in the dark but still products
requires energy. fat meat, fish, milk products,
8 Plant B has access to minerals from the soil. nuts, seeds
These minerals are required for growth, building vitamin fruit, vegetables, fish, dairy
cell components, and the formation of flowers. products
9a Xylem vessels (cells) mineral fish, milk products, fruit,
b It carries water and soluble minerals from the vegetables
roots up to the leaves.
10a How does the amount of carbon dioxide available
affect the amount of starch a leaf stores (how does
it affect the rate of photosynthesis in a leaf)?
b Leaf B (the leaf that received extra carbon dioxide).
© Oxford University Press 2013: this may be reproduced for class use solely for the purchaser’s institute 105
Checkpoint_Biology_TG_SB_Ans.indd 105 28/11/2013 16:03
7.2 Managing variables 2
Deficiency Main Missing
1 Measure 1 g of each food using an electronic
disease symptoms nutrient
balance. Measure 20 cm3 (or a similar volume)
of water into each of two boiling tubes scurvy bleeding gums vitamin C
(test tubes) and measure its starting temperature swollen legs
using a thermometer. Then burn each food little energy
underneath one tube of water and measure beri-beri partial paralysis vitamin B1
the end temperature. The food that causes the mental confusion
biggest temperature rise releases most energy
per gram. night difficulty seeing vitamin A
2 The volume of water heated: 20 cm3; the mass of blindness in low light
food burnt: 1 g; the distance between the burning levels
food and the tube: 5 cm. rickets softer bones that vitamin D
3 The results showed that the temperature of the are more likely calcium
water rose when the bread was burnt. They also to break or bend
showed that doubling the mass of food burnt
kwashiorkor muscle protein
doubled the temperature rise. This is evidence that
shrinkage
the method works because burning twice as much
swollen belly
food releases twice as much energy (the same
amount of energy per gram). anaemia tiredness iron
4 Use a larger volume of water; burn a smaller mass
of food.
3 Vitamin C is found in fruits and vegetables.
5 Any two from the following:
Sailors could not take these on long voyages as
Some of the energy released by the burning food
they would rot. They are also expensive.
could escape (heat the surrounding air instead of
4 Lemon juice contains vitamin C (which prevents
the water).
scurvy) but it is destroyed by boiling.
Some of the energy released heats the equipment,
5 Vitamin D is made when skin is exposed to
rather than the water.
sunlight. Countries further from the equator get
Some energy is lost whilst Eniola sets light to less sunshine so people there are more likely to
the food. have a vitamin D deficiency.
The food may stop burning before all its energy 6 Casimir Funk fed different chemicals from rice
has been released. skins to pigeons with (a similar disease to)
7.3 A balanced diet beri-beri. One of the chemicals cured the pigeons
1 You should eat more carbohydrates than other so he concluded that this vitamin was deficient in
nutrients. the diet of those with beri-beri.
2 Each type of protein contains a different combination 7.5 Choosing foods
of amino acids, so we need to eat a variety of 1 Anyone whose body mass is much higher than
proteins to get all the amino acids we need. average is considered obese.
3 Amino acids are small molecules that can be 2 Obesity increases the risk of having long-term
joined together to form the proteins needed to health problems such as diabetes, cancer, high
build and repair cells. blood pressure, and heart disease. These could
4 Fats contain fatty acids and some of these are cost billions to treat in the future.
essential for health. Fats also contain some 3 The average body mass is increasing in many
essential vitamins. countries because people rely more on takeaways
5 Eating too many sweets can cause tooth decay and processed foods, which contain lots of sugar,
and lead to obesity. salt, and saturated fat. People also do less exercise
40 because they use more energy-saving machines
6 × 8000 kJ ÷ 37 kJ per g = 86.5 g
100 and cars.
4 Any two from: stop TV companies from
7.4 Deficiencies advertising sugary or fatty foods; stop schools
1 Deficiency diseases are diseases that occur if you providing sugary or fatty foods; change the layout
don’t get enough of an essential nutrient. of cities to make them better suited for walking
and cycling; make sugary and fatty foods more
expensive; educate people to avoid obesity.
106 © Oxford University Press 2013: this may be reproduced for class use solely for the purchaser’s institute
Checkpoint_Biology_TG_SB_Ans.indd 106 28/11/2013 16:03
5 Extra nutrients are added to foods like bread to The sugary sweets caused a more rapid rise and
make it easier for people to get the vitamins and fall in blood glucose.
minerals they require without having to alter The cereal caused raised blood glucose levels
their diet. for longer.
6 We can increase the amount of vitamins in crops e Any one from the following.
by adding new genes to them. The starch in the cereal contains many glucose
7.6 Review molecules joined together.
1a Rice. The starch must be broken down in the student’s
b Chicken leg. digestive system before these glucose molecules
c Corn oil because it contains the highest amount can enter the blood.
of fat of the three foods, and fats release twice as The glucose from the sugary sweets doesn’t
much energy per gram as carbohydrates. have to be broken down and can enter the blood
50 straight away.
2a × 100 g = 50 g 10
100 6a × 12 000 kJ ÷ 16 kJ/g = 75 g
b Cheese contains a higher percentage of fat (than 100
other sources of protein). b 36 g × 37 kJ/g = 1332 kJ
c 25 – 10 = 15 g c 1332 kJ ÷ 12 000 kJ × 100 = 11.1%
3a Protein. d A diet high in saturated fat increases your risk of
b B may not get enough protein in their diet. developing heart disease.
4a Potato crisps because they have a higher fat e Oily fish contains a lot of unsaturated fat. A diet
content than crispbread, and fat releases twice high in unsaturated fats reduces your risk of
as much energy per gram as carbohydrates. developing heart disease.
b Measure out 1 g of each food and burn the food 7a 75 mg ÷ 25 mg/100 g = 300 g
under a test tube (boiling tube) of water. Measure b Accept any combination which gives at least
the temperature of the water before and after 0.9 mg of vitamin A, e.g. 100 g of carrots and
burning each food and calculate the temperature 22 g of spinach; 200 g of spinach.
rise. If the prediction is correct, then burning the c It would be greatly reduced.
potato crisps will cause the biggest increase in 8a Vitamin A.
temperature. b Iron.
c Any two from: volume of water used; mass of food c Protein.
burnt; distance between burning food and water. d Vitamin C.
d Any one from the following: 9a Orla has bowed legs/the bones in her legs
Some of the energy released by the burning food are curved.
could escape (heat the surrounding air instead of b Any two from the following:
the water). Rickets is caused by not getting enough vitamin D.
Your skin makes vitamin D when it receives
Some of the energy released heats the equipment,
direct sunlight.
rather than the water.
Orla has developed rickets because she isn’t
Some energy is lost whilst the food is set alight. getting enough sunlight.
The food may stop burning before all its energy 10a The source of the acid.
has been released. b Whether each sailor’s condition improved after
5a Her blood glucose levels. one week.
b Her blood glucose levels are lowest before c No – some of the acids made their condition worse.
breakfast and will not be affected by food eaten d The vitamin C in the citrus fruit cured the scurvy.
earlier in the day.
c Any one from: the mass of each food type 8 Digestion
eaten; the amount of exercise done during the
experiment; other foods or drinks consumed 8.1 The digestive system
during this three-hour period. 1 Most foods are made of complex molecules such
d Any two from the following: as starch, fats, and proteins. These are too big to
The sugary sweets caused a more rapid rise in pass from your digestive system into your blood/
blood glucose levels than the cereal. cells. Digestion breaks them down into smaller
The sugary sweets caused a higher peak in blood molecules that your cells can take in.
glucose levels than the cereal.
© Oxford University Press 2013: this may be reproduced for class use solely for the purchaser’s institute 107
Checkpoint_Biology_TG_SB_Ans.indd 107 28/11/2013 16:03
2 Fibre passes through your digestive system 8.3 Using enzymes
without getting broken down. The route it takes 1
is: gullet stomach small intestine large Type of Use in food manufacture
intestine rectum anus. enzyme
3 Mechanical digestion uses your teeth to break carbohydrase breaking down corn starch
solid food into smaller pieces that you can into a mixture of glucose and
swallow. Chemical digestion uses enzymes to fructose for processed foods
break large food molecules into smaller ones.
protease turning milk into cheese
4 Saliva contains an enzyme that begins the
breakdown of starch. It also makes food slippery lipase flavouring cheese converting
so it is easier to swallow. vegetable oils into butter or
5 Food is mixed with acid in your stomach, to margarine adding omega-3 and
destroy microbes; it is also mixed with an enzyme omega-6 fatty acids to foods
to start protein digestion, and turned into a
smooth paste.
6 Most large molecules are digested in the small 2
intestine using enzymes made in the pancreas
and the small intestine itself. Once broken down, water
these small molecules are absorbed into the
bloodstream.
7 Small food molecules are absorbed by the walls enzyme enzyme
of the small intestine and pass into the blood. The maltose this makes glucose
blood carries them to cells all over the body. approaches maltose react molecules
the enzyme with water separate
8.2 Enzymes more easily
1 The term ‘biological’ means they are made by
living cells. The term ‘catalysts’ means that they 3 Enzymes remain unchanged at the end of a
speed up the rate of chemical reactions. reaction so the same enzyme molecule can be
2 Enzymes can only help molecules on the surfaces of used again and again.
food particles to break down. Chewing food breaks 4 Each enzyme has a different active site which
it into smaller pieces. This increases its surface area, allows it to catalyse a specific reaction. By
so more of it can be broken down at once. investigating the enzymes produced by different
3 Fat molecules stick together in large globules. microbes we can find biological catalysts to speed
Bile emulsifies the fats in the small intestine. This up the reactions that make everything we need.
breaks large fat droplets into smaller ones which
8.4 Review
mix with water. It increases the surface area of the
1a E
fat so that enzymes can begin to break them down
b C
more rapidly.
c B
4 d A
Nutrient Enzyme used Organ/s where
e F
to digest it digestion takes
2a Stomach.
place
b Gullet.
carbohydrate carbohydrase mouth, small c Large intestine.
(amylase) intestine d Stomach.
protein protease stomach, small e Mouth.
intestine f Small intestine.
3a They grind and chew food into smaller pieces
fat lipase small intestine (mechanical digestion). This increases its surface
area so enzymes can break down the large
molecules in the food more easily.
b Saliva makes food slippery so it can pass
more easily down your gullet. It also contains
amylase to break down starch into smaller
sugar molecules.
108 © Oxford University Press 2013: this may be reproduced for class use solely for the purchaser’s institute
Checkpoint_Biology_TG_SB_Ans.indd 108 28/11/2013 16:03
4 Glucose molecules are small so can pass This is because enzymes only work at the surface
directly into your blood and be taken straight of a solid, and breaking the gelatin into tiny
to cells for respiration. Starch molecules must pieces increases its surface area.
be broken down by enzymes in the mouth and This allows more large molecules to be broken
small intestine before the glucose molecules are down at once.
released and can be absorbed into your blood and
f The mouth.
this takes longer.
5a The small intestine.
b Any three from the following: 9 Circulation
Undigested food (fibre) passes into your large 9.1 Blood
intestine.
The large intestine absorbs water to make fibre 1
Blood Main function
more solid. component
Fibre is stored in your rectum as part of
your faeces. red blood cell Picks up oxygen in the lungs
and transports it to every
Fibre is excreted from your anus as part of
other part of the body.
your faeces.
Bacteria in your large intestine use the fibre to white blood cell Helps to destroy
make vitamins that your body cells need. micro-organisms.
6a Large intestine and small intestine. platelet Congregates around
b Mouth, stomach, and small intestine. damaged blood vessels and
7a B helps to seal cuts.
b D plasma Carries nutrients, carbon
8a The indicator colour. dioxide, and waste products
b The enzyme broke down the protein into amino in your blood.
acids, so the indicator did not turn lilac. Water
cannot break down protein so the indicator 2 Students should draw a side view of a red blood
turned lilac. cell like the one on page 112 of the Student book.
9a Glucose molecules are small enough to diffuse 3 Their biconcave shape makes them flexible and
through the walls of the model gut and into lets them squeeze through tiny capillaries. Their
the beaker. shape also gives them a large surface area so
b Starch molecules are too big to pass through the they can pick up oxygen quickly. They are full
walls of the model gut. They would have to be of haemoglobin which binds oxygen in the lungs
broken down into glucose by enzymes first. and releases it in other tissues.
c The starch was broken down into glucose 4
molecules by the amylase (enzyme/carbohydrase) Substance From To
in the saliva. oxygen lungs every cell
d Blood.
10a This is the normal human body temperature so the carbon dioxide every cell lungs
protease should work best at this temperature. digested food small intestine every cell
b Changed: type of protease – normal or boiled.
urea liver kidneys
Observed: the appearance of the gelatin cube after
4 hours. 5 Micro-organisms grow and divide quickly in
c Any two from: the temperature; the time it was blood because it is warm and contains lots of
left for; the size of the gelatin cubes; the volume nutrients, including glucose, which they can use
of protease added. for respiration.
d The protein that had normal pepsin added to
it was completely digested. The boiled pepsin 9.2 Anaemia
did not digest the protein at all. This is because 1 Healthy people have a range of red cell counts but
boiling enzymes like pepsin causes them to most lie within a certain range.
denature so they cannot work. 2 No – her red cell count is 3 billion cells per dm3,
e Any two from the following: which is below the normal range (3.8–5.0 billion
The table shows that it took more than twice as cells per dm3).
long to completely digest the gelatin when it was 3 No – her haemoglobin level is 93 g per dm3, which
in a single cube. is below the normal range (110–150 g per dm3).
© Oxford University Press 2013: this may be reproduced for class use solely for the purchaser’s institute 109
Checkpoint_Biology_TG_SB_Ans.indd 109 28/11/2013 16:03
4 They are paler than normal red cells. 2
Before After training
5a Students should have five values between 5.5 and
training
7.5 mm.
b Their average values should be between 6 and resting heart rate 70–75 60–65
7 mm. (beats/minute)
c Students should have five values between 6.5 and maximum heart 170 135
8.5 mm and an average value between 7 and 8 mm. rate (beats/minute)
6 Sara’s red cells are smaller and paler than
normal cells. recovery time 9 4
7a 15 mm (minutes)
b 50 mm
15 × 100% 3 The heart rate drops as the volume of oxygen
c Packed cell volume = = 30%
50 blood can carry increases. This means that there is
8 Yes – Sara’s packed cell volume is lower than a negative correlation between the heart rate during
normal (36–46%) which agrees with the results exercise and the oxygen content of the blood.
from her other tests. 9.5 Diet and fitness
9.3 The circulatory system 1 Students should draw simple cross-sections of
1 The heart pumps blood to the lungs to collect two blood vessels. The one labelled ‘normal’
oxygen. This blood returns to the heart to be should be clear in the centre. The other should be
pumped to every other part of the body. almost blocked by plaque.
2 The right side. 2 Plaque is made of fat, cholesterol, and blood cells.
3 Blood (low in oxygen) leaves capillaries in the 3 Plaque narrows arteries and raises blood
muscles. The capillaries join to form veins. pressure. It can reduce blood flow to the body’s
Veins join and carry blood to the right side of tissues and organs. This can cut their supplies of
your heart. The heart pumps this blood (low in glucose and oxygen and can cause them to stop
oxygen) through arteries to capillaries in the working properly. This is particularly dangerous
lungs. Red blood cells pick up oxygen there. in arteries supplying the heart, as it could cause
The blood (now rich in oxygen) travels through a heart attack.
veins back to the heart. Then the heart pumps 4 Consistently high blood pressure readings suggest
this oxygen-rich blood through arteries to return that the arteries have become narrower. The heart
it to capillaries in the muscles. has to pump much harder to get blood through a
narrower tube.
4 vein where blood
has most oxygen
5 Heart attacks and strokes can both be caused by
a blockage in an artery. If an artery supplying
your heart muscle is blocked by plaque, blood
left flow to the heart is reduced. This can cause part of
heart small the heart muscle to die. If an artery that supplies
lungs muscles
right intestine your brain is blocked it can cause part of your
heart brain to die.
6 By changing their diet, people can avoid being
overweight, eating unhealthy food, and having a
artery where blood high salt intake.
has least oxygen
9.6 Review
9.4 Identifying trends 1a C
1 Students should make a copy of the graph on b A
page 118 of the Student book and describe the c B
graph, e.g. his maximum heart rate after exercise 2a C
was 170 beats per minute. His heart rate dropped b A
quickly in the first 4 minutes after exercise 3 A – oxygen; B – glucose.
(to 95 bpm) and then more slowly until it reached 4a Plasma.
his resting heart rate (between 70 and 75 bpm) b Any two from: carbon dioxide; nutrients
after 9 minutes. (glucose); urea (waste products).
5a Lungs
b C, D
110 © Oxford University Press 2013: this may be reproduced for class use solely for the purchaser’s institute
Checkpoint_Biology_TG_SB_Ans.indd 110 28/11/2013 16:03
6a After 5 minutes. of your body. It picks up oxygen in the lungs, and
b When she exercises, her muscles need more then veins return to the heart which pumps blood
glucose and oxygen so they can release more full of oxygen through all your other arteries.
energy using respiration. Her heart has to pump/
10.2 Respiration and gas exchange
beat more times per minute to get blood to her
1 Respiration;
muscles fast enough.
glucose + oxygen carbon dioxide + water
c At 26 minutes.
2 Gases are exchanged in the lungs so the
7a An artery.
percentage of carbon dioxide increases and the
b B
percentage that is oxygen decreases.
c C (a capillary) because small molecules such as
3 Your body needs more energy when it is exercising,
glucose and oxygen need to diffuse through their
so its muscles can contract more strongly/quickly.
walls very rapidly.
Muscle cells release this energy by respiring more
8a Their heart rates rose to increase the blood flow to
quickly so more oxygen is required.
their muscles.
4a 0.3 dm3/min
b Student B because their resting heart rate is lower
b 2.6 – 0.3 = 2.5 dm3/min
and it does not increase so much during exercise.
c 3 breaths
c Take more frequent exercise that raises their heart
d 12 breaths per minute
rate such as running or swimming.
e 0.5 dm3
9a A, the right-hand side (shown on the left in
f His breathing rate increased (to 16 breaths per
the image).
minute) and the volume of each breath increased
b D, E
(to 3.0–3.2 dm3).
10a B
b A 10.3 Anaerobic respiration
11a It has just come from the lungs, where it picked 1 Most respiration takes place in mitochondria. The
up oxygen. heart needs a lot of energy to pump blood around
b B the body, so needs to have lots of mitochondria.
c C 2
12a Valve. Aerobic respiration Anaerobic
b It ensures that blood only flows in one direction. respiration
releases all the energy releases 5% of the
10 Respiration and gas exchange stored in glucose energy from glucose
needs oxygen to doesn’t need oxygen
10.1 Lungs
release energy from to release energy from
1 Your intercostal muscles and diaphragm make
glucose glucose
you breathe.
2 They work together to increase the volume of used in long-distance used in sprints
your chest. The intercostal muscles contract running
to bring your ribs up and out. Your diaphragm can be used can only be used for a
contracts and flattens. The increased volume continuously short time
makes air rush into your lungs.
3 Lungs contain air so they are less dense than water. produces carbon produces lactic acid
4 Students should describe the route an oxygen dioxide
molecule takes to get into the blood, e.g. I enter
3 Anaerobic respiration allows you to release energy
the body through the nose/mouth. I pass down
from glucose much faster than is possible with
the trachea. I choose between two paths to
aerobic respiration. This is useful when energy is
lungs, one through each bronchus. The bronchus
needed very quickly, e.g. when sprinting.
keeps branching into many smaller tubes, the
4a Fast twitch.
bronchioles. These tubes get narrower until I
b Slow twitch.
reach a tiny air sac – an alveolus. I dissolve in its
c Slow-twitch fibres have many capillaries so
moist lining and diffuse through its thin walls into
oxygen can diffuse into the muscle cells/fibres
the bloodstream.
much more rapidly.
5 The arteries that carry blood into the lungs should
d A sprinter has a greater proportion of fast-twitch
be coloured blue. Normally arteries carry blood
fibres, which can produce stronger contractions,
that is full of oxygen, but the arteries to your lungs
allowing them to run faster.
are carrying blood that has returned from the rest
5 A cheetah would have mainly fast-twitch fibres.
© Oxford University Press 2013: this may be reproduced for class use solely for the purchaser’s institute 111
Checkpoint_Biology_TG_SB_Ans.indd 111 28/11/2013 16:03
10.4 Smoking and lung damage That means your blood can’t get enough
oxygen. That’s why you are finding it hard to
1
Chemical Damage caused breathe. If it gets any worse your body will not
tar Paralyses cilia, leading to a build- get enough oxygen to survive. This is a very
up of mucus, causing coughing and dangerous situation so we want to start treatment
increasing the chance of infection. immediately to remove the blockage.
6 Students should write what they would explain to
Increases the risk of developing
the patient, e.g. there is a build-up of sticky mucus
lung cancer.
in the tubes that carry air into your lungs. Some
carbon Binds to red blood cells, reducing of the cells inside your lungs act like little brushes
monoxide the amount of oxygen they can carry. and sweep this mucus out. Unfortunately your
nicotine Acts on brain cells and makes mucus is thicker and more sticky then normal – a
people addicted to cigarettes. bit like honey. It is blocking the tubes and making
it hard for you to take enough oxygen in. This is
Narrows blood vessels, and why you are finding it hard to breathe. We have
increases your risk of having a some medication that will make your mucus
heart attack or stroke. thinner. Then your lungs will keep themselves
clean and you will breathe more easily.
2 The baby is more likely to be smaller than average.
3 Smoking is most damaging during the final 10.6 Review
months of pregnancy. 1a E
4a The smoker’s alveolar walls have broken down. b D
The individual alveoli have combined to form c A
larger clumps. This has reduced the surface area d B
available for gas exchange. e C
b Their oxygen uptake will be reduced because gas 2a Alveoli.
exchange will be slower. b Bronchus.
5 Nicotine is addictive, so their cells rely on c Bronchioles.
nicotine to function normally. 3a Trachea and bronchi.
b The diaphragm.
10.5 Communicating findings
c Air rushes in and the lungs inflate.
1 Lower – the average value for her height is
d Any one from: the bronchioles; the intercostal
425 dm3; her PEF is only 320 dm3.
muscles; the alveoli.
2 Kemi’s bronchioles are easily irritated by
4 E, C, B, D, A
substances in the air. They produce more mucus
5a X alveolus; Y capillary.
which clogs up the bronchioles and makes them
b A oxygen; B carbon dioxide.
narrower. This makes it harder for air to get into
c This allows the air in the alveolus and the blood
and out of the lungs.
to get very close together, which speeds up
3 Students should draw simplified versions of the
diffusion/gas exchange.
normal and constricted bronchioles shown on
6a Her heart and lungs worked harder. Her heart
page 133 of the Student book.
beat more quickly and she took more breaths
4 Students should write what they would explain
per minute
to Kemi, e.g. your peak expiratory flow (PEF)
b The heart needs to pump faster to ensure that
is lower than the average value for someone of
enough oxygen is delivered to the muscle cells
your height. Your PEF value is below the blue
for respiration. The breaths per minute need
line, which means that it is also lower than 95%
to increase to allow oxygen to diffuse into the
of people who are the same height as you. This
blood rapidly.
means that you aren’t able to blow air out of your
7a B
lungs as quickly as they can. The tubes that take
b A
air into your lungs are narrower than normal –
c C
like straws that have been squeezed shut. Your
8a Tar.
tubes are easily irritated by things in the air. They
b Any one from: can cause lung cancer; can cause
produce more mucus and become narrower.
bronchitis; can cause emphysema; can reduce
5 Students should write what they would explain
gas exchange.
to the patient, e.g. we have looked at the results
c It is acidic.
of your scan and we have found a blood clot. It
d It is addictive.
is blocking the blood flow to one of your lungs.
112 © Oxford University Press 2013: this may be reproduced for class use solely for the purchaser’s institute
Checkpoint_Biology_TG_SB_Ans.indd 112 28/11/2013 16:03
9a They waft it up the tubes in your lungs towards 6 The fetus is especially vulnerable to infections
your throat, to be swallowed. and drugs during the first twelve weeks of
b Mucus traps microbes. If the cilia are paralysed, pregnancy, when its organs are developing. As
they are unable to move the microbes out of your mothers can take up to eight weeks to realise that
lungs, so the microbes multiply there and cause they are pregnant, they could continue to take
an infection. drugs and drink alcohol during this time, which
10a Glucose + oxygen carbon dioxide + water can harm the developing fetus.
b Respiration releases energy, which cells need to
11.3 Twins
stay alive.
1 Students should draw diagrams like those on
11a Mass of air.
page 140 of the Student book to show non-identical
b Any one from: number of breaths taken; age of
twins forming from two separate fertilised eggs
participants; size/type of balloon.
and identical twins forming when one fertilised
c Yes – on average, the 10 smokers blew out a
egg splits.
lower mass of air than the non-smokers.
2 Her ovaries would have released two eggs, which
12a 3 dm3
both got fertilised. One of the fertilised eggs
b 5 dm3
divided and split early on in development. This
c 12 breaths per minute
produced two identical twins. The other fertilised
d 18 breaths per minute
egg developed into the baby boy.
e His breathing is faster and deeper during exercise.
3a 16
b Any one from the following:
11 Reproduction and fetal Single babies have a higher average birth mass
development than twin babies.
A greater percentage of twin babies have a birth
11.1 Reproduction mass lower than 3 kg.
1 A sperm nucleus from the father enters an egg c The average pregnancy for a single baby is five
cell from the mother and the sperm and egg nuclei weeks longer than for twins.
fuse to form a fertilised egg. 4 Poor vision and hearing problems are much more
2 Ovary oviduct uterus. common in babies with a birth mass below 1 kg.
3 An egg is released approximately once a month. 5 Premature babies often need to be put in an
4 Testes sperm ducts penis vagina incubator to keep them warm, feed them and help
uterus oviduct. them breathe. This equipment (and the training
5 Fertilisation usually happens in the oviduct. needed to use it) is expensive.
6 Eggs and sperm die if they don’t meet.
11.4 Adolescence
7 A baby is called an embryo when it first starts
1 Puberty prepares your body for reproduction.
to grow.
2 Puberty starts when sex hormones are produced
8 A streamlined head and tail help sperm to
and released into your blood by your testes
swim well.
or ovaries.
9 Eggs have a large food store which the embryo
3 Hormones are chemical messengers which travel
needs for growth.
around your body in blood.
11.2 Fetal development 4 The sex hormones released during puberty affect
1 An embryo implants one week after fertilisation. cells in many different parts of your body.
2 As an embryo turns into a fetus its cells start to 5 Girls notice a flow of blood through their vagina
specialise and form different tissues and organs. for 3 or 4 days every month.
3 Any one from the following: 6 An egg begins to mature in one of the ovaries
The bag of fluid around the fetus protects it from a new uterus lining builds up an egg is released
knocks and bumps. It gives the fetus space to from one of the ovaries a thick uterus lining is
practise moving, swallowing, and breathing. maintained ready for an embryo to implant in
4 The placenta brings the blood of the fetus close to if an embryo does not implant, the thick lining of
its mother’s blood so that nutrients and oxygen can the uterus breaks down bleeding occurs.
diffuse between the two/into the fetal blood supply. 7 Your sex hormones can upset your body’s timer
5 Some drugs/medicines can diffuse across the and make you feel tired in the morning.
placenta from the mother’s blood to the baby’s.
These drugs can harm the developing fetus.
© Oxford University Press 2013: this may be reproduced for class use solely for the purchaser’s institute 113
Checkpoint_Biology_TG_SB_Ans.indd 113 28/11/2013 16:03
11.5 Review 12 Drugs and disease
1a Sperm cell.
b Testes. 12.1 Drugs
c Egg cell. 1a Any one from: caffeine; nicotine.
d Ovaries. b alcohol.
2a Fertilisation. 2a Brain, lungs, testes.
b Oviduct. b Liver, heart.
3a Testes. c Brain.
b Penis. 3 Their brains receive altered signals from their
4a Ovaries. sense organs. This changes the way they see and
b Vagina. hear things.
c Uterus. 4 Alcohol slows down your reactions (increases
d Vagina. your reaction time) so Joshua would respond
5 C E D B A more slowly to people and actions during the
6a Boys. match. He could also become more aggressive,
b Girls. get involved with rougher tackles and injure
c Both. himself and others or get sent off the pitch.
d Girls. 12.2 Disease
7a B
b A 1
Situation Disease that
c C could be caught
d A
walking into a pond in Africa, bilharzia
8a Any one from: a sperm’s streamlined head
South-East Asia, or the
makes swimming easier; a sperm’s tail allows
Middle East with bare legs
it to swim.
b Enzymes in a sperm’s head help it penetrate living near a stream in Africa river blindness
the egg. eating contaminated food in worms
c The sperm cell’s nucleus fuses with the egg to a tropical country
fertilise it.
9a The egg is usually released on day 14 of the sleeping in a crowded room tuberculosis
menstrual cycle. where there may be carriers
b Bleeding begins on day 1 of the menstrual cycle. of the disease
c Ovulation is most likely on 19 May. having sex without using gonorrhoea
10a B a condom chlamydia
b C
c D 2 If someone has no symptoms of the disease, they
d A don’t know they have it. This means they don’t seek
e Any one from: protects the baby from knocks; treatment and will pass the disease to other people.
allows the baby to practise moving. 3 Infectious diseases can cause children to perform
f Any one from: carries fetal blood to and from the less well at school, making it harder for them to
placenta; allows the fetus to collect nutrients and succeed and get good jobs. Infectious diseases
oxygen from the placenta. cause poor health, which means children are not
11a B able to go to school and parents are not able to work
b C
12.3 Defence against disease
c A
1 Any two from: breathed in; swallowed in food or
12a A
drink; picked up when you touch something and
b B
then passed to your mouth, nose, or eyes; through
c A
a break in your skin into your blood.
d A
2 Cholera is found in victims’ faeces. If sewage
13a As the pregnancy gets longer, the mass of the
water is not treated, drinking water can be
baby increases.
contaminated.
b Yes. The babies of smoking mothers have a lower
3 Microbes are kept out of your alimentary canal
mass throughout pregnancy.
by stomach acid. It destroys most of the microbes
c Alcohol.
you take in with food and drink.
Microbes are kept out of your lungs by mucus,
which traps the microbes that you breathe in.
114 © Oxford University Press 2013: this may be reproduced for class use solely for the purchaser’s institute
Checkpoint_Biology_TG_SB_Ans.indd 114 28/11/2013 16:03
4 Phagocytes surround bacteria with their In the over 35 category, more than twice as
cytoplasm and digest them. many men than women drink more than the
5 If phagocytes aren’t able to deal with an infection, recommended amount.
antibodies are produced. Some attach to pathogens Under 35s drink more than over 35s.
and destroy them. Others help phagocytes to find
3a Shorter.
the pathogens and destroy them.
b Before caffeine 28.3 cm; after caffeine 21.3 cm.
6 HIV infects some white blood cells and instructs
c The caffeine shortened his reaction time.
them to produce lots more HIV particles. These
d Repeat his experiment more times to make the
burst out and infect other white blood cells. This
average more reliable.
weakens the immune system. Once the number of
e Alcohol would increase the distance the ruler
white blood cells in your body has dropped to a
dropped before it was caught.
certain point, the disease is known as AIDS.
4a This allows her to establish her resting heart rate
7 People with AIDS have a lower number of white
before caffeine.
blood cells so they cannot fight infections easily.
b Yes – all her heart rate measurements are higher
12.4 Boosting your immunity after taking caffeine, by 4–10 bpm.
1 Bacteria reproduce very quickly – they can divide c She could repeat the test using pure caffeine, or
and double in number in less than 30 minutes, compare the results with results obtained after
using the nutrients in your body. drinking cola with no caffeine in it to see if the
2 It takes a couple of days for bacteria to multiply results were the same.
and produce a large enough population to make 5a 7
you ill. b 28
3 Once you have been exposed to a pathogen, your c Blood alcohol rises rapidly in the first hour
white blood cells remember how to make antibodies after drinking alcohol. After one hour, the blood
against it. If the same pathogen infects you again, alcohol levels begin to fall; from 1.5 to 0.1 g/dm3.
these antibodies are made very quickly. This means (Numbers from the graph must be used to award
that the pathogens can be destroyed before their all three marks.)
population gets big enough to make you ill. d At least 6 hours 30 minutes.
4 Vaccines contain weak or damaged pathogens. 6a Average birth mass.
5 You become immunised when you are injected b Smoking.
with a vaccine. Vaccines contain weak or dead c The children of mothers who drink alcohol when
pathogens, so they don’t make you ill, but your pregnant have lower test scores in maths and
white cells make antibodies. When the live reading by about 10 units.
pathogen infects you later, your white cells 7a Malaria.
can produce the right antibodies very quickly. b Far more children between the ages of 0 and 4 die
This destroys all the pathogens before they can from malaria than those 5 years and over (around
make you ill. 980 000 compared with around 150 000).
6 Colds and flu are caused by viruses. Antibiotics c Polio. It is spread only by infected humans, and
only destroy bacteria. is only found in a few countries, which means it
7 Some pathogens are resistant to certain types of is easier to vaccinate the people who could catch
antibiotic. Hospitals test different antibiotics to disease from the infected people.
find out which are best for treating each infection. d If infected people have no symptoms they are less
8 Some bacteria are tougher than others. They won’t likely to seek treatment.
be killed by the first few doses of antibiotics. These
bacteria have a greater resistance to the antibiotic. Stage 8 Review
If the antibiotic course is not completed, these
1a Students should draw the apparatus shown at the
bacteria survive and reproduce. This creates a
top of page 156 of the Student book without the
large number of bacteria that are resistant to the
solution to remove carbon dioxide.
antibiotic, so it is no longer any use.
b She should test the leaves for starch by adding
12.5 Review iodine.
1a A, B c The leaves should turn blue-black on the control
b A, C plant but stay brown on the plant without carbon
2 Any two from the following. dioxide.
In the under 35 category, nearly twice as 2a C, A, B, D.
many men as women drink more than the b Minerals.
recommended amount. c By closing its stomata.
© Oxford University Press 2013: this may be reproduced for class use solely for the purchaser’s institute 115
Checkpoint_Biology_TG_SB_Ans.indd 115 28/11/2013 16:03
3a B fats and C carbohydrates. 5 Test 3 shows that plants can only make their
b A proteins and E minerals. own food if they have carbon dioxide around
c A proteins, D vitamins, and E minerals. their leaves.
d 20% 6 On a sunny day the amount of oxygen in the
4a Cheese. air around sugar cane should increase as more
b Starch and glucose. oxygen is produced by photosynthesis (than the
c 200 g plant uses for respiration).
d 5.11 g
13.2 Preliminary tests
5a D, E
1 Does the colour of light affect the rate of
b C, D
photosynthesis (the time a leaf disc takes to
c Any one from: carbon dioxide; glucose; nutrients.
collect enough oxygen to make it rise)?
d The walls need to be thinner so that oxygen can
2 Salma thinks that green light is no good for
diffuse into the capillaries in other tissues quickly
photosynthesis because plants are green.
and easily.
This shows that they absorb red and blue light
6 It rises.
but reflect greeen.
7a Large molecules like starch need to be broken
3 Students should produce a diagram of the
down into smaller molecules like glucose which
apparatus shown on page 160 of the Student book.
can diffuse into cells/the blood.
4 Leaf discs sink when the air is sucked out of them.
b In the mouth.
As they photosynthesise, oxygen builds up in the
c Blood.
discs and they start to float again. The faster the rate
d Glucose.
of photosynthesis, the less time they take to float.
e Any one from: 37 °C is the normal human body
5 Preliminary tests check that the method works
temperature; the enzyme works fastest at 37 °C.
and the controlled variables have suitable values.
8a Tar.
6 The light from each filter might have a different
b Carbon monoxide.
intensity. There could be other variables she did
c Nicotine.
not control.
d Carbon monoxide.
e Any two from: the heart’s muscle cells would not 13.3 Plant growth
receive enough glucose and oxygen; the muscles 1 Minerals are added to the water used in
could not respire; the muscles would run out hydroponic systems.
of energy. 2 Plants take the elements nitrogen, potassium,
9a B ovary. phosphorus, and magnesium from minerals.
b A oviduct. 3 Purple leaves and few roots show a plant is short
c C uterus. of phosphorus.
d Any one from: during days 1–4 the lining of the 4 A plant that is short of potassium has poor flower
uterus was breaking down; the woman was having and fruit growth, and older leaves wilt and lose
a period. their colour.
e Day 14. 5 Plants can’t grow properly without nitrogen
because they use it to make proteins to build
13 Plants 6
new cells.
Plant one group of rice plants in normal soil
13.1 Photosynthesis and another group in soil that is short of
1 Animals depend on plants for oxygen and for the magnesium. Make sure both groups receive the
food they use as a source of energy and building same conditions of other minerals, light, water,
materials. temperature, and carbon dioxide. Compare
2 Carbon dioxide enters a leaf through stomata on the appearance of the groups after 2 weeks
its underside and diffuses to the the chloroplasts (any suitable time).
in its cells. Water is carried from roots to leaves, 13.4 Phytoextraction
through xylem vessels in the veins, and then 1 Some metals need to be removed from soil or
diffuses into every cell. water because they are toxic.
3 If seedlings are kept in the dark they produce tall, 2 Hyperaccumulators can absorb a lot of metal and
weak shoots and tiny yellow leaves and they only it doesn’t harm them.
survive for a few days. If part of a leaf is covered 3 To remove metals from soil, grow
it does not make starch. hyperaccumulators, harvest the plants, and burn
4 Test 1 shows that plants can only make their own them to trap the metal in a small amount of ash.
food in the green parts of leaves. Repeat until the soil is clean.
116 © Oxford University Press 2013: this may be reproduced for class use solely for the purchaser’s institute
Checkpoint_Biology_TG_SB_Ans.indd 116 28/11/2013 16:03
4 Plant the ferns (hyperaccumulators) along river e The leaves of plants grown without magnesium
banks to take poisonous arsenic from the water. would be white, yellow, or paler.
5a B
13.5 Flowers
b E
1 Students should draw stamens and a carpel like
c F
those in the insect-pollinated flower shown on
d C
page 166 of the Student book and a second set
e D
like those in the wind-pollinated flower shown on
f A
page 167 of the Student book.
6 Any two from the following:
2 Insect-pollinated flowers have brightly coloured
Insect-pollinated flowers have brightly coloured
petals and produce nectar to attract the insects. In
petals.
wind-pollinated flowers, the anthers hang down
Insect-pollinated flowers have nectaries/produce
to catch the wind and the stigmas are feathery to
nectar to attract the insects.
catch pollen.
Wind-pollinated flowers have anthers that hang
3 Wind-pollinated flowers produce smaller,
down to catch the wind.
lighter pollen.
4 Flowers can make self-pollination difficult by Wind-pollinated flowers have feathery stigmas to
producing their male and female gametes at catch pollen.
different times. Wind-pollinated flowers produce smaller,
5 Pollination occurs when pollen lands on the lighter pollen.
stigma. Fertilisation occurs (after a pollen tube 7a The concentration of the sugar solution the pollen
grows down to the ovule) when the nucleus of the was placed in.
male gamete fuses with the egg cell nucleus. b 80%
13.6 Seed dispersal c Repeat the test.
1 Seeds germinate when they have water, a suitable 8a A, E
temperature, and oxygen. b B
2 Seedlings have a better chance of survival if they c C, F
grow a long way from their parent plant, because d D
this reduces competition between plants of the
same species. 14 Adaptation and survival
3 Students should produce three diagrams: a small
fruit, with either wings or a parachute, that could 14.1 Adaptation
be carried by the wind; a large floating fruit, with 1 An adaptation is a characteristic (physical feature
air inside it, that could be carried by water; and or behaviour) that helps an organism survive.
fruit with a sticky coat of hooks that could be 2a Any two of the following: forward-facing eyes;
carried by animals. sharp teeth; camouflage; streamlined shape.
b Any two of the following: forward-facing eyes;
13.7 Review sharp beak; streamlined shape; strong claws.
1 A water (minerals). c Any two of the following: eyes on the front of
B carbon dioxide. their heads to judge distances; large ears; good
C light. sense of smell; grasping feet; long arms.
D glucose (starch). d Any two of the following: eyes on the sides of
E oxygen. their heads; large ears; good sense of smell;
2 a and c are correct. camouflage; speed; living in herds.
3a The grams of plant biomass produced increased as e Any two of the following: forward-facing eyes;
the carbon dioxide percentage in the air increased. sharp teeth; sharp claws; speed; streamlined
b Carbon dioxide + water glucose + oxygen shape; camouflage; hunting in packs.
c Carbon dioxide is essential for photosynthesis
but there is very little in the air. When more is 14.2 Extreme adaptations
provided, the rate of photosynthesis increases. 1 Students should produce a labelled drawing of a
d To increase reliability the tests (measurements) desert plant with at least two of these adaptations:
should be repeated. long horizontal roots; a very long vertical root;
4a Any one from: the volume; the temperature. thick stems; small fleshy leaves; spines or
b Any one from: the number of leaves; the sizes of waxy coatings.
the leaves; the length of the seedling. 2 Small animals survive without drinking because
c Nitrogen. they store fat, stay underground during the day,
d To make proteins. extract water from food, avoid sweating, and
produce concentrated urine.
© Oxford University Press 2013: this may be reproduced for class use solely for the purchaser’s institute 117
Checkpoint_Biology_TG_SB_Ans.indd 117 28/11/2013 16:03
3 Arctic animals conserve heat because they have b Electronic tags, studying their tracks, or direct
rounded bodies and thick layers of fat and fur. observation could be used to study the migration
Most are large but smaller animals burrow under of wildebeest.
the snow. c Automatic cameras or studying their tracks could be
4 In milder winters, when there is less snow, fewer used to study shy mammals in a tropical rainforest.
lemmings survive because there is nothing to d Electronic tags could be used to study whale
burrow under and no protection from icy winds. migration.
e The number of arctic foxes in a habitat could be
14.3 Survival
studied by observing their tracks.
1 Many plant species move towards the poles as
3 Studying animal faeces can show which animals
the climate warms because their seeds survive in
are present and what they eat.
cooler places.
4 Long-term observations of a group of animals can
2 Climate change could affect our food supply
show how they behave and what their social lives
because the world’s three main crops – maize,
are like.
wheat, and rice – are not adapted to hot, dry
conditions. 14.6 Review
3 Global warming has reduced the number of seals 1 A – desert; B – rainforest; C – grassland;
that polar bears catch because the ice they hunt D – arctic region.
from melts earlier. 2 Any three from: forward-facing eyes; sharp beak;
4 Between 1990 and 2000, adelie penguin numbers streamlined shape for speed; strong claws.
dropped and chinstrap penguin numbers rose. 3a Fox A is camouflaged against soil in summer and
5 Adelie penguins find it harder to catch their food snow in winter.
when there is less ice. b Fox B has large ears to cool its blood.
6 Adelies breed later because there is more snow 4 The long root collects water from deep
now and they wait until the snow has melted. underground. The swollen leaves store water.
7 Adelie chicks have less chance of survival 5 Wide feet stop the camel sinking in loose sand
because small chicks lose their heat more quickly and the polar bear sinking in loose snow.
and have smaller food stores. 6 Any two from the following:
The long root collects water from deep
14.4 Sampling techniques
underground.
1 To estimate the size of a rabbit population
The surface roots collects water when it rains.
scientists could: set traps; mark the animals they
The chemical prevents other plants from
capture; release them; capture another sample;
competing with it for water.
calculate what fraction of the second sample is
7 Decorator crabs cover their shells with corals, sea
marked; divide the number marked at the start by
anemones, seaweeds, and sponges to camouflage
this fraction.
themselves from predators.
2 To estimate the number of plants on 1000 m2 of
8a The average beak length increases as the
land: place 10 or more 1 m2 quadrats in random
temperature of the environment increases.
positions over the land; count the plants in each
b Birds can increase heat loss by having a longer
quadrat; calculate the average number of plants
beak in warmer climates or reduce heat loss in
per quadrat; multiply by 1000 to estimate the
cold climates by having a shorter beak.
total population.
9a Plant B is better adapted to the dim light under
3 Students should sketch a pitfall trap like the
the tree.
one at the top of page 179 of the Student book.
b Any one from: collect data around other trees;
They should state that it is designed to catch any
repeat the investigation.
invertebrates that run along the ground.
10a The minimum area of sea ice in the Arctic
4 The percentage plant cover increases as the
dropped by 4.7 millions of m2.
distance from the tree increases.
b Narwhals could be endangered if the sea ice
5 Trees stop light reaching the ground, so few
disappears because they will not be able to feed
plants can grow near trees.
under sea ice where their predators can’t catch them.
14.5 Studying the natural world 11a Seema threw the quadrat over her shoulder so that
1 Ecologists study animals in their environments it would land in a random position.
by: direct observation; studying their tracks; using b The total number of poisonous plants growing
automatic cameras; using electronic tags. in the square of grass is the average number in
2a Automatic cameras could show how a lioness one quadrat multiplied by the total area (50 m2),
brings up her cubs. which is 100.
c She could repeat the test in more positions.
118 © Oxford University Press 2013: this may be reproduced for class use solely for the purchaser’s institute
Checkpoint_Biology_TG_SB_Ans.indd 118 28/11/2013 16:03
12a There were fewer attacks on the model snakes 15.3 Decomposers
with triangular heads than the model snakes with 1 Any two from: fungi and bacteria; invertebrates
flat heads. such as worms, slugs, snails, and fly larvae.
b The grass snakes deter predators by making 2 Most of the food chains in the mangroves depend
themselves look more like dangerous vipers. on decomposers because most mangrove leaves
13 100 fish. are not eaten by herbivores. They fall into the
water where they are decomposed.
15 Energy flow 3 Mangrove forests are important to local people
because they provide building materials, fuel,
15.1 Food webs medicines, and food, and the waters around them
1 spiders are rich fishing grounds.
4 Mangrove forests are important to the Earth
as a whole because they produce new biomass
as fast as tropical rainforests, and have a high
beetles and their larvae
biodiversity.
5 The carbon in rotting leaves can get back into
the air when decomposers respire or when the
snails woodlice millipedes animals that feed on them respire.
6 Decomposers allow life to continue by recycling
the elements (minerals) that make up the bodies.
dead leaves 7 Phytoplankton grow faster in shallow coastal
waters because rivers bring a constant supply of
2 The secondary consumers are beetles and minerals to them.
their larvae.
3 Snails, woodlice, and millipedes make up the 15.4 Changing populations
second trophic level. 1 The population of an animal species might suddenly
4 The producers at the starts of food chains are increase if they move into a new environment, where
plants (algae or phytoplankton). there is plenty of food and no predators.
5 The arrows in a food web represent the energy 2 Three things that could reduce the population of
passed from producers to consumers. an animal species are lack of food, disease, or
pollution (or predators).
15.2 Energy flow 3 Populations stay small if their death rate the same
1 Students should draw a pyramid composed of: as their birth rate.
a 15 cm wide block labelled acacia trees, a 2 cm 4 Humans populations use energy and materials as
wide block labelled giraffes, and 1 cm wide block well as food and water.
labelled lion. 5 Sustainable development provides everything
2 Students should draw a pyramid composed of, humans need without damaging the environment.
from the bottom upwards: a 5 cm wide block 6 Animals are interdependent if one animal affects
labelled acacia trees, a 10 cm block labelled the survival of the other, such as a predator and
impalas, and a 1 cm wide block labelled cheetahs. its prey.
3 Most of the energy in the food that impalas eat is 7 The numbers of caribou and wolves in the Arctic
used for respiration. rise and fall in cycles because the animals are
4 Students should draw a pyramid composed of, interdependent. Wolves eat caribou so the number
from the bottom upwards: a 200 mm wide block of caribou drops. Then wolf numbers drop too
labelled acacia trees, a 15 mm wide block labelled because they have less food – they starve or raise
giraffes, and 1.5 mm wide block labelled lion. fewer offspring. This gives the caribou a chance
5 Students should draw a pyramid composed of, from to breed and raise offspring. Then predator
the bottom upwards: a 100 mm wide block labelled numbers increase and the cycle begins again.
grass plants, a 5 mm block labelled impalas, and a 8 Populations are more likely to stay the same
0.5 mm wide block labelled cheetah. size where there is more biodiversity because
6 Prey animals are present in the higher numbers. predators can eat several different prey species. If
7 Pyramids of biomass are always shaped like one disappears, they can eat something else.
pyramids – the mass of producers is greater
than the mass of herbivores, and the mass of 15.5 Facing extinction
herbivores is greater than the mass of carnivores. 1 Invasive species are successful because they grow
8 Big carnivores such as lions need a large territory quickly, reproduce quickly, survive in a wide range
with plenty of vegetation to support a large of habitats, eat anything, or beat other species in
number of prey animals. the competition for food and spaces to live.
© Oxford University Press 2013: this may be reproduced for class use solely for the purchaser’s institute 119
Checkpoint_Biology_TG_SB_Ans.indd 119 28/11/2013 16:03
2 A species is more likely to become extinct if it 4a B
is only found in a few places, reproduces very b A
slowly, faces a new predator, or has its food c The biomass of secondary consumers is always
supply reduced by a new competitor. lower than the biomass of primary consumers
3 The number of tree snakes carried on rising when because primary consumers use most of the
the bird population on Guam dropped because energy in their food for respiration. Only a small
they swapped to eating other animals (lizards). percentage is passed to the next trophic level.
4 The number of spiders on Guam has risen 5 Statements a, c, and d are true.
because the tree snakes have eaten their predators 6a 2
(lizards and insect-eating birds). b 3
5 Destroying the spiders could ruin the island c 4
because there would be fewer predators to control d 1
the insect population. Leaf-eating insects could 7 The same area of land can feed more people if
destroy the island’s vegetation. they eat cereals instead of meat because cereals
6 The forests on Guam are likely to change in the occupy a lower trophic level. Energy is lost at
future because many of Guam’s tree seeds were each trophic level (through respiration) so the
dispersed by birds that are now extinct. The seeds total biomass in higher trophic levels drops.
can’t grow successfully if they are not dispersed. 8a B
b D
15.6 Maintaining biodiversity
c Where the population starts to drop because
1 An ecosystem has a high biodiversity if it
deaths exceed births.
contains many different species.
d Any two from: pollution; disease; shortage of
2 We should limit the amount of forest cleared for
food; predators.
farming because farmland produces less biomass
9a Decomposition.
per m2 and has a much lower biodiversity.
b Decomposers.
3 A rainforest can absorb more of the sunlight
c Any two from: bacteria; fungi; invertebrates such
that reaches it than the crops on farmland can
as worms, slugs, snails, and fly larvae.
because it contains a mixture of plants that each
d Decomposers release minerals from plant and
need different growing conditions. Some absorb
animal wastes so they can be reused by plants.
the dim light that the trees above them don’t use.
They also return carbon dioxide to the air.
4 It is useful to have many different varieties of
10a B
each crop plant because a disease that affects one
b C
variety is unlikely to infect them all.
c D
5 Animals can breed with other animals from other
d E
countries because their sperm can be frozen and
11a The zooplankton biomass could decrease
flown around the world.
between June and July because they have fewer
15.7 Review phytoplankton to feed on.
1a Students should produce a sketch to illustrate b Any two from: lack of light (for photosynthesis);
the following food chain: plant insect lack of carbon dioxide; lack of minerals; an
lizard fox. unsuitable temperature.
b The number of lizards would increase if the foxes
all died.
2a Any one from: squid; penguin; seal.
16 Human influences
b Any one from: krill; squid; penguin. 16.1 Air pollution
c Krill. 1 Acid rain is caused by sulfur dioxide and oxides
d Penguin of nitrogen. Sulfur dioxide is released when fuels
e Krill. burn and when metals are extracted. Cars release
f Phytoplankton oxides of nitrogen.
g Seal. 2 Many lichens cannot survive in polluted air so
3a The number of offspring puffins can raise could the varieties of lichen species present shows how
fall because there are fewer prey for them to catch. clean the air is.
b Now there are fewer herrings, sharks have a 3 Acid rain damages plants in three ways: it makes
bigger supply of zooplankton. soil more acidic which can stop plants getting
c If global warming reduces the biomass of essential mineral elements; it dissolves aluminium
phytoplankton in the oceans, populations will from rocks, which can poison plants; it damages
drop in the rest of the food web because there will leaves and seeds, so pathogens can infect plants
less food (energy) available to feed them. more easily.
120 © Oxford University Press 2013: this may be reproduced for class use solely for the purchaser’s institute
Checkpoint_Biology_TG_SB_Ans.indd 120 28/11/2013 16:03
4 Air pollution has increased in the past 100 years 5 Countries can earn money from sustainable
because the human population is larger, we have forests by encouraging tourists to visit them and
more cars, and we burn more fuels. selling rainforest products such as fruits and nuts.
6 Wealthy countries can help to save forests by
16.2 How scientists work
using fewer resources. To do this they need to
1 Carbon dioxide could make Earth warmer by
limit population growth, reuse products and
preventing heat from leaving the atmosphere.
recycle materials, use energy more efficiently so
2 Arrhenius predicted that doubling the amount
less fuel is needed, and make farms more efficient
of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere would make
so less land is needed for crops.
it 5 °C warmer.
3 One piece of evidence that supports this prediction is 16.5 Review
that the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere, 1a B, C
and its temperature, are both increasing. b A, D
4 Some scientists don’t agree that humans cause c Sulfur dioxide; oxides of nitrogen
global warming. They argue that natural events d Sewage; fertiliser
have a bigger effect on our atmosphere. e B, C
5 As the Earth warms there could be more storms, f Acid rain could be killing the trees.
droughts, and heatwaves. 2a Humans add sulfur dioxide to the air by burning
6 The IPCC studies evidence from thousands fossil fuels, especially coal.
of scientists all over the world and publishes b When the amount of sulfur dioxide in the air
conclusions. rises, the number of deaths rises.
c Sulfur dioxide damages the lungs.
16.3 Water pollution
d Reducing acid rain an international problem
1 Fertilisers make plants and algae grow faster by
because winds carry acidic gases from one
providing extra minerals.
country to another.
2 Eutrophication happens when fertiliser enters
3a Walls have more lichen species growing on them.
water, algae multiply rapidly and block off
b The greater the distance from the city centre, the
the light, plants below the surface die, micro-
more different lichen species are found.
organisms use up oxygen as they decompose dead
c The main source of air pollution in cities is traffic.
plants, and finally fish die from a lack of oxygen.
d Tall, bushy lichens most likely to be found in the
3 We can stop sewage polluting rivers by storing
country (in unpolluted areas).
it in huge tanks while micro-organisms break its
4 From least to most polluted the samples are:
contents down.
B, A, C.
4 Invertebrates can be used to monitor water
5a B
pollution because they act as living indicators.
b The oxygen concentration is lower at site B
Many species cannot survive in polluted water, so
because there are more decomposers using the
the species present show how polluted the water is.
oxygen for respiration.
16.4 Saving rainforests 6a The mass of bacteria could increase 2 km from the
1 A growing population removes trees for many town centre because there is sewage or rotting plant
reasons: to grow food; to keep farm animals; to material in the water (causing eutrophication).
remove metal ores, oil, or coal from the ground; b The extra bacteria could reduce the number of
to use the wood as a fuel or building material; to fish in the river by lowering the water’s oxygen
grow food crops to sell to other countries; to grow concentration as they respire.
biofuels to sell to other countries; to build new 7 Tench would survive best in water polluted with
roads and houses. sewage because they require least oxygen.
2 Other countries encourage tropical countries 8a The animals would lose their habitat.
to remove forests by buying crops grown in b Heavy rains could wash soil away from the
deforested areas. hillside (cause erosion).
3 Deforestation damages the local environment by: 9a 15%
destroying habitats; removing people’s access to b Any two from the following:
the food and fuel the forest provided; making the Deforestation reduces photosynthesis.
local climate warmer, windier, and drier; making The roots and branches left behind add carbon
soil erosion more common; making rivers flood dioxide to the atmosphere as they decompose.
more easily. The machinery used for deforestation burns
4 Deforestation affects the world’s climate by fossil fuels.
adding carbon dioxide to the atmosphere and The fires used to remove the trees add carbon
increasing global warming. dioxide to the atmosphere.
© Oxford University Press 2013: this may be reproduced for class use solely for the purchaser’s institute 121
Checkpoint_Biology_TG_SB_Ans.indd 121 28/11/2013 16:03
10a Any two from the following: 4 Students should modify the branching key
It reduces biodiversity. produced for question 3 to start with the question:
It reduces photosynthesis. does it roar?
It increases global warming. Does it roar?
b Any two ways of limiting the need to remove YES NO
trees to grow crops such as the following:
Limit population growth. Does it have Does it have
Make farms more efficient so less land is needed stripes? spots?
for crops. NO YES YES NO
Encourage tourists to visit the forest, to provide
local employment. Does it have tiger cheetah caracal
Harvest rainforest products such as fruits and nuts spots?
for export. YES NO
Encourage wealthy people to buy trees in the
leopard lion
forest and protect them.
17.2 What makes us different?
17 Variation and classification 1 Each egg and sperm cell contains half of each
parent’s genes. These combine to give each
17.1 Using keys
embryo a full set of genes.
1 2 The genes you inherit from your parents are
1. Does it have yes see 2
spots? copied each time a cell divides, so every cell in
no see 3 your body has a complete set.
2. Are its spots yes leopard 3 Each egg and sperm cell contains half of each
in groups? parent’s genes – a random selection – so each
no cheetah
child inherits a different combination of genes
3. Are its ears yes caracal from the same parents.
pointed? 4 Identical twins look the same when they are
no lion
young because they have identical genes and
2 Does it have these control their characteristics.
spots? 5 One human characteristic controlled only by
YES NO genes is your blood group.
6 Any two examples: height, body mass, intelligence.
Are its spots Are its ears 7 Any example of a characteristic influenced only
in groups? pointed? by the environment, e.g. language spoken.
YES NO YES NO 17.3 Chromosomes
1 Students should produce a labelled diagram like
leopard cheetah caracal lion
the one at the bottom of page 212 of the Student
3 Students should modify the branching key book showing genes on chromosomes in the
produced for question 2 to include a tiger, e.g. nucleus of a cell.
Does it have
2 The nucleus of a human cell contains 23 pairs of
spots? chromosomes or 46 individual chromosomes.
YES NO 3 You have two copies of every gene because the
chromosomes in each pair carry the same genes.
Are its spots Does it have We inherit one set from each parent.
in groups? stripes? 4 Sex cells (eggs and sperm) each contain one
YES NO YES NO chromosome from each pair – 23 individual
chromosomes.
leopard cheetah tiger Are its ears 5 A fertilised egg cell with two X chromosomes
pointed? produces a girl and one with an X and a Y
YES NO chromosome produces a boy.
6 Parents are equally likely to have a girl or a
caracal lion boy because half a man’s sperm cells carry
an X chromosome and the other half carry a
Y chromosome.
122 © Oxford University Press 2013: this may be reproduced for class use solely for the purchaser’s institute
Checkpoint_Biology_TG_SB_Ans.indd 122 28/11/2013 16:03
17.4 Investigating inheritance 17.6 Developing a theory
1 Mendel’s second-generation pea plants only 1 Students should describe an observation that
inherited their height from one of their parents. suggests species change over time, e.g. many fossils
They were all tall. None were short. are similar to modern animals, but not identical.
2 Mendel made his tall and short plants fertilise each 2 In the Galapagos Islands, there are different
other by preventing self-pollination and using a mockingbirds and finches on different islands.
brush to transfer the chosen pollen to their flowers. 3 Students should sketch two beaks. One should
3 The gene that makes peas tall must be a dominant be long and pointed and labelled ‘suitable for
gene because plants are tall even when they only collecting insects’. The other should be short and
have one copy of the gene. wide and labelled ‘suitable for crunching seeeds
4 The second-generation plants inherit a gene from and nuts’.
each parent so they have both sorts: T and t. The T 4 The finches with the beaks that suit the food
version is dominant so the pea plants are all tall. available will collect more food, so they are more
5 Each of the second generation plants makes two likely to survive.
sorts of sex cell. On average, half carry T and 5 Selective breeding occurs when humans choose
half carry t genes. Male sex cells carrying t genes which members of a species breed and produce
could fertilise female sex cells with the same offspring. Natural selection occurs when
gene. The offspring would have tt genes so they environmental factors, such as the availability of
would be short. food, select which individuals survive and reproduce.
6 17.7 Darwin’s theory of evolution
t t
eggs pollen 1 Plants and animals keep producing offspring, but
their total numbers usually stay the same because
T tt t most of their offspring don’t survive.
2 Plants compete for patches of soil, water, and
sunlight, and animals compete for food and
Tt tt
places to live.
3 Some animals are more likely to survive than
Tt others because they are better adapted to their
environment.
4 Students should name a characteristic that could
1 in 2 or 50% improve an animal’s chance of surviving for long
of the offspring will be tall. enough to reproduce, e.g. the ability to run fast to
catch prey or escape from predators.
17.5 Selective breeding 5 Evolution by natural selection could have made
1 Members of a species show a lot of variation modern cheetahs run faster than their ancestors
because they inherit unique combinations of over many generations, e.g. the speeds of
genes from their parents. cheetahs vary. A fast cheetah catches more prey.
2 Selective breeding involves three steps: decide This allows them to feed more offspring. So their
what characteristics you want the next generation speed passes to the next generation. Over time
to have; choose parents that have some of these this characteristic becomes more common.
features and breed them together; select the
offspring with the characteristics you prefer and 17.8 Moving genes
breed these together. The process needs to be 1 Genetic engineering adds genes to cells.
repeated over many generations. 2 Genetic engineering is easier in bacteria because
3 Selective breeding is useful to farmers because it their cells are simpler, their genes are loose in the
has produced better farm animals and crops. cytoplasm, and they reproduce very rapidly.
4 Selective breeding has produced cows that give 3 Students should produce a series of labelled
more milk, resist disease, or are stronger. diagrams, like those at the top of page 223 of
5 Selective breeding can produce cereal crops the Student book, to explain how new genes are
such as maize with bigger seeds (so more food is transferred to bacteria.
grown on the same amount of land). 4 Genetic engineering can make micro-organisms
more useful by giving them genes that make them
produce products we need.
© Oxford University Press 2013: this may be reproduced for class use solely for the purchaser’s institute 123
Checkpoint_Biology_TG_SB_Ans.indd 123 28/11/2013 16:03
5 Some people worry about genetically engineered 7a The population changed from 1% black to
plants because their pollen or seeds could 90% black.
contaminate food crops or cause other problems b Light moths.
we can’t predict. Genetically engineered bacteria c Light moths could be seen more easily on the
grow indoors in large tanks and few people worry darker tree trunks so birds caught more of them.
about them escaping. The dark moths were more likely to survive and
produce offspring.
17.9 Using genes
8 a and c are true.
1 Most of the medicines used to treat malaria no
9a A
longer work because the protozoa that cause
b C
malaria have developed resistance to them.
c Genes.
2 Artemisinin comes from a Chinese plant. It is
d Different foods were available on each island. The
expensive because it is difficult to extract from
birds with the best adapted beaks survived and
the plant.
passed the genes that controlled their beak shape
3 Selective breeding could be used to make
to their offspring.
artemisinin cheaper by producing new varieties of
e The finches evolved from the same group
the plant that contain more artemisinin.
of finches.
4 The genes that plants use to make artimisinin can
10 Any two from the following:
be put into yeast cells. Then the yeast cells can
Armadillos showed variation.
be grown in tanks all over the world to produce
Those with the biggest claws dug more insects
artemisinin quickly.
out of the soil.
5 Governments and charities need to raise money to
They survived and passed their genes to their
tackle malaria because it costs billions to find new
offspring.
medicines and most malaria victims are too poor
Over time, bigger claws became more common.
to pay for them.
17.10 Review
1 A – dragonfly larva.
Stage 9 Review
B – stonefly larva. 1a Photosynthesis.
C – damselfly larva. b Both.
2a A – water mite. c Photosynthesis.
C – water boatman. d Photosynthesis.
E – midge larva. e Respiration.
b Students should produce a question that will f Both.
distinguish between invertebrates B and D, 2 B
e.g. how many tail filaments does it have? 3a 30 °C
3a Any one from: dark hair; eyebrow shape; ear b Any two from:light intensity; water supply;
shape; nose shape; large eyes. mineral supply; carbon dioxide supply.
b Any one from: mouth shape; straight hair. c Any one from: have more seedlings in each
c Karis looks a bit like each parent because she group; repeat/duplicate the measurements.
inherited genes from each of them, and genes 4a B produces pollen (male sex cells); A collects
control characteristics. pollen (so the male sex cell can fertilise the ovule
4a Nucleus. to produce a seed).
b The genes are copied so that each cell gets a b Nectar and coloured petals are used to attract
full set. insects but this flower is wind pollinated.
c Each egg or sperm cell contains half the normal 5a Pollen lands on the stigma.
number of genes. b Any two from the following.
d The genes in the parents’ egg and sperm cells A pollen tube grows down (through the style) to
combine during fertilisation to give each embryo an ovule.
a full set of genes. The nucleus of the male sex cell (gamete) moves
5 Different breeds of dog are produced by selective down the pollen tube.
breeding. The nucleus of the male sex cell (gamete) enters
6 Breed varieties A and C together; select the an egg cell.
offspring with the shortest stems and highest The nucleus of the male sex cell (gamete) fuses
mass of grain, and breed these together; repeat the with the egg cell nucleus.
process over many generations. c 28–32 oC
d They could drop because fewer egg cells would
be fertilised.
124 © Oxford University Press 2013: this may be reproduced for class use solely for the purchaser’s institute
Checkpoint_Biology_TG_SB_Ans.indd 124 28/11/2013 16:03
6a The number of seeds per dish. 9 A arachnid; B mollusc; C crustacean.
b Any one from: the fewer seeds per dish, the 10a Carbon dioxide + water glucose + oxygen
greater their chance of survival; the closer b Grasshoppers.
together seeds are grown, the smaller their chance c Only a small fraction of the biomass in each
of survival. trophic level is passed to the animals that
c Any two from: light; water; minerals; carbon consume it, so the total biomass in a higher
dioxide trophic level is always less than in a lower one.
d Any three from: wind; water; animals; d Decomposers break down dead plants and
exploding pods. animals to release the energy they need.
7a To make chlorophyll. 11 They inherited genes from each parent. Genes
b To make protein. influence most of our characteristics by
c A – nitrogen; B – magnesium; C – phosphorus. controlling our cells.
8 Desert because they are waterproof, camouflaged
against orange sand, and capable of surviving for
months without eating or drinking.
© Oxford University Press 2013: this may be reproduced for class use solely for the purchaser’s institute 125
Checkpoint_Biology_TG_SB_Ans.indd 125 28/11/2013 16:03
You might also like
- SlideDoc - Us-Diagnostic Natural Science 4 Primary Byme - Plants - TreesDocument2 pagesSlideDoc - Us-Diagnostic Natural Science 4 Primary Byme - Plants - TreesJuanA.RodriguezGonzalez100% (7)
- A MathematicalModelof The Hemoglobin-OxygenDissociationCurve of Human Blood and of The Partial Pressure As A Function or TemperatureDocument6 pagesA MathematicalModelof The Hemoglobin-OxygenDissociationCurve of Human Blood and of The Partial Pressure As A Function or TemperatureakbianchessiNo ratings yet
- 2210 ABO Worksheet-1Document3 pages2210 ABO Worksheet-1Lida LindstromNo ratings yet
- Daily Lesson Plan SCIENCE 4 WEEK 3Document24 pagesDaily Lesson Plan SCIENCE 4 WEEK 3Carol Gelbolingo100% (2)
- Compelet Biology Sec1 SB Answers (S.A.files ?)Document34 pagesCompelet Biology Sec1 SB Answers (S.A.files ?)Suha AlgharazNo ratings yet
- Activity 3.1 Factors Affecting EcosystemDocument2 pagesActivity 3.1 Factors Affecting EcosystemAT4-11 HUMSS 2 CEDRICK ILAONo ratings yet
- Sci Mod3 1Document11 pagesSci Mod3 1Pauline Jane FernandezNo ratings yet
- U2 Ans CoursebookDocument2 pagesU2 Ans CoursebookKshitij SoniNo ratings yet
- Science 4 LessonplanDocument4 pagesScience 4 LessonplanDanieta Salas PerezNo ratings yet
- All About PlantsDocument14 pagesAll About Plantsapi-234860390No ratings yet
- Ans Biology Work Book1Document26 pagesAns Biology Work Book1Aly HassanNo ratings yet
- Learning Area Grade Level Quarter Date: TLE-Agri Crop Nine ThreeDocument4 pagesLearning Area Grade Level Quarter Date: TLE-Agri Crop Nine ThreeÁthymosNo ratings yet
- STD - Iii Sub - Science CH - Plants in Our SurroundingsDocument3 pagesSTD - Iii Sub - Science CH - Plants in Our SurroundingsSudip GhoshNo ratings yet
- Science-6B-Week12-Adaptation of PlantsDocument3 pagesScience-6B-Week12-Adaptation of PlantsOlivia Maria ThomasNo ratings yet
- Answers Chapter 6Document44 pagesAnswers Chapter 6lunalabrijnNo ratings yet
- Plant PhysiologyDocument3 pagesPlant PhysiologyNica CordovaNo ratings yet
- Grades 2 and Up Plant RootsDocument17 pagesGrades 2 and Up Plant RootsAnubhav KashyapNo ratings yet
- Sci7 Unit B Unit ReviewDocument16 pagesSci7 Unit B Unit Reviewapi-242221534No ratings yet
- G3 - LSR - 2Y - 3.01 Plants and Trees GrowingDocument14 pagesG3 - LSR - 2Y - 3.01 Plants and Trees GrowingPhạm SửuNo ratings yet
- Getting To Know PlantsDocument29 pagesGetting To Know Plantsashutoshbombatkar2No ratings yet
- Science Unit 1Document14 pagesScience Unit 1SadakatMalihaNo ratings yet
- TLE-Agriculture and Fishery Arts: Quarter 3 Week 7-8 - Module 6Document11 pagesTLE-Agriculture and Fishery Arts: Quarter 3 Week 7-8 - Module 6Lara FloresNo ratings yet
- DoCN Housplant GuideDocument9 pagesDoCN Housplant GuideJunior ArreseNo ratings yet
- Cot Science 4 q2 w3Document54 pagesCot Science 4 q2 w3Frit ZieNo ratings yet
- First Book of Plant 00 Dick RichDocument98 pagesFirst Book of Plant 00 Dick RichjeubrasilNo ratings yet
- Lesson 27 Terrestrial PlantsDocument3 pagesLesson 27 Terrestrial PlantsMaricel Cebrero Santiago100% (4)
- Good Example Research PaperDocument9 pagesGood Example Research Paperapi-370973922No ratings yet
- Science - Other Ways of Classifying PlantsDocument7 pagesScience - Other Ways of Classifying PlantsRien Jing TianNo ratings yet
- G3 - LSR - 1G - 3.03 Where Plants and Animals LiveDocument14 pagesG3 - LSR - 1G - 3.03 Where Plants and Animals LiveNguyệt Ánh - Lucy TăngNo ratings yet
- Science Class With Miss RJDocument31 pagesScience Class With Miss RJOktaviana PusparaniNo ratings yet
- Lant Ingdom: Big PictureDocument2 pagesLant Ingdom: Big PicturehenryNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 WorksheetsDocument4 pagesUnit 5 WorksheetsenkarniNo ratings yet
- Science Chapter 6Document13 pagesScience Chapter 6GM EstradaNo ratings yet
- DLP - Aquatic and Terrestrial PlantsDocument7 pagesDLP - Aquatic and Terrestrial PlantsCLARKDOREAL CANTURIAS100% (2)
- Insight Link 6 - Answer Keys - WBDocument19 pagesInsight Link 6 - Answer Keys - WBElvie ColladoNo ratings yet
- CL 6 - SciDocument2 pagesCL 6 - SciK BhaiNo ratings yet
- Grade.4 ch.1, l.3Document26 pagesGrade.4 ch.1, l.3Hibara AliNo ratings yet
- Roots_of_Desert_Plants Sonoran DesertDocument2 pagesRoots_of_Desert_Plants Sonoran Desertanenyasha.guveyaNo ratings yet
- Plants Knowledge Organiser v1Document1 pagePlants Knowledge Organiser v1Catherine Dharshini LabrooyNo ratings yet
- TERM - 2 Notes & Work Book - Grade 8Document12 pagesTERM - 2 Notes & Work Book - Grade 8Hano MohdNo ratings yet
- Indian Educational School Bharatiya Vidya Bhavan, Kuwait Subject: Science Practice Worksheet Answer KeyDocument3 pagesIndian Educational School Bharatiya Vidya Bhavan, Kuwait Subject: Science Practice Worksheet Answer KeyRAJ STUDY WIZARDNo ratings yet
- How PlantsDocument3 pagesHow PlantsDanjenica Desoloc AsehanNo ratings yet
- Grade 3 Science - Plant - Parts of Leaves Different Types of Leaves - UNIT 1Document4 pagesGrade 3 Science - Plant - Parts of Leaves Different Types of Leaves - UNIT 1Surbhi BhatiaNo ratings yet
- AS - SSD - IV - EVS - Types of PlantsDocument4 pagesAS - SSD - IV - EVS - Types of PlantswasundesagarNo ratings yet
- PlantsDocument50 pagesPlantsMark JuliusNo ratings yet
- Basics of Indoor GardeningDocument9 pagesBasics of Indoor Gardeningمصطفى جاسمNo ratings yet
- Secondary-1 Bio Unit-1 Plants TextDocument9 pagesSecondary-1 Bio Unit-1 Plants TextMay Nyein ChanNo ratings yet
- Activity: Group Function Energy SourceDocument4 pagesActivity: Group Function Energy SourceKirstelle SarabilloNo ratings yet
- FRST 200 Seedling Lab ReportDocument13 pagesFRST 200 Seedling Lab ReportKaysha ReederNo ratings yet
- FOLLETO SCIENCE 2doDocument36 pagesFOLLETO SCIENCE 2doBodaq Decoracion De Interiores Papel TapizNo ratings yet
- Excerpt PDFDocument10 pagesExcerpt PDFerikNo ratings yet
- Science - 1 - WB AnsDocument12 pagesScience - 1 - WB AnsPaPa HeinNo ratings yet
- Answer Key For Class 8 J Biology J Transport in PlantsDocument3 pagesAnswer Key For Class 8 J Biology J Transport in Plantsgea1300015No ratings yet
- Q3 - Science - LessonDocument22 pagesQ3 - Science - LessonHF ManigbasNo ratings yet
- L2 Finals Plant Cell and Plant CharacteristicsDocument32 pagesL2 Finals Plant Cell and Plant CharacteristicsdonglmodestoNo ratings yet
- GK-I (Science) - Unit 7 Plants - p.48-54Document7 pagesGK-I (Science) - Unit 7 Plants - p.48-54عبیرہ کیانیNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Plants Organ SystemDocument32 pages1.2 Plants Organ SystemkitsujinnNo ratings yet
- Plant Needs and Growing Conditions: Give It ADocument30 pagesPlant Needs and Growing Conditions: Give It AAdyangNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in ScienceDocument6 pagesLesson Plan in Scienceesang quettNo ratings yet
- Looking After Plants: 1.1 Plants and Their PartsDocument10 pagesLooking After Plants: 1.1 Plants and Their PartsUbaid KhanNo ratings yet
- Week 6 Reproduction - Print Page 5-8Document8 pagesWeek 6 Reproduction - Print Page 5-8Hart OlpendaNo ratings yet
- Camp's Botany by the Numbers: A comprehensive study guide in outline form for advanced biology courses, including AP, IB, DE, and college courses.From EverandCamp's Botany by the Numbers: A comprehensive study guide in outline form for advanced biology courses, including AP, IB, DE, and college courses.No ratings yet
- Unit 3 WorksheetDocument13 pagesUnit 3 WorksheetAly HassanNo ratings yet
- Advanced Animations in Animate CCDocument10 pagesAdvanced Animations in Animate CCAly HassanNo ratings yet
- Grade-5 Chapter-7 Answer KeyDocument2 pagesGrade-5 Chapter-7 Answer KeyAly HassanNo ratings yet
- G 7 3.11 Tissues and OrganDocument3 pagesG 7 3.11 Tissues and OrganAly HassanNo ratings yet
- Ans Biology Work Book1Document26 pagesAns Biology Work Book1Aly HassanNo ratings yet
- 3.10 NervesDocument2 pages3.10 NervesAly HassanNo ratings yet
- WB Unit 1Document9 pagesWB Unit 1Aly HassanNo ratings yet
- Answer - Physics - Work Book 1Document21 pagesAnswer - Physics - Work Book 1Aly HassanNo ratings yet
- Capaian Kinerja Peserta RSDocument14 pagesCapaian Kinerja Peserta RSAyu AzrinaNo ratings yet
- Cerebral Circulation Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument5 pagesCerebral Circulation Anatomy and PhysiologyMayrjun Lo JacosalemNo ratings yet
- Who BCT Bts 01 3Document37 pagesWho BCT Bts 01 3Deo Tarigan SilangitNo ratings yet
- Survey Kompetitor Oktober 2021Document9 pagesSurvey Kompetitor Oktober 2021Velin AzzahraNo ratings yet
- Mock Test For Entrance ExamDocument19 pagesMock Test For Entrance ExamAeris Strong100% (1)
- Pada Wanita MenstruasiDocument7 pagesPada Wanita MenstruasiLab RS MMCNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument6 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyJulianne B. Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- PBMC Isolation ProtocolDocument1 pagePBMC Isolation ProtocolKartik BhamidipatiNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: Biology 0610/22Document16 pagesCambridge IGCSE: Biology 0610/22Aisha YousifNo ratings yet
- 5 Patcharee Komvilaisak - Approaching To Pancytopenia 24112017Document43 pages5 Patcharee Komvilaisak - Approaching To Pancytopenia 24112017Satvik BansalNo ratings yet
- Discuss The Indications and Complications of Blood TransfusionDocument32 pagesDiscuss The Indications and Complications of Blood TransfusionYetunde Shakirat Amoo-Tella100% (1)
- Multifibren UDocument6 pagesMultifibren UJoseline Alejandra Bravo Bravo0% (1)
- Define Arteries, Veins and Capillaries. Explain The Differences Between ThemDocument5 pagesDefine Arteries, Veins and Capillaries. Explain The Differences Between Themzeenat gaziNo ratings yet
- SGBAU B.Pharm 1 SEM Human-Anatomy-n-Physiology-I 2018Document2 pagesSGBAU B.Pharm 1 SEM Human-Anatomy-n-Physiology-I 2018Abhay DeulkarNo ratings yet
- Effect of Tranexamic Acid On Blood Loss in Pediatric Cardiac Surgery: A Randomized TrialDocument8 pagesEffect of Tranexamic Acid On Blood Loss in Pediatric Cardiac Surgery: A Randomized TrialBetão AviãoNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Methods For Analyzing Monoclonal Proteins - UpToDateDocument50 pagesLaboratory Methods For Analyzing Monoclonal Proteins - UpToDatechali90No ratings yet
- PBSDocument72 pagesPBSKavi KaviNo ratings yet
- ABO Blood Typing: Forward Typing (Glass Slide Method)Document2 pagesABO Blood Typing: Forward Typing (Glass Slide Method)Marj MendezNo ratings yet
- MK Hematology-LeukemiasDocument35 pagesMK Hematology-LeukemiasMoses Jr KazevuNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Three Plant Extracts ActivityDocument106 pagesEvaluation of Three Plant Extracts ActivityDrmirfat AlkashifNo ratings yet
- International Health Olympiad Reference Book Juniors PDFDocument188 pagesInternational Health Olympiad Reference Book Juniors PDFRajesh KrishnanNo ratings yet
- No Risk ScoreDocument4 pagesNo Risk ScorehenrisaatjianNo ratings yet
- Citizen CharterDocument21 pagesCitizen CharterVedhanayagiNo ratings yet
- 1996 Biology Paper I Marking SchemeDocument13 pages1996 Biology Paper I Marking Schemetramysss80% (5)
- Evaluation of The Ruminant Complete Blood Dell CountDocument26 pagesEvaluation of The Ruminant Complete Blood Dell CountDirección Científica Laboratorio VitalabNo ratings yet
- LAS Science 4 MELC 1 Q2 Week1Document10 pagesLAS Science 4 MELC 1 Q2 Week1Jing Pelingon Carten86% (7)
- Blood Grouping Brochure 2013 - Priced PDFDocument8 pagesBlood Grouping Brochure 2013 - Priced PDFmwenyeweNo ratings yet
- Biology Paper 1Document32 pagesBiology Paper 1Cameron DaviesNo ratings yet