Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
46 viewsStylistic Devises & Their Effects
Stylistic Devises & Their Effects
Uploaded by
Pranav BISUMBHERThis document defines and provides examples of common stylistic devices used in writing and their effects. It discusses devices such as alliteration, antithesis, hyperbole, metaphor, simile, onomatopoeia, personification, repetition, emotive language, flashback, foreshadowing, rhetorical questions, and the use of informal vs formal language. The document explains that these devices can be used to grab a reader's attention, emphasize ideas, create vivid imagery, persuade readers, build suspense, and establish different tones.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Scion 2e - Demigod (Manuscript)Document280 pagesScion 2e - Demigod (Manuscript)JeanJ7T50% (2)
- Butoh - Shades of DarknessDocument105 pagesButoh - Shades of DarknessVarinia Lourdes Barrantes Segura100% (4)
- Rhetorical Choices and Effect Matching GameDocument4 pagesRhetorical Choices and Effect Matching Gamecarolinethouin10No ratings yet
- Young-And-Dyslexic-Techniques-Table-To-Go-With-Ppt 2Document1 pageYoung-And-Dyslexic-Techniques-Table-To-Go-With-Ppt 2Jjrl50% (2)
- Stylistic Devices & Their EffectsDocument5 pagesStylistic Devices & Their EffectsmaliathNo ratings yet
- Eng Year 05 Judging Standards Assessment Pointers Web Version 1Document3 pagesEng Year 05 Judging Standards Assessment Pointers Web Version 1api-248888410No ratings yet
- Literary TechniquesDocument2 pagesLiterary TechniquesSohania RoopaiNo ratings yet
- English Language and Literature Key Terms DictionaryDocument7 pagesEnglish Language and Literature Key Terms Dictionarysynxz2kNo ratings yet
- Week 1 HandoutsDocument4 pagesWeek 1 Handoutstwihlr.69No ratings yet
- Table of Stylistic Devices - Posters OnlyDocument5 pagesTable of Stylistic Devices - Posters OnlyAddie LakeNo ratings yet
- Figurative LanguageDocument2 pagesFigurative LanguageNoel Krish ZacalNo ratings yet
- Language AnalysisDocument3 pagesLanguage AnalysisFahim MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Linguistic DevicesDocument16 pagesLinguistic DevicesFahim MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Creative Writing - Q1 - M4Document10 pagesCreative Writing - Q1 - M4Aldous AngcayNo ratings yet
- Diction: Type What It Is + Example Writer's Purpose Effect On Audience Slang Jargon FormalDocument3 pagesDiction: Type What It Is + Example Writer's Purpose Effect On Audience Slang Jargon FormalAisyah AlkatiriNo ratings yet
- Better Team On The Day: The Slippery Slithering SnakeDocument4 pagesBetter Team On The Day: The Slippery Slithering SnakenerdasdasdNo ratings yet
- Elements of A NarrativeDocument2 pagesElements of A NarrativeSecret SecretNo ratings yet
- Writing Sentences With ImpactDocument3 pagesWriting Sentences With ImpactBruno RibeiroNo ratings yet
- Rhetorical Appeal: Ethos (Inspiring Trust in The Author or Speaker)Document5 pagesRhetorical Appeal: Ethos (Inspiring Trust in The Author or Speaker)Christopher CharlesNo ratings yet
- Additional Authors Craft Notes WhyDocument2 pagesAdditional Authors Craft Notes WhyMohamedNo ratings yet
- Mystery and SuspenceDocument10 pagesMystery and Suspencemaya.a.shaker.1No ratings yet
- Analyze Literary and Nonfiction TextsDocument5 pagesAnalyze Literary and Nonfiction TextsWayne HNo ratings yet
- Paper 1 Text Type and TermsDocument9 pagesPaper 1 Text Type and TermsSoham AherNo ratings yet
- A Home in Fiction - Gerlaldine BrooksDocument5 pagesA Home in Fiction - Gerlaldine BrooksZhou.Zhang2No ratings yet
- English Quarter 2 ReviewerDocument4 pagesEnglish Quarter 2 ReviewerEugenio MuellaNo ratings yet
- 8ENG Shaun Tan Creative Writing Skills BookletDocument24 pages8ENG Shaun Tan Creative Writing Skills Bookletdemoskull1235No ratings yet
- Response Elements Constructing Meaning: Element Questions For DiscussionDocument5 pagesResponse Elements Constructing Meaning: Element Questions For Discussionapi-295217355No ratings yet
- 1849511Document10 pages1849511Rohan ReddyNo ratings yet
- Literary DevicesDocument37 pagesLiterary DevicesLy VõNo ratings yet
- Anaphora: Similes and MetaphorsDocument2 pagesAnaphora: Similes and MetaphorsBrigandia PetersNo ratings yet
- Year 8 Literary Techniques GlossaryDocument3 pagesYear 8 Literary Techniques GlossaryMUBASHIR HUSSAINNo ratings yet
- 4th Grade Studies Guides All SubjectsDocument44 pages4th Grade Studies Guides All Subjectsapi-505796786No ratings yet
- Identify The Structure, Purpose and Language Features of Different Text Types (E.g. Narrative, Information Report, Procedure Argument)Document13 pagesIdentify The Structure, Purpose and Language Features of Different Text Types (E.g. Narrative, Information Report, Procedure Argument)Jaz Zele50% (2)
- Writer's EffectDocument2 pagesWriter's EffectAhmed YaqootNo ratings yet
- Gcse Paper 2Document4 pagesGcse Paper 2alexNo ratings yet
- Analyze Figurative Language: IntroduceDocument5 pagesAnalyze Figurative Language: IntroduceSarah AliNo ratings yet
- Knowing The Language of Creative Writing 2Document1 pageKnowing The Language of Creative Writing 2JM AsisNo ratings yet
- Annotation Strategy Sticky Notes InstructionDocument10 pagesAnnotation Strategy Sticky Notes Instructionapi-608966375No ratings yet
- Term Effect/Uses: A Cliché Are Actions and Events That Are Predictable Since There Are Past EventsDocument3 pagesTerm Effect/Uses: A Cliché Are Actions and Events That Are Predictable Since There Are Past EventsWilliamNo ratings yet
- Writers Effect - Picture YourselfDocument3 pagesWriters Effect - Picture Yourselfvinit dhageNo ratings yet
- English Paper 1 TechqniuesDocument9 pagesEnglish Paper 1 Techqniueslailaamramin137No ratings yet
- 612le 05 SC Identifyfiglang SCDocument5 pages612le 05 SC Identifyfiglang SCSayde BetancourtNo ratings yet
- (GR) Devices Writers Use To Create EffectsDocument4 pages(GR) Devices Writers Use To Create EffectshariNo ratings yet
- Literary Devices 1. Alliteration - Alliteration Is TheDocument5 pagesLiterary Devices 1. Alliteration - Alliteration Is TheDona Sabucdalao SacoteNo ratings yet
- English Language Revision by Jodie FisherDocument19 pagesEnglish Language Revision by Jodie Fishermehtaaarav1116No ratings yet
- Handout 1 - Overview of Narrative TechniquesDocument5 pagesHandout 1 - Overview of Narrative TechniquesWalter WhiteNo ratings yet
- Anglophone Countries Literature I: "Year of The Universalization of Health"Document4 pagesAnglophone Countries Literature I: "Year of The Universalization of Health"Mire MartinezNo ratings yet
- Lecture Eapp 1ST Quarter Week 2 3PDF 1Document3 pagesLecture Eapp 1ST Quarter Week 2 3PDF 1Joana IrishNo ratings yet
- Write On or Write OffDocument1 pageWrite On or Write Offsimor4780No ratings yet
- 2243persuasive TechniquesDocument5 pages2243persuasive TechniquesWen You ChanNo ratings yet
- Literary DevicesDocument3 pagesLiterary DevicesMara BravoNo ratings yet
- Lang Arts-2Document8 pagesLang Arts-2biriginpeterNo ratings yet
- Name: Lyka Nicole J. Dorado Section: C15 Group: GREEN Date: September 18, 2020Document1 pageName: Lyka Nicole J. Dorado Section: C15 Group: GREEN Date: September 18, 2020Lyka Nicole DoradoNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Creative WritingDocument4 pagesUnit 1 - Creative WritingBecca Olorvida-Roquid100% (1)
- Monsters Are Due On Maple Street. Lesson - StoryDocument24 pagesMonsters Are Due On Maple Street. Lesson - StoryRENATA AMETNo ratings yet
- Ib Texts FeaturesDocument31 pagesIb Texts FeaturesPhương Anh Cao HoàngNo ratings yet
- Ronaldo Aguilar - Creative Writing WorksheetDocument10 pagesRonaldo Aguilar - Creative Writing Worksheetapi-741758305No ratings yet
- Glossary of Literary TermsDocument2 pagesGlossary of Literary TermsInayaNo ratings yet
- Prefinal Lesson2 Literary - DevicesDocument18 pagesPrefinal Lesson2 Literary - DevicesCarina Margallo CelajeNo ratings yet
- Language and StructureDocument9 pagesLanguage and StructureZakariah ArhinNo ratings yet
- How Does Reading Aloud Improve WritingDocument15 pagesHow Does Reading Aloud Improve WritingGhareib KhatemNo ratings yet
- Y11 Persuasive Writing Devices BookletDocument7 pagesY11 Persuasive Writing Devices BookletJack LarkinNo ratings yet
- The Company You Don't Keep - Corporate SuccessionDocument8 pagesThe Company You Don't Keep - Corporate SuccessionPranav BISUMBHERNo ratings yet
- Creative SuccessionDocument14 pagesCreative SuccessionPranav BISUMBHERNo ratings yet
- Pre-Admission Math Assessment - SampleDocument13 pagesPre-Admission Math Assessment - SamplePranav BISUMBHERNo ratings yet
- Concluding QuestionsDocument7 pagesConcluding QuestionsPranav BISUMBHERNo ratings yet
- The Main Features of A Synovial JointDocument3 pagesThe Main Features of A Synovial JointPranav BISUMBHERNo ratings yet
- DL Letter - Pran 9rDocument2 pagesDL Letter - Pran 9rPranav BISUMBHERNo ratings yet
- 2021 October - November TimetableDocument8 pages2021 October - November TimetablePranav BISUMBHERNo ratings yet
- DNT NotesDocument12 pagesDNT NotesPranav BISUMBHERNo ratings yet
- The Return of The KingsDocument19 pagesThe Return of The KingsPranav BISUMBHERNo ratings yet
- Geo Revision For TestDocument11 pagesGeo Revision For TestPranav BISUMBHERNo ratings yet
- DNT NotesDocument9 pagesDNT NotesPranav BISUMBHERNo ratings yet
- Form For Confirmation of Funds For Purchase of Items Under Standard List - SS ResidenceDocument2 pagesForm For Confirmation of Funds For Purchase of Items Under Standard List - SS ResidencePranav BISUMBHERNo ratings yet
- Review On Hotel Sophy Hyde ParkDocument1 pageReview On Hotel Sophy Hyde ParkPranav BISUMBHERNo ratings yet
- Book ReportDocument3 pagesBook ReportPranav BISUMBHERNo ratings yet
- Animal Cells and Plant CellsDocument4 pagesAnimal Cells and Plant CellsPranav BISUMBHERNo ratings yet
- Term 2 Math Revision TestDocument8 pagesTerm 2 Math Revision TestPranav BISUMBHERNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education (9-1)Document20 pagesCambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education (9-1)Pranav BISUMBHERNo ratings yet
- Covering Letter For Purchase F Household Items For Ss ResidenceDocument3 pagesCovering Letter For Purchase F Household Items For Ss ResidencePranav BISUMBHERNo ratings yet
- Have You Ever Succeeded Someone Else in A Role or PositionDocument5 pagesHave You Ever Succeeded Someone Else in A Role or PositionPranav BISUMBHERNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education (9-1)Document26 pagesCambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education (9-1)Pranav BISUMBHERNo ratings yet
- Evaluating My 3 Designs of An Interior of A CafeDocument5 pagesEvaluating My 3 Designs of An Interior of A CafePranav BISUMBHERNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of The Gas Exchange SystemDocument4 pagesStructure and Function of The Gas Exchange SystemPranav BISUMBHERNo ratings yet
- 2nd Test of EnglishDocument5 pages2nd Test of EnglishPranav BISUMBHERNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education (9-1)Document18 pagesCambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education (9-1)Pranav BISUMBHERNo ratings yet
- The Effects of The Age of ExplorationDocument2 pagesThe Effects of The Age of ExplorationPranav BISUMBHERNo ratings yet
- Technique and StyleDocument3 pagesTechnique and StylePranav BISUMBHERNo ratings yet
- Natural Selection Leads To EvolutionDocument3 pagesNatural Selection Leads To EvolutionPranav BISUMBHERNo ratings yet
- Prince Henry - The Navigator (Homework)Document2 pagesPrince Henry - The Navigator (Homework)Pranav BISUMBHERNo ratings yet
- The Main Features of A Synovial JointDocument5 pagesThe Main Features of A Synovial JointPranav BISUMBHERNo ratings yet
- The Agricultural Revolution - NotesDocument5 pagesThe Agricultural Revolution - NotesPranav BISUMBHERNo ratings yet
- 27 Saira Scientist by Muhammed Zafar Iqbal 2003 PDFDocument119 pages27 Saira Scientist by Muhammed Zafar Iqbal 2003 PDFhermione grangerNo ratings yet
- English 7, 9 and 10Document10 pagesEnglish 7, 9 and 10MaryGraceCuynoNo ratings yet
- Varga TXTBK 2010Document100 pagesVarga TXTBK 2010Iza PagkalinawanNo ratings yet
- Lit 04Document3 pagesLit 04westcoastlifeNo ratings yet
- Waaagh! AzhagDocument3 pagesWaaagh! AzhagZioAnthros0% (1)
- Rethorical DevicesDocument6 pagesRethorical DevicesLaura CavarrettaNo ratings yet
- María B2 Julio 2017Document17 pagesMaría B2 Julio 2017FranNo ratings yet
- Huck Finn SatireDocument2 pagesHuck Finn Satireapi-354511981No ratings yet
- D&D 5e Homebrew Compilation - CompressedDocument1 pageD&D 5e Homebrew Compilation - CompressedLeonis AngelisNo ratings yet
- Through A GlassDocument2 pagesThrough A GlassNeziah Raborar BugnaNo ratings yet
- Interpreting Information From TextsDocument3 pagesInterpreting Information From Textsapi-272887345100% (1)
- DocumentDocument17 pagesDocumentRomanNo ratings yet
- King Lear in Zebulon County: Archive - TodayDocument4 pagesKing Lear in Zebulon County: Archive - TodayRobertt MosheNo ratings yet
- Elements of A StoryDocument25 pagesElements of A Storycaren santosNo ratings yet
- The Territorialization of The Imaginary in Latin America. Amaryll ChanadyDocument11 pagesThe Territorialization of The Imaginary in Latin America. Amaryll ChanadyEsmeralda ArredondoNo ratings yet
- Quiz Personal LetterDocument3 pagesQuiz Personal LetterNurida LatipahNo ratings yet
- Part 1: All Tenses Fill in The Correct Form of The Verb GivenDocument3 pagesPart 1: All Tenses Fill in The Correct Form of The Verb GivenVan Ngo Le KhanhNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 - AdjectivesDocument3 pagesLesson 3 - AdjectivesAkbarul Amin100% (2)
- Themes of Kite Runner: A Project Report OnDocument10 pagesThemes of Kite Runner: A Project Report OnShubhankar ThakurNo ratings yet
- Broken Verses - Discussion GuideDocument4 pagesBroken Verses - Discussion GuideHoughton Mifflin HarcourtNo ratings yet
- The Strangeness of Christabel - La CassagnereDocument6 pagesThe Strangeness of Christabel - La CassagnereRuby GraceNo ratings yet
- Creative NonFiction Module Lesson 1Document7 pagesCreative NonFiction Module Lesson 1honeylyn moncatarNo ratings yet
- And So It Goes: Life According To Kurt VonnegutDocument2 pagesAnd So It Goes: Life According To Kurt Vonnegutcoolth2No ratings yet
- English Literature PDFDocument20 pagesEnglish Literature PDFNargis SheikhNo ratings yet
- 21st Lit. Q2 M2Document19 pages21st Lit. Q2 M2jasperklientricoNo ratings yet
- GreekDocument135 pagesGreekvmishkaNo ratings yet
- Gramatica-Limbii-Engleze 3 PDFDocument44 pagesGramatica-Limbii-Engleze 3 PDFpasunuNo ratings yet
Stylistic Devises & Their Effects
Stylistic Devises & Their Effects
Uploaded by
Pranav BISUMBHER0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
46 views2 pagesThis document defines and provides examples of common stylistic devices used in writing and their effects. It discusses devices such as alliteration, antithesis, hyperbole, metaphor, simile, onomatopoeia, personification, repetition, emotive language, flashback, foreshadowing, rhetorical questions, and the use of informal vs formal language. The document explains that these devices can be used to grab a reader's attention, emphasize ideas, create vivid imagery, persuade readers, build suspense, and establish different tones.
Original Description:
Original Title
STYLISTIC DEVISES & THEIR EFFECTS
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document defines and provides examples of common stylistic devices used in writing and their effects. It discusses devices such as alliteration, antithesis, hyperbole, metaphor, simile, onomatopoeia, personification, repetition, emotive language, flashback, foreshadowing, rhetorical questions, and the use of informal vs formal language. The document explains that these devices can be used to grab a reader's attention, emphasize ideas, create vivid imagery, persuade readers, build suspense, and establish different tones.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
46 views2 pagesStylistic Devises & Their Effects
Stylistic Devises & Their Effects
Uploaded by
Pranav BISUMBHERThis document defines and provides examples of common stylistic devices used in writing and their effects. It discusses devices such as alliteration, antithesis, hyperbole, metaphor, simile, onomatopoeia, personification, repetition, emotive language, flashback, foreshadowing, rhetorical questions, and the use of informal vs formal language. The document explains that these devices can be used to grab a reader's attention, emphasize ideas, create vivid imagery, persuade readers, build suspense, and establish different tones.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
STYLISTIC DEVISES & THEIR EFFECTS
Stylistic Devises Definition Effect
Alliteration Repetition of initial consonant Grabs reader’s attention, sort of
sound. punctuates words.
Also creates mood for e.g. if it’s
an ‘s’ sound, maybe shows
snakelike quantity or hissing.
Perhaps slyness of the narrator
Antithesis Having two opposite ideas in a Emphasizes ideas.
sentence. “One small step for Makes it easier to understand
man, one giant leap for the point being made or the
mankind.” complexity of the situation.
Hyperbole Exaggeration of ideas. Create amusing effect.
Common human feelings sound
remarkable.
Can also create contrast if
something is described using
exaggeration and the next
thing isn’t. This attracts
reader’s attention.
Helps visualize.
Metaphor Comparing two things without Gives readers another way of
using the words “like” or “as” thinking about something.
Creates an image for the
reader.
Make it easier to understand
what the reader is saying
(mostly applies to similes).
Simile Comparing two things Same effect as mentioned for
using the words “like” or “as” the metaphor
Onomatopoeia A word which imitates the Helps readers hear the sounds,
natural sound of things like allowing them to enter the
“buzzing”, “rustling” or even author’s world.
“meow”.
Personification When an idea or animal is given Helps readers empathize with
human characteristics. “The sky non-human characters.
weeps.” Gives deeper meanings as well.
Repetition Repeating words or phrases. To grab the reader’s attention.
(There are actually many For e.g. repeating a line.
different types of repetition like Emphasize and create rhythm.
anaphora and epiphora.)
Emotive It refers to word choices that To persuade the reader or
language are intended to get an listener to share the writer’s
emotional reaction or arouse an point of view.
emotion.
Flashback The story begins with a To hook the reader from the
flashback that starts the reader very first sentence
off in the middle of the action
Foreshadowing A technique in which a writer Makes your reader wonder
includes hints in the text letting what will happen next and
readers know what will happen keeps them reading to find out.
at the end of the story. Build dramatic tension and
suspense throughout their
stories.
Rhetorical A question which is meant to be Emphasize a point being made.
Question unanswered. Mostly used to as an effect.
Used to persuade people.
Informal Personal, colloquial sort of Writing becomes more casual
language language. and relaxed.
Sets up close relationship with
reader because it appeals to us.
It’s speaking at our level
Formal Doesn’t use colloquialism, Makes text more authoritative
language contractions or first-person. and powerful.
Passive voice Make your writing more interesting to read
active voice Makes your writing clearer and aids the reader in visualizing
what's happening, especially when you use vivid action verbs.
Short/long Short sentences may make it more authoritative like an order.
sentences Could also give more clearness.
Long sentences may sound formal or even conversational.
You might also like
- Scion 2e - Demigod (Manuscript)Document280 pagesScion 2e - Demigod (Manuscript)JeanJ7T50% (2)
- Butoh - Shades of DarknessDocument105 pagesButoh - Shades of DarknessVarinia Lourdes Barrantes Segura100% (4)
- Rhetorical Choices and Effect Matching GameDocument4 pagesRhetorical Choices and Effect Matching Gamecarolinethouin10No ratings yet
- Young-And-Dyslexic-Techniques-Table-To-Go-With-Ppt 2Document1 pageYoung-And-Dyslexic-Techniques-Table-To-Go-With-Ppt 2Jjrl50% (2)
- Stylistic Devices & Their EffectsDocument5 pagesStylistic Devices & Their EffectsmaliathNo ratings yet
- Eng Year 05 Judging Standards Assessment Pointers Web Version 1Document3 pagesEng Year 05 Judging Standards Assessment Pointers Web Version 1api-248888410No ratings yet
- Literary TechniquesDocument2 pagesLiterary TechniquesSohania RoopaiNo ratings yet
- English Language and Literature Key Terms DictionaryDocument7 pagesEnglish Language and Literature Key Terms Dictionarysynxz2kNo ratings yet
- Week 1 HandoutsDocument4 pagesWeek 1 Handoutstwihlr.69No ratings yet
- Table of Stylistic Devices - Posters OnlyDocument5 pagesTable of Stylistic Devices - Posters OnlyAddie LakeNo ratings yet
- Figurative LanguageDocument2 pagesFigurative LanguageNoel Krish ZacalNo ratings yet
- Language AnalysisDocument3 pagesLanguage AnalysisFahim MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Linguistic DevicesDocument16 pagesLinguistic DevicesFahim MuhammadNo ratings yet
- Creative Writing - Q1 - M4Document10 pagesCreative Writing - Q1 - M4Aldous AngcayNo ratings yet
- Diction: Type What It Is + Example Writer's Purpose Effect On Audience Slang Jargon FormalDocument3 pagesDiction: Type What It Is + Example Writer's Purpose Effect On Audience Slang Jargon FormalAisyah AlkatiriNo ratings yet
- Better Team On The Day: The Slippery Slithering SnakeDocument4 pagesBetter Team On The Day: The Slippery Slithering SnakenerdasdasdNo ratings yet
- Elements of A NarrativeDocument2 pagesElements of A NarrativeSecret SecretNo ratings yet
- Writing Sentences With ImpactDocument3 pagesWriting Sentences With ImpactBruno RibeiroNo ratings yet
- Rhetorical Appeal: Ethos (Inspiring Trust in The Author or Speaker)Document5 pagesRhetorical Appeal: Ethos (Inspiring Trust in The Author or Speaker)Christopher CharlesNo ratings yet
- Additional Authors Craft Notes WhyDocument2 pagesAdditional Authors Craft Notes WhyMohamedNo ratings yet
- Mystery and SuspenceDocument10 pagesMystery and Suspencemaya.a.shaker.1No ratings yet
- Analyze Literary and Nonfiction TextsDocument5 pagesAnalyze Literary and Nonfiction TextsWayne HNo ratings yet
- Paper 1 Text Type and TermsDocument9 pagesPaper 1 Text Type and TermsSoham AherNo ratings yet
- A Home in Fiction - Gerlaldine BrooksDocument5 pagesA Home in Fiction - Gerlaldine BrooksZhou.Zhang2No ratings yet
- English Quarter 2 ReviewerDocument4 pagesEnglish Quarter 2 ReviewerEugenio MuellaNo ratings yet
- 8ENG Shaun Tan Creative Writing Skills BookletDocument24 pages8ENG Shaun Tan Creative Writing Skills Bookletdemoskull1235No ratings yet
- Response Elements Constructing Meaning: Element Questions For DiscussionDocument5 pagesResponse Elements Constructing Meaning: Element Questions For Discussionapi-295217355No ratings yet
- 1849511Document10 pages1849511Rohan ReddyNo ratings yet
- Literary DevicesDocument37 pagesLiterary DevicesLy VõNo ratings yet
- Anaphora: Similes and MetaphorsDocument2 pagesAnaphora: Similes and MetaphorsBrigandia PetersNo ratings yet
- Year 8 Literary Techniques GlossaryDocument3 pagesYear 8 Literary Techniques GlossaryMUBASHIR HUSSAINNo ratings yet
- 4th Grade Studies Guides All SubjectsDocument44 pages4th Grade Studies Guides All Subjectsapi-505796786No ratings yet
- Identify The Structure, Purpose and Language Features of Different Text Types (E.g. Narrative, Information Report, Procedure Argument)Document13 pagesIdentify The Structure, Purpose and Language Features of Different Text Types (E.g. Narrative, Information Report, Procedure Argument)Jaz Zele50% (2)
- Writer's EffectDocument2 pagesWriter's EffectAhmed YaqootNo ratings yet
- Gcse Paper 2Document4 pagesGcse Paper 2alexNo ratings yet
- Analyze Figurative Language: IntroduceDocument5 pagesAnalyze Figurative Language: IntroduceSarah AliNo ratings yet
- Knowing The Language of Creative Writing 2Document1 pageKnowing The Language of Creative Writing 2JM AsisNo ratings yet
- Annotation Strategy Sticky Notes InstructionDocument10 pagesAnnotation Strategy Sticky Notes Instructionapi-608966375No ratings yet
- Term Effect/Uses: A Cliché Are Actions and Events That Are Predictable Since There Are Past EventsDocument3 pagesTerm Effect/Uses: A Cliché Are Actions and Events That Are Predictable Since There Are Past EventsWilliamNo ratings yet
- Writers Effect - Picture YourselfDocument3 pagesWriters Effect - Picture Yourselfvinit dhageNo ratings yet
- English Paper 1 TechqniuesDocument9 pagesEnglish Paper 1 Techqniueslailaamramin137No ratings yet
- 612le 05 SC Identifyfiglang SCDocument5 pages612le 05 SC Identifyfiglang SCSayde BetancourtNo ratings yet
- (GR) Devices Writers Use To Create EffectsDocument4 pages(GR) Devices Writers Use To Create EffectshariNo ratings yet
- Literary Devices 1. Alliteration - Alliteration Is TheDocument5 pagesLiterary Devices 1. Alliteration - Alliteration Is TheDona Sabucdalao SacoteNo ratings yet
- English Language Revision by Jodie FisherDocument19 pagesEnglish Language Revision by Jodie Fishermehtaaarav1116No ratings yet
- Handout 1 - Overview of Narrative TechniquesDocument5 pagesHandout 1 - Overview of Narrative TechniquesWalter WhiteNo ratings yet
- Anglophone Countries Literature I: "Year of The Universalization of Health"Document4 pagesAnglophone Countries Literature I: "Year of The Universalization of Health"Mire MartinezNo ratings yet
- Lecture Eapp 1ST Quarter Week 2 3PDF 1Document3 pagesLecture Eapp 1ST Quarter Week 2 3PDF 1Joana IrishNo ratings yet
- Write On or Write OffDocument1 pageWrite On or Write Offsimor4780No ratings yet
- 2243persuasive TechniquesDocument5 pages2243persuasive TechniquesWen You ChanNo ratings yet
- Literary DevicesDocument3 pagesLiterary DevicesMara BravoNo ratings yet
- Lang Arts-2Document8 pagesLang Arts-2biriginpeterNo ratings yet
- Name: Lyka Nicole J. Dorado Section: C15 Group: GREEN Date: September 18, 2020Document1 pageName: Lyka Nicole J. Dorado Section: C15 Group: GREEN Date: September 18, 2020Lyka Nicole DoradoNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Creative WritingDocument4 pagesUnit 1 - Creative WritingBecca Olorvida-Roquid100% (1)
- Monsters Are Due On Maple Street. Lesson - StoryDocument24 pagesMonsters Are Due On Maple Street. Lesson - StoryRENATA AMETNo ratings yet
- Ib Texts FeaturesDocument31 pagesIb Texts FeaturesPhương Anh Cao HoàngNo ratings yet
- Ronaldo Aguilar - Creative Writing WorksheetDocument10 pagesRonaldo Aguilar - Creative Writing Worksheetapi-741758305No ratings yet
- Glossary of Literary TermsDocument2 pagesGlossary of Literary TermsInayaNo ratings yet
- Prefinal Lesson2 Literary - DevicesDocument18 pagesPrefinal Lesson2 Literary - DevicesCarina Margallo CelajeNo ratings yet
- Language and StructureDocument9 pagesLanguage and StructureZakariah ArhinNo ratings yet
- How Does Reading Aloud Improve WritingDocument15 pagesHow Does Reading Aloud Improve WritingGhareib KhatemNo ratings yet
- Y11 Persuasive Writing Devices BookletDocument7 pagesY11 Persuasive Writing Devices BookletJack LarkinNo ratings yet
- The Company You Don't Keep - Corporate SuccessionDocument8 pagesThe Company You Don't Keep - Corporate SuccessionPranav BISUMBHERNo ratings yet
- Creative SuccessionDocument14 pagesCreative SuccessionPranav BISUMBHERNo ratings yet
- Pre-Admission Math Assessment - SampleDocument13 pagesPre-Admission Math Assessment - SamplePranav BISUMBHERNo ratings yet
- Concluding QuestionsDocument7 pagesConcluding QuestionsPranav BISUMBHERNo ratings yet
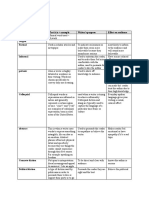
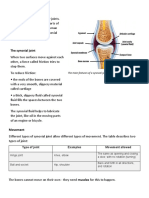
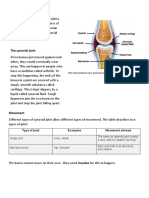
- The Main Features of A Synovial JointDocument3 pagesThe Main Features of A Synovial JointPranav BISUMBHERNo ratings yet
- DL Letter - Pran 9rDocument2 pagesDL Letter - Pran 9rPranav BISUMBHERNo ratings yet
- 2021 October - November TimetableDocument8 pages2021 October - November TimetablePranav BISUMBHERNo ratings yet
- DNT NotesDocument12 pagesDNT NotesPranav BISUMBHERNo ratings yet
- The Return of The KingsDocument19 pagesThe Return of The KingsPranav BISUMBHERNo ratings yet
- Geo Revision For TestDocument11 pagesGeo Revision For TestPranav BISUMBHERNo ratings yet
- DNT NotesDocument9 pagesDNT NotesPranav BISUMBHERNo ratings yet
- Form For Confirmation of Funds For Purchase of Items Under Standard List - SS ResidenceDocument2 pagesForm For Confirmation of Funds For Purchase of Items Under Standard List - SS ResidencePranav BISUMBHERNo ratings yet
- Review On Hotel Sophy Hyde ParkDocument1 pageReview On Hotel Sophy Hyde ParkPranav BISUMBHERNo ratings yet
- Book ReportDocument3 pagesBook ReportPranav BISUMBHERNo ratings yet
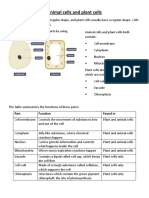
- Animal Cells and Plant CellsDocument4 pagesAnimal Cells and Plant CellsPranav BISUMBHERNo ratings yet
- Term 2 Math Revision TestDocument8 pagesTerm 2 Math Revision TestPranav BISUMBHERNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education (9-1)Document20 pagesCambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education (9-1)Pranav BISUMBHERNo ratings yet
- Covering Letter For Purchase F Household Items For Ss ResidenceDocument3 pagesCovering Letter For Purchase F Household Items For Ss ResidencePranav BISUMBHERNo ratings yet
- Have You Ever Succeeded Someone Else in A Role or PositionDocument5 pagesHave You Ever Succeeded Someone Else in A Role or PositionPranav BISUMBHERNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education (9-1)Document26 pagesCambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education (9-1)Pranav BISUMBHERNo ratings yet
- Evaluating My 3 Designs of An Interior of A CafeDocument5 pagesEvaluating My 3 Designs of An Interior of A CafePranav BISUMBHERNo ratings yet
- Structure and Function of The Gas Exchange SystemDocument4 pagesStructure and Function of The Gas Exchange SystemPranav BISUMBHERNo ratings yet
- 2nd Test of EnglishDocument5 pages2nd Test of EnglishPranav BISUMBHERNo ratings yet
- Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education (9-1)Document18 pagesCambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education (9-1)Pranav BISUMBHERNo ratings yet
- The Effects of The Age of ExplorationDocument2 pagesThe Effects of The Age of ExplorationPranav BISUMBHERNo ratings yet
- Technique and StyleDocument3 pagesTechnique and StylePranav BISUMBHERNo ratings yet
- Natural Selection Leads To EvolutionDocument3 pagesNatural Selection Leads To EvolutionPranav BISUMBHERNo ratings yet
- Prince Henry - The Navigator (Homework)Document2 pagesPrince Henry - The Navigator (Homework)Pranav BISUMBHERNo ratings yet
- The Main Features of A Synovial JointDocument5 pagesThe Main Features of A Synovial JointPranav BISUMBHERNo ratings yet
- The Agricultural Revolution - NotesDocument5 pagesThe Agricultural Revolution - NotesPranav BISUMBHERNo ratings yet
- 27 Saira Scientist by Muhammed Zafar Iqbal 2003 PDFDocument119 pages27 Saira Scientist by Muhammed Zafar Iqbal 2003 PDFhermione grangerNo ratings yet
- English 7, 9 and 10Document10 pagesEnglish 7, 9 and 10MaryGraceCuynoNo ratings yet
- Varga TXTBK 2010Document100 pagesVarga TXTBK 2010Iza PagkalinawanNo ratings yet
- Lit 04Document3 pagesLit 04westcoastlifeNo ratings yet
- Waaagh! AzhagDocument3 pagesWaaagh! AzhagZioAnthros0% (1)
- Rethorical DevicesDocument6 pagesRethorical DevicesLaura CavarrettaNo ratings yet
- María B2 Julio 2017Document17 pagesMaría B2 Julio 2017FranNo ratings yet
- Huck Finn SatireDocument2 pagesHuck Finn Satireapi-354511981No ratings yet
- D&D 5e Homebrew Compilation - CompressedDocument1 pageD&D 5e Homebrew Compilation - CompressedLeonis AngelisNo ratings yet
- Through A GlassDocument2 pagesThrough A GlassNeziah Raborar BugnaNo ratings yet
- Interpreting Information From TextsDocument3 pagesInterpreting Information From Textsapi-272887345100% (1)
- DocumentDocument17 pagesDocumentRomanNo ratings yet
- King Lear in Zebulon County: Archive - TodayDocument4 pagesKing Lear in Zebulon County: Archive - TodayRobertt MosheNo ratings yet
- Elements of A StoryDocument25 pagesElements of A Storycaren santosNo ratings yet
- The Territorialization of The Imaginary in Latin America. Amaryll ChanadyDocument11 pagesThe Territorialization of The Imaginary in Latin America. Amaryll ChanadyEsmeralda ArredondoNo ratings yet
- Quiz Personal LetterDocument3 pagesQuiz Personal LetterNurida LatipahNo ratings yet
- Part 1: All Tenses Fill in The Correct Form of The Verb GivenDocument3 pagesPart 1: All Tenses Fill in The Correct Form of The Verb GivenVan Ngo Le KhanhNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 - AdjectivesDocument3 pagesLesson 3 - AdjectivesAkbarul Amin100% (2)
- Themes of Kite Runner: A Project Report OnDocument10 pagesThemes of Kite Runner: A Project Report OnShubhankar ThakurNo ratings yet
- Broken Verses - Discussion GuideDocument4 pagesBroken Verses - Discussion GuideHoughton Mifflin HarcourtNo ratings yet
- The Strangeness of Christabel - La CassagnereDocument6 pagesThe Strangeness of Christabel - La CassagnereRuby GraceNo ratings yet
- Creative NonFiction Module Lesson 1Document7 pagesCreative NonFiction Module Lesson 1honeylyn moncatarNo ratings yet
- And So It Goes: Life According To Kurt VonnegutDocument2 pagesAnd So It Goes: Life According To Kurt Vonnegutcoolth2No ratings yet
- English Literature PDFDocument20 pagesEnglish Literature PDFNargis SheikhNo ratings yet
- 21st Lit. Q2 M2Document19 pages21st Lit. Q2 M2jasperklientricoNo ratings yet
- GreekDocument135 pagesGreekvmishkaNo ratings yet
- Gramatica-Limbii-Engleze 3 PDFDocument44 pagesGramatica-Limbii-Engleze 3 PDFpasunuNo ratings yet