Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Calcium Gluconate Lasix
Calcium Gluconate Lasix
Uploaded by
Christian Dave EndinoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Calcium Gluconate Lasix
Calcium Gluconate Lasix
Uploaded by
Christian Dave EndinoCopyright:
Available Formats
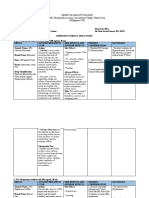
Mindanao State University – Iligan Institute of Technology Student: _________________________
COLLEGE OF NURSING Block:___________
PHARMACOLOGICAL MANAGEMENT
DRUG STUDY
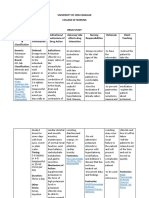
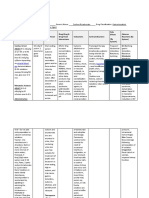
Brand Name: _____________________Kalcinate____________ Generic Name: ___________Calcium Glucoante__________________ Drug Classification: Electrolytand
replacement solution
Dosage, Route & Frequency Drug-Drug & Adverse
Side Effects
Drug Action Drug-Food Indications Contraindications Reactions (By
Recommended Prescribed (By System)
Interactions System)
Contains 90 mg or 4.5 9% Ca or 4.5 mEq/g Calcium is an Drug-Food: Cereals, PO, IV: Treatment and Hypercalcemia; Renal CNS: tingling CV: bradycardia,
mEq of elemental essential element spinach, orrhubarb prevention of calculi; Ventricular sensation arrhythmia, cardiac
calcium/g for regulating the may decrease the hypocalcemia. PO: fibrillation; Concurrent arrest.
excitation threshold absorption of Adjunct in the use of calcium CV: mild drop of BP
of nerve muscle, calcium supplement prevention of supplements (calcium F & E: hypercalcemia
GI: irritation,
cardiac function, postmenopausal acetate).
Injection: 10% Drug-Drug: constipation,
maintenance of osteoporosis. IV:
solution in 10-ml Hypercalcemia Use Cautiously in: nausea, vomiting,
renal function. Emergency treatment
ampules and vials, 10 increase the risk of Patients receiving thirst, abdominal
of hyperkalemia and
ml or 50 ml vials Replaces calcium digoxin toxicity. digitalis glycosides; pain
hypermagnesemia
and maintains Chronic use with and adjunct in cardiac Severe respiratory
Powder for oral
calcium leve. antacids in renal arrest or calcium insufficiency; Renal
suspension 15 ml
insufficiency may channel blocking disease; Cardiac
Tablets: 500 mg, 650 lead to milk-alkali agent toxicity disease; OB:
ml, 1 g syndrome. (calcium chloride, Hypercalcemia may
calcium gluconate increase risk of
Excessive amounts maternal and fetal
may decrease the complications;
effects of calcium Lactation: Breast
channel blockers. feeding not expected
to harm infant
Calcium
provided that serum
supplements,
calcium levels
including calcium-
containing antacids,
may increase risk of monitored.
hypercalcemia; avoid
concurrent use.
Responsibilities in the Nursing Process (ADPIE) Responsibilities in the Nursing Process (ADPIE)
ASSESSMENT IMPLEMENTAITON
Assess IV site for patency. IV Push: Administer slowly by IV push. Rate: Maximum administration rate for adults
Monitor BP, pulse, and ECG frequently throughout parenteral therapy. May cause is 1.5– 2 mL/ min.
vasodilation with resulting hypotension, bradycardia, arrhythmias, and cardiac Continuous Infusion: May be further diluted in 1000 mL of D5W, D10W, D20W,
arrest. D5/0.9% NaCl, 0.9% NaCl, D5/LR, or LR.
Monitor serum calcium or ionized calcium, chloride, sodium, potassium, Rate: Administer at a rate not to exceed 200 mg/ min over 12– 24 hr
magnesium, albumin, and parathyroid hormone (PTH) concentrations before and Monitor electrolyte level throughout therapy.
periodically during therapy for treatment of hypocalcemia.
EVALUATION
DIAGNOSIS
Increase in serum calcium levels.
Imbalanced nutrition: less than body requirements (Indications) Decrease in the signs and symptoms of hypocalcemia
Risk for injury related to osteoporosis or electrolyte imbalance (Indications)
PLANNING
Patient’s calcium level will increase as evidence by laboratory result.
In Patient will display decrease in signs and symptoms of hypocalcemia.
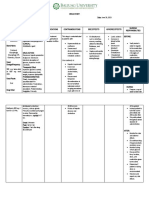
Mindanao State University – Iligan Institute of Technology Student: _________________________
COLLEGE OF NURSING Block:___________
PHARMACOLOGICAL MANAGEMENT
DRUG STUDY
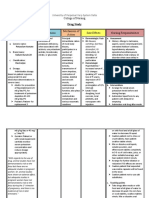
Brand Name: ____________________Lasix________ Generic Name: ______________Furosemide_______________ Drug Classification:__________Diuretics___________
Dosage, Route & Frequency Drug-Drug & Adverse
Side Effects
Drug Action Drug-Food Indications Contraindications Reactions (By
Recommended Prescribed (By System)
Interactions System)
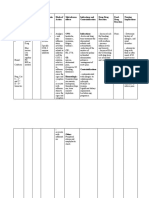
EDEMA: M, IV Inhibits the Increase risk of Edema due to heart Hypersensitivity; CNS: blurred vision, DERM: erythema,
(Adults): 20– 40 mg, reabsorption of hypotension with failure, hepatic Cross-sensitivity with dizziness, headache, stevens-johnson
may repeat in 1– 2 hr sodium and chloride anti-hypertensives, impairment, or renal thiazides and vertigo syndrome, toxic
and increase by 20 from the loop of nitrates, or acute disease. sulfonamides may epidermal necrolysis
mg every 1– 2 hr until Henle and distal ingestion of alcohol. Hypertension. occur; Hepatic coma or CV: hypotension
response is obtained, renal tubule. Increase risk of anuria; Some liquid HEMAT: aplastic
maintenance dose Increases renal hypokalemia with products may contain GI: anorexia, anemia,
may be given q 6– 12 excretion of water, other diuretics, alcohol, avoid in constipation, dry agranulocytosis
hr; Continuous sodium, chloride, amphotericin B, patients with alcohol mouth, diarrhea
infusion—Bolus 0.1 magnesium, stimulant laxatives, intolerance
mg/kg followed by potassium, and and corticosteroids.
0.1 mg/kg/hr, double calcium. Hypokalemia may
q 2 hr to a maximum Effectiveness increase risk of
of 0.4 mg/ kg/hr. persists in impaired digoxin toxicity and
renal function increase risk of
HYPERTENSION arrhythmia in
PO (Adults): 40 twice patients taking drugs
daily initially (when that prolong
added to regimen,
decrease dose of
other
antihypertensives by
50%); adjust further
dosing based on
response.
Responsibilities in the Nursing Process (ADPIE) Responsibilities in the Nursing Process (ADPIE)
ASSESSMENT PLANNING
Assess fluid status. Patient will be able to have an increase of urinary output, decrease in edema
Assess vs and BP.
Assess patients receiving digoxin for anorexia, nausea, vomiting, muscle IMPLEMETATION
cramps, paresthesia, and confusion. PO: May be taken with food or milk to minimize gastric irritation. Tablets may
assess for allergy to sulfonamides. be crushed if patient has difficulty swallowing.
DIAGNOSIS Do not administer discolored solution or tablets.
Excess fluid volume (Indications) IV Push: Diluent: Administer undiluted (larger doses may be diluted and
Deficient fluid volume (Side Effects) administered as intermittent infusion
EVALUATION
Decrease in edema, BP.
Increase in urinary output.
You might also like
- Project Hse PlanDocument35 pagesProject Hse PlanNana Barima100% (5)
- DS (Calcium + Vit. D)Document6 pagesDS (Calcium + Vit. D)Mary April MendezNo ratings yet
- Calcium CarbonateDocument1 pageCalcium CarbonateMikko EnocNo ratings yet
- CALCITRIOLDocument2 pagesCALCITRIOLdesshe09No ratings yet
- Calcium GluconateDocument1 pageCalcium GluconateMary Reigns BuhatNo ratings yet
- KCL TabDocument3 pagesKCL TabGermin CesaNo ratings yet
- Calcium Gluconate: (Kal-See-Um Gloo-Koh-Nate)Document3 pagesCalcium Gluconate: (Kal-See-Um Gloo-Koh-Nate)govind_soni_15No ratings yet
- Calcium AcetateDocument3 pagesCalcium AcetateKIM NAMJOON'S PEACHES & CREAM100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument18 pagesDrug StudyAngelou Joefred CongresoNo ratings yet
- Lida AjocDocument10 pagesLida AjocEzra Knight Llesis AcebedoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Calcium Gluconate)Document2 pagesDrug Study (Calcium Gluconate)Andrea Albester GarinoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug Studyxllxxcxm -No ratings yet
- Rationale:: Drug MOA Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing Implication AssessmentDocument3 pagesRationale:: Drug MOA Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing Implication AssessmentTrishia Mae GallardoNo ratings yet
- 10% W/V Calcium Gluconate Inj.: B - BraunDocument2 pages10% W/V Calcium Gluconate Inj.: B - BraunFatma HossamNo ratings yet
- Calcium Gluconate 10 Injection B.P DR 1433675212243Document2 pagesCalcium Gluconate 10 Injection B.P DR 1433675212243Ayash Kant HotaNo ratings yet
- AcetazolamideDocument2 pagesAcetazolamideLIEZEL GRACE VELAYONo ratings yet
- Sodium Bicarbonate Drug StudyDocument4 pagesSodium Bicarbonate Drug StudyAngelou Joefred CongresoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument11 pagesDrug Studyfaula rocamoraNo ratings yet
- Vancomycin DRUGSTUDYDocument3 pagesVancomycin DRUGSTUDYEmagra AzilNo ratings yet
- Sodium BicarbonateDocument20 pagesSodium BicarbonateChristian Dave EndinoNo ratings yet
- Final ColistinDocument3 pagesFinal ColistinGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- Drugana IIIJDocument7 pagesDrugana IIIJNikki DarleneNo ratings yet
- Drug Study-MsGO4 (A)Document3 pagesDrug Study-MsGO4 (A)Ronel ResurricionNo ratings yet
- Calcium GluconateDocument2 pagesCalcium GluconateMae Ann Bueno Castillon100% (1)
- CaCO3 Drug StudDocument2 pagesCaCO3 Drug StudAubrey SungaNo ratings yet
- MV FeSO4 Drug StudyDocument2 pagesMV FeSO4 Drug StudyZiaNo ratings yet
- Tablet For KidneyDocument1 pageTablet For KidneyAbdul Wahaab KhokharNo ratings yet
- StudyDocument5 pagesStudyWestley RubinoNo ratings yet
- Medici Di Makati College 1061 Metropolitan Avenue, San Antonio Village, Makati City, Philippines 1200Document18 pagesMedici Di Makati College 1061 Metropolitan Avenue, San Antonio Village, Makati City, Philippines 1200Andee SalegonNo ratings yet
- Drug Therapy of DM - Oral Antidiabetic DrugsDocument3 pagesDrug Therapy of DM - Oral Antidiabetic DrugsSurria Suguna15No ratings yet
- 1magsu 2methergineDocument5 pages1magsu 2metherginelaiza_lumbaNo ratings yet
- OMEPRAZOLEDocument1 pageOMEPRAZOLERheza0% (1)
- Class: Calcium Salts: Agent(s) Common Uses Contraindications Route/Dosage Onset of Action InteractionsDocument8 pagesClass: Calcium Salts: Agent(s) Common Uses Contraindications Route/Dosage Onset of Action InteractionsAlano S. LimgasNo ratings yet
- Simvastatin (Zocor)Document2 pagesSimvastatin (Zocor)Mikaela Gabrielle GeraliNo ratings yet
- DRUGSTUDYDocument6 pagesDRUGSTUDYMauriceNo ratings yet
- Metformin Drug StudyDocument2 pagesMetformin Drug StudyArone SebastianNo ratings yet
- AcetazolamideDocument2 pagesAcetazolamideAlexandra Antondy0% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyJanika BecieraNo ratings yet
- Ob Ward Rle Drug StudyDocument3 pagesOb Ward Rle Drug StudyArisza Shane B.No ratings yet
- Drugstudy Ms. IbaleDocument23 pagesDrugstudy Ms. IbaleNabor, MelagroseNo ratings yet
- Final Magnesium SulfateDocument3 pagesFinal Magnesium SulfateGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Drug Name Classificatio N Dosage/ Prepatarion Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument4 pagesDrug Study Drug Name Classificatio N Dosage/ Prepatarion Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesTheresa AbrilloNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyTheresa AbrilloNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Drug Name Classificatio N Dosage/ Prepatarion Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument4 pagesDrug Study Drug Name Classificatio N Dosage/ Prepatarion Indication Contraindication Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesTheresa AbrilloNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument10 pagesDrug StudyJashtine JingcoNo ratings yet
- PHRM TemplateDocument4 pagesPHRM TemplateRichard SakyiamahNo ratings yet
- AcetazolamideDocument4 pagesAcetazolamideAnkit RuhilNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudymayanngeloNo ratings yet
- Medications and Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument6 pagesMedications and Nursing ResponsibilitiesDarla JoyceNo ratings yet
- Oral-Revalida GDocument19 pagesOral-Revalida GJasmine CorreosNo ratings yet
- College of Nursing: Cebu Normal UniversityDocument4 pagesCollege of Nursing: Cebu Normal UniversityFaye Andrea FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Generic NameDocument5 pagesGeneric NameJanika BecieraNo ratings yet
- DKASystem DisorderDocument1 pageDKASystem DisorderAA DDNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Mechanism of Action Indications Contraindication Side Effects Nursing Responsibilities Generic Name: BeforeDocument5 pagesName of Drug Mechanism of Action Indications Contraindication Side Effects Nursing Responsibilities Generic Name: BeforeWestley RubinoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - Colon CancerDocument4 pagesDrug Study - Colon Cancerbea pegadNo ratings yet
- X. Medical ManagementDocument12 pagesX. Medical ManagementXy-Za Roy MarieNo ratings yet
- Drug Study NOt COmpleteDocument6 pagesDrug Study NOt COmpletejiellianemaeNo ratings yet
- Vitamin KDocument3 pagesVitamin KJaye Aprile Adrianne KuizonNo ratings yet
- Drug SDocument2 pagesDrug SJane CasiquinNo ratings yet
- CalciumDocument2 pagesCalciumNoah Kent MojicaNo ratings yet
- Case Study #7Document22 pagesCase Study #7Christian Dave EndinoNo ratings yet
- CASE 2 - Heat StrokeDocument26 pagesCASE 2 - Heat StrokeChristian Dave EndinoNo ratings yet
- Case 6Document41 pagesCase 6Christian Dave EndinoNo ratings yet
- Abc Case 5Document19 pagesAbc Case 5Christian Dave EndinoNo ratings yet
- Uses of ICT in Our Daily LivesDocument1 pageUses of ICT in Our Daily LivesChristian Dave EndinoNo ratings yet
- Module 6 - PDFDocument17 pagesModule 6 - PDFChristian Dave EndinoNo ratings yet
- DopamineDocument3 pagesDopamineChristian Dave EndinoNo ratings yet
- Ict EssayDocument3 pagesIct EssayChristian Dave EndinoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument32 pagesDrug StudyChristian Dave EndinoNo ratings yet
- AtropineDocument3 pagesAtropineChristian Dave EndinoNo ratings yet
- AmiodaroneDocument4 pagesAmiodaroneChristian Dave EndinoNo ratings yet
- VasopressinDocument3 pagesVasopressinChristian Dave EndinoNo ratings yet
- NCDs Among TeenagerDocument13 pagesNCDs Among TeenagerChristian Dave EndinoNo ratings yet
- Sodium BicarbonateDocument20 pagesSodium BicarbonateChristian Dave EndinoNo ratings yet
- Guptautkarsh@dsnlu Ac inDocument2 pagesGuptautkarsh@dsnlu Ac inUTKARSH GUPTANo ratings yet
- Cure Tooth Decay - How To Prevent & Cure Tooth Decay & Cavities Naturally in The Comfort of Your Own Home (Cure Tooth, Cure Tooth Decay, Tooth Decay Cure, ... Whitening, Teeth Health, Teeth Healing)Document38 pagesCure Tooth Decay - How To Prevent & Cure Tooth Decay & Cavities Naturally in The Comfort of Your Own Home (Cure Tooth, Cure Tooth Decay, Tooth Decay Cure, ... Whitening, Teeth Health, Teeth Healing)Hendrik Danu67% (3)
- FMcase 1Document24 pagesFMcase 1Ryan Townsend100% (2)
- Siemens Bullet Train Feasibility Report For PakistanDocument153 pagesSiemens Bullet Train Feasibility Report For Pakistansyed usman wazirNo ratings yet
- Health Education and Health Promotion - OkanegaraDocument40 pagesHealth Education and Health Promotion - OkanegaraKristian Dwi CahyaNo ratings yet
- Name Product Link For Clients To UseDocument46 pagesName Product Link For Clients To UseGerry GimenaNo ratings yet
- CASESDocument24 pagesCASESMuhammed FirozNo ratings yet
- 8 - Blood Banking and SerologyDocument4 pages8 - Blood Banking and SerologyRanndolf Javier80% (5)
- Beast Mentality E-BookDocument40 pagesBeast Mentality E-BookMilton DesignerNo ratings yet
- CRANIOTOMYDocument5 pagesCRANIOTOMYJesha PlatigueNo ratings yet
- 4th Quarter WeeklyDocument15 pages4th Quarter WeeklyAlvior Elipane EirolNo ratings yet
- 2016-06-02 Map Re SVEC PCB Ballasts, Primary ContaminationDocument1 page2016-06-02 Map Re SVEC PCB Ballasts, Primary ContaminationLynsiNo ratings yet
- DCW PPT Re MCW Gender & GovDocument65 pagesDCW PPT Re MCW Gender & Goverick auza100% (1)
- Anatomy Lab Safety Contract 1Document3 pagesAnatomy Lab Safety Contract 1api-291794000No ratings yet
- Clinical Outcome PDF Update 2010Document62 pagesClinical Outcome PDF Update 2010Breno Mendes CardosoNo ratings yet
- Health Care Workers Systems of Safety - ENGLISHDocument20 pagesHealth Care Workers Systems of Safety - ENGLISHdorry_coshnetNo ratings yet
- Eng QP FormatDocument15 pagesEng QP Formatpriyansh asnaniNo ratings yet
- 3 - Updated Undertaking For EmployerDocument1 page3 - Updated Undertaking For EmployerRamnuj Orecul SoralcNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan - NCP-PIHDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan - NCP-PIHAally ChandraNo ratings yet
- Architects-Behaving-Badly3 Harvard Design MagazineDocument3 pagesArchitects-Behaving-Badly3 Harvard Design MagazineJelena SavicNo ratings yet
- INTRO-TO-ANATOMY - PHYSIOLOGY LectureDocument30 pagesINTRO-TO-ANATOMY - PHYSIOLOGY LectureJulie anne De jesusNo ratings yet
- Avascular NecrosisDocument44 pagesAvascular NecrosisRohit NathNo ratings yet
- 153 - 158 - 23 - PDF 2023 Jun 20 16 51 8Document17 pages153 - 158 - 23 - PDF 2023 Jun 20 16 51 8harshNo ratings yet
- 2020-Observership ApplicationDocument10 pages2020-Observership ApplicationShirley RamirezNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology, Pathology, Genetics: QP Code: BNN203Document1 pagePharmacology, Pathology, Genetics: QP Code: BNN203Mamta KumariNo ratings yet
- Biotechnology Safety Law enDocument40 pagesBiotechnology Safety Law enSunnyNo ratings yet
- Worksheet - Digestive System - 2020-21Document9 pagesWorksheet - Digestive System - 2020-21riddhiNo ratings yet
- 12th Zoolgy Guess Paper 2021 PDFDocument3 pages12th Zoolgy Guess Paper 2021 PDFMir FozAnNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Pridiction Using Machine LearningDocument31 pagesDiabetes Pridiction Using Machine LearningAbhishekNo ratings yet