Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Kat (Pat) - X Class - Ws - 3 - Solutions
Kat (Pat) - X Class - Ws - 3 - Solutions
Uploaded by
saatvikCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- The Geometry and Cohomology of Some Simple Shimura Varieties. (AM-151), Volume 151From EverandThe Geometry and Cohomology of Some Simple Shimura Varieties. (AM-151), Volume 151No ratings yet
- TN Primary Care Physicians COMPLAINT (Exhibits Attached)Document89 pagesTN Primary Care Physicians COMPLAINT (Exhibits Attached)HLMeditNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity PDFDocument82 pagesCurrent Electricity PDFKarna SriNo ratings yet
- Local Current in The HomeDocument108 pagesLocal Current in The Homeopsaurabh404No ratings yet
- SR Sankalp Super Grand-1!14!04-24 - PDF - QPDocument12 pagesSR Sankalp Super Grand-1!14!04-24 - PDF - QPrangaraonaidu011No ratings yet
- Neet PaperDocument20 pagesNeet Paperamoodiamna04No ratings yet
- 006 Power in DC CircuitsDocument4 pages006 Power in DC CircuitsBen KellyNo ratings yet
- 24.01.23 - SR MPC (Cio& Cao) - Jee Main Model - gtm-20 - QP - An - FinalDocument17 pages24.01.23 - SR MPC (Cio& Cao) - Jee Main Model - gtm-20 - QP - An - FinalAnuraag KumarNo ratings yet
- 04 09 21 SR.C 120, C Ipl & Ipl Ic (Incom) Jee Main WTM 12 Q.paperDocument18 pages04 09 21 SR.C 120, C Ipl & Ipl Ic (Incom) Jee Main WTM 12 Q.papernithila bhaskerNo ratings yet
- February 1 - MorningDocument12 pagesFebruary 1 - Morningadhyayan.learning.2021No ratings yet
- Linear Circuit Analysis: Chapter # 2: Basic LawsDocument60 pagesLinear Circuit Analysis: Chapter # 2: Basic Lawsrizwanspirit11No ratings yet
- Formulas and Constants: 13.1 Electrical Properties of CircuitsDocument7 pagesFormulas and Constants: 13.1 Electrical Properties of CircuitsGerardo Muñoz UrbinaNo ratings yet
- Cls Aipmt 19 20 Xii Phy Study Package 1 Level 2 Chapter 2Document32 pagesCls Aipmt 19 20 Xii Phy Study Package 1 Level 2 Chapter 2sona babuNo ratings yet
- Electricity Practice Sheet Solution: So, Equivalent Resistance of Three Bulbs in Parallel Will BeDocument5 pagesElectricity Practice Sheet Solution: So, Equivalent Resistance of Three Bulbs in Parallel Will BeAditya DuttNo ratings yet
- Important Questions For CBSE Class 12 Physics Chapter 3Document62 pagesImportant Questions For CBSE Class 12 Physics Chapter 3sudhanshu narvekarNo ratings yet
- 0102 Physics Paper With Answer MorningDocument5 pages0102 Physics Paper With Answer Morningspicypip123No ratings yet
- 01-07-2023 - Sr. C-IPL - Jee-Mains - WTM-08 - Q PaperDocument20 pages01-07-2023 - Sr. C-IPL - Jee-Mains - WTM-08 - Q PaperGowri ShankarNo ratings yet
- 07.04.18 - Current Electricity - PMDDocument8 pages07.04.18 - Current Electricity - PMDM JEEVARATHNAM NAIDUNo ratings yet
- Fianl 12th SOF-NSO-Stage-1 SET-B Solutions 2016Document25 pagesFianl 12th SOF-NSO-Stage-1 SET-B Solutions 2016RajuNo ratings yet
- Ari 12 CH 3 Current ElectricityDocument48 pagesAri 12 CH 3 Current ElectricitysitaramroyalNo ratings yet
- ????? ????????? ??? ??????? ???????? Docx - Ar.enDocument7 pages????? ????????? ??? ??????? ???????? Docx - Ar.eng4hb4zvt9bNo ratings yet
- SR Inter Ipe Question Bank Chapter-Vi (Current Electricity)Document21 pagesSR Inter Ipe Question Bank Chapter-Vi (Current Electricity)sojakoj867No ratings yet
- 06-05-2024 - Isr - Iit - Star Co SC - (Model - A & B) - WTM-34 - QP FinalDocument22 pages06-05-2024 - Isr - Iit - Star Co SC - (Model - A & B) - WTM-34 - QP Finaljirav34275No ratings yet
- 2 CurrentElectricityExe PCDocument44 pages2 CurrentElectricityExe PCAditya KapooorNo ratings yet
- Aakash CPP - 3Document34 pagesAakash CPP - 3Rishi ShuklaNo ratings yet
- FTS 7 (Code A) - 10 04 2020 PDFDocument17 pagesFTS 7 (Code A) - 10 04 2020 PDFkavyareddyNo ratings yet
- Alternating Current DPP 02 Manish Raj Sir Neet Crash Course RelaunchDocument2 pagesAlternating Current DPP 02 Manish Raj Sir Neet Crash Course Relaunchabu326274No ratings yet
- Ans Bank For PrelimsDocument7 pagesAns Bank For PrelimssahilNo ratings yet
- Online Neet/Jeemain Exam Physics: Electromagnetic Induction & AC (HOME WORK)Document5 pagesOnline Neet/Jeemain Exam Physics: Electromagnetic Induction & AC (HOME WORK)Haa KksakNo ratings yet
- Lab 3 AecDocument7 pagesLab 3 Aecpeter parkerNo ratings yet
- Network Theory: Presented byDocument29 pagesNetwork Theory: Presented bySapata KumarNo ratings yet
- Medical Question Paper 2204Document20 pagesMedical Question Paper 2204sumit kumarNo ratings yet
- Aakash CPP - 2Document43 pagesAakash CPP - 2Rishi Shukla100% (1)
- R-2R LadderDocument4 pagesR-2R Laddercarrotcucumber20No ratings yet
- PCBTest 1Document24 pagesPCBTest 1Bala ChinnappaNo ratings yet
- Ioqp 2021 22 Part I SolutionDocument11 pagesIoqp 2021 22 Part I SolutionJyoti DhillonNo ratings yet
- DPP-20 - Emi Jee MainsDocument7 pagesDPP-20 - Emi Jee MainsPpoNo ratings yet
- Modelling of Induction Motor PDFDocument42 pagesModelling of Induction Motor PDFsureshNo ratings yet
- NEET UG Physics Current Electricity MCQs PDFDocument54 pagesNEET UG Physics Current Electricity MCQs PDFKarthick .aNo ratings yet
- Topic2 - Resistive Circuits - Part 2Document26 pagesTopic2 - Resistive Circuits - Part 2jeanniejayeadsNo ratings yet
- UNIT - 1 Differential Calculus 1 (21MA1BSCDE) 2021-22Document7 pagesUNIT - 1 Differential Calculus 1 (21MA1BSCDE) 2021-22Jai VishnuNo ratings yet
- 64e48eeaf4cb5500180a97d7 ## Electromagnetic Induction Practice SheetDocument14 pages64e48eeaf4cb5500180a97d7 ## Electromagnetic Induction Practice SheetdevanshbcollabNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document5 pagesLecture 3none. xNo ratings yet
- Physics II Chapter 6 PDFDocument10 pagesPhysics II Chapter 6 PDFrenNo ratings yet
- Practice Test 04 - Test Paper - Lakshya NEET Fastrack 2024Document19 pagesPractice Test 04 - Test Paper - Lakshya NEET Fastrack 2024Janhavi kulkarniNo ratings yet
- Narayana 26 05 2022 OUTGOING SR JEE MAIN MODEL GTM 3 QP FINAL QuesDocument18 pagesNarayana 26 05 2022 OUTGOING SR JEE MAIN MODEL GTM 3 QP FINAL Quesmanol sahooNo ratings yet
- Classroom Contact Programme: Pre-Medical: Enthusiast Course (Phase: Meq)Document31 pagesClassroom Contact Programme: Pre-Medical: Enthusiast Course (Phase: Meq)shainasinghdhaniaNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity-09-Subjective and Objective SolutionsDocument26 pagesCurrent Electricity-09-Subjective and Objective SolutionsRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- PHYS 102 - General Physics II Midterm Exam 2 Solutions: V V P R R PDocument2 pagesPHYS 102 - General Physics II Midterm Exam 2 Solutions: V V P R R PNano SuyatnoNo ratings yet
- AC Current & Semiconductors: L5 by Ahmed AtlamDocument23 pagesAC Current & Semiconductors: L5 by Ahmed AtlamAhmed AtlamNo ratings yet
- SR - Part Test-2 Q.paperDocument12 pagesSR - Part Test-2 Q.paperM JEEVARATHNAM NAIDUNo ratings yet
- 3852Document27 pages3852Wana BilaNo ratings yet
- Paper 1 - JEEADV2019Document18 pagesPaper 1 - JEEADV2019vivek.vmcavNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity (SMTP) (Ans)Document11 pagesCurrent Electricity (SMTP) (Ans)Dionysius LeowNo ratings yet
- Jee Mainpapersol2018 PDFDocument22 pagesJee Mainpapersol2018 PDFBhoopesh KayapakNo ratings yet
- All India Test Series Full Syllabus Test-07 - NEET - 04-05-2023 - QuestionsDocument17 pagesAll India Test Series Full Syllabus Test-07 - NEET - 04-05-2023 - QuestionsMusical MaanishNo ratings yet
- Hukum Coulomb Dan Medan ListrikDocument66 pagesHukum Coulomb Dan Medan Listrikdavid purbaNo ratings yet
- Neet Full Test - 01 Time:3 Hours Full Mark: 720Document24 pagesNeet Full Test - 01 Time:3 Hours Full Mark: 720Shaba TaskeenNo ratings yet
- Raghu Engineering College: AutonomousDocument24 pagesRaghu Engineering College: AutonomousmkrNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS JEE 27th Jan Shift 2Document9 pagesPHYSICS JEE 27th Jan Shift 2hasan.mohamed2305No ratings yet
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterNo ratings yet
- United India Insurance Company Limited: M/ Weld Care NDT Inspection ServicesDocument3 pagesUnited India Insurance Company Limited: M/ Weld Care NDT Inspection ServicesDeepan RajNo ratings yet
- Law600 Foundation Group2Document68 pagesLaw600 Foundation Group2Nadine DiamanteNo ratings yet
- 1.1 - Application - LitvinovDocument12 pages1.1 - Application - LitvinovDmiNo ratings yet
- Challenges For Foreign Banks Entering India Open New Opportunities For Consulting Firms PDFDocument11 pagesChallenges For Foreign Banks Entering India Open New Opportunities For Consulting Firms PDFTanu SinghNo ratings yet
- BomBay Port Trust Case (16909)Document24 pagesBomBay Port Trust Case (16909)Pragya RaniNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For You May Ask Yourself An Introduction To Thinking Like A Sociologist 6th Edition Dalton Conley Isbn 10 0393674185 Isbn 9780393674187Document18 pagesTest Bank For You May Ask Yourself An Introduction To Thinking Like A Sociologist 6th Edition Dalton Conley Isbn 10 0393674185 Isbn 9780393674187tammyshaffer12052000mfe93% (14)
- Credit CreationDocument46 pagesCredit Creationrizw_anNo ratings yet
- TES Sharing Agreement 2022-2023Document2 pagesTES Sharing Agreement 2022-2023Sherwin Sioco IbongNo ratings yet
- Media and Ent Law RequiremntsDocument83 pagesMedia and Ent Law RequiremntsAnuj SunejaNo ratings yet
- 2021 Production Goal Chart - IndiaDocument3 pages2021 Production Goal Chart - IndiaVidhyaNo ratings yet
- Data 2Document22 pagesData 2Ravi RadheyNo ratings yet
- Deloitte UK 2021 Hot Topics in IT Internal AuditDocument46 pagesDeloitte UK 2021 Hot Topics in IT Internal AuditkosmoguyNo ratings yet
- 2019LLB052 - 1PC I - 3rd SemDocument16 pages2019LLB052 - 1PC I - 3rd Semshloka dikshitNo ratings yet
- Corruption Perceptions Index 2010Document12 pagesCorruption Perceptions Index 2010NDTVNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Grade and Section: 9-WISDOM Adviser: Prilyn S. AlbaricoDocument13 pagesDepartment of Education: Grade and Section: 9-WISDOM Adviser: Prilyn S. Albaricoprilyn albaricoNo ratings yet
- Clearance PDFDocument1 pageClearance PDFJane DeckerNo ratings yet
- Complaint Based On Actionable DocumentDocument7 pagesComplaint Based On Actionable DocumentAnnievin HawkNo ratings yet
- Week 3 DigestsDocument45 pagesWeek 3 DigestsTony TopacioNo ratings yet
- I. Exemptions 1.1. Insanity / Imbecility: Crim 1 SyllabusDocument2 pagesI. Exemptions 1.1. Insanity / Imbecility: Crim 1 SyllabusJohn Rey FerarenNo ratings yet
- RECTIFICATION - ENG Power No Mistake Aishwaryam Garden Plot No.7Document2 pagesRECTIFICATION - ENG Power No Mistake Aishwaryam Garden Plot No.7Gokulakrishnan SelvarajanNo ratings yet
- Crim I DigestsDocument7 pagesCrim I DigestsBinkee Villarama0% (1)
- Job Description - CRODocument1 pageJob Description - CROPeeush ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- BIR Ruling 023-09Document5 pagesBIR Ruling 023-09Juno Geronimo100% (2)
- Business Letter WritingDocument8 pagesBusiness Letter WritingMonahil FatimaNo ratings yet
- Komparasi 2Document11 pagesKomparasi 2rizky kunNo ratings yet
- Part I: Multiple - Choise Questions Choose The Only One Right Answer For Each QuestionDocument7 pagesPart I: Multiple - Choise Questions Choose The Only One Right Answer For Each QuestionHa TranNo ratings yet
- St. Mary's Farm v. Prime Real Properties (Teresa)Document10 pagesSt. Mary's Farm v. Prime Real Properties (Teresa)Lourdes LescanoNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Manila: Supreme CourtDocument2 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Manila: Supreme CourtDatu Arumpac100% (1)
- Cas-Letter-Request-Form (Vikas)Document2 pagesCas-Letter-Request-Form (Vikas)VikasNo ratings yet
Kat (Pat) - X Class - Ws - 3 - Solutions
Kat (Pat) - X Class - Ws - 3 - Solutions
Uploaded by
saatvikOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Kat (Pat) - X Class - Ws - 3 - Solutions
Kat (Pat) - X Class - Ws - 3 - Solutions
Uploaded by
saatvikCopyright:
Available Formats
KAT (PAT) – W.
S – 3 - SOLUTIONS
KAT (PAT) – WORK SHEET - 3 :: SOLUTIONS
CURRENT ELECTRICITY
X - CLASS
q w v
1. i , q it , v , R
t q i
2. If collisions decreases then resistance also decreases hence current increases.
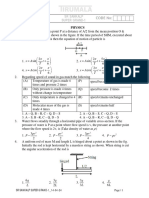
3.
R i1 4R
i i
v1 A i2 B
2R v 2
4R, 2R are parallel
1 1 1 6R 3
2
R eff 4R 2R 8R 4R
4R
R eff
3
4R
and R are in series
3
4R 7R
R eff R
3 3
E3
l
7R
We know
E v1 v2
v2 E v1 E iR
3E 4E
E .R
7R 7
But v2 2R i2
4E 2E
i2
7 2R 7R
4. i neAVd
i1 A1 Vd1
i 2 A 2 Vd 2
i A V
2i 2A Vd 2
Vd 2 V
5. from V IR
Current depends on both potential difference applied and Resistance of the wire
Sri Chaitanya School 1 No.1 School in India
KAT (PAT) – W.S – 3 - SOLUTIONS
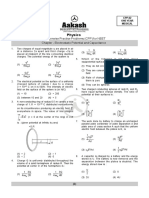
6.
V T2
T1
90
I
R1 tan
R 2 tan 90 cot
cos sin
R 2 R 1 cot tan
sin cos
cos 2 sin 2 2.cos 2
cos .sin sin 2
2 cot 2
R 2 R1 2cot 2
T2 T1 cot 2
7. R l2
l2 R
R2
4 4
R R R
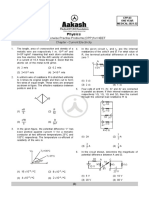
8. (1)
R
R
(2)
R
R R
(3)
R
R
R
(4)
R
Second method:
1) For equal resistors the number of easy of different combinations of these
resistance is 2n 1
2) For an equal resistors of different combinations of these resistance is 2n
9. They are parallel
q 900
10. i 3/2 1.5A
t 10 60
11. By conceptual
12. By conceptual
1
13. a) R
A
b) Specific resistance depends on nature of material
14. In conducting materials electrons respond to electric change or heat energy. So metals are good
conductors of current and heat energy
15. Assertion: If the current has to flow between two points, Potential difference should exist between
them.
Reason: Ohm’s law can be stated as
“The potential difference across a current carrying conductor is directly proportional to the current
passing through it, when the temperature of the current kept constant”
Sri Chaitanya School 2 No.1 School in India
KAT (PAT) – W.S – 3 - SOLUTIONS
16. In case of electric current area of the conductor is not considered current
density depends on cross sectional area of the conductor
i
j
A cos
i jA cos
Thus current density is a vector
17. Reciprocal of resistance conductance
18. Kirchhoff’s first law follows law of conservation of charge
19. Kirchhoff’s second law follows law of conservation of energy
20. Reciprocal of resistivity conductivity
***
Sri Chaitanya School 3 No.1 School in India
You might also like
- The Geometry and Cohomology of Some Simple Shimura Varieties. (AM-151), Volume 151From EverandThe Geometry and Cohomology of Some Simple Shimura Varieties. (AM-151), Volume 151No ratings yet
- TN Primary Care Physicians COMPLAINT (Exhibits Attached)Document89 pagesTN Primary Care Physicians COMPLAINT (Exhibits Attached)HLMeditNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity PDFDocument82 pagesCurrent Electricity PDFKarna SriNo ratings yet
- Local Current in The HomeDocument108 pagesLocal Current in The Homeopsaurabh404No ratings yet
- SR Sankalp Super Grand-1!14!04-24 - PDF - QPDocument12 pagesSR Sankalp Super Grand-1!14!04-24 - PDF - QPrangaraonaidu011No ratings yet
- Neet PaperDocument20 pagesNeet Paperamoodiamna04No ratings yet
- 006 Power in DC CircuitsDocument4 pages006 Power in DC CircuitsBen KellyNo ratings yet
- 24.01.23 - SR MPC (Cio& Cao) - Jee Main Model - gtm-20 - QP - An - FinalDocument17 pages24.01.23 - SR MPC (Cio& Cao) - Jee Main Model - gtm-20 - QP - An - FinalAnuraag KumarNo ratings yet
- 04 09 21 SR.C 120, C Ipl & Ipl Ic (Incom) Jee Main WTM 12 Q.paperDocument18 pages04 09 21 SR.C 120, C Ipl & Ipl Ic (Incom) Jee Main WTM 12 Q.papernithila bhaskerNo ratings yet
- February 1 - MorningDocument12 pagesFebruary 1 - Morningadhyayan.learning.2021No ratings yet
- Linear Circuit Analysis: Chapter # 2: Basic LawsDocument60 pagesLinear Circuit Analysis: Chapter # 2: Basic Lawsrizwanspirit11No ratings yet
- Formulas and Constants: 13.1 Electrical Properties of CircuitsDocument7 pagesFormulas and Constants: 13.1 Electrical Properties of CircuitsGerardo Muñoz UrbinaNo ratings yet
- Cls Aipmt 19 20 Xii Phy Study Package 1 Level 2 Chapter 2Document32 pagesCls Aipmt 19 20 Xii Phy Study Package 1 Level 2 Chapter 2sona babuNo ratings yet
- Electricity Practice Sheet Solution: So, Equivalent Resistance of Three Bulbs in Parallel Will BeDocument5 pagesElectricity Practice Sheet Solution: So, Equivalent Resistance of Three Bulbs in Parallel Will BeAditya DuttNo ratings yet
- Important Questions For CBSE Class 12 Physics Chapter 3Document62 pagesImportant Questions For CBSE Class 12 Physics Chapter 3sudhanshu narvekarNo ratings yet
- 0102 Physics Paper With Answer MorningDocument5 pages0102 Physics Paper With Answer Morningspicypip123No ratings yet
- 01-07-2023 - Sr. C-IPL - Jee-Mains - WTM-08 - Q PaperDocument20 pages01-07-2023 - Sr. C-IPL - Jee-Mains - WTM-08 - Q PaperGowri ShankarNo ratings yet
- 07.04.18 - Current Electricity - PMDDocument8 pages07.04.18 - Current Electricity - PMDM JEEVARATHNAM NAIDUNo ratings yet
- Fianl 12th SOF-NSO-Stage-1 SET-B Solutions 2016Document25 pagesFianl 12th SOF-NSO-Stage-1 SET-B Solutions 2016RajuNo ratings yet
- Ari 12 CH 3 Current ElectricityDocument48 pagesAri 12 CH 3 Current ElectricitysitaramroyalNo ratings yet
- ????? ????????? ??? ??????? ???????? Docx - Ar.enDocument7 pages????? ????????? ??? ??????? ???????? Docx - Ar.eng4hb4zvt9bNo ratings yet
- SR Inter Ipe Question Bank Chapter-Vi (Current Electricity)Document21 pagesSR Inter Ipe Question Bank Chapter-Vi (Current Electricity)sojakoj867No ratings yet
- 06-05-2024 - Isr - Iit - Star Co SC - (Model - A & B) - WTM-34 - QP FinalDocument22 pages06-05-2024 - Isr - Iit - Star Co SC - (Model - A & B) - WTM-34 - QP Finaljirav34275No ratings yet
- 2 CurrentElectricityExe PCDocument44 pages2 CurrentElectricityExe PCAditya KapooorNo ratings yet
- Aakash CPP - 3Document34 pagesAakash CPP - 3Rishi ShuklaNo ratings yet
- FTS 7 (Code A) - 10 04 2020 PDFDocument17 pagesFTS 7 (Code A) - 10 04 2020 PDFkavyareddyNo ratings yet
- Alternating Current DPP 02 Manish Raj Sir Neet Crash Course RelaunchDocument2 pagesAlternating Current DPP 02 Manish Raj Sir Neet Crash Course Relaunchabu326274No ratings yet
- Ans Bank For PrelimsDocument7 pagesAns Bank For PrelimssahilNo ratings yet
- Online Neet/Jeemain Exam Physics: Electromagnetic Induction & AC (HOME WORK)Document5 pagesOnline Neet/Jeemain Exam Physics: Electromagnetic Induction & AC (HOME WORK)Haa KksakNo ratings yet
- Lab 3 AecDocument7 pagesLab 3 Aecpeter parkerNo ratings yet
- Network Theory: Presented byDocument29 pagesNetwork Theory: Presented bySapata KumarNo ratings yet
- Medical Question Paper 2204Document20 pagesMedical Question Paper 2204sumit kumarNo ratings yet
- Aakash CPP - 2Document43 pagesAakash CPP - 2Rishi Shukla100% (1)
- R-2R LadderDocument4 pagesR-2R Laddercarrotcucumber20No ratings yet
- PCBTest 1Document24 pagesPCBTest 1Bala ChinnappaNo ratings yet
- Ioqp 2021 22 Part I SolutionDocument11 pagesIoqp 2021 22 Part I SolutionJyoti DhillonNo ratings yet
- DPP-20 - Emi Jee MainsDocument7 pagesDPP-20 - Emi Jee MainsPpoNo ratings yet
- Modelling of Induction Motor PDFDocument42 pagesModelling of Induction Motor PDFsureshNo ratings yet
- NEET UG Physics Current Electricity MCQs PDFDocument54 pagesNEET UG Physics Current Electricity MCQs PDFKarthick .aNo ratings yet
- Topic2 - Resistive Circuits - Part 2Document26 pagesTopic2 - Resistive Circuits - Part 2jeanniejayeadsNo ratings yet
- UNIT - 1 Differential Calculus 1 (21MA1BSCDE) 2021-22Document7 pagesUNIT - 1 Differential Calculus 1 (21MA1BSCDE) 2021-22Jai VishnuNo ratings yet
- 64e48eeaf4cb5500180a97d7 ## Electromagnetic Induction Practice SheetDocument14 pages64e48eeaf4cb5500180a97d7 ## Electromagnetic Induction Practice SheetdevanshbcollabNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document5 pagesLecture 3none. xNo ratings yet
- Physics II Chapter 6 PDFDocument10 pagesPhysics II Chapter 6 PDFrenNo ratings yet
- Practice Test 04 - Test Paper - Lakshya NEET Fastrack 2024Document19 pagesPractice Test 04 - Test Paper - Lakshya NEET Fastrack 2024Janhavi kulkarniNo ratings yet
- Narayana 26 05 2022 OUTGOING SR JEE MAIN MODEL GTM 3 QP FINAL QuesDocument18 pagesNarayana 26 05 2022 OUTGOING SR JEE MAIN MODEL GTM 3 QP FINAL Quesmanol sahooNo ratings yet
- Classroom Contact Programme: Pre-Medical: Enthusiast Course (Phase: Meq)Document31 pagesClassroom Contact Programme: Pre-Medical: Enthusiast Course (Phase: Meq)shainasinghdhaniaNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity-09-Subjective and Objective SolutionsDocument26 pagesCurrent Electricity-09-Subjective and Objective SolutionsRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- PHYS 102 - General Physics II Midterm Exam 2 Solutions: V V P R R PDocument2 pagesPHYS 102 - General Physics II Midterm Exam 2 Solutions: V V P R R PNano SuyatnoNo ratings yet
- AC Current & Semiconductors: L5 by Ahmed AtlamDocument23 pagesAC Current & Semiconductors: L5 by Ahmed AtlamAhmed AtlamNo ratings yet
- SR - Part Test-2 Q.paperDocument12 pagesSR - Part Test-2 Q.paperM JEEVARATHNAM NAIDUNo ratings yet
- 3852Document27 pages3852Wana BilaNo ratings yet
- Paper 1 - JEEADV2019Document18 pagesPaper 1 - JEEADV2019vivek.vmcavNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity (SMTP) (Ans)Document11 pagesCurrent Electricity (SMTP) (Ans)Dionysius LeowNo ratings yet
- Jee Mainpapersol2018 PDFDocument22 pagesJee Mainpapersol2018 PDFBhoopesh KayapakNo ratings yet
- All India Test Series Full Syllabus Test-07 - NEET - 04-05-2023 - QuestionsDocument17 pagesAll India Test Series Full Syllabus Test-07 - NEET - 04-05-2023 - QuestionsMusical MaanishNo ratings yet
- Hukum Coulomb Dan Medan ListrikDocument66 pagesHukum Coulomb Dan Medan Listrikdavid purbaNo ratings yet
- Neet Full Test - 01 Time:3 Hours Full Mark: 720Document24 pagesNeet Full Test - 01 Time:3 Hours Full Mark: 720Shaba TaskeenNo ratings yet
- Raghu Engineering College: AutonomousDocument24 pagesRaghu Engineering College: AutonomousmkrNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS JEE 27th Jan Shift 2Document9 pagesPHYSICS JEE 27th Jan Shift 2hasan.mohamed2305No ratings yet
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterNo ratings yet
- United India Insurance Company Limited: M/ Weld Care NDT Inspection ServicesDocument3 pagesUnited India Insurance Company Limited: M/ Weld Care NDT Inspection ServicesDeepan RajNo ratings yet
- Law600 Foundation Group2Document68 pagesLaw600 Foundation Group2Nadine DiamanteNo ratings yet
- 1.1 - Application - LitvinovDocument12 pages1.1 - Application - LitvinovDmiNo ratings yet
- Challenges For Foreign Banks Entering India Open New Opportunities For Consulting Firms PDFDocument11 pagesChallenges For Foreign Banks Entering India Open New Opportunities For Consulting Firms PDFTanu SinghNo ratings yet
- BomBay Port Trust Case (16909)Document24 pagesBomBay Port Trust Case (16909)Pragya RaniNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For You May Ask Yourself An Introduction To Thinking Like A Sociologist 6th Edition Dalton Conley Isbn 10 0393674185 Isbn 9780393674187Document18 pagesTest Bank For You May Ask Yourself An Introduction To Thinking Like A Sociologist 6th Edition Dalton Conley Isbn 10 0393674185 Isbn 9780393674187tammyshaffer12052000mfe93% (14)
- Credit CreationDocument46 pagesCredit Creationrizw_anNo ratings yet
- TES Sharing Agreement 2022-2023Document2 pagesTES Sharing Agreement 2022-2023Sherwin Sioco IbongNo ratings yet
- Media and Ent Law RequiremntsDocument83 pagesMedia and Ent Law RequiremntsAnuj SunejaNo ratings yet
- 2021 Production Goal Chart - IndiaDocument3 pages2021 Production Goal Chart - IndiaVidhyaNo ratings yet
- Data 2Document22 pagesData 2Ravi RadheyNo ratings yet
- Deloitte UK 2021 Hot Topics in IT Internal AuditDocument46 pagesDeloitte UK 2021 Hot Topics in IT Internal AuditkosmoguyNo ratings yet
- 2019LLB052 - 1PC I - 3rd SemDocument16 pages2019LLB052 - 1PC I - 3rd Semshloka dikshitNo ratings yet
- Corruption Perceptions Index 2010Document12 pagesCorruption Perceptions Index 2010NDTVNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Grade and Section: 9-WISDOM Adviser: Prilyn S. AlbaricoDocument13 pagesDepartment of Education: Grade and Section: 9-WISDOM Adviser: Prilyn S. Albaricoprilyn albaricoNo ratings yet
- Clearance PDFDocument1 pageClearance PDFJane DeckerNo ratings yet
- Complaint Based On Actionable DocumentDocument7 pagesComplaint Based On Actionable DocumentAnnievin HawkNo ratings yet
- Week 3 DigestsDocument45 pagesWeek 3 DigestsTony TopacioNo ratings yet
- I. Exemptions 1.1. Insanity / Imbecility: Crim 1 SyllabusDocument2 pagesI. Exemptions 1.1. Insanity / Imbecility: Crim 1 SyllabusJohn Rey FerarenNo ratings yet
- RECTIFICATION - ENG Power No Mistake Aishwaryam Garden Plot No.7Document2 pagesRECTIFICATION - ENG Power No Mistake Aishwaryam Garden Plot No.7Gokulakrishnan SelvarajanNo ratings yet
- Crim I DigestsDocument7 pagesCrim I DigestsBinkee Villarama0% (1)
- Job Description - CRODocument1 pageJob Description - CROPeeush ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- BIR Ruling 023-09Document5 pagesBIR Ruling 023-09Juno Geronimo100% (2)
- Business Letter WritingDocument8 pagesBusiness Letter WritingMonahil FatimaNo ratings yet
- Komparasi 2Document11 pagesKomparasi 2rizky kunNo ratings yet
- Part I: Multiple - Choise Questions Choose The Only One Right Answer For Each QuestionDocument7 pagesPart I: Multiple - Choise Questions Choose The Only One Right Answer For Each QuestionHa TranNo ratings yet
- St. Mary's Farm v. Prime Real Properties (Teresa)Document10 pagesSt. Mary's Farm v. Prime Real Properties (Teresa)Lourdes LescanoNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Manila: Supreme CourtDocument2 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Manila: Supreme CourtDatu Arumpac100% (1)
- Cas-Letter-Request-Form (Vikas)Document2 pagesCas-Letter-Request-Form (Vikas)VikasNo ratings yet