Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Connected Particles Student Notes - Lifts 2022-06-27 15 - 47 - 18
Connected Particles Student Notes - Lifts 2022-06-27 15 - 47 - 18
Uploaded by
Dean MillarOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Connected Particles Student Notes - Lifts 2022-06-27 15 - 47 - 18
Connected Particles Student Notes - Lifts 2022-06-27 15 - 47 - 18
Uploaded by
Dean MillarCopyright:
Available Formats
Reaction
If twobodies are in direct contact then they exertan equal but opposite
reactiononthe other R2
E o
R2
now
e o r
momma mg r my
the force due to a mass actingon anotherbody is its reaction not its weight
Uninhutively
A weightonlyactson the body ofthatmass
Note on lifts the maximum downwards acceleration is 9.8ms as that represents a body
infreefall
Journey of a lift
goingotO
equilibrium
re
re
equilibria
r
ve te
equilibrium
v
goingdowrimT
Static equilibrium ko
In equilibrium the reaction bythe person will equaltheirweight
andthe tension willequal the totalweightof the system
omg
R ng O R mg
4mg
Upwards acceleration upwards motion
As theobjectsare incontact theyhave thesame acceleration
Theeffect on the person will be
me
µ
o K mg ma
R2Mg re mg ma lie it is greater Why Becausethereach
is outweighing the weight to cause an
acceleration
Dynamic equilibrium constant velocity
As in position R mg
Deceleration downwards acceleration upwards motion
T
a R mg MC a
r
R mg ma
v
va
om Recallthat Rz0 for objects to be in contact so a eg
Weknowthis to betrue as theropecannot push the lift downwards
Rs99 sothe maximum downwards acceleration of the lift mustbe g
Static Cas
Downwards acceleration downwardsmotion as
Dynamic equilibrium constantvelocity as
Upwards acceleration downwardsvelocity as
staticEquilibrium as
Broken
rope
inthecasethattheropebreakstherewillbenotensionactingonthelift
Bothbodieswillexperience accelerationdueonlyto gravity
Theeffectontheobjectinthelifewillbe
m Eg Rmg mg
ing R 0
Boththeperson
andtheliftareinfreefanTheliftisnotexerting
anyforceonmeobject thisisclearlytrueasthe objecthasreachedin
maximumdownwardsacceleration possible dueonlyto weight
Notethe
liftcanalso technical
feelawif its downwards carmotiondownwards or deceleration
formotion
acceleration
experience
upwards isequaltog
ta
vg T cm1mg cmmy
Mm
T o
cm
ing
Examples
A person of mass 100 kg stands in a lift.
What is the force exerted by the lift oor on the person when the lift is:
i) moving upwards at 3 ms-1
ii) moving downwards at 4 ms-1
A man enters an elevator holding two boxes - one on top of the other. The top box has a mass
of 6.0 kg and the bottom box has a mass of 8.0 kg. The man sets the two boxes on a metric
scale sitting on the oor. When accelerating upward from rest, the man observes that the scale
reads a value of 166 N; this is the upward force upon the bottom box. Determine the
acceleration of the elevator (and boxes) and determine the forces acting between the boxes.
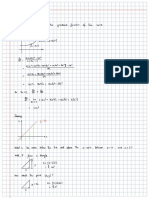
Two boxes are held together by a strong wire and attached to the ceiling of an elevator by
a second wire (see diagram). The mass of the top box is 14.2 kg; the mass of the bottom
box is 10.4 kg. The elevator accelerates upwards at 2.84 m/s2. (Assume the wire is relatively
massless.)
(a) Find the tension in the top wire (connecting points A and B).
(b) Find the tension in the bottom wire (connecting points C and D).
Exercise 2
You might also like
- LAB REPORT FlowmeterDocument31 pagesLAB REPORT Flowmeterahlan wasahlan82% (28)
- Moving SHT VesselsDocument19 pagesMoving SHT Vesselsmorsid aliudinNo ratings yet
- NLMWS67Document17 pagesNLMWS67Venky reddyNo ratings yet
- m1 Kinematics…. Copy (2) Copy (2) Copy (3)(1)Document27 pagesm1 Kinematics…. Copy (2) Copy (2) Copy (3)(1)AbidManNo ratings yet
- Iroduct: VelocityDocument5 pagesIroduct: VelocityIsmailchattha100No ratings yet
- Newtons Laws and MotionDocument11 pagesNewtons Laws and Motionvictoria kairooNo ratings yet
- Chương 6Document33 pagesChương 6Linh ThuậnNo ratings yet
- 2.2 Forces - and - FrictionDocument2 pages2.2 Forces - and - FrictionEjaz AhmadNo ratings yet
- (Combined PDF 4.0) - NLM - Class 11Document353 pages(Combined PDF 4.0) - NLM - Class 11Japjeet Singh KhurmiNo ratings yet
- Linear Momentum 1Document5 pagesLinear Momentum 1samcj4realNo ratings yet
- Oscillations Chapter 15: Simple Harmonic MotionDocument12 pagesOscillations Chapter 15: Simple Harmonic MotionmohidNo ratings yet
- Draft Draft: Attracted To The EarthDocument1 pageDraft Draft: Attracted To The EarthChian Kuok TingNo ratings yet
- Understanding Frictional Forces: AS Physics Revision Notes OnDocument3 pagesUnderstanding Frictional Forces: AS Physics Revision Notes OnmiltonNo ratings yet
- Stokes Law and ViscosityDocument3 pagesStokes Law and ViscosityPhilip MooreNo ratings yet
- Ch2 HandwrittenDocument4 pagesCh2 HandwrittenlilliaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3-DynamicsDocument1 pageChapter 3-DynamicsantonstefanbiehlerNo ratings yet
- (L1) - (JLD 2.0) - NLM - 14th JulyDocument92 pages(L1) - (JLD 2.0) - NLM - 14th JulyRaman BajajNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Fall2014 PDFDocument26 pagesChapter 5 Fall2014 PDFEdgar FigueroaNo ratings yet
- NLM 1Document56 pagesNLM 1Vrushant ParmarNo ratings yet
- (H2 PHY) Chapter 4 - ForcesDocument42 pages(H2 PHY) Chapter 4 - ForcesBaskar Dharshan (Punggolss)No ratings yet
- Circular Motion: Round and RoundDocument6 pagesCircular Motion: Round and RoundFarogh HamidNo ratings yet
- Science Power Point (Intro To Forces-Upper KS2)Document23 pagesScience Power Point (Intro To Forces-Upper KS2)Riya DeleneNo ratings yet
- Day 4 Laws of MotionDocument14 pagesDay 4 Laws of MotionRaj KumarNo ratings yet
- Dynamics: Second Semester 1442HDocument37 pagesDynamics: Second Semester 1442HKhalid AlqahtaniNo ratings yet
- 3 DynamicsDocument62 pages3 Dynamicsamandeep kaurNo ratings yet
- 2018 19 Q3 Phys114 L16 Torque and Center of GravityDocument21 pages2018 19 Q3 Phys114 L16 Torque and Center of GravityDestiny SumaniNo ratings yet
- FSMQ Force Diagrams PDFDocument6 pagesFSMQ Force Diagrams PDFgrace_lo_1No ratings yet
- Prog Pecutan Akhir Topic 7.1 - 7.3Document29 pagesProg Pecutan Akhir Topic 7.1 - 7.3farha2681No ratings yet
- Glenn B. Stracher Chapter6Document35 pagesGlenn B. Stracher Chapter6Lorraine QuijanoNo ratings yet
- Waves and Optics - ReviewerDocument15 pagesWaves and Optics - ReviewerJoshua QuimsonNo ratings yet
- 2.4 Momentum & ImpulseDocument11 pages2.4 Momentum & ImpulsefeeyonahNo ratings yet
- Week 1 PPT Lecture - Ch14 Phy097 (Compatibility Mode)Document40 pagesWeek 1 PPT Lecture - Ch14 Phy097 (Compatibility Mode)Anonymous nZo3uhY8uRNo ratings yet
- H2 Chapter 6 Circular Motion SummaryDocument1 pageH2 Chapter 6 Circular Motion SummaryDelania JohnNo ratings yet
- Impulse and MomentumDocument9 pagesImpulse and MomentumJancis TugadeNo ratings yet
- Engineering Dynamics: Chapter - Kinetics ParticlesDocument17 pagesEngineering Dynamics: Chapter - Kinetics ParticlesAbdillah AbassNo ratings yet
- Ch-7 FrictionDocument15 pagesCh-7 Frictionprabhunics26No ratings yet
- GR9 - Q4 - Lesson 1 - Motion in One DimensionDocument5 pagesGR9 - Q4 - Lesson 1 - Motion in One DimensionJerome HizonNo ratings yet
- 2.5 Effects of ForcesDocument8 pages2.5 Effects of ForcesNURUL FAEZAH BINTI MUSTAPA MoeNo ratings yet
- Relative Equilibrium of LiquidsDocument15 pagesRelative Equilibrium of LiquidsLarissa RiveraNo ratings yet
- 12A.3 Forces NSDocument4 pages12A.3 Forces NSnishka.sheikNo ratings yet
- Mass Attach To SpringDocument2 pagesMass Attach To SpringshahidjhyuNo ratings yet
- Learning Material - 03Document6 pagesLearning Material - 03Vincent VasquezNo ratings yet
- L04 Control Systems - Modeling of Mechanical SystemsDocument5 pagesL04 Control Systems - Modeling of Mechanical SystemsJezzrel Xandy BalmesNo ratings yet
- Nim Short NotesDocument6 pagesNim Short Noteshumairaparkar6No ratings yet
- Ee Fall 2022 - For StudentsDocument17 pagesEe Fall 2022 - For Students加赛 郭No ratings yet
- Drag Force in External Flows Lesson 2 Handout PDFDocument18 pagesDrag Force in External Flows Lesson 2 Handout PDFArjun LalitNo ratings yet
- White Paper 1403-How Gyros Create Stabilizing-TorqueDocument13 pagesWhite Paper 1403-How Gyros Create Stabilizing-TorqueSangam PatariNo ratings yet
- CBSE-XI Physics - Chap-4-6Document43 pagesCBSE-XI Physics - Chap-4-6himeshs298No ratings yet
- Week 4 - Skate Park Phet LabDocument3 pagesWeek 4 - Skate Park Phet LabSavannah RoseNo ratings yet
- Chapter3 RememberDocument1 pageChapter3 Rememberyue yueNo ratings yet
- Rotational Equilibrium and Rotational DynamicsDocument8 pagesRotational Equilibrium and Rotational DynamicsNathalie SerafinNo ratings yet
- Physical World Lecture Notes Week 11 Day 1 - Instructors (2023)Document43 pagesPhysical World Lecture Notes Week 11 Day 1 - Instructors (2023)Harshitha DavanamNo ratings yet
- NLM Lec1Document47 pagesNLM Lec1mohammadhamidakhlaqueNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium and Rotational DynamicsDocument8 pagesEquilibrium and Rotational DynamicsJohannesNo ratings yet
- 9,10 Physics FormulaDocument14 pages9,10 Physics Formulakhubsorart dunyaNo ratings yet
- CBSE-XI Physics - Chap-4 (Laws of Motion)Document14 pagesCBSE-XI Physics - Chap-4 (Laws of Motion)Shubhrojyoti MitraNo ratings yet
- Tensile PropertiesDocument42 pagesTensile Propertiesbdemperor1508No ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Buoyancy and StabilityDocument21 pagesLecture 3 Buoyancy and StabilityKokoy Mae Straw100% (1)
- Motion in One DimensionDocument17 pagesMotion in One DimensionSrikant SubramanianNo ratings yet
- Open Channel FlowDocument170 pagesOpen Channel FlowVishwajeet kashyapNo ratings yet
- Summer-2016 WJECDocument96 pagesSummer-2016 WJECDean MillarNo ratings yet
- WJEC Summer-2012Document71 pagesWJEC Summer-2012Dean MillarNo ratings yet
- WJEC Summer-2011Document74 pagesWJEC Summer-2011Dean MillarNo ratings yet
- Differentiation 2022-02-07 10 - 49 - 14Document12 pagesDifferentiation 2022-02-07 10 - 49 - 14Dean MillarNo ratings yet
- Definite IntegrationDocument10 pagesDefinite IntegrationDean MillarNo ratings yet
- Znotes CAIE A2 Level Further Maths Further MechanicsDocument15 pagesZnotes CAIE A2 Level Further Maths Further MechanicsfsffsffdsgfsdNo ratings yet
- Circular Motion & Centripetal Force: StarterDocument12 pagesCircular Motion & Centripetal Force: StarterJhezreel MontefalcoNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Conceptual Questions: Chapter 3 Kinematics in Two or Three Dimensions VectorsDocument18 pages3.1 Conceptual Questions: Chapter 3 Kinematics in Two or Three Dimensions VectorsnourNo ratings yet
- Srisailam Boillaert MasonDocument8 pagesSrisailam Boillaert MasonzuenboNo ratings yet
- Jacketed PipingDocument3 pagesJacketed PipingHmd MokhtariNo ratings yet
- Curriculum-Mapping PHYSICS 9Document8 pagesCurriculum-Mapping PHYSICS 9kristinebarredoNo ratings yet
- Science 7 Q3 Periodic Exam Blooms Taxo With Answer KeyDocument8 pagesScience 7 Q3 Periodic Exam Blooms Taxo With Answer KeyPantz Revibes PastorNo ratings yet
- Clutches & BrakesDocument19 pagesClutches & BrakesterratempestNo ratings yet
- Lab Report LinearMotionDocument7 pagesLab Report LinearMotionAshley StraubNo ratings yet
- Tigist CFD Lab ReportDocument23 pagesTigist CFD Lab Reportdaniel hambissaNo ratings yet
- 6RB7-1200X550-Pin Support PDFDocument8 pages6RB7-1200X550-Pin Support PDFOmer HayatNo ratings yet
- MCG4308 Lec4Document25 pagesMCG4308 Lec4Christian PaultreNo ratings yet
- Presstresed Concrete Assignment-01Document12 pagesPresstresed Concrete Assignment-01Natinael WoldeNo ratings yet
- 7.turbulent Pipe Flow - Set 2Document5 pages7.turbulent Pipe Flow - Set 2ahm531No ratings yet
- Anchor Bolt and Shear Key DesignDocument3 pagesAnchor Bolt and Shear Key DesignsvgkraoNo ratings yet
- 6.thermo TD Relations Objective by RajputDocument3 pages6.thermo TD Relations Objective by RajputMuruganantham MajesticNo ratings yet
- Advanced Finite Element Analysis Prof. R. Krishnakumar Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, MadrasDocument22 pagesAdvanced Finite Element Analysis Prof. R. Krishnakumar Department of Mechanical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, MadrasdurgaraokamireddyNo ratings yet
- Study of The Performance Envelope of A Variable Sweep Wing PDFDocument118 pagesStudy of The Performance Envelope of A Variable Sweep Wing PDFPavan KumarNo ratings yet
- StressDocument13 pagesStressLenielle AmatosaNo ratings yet
- Fracture Strength and Fatigue of Polysilicon Determined by A Novel Thermal ActuatorDocument7 pagesFracture Strength and Fatigue of Polysilicon Determined by A Novel Thermal ActuatorIhsanNo ratings yet
- 1997 Book DynamicsForEngineersDocument918 pages1997 Book DynamicsForEngineersRicardo Teixeira100% (3)
- Mid Term Examination Solved MCQS BY Mehran Ali Shah PHY101-Physics Mostly From MID TERMDocument14 pagesMid Term Examination Solved MCQS BY Mehran Ali Shah PHY101-Physics Mostly From MID TERMMulazimNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document8 pagesUnit 1harinathNo ratings yet
- Dynamics Lab: Department of Production EngineeringDocument13 pagesDynamics Lab: Department of Production EngineeringAditi RayNo ratings yet
- 2nd Quarter Summative Test in Physics 1Document2 pages2nd Quarter Summative Test in Physics 1Eoine Kyle BayubayNo ratings yet
- Physics Paper 1 Grade 11 Exemplar Paper 2007Document13 pagesPhysics Paper 1 Grade 11 Exemplar Paper 2007Teshar WhyAwire SolankiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Electrostatic Field TheoryDocument11 pagesChapter 4 Electrostatic Field TheoryTynoh MusukuNo ratings yet
- Ultimate Bearing Capacity of Foundation On Clays - MeyerhofDocument3 pagesUltimate Bearing Capacity of Foundation On Clays - Meyerhofsreekx0073916100% (1)
- Slab Analysis of Ring Rolling AssumingConstantShearFrictionDocument7 pagesSlab Analysis of Ring Rolling AssumingConstantShearFrictionMatteo Dalla Vecchia100% (1)