Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 viewsMiñano - (OS 204) PN 6 - Pharynx and Larynx
Miñano - (OS 204) PN 6 - Pharynx and Larynx
Uploaded by
Marion Rodelle MiñanoThe document summarizes the anatomy and functions of the pharynx and larynx. It describes their divisions, boundaries, blood supply, lymphatic drainage, and roles in swallowing, phonation, and speech. Key structures are defined, including the tonsils, adenoid, uvula, vocal folds, and cartilages of the larynx like the thyroid, cricoid, and hyoid bones. Muscles that control the pharyngeal walls and larynx are also mentioned.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Anatomy and Physiology of The AirwayDocument42 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Airwayiaa100% (1)
- Miñano - (OS 204) PN 6 - Pharynx and LarynxDocument2 pagesMiñano - (OS 204) PN 6 - Pharynx and LarynxMarion Rodelle MiñanoNo ratings yet
- The Oral Cavity: Prepared By: Katrina Zarina G. Roslin, D.M.DDocument14 pagesThe Oral Cavity: Prepared By: Katrina Zarina G. Roslin, D.M.DJp MUSICNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument6 pagesRespiratory SystemJed Kachel BugayongNo ratings yet
- Mouth Tongue and Salivary GlandsDocument52 pagesMouth Tongue and Salivary GlandsIrfan FalahNo ratings yet
- Oral CavityDocument48 pagesOral Cavityaysoncolline24No ratings yet
- The Oral CavityDocument55 pagesThe Oral CavityMeren NagaNo ratings yet
- The Human Respiratory SystemDocument83 pagesThe Human Respiratory SystemLia lylNo ratings yet
- Respiratory 5Document82 pagesRespiratory 5deoneprofNo ratings yet
- Oral CavityDocument105 pagesOral CavityAisha AbbasNo ratings yet
- Oral Cavity (Mouth Cavity) : Dr. Aymen Ahmed Warille DR Moahip MohamedDocument57 pagesOral Cavity (Mouth Cavity) : Dr. Aymen Ahmed Warille DR Moahip MohamedNada MohammedNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument93 pagesRespiratory SystemGritchen SilatNo ratings yet
- Miñano - (OS 204) PN 5 - Oral Cavity and PalateDocument2 pagesMiñano - (OS 204) PN 5 - Oral Cavity and PalateMarion Rodelle MiñanoNo ratings yet
- ThroatDocument100 pagesThroatChekole AdaneNo ratings yet
- Gi BNSDocument117 pagesGi BNSBibika MallaNo ratings yet
- Upper Respiratory Tract AnatomyDocument36 pagesUpper Respiratory Tract AnatomyNatalie HuiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Respiratory SystemDocument70 pagesChapter 6 Respiratory SystemWenzy Razzie cruzNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument89 pagesRespiratory SystemSuzuke Mae Nijo100% (1)
- RESPIRATORY (1)Document92 pagesRESPIRATORY (1)Mary Grace MacawileNo ratings yet
- Clinical Anatomy of ORAL CAVITY-2016 PDFDocument29 pagesClinical Anatomy of ORAL CAVITY-2016 PDFshagufta lailaNo ratings yet
- Prof. Hamiadji - Ear, Nose, Throat PDFDocument28 pagesProf. Hamiadji - Ear, Nose, Throat PDFSANDA NABILAH FATINNo ratings yet
- Upper Nasal Cavity and Chest WallDocument18 pagesUpper Nasal Cavity and Chest WallHessa AlamiraNo ratings yet
- 12 Respiratory System - ATFDocument43 pages12 Respiratory System - ATFLucas BarbosaNo ratings yet
- Pharynx: Upper Part: Widest - 3.5 CM, Non-Collapsible Middle Part: Narrow Lower End: Narrowest Part of GITDocument5 pagesPharynx: Upper Part: Widest - 3.5 CM, Non-Collapsible Middle Part: Narrow Lower End: Narrowest Part of GITdrpnnreddyNo ratings yet
- Digestion and Absorption by DR Yogesh Swami Nur 1Document45 pagesDigestion and Absorption by DR Yogesh Swami Nur 1chiragm1408No ratings yet
- Respiratory Notes (Tortora)Document3 pagesRespiratory Notes (Tortora)Eli MinchaiNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory System: SubtitleDocument89 pagesThe Respiratory System: SubtitleAaaNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory SystemDocument7 pagesThe Respiratory SystemVernice LopezNo ratings yet
- Oral Cavity and PharynxDocument6 pagesOral Cavity and PharynxStepyn SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Anatomi Dan Fisiologi Mulut Bp2Document47 pagesAnatomi Dan Fisiologi Mulut Bp2Aditya FirmansyahNo ratings yet
- Special Senses - Oral Cavity Etc.Document18 pagesSpecial Senses - Oral Cavity Etc.Dunkin DonutNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System With HighlightsDocument90 pagesRespiratory System With HighlightsReinand Joseff ServanoNo ratings yet
- Miñano - (OS 204) PN 2 - Skull and MandibleDocument2 pagesMiñano - (OS 204) PN 2 - Skull and MandibleMarion Rodelle MiñanoNo ratings yet
- The MouthDocument23 pagesThe MouthgcamaymayanNo ratings yet
- General AnatomyDocument30 pagesGeneral Anatomyassilshelig5No ratings yet
- 14 Anatomy of Larynx and PharynxDocument69 pages14 Anatomy of Larynx and PharynxsandyNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Tongue and Its Applied Aspects: Presented By: Niti SarawgiDocument77 pagesAnatomy of Tongue and Its Applied Aspects: Presented By: Niti SarawgideepNo ratings yet
- The Digestive System: Andi AnsharullahDocument37 pagesThe Digestive System: Andi AnsharullahAnonymous vUl83IptiSNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6-ADocument31 pagesLecture 6-AJayNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 Respiratory SystemDocument3 pagesChapter 15 Respiratory SystemRayumaaa100% (1)
- 16 The Mouth (Done)Document9 pages16 The Mouth (Done)osamaeNo ratings yet
- B-M of Human Teeth - 1Document10 pagesB-M of Human Teeth - 1Magd NabilNo ratings yet
- Pharynx IiDocument21 pagesPharynx IiHompreetha RajamanickamNo ratings yet
- Digestive System PearsonDocument179 pagesDigestive System PearsonJan Jesty CaiquetNo ratings yet
- SGD 5 Head & NeckDocument18 pagesSGD 5 Head & NeckFarena LazimNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory System ReviewerDocument6 pagesThe Respiratory System ReviewerJP LozadaNo ratings yet
- Pharynx: Dr. U OfforDocument29 pagesPharynx: Dr. U OfforugochukwuNo ratings yet
- Oral CavityDocument57 pagesOral CavityArif NabeelNo ratings yet
- Anaphy 12Document8 pagesAnaphy 12fio.maglaya13No ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Throat DR Oscar PresentasiDocument53 pagesAnatomy of The Throat DR Oscar Presentasiharyo wiryantoNo ratings yet
- A.S.a Chapter 12 - The Respiratory SystemDocument8 pagesA.S.a Chapter 12 - The Respiratory Systemkoshiaiko21No ratings yet
- Tongue AnatomyDocument3 pagesTongue Anatomykaruparthi sripravallikaNo ratings yet
- Sistem Respirasi Stikes WN PDFDocument107 pagesSistem Respirasi Stikes WN PDFEkafatikasariNo ratings yet
- Digestion Absorption MetabolismDocument12 pagesDigestion Absorption MetabolismEunice Villa CuñadaNo ratings yet
- PHARYNXDocument75 pagesPHARYNXDr. Janarthanan VNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument8 pagesRespiratory SystemHenry BuñagNo ratings yet
- HAP RespiratoryDocument4 pagesHAP Respiratorysmzw4r78sqNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory SystemDocument4 pagesThe Respiratory SysteminitaygracileshayneNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Pharynx: Keerthi Ns 2010 BATCHDocument21 pagesAnatomy of Pharynx: Keerthi Ns 2010 BATCHAdam NoheNo ratings yet
- Miñano - (OS 204) PN 1 - Anatomy of FaceDocument2 pagesMiñano - (OS 204) PN 1 - Anatomy of FaceMarion Rodelle MiñanoNo ratings yet
- Miñano - (OS 204) PN 2 - Skull and MandibleDocument2 pagesMiñano - (OS 204) PN 2 - Skull and MandibleMarion Rodelle MiñanoNo ratings yet
- Miñano - (OS 204) PN 5 - Oral Cavity and PalateDocument2 pagesMiñano - (OS 204) PN 5 - Oral Cavity and PalateMarion Rodelle MiñanoNo ratings yet
- Miñano - (OS 204) PN 4 - Parotid GlandDocument2 pagesMiñano - (OS 204) PN 4 - Parotid GlandMarion Rodelle MiñanoNo ratings yet
- Miñano - (OS 204) PN 3 - EarDocument3 pagesMiñano - (OS 204) PN 3 - EarMarion Rodelle MiñanoNo ratings yet
- Miñano - (OS 204) PN 3 - EarDocument2 pagesMiñano - (OS 204) PN 3 - EarMarion Rodelle MiñanoNo ratings yet
- Miñano - (OS 204) PN 2 - Skull and MandibleDocument2 pagesMiñano - (OS 204) PN 2 - Skull and MandibleMarion Rodelle MiñanoNo ratings yet
- Miñano - (OS 204) PN 1 - Anatomy of FaceDocument2 pagesMiñano - (OS 204) PN 1 - Anatomy of FaceMarion Rodelle MiñanoNo ratings yet
- Miñano - (OS 204) PN 6 - Pharynx and LarynxDocument2 pagesMiñano - (OS 204) PN 6 - Pharynx and LarynxMarion Rodelle MiñanoNo ratings yet
- Miñano - (OS 204) PN 5 - Oral Cavity and PalateDocument2 pagesMiñano - (OS 204) PN 5 - Oral Cavity and PalateMarion Rodelle MiñanoNo ratings yet
- Applying The Chronic Care Model in Low-Resource Settings Ada Dec2013Document44 pagesApplying The Chronic Care Model in Low-Resource Settings Ada Dec2013Wawan JokoNo ratings yet
- Waste Management Technologies in Japanese Cement Industry - From Manufacturing To EcofactuaringDocument6 pagesWaste Management Technologies in Japanese Cement Industry - From Manufacturing To EcofactuaringRati YuliarningsihNo ratings yet
- Climate and Consumption Pattern - Demand and Supply of Water District ConcessionairesDocument3 pagesClimate and Consumption Pattern - Demand and Supply of Water District ConcessionairesIJAERS JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Disguised UnemploymentDocument14 pagesDisguised UnemploymentAbhishek KumarNo ratings yet
- Al-Fasi Et Al.2015 PDFDocument8 pagesAl-Fasi Et Al.2015 PDFUmroh NuryantoNo ratings yet
- Erik Erikson: - Trust vs. MistrustDocument6 pagesErik Erikson: - Trust vs. MistrustWidya FitrianingrumNo ratings yet
- De Jong 2013 ACS Catalysis Catalysts For Production of Lower Olefins From Synthesis Gas - A Review PDFDocument20 pagesDe Jong 2013 ACS Catalysis Catalysts For Production of Lower Olefins From Synthesis Gas - A Review PDFSohail FarooqNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Chemistry 9701/33 March 2019Document7 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Chemistry 9701/33 March 2019Trang NguyenNo ratings yet
- Demolition Instructions With Heavy Duty Construction MachineryDocument2 pagesDemolition Instructions With Heavy Duty Construction Machinerymiraç burak navruzNo ratings yet
- The One Minute ManagerDocument20 pagesThe One Minute ManagerYashwant J100% (2)
- Gala MayDocument7 pagesGala MayRobert Ross DulayNo ratings yet
- Man#251 Rev BDocument10 pagesMan#251 Rev Bjuan dalmassoNo ratings yet
- NACE 2003 Cust Seminar 2006Document21 pagesNACE 2003 Cust Seminar 2006me.mantilla4148No ratings yet
- Anaesthesia Workstation 4Document120 pagesAnaesthesia Workstation 4john georgeNo ratings yet
- Take Home Quiz COVID 2020Document18 pagesTake Home Quiz COVID 2020Jamie RuzickaNo ratings yet
- HEALTH 9 QUARTER2 MODULE3 WeeK5-6Document9 pagesHEALTH 9 QUARTER2 MODULE3 WeeK5-6Heidee Basas100% (3)
- Cafe 77 Menu Sept NewDocument2 pagesCafe 77 Menu Sept NewAhmed SaklanNo ratings yet
- Singer BangladeshDocument16 pagesSinger BangladeshMahbubur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Health Problems Illnesses Sickness Ailments Injuries Pictionary Poster Vocabulary WorksheetDocument2 pagesHealth Problems Illnesses Sickness Ailments Injuries Pictionary Poster Vocabulary WorksheetTania Lopez100% (1)
- Common Pediatric Fractures Common Pediatric FracturesDocument67 pagesCommon Pediatric Fractures Common Pediatric FracturesJeane SuyantoNo ratings yet
- Case Study Format - PGTCNDocument2 pagesCase Study Format - PGTCNFitz JaminitNo ratings yet
- Especificaciones de Valvulas Normas APIDocument2 pagesEspecificaciones de Valvulas Normas APIÀngel Rodriguez0% (1)
- Respiratory FailureDocument29 pagesRespiratory Failureageng rusbaya0% (1)
- Polymer Materials From Recycled Plastic in Road ConstructionDocument7 pagesPolymer Materials From Recycled Plastic in Road ConstructionYuv RajNo ratings yet
- 3 - Cardiovascular System PDFDocument54 pages3 - Cardiovascular System PDFMSKCNo ratings yet
- Bengkel Biologi SmartGDocument6 pagesBengkel Biologi SmartGK XuanNo ratings yet
- 319 6904116 Om 10 05 PDFDocument136 pages319 6904116 Om 10 05 PDFvatasaNo ratings yet
- Vessel Design (External Loads) 2 PDFDocument50 pagesVessel Design (External Loads) 2 PDFEzekielNo ratings yet
- Concept Questions From Marine BiologyDocument2 pagesConcept Questions From Marine BiologyJameeNo ratings yet
- 6 Sulangan Farm and Farmers ProfileDocument37 pages6 Sulangan Farm and Farmers ProfilePhen MontalboNo ratings yet
Miñano - (OS 204) PN 6 - Pharynx and Larynx
Miñano - (OS 204) PN 6 - Pharynx and Larynx
Uploaded by
Marion Rodelle Miñano0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views2 pagesThe document summarizes the anatomy and functions of the pharynx and larynx. It describes their divisions, boundaries, blood supply, lymphatic drainage, and roles in swallowing, phonation, and speech. Key structures are defined, including the tonsils, adenoid, uvula, vocal folds, and cartilages of the larynx like the thyroid, cricoid, and hyoid bones. Muscles that control the pharyngeal walls and larynx are also mentioned.
Original Description:
Original Title
Miñano_[OS 204] PN 6 - Pharynx and Larynx
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document summarizes the anatomy and functions of the pharynx and larynx. It describes their divisions, boundaries, blood supply, lymphatic drainage, and roles in swallowing, phonation, and speech. Key structures are defined, including the tonsils, adenoid, uvula, vocal folds, and cartilages of the larynx like the thyroid, cricoid, and hyoid bones. Muscles that control the pharyngeal walls and larynx are also mentioned.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views2 pagesMiñano - (OS 204) PN 6 - Pharynx and Larynx
Miñano - (OS 204) PN 6 - Pharynx and Larynx
Uploaded by
Marion Rodelle MiñanoThe document summarizes the anatomy and functions of the pharynx and larynx. It describes their divisions, boundaries, blood supply, lymphatic drainage, and roles in swallowing, phonation, and speech. Key structures are defined, including the tonsils, adenoid, uvula, vocal folds, and cartilages of the larynx like the thyroid, cricoid, and hyoid bones. Muscles that control the pharyngeal walls and larynx are also mentioned.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
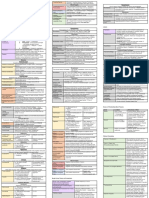
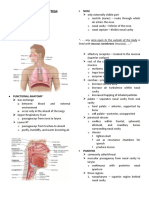
Marion Miñano OS 204 Portfolio Note 6 Pharynx & Larynx Tonsillar Nerves Derived fr/ tonsillar plexus of nerves;
nsillar plexus of nerves; Formed fr/
branches of glossopharyngeal and vagus nerves
Divisions of Pharynx and Larynx Blood Supply Hypopharynx
Tonsillar Branch of Sup pharyngeal constrictor muscle → Inf pole of Pos to larynx; Pharynx divides into larynx and esophagus
Division General Function Location Facial Artery palatine tonsil; Arterial twigs from Asc palatine A, Boundaries Pos – Bodies of C4-C6; Pos and Lat – Middle and inf
Nasopharynx Respiratory; Pos extension of nasal Lingual A, Desc palatine A, Ascending pharyngeal A pharyngeal constrictors; Internal – Palatophrayngeus &
Sometimes has nasal cavities; Level of External Palatine Soft palate → Lat surface of tonsil → Pharyngeal Stylopharyngeus
discharge sphenoid bone →soft Vein venous plexus → Int jug V Structures
palate Tonsillar Lymphatic Pass lat and inf to lymph nodes (near angle of Laryngeal Inlet Anterior wall; Enables comm bet laryngopharynx and
Oropharynx Digestive; Food and air Soft palate, base of Vessels mandible and jugulodigastric node) larynx
pass thru epiglottis, pos to Jugulodigastric/ Tonsilitis Piriform Fossa Depression of laryngopharyngeal cavity on either side of
tongue; Ant – Pos Tonsillar node laryngeal inlet; Lat bounded by med surfaces of thyroid
tongue; Pos – Pharyngeal Formed by palatine, lingual and pharyngeal tonsils; cartilage and thyrohyoid membrane
Pharyngeal mucosa Lymphatic Ring AI – lingual tonsil in pos part of tongue; Lat – Aryepiglottic Separates pisiform fossa fr/ laryngeal inlet
Larynx Breathing; Protection; Epiglottis → palatine and tubal tonsils; Pos and sup – Fold
Voice production Cricoid/subglottic pharyngeal tonsil
region; Housed in bony
cartilage Larynx
Hypopharynx Guides food into Behind and lat to Nasopharynx
esophagus larynx Passageway for air only; Pos – nose; Sup – soft palate Functions Located in anterior neck; Connects oropharynx w/
Boundaries Sup – soft palate; Inf – Base of tongue, Lat - trachea; Guards air passages to maintain airway;
Palatoglossal and palatopharyngeal arches Complex organ of voice production
Pharynx Structures Subdivisions Supraglottic (Area below tongue based above true
Adenoids Enlarged tonsil in mucus membrane of roof and pos vocal folds) - Epiglottis, Arytenoid, Aryepiglottic fold,
Functions wall of nasopharynx; Role in immunology in children; Vestibular fold
Swallowing Hyoid bone goes up → Larynx closes (epiglottis Usually absent in adults but present in cases of Glottic (Gap bet vocal folds) – Ventricle, Vocal fold,
covers inlet) → Hypophraynx → Cervical esophagus inflammation Ant and pos commissure
Phases of 1. Oral – mouth → oropharynx Eustachian Tubes Floor of nose coincides lat w/ Esutachian tube; Joins Subglottic (Below vocal fold until lower border of
Swallowing 2. Pharyngeal – food pushed by tongue middle ear to nasopharynx; Drainage and ventilation cricoid cartilage) – beyond is trachea
→soft palate elevated (closes of middle ear Laryngeal Skeleton
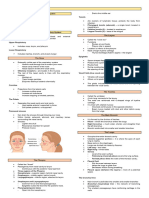
nasopharynx) → Pharynx → Larynx Nasopharyngeal Highly variable amount of lymphoid tissue Hyoid Bone U-shaped; Does not articulate w/ any other; Suspends
elevated Mucosa and anchors larynx; 3 unpaired: TEC, 3 paired:
3. Esophageal – Pushed to esophagus Nasal Choanae Paired opening bet nasal cavity and nasopharynx ArCoCu
Phonation Vocal cords apposed together → Vibration → Pharyngeal Tonsils “Adenoids” when enlarged; Mucus membrane of roof Unpaired/Single Cartilages
Sound; Requires power fr/ lungs, larynx as vibrator and pos wall of nasopharynx Thyroid Cartilage Largest; w/ sup and inf horns; Sup part lies opp C4
and a resonator (nose and nasal cavity) Salpingopharyngea Vertical; Covers salpinopharyngeal muscles; Lat wall vertebrae and attached to hyoid by thyrohyoid
Speech Entails respiration, phonation and articulation; l Fold of nasopharynx, inf to pharyngotympanic tube membrane
Consonants – tongue and palate; Vowels – vocal Uvula Middle of nasopharyngeal floor; Mallampati score Thyroid Membrane Made of CT; Thinner lat sides pierced by int laryngeal
cords w/ some resonance in nasal and oral cavity; (ease of intubation) – predicted using uvula size nerve and A; Drains into supraglottic; Ligaments –
Requires coordination and muscle control median thyrohyoid (thick), lateral thyrohyoid
Tubal Tonsil Collection of lymphoid tissue; Near nasopharyngeal
Muscles opening of pharyngotympanic tube Cricothyroid Joints Inferior horns of thyroid cart + Lat surface of cricoid
External Layer Pharyngeal Recess Slit-like proj located pos to torus of pharyngotympanic cartilage; Rotation and gliding = allows changes in
Constrict pharyngeal walls; Horizontal tube and salpingophrayngeal fold length of vocal fold
Superior Constrictors Pharyngeal branch of vagus (CN X); Pharyngeal Cricoid Cartilage Signet ring; Only compete ring to encircle airway;
plexus Thicker and stronger than thyroid; Attaches to cricoid
Middle Constrictors Pharyngeal branch of vagus (CN X); Pharyngeal ligament (median cricothyroid ligament), 1st tracheal
Oropharynx
plexus; Branches of external recurrent laryngeal ring (cricotracheal ligament)
Pos to oral cavity; Soft palate → Sup border of epiglottis; Comm w/ mouth via
nerve of vagus Epiglottic Cartilage Thin, leaf like; Only elastic cartilage; Flexibility to
OP isthmus
Inferior Constrictors Pharyngeal branch of vagus (CN X); Pharyngeal epiglottis; Ant – laryngeal inlet; Pos – root of tongue
Boundaries Ant – Pos 1/3 of tongue, Base of epiglottis, Border of
plexus; Branches of external recurrent laryngeal and hyoid; Attaches to thyroid laminae (thyro-epiglottic
head and soft palate; Pos – Pos pharyngeal wall; Lat –
nerve of vagus ligament), w/ hypo-epicglottic ligament
Ant and pos tonsillar pillars; Sup – Soft palate; Inf – Sup
Internal Layer border of epiglottis Paired Cartilages
Suspend hyoid; Elevates pharynx and larynx; Vertical Arytenoid Paired, 3-sided pyramidal; Joins w/ lat parts of sup
Structures
Palatopharyngeus Pharyngeal branch of vagus nerve (CN X); Cartilages border of cricoid cartilage; On top of cricoid cartilage;
Soft palate Elevated pos and sup against pharyngeal wall; Prevent
Pharyngeal plexus Opened – muscles at back proj down; Closed –
passage of food into nasal cavity
Salpingopharyngeus Pharyngeal branch of vagus nerve (CN X); muscles at side and front
Anterior and Palatoglossal – ant pillar; Palatopharyngeal – pos pillar
Pharyngeal plexus Apex Bears corniculate cartilage; Attaches to aryepiglottic
Posterior
Stylopharyngeus Glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX) Tonsillar Pillars fold
Innervation Palatine Tonsils Masses of lymph tissue on each side of oropharynx; Loc Vocal Process Provides pos attachment for vocal ligament
Pharyngeal plexus of Pharyngeal branches of vagus and in tonsillar fossa bet ant and pos tonsillar pillars Muscular Process Lever for pos and lat cricoarytenoid muscles
nerves glossopharyngeal nerves, sympathetic branches fr/ Lingual Tonsils Masses of lymph tissue at base of tongue Cricoarytenoid Located bet bases of arytenoid cartilages and
superior cervical ganglion; Motor – fr/ vagus nerve Joint superolateral surf of lamina of cricoid cartilages;
Base of Tongue
(CN X); Sensory – fr/ glossopharyngeal nerve (CN Permits movement of arytenoid cartilages
IX) Posterior Deep layer of pharyngeal constrictors – Inf pharyngeal Corniculate Located pos of aryepiglottic fold, on top of arytenoid
Glossopharyngeal Innervates Pos tongue for taste and pain, Portions Pharyngeal Wall constrictors – level of larynx and nasophraynx Cartilages tower; Attaches to apices of arytenoid cartilage
Nerve (CN IX) of oropharynx Vallecula Fossa vet epiglottis and base of tongue Cuneiform Located bet epiglottis and arytenoid; Act as spacer;
Vagus Nerve (CN X) Innervates all Muscles of pharynx and soft palate, Waldeyer’s Collection of lymph tissue that form ringed arrangement; Cartilages Does not directly attach; Not always present
except stylopharyngeus and tensor veli palatini Tonsillar Ring Composed of Adenoid, Palatine tonsil, Lingual tonsil, Vocal Folds Control sound prod; Contains Vocal ligament and
Maxillary Nerve (CN Innervates Mucus membrane of anterior, Superior Tubal tonsils, Lateral pharyngeal bands; 1 st line of Vocalis muscle; Sharped edged folds
V2) nasopharynx defense vs. microorganisms Vocal Ligaments Junction of laminae of thyroid cartilage → Vocal
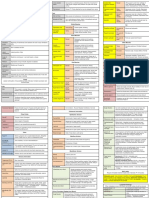
processes of arytenoid cartilage; Conus elasticus mandible Branch of inferior Zones of Penetrating Neck Trauma
encloses tracheal inlet except for rima glottidis I - Mylohyoid raphe and body alveolar nerve
Lateral Extension of conus elasticus bet vocal folds and sup of hyoid Zone Location Structures at Risk
Cricothyroid border of cricoid Geniohyoid O – Inferior mental spine of C1 via hypoglossal Zone 1 Root of neck; Cervical pleura; Apices of lungs;
Ligament mandible Clavicles/manubriu Thyroid & parathyroid glands;
Glottis Vocal apparatus; Makes up vocal folds and process w/ I – Body of hyoid m → Inf border of Trachea; Esophagus; Common
rima glottis Stylohyoid O – Styloid process of Stylohyoid branch of cricoid cartilage carotid arteries; Jugular veins;
Intrinsic Muscles temporal bone facial nerve Cervical region of vertebral
Focal point: Arytenoid cartilages (Rotate, adduct, abduct and move ant/pos I - Body of hyoid column
on sloping shoulder of cricoid cartilage) Digastric O – (Ant) Digastric fossa of Ant – Nerve to Zone 2 Cricoid cartilage → Superior poles of thyroid gland;
Innervations External Laryngeal Nerve – Cricothyroid; Internal mandible; (Pos) Mastoid mylohyoid, Branch of Angle of mandible Thyroid and cricoid cartilages;
Laryngeal Nerve – Everything else notch of temp bone inf alveolar nerve; Larynx; Laryngopharynx; Carotid
Laryngeal Inlet Opened – Thyroepiglottis; Closed – Aryepiglottis I – Intermediate tendon to Pos – Digastric arteries; Jugular veins;
Rima Glottidis Dialted – Posterior cricoarytenoid; Assisted – Lateral body and greater horn of (preparotid) branch of Esophagus; Cervical region of
cricoarytenoid; Closed – Inter-arytenoid hyoid facial nerve vertebral column
Vocal Cords Altered and tensed by vocalis; Lengthened – Innervation Zone 3 Angles of mandible Salivary glands; Oral and nasal
Cricothyroid; Shortened - Thyroarytenoid Superior Laryngeal Arises fr/ inferior vagal ganglion at superior end of superiorly cavities; Oropharynx;
Adductors Nerve carotid triangle Nasopharynx
Lateral Crico- O – Arch of cricoid cartilage Adducts vocal folds Internal Laryngeal Sensory; Larger; Pierces thyrohyoid membrane w/
arythenoid I – Vocal process of Nerve superior laryngeal A
arytenoid External Laryngeal Motor to cricothyroid; Smaller; Accompanies laryngeal Clinical Correlates
Transverse and O – 1 arytenoid cartilage Adducts arytenoid Nerve branch of inf thyroid artery; Descends pos to
Oblique Arytenoids I – Contralateral arytenoid cartilage sternothyroid muscle in company of sup thyroid A Cancer of Oropharynx May manifest as ear pain; Ear is
Abductors Recurrent Terminates as inferior laryngeal nerve; Sensory – innervated by trigeminal nerve (CN
Posterior Crico- O – Pos surface of lamina of Abducts vocal fold Laryngeal Nerve mucus membrane below vocal cords; Motor – all V)
arytenoid cricoid cartilage intrinsic muscles of larynx, except for cricothyroid and Injury to Vagus and Dysfunction in swallowing and voice;
I – Muscular process of part of arytenoid muscles; R loops around R subclav A Glossopharyngeal Nerves If patient can swallow but has hoarse
arytenoid cartilage Inferior Laryngeal Primary motor nerve; Enters larynx by passing deep to voice, lesion may be in more distal
Sphincters Nerve inf border of inf pharyngeal constrictor and med to branch of vagus nerve
Closes laryngeal inlet (protective); Brings aryepiglottic folds together and pulls lamina of thyroid cartilage Injury to Recurrent Laryngeal Nerves Risk during neck surgery; Right – Inf
arytenoid cartilage towards epiglottis (strongest reflex) Anterior branch of Innervates lat crico-arytenoid, thryo-arytenoid, vocalis, thyroid A and branches; Hoarseness
Aryepiglottic O – Arytenoid cartilage Recurrent laryngeal Inf Laryngeal aryepiglottic and thyro-epiglottic of voice – sign of unilateral injury;
I - Epiglottis nerve; Closes Nerve Temporary disturbance in voice and
vestibule of larynx Posterior branch of Innervates pos crico-arytenoid, transverse and oblique laryngeal spasm may also occur
during swallow Inf Laryngeal arytenoid Injury to Laryngeal Nerve Paralysis of vocal folds = unable to
Tensors Nerve adduct to meet normal vocal fold →
Pitch of voice is raised; Pulls thyroid cartilage toward arch of cricoid cartilage Blood Supply poor voice
Cricothyroid O – AL part of cricoid Ext laryngeal nerve; Superior Laryngeal Supplies internal surface of larynx Dysplasia of Vocal Fold Transformation from respiratory
cartilage Stretches and tenses Artery epithelium to squamous due to
I – Inf margin and inf horn of vocal ligament Cricothyroid Artery Supplies cricothyroid muscle smoking or acid reflux; Uncontrolled
thyroid cartilage Inferior Laryngeal Supplies mucus membrane and inferior muscles mitosis
Relaxers Artery Fractures of Laryngeal Skeleton Result from blows received in sports
Lower pitch of voice; Pulls arytenoid cartilages toward thyroid angle Superior Laryngeal Joins superior thyroid vein Drains to internal or compression by shoulder strap
Thyro-artenoid O – Lower hald of pos aspect Relaxes vocal Vein jugular vein during accident; Produce
of angle of thyroid laminae ligament Inferior Laryngeal Joins inferior thyroid vein Drains to left submucous hemorrhage and edema,
and cricothyroid ligament Vein brachiocephalic vein respiratory obstruction, hoarseness
I – AL arytenoid surface and sometimes temporary inability to
Vocalis O – Lat surface of vocal Relaxes pos vocal speak
process of arytenoid cartilage ligament while Body Cover Theory of Production Cricothyrotomy Extreme emergencies; Insert large
I – Ipsilateral vocal ligament maintain tension in bore needle thru cricothyroid
anterior part Body cover composition of deep Dictate frequency of voice ligament to permit fast entry of air;
Extrinsic Muscles Faster than tracheostomy and
layer of lamina propria/vocal
Infrahyoid ligament and vocalis muscle cervical spine manipulation is usually
Depresses hyoid and larynx unnecessary
Superficial layer of lamina propria Dictate character of voice
Sternohyoid O – Manubrium and medial C1-C3 and epithelium Tracheostomy Upper airway obstruction/ respiratory
end of clavicle failure; Opening made in trachea bet
Voice can be produced w/out moving Because of Bernoulli effect – air
I – Body of hyoid 1st and 2nd tracheal rings; Inferior
arytenoids passing thru lumen → cause larynx
thyroid veins, Thyroid ima artery,
Omohyoid O – Manubrium and medial C1-C3 to close
Left brachiocephalic vein, Jugular
end of clavicle Reinke’s Space Bet vocal ligament and vocalis;
venous arch, Pleurae, Thymus
I - Body of hyoid Where mucosa and lamina propria
Cancer of Larynx Persons who smoke cigarettes;
Sternothyroid O – Pos surface of C2-C3 can glide; Vibrates; Mucosal wave
Enlarged pretracheal or paratracheal
manubrium w/c will result to character of voice
lymph nodes; Laryngectomy and
I – Oblique line of thyroid cart True Vocal Cords (Glottis, Glottic Produce voice; Squamous NK
vocal rehab may be performed
Thyrohyoid O – Oblique line of thyroid C1 via hypoglossal Fold) epithelium; Varying levels of stiffness
Foreign Bodies in Laryngopharynx Sharp food objects may pierce
cart provided by vocal ligament and
mucus membrane of piriform fossae
I - Inf border of body and vocalis
and injure internal laryngeal nerve;
greater horn of hyoid Vocal ligament String-like; Hard CT at edge of true
Numbness of laryngeal mucous
Suprahyoid vocal cord
membrane (as far as vocal folds)
Elevates hyoid and larynx
Mylohyoid O –Mylohyoid line of Nerve to mylohyoid;
You might also like
- Anatomy and Physiology of The AirwayDocument42 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Airwayiaa100% (1)
- Miñano - (OS 204) PN 6 - Pharynx and LarynxDocument2 pagesMiñano - (OS 204) PN 6 - Pharynx and LarynxMarion Rodelle MiñanoNo ratings yet
- The Oral Cavity: Prepared By: Katrina Zarina G. Roslin, D.M.DDocument14 pagesThe Oral Cavity: Prepared By: Katrina Zarina G. Roslin, D.M.DJp MUSICNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument6 pagesRespiratory SystemJed Kachel BugayongNo ratings yet
- Mouth Tongue and Salivary GlandsDocument52 pagesMouth Tongue and Salivary GlandsIrfan FalahNo ratings yet
- Oral CavityDocument48 pagesOral Cavityaysoncolline24No ratings yet
- The Oral CavityDocument55 pagesThe Oral CavityMeren NagaNo ratings yet
- The Human Respiratory SystemDocument83 pagesThe Human Respiratory SystemLia lylNo ratings yet
- Respiratory 5Document82 pagesRespiratory 5deoneprofNo ratings yet
- Oral CavityDocument105 pagesOral CavityAisha AbbasNo ratings yet
- Oral Cavity (Mouth Cavity) : Dr. Aymen Ahmed Warille DR Moahip MohamedDocument57 pagesOral Cavity (Mouth Cavity) : Dr. Aymen Ahmed Warille DR Moahip MohamedNada MohammedNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument93 pagesRespiratory SystemGritchen SilatNo ratings yet
- Miñano - (OS 204) PN 5 - Oral Cavity and PalateDocument2 pagesMiñano - (OS 204) PN 5 - Oral Cavity and PalateMarion Rodelle MiñanoNo ratings yet
- ThroatDocument100 pagesThroatChekole AdaneNo ratings yet
- Gi BNSDocument117 pagesGi BNSBibika MallaNo ratings yet
- Upper Respiratory Tract AnatomyDocument36 pagesUpper Respiratory Tract AnatomyNatalie HuiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Respiratory SystemDocument70 pagesChapter 6 Respiratory SystemWenzy Razzie cruzNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument89 pagesRespiratory SystemSuzuke Mae Nijo100% (1)
- RESPIRATORY (1)Document92 pagesRESPIRATORY (1)Mary Grace MacawileNo ratings yet
- Clinical Anatomy of ORAL CAVITY-2016 PDFDocument29 pagesClinical Anatomy of ORAL CAVITY-2016 PDFshagufta lailaNo ratings yet
- Prof. Hamiadji - Ear, Nose, Throat PDFDocument28 pagesProf. Hamiadji - Ear, Nose, Throat PDFSANDA NABILAH FATINNo ratings yet
- Upper Nasal Cavity and Chest WallDocument18 pagesUpper Nasal Cavity and Chest WallHessa AlamiraNo ratings yet
- 12 Respiratory System - ATFDocument43 pages12 Respiratory System - ATFLucas BarbosaNo ratings yet
- Pharynx: Upper Part: Widest - 3.5 CM, Non-Collapsible Middle Part: Narrow Lower End: Narrowest Part of GITDocument5 pagesPharynx: Upper Part: Widest - 3.5 CM, Non-Collapsible Middle Part: Narrow Lower End: Narrowest Part of GITdrpnnreddyNo ratings yet
- Digestion and Absorption by DR Yogesh Swami Nur 1Document45 pagesDigestion and Absorption by DR Yogesh Swami Nur 1chiragm1408No ratings yet
- Respiratory Notes (Tortora)Document3 pagesRespiratory Notes (Tortora)Eli MinchaiNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory System: SubtitleDocument89 pagesThe Respiratory System: SubtitleAaaNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory SystemDocument7 pagesThe Respiratory SystemVernice LopezNo ratings yet
- Oral Cavity and PharynxDocument6 pagesOral Cavity and PharynxStepyn SalvadorNo ratings yet
- Anatomi Dan Fisiologi Mulut Bp2Document47 pagesAnatomi Dan Fisiologi Mulut Bp2Aditya FirmansyahNo ratings yet
- Special Senses - Oral Cavity Etc.Document18 pagesSpecial Senses - Oral Cavity Etc.Dunkin DonutNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System With HighlightsDocument90 pagesRespiratory System With HighlightsReinand Joseff ServanoNo ratings yet
- Miñano - (OS 204) PN 2 - Skull and MandibleDocument2 pagesMiñano - (OS 204) PN 2 - Skull and MandibleMarion Rodelle MiñanoNo ratings yet
- The MouthDocument23 pagesThe MouthgcamaymayanNo ratings yet
- General AnatomyDocument30 pagesGeneral Anatomyassilshelig5No ratings yet
- 14 Anatomy of Larynx and PharynxDocument69 pages14 Anatomy of Larynx and PharynxsandyNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Tongue and Its Applied Aspects: Presented By: Niti SarawgiDocument77 pagesAnatomy of Tongue and Its Applied Aspects: Presented By: Niti SarawgideepNo ratings yet
- The Digestive System: Andi AnsharullahDocument37 pagesThe Digestive System: Andi AnsharullahAnonymous vUl83IptiSNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6-ADocument31 pagesLecture 6-AJayNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 Respiratory SystemDocument3 pagesChapter 15 Respiratory SystemRayumaaa100% (1)
- 16 The Mouth (Done)Document9 pages16 The Mouth (Done)osamaeNo ratings yet
- B-M of Human Teeth - 1Document10 pagesB-M of Human Teeth - 1Magd NabilNo ratings yet
- Pharynx IiDocument21 pagesPharynx IiHompreetha RajamanickamNo ratings yet
- Digestive System PearsonDocument179 pagesDigestive System PearsonJan Jesty CaiquetNo ratings yet
- SGD 5 Head & NeckDocument18 pagesSGD 5 Head & NeckFarena LazimNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory System ReviewerDocument6 pagesThe Respiratory System ReviewerJP LozadaNo ratings yet
- Pharynx: Dr. U OfforDocument29 pagesPharynx: Dr. U OfforugochukwuNo ratings yet
- Oral CavityDocument57 pagesOral CavityArif NabeelNo ratings yet
- Anaphy 12Document8 pagesAnaphy 12fio.maglaya13No ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Throat DR Oscar PresentasiDocument53 pagesAnatomy of The Throat DR Oscar Presentasiharyo wiryantoNo ratings yet
- A.S.a Chapter 12 - The Respiratory SystemDocument8 pagesA.S.a Chapter 12 - The Respiratory Systemkoshiaiko21No ratings yet
- Tongue AnatomyDocument3 pagesTongue Anatomykaruparthi sripravallikaNo ratings yet
- Sistem Respirasi Stikes WN PDFDocument107 pagesSistem Respirasi Stikes WN PDFEkafatikasariNo ratings yet
- Digestion Absorption MetabolismDocument12 pagesDigestion Absorption MetabolismEunice Villa CuñadaNo ratings yet
- PHARYNXDocument75 pagesPHARYNXDr. Janarthanan VNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument8 pagesRespiratory SystemHenry BuñagNo ratings yet
- HAP RespiratoryDocument4 pagesHAP Respiratorysmzw4r78sqNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory SystemDocument4 pagesThe Respiratory SysteminitaygracileshayneNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Pharynx: Keerthi Ns 2010 BATCHDocument21 pagesAnatomy of Pharynx: Keerthi Ns 2010 BATCHAdam NoheNo ratings yet
- Miñano - (OS 204) PN 1 - Anatomy of FaceDocument2 pagesMiñano - (OS 204) PN 1 - Anatomy of FaceMarion Rodelle MiñanoNo ratings yet
- Miñano - (OS 204) PN 2 - Skull and MandibleDocument2 pagesMiñano - (OS 204) PN 2 - Skull and MandibleMarion Rodelle MiñanoNo ratings yet
- Miñano - (OS 204) PN 5 - Oral Cavity and PalateDocument2 pagesMiñano - (OS 204) PN 5 - Oral Cavity and PalateMarion Rodelle MiñanoNo ratings yet
- Miñano - (OS 204) PN 4 - Parotid GlandDocument2 pagesMiñano - (OS 204) PN 4 - Parotid GlandMarion Rodelle MiñanoNo ratings yet
- Miñano - (OS 204) PN 3 - EarDocument3 pagesMiñano - (OS 204) PN 3 - EarMarion Rodelle MiñanoNo ratings yet
- Miñano - (OS 204) PN 3 - EarDocument2 pagesMiñano - (OS 204) PN 3 - EarMarion Rodelle MiñanoNo ratings yet
- Miñano - (OS 204) PN 2 - Skull and MandibleDocument2 pagesMiñano - (OS 204) PN 2 - Skull and MandibleMarion Rodelle MiñanoNo ratings yet
- Miñano - (OS 204) PN 1 - Anatomy of FaceDocument2 pagesMiñano - (OS 204) PN 1 - Anatomy of FaceMarion Rodelle MiñanoNo ratings yet
- Miñano - (OS 204) PN 6 - Pharynx and LarynxDocument2 pagesMiñano - (OS 204) PN 6 - Pharynx and LarynxMarion Rodelle MiñanoNo ratings yet
- Miñano - (OS 204) PN 5 - Oral Cavity and PalateDocument2 pagesMiñano - (OS 204) PN 5 - Oral Cavity and PalateMarion Rodelle MiñanoNo ratings yet
- Applying The Chronic Care Model in Low-Resource Settings Ada Dec2013Document44 pagesApplying The Chronic Care Model in Low-Resource Settings Ada Dec2013Wawan JokoNo ratings yet
- Waste Management Technologies in Japanese Cement Industry - From Manufacturing To EcofactuaringDocument6 pagesWaste Management Technologies in Japanese Cement Industry - From Manufacturing To EcofactuaringRati YuliarningsihNo ratings yet
- Climate and Consumption Pattern - Demand and Supply of Water District ConcessionairesDocument3 pagesClimate and Consumption Pattern - Demand and Supply of Water District ConcessionairesIJAERS JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Disguised UnemploymentDocument14 pagesDisguised UnemploymentAbhishek KumarNo ratings yet
- Al-Fasi Et Al.2015 PDFDocument8 pagesAl-Fasi Et Al.2015 PDFUmroh NuryantoNo ratings yet
- Erik Erikson: - Trust vs. MistrustDocument6 pagesErik Erikson: - Trust vs. MistrustWidya FitrianingrumNo ratings yet
- De Jong 2013 ACS Catalysis Catalysts For Production of Lower Olefins From Synthesis Gas - A Review PDFDocument20 pagesDe Jong 2013 ACS Catalysis Catalysts For Production of Lower Olefins From Synthesis Gas - A Review PDFSohail FarooqNo ratings yet
- Cambridge Assessment International Education: Chemistry 9701/33 March 2019Document7 pagesCambridge Assessment International Education: Chemistry 9701/33 March 2019Trang NguyenNo ratings yet
- Demolition Instructions With Heavy Duty Construction MachineryDocument2 pagesDemolition Instructions With Heavy Duty Construction Machinerymiraç burak navruzNo ratings yet
- The One Minute ManagerDocument20 pagesThe One Minute ManagerYashwant J100% (2)
- Gala MayDocument7 pagesGala MayRobert Ross DulayNo ratings yet
- Man#251 Rev BDocument10 pagesMan#251 Rev Bjuan dalmassoNo ratings yet
- NACE 2003 Cust Seminar 2006Document21 pagesNACE 2003 Cust Seminar 2006me.mantilla4148No ratings yet
- Anaesthesia Workstation 4Document120 pagesAnaesthesia Workstation 4john georgeNo ratings yet
- Take Home Quiz COVID 2020Document18 pagesTake Home Quiz COVID 2020Jamie RuzickaNo ratings yet
- HEALTH 9 QUARTER2 MODULE3 WeeK5-6Document9 pagesHEALTH 9 QUARTER2 MODULE3 WeeK5-6Heidee Basas100% (3)
- Cafe 77 Menu Sept NewDocument2 pagesCafe 77 Menu Sept NewAhmed SaklanNo ratings yet
- Singer BangladeshDocument16 pagesSinger BangladeshMahbubur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Health Problems Illnesses Sickness Ailments Injuries Pictionary Poster Vocabulary WorksheetDocument2 pagesHealth Problems Illnesses Sickness Ailments Injuries Pictionary Poster Vocabulary WorksheetTania Lopez100% (1)
- Common Pediatric Fractures Common Pediatric FracturesDocument67 pagesCommon Pediatric Fractures Common Pediatric FracturesJeane SuyantoNo ratings yet
- Case Study Format - PGTCNDocument2 pagesCase Study Format - PGTCNFitz JaminitNo ratings yet
- Especificaciones de Valvulas Normas APIDocument2 pagesEspecificaciones de Valvulas Normas APIÀngel Rodriguez0% (1)
- Respiratory FailureDocument29 pagesRespiratory Failureageng rusbaya0% (1)
- Polymer Materials From Recycled Plastic in Road ConstructionDocument7 pagesPolymer Materials From Recycled Plastic in Road ConstructionYuv RajNo ratings yet
- 3 - Cardiovascular System PDFDocument54 pages3 - Cardiovascular System PDFMSKCNo ratings yet
- Bengkel Biologi SmartGDocument6 pagesBengkel Biologi SmartGK XuanNo ratings yet
- 319 6904116 Om 10 05 PDFDocument136 pages319 6904116 Om 10 05 PDFvatasaNo ratings yet
- Vessel Design (External Loads) 2 PDFDocument50 pagesVessel Design (External Loads) 2 PDFEzekielNo ratings yet
- Concept Questions From Marine BiologyDocument2 pagesConcept Questions From Marine BiologyJameeNo ratings yet
- 6 Sulangan Farm and Farmers ProfileDocument37 pages6 Sulangan Farm and Farmers ProfilePhen MontalboNo ratings yet