Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views13 - L-16 (NKD) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)
13 - L-16 (NKD) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)
Uploaded by
CharkThe document discusses filters used in converter circuits to reduce harmonic content in output voltage and current waveforms. It explains that an inductor connected in series with the load can reduce harmonic components in current, while a capacitor in parallel can stabilize voltage. Optimal filtering requires a combination of inductor, capacitor, and resistor. A single-stage low-pass LC filter is then described for a diode bridge converter, where the inductor value must be high enough to filter the lowest harmonic frequency. The capacitive reactance is set to the total load impedance divided by 10 for effective filtering.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- ZF Cruisecommand User ManualDocument240 pagesZF Cruisecommand User ManualSoesanto Tirtoprodjo100% (3)
- Healing Is Voltage - Healing Eye DiseasesDocument219 pagesHealing Is Voltage - Healing Eye DiseasesAndrea Sirah90% (10)
- LC Ladder Matching NetworksDocument33 pagesLC Ladder Matching NetworksCarriceiros Tour100% (1)
- CTE FM CatalogDocument95 pagesCTE FM CatalogTatesz100% (1)
- Lect 6 Distribution Substation Design PDFDocument31 pagesLect 6 Distribution Substation Design PDFMohammed Shariq AyjazNo ratings yet
- 2013 Nissan Sentra LanDocument128 pages2013 Nissan Sentra LanFSR1407100% (1)
- TOFD Full NotesDocument80 pagesTOFD Full NotesRamesh mudunuri79% (14)
- Load Network Design Technique For Switched-Mode Tuned Class E Power AmplifiersDocument23 pagesLoad Network Design Technique For Switched-Mode Tuned Class E Power AmplifiersJong-RyulNo ratings yet
- Full Wave RectifierDocument10 pagesFull Wave RectifierVenkata PavanNo ratings yet
- AimDocument12 pagesAimkarakeriNo ratings yet
- Omega Type ETB-29 Lab Manual (CURAJ)Document18 pagesOmega Type ETB-29 Lab Manual (CURAJ)McMillerNo ratings yet
- ( (Overdamped Voltage Response) )Document12 pages( (Overdamped Voltage Response) )Hayder AliNo ratings yet
- Case Study: Complex Impedance: Electronic FiltersDocument4 pagesCase Study: Complex Impedance: Electronic FiltersDaniel SolhNo ratings yet
- Freq Compensation Tech LdoDocument4 pagesFreq Compensation Tech LdoManish SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Case Study: Complex Impedance: Electronic FiltersDocument4 pagesCase Study: Complex Impedance: Electronic FiltersEbookcrazeNo ratings yet
- Application Note AN-1160: Design of Resonant Half-Bridge Converter Using IRS2795 (1,2) Control ICDocument32 pagesApplication Note AN-1160: Design of Resonant Half-Bridge Converter Using IRS2795 (1,2) Control ICcumshotNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Power Supplies and Amplifiers NotesDocument13 pagesModule 1 Power Supplies and Amplifiers Notesayushsingh102005No ratings yet
- Two Inductively Coupled RLC CircuitsDocument4 pagesTwo Inductively Coupled RLC CircuitsAshutoshMishraNo ratings yet
- RC Circuit: Natural Response Complex Impedance Series CircuitDocument12 pagesRC Circuit: Natural Response Complex Impedance Series CircuitKrishanu ModakNo ratings yet
- Simple LC Filter IIDocument3 pagesSimple LC Filter IIdhananjaymohapatra2009No ratings yet
- An-721 Impedance Matching Networks Applied To RF Power TransistorsDocument16 pagesAn-721 Impedance Matching Networks Applied To RF Power TransistorsEdward YanezNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics 1: ENEL371S2Document30 pagesPower Electronics 1: ENEL371S2bpd21No ratings yet
- RLC TransientDocument7 pagesRLC TransientAlamaskhan PathanNo ratings yet
- ClampDocument8 pagesClampGaetano GaetanoNo ratings yet
- Some Applications of Differential Equations in RL-RC Electrical CircuitDocument12 pagesSome Applications of Differential Equations in RL-RC Electrical CircuitArindam MondalNo ratings yet
- Wideband TransformersDocument6 pagesWideband TransformersA. VillaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 02Document21 pagesLecture 02Abd El-Rahman DabbishNo ratings yet
- Experiment 12: AC Circuits - RLC CircuitDocument5 pagesExperiment 12: AC Circuits - RLC CircuitAhmed SalehNo ratings yet
- RLC CircuitDocument9 pagesRLC CircuitHemangee PurohitNo ratings yet
- Basic Electricity: University of Manchester Department of Computer ScienceDocument14 pagesBasic Electricity: University of Manchester Department of Computer Scienceabinash_pattanaik41No ratings yet
- RLC NotesDocument4 pagesRLC Noteskerala pscNo ratings yet
- 3 RectifiersDocument30 pages3 RectifiersYahya MareiNo ratings yet
- 03 Diode Rectifier ProjectDocument11 pages03 Diode Rectifier ProjectManju NathNo ratings yet
- ALLAH The Most Merciful, The Most Beneficent"Document39 pagesALLAH The Most Merciful, The Most Beneficent"api-19788618No ratings yet
- Electronic FilterDocument11 pagesElectronic FilterPrabuddha ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Ecn RLCPDocument11 pagesEcn RLCPharshsuryawanshi2021No ratings yet
- Advance ElectronicsDocument8 pagesAdvance ElectronicswazidulNo ratings yet
- Design and Simulation of Electrical Vehicle (EV) Power SupplyDocument5 pagesDesign and Simulation of Electrical Vehicle (EV) Power SupplyRAJESHNo ratings yet
- EE-221-Review of DC CircuitsDocument51 pagesEE-221-Review of DC CircuitsSean Ng100% (1)
- Analysis and Design of The Resonant Converter For Low Output Current RippleDocument9 pagesAnalysis and Design of The Resonant Converter For Low Output Current Rippleroughdraft2020No ratings yet
- RL & RCDocument43 pagesRL & RCThilaga MohanNo ratings yet
- Mod 4 Book 2 Transistors Intergrated Circuits Printed Circuit BoardsDocument61 pagesMod 4 Book 2 Transistors Intergrated Circuits Printed Circuit Boardsranjit prasadNo ratings yet
- Capacitor Input FilterDocument2 pagesCapacitor Input FilterAgbarakwe Ikechukwu100% (1)
- Unit-I Resonance: 2 Marks Questions and AnswersDocument14 pagesUnit-I Resonance: 2 Marks Questions and AnswersyaminiNo ratings yet
- Control S Lec 12-18Document7 pagesControl S Lec 12-18Aloysious Aries GonzagaNo ratings yet
- Davoli Model 207Document5 pagesDavoli Model 207honzah.karnevalNo ratings yet
- A18EE2001 - IA2 Sample Questions : Answer Red ColouredDocument6 pagesA18EE2001 - IA2 Sample Questions : Answer Red ColouredanNo ratings yet
- Colpitts OscillatorDocument4 pagesColpitts OscillatorjoNo ratings yet
- Enginering AnalysisDocument11 pagesEnginering Analysisamr3repy4No ratings yet
- CH 2Document27 pagesCH 2dawitdabale09No ratings yet
- Tdc-La 2018 8511669Document5 pagesTdc-La 2018 8511669Asad HameedNo ratings yet
- Analog Measuring InstrumentsDocument43 pagesAnalog Measuring Instrumentsmuvvala charithaNo ratings yet
- 241 RLC Circuit Ac SourceDocument14 pages241 RLC Circuit Ac SourceWsma AmswNo ratings yet
- LLC Resonant Converter 1713008423Document10 pagesLLC Resonant Converter 1713008423im.pavantomarNo ratings yet
- Q. What Do You Mean by Half Wave Rectification and Full Wave Rectification?Document5 pagesQ. What Do You Mean by Half Wave Rectification and Full Wave Rectification?Huidrom SharatNo ratings yet
- 2.06 Ripple Factor of Inductor FilterDocument2 pages2.06 Ripple Factor of Inductor FilterVamsiMadupu100% (6)
- LCL Filters For A Grid Emulator Application - Comparative Study of Active Damping TechniquesDocument6 pagesLCL Filters For A Grid Emulator Application - Comparative Study of Active Damping TechniquesUzhansEell-neinoNo ratings yet
- Aims of The Exercise: EquipmentDocument3 pagesAims of The Exercise: Equipmentwala alabedNo ratings yet
- Transfer FunctionDocument15 pagesTransfer FunctionVarli ArsolNo ratings yet
- RC CircuitsDocument37 pagesRC CircuitsNoviNo ratings yet
- Easy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2019-2023)From EverandEasy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2019-2023)No ratings yet
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterNo ratings yet
- Easy(er) Electrical Principles for Extra Class Ham License (2012-2016)From EverandEasy(er) Electrical Principles for Extra Class Ham License (2012-2016)No ratings yet
- 6 - L-25 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page6 - L-25 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 9 - L-26 (SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page9 - L-26 (SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 4 - L-26 (SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page4 - L-26 (SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 13 - L-24 (DK&SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page13 - L-24 (DK&SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 3 - L-26 (SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page3 - L-26 (SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 8 - L-26 (SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page8 - L-26 (SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 12 - L-24 (DK&SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page12 - L-24 (DK&SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 3 - L-25 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page3 - L-25 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 5 - L-25 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page5 - L-25 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 10 - L-25 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page10 - L-25 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 4 - L-25 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page4 - L-25 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 5 - L-26 (SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page5 - L-26 (SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 7 - L-25 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page7 - L-25 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 9 - L-23 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page9 - L-23 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 4 - L-24 (DK&SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page4 - L-24 (DK&SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 10 - L-23 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page10 - L-23 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 12 - L-23 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page12 - L-23 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 13 - L-23 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page13 - L-23 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 14 - L-24 (DK&SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page14 - L-24 (DK&SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 15 - L-24 (DK&SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page15 - L-24 (DK&SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 11 - L-23 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page11 - L-23 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 5 - L-24 (DK&SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page5 - L-24 (DK&SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 10 - L-24 (DK&SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page10 - L-24 (DK&SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 8 - L-23 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page8 - L-23 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 6 - L-23 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page6 - L-23 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 5 - L-23 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page5 - L-23 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 3 - L-23 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page3 - L-23 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 4 - L-23 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page4 - L-23 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 12 - L-22 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page12 - L-22 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 7 - L-22 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page7 - L-22 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- Lavadora Frigidaire Gb7nc60hdDocument15 pagesLavadora Frigidaire Gb7nc60hdHernan Vallenilla Rumildo MixNo ratings yet
- HI - 93703 Manual TurbidimetroDocument13 pagesHI - 93703 Manual Turbidimetrojesica31No ratings yet
- Everyday Electronics 1992 06Document76 pagesEveryday Electronics 1992 06god2pcsNo ratings yet
- Motor Protection: 5.08kV, 7.2kV AND 15.5kV Bolt-In FusesDocument4 pagesMotor Protection: 5.08kV, 7.2kV AND 15.5kV Bolt-In FusesRafael LopezNo ratings yet
- Using Broken Delta Protection For Earth FaultsDocument1 pageUsing Broken Delta Protection For Earth Faultsm khNo ratings yet
- Jinko-Solar Eagle-Plus 340P-360P 72cells 34700Document2 pagesJinko-Solar Eagle-Plus 340P-360P 72cells 34700rockydark0% (1)
- Synopsis - Substation ModernizationDocument2 pagesSynopsis - Substation ModernizationajayecomNo ratings yet
- EN - ACS800-307 V992 and ACS800-507 V992 HW Manual - BDocument92 pagesEN - ACS800-307 V992 and ACS800-507 V992 HW Manual - BINDRANIL DEYNo ratings yet
- Infinity: Audiomax™ Lx1721 / 1722Document14 pagesInfinity: Audiomax™ Lx1721 / 1722Malith UdayangaNo ratings yet
- Metal Ligand Bonding in Transition Metal Complexes Part 1Document4 pagesMetal Ligand Bonding in Transition Metal Complexes Part 1Swati JadhavNo ratings yet
- Schneider Electric - PowerLogic-Power-Meters-PM3000 - METSEPM3250Document4 pagesSchneider Electric - PowerLogic-Power-Meters-PM3000 - METSEPM3250techhustler2No ratings yet
- Ipd 66031Document42 pagesIpd 66031HannOtto StoreNo ratings yet
- BBU Quick Installation Guide (V100R005C10 - 04) (PDF) - ENDocument7 pagesBBU Quick Installation Guide (V100R005C10 - 04) (PDF) - ENCarlitos GuevaraNo ratings yet
- Analog MultiplexerDocument13 pagesAnalog MultiplexerSanjoy PandaNo ratings yet
- LM1201 Video Amplifier System: General DescriptionDocument16 pagesLM1201 Video Amplifier System: General DescriptionVicenteNo ratings yet
- SYSTEM Info (L3 Messages) 2GDocument43 pagesSYSTEM Info (L3 Messages) 2GWuhayb Mohsin MirzaNo ratings yet
- What Does XDSL and ADSL Mean?: ArticleDocument9 pagesWhat Does XDSL and ADSL Mean?: ArticleIas Aspirant AbhiNo ratings yet
- TC 0909Document3 pagesTC 0909takzy007No ratings yet
- Led TV: Service ManualDocument53 pagesLed TV: Service ManualMauricio PérezNo ratings yet
- Gps TrackingDocument3 pagesGps TrackingImaniNo ratings yet
- Inverter MoudlesDocument63 pagesInverter Moudlesknighthood4allNo ratings yet
- ET4117 Electrical Machines and Drives Lecture5Document31 pagesET4117 Electrical Machines and Drives Lecture5farhan beighNo ratings yet
- Position Tracking System With Brushless DC Motor: Keywords: BLDC Motor Hall Sensors PID ControllerDocument5 pagesPosition Tracking System With Brushless DC Motor: Keywords: BLDC Motor Hall Sensors PID ControllerMyat AungNo ratings yet
- Service Manual Daikin Altherma LT-DDocument160 pagesService Manual Daikin Altherma LT-DSlobodan GerićNo ratings yet
13 - L-16 (NKD) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)
13 - L-16 (NKD) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)
Uploaded by
Chark0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views1 pageThe document discusses filters used in converter circuits to reduce harmonic content in output voltage and current waveforms. It explains that an inductor connected in series with the load can reduce harmonic components in current, while a capacitor in parallel can stabilize voltage. Optimal filtering requires a combination of inductor, capacitor, and resistor. A single-stage low-pass LC filter is then described for a diode bridge converter, where the inductor value must be high enough to filter the lowest harmonic frequency. The capacitive reactance is set to the total load impedance divided by 10 for effective filtering.
Original Description:
13_L-16(NKD)(PE) ((EE)NPTEL)
Original Title
13_L-16(NKD)(PE) ((EE)NPTEL)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses filters used in converter circuits to reduce harmonic content in output voltage and current waveforms. It explains that an inductor connected in series with the load can reduce harmonic components in current, while a capacitor in parallel can stabilize voltage. Optimal filtering requires a combination of inductor, capacitor, and resistor. A single-stage low-pass LC filter is then described for a diode bridge converter, where the inductor value must be high enough to filter the lowest harmonic frequency. The capacitive reactance is set to the total load impedance divided by 10 for effective filtering.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
2 views1 page13 - L-16 (NKD) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)
13 - L-16 (NKD) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)
Uploaded by
CharkThe document discusses filters used in converter circuits to reduce harmonic content in output voltage and current waveforms. It explains that an inductor connected in series with the load can reduce harmonic components in current, while a capacitor in parallel can stabilize voltage. Optimal filtering requires a combination of inductor, capacitor, and resistor. A single-stage low-pass LC filter is then described for a diode bridge converter, where the inductor value must be high enough to filter the lowest harmonic frequency. The capacitive reactance is set to the total load impedance divided by 10 for effective filtering.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
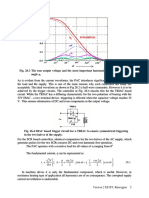
may also be explained in the following way.
The voltage across the capacitor changes as per the
input voltage, which is the output voltage of the converter, fed to it, and the capacitor voltage
tries to stabilize at the overage value of the output voltage, as the capacitor voltage decreases,
load resistance being connected across it.
Same is the case with the filter used to reduce the harmonic content of the output current
waveform for the above converters with resistive (R) load. Instead of a capacitor in parallel, an
inductor (L) is connected in series with the load. The reactance of the inductor increases, thus
reducing the harmonic component in the current waveform. Here, a smaller value of the inductor
is needed to filter higher harmonics, for example a three-phase bridge converter. These are all
simple cases, known to those, who have studied the circuit (network) theory. Also, by Faraday’s
laws, induced voltage (emf) appears across the inductor, L, when the current through it changes,
and the sign of it opposes the cause, thus opposing the changes in current. So, the current is not
allowed to change much, as an inductor is placed in series with the load. In actual practice, a
combination of L, C & R is needed to get an optimum filter needed to reduce or eliminate the
harmonics in both output voltage and current waveforms.
Low Pass (L-C) Filter
A passive low pass filter is the ideal choice. But two problems arise; one is the voltage level,
the other is the power or current level. All the elements used, L C or R must be properly rated for
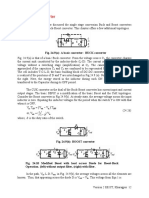
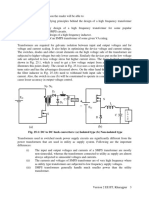
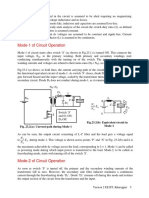
the voltage or current level as needed. A single stage filter (L-C) is used to reduce the harmonic
components in both voltage and current waveforms of a single phase full wave diode bridge
converter with resistive (RL) load as shown in Fig. 16.5(a). It may be noted that, for the lowest
harmonic frequency of 100 Hz, the value of the inductor needed is high, needing an iron-cored
coil. The size also may be large, if the power or current level is high. As stated earlier, such that
nth harmonic ripple content passes through the filter capacitor (C), the impedance of the series
path must be much greater than that of the capacitance, i.e.,
1
ZL = ( R L ) + ( n ω L ) >>
2 2
n ωC
The condition to be satisfied is
10
ZL = or ZL 10 = 1 ( n ω C )
n ωC
and the effect of load is negligible. As shown, the capacitive reactance chosen is total load
impedance divided by a factor of 10
The advantages are small ripple factor with just a single stage (L-C) used, with higher dc
output voltage. The main advantage is poor voltage regulation, also resulting in higher peak
anode current and peak inverse voltage rating.
Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 13
You might also like
- ZF Cruisecommand User ManualDocument240 pagesZF Cruisecommand User ManualSoesanto Tirtoprodjo100% (3)
- Healing Is Voltage - Healing Eye DiseasesDocument219 pagesHealing Is Voltage - Healing Eye DiseasesAndrea Sirah90% (10)
- LC Ladder Matching NetworksDocument33 pagesLC Ladder Matching NetworksCarriceiros Tour100% (1)
- CTE FM CatalogDocument95 pagesCTE FM CatalogTatesz100% (1)
- Lect 6 Distribution Substation Design PDFDocument31 pagesLect 6 Distribution Substation Design PDFMohammed Shariq AyjazNo ratings yet
- 2013 Nissan Sentra LanDocument128 pages2013 Nissan Sentra LanFSR1407100% (1)
- TOFD Full NotesDocument80 pagesTOFD Full NotesRamesh mudunuri79% (14)
- Load Network Design Technique For Switched-Mode Tuned Class E Power AmplifiersDocument23 pagesLoad Network Design Technique For Switched-Mode Tuned Class E Power AmplifiersJong-RyulNo ratings yet
- Full Wave RectifierDocument10 pagesFull Wave RectifierVenkata PavanNo ratings yet
- AimDocument12 pagesAimkarakeriNo ratings yet
- Omega Type ETB-29 Lab Manual (CURAJ)Document18 pagesOmega Type ETB-29 Lab Manual (CURAJ)McMillerNo ratings yet
- ( (Overdamped Voltage Response) )Document12 pages( (Overdamped Voltage Response) )Hayder AliNo ratings yet
- Case Study: Complex Impedance: Electronic FiltersDocument4 pagesCase Study: Complex Impedance: Electronic FiltersDaniel SolhNo ratings yet
- Freq Compensation Tech LdoDocument4 pagesFreq Compensation Tech LdoManish SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Case Study: Complex Impedance: Electronic FiltersDocument4 pagesCase Study: Complex Impedance: Electronic FiltersEbookcrazeNo ratings yet
- Application Note AN-1160: Design of Resonant Half-Bridge Converter Using IRS2795 (1,2) Control ICDocument32 pagesApplication Note AN-1160: Design of Resonant Half-Bridge Converter Using IRS2795 (1,2) Control ICcumshotNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Power Supplies and Amplifiers NotesDocument13 pagesModule 1 Power Supplies and Amplifiers Notesayushsingh102005No ratings yet
- Two Inductively Coupled RLC CircuitsDocument4 pagesTwo Inductively Coupled RLC CircuitsAshutoshMishraNo ratings yet
- RC Circuit: Natural Response Complex Impedance Series CircuitDocument12 pagesRC Circuit: Natural Response Complex Impedance Series CircuitKrishanu ModakNo ratings yet
- Simple LC Filter IIDocument3 pagesSimple LC Filter IIdhananjaymohapatra2009No ratings yet
- An-721 Impedance Matching Networks Applied To RF Power TransistorsDocument16 pagesAn-721 Impedance Matching Networks Applied To RF Power TransistorsEdward YanezNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics 1: ENEL371S2Document30 pagesPower Electronics 1: ENEL371S2bpd21No ratings yet
- RLC TransientDocument7 pagesRLC TransientAlamaskhan PathanNo ratings yet
- ClampDocument8 pagesClampGaetano GaetanoNo ratings yet
- Some Applications of Differential Equations in RL-RC Electrical CircuitDocument12 pagesSome Applications of Differential Equations in RL-RC Electrical CircuitArindam MondalNo ratings yet
- Wideband TransformersDocument6 pagesWideband TransformersA. VillaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 02Document21 pagesLecture 02Abd El-Rahman DabbishNo ratings yet
- Experiment 12: AC Circuits - RLC CircuitDocument5 pagesExperiment 12: AC Circuits - RLC CircuitAhmed SalehNo ratings yet
- RLC CircuitDocument9 pagesRLC CircuitHemangee PurohitNo ratings yet
- Basic Electricity: University of Manchester Department of Computer ScienceDocument14 pagesBasic Electricity: University of Manchester Department of Computer Scienceabinash_pattanaik41No ratings yet
- RLC NotesDocument4 pagesRLC Noteskerala pscNo ratings yet
- 3 RectifiersDocument30 pages3 RectifiersYahya MareiNo ratings yet
- 03 Diode Rectifier ProjectDocument11 pages03 Diode Rectifier ProjectManju NathNo ratings yet
- ALLAH The Most Merciful, The Most Beneficent"Document39 pagesALLAH The Most Merciful, The Most Beneficent"api-19788618No ratings yet
- Electronic FilterDocument11 pagesElectronic FilterPrabuddha ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Ecn RLCPDocument11 pagesEcn RLCPharshsuryawanshi2021No ratings yet
- Advance ElectronicsDocument8 pagesAdvance ElectronicswazidulNo ratings yet
- Design and Simulation of Electrical Vehicle (EV) Power SupplyDocument5 pagesDesign and Simulation of Electrical Vehicle (EV) Power SupplyRAJESHNo ratings yet
- EE-221-Review of DC CircuitsDocument51 pagesEE-221-Review of DC CircuitsSean Ng100% (1)
- Analysis and Design of The Resonant Converter For Low Output Current RippleDocument9 pagesAnalysis and Design of The Resonant Converter For Low Output Current Rippleroughdraft2020No ratings yet
- RL & RCDocument43 pagesRL & RCThilaga MohanNo ratings yet
- Mod 4 Book 2 Transistors Intergrated Circuits Printed Circuit BoardsDocument61 pagesMod 4 Book 2 Transistors Intergrated Circuits Printed Circuit Boardsranjit prasadNo ratings yet
- Capacitor Input FilterDocument2 pagesCapacitor Input FilterAgbarakwe Ikechukwu100% (1)
- Unit-I Resonance: 2 Marks Questions and AnswersDocument14 pagesUnit-I Resonance: 2 Marks Questions and AnswersyaminiNo ratings yet
- Control S Lec 12-18Document7 pagesControl S Lec 12-18Aloysious Aries GonzagaNo ratings yet
- Davoli Model 207Document5 pagesDavoli Model 207honzah.karnevalNo ratings yet
- A18EE2001 - IA2 Sample Questions : Answer Red ColouredDocument6 pagesA18EE2001 - IA2 Sample Questions : Answer Red ColouredanNo ratings yet
- Colpitts OscillatorDocument4 pagesColpitts OscillatorjoNo ratings yet
- Enginering AnalysisDocument11 pagesEnginering Analysisamr3repy4No ratings yet
- CH 2Document27 pagesCH 2dawitdabale09No ratings yet
- Tdc-La 2018 8511669Document5 pagesTdc-La 2018 8511669Asad HameedNo ratings yet
- Analog Measuring InstrumentsDocument43 pagesAnalog Measuring Instrumentsmuvvala charithaNo ratings yet
- 241 RLC Circuit Ac SourceDocument14 pages241 RLC Circuit Ac SourceWsma AmswNo ratings yet
- LLC Resonant Converter 1713008423Document10 pagesLLC Resonant Converter 1713008423im.pavantomarNo ratings yet
- Q. What Do You Mean by Half Wave Rectification and Full Wave Rectification?Document5 pagesQ. What Do You Mean by Half Wave Rectification and Full Wave Rectification?Huidrom SharatNo ratings yet
- 2.06 Ripple Factor of Inductor FilterDocument2 pages2.06 Ripple Factor of Inductor FilterVamsiMadupu100% (6)
- LCL Filters For A Grid Emulator Application - Comparative Study of Active Damping TechniquesDocument6 pagesLCL Filters For A Grid Emulator Application - Comparative Study of Active Damping TechniquesUzhansEell-neinoNo ratings yet
- Aims of The Exercise: EquipmentDocument3 pagesAims of The Exercise: Equipmentwala alabedNo ratings yet
- Transfer FunctionDocument15 pagesTransfer FunctionVarli ArsolNo ratings yet
- RC CircuitsDocument37 pagesRC CircuitsNoviNo ratings yet
- Easy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2019-2023)From EverandEasy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2019-2023)No ratings yet
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterNo ratings yet
- Easy(er) Electrical Principles for Extra Class Ham License (2012-2016)From EverandEasy(er) Electrical Principles for Extra Class Ham License (2012-2016)No ratings yet
- 6 - L-25 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page6 - L-25 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 9 - L-26 (SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page9 - L-26 (SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 4 - L-26 (SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page4 - L-26 (SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 13 - L-24 (DK&SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page13 - L-24 (DK&SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 3 - L-26 (SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page3 - L-26 (SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 8 - L-26 (SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page8 - L-26 (SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 12 - L-24 (DK&SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page12 - L-24 (DK&SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 3 - L-25 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page3 - L-25 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 5 - L-25 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page5 - L-25 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 10 - L-25 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page10 - L-25 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 4 - L-25 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page4 - L-25 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 5 - L-26 (SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page5 - L-26 (SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 7 - L-25 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page7 - L-25 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 9 - L-23 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page9 - L-23 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 4 - L-24 (DK&SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page4 - L-24 (DK&SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 10 - L-23 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page10 - L-23 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 12 - L-23 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page12 - L-23 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 13 - L-23 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page13 - L-23 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 14 - L-24 (DK&SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page14 - L-24 (DK&SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 15 - L-24 (DK&SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page15 - L-24 (DK&SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 11 - L-23 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page11 - L-23 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 5 - L-24 (DK&SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page5 - L-24 (DK&SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 10 - L-24 (DK&SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page10 - L-24 (DK&SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 8 - L-23 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page8 - L-23 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 6 - L-23 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page6 - L-23 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 5 - L-23 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page5 - L-23 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 3 - L-23 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page3 - L-23 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 4 - L-23 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page4 - L-23 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 12 - L-22 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page12 - L-22 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 7 - L-22 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page7 - L-22 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- Lavadora Frigidaire Gb7nc60hdDocument15 pagesLavadora Frigidaire Gb7nc60hdHernan Vallenilla Rumildo MixNo ratings yet
- HI - 93703 Manual TurbidimetroDocument13 pagesHI - 93703 Manual Turbidimetrojesica31No ratings yet
- Everyday Electronics 1992 06Document76 pagesEveryday Electronics 1992 06god2pcsNo ratings yet
- Motor Protection: 5.08kV, 7.2kV AND 15.5kV Bolt-In FusesDocument4 pagesMotor Protection: 5.08kV, 7.2kV AND 15.5kV Bolt-In FusesRafael LopezNo ratings yet
- Using Broken Delta Protection For Earth FaultsDocument1 pageUsing Broken Delta Protection For Earth Faultsm khNo ratings yet
- Jinko-Solar Eagle-Plus 340P-360P 72cells 34700Document2 pagesJinko-Solar Eagle-Plus 340P-360P 72cells 34700rockydark0% (1)
- Synopsis - Substation ModernizationDocument2 pagesSynopsis - Substation ModernizationajayecomNo ratings yet
- EN - ACS800-307 V992 and ACS800-507 V992 HW Manual - BDocument92 pagesEN - ACS800-307 V992 and ACS800-507 V992 HW Manual - BINDRANIL DEYNo ratings yet
- Infinity: Audiomax™ Lx1721 / 1722Document14 pagesInfinity: Audiomax™ Lx1721 / 1722Malith UdayangaNo ratings yet
- Metal Ligand Bonding in Transition Metal Complexes Part 1Document4 pagesMetal Ligand Bonding in Transition Metal Complexes Part 1Swati JadhavNo ratings yet
- Schneider Electric - PowerLogic-Power-Meters-PM3000 - METSEPM3250Document4 pagesSchneider Electric - PowerLogic-Power-Meters-PM3000 - METSEPM3250techhustler2No ratings yet
- Ipd 66031Document42 pagesIpd 66031HannOtto StoreNo ratings yet
- BBU Quick Installation Guide (V100R005C10 - 04) (PDF) - ENDocument7 pagesBBU Quick Installation Guide (V100R005C10 - 04) (PDF) - ENCarlitos GuevaraNo ratings yet
- Analog MultiplexerDocument13 pagesAnalog MultiplexerSanjoy PandaNo ratings yet
- LM1201 Video Amplifier System: General DescriptionDocument16 pagesLM1201 Video Amplifier System: General DescriptionVicenteNo ratings yet
- SYSTEM Info (L3 Messages) 2GDocument43 pagesSYSTEM Info (L3 Messages) 2GWuhayb Mohsin MirzaNo ratings yet
- What Does XDSL and ADSL Mean?: ArticleDocument9 pagesWhat Does XDSL and ADSL Mean?: ArticleIas Aspirant AbhiNo ratings yet
- TC 0909Document3 pagesTC 0909takzy007No ratings yet
- Led TV: Service ManualDocument53 pagesLed TV: Service ManualMauricio PérezNo ratings yet
- Gps TrackingDocument3 pagesGps TrackingImaniNo ratings yet
- Inverter MoudlesDocument63 pagesInverter Moudlesknighthood4allNo ratings yet
- ET4117 Electrical Machines and Drives Lecture5Document31 pagesET4117 Electrical Machines and Drives Lecture5farhan beighNo ratings yet
- Position Tracking System With Brushless DC Motor: Keywords: BLDC Motor Hall Sensors PID ControllerDocument5 pagesPosition Tracking System With Brushless DC Motor: Keywords: BLDC Motor Hall Sensors PID ControllerMyat AungNo ratings yet
- Service Manual Daikin Altherma LT-DDocument160 pagesService Manual Daikin Altherma LT-DSlobodan GerićNo ratings yet