Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cytogen Reviewer
Cytogen Reviewer
Uploaded by
Jolan Fernando Herce0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views6 pagesThe document summarizes key aspects of cell structure and function. It describes the basic unit and functions of cells, including synthesis of molecules, communication, metabolism, and reproduction. It outlines the structures and functions of organelles like the cell membrane, nucleus, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, and lysosomes. It explains how molecules pass through the cell membrane via diffusion, channels, carrier molecules, and vesicles. It also describes osmosis and different types of osmotic solutions. Finally, it provides an overview of cell structures and their locations and functions.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document summarizes key aspects of cell structure and function. It describes the basic unit and functions of cells, including synthesis of molecules, communication, metabolism, and reproduction. It outlines the structures and functions of organelles like the cell membrane, nucleus, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, and lysosomes. It explains how molecules pass through the cell membrane via diffusion, channels, carrier molecules, and vesicles. It also describes osmosis and different types of osmotic solutions. Finally, it provides an overview of cell structures and their locations and functions.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views6 pagesCytogen Reviewer
Cytogen Reviewer
Uploaded by
Jolan Fernando HerceThe document summarizes key aspects of cell structure and function. It describes the basic unit and functions of cells, including synthesis of molecules, communication, metabolism, and reproduction. It outlines the structures and functions of organelles like the cell membrane, nucleus, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, and lysosomes. It explains how molecules pass through the cell membrane via diffusion, channels, carrier molecules, and vesicles. It also describes osmosis and different types of osmotic solutions. Finally, it provides an overview of cell structures and their locations and functions.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 6
Topic 1: Cytology (Cells to Mitosis) plants energy
Functions: Cell Structure:
• Basic unit of life • Organelles:
- specialized structures in cells that
• Synthesis of molecules
perform specific functions
• Communication - Ex. Nucleus, mitochondria,
ribosomes, etc.
• Cell metabolism and energy release
• Cytoplasm:
• Reproduction and inheritance (DNA)
jelly-like substance that holds organelles
Cell Part & its Function:
● Cell Membrane
● Cell membrane- control what enters
- Outermost component of cell
and leaves the cell
● Nuclear membrane- control what Function:
enters and leaves the nucleus - Selective barrier
● Nucleus- control center of the cell - Encloses Cytoplasm
● Chromosomes- genetic information ● Extracellular: material outside cell
in the nucleus ● Intracellular: material inside cell
● Endoplasmic Reticulum- transport Structure of Cell Membrane
system in cell
• Called Fluid Mosaic Model
● Ribosomes- organelle that makes
proteins • Made of phospholipids and proteins
● Golgi Body- organelle that packages
• Phospholipids form a double layer or
proteins bilayer
● Vacuole- stores water/waste
● Lysosome- breaks down old cell • Phospholipids contain 2 regions:
parts polar and nonpolar
● Mitochondria- organelle for cellular • Polar regions:
respiration- provides energy - “heads”
● Cytoplasm- jelly like fluid - hydrophilic (H2O loving)
—----------plant cells (addition yung nasa - exposed to H2O
baba same meaning lang naman)
• Nonpolar regions:
● Vacuole- it stores material like
- “tails”
water
- hydrophobic (H2O fearing)
● Cell Wall- support/protect plant
cells - away from H2O
● Chloroplasts- captures light to give
channels
3. Carrier molecules:
- bind to molecules, transport them
across, and drop them off - Ex.
glucose
4. Vesicles:
- can transport a variety of
materials
- fuse with cell membrane
Diffusion
● movement of molecules from areas
of high to low concentration
● Solution: solid, liquid, or gas that
contains one or more solutes
● Solute: substance added to solvent
that dissolves
● Solvent: substance such as H2O that
solute is being added to
Movement through Cell Membrane Ex. Add salt to H2O. H2O =solvent,
• Cell membrane selectively determines salt=solute, mixture=solution
what can pass in and out of the cell.
● Concentration gradient:
• Enzymes, glycogen, and potassium are
found in higher concentrations INSIDE - measures conc. difference at 2 points
the cell. - greater the distance the faster the solute
will travel
• Sodium, calcium, and chloride are ● Filtration:
found in higher concentrations
- movement of fluid through a
OUTSIDE the cell.
partition with holes
Ways molecules Pass through Cell
Mediated Transport Mechanisms
Membrane
1. Directly through (diffusion): Facilitated diffusion:
- diffusion with aid of a carrier
O2 and CO2 (small molecules)
molecule
2. Membrane channels:
- requires no ATP
- proteins that extend from one Active transport:
side of cell membrane to other
- moves substances from low to high
- size, shape, and charge (+/-) conc.
determine what can go through
- requires ATP
- Ex. Na+ passes through Na+ - Ex. Sodium-potassium pump
● Nucleus
Osmosis Location: center of cell
- diffusion of water across a cell Characteristic: all cells contain nucleus at
membrane some point
- Osmotic pressure: Function: houses DNA
force required to prevent movement of ● Nuclear envelope:
water across cell membrane Location: edge of nucleus
Types of Osmotic Solutions ● Nuclear pores:
Hypotonic solution: Location: surface of nucleus
- lower conc. of solutes outside cell Function: where materials pass in and out
- higher conc. of H2O outside cell of nucleus
- H2O moves into cell ● Chromosome:
- lysis (burst) Location: inside nucleus
Hypertonic solution: Characteristic: made of DNA and proteins
- higher conc. of solutes outsidecell Function: part of genetic makeup
- higher conc. H2O inside cell ● Chromatin:
- H2O moves out Location: inside nucleus
- crenation (shrinks) Characteristic: loosely coiled chromosomes
Isotonic solution: ● Nucleolus
- equal conc. of solutes Location: in nucleus
- water doesn’t move Function: produce ribosomes
- cell remains intact ● Ribosome
Endocytosis Location: attached to RER or cytoplasm
- process that brings materials into Function: produce proteins
cell using vesicles ● RER (Rough Endoplasmic
2 types Reticulum)
- Phagocytosis: cell eating (solid particles) Location: cytoplasm
- Pinocytosis: cell drinking (liquid particles) Characteristic: membranes with ribosomes
Exocytosis attached
- process that carries materials out of Function: site of protein synthesis
cell using vesicles ● SER (Smooth Endoplasmic
Reticulum)
Cell Structures: Location: cytoplasm
● Cytoplasm Characteristic: membranes with no
Location: inside cell ribosomes
Characteristic: jelly-like fluid Function: site of lipid synthesis (Ex.
Function: give cell shape and hold Cholesterol)
organelles in place ● Golgi apparatus
Location: cytoplasm Microtubules:
Characteristic: closely, packed stacks of - largest diameter
membranes - provide structural support
Function: collect, sort, package, and - form cilia and flagella
distribute proteins and lipids Intermediate filaments:
● Secretory vesicle - medium diameter
Location: cytoplasm - maintain cell shape
Function: distributes materials out of cell Microfilaments:
● Lysosome - smallest diameter
Location: cytoplasm - involved in cell movement
Function: enzymes that digest foreign
material Whole Cell Activity
● Mitochondria - A cell’s characteristics are
Location: cytoplasm determined by the type of proteins
Characteristic: contains folds (cristae) produced
Function: produces ATP - Proteins’ function is determined by
● Cilia genetics
Location: cell surface - Information in DNA provides the cell
Characteristic: many per cell with a code for its cellular processes
Function: move materials across cell’s DNA
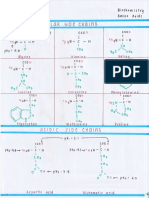
surface - double helix in nucleus
- composed of nucleotides
● Flagella - contains 5 carbon sugar (deoxyribose,
Location: cell surface nitrogen base, phosphate)
Characteristic: 1 per cell
Function: move cell, Ex. sperm Flow of Genetic Information:
● Microvilli - Also called Central Dogma
Location: cell surface Occurs in three stages:
Characteristic: shorter than cilia ● DNA replication
Function: increase surface area ● Transcription
● Cytoskeleton ● Translation
- cell’s framework
- made of proteins DNA Replication
Functions:
- provide support
- hold organelles in place
- enable cell to change shape
Types of Cytoskeleton
- codons: set of 3 nucleotide bases that
code for a particular amino acid
● Translation
- process by mRNA is converted into amino
acids (polypeptides)
- produces proteins
- codons pair with anticodons
- anticodons: 3 nucleotide bases carried by
tRNA
Cell Division (Mitosis)
- formation of 2 daughter cells from a
single parent cell
- uses mitosis and meiosis
- each cell (except sperm and egg)
contains 46 chromosomes (diploid)
- sperm and egg contain 23 chromosomes
65
Mitosis
- cell division that occurs in all cells except
sex cells
- forms 2 daughter cells
● Gene Expression Components of Mitosis
- information in DNA directs protein Chromatid:
synthesis - 2 strands of chromosomes that are
- proteins provide code for gene expression genetically identical
- enzymes regulate chemical reactions Centromere:
- uses transcription and translation - where 2 chromatids are connected
● Transcription Centrioles:
- process by which DNA is “read” - small organelle composed of 9
- occurs in ribosomes triplets
- produces mRNA (messenger RNA) Stages in Mitosis
- mRNA contains codons 1. Interphase:
- time between cell divisions
- DNA is in strands (chromatin)
- DNA replication occurs
2. Prophase:
- chromatin condenses into
chromosomes
- centrioles move to opposite ends
3. Metaphase:
- chromosomes align
4. Anaphase:
- chromatids separate to form 2 sets
of chromosomes
- chromosomes move towards
centrioles
5. Telophase:
- chromosomes disperse
- nuclear envelopes and nucleoli form
- cytoplasm divides to form 2 cells
You might also like
- Basic in Obstetrics and Gynecology 4th PDFDocument384 pagesBasic in Obstetrics and Gynecology 4th PDFsandraamo100% (2)
- Molecular Biology of The Cell, 5th EditionDocument82 pagesMolecular Biology of The Cell, 5th EditionBee Nunes25% (67)
- Anatomy and Physiology - Review NotesDocument11 pagesAnatomy and Physiology - Review NotesKennethNo ratings yet
- 3A Cell Structure and FunctionDocument64 pages3A Cell Structure and FunctionSandra Reyes CervantesNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and FunctionsDocument10 pagesCell Structure and FunctionsQsh SinoroNo ratings yet
- Cells and TissuesDocument5 pagesCells and TissuesEARLRYAN TUMBALENo ratings yet
- Reviewer (Cells)Document6 pagesReviewer (Cells)Sophia Mae ClavecillaNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Cells ReviewerDocument3 pagesAnaphy Cells ReviewerPlacido Edgar MagaNo ratings yet
- 2020 P Bio - Biology Preliminary Notes To SyllabusDocument36 pages2020 P Bio - Biology Preliminary Notes To SyllabusAnahita MerazNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Chapter 3Document13 pagesAnaphy Chapter 3vtangarocan33932No ratings yet
- Cell Structure Lec.3 2 - TaggedDocument28 pagesCell Structure Lec.3 2 - TaggedbaderNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane TransportDocument75 pagesCell Membrane Transportvinay chaudhary100% (1)
- Chapter 2 Transes CellsDocument9 pagesChapter 2 Transes CellsAzy Joy ViñasNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3: Cell Structures and Their Functions CellDocument2 pagesCHAPTER 3: Cell Structures and Their Functions CellCELLINA CLARISSE DE LEONNo ratings yet
- Chapt 3Document7 pagesChapt 3Chelsea MansuetoNo ratings yet
- Cellular Level of OrganizationDocument76 pagesCellular Level of OrganizationCherub DaramanNo ratings yet
- 2 CellsDocument11 pages2 CellsmargaretNo ratings yet
- Cells: Electron MicroscopeDocument7 pagesCells: Electron MicroscopeGabriela ZahiuNo ratings yet
- CellDocument8 pagesCellVivaMapwaNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Lec 3Document5 pagesAnaphy Lec 3khayennekemdumas.24No ratings yet
- Biology Unit Chapters 2 and 3 Plus IBDocument164 pagesBiology Unit Chapters 2 and 3 Plus IBallie3d100% (1)
- Anaphy Chapter 3Document10 pagesAnaphy Chapter 3Akemi LeeNo ratings yet
- Biology Notes: Gifty VargheseDocument18 pagesBiology Notes: Gifty VargheseGvNo ratings yet
- Happ Lec Chapter 3Document9 pagesHapp Lec Chapter 3Raniel SilimNo ratings yet
- 2.lecture 2 - Cell Structure and Function of Organelles PDFDocument73 pages2.lecture 2 - Cell Structure and Function of Organelles PDFMuhammad Danial HasanNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane, Mitochondria & Nucleus Pertemuan 3Document39 pagesCell Membrane, Mitochondria & Nucleus Pertemuan 3Rizky BluesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Cell Structures and Their FunctionsDocument6 pagesChapter 3: Cell Structures and Their FunctionsRayumaaaNo ratings yet
- Prelim Syllabus NotesDocument22 pagesPrelim Syllabus NotesChamsNo ratings yet
- Cells Structure and Their Functions: Mary Winrose B. Tia, RNDocument60 pagesCells Structure and Their Functions: Mary Winrose B. Tia, RNFeah DaydayNo ratings yet
- 7 Transport-Mechanism2Document62 pages7 Transport-Mechanism2aldrin braganzaNo ratings yet
- Cell 1. DiffusionDocument11 pagesCell 1. DiffusionJhoannah DimayugaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Cells & TissuesDocument17 pagesLesson Cells & TissuesJulianne P. VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- AS Level Cells and Cell StructuresDocument54 pagesAS Level Cells and Cell StructuresRamya MalariniNo ratings yet
- 3 Cell Structures FunctionsDocument2 pages3 Cell Structures FunctionsPia Clarisse Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Physio Mga TermsDocument6 pagesPhysio Mga TermsLei FernandezNo ratings yet
- Cell MembraneDocument26 pagesCell MembraneCookies and ReiNo ratings yet
- Cellular Level ReviewerDocument12 pagesCellular Level ReviewerChloe Mikaela MonsantoNo ratings yet
- Animal Cells and TissuesDocument85 pagesAnimal Cells and TissuesnalakaNo ratings yet
- Genbio 1 Review Cell To Cell TransportDocument4 pagesGenbio 1 Review Cell To Cell TransportSofia Monica MontadasNo ratings yet
- 9.4. CellDocument88 pages9.4. CellTUĞRUL ERGÜLNo ratings yet
- Ultimate Biology Revision Notes For O-LevelDocument63 pagesUltimate Biology Revision Notes For O-Leveltanmay.g1474No ratings yet
- General Science Reviewer For LET 2022Document117 pagesGeneral Science Reviewer For LET 2022Elaine May Cabunoc GalvezNo ratings yet
- Reviewer For Genbio 3RD QTRDocument6 pagesReviewer For Genbio 3RD QTRvmargajavierNo ratings yet
- Component of Cell MembraneDocument65 pagesComponent of Cell MembraneAthena YshelleNo ratings yet
- Membranes and Transport: SlidesDocument31 pagesMembranes and Transport: SlidesZohal HayeriNo ratings yet
- The Cell and Plasma MembraneDocument7 pagesThe Cell and Plasma MembraneFrederick ManaigNo ratings yet
- General Biology Exam ReviewerDocument31 pagesGeneral Biology Exam ReviewerRayyyNo ratings yet
- Combined Powerpoints On Cells 2017Document66 pagesCombined Powerpoints On Cells 2017api-242405009No ratings yet
- Cell Structure NotesDocument29 pagesCell Structure Notesjuan esteban MonroyNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 2 Cellular and Chemical Organisation GN - ConceptualDocument74 pagesLECTURE 2 Cellular and Chemical Organisation GN - Conceptualjty4mkp59xNo ratings yet
- CGEN - 100 - #2-Parts of A CellDocument2 pagesCGEN - 100 - #2-Parts of A CellEricka MasakayanNo ratings yet
- Class Notes Cell Membrane Questions/Main IdeaDocument2 pagesClass Notes Cell Membrane Questions/Main IdeaLeasxz ZxsaelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 ReveiwerDocument8 pagesChapter 3 ReveiwerrizzamaegomezoctavianoNo ratings yet
- Transport Mec Hanisms in Biological MembranesDocument51 pagesTransport Mec Hanisms in Biological Membranesjm earlytepNo ratings yet
- Cell Bio Chapter 5Document23 pagesCell Bio Chapter 5busachala517No ratings yet
- Cell Structure and FunctionDocument66 pagesCell Structure and FunctionMark Anthony CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Lec. 2 Chapter 3 (Cell)Document30 pagesLec. 2 Chapter 3 (Cell)Mary Gwen CasuncadNo ratings yet
- Cell MembraneDocument41 pagesCell MembraneBima ArisandiNo ratings yet
- WEEK 3 Cell Structures and PhysiologyDocument9 pagesWEEK 3 Cell Structures and PhysiologyMarjorie Lyka LingatNo ratings yet
- Cell MembraneDocument23 pagesCell MembraneSadaf JavedNo ratings yet
- CellsDocument4 pagesCellsAIRENA RAIN TAMPOSNo ratings yet
- APznzab7n0tTt9B3o6nrEulLujxEm FmBRigdivDocument2 pagesAPznzab7n0tTt9B3o6nrEulLujxEm FmBRigdivJolan Fernando HerceNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Herce Bsmt2bDocument1 pageBiochemistry Herce Bsmt2bJolan Fernando HerceNo ratings yet
- Background of The ProjectDocument2 pagesBackground of The ProjectJolan Fernando HerceNo ratings yet
- 20 Amino Acids Herce Bsmt2bDocument2 pages20 Amino Acids Herce Bsmt2bJolan Fernando HerceNo ratings yet
- Homework 1 Herce Bsmt2bDocument1 pageHomework 1 Herce Bsmt2bJolan Fernando HerceNo ratings yet
- Biochem Herce Bsmt2bDocument3 pagesBiochem Herce Bsmt2bJolan Fernando HerceNo ratings yet
- Letter of Two Students For InterviewDocument1 pageLetter of Two Students For InterviewJolan Fernando HerceNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 Herce Bsmt1bDocument1 pageActivity 1 Herce Bsmt1bJolan Fernando HerceNo ratings yet
- SEATWORK1Document2 pagesSEATWORK1Jolan Fernando HerceNo ratings yet
- Activity On Endocrinology HERCE BSMT1BDocument1 pageActivity On Endocrinology HERCE BSMT1BJolan Fernando HerceNo ratings yet
- ACFrOgBSxI6Havvmnh9Te1qpS qBO9uYA HesicDocument6 pagesACFrOgBSxI6Havvmnh9Te1qpS qBO9uYA HesicJolan Fernando HerceNo ratings yet
- Assessment QuestionnaireDocument3 pagesAssessment QuestionnaireJolan Fernando HerceNo ratings yet
- Cytogen FnalsDocument17 pagesCytogen FnalsJolan Fernando HerceNo ratings yet
- Activity Lab Sheet 4Document5 pagesActivity Lab Sheet 4Jolan Fernando HerceNo ratings yet
- Script For StepsDocument5 pagesScript For StepsJolan Fernando HerceNo ratings yet
- Activity 8 - HERCE - BSMT1BDocument3 pagesActivity 8 - HERCE - BSMT1BJolan Fernando HerceNo ratings yet
- Covid19 Pandemic - HerceDocument6 pagesCovid19 Pandemic - HerceJolan Fernando HerceNo ratings yet
- Medical Quackery and Folk MedicinesDocument2 pagesMedical Quackery and Folk MedicinesJolan Fernando HerceNo ratings yet
- Group Learning ActivityDocument3 pagesGroup Learning ActivityJolan Fernando HerceNo ratings yet
- Practical Test-Balancing and Types of Chemical RXNDocument1 pagePractical Test-Balancing and Types of Chemical RXNJolan Fernando HerceNo ratings yet
- Steps in Foodborne OutbreakDocument2 pagesSteps in Foodborne OutbreakJolan Fernando HerceNo ratings yet
- Biostat and Epi Transes SophomoresDocument60 pagesBiostat and Epi Transes SophomoresJolan Fernando HerceNo ratings yet
- QajjquoisiDocument41 pagesQajjquoisiJolan Fernando HerceNo ratings yet
- Bio ModelDocument12 pagesBio ModelDouuNo ratings yet
- Biology (Midterm, Hki 2021-2022) 1Document4 pagesBiology (Midterm, Hki 2021-2022) 1Nhi TrầnNo ratings yet
- Perfusion Cell Culture ProcessesDocument19 pagesPerfusion Cell Culture ProcessesPosh Arts and CraftsNo ratings yet
- Protein - Britannica Online Encyclopedia PDFDocument46 pagesProtein - Britannica Online Encyclopedia PDFanant mishraNo ratings yet
- Science 10 3rd Quarter Exam - PDF - Messenger Rna - RibosomeDocument1 pageScience 10 3rd Quarter Exam - PDF - Messenger Rna - RibosomeKedir MohammedNo ratings yet
- 02 Lecture Presentation (Bio20-1, Mapua Institute of Technology)Document47 pages02 Lecture Presentation (Bio20-1, Mapua Institute of Technology)Christelle ZuluetaNo ratings yet
- Origins of Life On The Earth and in The CosmosDocument585 pagesOrigins of Life On The Earth and in The CosmosSveti Jeronim100% (3)
- Vaccines 08 00764Document19 pagesVaccines 08 00764Mai Chi PhạmNo ratings yet
- 2nd Puc Biology Reasoning Questions BotanyDocument4 pages2nd Puc Biology Reasoning Questions BotanyRasheed AhmedNo ratings yet
- EOC BookletDocument33 pagesEOC BookletHalden LinNo ratings yet
- Performance Task On Nucleic AcidsDocument3 pagesPerformance Task On Nucleic AcidsPrincess Mejia De VeraNo ratings yet
- Griffiths Introduction To Genetic Analysis 12th EditionDocument3,002 pagesGriffiths Introduction To Genetic Analysis 12th Editionmartin.kv4No ratings yet
- GeneticsDocument55 pagesGeneticsJonathan Carlisle CheungNo ratings yet
- Lets SeeDocument986 pagesLets SeeShehnaaz KhanNo ratings yet
- Orca Share Media1662355444548 6972424090491517852Document9 pagesOrca Share Media1662355444548 6972424090491517852Mic Houston Mar T. ParroNo ratings yet
- 7.3 Translation Nucleic Acid To Polypeptide-Student Sheet PDFDocument3 pages7.3 Translation Nucleic Acid To Polypeptide-Student Sheet PDFMajdalen AzouzNo ratings yet
- Central Dogma of Biology Answer KeyDocument5 pagesCentral Dogma of Biology Answer KeyMusah Lamusah AlaleNo ratings yet
- 2nd Edition Biochemistry Medicomama's QBDocument55 pages2nd Edition Biochemistry Medicomama's QBkvmokshithreddy0708No ratings yet
- Sample Exam2 PDFDocument4 pagesSample Exam2 PDFLorraine M. Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Unit: Genetics and Biotechnology: NYCTA Unit Plan TemplateDocument9 pagesUnit: Genetics and Biotechnology: NYCTA Unit Plan Templateapi-466659492No ratings yet
- COMP90016 2023 06 Data SourcesDocument64 pagesCOMP90016 2023 06 Data SourcesLynn CHENNo ratings yet
- Fermentation: Optimize Bio-Ethanol Production: Property Of: Joie Mga Hampas Lupa Bigyan Niyo Ko NG Ice CreamDocument10 pagesFermentation: Optimize Bio-Ethanol Production: Property Of: Joie Mga Hampas Lupa Bigyan Niyo Ko NG Ice CreamjoieNo ratings yet
- Biocell BlankDocument139 pagesBiocell BlankAchraf RabadiNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 Protein SynthesisDocument8 pagesLesson 5 Protein SynthesisMarc Laurence LadoresNo ratings yet
- Molecular Biology All McqsDocument76 pagesMolecular Biology All Mcqssanullah123khan.13No ratings yet
- PTS 2024 Preparatory Test 33 Solutions EngDocument28 pagesPTS 2024 Preparatory Test 33 Solutions EngPJ 123No ratings yet
- BIF501-Bioinformatics-II Solved Questions FINAL TERM (PAST PAPERS)Document23 pagesBIF501-Bioinformatics-II Solved Questions FINAL TERM (PAST PAPERS)Awais BhuttaNo ratings yet
- Nucleic Acids MODULEDocument6 pagesNucleic Acids MODULEJulius Memeg PanayoNo ratings yet