Professional Documents
Culture Documents
3 Symbols
3 Symbols
Uploaded by
ArdenCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Electrical Systems in A BuildingDocument30 pagesElectrical Systems in A Buildingpipeds100% (6)
- Jenkins Lab Guide: 172-172, 5th Floor Old Mahabalipuram Road (Above Axis Bank-PTC Bus Stop) Thuraipakkam Chennai 600097Document45 pagesJenkins Lab Guide: 172-172, 5th Floor Old Mahabalipuram Road (Above Axis Bank-PTC Bus Stop) Thuraipakkam Chennai 600097thecoinmaniac hodlNo ratings yet
- Big Data in PracticeDocument23 pagesBig Data in PracticevikasNo ratings yet
- MS DOS HackingDocument7 pagesMS DOS Hackingapi-3715801100% (1)
- Basic ElectronicsDocument8 pagesBasic ElectronicsJerry IsaacNo ratings yet
- Active and Passive Electrical ComponentsDocument7 pagesActive and Passive Electrical ComponentsHannahNo ratings yet
- Com 223, WK 4-5Document28 pagesCom 223, WK 4-5Emmanuel ChristianNo ratings yet
- Component 1Document5 pagesComponent 1Ha FaiazNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronic ComponentsDocument5 pagesBasic Electronic ComponentsHa FaiazNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronic Components and Test EquipmentDocument16 pagesBasic Electronic Components and Test EquipmentkamleshyadavmoneyNo ratings yet
- Electronics and Electrical SymbolsDocument10 pagesElectronics and Electrical SymbolsmardyNo ratings yet
- Table of ContentsDocument5 pagesTable of ContentsHa FaiazNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronic CompoentsDocument13 pagesBasic Electronic CompoentsMurali Krishna VelavetiNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronic ComponentsDocument10 pagesBasic Electronic ComponentsEDEN JIMENEZNo ratings yet
- Electronic ComponentsDocument6 pagesElectronic ComponentsKumar KumarrNo ratings yet
- GCSE Electronics Summary: 1. Basic ElectricityDocument4 pagesGCSE Electronics Summary: 1. Basic ElectricitytheedisoncureNo ratings yet
- Unit - I Electrical - BeeeDocument27 pagesUnit - I Electrical - BeeeBubblee BennuNo ratings yet
- Electronic Component - Wikipedia PDFDocument48 pagesElectronic Component - Wikipedia PDFNivas.B100% (1)
- Active Components: These Components Are Those That Have Gain or Directionality.,, Logic GatesDocument4 pagesActive Components: These Components Are Those That Have Gain or Directionality.,, Logic GatesHa FaiazNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronic Components in AutomotiveDocument11 pagesBasic Electronic Components in Automotivedray09No ratings yet
- Name of Electrical Symbols PDFDocument6 pagesName of Electrical Symbols PDFHarsh MittalNo ratings yet
- Basic Concept of DiodesDocument6 pagesBasic Concept of DiodesJANUBAS, GLORIBETH L.No ratings yet
- Electrical SymbolsDocument18 pagesElectrical SymbolsIdzard Morais100% (1)
- Electronic Component: Discrete Device or Physical Entity in AnDocument14 pagesElectronic Component: Discrete Device or Physical Entity in AnyirzebamleNo ratings yet
- Computer Systems Servicing (NCII) Quarter 4 Module 1 Testing Electronic Components (Tec)Document12 pagesComputer Systems Servicing (NCII) Quarter 4 Module 1 Testing Electronic Components (Tec)Xyreel LagurasNo ratings yet
- Electronic ComponentDocument11 pagesElectronic ComponentVinay SinghNo ratings yet
- Electronic Components (Active vs. Passive)Document5 pagesElectronic Components (Active vs. Passive)Djinn CooNo ratings yet
- Circuit Symbols of Electronic ComponentsDocument8 pagesCircuit Symbols of Electronic ComponentsCasandra ClarkNo ratings yet
- Reviewer: Electronics & Communication EngineeringDocument6 pagesReviewer: Electronics & Communication EngineeringAshley De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Electronic ComponentDocument13 pagesElectronic ComponentmcmusbixNo ratings yet
- Digital Logic Design Lesson 04 - Resistor Color Coding (2021)Document5 pagesDigital Logic Design Lesson 04 - Resistor Color Coding (2021)Jong Suk LeeNo ratings yet
- Electronics 15.1 Resource GuideDocument58 pagesElectronics 15.1 Resource Guidemister8829No ratings yet
- Lab Practice-1 (Circuit Symbols)Document7 pagesLab Practice-1 (Circuit Symbols)awien28No ratings yet
- Electrical Symbols & Electronic SymbolsDocument6 pagesElectrical Symbols & Electronic SymbolsAhmad Bin Ismail KhanNo ratings yet
- Electronic Circuit DEMODocument33 pagesElectronic Circuit DEMORianne Lore ArueloNo ratings yet
- Basics of ElectronicsDocument23 pagesBasics of Electronicsnonake8617No ratings yet
- Ele DevicesDocument3 pagesEle DevicesSatyaNo ratings yet
- Eee 1003 VitDocument71 pagesEee 1003 VitAlok100% (1)
- Difference Between Active and Passive Components (In Electronics)Document12 pagesDifference Between Active and Passive Components (In Electronics)jackNo ratings yet
- Eec 115 Experiment I & IiDocument12 pagesEec 115 Experiment I & IiOreoluwa OmiyaleNo ratings yet
- EQUIPMENT2536Document1 pageEQUIPMENT2536Amresh KumarNo ratings yet
- Circuit Symbols of Electronic ComponentsDocument8 pagesCircuit Symbols of Electronic ComponentsEBENo ratings yet
- Electrical and Electronic Circuit and DevicesDocument2 pagesElectrical and Electronic Circuit and DevicesjgecainNo ratings yet
- Electrical & Electronic SymbolsDocument7 pagesElectrical & Electronic Symbolsecruz_yhwhNo ratings yet
- TransistorsDocument6 pagesTransistorsdeepakvasavaNo ratings yet
- Unit Four (Cuarta Unidad)Document7 pagesUnit Four (Cuarta Unidad)Madewill DuránNo ratings yet
- 3 TcHxW6S6 k3B8VuouvuA Mod2 Devices QC Whiteoutsremoved Mar 2021Document173 pages3 TcHxW6S6 k3B8VuouvuA Mod2 Devices QC Whiteoutsremoved Mar 2021Umair Ejaz ButtNo ratings yet
- Electronic Component: Adding Citations To Reliable SourcesDocument26 pagesElectronic Component: Adding Citations To Reliable SourcesShimadzu SPMINo ratings yet
- Beato Bscpe3b Cedd Act3 EditedDocument2 pagesBeato Bscpe3b Cedd Act3 EditedBeato MichaelNo ratings yet
- Electrical Symbols & Electronic SymbolsDocument6 pagesElectrical Symbols & Electronic SymbolsJeric Gader BriosoNo ratings yet
- Ee AssignmentDocument4 pagesEe AssignmentCarloen S. LadreraNo ratings yet
- Electrical / Electronics: After Studying This Chapter, You Will Be Familiar WithDocument15 pagesElectrical / Electronics: After Studying This Chapter, You Will Be Familiar WithjohnNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of EleectronicsDocument32 pagesFundamentals of EleectronicsPillo Pillo PilloNo ratings yet
- Activity2 - ELECTRONIC SYMBOLSDocument3 pagesActivity2 - ELECTRONIC SYMBOLSgil valerioNo ratings yet
- Basic CompDocument27 pagesBasic Compitamar_123No ratings yet
- Electrical SymbolsDocument6 pagesElectrical SymbolsAnant Catalyst ShuklaNo ratings yet
- 3 FC 93 D 5Document3 pages3 FC 93 D 5wkanda techNo ratings yet
- Electrical SymbolsDocument7 pagesElectrical SymbolsZativa AlyaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Symbols & Electronic SymbolsDocument7 pagesElectrical Symbols & Electronic SymbolsSilviu IlNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering SymbolDocument8 pagesElectrical Engineering SymbolAnupam BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Electronics ComponentsDocument13 pagesElectronics ComponentsJimmy Makiling PamugasNo ratings yet
- Etrobility Latform: Installation & User GuideDocument30 pagesEtrobility Latform: Installation & User GuideYoel ArmasNo ratings yet
- Barmex Bandas Catalogo Roulunds 416296Document154 pagesBarmex Bandas Catalogo Roulunds 416296peibolrz100% (2)
- L&T MCCB Product CatalougeDocument84 pagesL&T MCCB Product CatalougeKishore Krishna92% (13)
- 2SC2458Document5 pages2SC2458Rolando P BartolomeNo ratings yet
- Refval 1209Document40 pagesRefval 1209LuisNo ratings yet
- Microsoft SQL Server 2019: Licensing GuideDocument38 pagesMicrosoft SQL Server 2019: Licensing GuidemistersatNo ratings yet
- Universal Audio UAD Lexicon 224Document1 pageUniversal Audio UAD Lexicon 224Zizja TurtleNo ratings yet
- Office Scripts With ChatGPTDocument13 pagesOffice Scripts With ChatGPTRobin KavalonNo ratings yet
- Web Tech PresentationDocument48 pagesWeb Tech PresentationSimbarashe HlanyaNo ratings yet
- Memory Hierarchy - CachesDocument51 pagesMemory Hierarchy - CachesAmanda Judy AndradeNo ratings yet
- Programming Software: Instruction ManualDocument65 pagesProgramming Software: Instruction Manualm irfan jalilNo ratings yet
- SSP 272 Phaeton ObpsDocument37 pagesSSP 272 Phaeton Obpsภูเก็ต เป็นเกาะNo ratings yet
- Modeling and Thermal Simulation of A PHEV Battery Module With Cylindrical LFP CellsDocument11 pagesModeling and Thermal Simulation of A PHEV Battery Module With Cylindrical LFP CellsNavamani PrakashNo ratings yet
- Director Operations Logistics Inventory in New York City Resume Jon LapDocument2 pagesDirector Operations Logistics Inventory in New York City Resume Jon LapJon LapNo ratings yet
- Sensor Based Automated Irrigation System With Iot A Technical ReviewDocument4 pagesSensor Based Automated Irrigation System With Iot A Technical ReviewJhanina CapicioNo ratings yet
- OFA-CF - Workbook - PreWeek - Day 1Document13 pagesOFA-CF - Workbook - PreWeek - Day 1beanbeanNo ratings yet
- Unseen Class Discovery in Open-World Classification: A Project ReportDocument48 pagesUnseen Class Discovery in Open-World Classification: A Project ReportpoojaNo ratings yet
- Sustainable in Bahrain-Thesis PDFDocument12 pagesSustainable in Bahrain-Thesis PDFTarek AbbasNo ratings yet
- AD-19-06 Rev 2 OHS Technical QuestionnaireDocument15 pagesAD-19-06 Rev 2 OHS Technical QuestionnairejesusNo ratings yet
- DbSpectra Catalog 17.2Document109 pagesDbSpectra Catalog 17.2michaelethompson100% (1)
- Test Physical Standby With FlashbackDocument3 pagesTest Physical Standby With FlashbackSyed NaumanNo ratings yet
- EEN 443 Communication Systems II ADocument2 pagesEEN 443 Communication Systems II AjulioNo ratings yet
- Catalogo AVTRON EncodersDocument32 pagesCatalogo AVTRON EncodersMiguel Ángel Castillo HernándezNo ratings yet
- Configuring An LDAP AAA Server: Selected ASDM VPN Procedures, Version 5.2 (1) OL-10670-01Document14 pagesConfiguring An LDAP AAA Server: Selected ASDM VPN Procedures, Version 5.2 (1) OL-10670-01Khalil NiniNo ratings yet
- FSB - L4 - LARAEFSB2020-31 - Moto E6s Moto G8 Power Lite - Device Starting To MTK Test Mode ScreenDocument3 pagesFSB - L4 - LARAEFSB2020-31 - Moto E6s Moto G8 Power Lite - Device Starting To MTK Test Mode ScreenSaúl ríosNo ratings yet
- Cummins Diessel Engine m11 Troubleshooting and Repair ManualDocument20 pagesCummins Diessel Engine m11 Troubleshooting and Repair Manualevelyn100% (58)
- Solid Seismic CableDocument6 pagesSolid Seismic CablechenxqNo ratings yet
3 Symbols
3 Symbols
Uploaded by
ArdenOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
3 Symbols
3 Symbols
Uploaded by
ArdenCopyright:
Available Formats
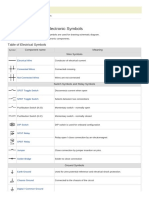
Module 1 – Fundamentals of Electricity and Electronics 1
ELECTRONIC/SCHEMATIC SYMBOL
An electronic symbol is a pictogram used to
represent various electrical and electronic devices
in a schematic diagram of an electrical
or electronic circuit.
Graphical symbols not only identify a
components position but the type of electrical
element too, whether it’s resistive, inductive,
capacitive, mechanical, etc. Thus in circuit
diagrams and schematics, graphical symbols
identify and represent electrical and electronic
devices and show how they are electrically
connected together while drawing lines between
them represents the wires or component leads.
The connecting leads or pins of a component in
a schematic diagram can be identified using letters
or abreviations. For example, the connecting leads
of a bipolar junction transistor, (BJT) are identified
as E (emitter), B (base), and C (collector). Arrows
are also used within schematic symbols to indicate
the direction of current flow around a circuit or
through a component, or are used as part of their
graphical symbol to show that the components has
a variable or adjustable value. For example, a
potentiometer or rheostat.
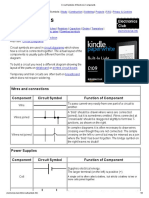
Basic Electricity and Electronics
Module 1 – Fundamentals of Electricity and Electronics 2
Although electrical components are
represented by universally accepted schematic
symbols, there are a number of variants and
alternative symbols used throughout the world to
represent the same electrical component or device.
For example, the IEC (International
Electrotechnical Commission) have one set of
symbols, while the IEEE (Institute of Electrical and
Electronics Engineers) have an alternative set of
symbols for the same component.
Basic Electricity and Electronics
Module 1 – Fundamentals of Electricity and Electronics 3
Basic Electricity and Electronics
Module 1 – Fundamentals of Electricity and Electronics 4
Basic Electricity and Electronics
Module 1 – Fundamentals of Electricity and Electronics 5
Basic Electricity and Electronics
Module 1 – Fundamentals of Electricity and Electronics 6
Basic Electricity and Electronics
Module 1 – Fundamentals of Electricity and Electronics 7
Basic Electricity and Electronics
Module 1 – Fundamentals of Electricity and Electronics 8
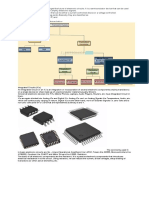
Passive Electronic Components
Passive electronic components are those that
don’t have the ability to control electric current by
means of another electrical signal. Examples of passive
electronic components are capacitors, resistors,
inductors, transformers, and some diodes.
Electromechanical
Basic Components
Components
Piezoelectric devices
Resistors (All Types) Crystals
Capacitors (All Resonators
Types) Terminals and
Inductors / Coil Connectors
Memristor / Network Cables
Sensors Switches
Detectors Circuit Protection
Transducers Devices
Antennas PCB
Assembly Modules Mechanical Devices
such as a Fan, Lamp
Basic Electricity and Electronics
Module 1 – Fundamentals of Electricity and Electronics 9
Active Electronic Components
Active electronic components are those that can
control the flow of electricity.
Active Electronic Components
Diodes Photo Vacuum Tubes
Rectifier Diode Transistor Rectifier Tubes
Schottky Diode Darlington Digital Circuit
Zener Diode
Transistor Analog Circuit
Compound Current Sensor
Varicap
Varactor
Transistor BGA Packages
Composition Processor
Transistors
MOSFET
Transistors Ignitron
CRT / LCD / Unipolar / Bipolar
(FET)
VFD / TFT/ Diode
JFET LED
ICs Hall Effect Sensor
Emitters Thyratron
Power ICs Battery / PS
Solar PV Cell Optoelectronic
Electric Gas discharge tube
Thyristors Generator
Basic Electricity and Electronics
You might also like
- Electrical Systems in A BuildingDocument30 pagesElectrical Systems in A Buildingpipeds100% (6)
- Jenkins Lab Guide: 172-172, 5th Floor Old Mahabalipuram Road (Above Axis Bank-PTC Bus Stop) Thuraipakkam Chennai 600097Document45 pagesJenkins Lab Guide: 172-172, 5th Floor Old Mahabalipuram Road (Above Axis Bank-PTC Bus Stop) Thuraipakkam Chennai 600097thecoinmaniac hodlNo ratings yet
- Big Data in PracticeDocument23 pagesBig Data in PracticevikasNo ratings yet
- MS DOS HackingDocument7 pagesMS DOS Hackingapi-3715801100% (1)
- Basic ElectronicsDocument8 pagesBasic ElectronicsJerry IsaacNo ratings yet
- Active and Passive Electrical ComponentsDocument7 pagesActive and Passive Electrical ComponentsHannahNo ratings yet
- Com 223, WK 4-5Document28 pagesCom 223, WK 4-5Emmanuel ChristianNo ratings yet
- Component 1Document5 pagesComponent 1Ha FaiazNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronic ComponentsDocument5 pagesBasic Electronic ComponentsHa FaiazNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronic Components and Test EquipmentDocument16 pagesBasic Electronic Components and Test EquipmentkamleshyadavmoneyNo ratings yet
- Electronics and Electrical SymbolsDocument10 pagesElectronics and Electrical SymbolsmardyNo ratings yet
- Table of ContentsDocument5 pagesTable of ContentsHa FaiazNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronic CompoentsDocument13 pagesBasic Electronic CompoentsMurali Krishna VelavetiNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronic ComponentsDocument10 pagesBasic Electronic ComponentsEDEN JIMENEZNo ratings yet
- Electronic ComponentsDocument6 pagesElectronic ComponentsKumar KumarrNo ratings yet
- GCSE Electronics Summary: 1. Basic ElectricityDocument4 pagesGCSE Electronics Summary: 1. Basic ElectricitytheedisoncureNo ratings yet
- Unit - I Electrical - BeeeDocument27 pagesUnit - I Electrical - BeeeBubblee BennuNo ratings yet
- Electronic Component - Wikipedia PDFDocument48 pagesElectronic Component - Wikipedia PDFNivas.B100% (1)
- Active Components: These Components Are Those That Have Gain or Directionality.,, Logic GatesDocument4 pagesActive Components: These Components Are Those That Have Gain or Directionality.,, Logic GatesHa FaiazNo ratings yet
- Basic Electronic Components in AutomotiveDocument11 pagesBasic Electronic Components in Automotivedray09No ratings yet
- Name of Electrical Symbols PDFDocument6 pagesName of Electrical Symbols PDFHarsh MittalNo ratings yet
- Basic Concept of DiodesDocument6 pagesBasic Concept of DiodesJANUBAS, GLORIBETH L.No ratings yet
- Electrical SymbolsDocument18 pagesElectrical SymbolsIdzard Morais100% (1)
- Electronic Component: Discrete Device or Physical Entity in AnDocument14 pagesElectronic Component: Discrete Device or Physical Entity in AnyirzebamleNo ratings yet
- Computer Systems Servicing (NCII) Quarter 4 Module 1 Testing Electronic Components (Tec)Document12 pagesComputer Systems Servicing (NCII) Quarter 4 Module 1 Testing Electronic Components (Tec)Xyreel LagurasNo ratings yet
- Electronic ComponentDocument11 pagesElectronic ComponentVinay SinghNo ratings yet
- Electronic Components (Active vs. Passive)Document5 pagesElectronic Components (Active vs. Passive)Djinn CooNo ratings yet
- Circuit Symbols of Electronic ComponentsDocument8 pagesCircuit Symbols of Electronic ComponentsCasandra ClarkNo ratings yet
- Reviewer: Electronics & Communication EngineeringDocument6 pagesReviewer: Electronics & Communication EngineeringAshley De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Electronic ComponentDocument13 pagesElectronic ComponentmcmusbixNo ratings yet
- Digital Logic Design Lesson 04 - Resistor Color Coding (2021)Document5 pagesDigital Logic Design Lesson 04 - Resistor Color Coding (2021)Jong Suk LeeNo ratings yet
- Electronics 15.1 Resource GuideDocument58 pagesElectronics 15.1 Resource Guidemister8829No ratings yet
- Lab Practice-1 (Circuit Symbols)Document7 pagesLab Practice-1 (Circuit Symbols)awien28No ratings yet
- Electrical Symbols & Electronic SymbolsDocument6 pagesElectrical Symbols & Electronic SymbolsAhmad Bin Ismail KhanNo ratings yet
- Electronic Circuit DEMODocument33 pagesElectronic Circuit DEMORianne Lore ArueloNo ratings yet
- Basics of ElectronicsDocument23 pagesBasics of Electronicsnonake8617No ratings yet
- Ele DevicesDocument3 pagesEle DevicesSatyaNo ratings yet
- Eee 1003 VitDocument71 pagesEee 1003 VitAlok100% (1)
- Difference Between Active and Passive Components (In Electronics)Document12 pagesDifference Between Active and Passive Components (In Electronics)jackNo ratings yet
- Eec 115 Experiment I & IiDocument12 pagesEec 115 Experiment I & IiOreoluwa OmiyaleNo ratings yet
- EQUIPMENT2536Document1 pageEQUIPMENT2536Amresh KumarNo ratings yet
- Circuit Symbols of Electronic ComponentsDocument8 pagesCircuit Symbols of Electronic ComponentsEBENo ratings yet
- Electrical and Electronic Circuit and DevicesDocument2 pagesElectrical and Electronic Circuit and DevicesjgecainNo ratings yet
- Electrical & Electronic SymbolsDocument7 pagesElectrical & Electronic Symbolsecruz_yhwhNo ratings yet
- TransistorsDocument6 pagesTransistorsdeepakvasavaNo ratings yet
- Unit Four (Cuarta Unidad)Document7 pagesUnit Four (Cuarta Unidad)Madewill DuránNo ratings yet
- 3 TcHxW6S6 k3B8VuouvuA Mod2 Devices QC Whiteoutsremoved Mar 2021Document173 pages3 TcHxW6S6 k3B8VuouvuA Mod2 Devices QC Whiteoutsremoved Mar 2021Umair Ejaz ButtNo ratings yet
- Electronic Component: Adding Citations To Reliable SourcesDocument26 pagesElectronic Component: Adding Citations To Reliable SourcesShimadzu SPMINo ratings yet
- Beato Bscpe3b Cedd Act3 EditedDocument2 pagesBeato Bscpe3b Cedd Act3 EditedBeato MichaelNo ratings yet
- Electrical Symbols & Electronic SymbolsDocument6 pagesElectrical Symbols & Electronic SymbolsJeric Gader BriosoNo ratings yet
- Ee AssignmentDocument4 pagesEe AssignmentCarloen S. LadreraNo ratings yet
- Electrical / Electronics: After Studying This Chapter, You Will Be Familiar WithDocument15 pagesElectrical / Electronics: After Studying This Chapter, You Will Be Familiar WithjohnNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of EleectronicsDocument32 pagesFundamentals of EleectronicsPillo Pillo PilloNo ratings yet
- Activity2 - ELECTRONIC SYMBOLSDocument3 pagesActivity2 - ELECTRONIC SYMBOLSgil valerioNo ratings yet
- Basic CompDocument27 pagesBasic Compitamar_123No ratings yet
- Electrical SymbolsDocument6 pagesElectrical SymbolsAnant Catalyst ShuklaNo ratings yet
- 3 FC 93 D 5Document3 pages3 FC 93 D 5wkanda techNo ratings yet
- Electrical SymbolsDocument7 pagesElectrical SymbolsZativa AlyaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Symbols & Electronic SymbolsDocument7 pagesElectrical Symbols & Electronic SymbolsSilviu IlNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering SymbolDocument8 pagesElectrical Engineering SymbolAnupam BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Electronics ComponentsDocument13 pagesElectronics ComponentsJimmy Makiling PamugasNo ratings yet
- Etrobility Latform: Installation & User GuideDocument30 pagesEtrobility Latform: Installation & User GuideYoel ArmasNo ratings yet
- Barmex Bandas Catalogo Roulunds 416296Document154 pagesBarmex Bandas Catalogo Roulunds 416296peibolrz100% (2)
- L&T MCCB Product CatalougeDocument84 pagesL&T MCCB Product CatalougeKishore Krishna92% (13)
- 2SC2458Document5 pages2SC2458Rolando P BartolomeNo ratings yet
- Refval 1209Document40 pagesRefval 1209LuisNo ratings yet
- Microsoft SQL Server 2019: Licensing GuideDocument38 pagesMicrosoft SQL Server 2019: Licensing GuidemistersatNo ratings yet
- Universal Audio UAD Lexicon 224Document1 pageUniversal Audio UAD Lexicon 224Zizja TurtleNo ratings yet
- Office Scripts With ChatGPTDocument13 pagesOffice Scripts With ChatGPTRobin KavalonNo ratings yet
- Web Tech PresentationDocument48 pagesWeb Tech PresentationSimbarashe HlanyaNo ratings yet
- Memory Hierarchy - CachesDocument51 pagesMemory Hierarchy - CachesAmanda Judy AndradeNo ratings yet
- Programming Software: Instruction ManualDocument65 pagesProgramming Software: Instruction Manualm irfan jalilNo ratings yet
- SSP 272 Phaeton ObpsDocument37 pagesSSP 272 Phaeton Obpsภูเก็ต เป็นเกาะNo ratings yet
- Modeling and Thermal Simulation of A PHEV Battery Module With Cylindrical LFP CellsDocument11 pagesModeling and Thermal Simulation of A PHEV Battery Module With Cylindrical LFP CellsNavamani PrakashNo ratings yet
- Director Operations Logistics Inventory in New York City Resume Jon LapDocument2 pagesDirector Operations Logistics Inventory in New York City Resume Jon LapJon LapNo ratings yet
- Sensor Based Automated Irrigation System With Iot A Technical ReviewDocument4 pagesSensor Based Automated Irrigation System With Iot A Technical ReviewJhanina CapicioNo ratings yet
- OFA-CF - Workbook - PreWeek - Day 1Document13 pagesOFA-CF - Workbook - PreWeek - Day 1beanbeanNo ratings yet
- Unseen Class Discovery in Open-World Classification: A Project ReportDocument48 pagesUnseen Class Discovery in Open-World Classification: A Project ReportpoojaNo ratings yet
- Sustainable in Bahrain-Thesis PDFDocument12 pagesSustainable in Bahrain-Thesis PDFTarek AbbasNo ratings yet
- AD-19-06 Rev 2 OHS Technical QuestionnaireDocument15 pagesAD-19-06 Rev 2 OHS Technical QuestionnairejesusNo ratings yet
- DbSpectra Catalog 17.2Document109 pagesDbSpectra Catalog 17.2michaelethompson100% (1)
- Test Physical Standby With FlashbackDocument3 pagesTest Physical Standby With FlashbackSyed NaumanNo ratings yet
- EEN 443 Communication Systems II ADocument2 pagesEEN 443 Communication Systems II AjulioNo ratings yet
- Catalogo AVTRON EncodersDocument32 pagesCatalogo AVTRON EncodersMiguel Ángel Castillo HernándezNo ratings yet
- Configuring An LDAP AAA Server: Selected ASDM VPN Procedures, Version 5.2 (1) OL-10670-01Document14 pagesConfiguring An LDAP AAA Server: Selected ASDM VPN Procedures, Version 5.2 (1) OL-10670-01Khalil NiniNo ratings yet
- FSB - L4 - LARAEFSB2020-31 - Moto E6s Moto G8 Power Lite - Device Starting To MTK Test Mode ScreenDocument3 pagesFSB - L4 - LARAEFSB2020-31 - Moto E6s Moto G8 Power Lite - Device Starting To MTK Test Mode ScreenSaúl ríosNo ratings yet
- Cummins Diessel Engine m11 Troubleshooting and Repair ManualDocument20 pagesCummins Diessel Engine m11 Troubleshooting and Repair Manualevelyn100% (58)
- Solid Seismic CableDocument6 pagesSolid Seismic CablechenxqNo ratings yet