Professional Documents
Culture Documents
DelaCruz AlbertBryan Activity#6 MED3
DelaCruz AlbertBryan Activity#6 MED3
Uploaded by
AlbertOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
DelaCruz AlbertBryan Activity#6 MED3
DelaCruz AlbertBryan Activity#6 MED3
Uploaded by
AlbertCopyright:
Available Formats
Dela Cruz, Albert Bryan R.
BSMT - 1 | March 5, 2022
Human Histology (MED 3)
Activity #6
Integumentary System
Using the same format, do the following activities:
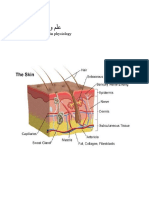
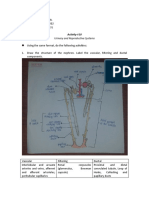
1. Illustrate and label human skin.
2. Identify the following cells and give their specific function.
Melanocytes
The melanocytes are irregular-shaped, neural crest-derived cells
which have many processes and extend between the epithelial cells
of stratum basale and stratum spinosum. Melanocytes are
responsible for the production of melanin, a group of brown-black
(eumelanin) and yellow-red (pheomelanin) primarily responsible to
the pigmentation of the skin and hair.
Merkel cells
Langerhans cells
3. Differentiate apocrine sweat glands and eccrine sweat glands.
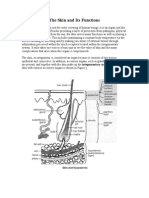
One of the glands found in our body are the sweat glands. As its name
suggests, sweat glands or sudoriferous glands, are exocrine glands found in
in many areas of the skin that produces sweat. There are two types of sweat
glands, the eccrine and apocrine. The eccrine or merocrine sweat glands are
found in almost every part of the skin (most numerous in palms and soles),
and are considered as the most common type. In this sweat gland, the
sweat produced is thin watery with little salts. On the other hand, the
apocrine sweat glands are found in the groin, the scalp and the armpits.
Unlike the eccrine sweat glands, the apocrine sweat glands produce thick
secretions that contain organic substances, which usually has odor.
4. What are sebaceous glands? What do they secrete and to what structures are
they most associated?
Another type of gland present in the integumentary system are the
sebaceous glands. These are simple, acinar glands that are usually
connected by a duct to the upper part of the hair follicles. It is responsible
to the production of sebum, a white, fatty substance that contains lipids.
The produced sebum of the sebaceous glands helps in lubricating and
preventing moisture loss in the hair and skin, and in trapping microbes and
bacteria. Sebaceous glands are considered apocrine since sebum is released
by the lysis and death of secretory cells.
5. Identify the following receptors and give their specific functions.
Free nerve endings
Merkel's ending
Meissner corpuscles
Pacinian corpuscles
You might also like
- Integumentary System: Quick Review Notes Chapter 5From EverandIntegumentary System: Quick Review Notes Chapter 5Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Bercadez, Ma. Benita GROUP 1 - BSN 1 I - Laboratory Exercise No. 4 5Document15 pagesBercadez, Ma. Benita GROUP 1 - BSN 1 I - Laboratory Exercise No. 4 5Ma. Benita BercadezNo ratings yet
- The Physiology of The SkinDocument39 pagesThe Physiology of The SkinElvisNo ratings yet
- Skin Anatomy: Prof: Shekhar TeliDocument21 pagesSkin Anatomy: Prof: Shekhar TeliShekhar TeliNo ratings yet
- Presentation About Skin PhysiologyDocument9 pagesPresentation About Skin PhysiologyWalaa Bani IrheadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Integumentary SystemDocument9 pagesChapter 6 Integumentary SystemKier Liboon EcleNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument13 pagesIntegumentary System Anatomy and PhysiologyKBD0% (1)
- Physiology of Skin-1Document27 pagesPhysiology of Skin-1stephenotibu03No ratings yet
- 3 The Integumentary System: Section IDocument18 pages3 The Integumentary System: Section IVõ ĐứcNo ratings yet
- Nursing Department: The Integumentary Systemزاهجل اDocument34 pagesNursing Department: The Integumentary Systemزاهجل اوجد عمرNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Holes Essentials of Human Anatomy Physiology 14th Edition Charles WelshDocument5 pagesSolution Manual For Holes Essentials of Human Anatomy Physiology 14th Edition Charles WelshCristianRodriguezpawry100% (84)
- Chapter 5 IntegumentaryDocument8 pagesChapter 5 IntegumentaryClark Jeth VicenteNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Integumentary SystemDocument4 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Integumentary Systemmao4evah0% (1)
- Integumentary SystemDocument18 pagesIntegumentary SystemRenjyl Gay DeguinionNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Integumentary SystemDocument5 pagesAnatomy of The Integumentary SystemSmol PadernalNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System Lab Report 1Document12 pagesIntegumentary System Lab Report 1api-374265257No ratings yet
- TUGAS Agus SusantoDocument3 pagesTUGAS Agus SusantoAgus Tiwansyah AbunasibNo ratings yet
- Skin PhysiologyDocument7 pagesSkin PhysiologyYash PandeyNo ratings yet
- The Integumentary SystemDocument12 pagesThe Integumentary Systemmiftahukhamis1No ratings yet
- II Integumentary SystemDocument51 pagesII Integumentary SystemRosa DeveraNo ratings yet
- Integumentary-SystemDocument3 pagesIntegumentary-SystemCharisse Elica LucasNo ratings yet
- The Integumentary System - Cliffnotes A&pDocument4 pagesThe Integumentary System - Cliffnotes A&pdbelmerNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Activity - Integumentary SystemDocument6 pagesLaboratory Activity - Integumentary SystemJaw LastNo ratings yet
- IntegumentaryDocument15 pagesIntegumentaryhayascent hilarioNo ratings yet
- SkinDocument1 pageSkinamy28stewartNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System ReportingDocument49 pagesIntegumentary System Reportingalmira garciaNo ratings yet
- Mammalian Anatomy and Physiology Reading MaterialDocument76 pagesMammalian Anatomy and Physiology Reading Materialtemesgenamare267No ratings yet
- Accessory Structures (REVISED)Document2 pagesAccessory Structures (REVISED)CARL JOSHUA DAODAOENNo ratings yet
- Physiology of The Skin: Dr. Mohamed HassanDocument45 pagesPhysiology of The Skin: Dr. Mohamed HassanSAKARIYE MAXAMEDNo ratings yet
- Structure SkincolorDocument32 pagesStructure SkincolorHelping Five (H5)No ratings yet
- Skin 2012Document21 pagesSkin 2012loulou612No ratings yet
- Skin and Body Membranes: Human Anatomy and Physiology Mr. MccammonDocument36 pagesSkin and Body Membranes: Human Anatomy and Physiology Mr. MccammonMaryamAlEmadiNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System and SkeletalDocument21 pagesIntegumentary System and SkeletalApril MaeNo ratings yet
- INTEGUMENTARY SYsTEMDocument42 pagesINTEGUMENTARY SYsTEMGabNo ratings yet
- Wk6 Integumentary System IIIDocument3 pagesWk6 Integumentary System IIILindenScholesNo ratings yet
- 0rder 427 Anatomy-Chapter 5 AssignmentDocument9 pages0rder 427 Anatomy-Chapter 5 Assignmentjoshua chegeNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System Lab Report: Lauren WilleyDocument5 pagesIntegumentary System Lab Report: Lauren Willeyapi-296594594100% (1)
- Skin and Breast HistologyDocument8 pagesSkin and Breast HistologyPraveena MoganNo ratings yet
- Skin (Integumentary System)Document16 pagesSkin (Integumentary System)sweet_toxiqueNo ratings yet
- Week 10 - Unit TaskDocument3 pagesWeek 10 - Unit TaskARRWEN DOMINIQUE YZABELLE TUAZONNo ratings yet
- The Integumentary SystemDocument23 pagesThe Integumentary Systemtareqhaddad123No ratings yet
- 3 The SkinDocument4 pages3 The SkinSenthereng MoaisiNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of SkinDocument25 pagesAnatomy of Skinaimi Batrisyia100% (1)
- Integumentary SystemDocument16 pagesIntegumentary SystemFlorinel B. LACATANNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of Sweat GlandDocument43 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Sweat GlandUjjwala VermaNo ratings yet
- Science6 Q2 W2 1Document9 pagesScience6 Q2 W2 1Matt The idkNo ratings yet
- Skin Lecture 2Document7 pagesSkin Lecture 2bv2328002No ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument22 pagesIntegumentary Systemnimfa t. plazaNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Pointers - Intregumentary OnlyDocument21 pagesAnaphy Pointers - Intregumentary OnlyDarwin DicoNo ratings yet
- 4 Ntegumentary SystemDocument8 pages4 Ntegumentary SystemAmanuel MaruNo ratings yet
- Skin SystemDocument14 pagesSkin SystemWannabee ChubyNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The SkinDocument40 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The SkinRicko Ciady100% (1)
- MODULE 4 Ana PhysioDocument11 pagesMODULE 4 Ana Physiojoshua ordenaNo ratings yet
- SkinDocument25 pagesSkinDJ DannyNo ratings yet
- Anatomy Lec.3Document6 pagesAnatomy Lec.3aminqasm111No ratings yet
- Accessory of Skin FunctionDocument3 pagesAccessory of Skin FunctiongrapikmsNo ratings yet
- Functions of The SkinDocument5 pagesFunctions of The SkinDenzow CalantocNo ratings yet
- Dermatology Notes Handbook of Medical inDocument22 pagesDermatology Notes Handbook of Medical inMian BazanNo ratings yet
- SKINDocument30 pagesSKINShafaqat Ghani Shafaqat GhaniNo ratings yet
- Hematology PresentationDocument13 pagesHematology PresentationAlbertNo ratings yet
- DelaCruz Albert SoAr2 PortfolioDocument15 pagesDelaCruz Albert SoAr2 PortfolioAlbertNo ratings yet
- DelaCruz Albert SoulmakingDocument1 pageDelaCruz Albert SoulmakingAlbertNo ratings yet
- DelaCruz Albert SCI1 BalancingDocument2 pagesDelaCruz Albert SCI1 BalancingAlbertNo ratings yet
- DelaCruz Albert VanGoghDocument1 pageDelaCruz Albert VanGoghAlbertNo ratings yet
- DelaCruz Albert SoulmakingDocument1 pageDelaCruz Albert SoulmakingAlbertNo ratings yet
- DelaCruz AlbertBryan TEM 02act1Document2 pagesDelaCruz AlbertBryan TEM 02act1AlbertNo ratings yet
- DelaCruz Albert Exercise7 ManualDocument3 pagesDelaCruz Albert Exercise7 ManualAlbertNo ratings yet
- DelaCruz Albert SoAr2 ArtisTechDocument2 pagesDelaCruz Albert SoAr2 ArtisTechAlbertNo ratings yet
- DelaCruz Albert Lecture6Document2 pagesDelaCruz Albert Lecture6AlbertNo ratings yet
- DelaCruz AlbertBryan TEM 02PETA1Document1 pageDelaCruz AlbertBryan TEM 02PETA1AlbertNo ratings yet
- DelaCruz Albert Exercise8 ManualDocument4 pagesDelaCruz Albert Exercise8 ManualAlbertNo ratings yet
- DelaCruz Albert Artist&ArtisanDocument1 pageDelaCruz Albert Artist&ArtisanAlbertNo ratings yet
- DelaCruz Albert Exercise1 ManualDocument4 pagesDelaCruz Albert Exercise1 ManualAlbertNo ratings yet
- DelaCruz Albert Exercise3 ManualDocument2 pagesDelaCruz Albert Exercise3 ManualAlbertNo ratings yet
- DelaCruz Albert Exercise6 ManualDocument4 pagesDelaCruz Albert Exercise6 ManualAlbertNo ratings yet
- DelaCruz Albert Exercise4 ManualDocument4 pagesDelaCruz Albert Exercise4 ManualAlbertNo ratings yet
- DelaCruz Albert Exercise2 ManualDocument3 pagesDelaCruz Albert Exercise2 ManualAlbertNo ratings yet
- DelaCruz AlbertBryan SCI1 Quiz5Document2 pagesDelaCruz AlbertBryan SCI1 Quiz5AlbertNo ratings yet
- DelaCruz Albert Exercise5Document2 pagesDelaCruz Albert Exercise5AlbertNo ratings yet
- DelaCruz AlbertBryan TEM 02PETA1Document1 pageDelaCruz AlbertBryan TEM 02PETA1AlbertNo ratings yet
- DelaCruz AlbertBryan Activity#10 MED3Document5 pagesDelaCruz AlbertBryan Activity#10 MED3AlbertNo ratings yet
- DelaCruz AlbertBryan Activity#9 MED3Document4 pagesDelaCruz AlbertBryan Activity#9 MED3AlbertNo ratings yet
- DelaCruz AlbertBryan Activity#8 MED3Document6 pagesDelaCruz AlbertBryan Activity#8 MED3AlbertNo ratings yet
- DelaCruz AlbertBryan Activity#7 MED3Document4 pagesDelaCruz AlbertBryan Activity#7 MED3AlbertNo ratings yet
- DelaCruz AlbertBryan Activity#5 MED3Document2 pagesDelaCruz AlbertBryan Activity#5 MED3AlbertNo ratings yet
- DelaCruz AlbertBryan TEM 01act1Document2 pagesDelaCruz AlbertBryan TEM 01act1AlbertNo ratings yet
- DelaCruz AlbertBryan Activity#4 MED3Document3 pagesDelaCruz AlbertBryan Activity#4 MED3AlbertNo ratings yet
- DelaCruz AlbertBryan Activity#3 MED3Document5 pagesDelaCruz AlbertBryan Activity#3 MED3AlbertNo ratings yet
- DelaCruz AlbertBryan Activity#2 MED3Document3 pagesDelaCruz AlbertBryan Activity#2 MED3AlbertNo ratings yet
- Stratum CorneumDocument4 pagesStratum CorneumMuh Firdaus Ar-RappanyNo ratings yet
- Anp2001 Skin Quiz PDFDocument19 pagesAnp2001 Skin Quiz PDFJerilee SoCute WattsNo ratings yet
- Literatura Algowhite (English)Document6 pagesLiteratura Algowhite (English)Maiko CarlosNo ratings yet
- Pathway Psoriasis 1Document1 pagePathway Psoriasis 1Yani Indri YaniNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology An Integrative Approach 2nd Edition Mckinley Test BankDocument54 pagesAnatomy and Physiology An Integrative Approach 2nd Edition Mckinley Test Banknicholasmcdonaldfwsgziecyt100% (33)
- Integumentary SystemDocument30 pagesIntegumentary SystemLourizMavericS.Samonte100% (1)
- 4 Ntegumentary SystemDocument8 pages4 Ntegumentary SystemAmanuel MaruNo ratings yet
- The Complete Integumentary System Study GuideDocument72 pagesThe Complete Integumentary System Study GuideDeborahMcCloudNo ratings yet
- 01 Basics On DermatopathologyDocument9 pages01 Basics On DermatopathologyCristina VajaituNo ratings yet
- What Is The Epidermis PDFDocument4 pagesWhat Is The Epidermis PDFlamarkaydotNo ratings yet
- 1 - The Skin's Function PDFDocument9 pages1 - The Skin's Function PDFskoahNo ratings yet
- Luka Thermal / Combustio / BurnDocument51 pagesLuka Thermal / Combustio / BurnPraty Dina MulyaNo ratings yet
- The Integumentary System Powerpoint PresentationDocument53 pagesThe Integumentary System Powerpoint PresentationGeulia RosalesNo ratings yet
- Principles of Human Anatomy 13Th Edition Tortora Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesPrinciples of Human Anatomy 13Th Edition Tortora Test Bank Full Chapter PDFmary.bethea195100% (15)
- Integumentary System (Skin & It'S Appendages)Document29 pagesIntegumentary System (Skin & It'S Appendages)explorerNo ratings yet
- PowerPoint - Presentation - About - Integumentary - SystemDocument27 pagesPowerPoint - Presentation - About - Integumentary - SystemPrayl Hope NapanoNo ratings yet
- Hole's Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology: David Shier Jackie Butler Ricki LewisDocument24 pagesHole's Essentials of Human Anatomy & Physiology: David Shier Jackie Butler Ricki LewisChristopher FrigoNo ratings yet
- Verruca VulgarisDocument5 pagesVerruca VulgarisDeba P SarmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Integumentary Study GuideDocument3 pagesChapter 5 Integumentary Study GuideSuperjunior8No ratings yet
- 12 Protection Support and Movement 1Document9 pages12 Protection Support and Movement 1Raiden EiNo ratings yet
- dms146 Slide Histology of Skin PDFDocument36 pagesdms146 Slide Histology of Skin PDFKarar AlaaNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument34 pagesIntegumentary SystemJerneth Nyka FloresNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System (Lecture Outline) PDFDocument4 pagesIntegumentary System (Lecture Outline) PDFAndrea Yzabell CortezNo ratings yet
- Gross Anatomy: The SkinDocument5 pagesGross Anatomy: The SkinkurarinnnNo ratings yet
- Histology of SkinDocument33 pagesHistology of SkinH R A K Kulathilaka75% (4)
- Avene DpigmentDocument10 pagesAvene DpigmentTina TinaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of SkinDocument12 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Skinjose abadNo ratings yet
- IT 3 - Histofisiologi KulitDocument62 pagesIT 3 - Histofisiologi KulitJennifer FinnaliaNo ratings yet
- Skin Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument5 pagesSkin Anatomy and PhysiologyKhan KamaalNo ratings yet
- Part 3 - Anatomy of The SkinDocument23 pagesPart 3 - Anatomy of The SkinAmal Naeem JHNo ratings yet