Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MHSB Lab - Brainstem External Features
MHSB Lab - Brainstem External Features
Uploaded by
Vee ManahanOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
MHSB Lab - Brainstem External Features
MHSB Lab - Brainstem External Features
Uploaded by
Vee ManahanCopyright:
Available Formats
2024 Brainstem - External Features (Lab)
OLFU MEDICINE MHSB - FINALS | Dr. Gironella| May 27, 2021
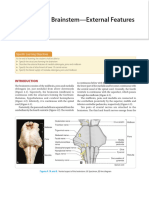
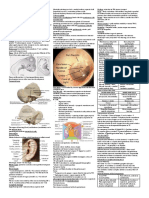
EXTERNAL FEATURES OF THE BRAINSTEM
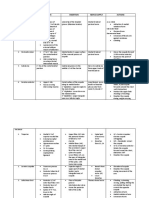
BRAINSTEM
MIDBRAIN
• Consists of short segment of brainstem between the pons and nuclei of
diencephalon
ITER /CEREBRAL AQUEDUCT space in the middle of midrain and
communication between the 3d ventricle and 4th ventricle
ANTERIOR
monami | 1 of 6
PONS
CRUS CEREBRI OF THE bag of fibers
MIDBRAIN / CEREBRAL PEDUNCLE
space that separates two cerebra
INTERPEDUNCULAR FOSSA peduncles
exits on the sides of interpeduncular
fossa and emerge on the surface of
OCULOMOTOR NERVE (CN 3)
transverese groove betwen pons and
midbrain
POSTERIOR
a large tissue that is located above the medulla and on the ventral surface of
brainstem, cerebral peduncles will pass through the pons and caudally it will
emerge towards the pyramid (pathway of fibers)
ANTERIOR
• occupying the anterior aspect
• extending along the midline and
BASAL SULCUS / BASILAR SULCUS coincides with the course of basilar
artery
• exits form the inferior pontine
sulcus on the caudal end of the
pons— very close to the pyramid
rostral pair • when viewing it on a lateral side,
which will connect through the the transverse fibers of pons
SUPERIOR COLLICULUS brachium of superior colliculus to ADBUCENS NERVE (CN 6)
converge to form a compact lateral
lateral geniculate for vision bundle known as middle
(visual pathway) cerebellar peduncle (brachium
pontis) that attach the pons on the
through brachium of inferior colliculi
overlying cerebellum
INFERIOR COLLICULUS will connect to medial geniculate
which is part of the auditory pathway compact lateral bundle formed by
MIDDLE CEREBELLAR PEDUNCLE / converging of transverse fibers of
PINEAL BODY part of epithalamus
BRACHIUM PONTIS pons that attach the pons to the
overlying cerebellum
• smallest of all cranial nerve
• emerges from posterior surface just
• on the lateral side
TROCHLEAR NERVE behind the inferior colliculus
• formed between caudal border of
(emerges posteriorly and goes
middle cerebellar peduncle the
anteriorly)
CEREBELLUM PONTINE ANGLE adjoining cerebellum, upper part of
medulla
• Facial nerve and vestibulocochlear
nerves are found here ( CN 7 & 8)
• penetrate brachium pontis near the
middle of lateral surface of pons
TRIGEMINAL NERVE (CN 5) • sensory portion is larger as
compared to the motor portion
monami | 2 of 6
MEDULLA OBLONGATA / BULB
• Constitutes the most caudal part o f the brain stem and continues with the
spinal cord at the foramen magnum
• extends rostrally about 2.5 cm caudal to the pons
• central canal of spinal cords is continues through the 4th ventricle at the
point called obex
• rostral part of the medulla forms the oor of 4th ventricle
ANTERIOR
• formed by pyramidal tracts of
corticospinal and corticobulbar
tracts
• forms 2 longitudinal ridges on
eother side of ventral median
PYRAMID ssure / antero-median ssure
• there is a decussation or crossing
over of the pyramids and
obliterating the anteromedian
fissure at the extreme caudal end of
medulla oblongata
VENTROLATERAL SULCUS where rootlets of hypoglossal nerve
(12) emerge
• cranial nerves are seen
• radicalsof cranial portion of
accessory nerve (11)
DORSOLATERAL SULCUS
• vagus nerve (10)
• glossopharyngeal nerve (9)
POSTERIOR POSTERIOR
posterior surface of the pons forms the rostral part of the 4th ventricle
red triangle - behind of ponds
yellow broken lines - behind medulla oblongata
at its widest point, this triangle area contains ponto-medullary junctions and
the lateral recesses of the ventricles
medial eminence and facial colliculus are also seen here
• is actually made up of the fibers of
the facial nerve and nucleus of
FACIAL COLLICULUS
abducens nerve
• bundles of fibers
• forms the walls of 4th ventricle
SUPERIOR CEREBELLAR
• together with the cerebellar vermis
PEDUNCLE
and anterior medullary bellum
forms the roof of the 4th ventricle
DORSAL MEDIAN SULCUS space in between / middle
SULCUS LIMITANS space lateral to the median emience
monami | 3 of 6
fi
fi
fl
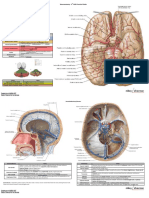
REVIEW USING ACTUAL SLIDES
FASCICULUS GRACILIS & FASCICULUS CUNEATUS - which for an eminence cerebral peduncle
or elevation known as gracile tubercle or clava and cuneate tubercle interopeduncular
fossa
communication between 4th
OBEX ventricle and central canal of spinal pons
cord
basilar sulcus CN V
vagal trigon
LATERAL ELEVATION contains dorsal motor nucleus of the
vagus (black circle)
antrolateral sulcus
hypoglossal trigon
MEDIAL ELEVATION contains hypoglossal nucleus (white ventral median
circle) pyramid
ssure
bun of fibers which are ridges formed
by fibers passing through the
cerebellum
STRIA MEDULLARIS proceed laterally (lateral portion is in
pink squares) and opening of
foramen of Lusca to allow CSF to
flow to the subarachnoid space
drain the CSF towards the
FORAMEN OF MAGENDI
subarachnoid space
superior colliculus
inferior colliculus
superior medullary
velum
middle cerebral
peduncle
superior cerebral
peduncle
inferior cerebral
medial peduncle
eminence
facial
dosro median
folliculus
sulcus
vestibular
clava cuneate tubercle
area
monami | 4 of 6
fi
superior colliculus
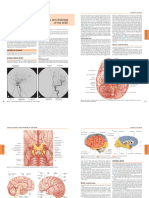
ANTERIOR VIEW:
RED PIN - interpeduncular fossa POSTERIOR VIEW:
GREEN PIN - crus cerebri / cerebral peduncle PINK PIN - inferior colliculus
PURPLE PIN - pons
WHITE PIN - anteromedian fissure
PURPLE PIN - Pyrami
POSTERIOR VIEW: RED PIN - olive
BLUE PIN - vestibular area
PINK PIN - medial elevation / hypoglossal trigon
PURPLE PIN - lateral elevation / vaga trigon
RED PIN - inserted towards stria medullaris
GREEN PIN - dorso lateral sulcus
PURPLE PIN - dorsal median sulcus / posteromedian sulcus
RED PIN - dorsal intermediate sulcus
DIS & DMS LIMITS FASCICULUS GRACILIS
DIS & DSL LIMITS FASCICULUS CUNEATUS
monami
POSTERIOR VIEW:
GREEN PIN - clava (elevation of fasciculus gracilis) | 5 of 6
PURPLE PIN - cuneate tubercle (elevation of fasciculus cuneatus)
RED PIN - obex
pontomedullary junction (space between pons & medulla oblongata)
posterolateral sulcus
anteromedian sulcus
anterolateral sulcus
superior cerebellar peduncle
middle cerebellar peduncle
inferior cerebellar peduncle
monami | 6 of 6
You might also like
- Barr's The Human Nervous System: An Anatomical Viewpoint: Kiernan, J. A Rajakumar, NagalingamDocument4 pagesBarr's The Human Nervous System: An Anatomical Viewpoint: Kiernan, J. A Rajakumar, NagalingamSaras Agrawal0% (1)
- Neuroanatomy Revision Notes PDFDocument7 pagesNeuroanatomy Revision Notes PDFTanya Tanu100% (1)
- Brain Stem NS2.2 FinalDocument16 pagesBrain Stem NS2.2 Finaldedhomosapien2No ratings yet
- Neuroanatomy NotesDocument8 pagesNeuroanatomy NotesJustine May Gervacio100% (1)
- Neuroanatomy PDFDocument12 pagesNeuroanatomy PDFM D100% (4)
- White MatterDocument13 pagesWhite MatterSamar Abd El-monaemNo ratings yet
- Head FactoidsDocument17 pagesHead FactoidsENo ratings yet
- Arm Approaches: Approach Internervous Plane Incision Superficial Dissection Deep Dissection DangersDocument2 pagesArm Approaches: Approach Internervous Plane Incision Superficial Dissection Deep Dissection DangersSaad Allah KabbanyNo ratings yet
- Brain and MeningesDocument5 pagesBrain and Meningesr74k8zgg8rNo ratings yet
- Additional Study Notes Brainstem - 2017Document4 pagesAdditional Study Notes Brainstem - 2017JustinNo ratings yet
- 01 Neuroscience: Gross Anatomy of The BrainDocument5 pages01 Neuroscience: Gross Anatomy of The BrainAsh CansanayNo ratings yet
- Neuroscience: Topic: MeningesDocument6 pagesNeuroscience: Topic: MeningesRoselle AbrazaldoNo ratings yet
- Knee ApproachesDocument1 pageKnee ApproachesAisha MousaNo ratings yet
- Peggy Mason Chapter 6 Brainstem Notes - For MergeDocument37 pagesPeggy Mason Chapter 6 Brainstem Notes - For MergeLydia RousseauNo ratings yet
- Muscle, Origin, InsertionDocument9 pagesMuscle, Origin, Insertionshananana1616No ratings yet
- Cerebellum Gross Appearance of The Cerebellum: Posterior Lobe), Which Is TheDocument10 pagesCerebellum Gross Appearance of The Cerebellum: Posterior Lobe), Which Is TheRafu DestajoNo ratings yet
- Protection of The CNSDocument4 pagesProtection of The CNSGrayson JamesNo ratings yet
- White Matter of The Cerebral HemispheresDocument50 pagesWhite Matter of The Cerebral HemispheresSandy MonirNo ratings yet
- The Vascular System Doc TulaganDocument10 pagesThe Vascular System Doc Tulagankûrñï såñskrùthîNo ratings yet
- 1.01 Anaphy Laboratory: The SkullDocument3 pages1.01 Anaphy Laboratory: The SkullONDONG, Zsarnainne P.No ratings yet
- Imaging Central Skull Base 2009 BorgesDocument28 pagesImaging Central Skull Base 2009 Borgesinasa nabilaNo ratings yet
- Brainstem Bravo AnnotatedDocument13 pagesBrainstem Bravo AnnotatedMia CadizNo ratings yet
- Brainstem - Activity SheetDocument12 pagesBrainstem - Activity SheetlindaNo ratings yet
- Axial and Appendicular BonesDocument9 pagesAxial and Appendicular BonesJuan Miguel TevesNo ratings yet
- Summary of Pathways 2020 5e and 6e MedNeuroDocument25 pagesSummary of Pathways 2020 5e and 6e MedNeuromaria fernandaNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System of VertebratesDocument33 pagesSkeletal System of VertebratesHannah BercasioNo ratings yet
- 48-Hour Chick Embryo: ST ND RDDocument29 pages48-Hour Chick Embryo: ST ND RDFerhaeeza KalayakanNo ratings yet
- Practs Reviewer - 3rd Shift (Mikey)Document3 pagesPracts Reviewer - 3rd Shift (Mikey)Madeline SibuloNo ratings yet
- Development of The Pig EmbryoDocument11 pagesDevelopment of The Pig Embryovada_soNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Brain Tutorial - John A. BealDocument78 pagesAnatomy of Brain Tutorial - John A. BealAnanda CondeNo ratings yet
- Face and Skull HolesDocument10 pagesFace and Skull HolesScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- BI 232 Lab 9Document17 pagesBI 232 Lab 9Cj LinceNo ratings yet
- Brain Stem FullDocument25 pagesBrain Stem FullCosplay AccountNo ratings yet
- Nur 194 - Care of Mother, Child, & AdolescentDocument43 pagesNur 194 - Care of Mother, Child, & AdolescentAileen Cagulada100% (1)
- Gray's Anatomy - The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice - Chap 19 Doc HijosaDocument8 pagesGray's Anatomy - The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice - Chap 19 Doc Hijosatiburciamd27No ratings yet
- Brainstem: External and Internal FeaturesDocument57 pagesBrainstem: External and Internal FeaturesJoaquin GuillermoNo ratings yet
- The Cerebellum (Revised)Document8 pagesThe Cerebellum (Revised)Ko HakuNo ratings yet
- Introduction & Organization of The Nervous System: Marlene Ricci Castillo, MD, FPCS, FpsgsDocument39 pagesIntroduction & Organization of The Nervous System: Marlene Ricci Castillo, MD, FPCS, FpsgsAfNo ratings yet
- Brain StemDocument19 pagesBrain StemSajid HussainNo ratings yet
- 6th Lecture - Physiology of The Brain Stem - CNS PhysiologyDocument13 pages6th Lecture - Physiology of The Brain Stem - CNS PhysiologyAnastasia SoareNo ratings yet
- 48 Hour Chick Reviewer PDFDocument5 pages48 Hour Chick Reviewer PDFSheanna May FuriaNo ratings yet
- NBSS CASE 6 - Cerebral Palsy and Mental RetardationDocument28 pagesNBSS CASE 6 - Cerebral Palsy and Mental RetardationbungadielaNo ratings yet
- Basal GangliaDocument3 pagesBasal GangliamakiscollegefilesNo ratings yet
- Bloqueos Miembro SuperiorDocument1 pageBloqueos Miembro SuperiorpimpollopittNo ratings yet
- Diploma in Occupational TherapyDocument47 pagesDiploma in Occupational TherapyAzmi Plus100% (2)
- The Cranial Cavity: Bony FeaturesDocument5 pagesThe Cranial Cavity: Bony FeaturesbibierabiaNo ratings yet
- Skeletal Systeeeeeeeehhhhhm Hyman: I. NotochordDocument6 pagesSkeletal Systeeeeeeeehhhhhm Hyman: I. NotochordMTCNo ratings yet
- PonsDocument61 pagesPonsAyberk ZorluNo ratings yet
- CN 4 6Document39 pagesCN 4 6Radityo Akhmedika FauzieNo ratings yet
- 2 01 Peripheral Nerves and Spinal Cord EDITED Dra DoqueniaDocument31 pages2 01 Peripheral Nerves and Spinal Cord EDITED Dra DoqueniaCRUZ Jill EraNo ratings yet
- 4 Cerebellum 2022Document40 pages4 Cerebellum 2022Gregory Wiggins100% (1)
- Vertebral Column of DogDocument3 pagesVertebral Column of DogEmit Rosary PenetranteNo ratings yet
- 1.12 ANATOMY - The Ears Surface Anatomy and Landmarks, External, Middle and Inner Portions, Blood Vessels and NervesDocument5 pages1.12 ANATOMY - The Ears Surface Anatomy and Landmarks, External, Middle and Inner Portions, Blood Vessels and NervesPaolo NaguitNo ratings yet
- B5M2Q1 CompilationDocument22 pagesB5M2Q1 CompilationMariel AbatayoNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Organ of Hearing and BalanceDocument1 pageAnatomy of The Organ of Hearing and BalanceJose Raphael Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Neuro Written I TablesDocument6 pagesNeuro Written I TablesSolomon Seth SallforsNo ratings yet
- Brainstem Simplified NotesDocument5 pagesBrainstem Simplified Noteslailatul husnaNo ratings yet
- Brainstem: Medulla OblongataDocument130 pagesBrainstem: Medulla OblongataBhawana BhatodiyaNo ratings yet
- Nervous System Reflexes and Senses: Physiology Lab-4 October, 2018Document21 pagesNervous System Reflexes and Senses: Physiology Lab-4 October, 2018Madhu LodhiNo ratings yet
- LARGE ANIMAL - Georgina Child - Large Animal Neurological Exam PDFDocument8 pagesLARGE ANIMAL - Georgina Child - Large Animal Neurological Exam PDFYaserAbbasiNo ratings yet
- Development of The Nervous SystemDocument27 pagesDevelopment of The Nervous Systemsalmankhan09215No ratings yet
- What Is The Difference Between Efferent and Afferent NervesDocument1 pageWhat Is The Difference Between Efferent and Afferent NervesranjuhiNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2: Genes and Behavior: Basic GeneticsDocument14 pagesLecture 2: Genes and Behavior: Basic GeneticsLaura BanksNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Coordination and ResponseDocument4 pagesChapter 3 - Coordination and ResponseMastura Muhamad MuktarNo ratings yet
- 4 Physiology of AnalyzersDocument50 pages4 Physiology of AnalyzerslenarioNo ratings yet
- The Neuromuscular Junction: Page 1. Introduction Page 2. GoalsDocument3 pagesThe Neuromuscular Junction: Page 1. Introduction Page 2. GoalsSteve EstebanNo ratings yet
- Bangert, M., Peschel, T., Schlaug, G., Rotte, M., Drescher, D., Hinrichs, H., ... & Altenmüller, E. (2006). Shared networks for auditory and motor processing in professional pianists- evidence from fMRI conjunction. Neuroimage, 30(3), 917-926.Document10 pagesBangert, M., Peschel, T., Schlaug, G., Rotte, M., Drescher, D., Hinrichs, H., ... & Altenmüller, E. (2006). Shared networks for auditory and motor processing in professional pianists- evidence from fMRI conjunction. Neuroimage, 30(3), 917-926.goni56509100% (1)
- Chapter 6 PerdevDocument11 pagesChapter 6 PerdevJamie Anne GarciaNo ratings yet
- Nervous Regulation of The Circulation and Rapid Control of Arterial PressureDocument2 pagesNervous Regulation of The Circulation and Rapid Control of Arterial Pressuremcwnotes100% (2)
- Textbook Inderbir Singh S Textbook of Human Neuroanatomy Fundamental and Clinical 10Th Edition Pritha S Bhuiyan Ebook All Chapter PDFDocument53 pagesTextbook Inderbir Singh S Textbook of Human Neuroanatomy Fundamental and Clinical 10Th Edition Pritha S Bhuiyan Ebook All Chapter PDFsheryl.jackson340100% (13)
- Cauda Equina SyndromeDocument22 pagesCauda Equina SyndromeZulzaire ZulkefliNo ratings yet
- Anatomyand Physiology Ratio Activity SAS 8-14Document8 pagesAnatomyand Physiology Ratio Activity SAS 8-14Clarisse Biagtan CerameNo ratings yet
- GC ANS Part II 2016 Phy2011Document25 pagesGC ANS Part II 2016 Phy2011Lisa KangNo ratings yet
- 9 - 10 - Cranial Nerves 1Document63 pages9 - 10 - Cranial Nerves 1jibnumajeedNo ratings yet
- Structural Organization of The Nervous SystemDocument14 pagesStructural Organization of The Nervous SystemGhaidaa SadeqNo ratings yet
- Cranial Nerve Mnemonics 101110.2Document13 pagesCranial Nerve Mnemonics 101110.2porphyrin rheniumNo ratings yet
- Sistem Saraf Motorik SensorikDocument36 pagesSistem Saraf Motorik Sensorikromzanr97No ratings yet
- Physiological Mechanisms of PainDocument7 pagesPhysiological Mechanisms of PainZAFFAR QURESHINo ratings yet
- ReflexesDocument37 pagesReflexesmishky19No ratings yet
- FCE 3204 Thinking SkillsDocument23 pagesFCE 3204 Thinking SkillsTey Boon KiatNo ratings yet
- Neurology 1 1 Long ExamDocument9 pagesNeurology 1 1 Long ExamNdor BariboloNo ratings yet
- Correlations Between Neurophysiological Activity in The Cortex and Short Term Behavior in The MonkeyDocument24 pagesCorrelations Between Neurophysiological Activity in The Cortex and Short Term Behavior in The MonkeyAvengingBrainNo ratings yet
- Function of The BrainDocument16 pagesFunction of The BrainJohn Matthew CrisostomoNo ratings yet
- Full Download Introduction To Psychology Gateways To Mind and Behavior With Concept Maps and Reviews 13th Edition Coon Solutions ManualDocument36 pagesFull Download Introduction To Psychology Gateways To Mind and Behavior With Concept Maps and Reviews 13th Edition Coon Solutions Manualcku4lcarter100% (37)
- Continuum Spinal Cord AnatomyDocument25 pagesContinuum Spinal Cord AnatomyslojnotakNo ratings yet
- Upper and Lower Motor NeuronDocument22 pagesUpper and Lower Motor NeuronJoshua Henrina100% (2)
- Neuro IDocument6 pagesNeuro IElenaNo ratings yet