Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chemical Reaction Notes
Chemical Reaction Notes
Uploaded by
alchriw0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views2 pages1. Chemical reactions involve the interaction of atoms, ions, molecules, or compounds to form or break chemical bonds, changing the relationship between atoms.
2. In synthesis reactions, two or more reactants combine to form a larger, more complex product, while decomposition reactions break down a reactant into simpler products.
3. Key types of chemical reactions include synthesis, decomposition, hydrolysis, anabolism, catabolism, dehydration, metabolism, and reversible reactions, which play important roles in biological processes like protein synthesis, digestion, and energy production.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1. Chemical reactions involve the interaction of atoms, ions, molecules, or compounds to form or break chemical bonds, changing the relationship between atoms.
2. In synthesis reactions, two or more reactants combine to form a larger, more complex product, while decomposition reactions break down a reactant into simpler products.
3. Key types of chemical reactions include synthesis, decomposition, hydrolysis, anabolism, catabolism, dehydration, metabolism, and reversible reactions, which play important roles in biological processes like protein synthesis, digestion, and energy production.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views2 pagesChemical Reaction Notes
Chemical Reaction Notes
Uploaded by
alchriw1. Chemical reactions involve the interaction of atoms, ions, molecules, or compounds to form or break chemical bonds, changing the relationship between atoms.
2. In synthesis reactions, two or more reactants combine to form a larger, more complex product, while decomposition reactions break down a reactant into simpler products.
3. Key types of chemical reactions include synthesis, decomposition, hydrolysis, anabolism, catabolism, dehydration, metabolism, and reversible reactions, which play important roles in biological processes like protein synthesis, digestion, and energy production.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
CHEMICAL REACTION
- atoms, ions, molecules, or compounds interact
either to form or to break chemical bonds.
- the substances that go into a chemical reaction are
called the reactants, and the substances produced at
the end of the reaction are known as the products.
DECOMPOSITION REACTIONS
- a reverse of a synthesis reaction
- larger reactant is chemically broken down into two
or more smaller products
HYDROLYSIS REACTION (water dissolution)
Three Important Points Made About Chemical
- process by which chemical compounds are broken
Reaction:
apart by the addition of water
1. In some reactions, less complex reactants are
- a reaction with a water molecule that breaks large
combined to form a larger, more complex product.
molecules into smaller ones
(ex. amino acids → protein molecule)
- water is split into two parts
2. In other reactions, a reactant can be broken down,
(ex. breakdown of disaccharide into glucose
or decomposed, into simpler, less complex products.
molecules)
(ex. carbohydrate molecule → glucose molecule)
3. Atoms are generally associated with other atoms
through chemical bonding or intermolecular forces;
therefore, to synthesize new products or break down
reactants, it is necessary to change the relationship
between atoms.
ANABOLISM
- all of the synthesis reactions that occur within the
Classification of Chemical Reactions
body are collective called anabolism
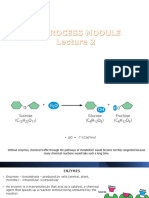
SYNTHESIS REACTION - synthesis of complex molecules
- when two or more reactants chemically combine to - growth, maintenance, and repair of the body could
form a new and larger product. not take place without anabolic reactions
- synthesis reactions produce the molecules
characteristic of life, such as ATP, proteins, CATABOLISM
carbohydrates, lipids, and nucleic acids. - decomposition reactions occurring in the body are
(ex1. formation of adenosine triphosphate) collectively called catabolism
- large, complex molecules in the body are broken
down into smaller, simple ones
- it includes digestion of food molecules in the
(ex2. protein synthesis) intestine and within cells, the breakdown of fat stores,
and the breakdown of foreign matter and
microorganisms in certain blood cells that protect the
body
DEHYDRATION REACTION (water out)
- the process of combination of two molecules with
the elimination of water molecule is called
dehydration synthesis.
- a chemical reaction in which a water molecule is
eliminated from the reactant molecule.
- synthesis reaction in which water is a product.
(ex2. combination of 2 amino acids to form a
dipeptide)
METABOLISM
- all of the anabolic and catabolic reactions in the
body are collectively defined as metabolism.
- describes all the chemical processes that go on
continuously inside your body to keep you alive and
your organs functioning normally, such as breathing,
repairing cells and digesting food. These chemical
processes require energy.
REVERSIBLE REACTIONS
- reaction can proceed from reactants to products or
from products to reactants
- when the rate of product formation is equal to
the rate of the reverse reaction, the reaction system is
said to be at equilibrium.
(ex.)
ENERGY
- the capacity to do work—that is, to move matter.
- energy can be subdivided into potential energy and
kinetic energy.
Potential energy
- stored energy that could do work but not doing so.
You might also like
- An Introduction To Medicinal Chemistry 7Th Edition Graham L Patrick Full ChapterDocument67 pagesAn Introduction To Medicinal Chemistry 7Th Edition Graham L Patrick Full Chaptermatthew.woodruff62688% (8)
- Principles of Cancer Biology 1st EditionDocument57 pagesPrinciples of Cancer Biology 1st Editiondarren.barnett949100% (53)
- Notes Dr. Wahid Wanis Biology ASFrom His BookDocument10 pagesNotes Dr. Wahid Wanis Biology ASFrom His BookBooks100% (1)
- 3.1 Synthesis of Biological Macromolecules Biology 2e OpenStaxDocument2 pages3.1 Synthesis of Biological Macromolecules Biology 2e OpenStaxAlodia PastorizoNo ratings yet
- BIOCHEM LEC (History and Introduction)Document8 pagesBIOCHEM LEC (History and Introduction)Mariyuh SkrtskrtNo ratings yet
- 2.1-2.6 Biology Review 1Document21 pages2.1-2.6 Biology Review 1Victoria FinolNo ratings yet
- Microbial Metabolism Metabolism - The Sum of All Chemical ReactionsDocument7 pagesMicrobial Metabolism Metabolism - The Sum of All Chemical ReactionsAGENT M.DNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1:synthesis of Biological MacromoleculesDocument12 pagesLesson 1:synthesis of Biological MacromoleculesExequiel Macalisang Ramientos Jr.No ratings yet
- Microbial Metabolism Lecture Part ADocument16 pagesMicrobial Metabolism Lecture Part AKashif IqbalNo ratings yet
- Lecture-4-Microbial Metabolism Lecture Part ADocument18 pagesLecture-4-Microbial Metabolism Lecture Part Aq4w2rgydvcNo ratings yet
- Intro To BiochemDocument13 pagesIntro To BiochemMarie A. BuyucanNo ratings yet
- BIOENERGETICS Notes 4Document3 pagesBIOENERGETICS Notes 4Hya LaniogNo ratings yet
- Metabolism (Compatibility Mode)Document13 pagesMetabolism (Compatibility Mode)Dark_KiroNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 2 Test Flash CardsDocument8 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Chapter 2 Test Flash Cardsmalenya1No ratings yet
- 1b - Intro To Macromolecules COMPLETEDocument2 pages1b - Intro To Macromolecules COMPLETEAaliyah AdenNo ratings yet
- 3.1: Synthesis of Biological MacromoleculesDocument2 pages3.1: Synthesis of Biological MacromoleculesElah TapangNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Chemistry of Life Review PacketDocument7 pagesUnit 2 Chemistry of Life Review PacketShannon ErdmanNo ratings yet
- Micropara TransesDocument13 pagesMicropara TransesKyla Marie BadanaNo ratings yet
- Microbial Metabolism: Catabolic and Anabolic ReactionsDocument16 pagesMicrobial Metabolism: Catabolic and Anabolic ReactionsApryll DarlineNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes Metabolism Part1Document9 pagesLecture Notes Metabolism Part1Oluwasegun ModupeNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Lesson 2Document18 pagesWeek 2 Lesson 2Yury DesuNo ratings yet
- 2 Chemical LifeDocument5 pages2 Chemical LifeEly FructuosoNo ratings yet
- 2.1.4 Biology Ocr ADocument5 pages2.1.4 Biology Ocr AFatima AfifiNo ratings yet
- Transes-Chap 2 - MicrobioDocument4 pagesTranses-Chap 2 - MicrobioFReyes KarylleNo ratings yet
- Physical Science-Finals ReviewerDocument18 pagesPhysical Science-Finals ReviewerPrecious Miracle Lucas SacataniNo ratings yet
- Biochem Lec Prelim FinalsDocument11 pagesBiochem Lec Prelim FinalsJullia SollezaNo ratings yet
- What Are Enzymes?: Every Organism Has Many Enzymes-More Than 3000 in A Single CellDocument7 pagesWhat Are Enzymes?: Every Organism Has Many Enzymes-More Than 3000 in A Single CellShane TamilNo ratings yet
- Chemical Foundations: Health Maintenance (Nutrition) - Vitamin, Minerals, Water IntakeDocument24 pagesChemical Foundations: Health Maintenance (Nutrition) - Vitamin, Minerals, Water IntakeShyenNo ratings yet
- Task 1Document8 pagesTask 1maryamshahzad489No ratings yet
- Unit Energy Releasing Pathways: StructureDocument33 pagesUnit Energy Releasing Pathways: StructureAD-MQNo ratings yet
- What Are Enzymes?: EnzymeDocument4 pagesWhat Are Enzymes?: EnzymeMark Jayson ContrerasNo ratings yet
- Transes Chap 1 MicrobioDocument4 pagesTranses Chap 1 MicrobioFReyes KarylleNo ratings yet
- Protein and Amino Acids 2Document5 pagesProtein and Amino Acids 2Mazine TakahashiNo ratings yet
- IntroDocument3 pagesIntroMary Rose AllinegNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: The Chemical Building Blocks of Life: Enantiomers . These Are Mirror Images of Each Other. MirroredDocument17 pagesChapter 3: The Chemical Building Blocks of Life: Enantiomers . These Are Mirror Images of Each Other. Mirroredapi-524244445No ratings yet
- Condensation Hydrolysis2Document13 pagesCondensation Hydrolysis2hpmx4shwx5No ratings yet
- Synthesis Reaction Definition BiologyDocument8 pagesSynthesis Reaction Definition Biologytrinasimmonssavannah100% (1)
- Las 3 ProteinsDocument2 pagesLas 3 ProteinsAntonio CharismaNo ratings yet
- Advance Biology: Quarter 3: Cell MetabolismDocument4 pagesAdvance Biology: Quarter 3: Cell MetabolismEmmanuel AzoresNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Enzymes and The Digestive SystemDocument11 pagesUnit 2 - Enzymes and The Digestive SystemKatherine NunnNo ratings yet
- Cholesterol Proteins Glycocalyx/carbohydrates: Phospholipid BilayerDocument11 pagesCholesterol Proteins Glycocalyx/carbohydrates: Phospholipid BilayerGreenard Imperial GualbertoNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry NCMA113 Midterm Notes PDocument3 pagesBiochemistry NCMA113 Midterm Notes PVaishnavi LoganathanNo ratings yet
- Exam 1 ReviewDocument14 pagesExam 1 ReviewLuzzuvannaNo ratings yet
- Enzymes 1Document20 pagesEnzymes 1Koushik KanjilalNo ratings yet
- Document 6Document11 pagesDocument 6kimberlyvalencia011112No ratings yet
- Molecular Biology of The CellDocument4 pagesMolecular Biology of The CellBuzoianu Maria100% (1)
- Las Q3 WK7 PDFDocument7 pagesLas Q3 WK7 PDFPerlyn Del Pilar OduyaNo ratings yet
- Chem 113 Introduction To Biochemistry Pt. 1Document11 pagesChem 113 Introduction To Biochemistry Pt. 1janson021cuteNo ratings yet
- BIOCHEMnotes 2Document3 pagesBIOCHEMnotes 2katNo ratings yet
- 2 Structure and Functions in Living OrganismsDocument36 pages2 Structure and Functions in Living OrganismsSam ShohetNo ratings yet
- CC-LEC-NOTES-1Document4 pagesCC-LEC-NOTES-1CDNo ratings yet
- LAS Physical Science Week 5Document7 pagesLAS Physical Science Week 5Shekaina Faith Cuizon LozadaNo ratings yet
- Unit. 1 MOLECULES OF LIFEDocument29 pagesUnit. 1 MOLECULES OF LIFEAntek WieNo ratings yet
- Enzymes:: Commented (1) : Im Going To Add The Notes From TheDocument5 pagesEnzymes:: Commented (1) : Im Going To Add The Notes From TheSarahNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document9 pagesChapter 6Georges SarkisNo ratings yet
- Enzymes Mechanism of Enzyme ActionDocument6 pagesEnzymes Mechanism of Enzyme Actionkl42c4300No ratings yet
- Cellular/molecular Biology ReviewDocument23 pagesCellular/molecular Biology ReviewStephen ByrneNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document18 pagesLecture 2warden tambiNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrates, Lipids, ProteinsDocument5 pagesCarbohydrates, Lipids, ProteinsJustine AsiloNo ratings yet
- Physical ScienceDocument2 pagesPhysical Sciencejerickpacia2000No ratings yet
- Enzyme ComponentsDocument36 pagesEnzyme ComponentsJanine CambaNo ratings yet
- Lipase LittlelaptopDocument53 pagesLipase LittlelaptopAjay LakshmananNo ratings yet
- A-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Biology Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Spanish ColonizationDocument3 pagesSpanish ColonizationalchriwNo ratings yet
- Pre-Colonial PhilippinesDocument2 pagesPre-Colonial PhilippinesalchriwNo ratings yet
- History RPHDocument3 pagesHistory RPHalchriwNo ratings yet
- Rph-Phil RevoDocument3 pagesRph-Phil RevoalchriwNo ratings yet
- TFN Midter-ExaminationDocument3 pagesTFN Midter-ExaminationalchriwNo ratings yet
- TFN Batt RevDocument8 pagesTFN Batt RevalchriwNo ratings yet
- Skeletal Anatomy NotesDocument7 pagesSkeletal Anatomy NotesalchriwNo ratings yet
- Midterm and Final Exam TFNDocument6 pagesMidterm and Final Exam TFNalchriwNo ratings yet
- Integumentary Anatomy NotesDocument6 pagesIntegumentary Anatomy NotesalchriwNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System NotesDocument6 pagesEndocrine System NotesalchriwNo ratings yet
- Quiz 7Document2 pagesQuiz 7юрий локтионовNo ratings yet
- AdenovirusDocument18 pagesAdenovirusNovika Ayuni RambeNo ratings yet
- Age of Child Vaccines Needed How and Where It Is GivenDocument1 pageAge of Child Vaccines Needed How and Where It Is GivenKwenaNo ratings yet
- Plant Cells Peroxisomes and Glyoxysomes PDFDocument7 pagesPlant Cells Peroxisomes and Glyoxysomes PDFmanoj_rkl_07No ratings yet
- Cell Viability AssayDocument6 pagesCell Viability AssayChristian Jayvon LalunaNo ratings yet
- Metagen OverviewDocument1 pageMetagen OverviewEvelyn Hernández ZúñigaNo ratings yet
- Biology Core Practical 6.1 DNA Amplification Using PCRDocument2 pagesBiology Core Practical 6.1 DNA Amplification Using PCRBenedicte Symcox100% (1)
- Bioinformatics I: Lecture NotesDocument180 pagesBioinformatics I: Lecture NotesDaniela GuardiaNo ratings yet
- How To Perform Successful CRISPR ExperimentsDocument24 pagesHow To Perform Successful CRISPR Experimentsprofessor85100% (1)
- Vaccination 790622035187Document1 pageVaccination 790622035187mohd jeffri bin yaakobNo ratings yet
- DNA TranslastionDocument2 pagesDNA TranslastionJoySe Merrera ÜNo ratings yet
- Gmo PampletDocument2 pagesGmo PampletMaui GupitaNo ratings yet
- Model Organisms: Course No. Zool. 205 Developmental Biology of AnimalsDocument2 pagesModel Organisms: Course No. Zool. 205 Developmental Biology of AnimalsSaad SakalNo ratings yet
- Biology 12 Unit 5 Dna Worksheet - Dna Strucuture 1Document2 pagesBiology 12 Unit 5 Dna Worksheet - Dna Strucuture 1api-338578874100% (1)
- Life Sciences Fundamentals and PracticeDocument167 pagesLife Sciences Fundamentals and PracticemoyayeNo ratings yet
- Chapter SevenDocument25 pagesChapter SevenTade GaromaNo ratings yet
- Cortaga Et Al. (2023) Mutations Associated With Fungicide Resistance in Colletotrichum Species: A ReviewDocument24 pagesCortaga Et Al. (2023) Mutations Associated With Fungicide Resistance in Colletotrichum Species: A ReviewfmdelacuevaNo ratings yet
- Redaccao ForenseDocument9 pagesRedaccao ForenseBrado AfricanoNo ratings yet
- Animal Performance and Stress Responses and Tolerance Limit PDFDocument16 pagesAnimal Performance and Stress Responses and Tolerance Limit PDFNgurah S. YasaNo ratings yet
- Bayern MunchenDocument23 pagesBayern MunchenKepa KepaNo ratings yet
- Gene Expression: Transcription and TranslationDocument1 pageGene Expression: Transcription and TranslationcccantaNo ratings yet
- Pda PicsDocument5 pagesPda PicsWilliam ChandraNo ratings yet
- MICROBIOLOGY & PATHOLOGY NuggetsDocument233 pagesMICROBIOLOGY & PATHOLOGY NuggetsFaraz SayedNo ratings yet
- Test 2 - Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins and Nucleic AcidsDocument7 pagesTest 2 - Carbohydrates, Lipids, Proteins and Nucleic AcidsChrisNo ratings yet
- Divan Problems ch16Document3 pagesDivan Problems ch16Merlin MerlinNo ratings yet
- Pemf FrequenciesDocument13 pagesPemf FrequenciescumbredinNo ratings yet
- Fragi 01 610406Document6 pagesFragi 01 610406msNo ratings yet