Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ANAPHY WEEK 4 (Notes)
ANAPHY WEEK 4 (Notes)
Uploaded by
Jamie Lynn BecaucoCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Pediatric ECG Survival Guide - FinalDocument21 pagesPediatric ECG Survival Guide - FinalEmily VlasikNo ratings yet
- Anaphy TissuesDocument4 pagesAnaphy TissuesYo1No ratings yet
- Module 2 TissuesDocument3 pagesModule 2 TissuesRaphael SevillaNo ratings yet
- HistologyDocument16 pagesHistologyHohai ConcepcionNo ratings yet
- MODULE 2.3 Tissue Level of OrganizationDocument12 pagesMODULE 2.3 Tissue Level of OrganizationKate Andrea PanizalesNo ratings yet
- Animal TissuesDocument75 pagesAnimal TissuesFaithlyn Riche YocorNo ratings yet
- TissuesDocument72 pagesTissuesFrelyn Tamba AndresNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissues NEW 1Document54 pagesAnimal Tissues NEW 1Jela AgengaNo ratings yet
- 6 - TissueDocument7 pages6 - TissueJocelyn AtisNo ratings yet
- Topic 4. Cells and Tissues Anatomy and Physiology Autosaved 1Document71 pagesTopic 4. Cells and Tissues Anatomy and Physiology Autosaved 1Janine Jerica JontilanoNo ratings yet
- 4 TissuesDocument124 pages4 TissuesJanette Monica Barrios100% (1)
- Epithelial-Tissues Lect.Document13 pagesEpithelial-Tissues Lect.adelbaneen31No ratings yet
- Vet Histo Notes Chap 2Document10 pagesVet Histo Notes Chap 2Mia Kristhyn Calinawagan SabanalNo ratings yet
- Epithelial Tissue (Compatibility Mode)Document40 pagesEpithelial Tissue (Compatibility Mode)StevenRafaelGarciaManingasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 AnaphyDocument3 pagesChapter 4 AnaphyKate MontenegroNo ratings yet
- BIO2OO - Introduction Tissues, Classification of Living Things & Ecology 1.1.0 Animal TissueDocument19 pagesBIO2OO - Introduction Tissues, Classification of Living Things & Ecology 1.1.0 Animal TissueMark SullivanNo ratings yet
- Tissue and Its ClassificationDocument6 pagesTissue and Its ClassificationPriyanjali Saini100% (1)
- General Biology R Q3Document16 pagesGeneral Biology R Q3Maysheil GalarceNo ratings yet
- BODY TISSUES Reviewer 3Document3 pagesBODY TISSUES Reviewer 3Jaira EmmarinaNo ratings yet
- T I S S U E: 4 Major Types of TissueDocument6 pagesT I S S U E: 4 Major Types of TissueMarla TurquezaNo ratings yet
- Histology Lec 1 & 2Document22 pagesHistology Lec 1 & 2Asma Ghazy100% (1)
- Epithelial TissueDocument71 pagesEpithelial TissueCharlesNo ratings yet
- TissueDocument22 pagesTissueRuhul Qudus NaimNo ratings yet
- Education Notes 2Document6 pagesEducation Notes 2Rwynn MemoryNo ratings yet
- TISSUESDocument28 pagesTISSUESSamuel BordohNo ratings yet
- 03-Epithelial TissuesDocument9 pages03-Epithelial TissuesRehab OmerNo ratings yet
- Animal TissuesDocument46 pagesAnimal TissuesKarthick GovindarajNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Part 2Document10 pagesChapter 3 Part 2Darla FlorendoNo ratings yet
- Skin Body Tissues and MembraneDocument50 pagesSkin Body Tissues and MembraneNaanmatha PuspanathanNo ratings yet
- Tissues ReviewerDocument5 pagesTissues ReviewerJoannah MarieNo ratings yet
- Ep It HeliumDocument24 pagesEp It HeliumKen AkiyamaNo ratings yet
- TissuesDocument91 pagesTissuesSon Ezekiel Gabriel I. BenitezNo ratings yet
- 3.tissue DmaDocument111 pages3.tissue DmaFaisal Mohamad100% (1)
- Epithelial TissueDocument10 pagesEpithelial Tissuememe bolongonNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 4 Tortora TissuesDocument68 pagesCHAPTER 4 Tortora TissuesKenken MijaresNo ratings yet
- Tissues: By: Ruth Abigail C. Valdez BSN, RNDocument62 pagesTissues: By: Ruth Abigail C. Valdez BSN, RNrJNo ratings yet
- Tissue (Notes) (1) 6roDocument4 pagesTissue (Notes) (1) 6romljnura3No ratings yet
- Epithelial TissueDocument5 pagesEpithelial TissueMiss KilmoryNo ratings yet
- Epithelial Tissue - Overview PDFDocument9 pagesEpithelial Tissue - Overview PDFAslak TorgersenNo ratings yet
- Humanhistologyreviewer PDFDocument8 pagesHumanhistologyreviewer PDFDen Angelica DungoNo ratings yet
- Bio HistologyDocument128 pagesBio HistologyYsabelle RamosNo ratings yet
- Animal TissuesDocument20 pagesAnimal TissuesRajesh Kanna A亗No ratings yet
- NothingDocument27 pagesNothingyoussef zareaNo ratings yet
- Tissues, Glands and Membranes: A. FunctionsDocument4 pagesTissues, Glands and Membranes: A. FunctionsRyan Cadorna FontanillaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 General HistologyDocument14 pagesLesson 2 General HistologyDanaNo ratings yet
- Struc. Organization in AnimalsDocument47 pagesStruc. Organization in AnimalsathuNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2Document18 pagesGeneral Biology 2ayah eliviaNo ratings yet
- General HistologyDocument29 pagesGeneral HistologyShalini SinghNo ratings yet
- Human Cell TypesDocument75 pagesHuman Cell Typesmegamemory14No ratings yet
- Tissue ReviewerDocument10 pagesTissue ReviewerDaniela Nicole Manibog Valentino100% (1)
- Microscopical Observation of Epithelial Tissue: Aim of The ExperimentDocument5 pagesMicroscopical Observation of Epithelial Tissue: Aim of The ExperimentCHIRAJIT KUNDUNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Tissue Level of OrganisationDocument66 pagesUnit 1 Tissue Level of Organisationkrystal1994100% (1)
- General Biology IIDocument6 pagesGeneral Biology IIFrederick SantosNo ratings yet
- HistologyDocument6 pagesHistologyMikaela Joy Villaflores CortesNo ratings yet
- lab 9 PDF Epithelial Tissuesم. رشا محمد شاكرDocument12 pageslab 9 PDF Epithelial Tissuesم. رشا محمد شاكرyamanuel25No ratings yet
- Epithelial TissueDocument11 pagesEpithelial TissueFadhil Hussam AhmedNo ratings yet
- Nimal TissueDocument35 pagesNimal TissueJesika GurungNo ratings yet
- Bahasa InggrisDocument5 pagesBahasa Inggrisahmad jamaluddinNo ratings yet
- Epithelial TissuesDocument31 pagesEpithelial Tissuesmuhammad ijazNo ratings yet
- Antecedent and PronounsDocument6 pagesAntecedent and PronounsJamie Lynn BecaucoNo ratings yet
- TFN ReviewerDocument8 pagesTFN ReviewerJamie Lynn BecaucoNo ratings yet
- Moods of The VerbDocument2 pagesMoods of The VerbJamie Lynn BecaucoNo ratings yet
- College EnglishDocument6 pagesCollege EnglishJamie Lynn BecaucoNo ratings yet
- Copernican RevolutionDocument4 pagesCopernican RevolutionJamie Lynn BecaucoNo ratings yet
- Pacemakers Cardiac External Invasive Electrodes TransvenousDocument6 pagesPacemakers Cardiac External Invasive Electrodes TransvenousEduardoNo ratings yet
- Head To Toe Assessment (Sept 12, 2022)Document1 pageHead To Toe Assessment (Sept 12, 2022)Kyle FernandezNo ratings yet
- Intradialytic Hypotension: Arwedi ArwantoDocument17 pagesIntradialytic Hypotension: Arwedi ArwantopiusiNo ratings yet
- Sickle Cell Disease (SCD) - Management Guidelines A5 Booklet A5 Booklet - Final-1Document64 pagesSickle Cell Disease (SCD) - Management Guidelines A5 Booklet A5 Booklet - Final-1Mtwe ZakayoNo ratings yet
- Soal Unstated Detailed QuestionsDocument4 pagesSoal Unstated Detailed QuestionsMaria Delina WijayaNo ratings yet
- Peritoneum 2022Document86 pagesPeritoneum 2022Tayyib KhanNo ratings yet
- Bailey & Love MCQs-EMQs in Surgery-Part - 2Document4 pagesBailey & Love MCQs-EMQs in Surgery-Part - 2JockerNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Cycle & Blood Vessels 2022-1Document8 pagesCardiac Cycle & Blood Vessels 2022-1krrish5906No ratings yet
- Nursing Acronyms Abbreviations TermsDocument5 pagesNursing Acronyms Abbreviations TermsMeyrheana Dorothy GaviolaNo ratings yet
- Medical Auditing Training: CPMA®: Practical Application WorkbookDocument32 pagesMedical Auditing Training: CPMA®: Practical Application WorkbookAnthony El HageNo ratings yet
- Relevant Equine Renal Anatomy, Physiology and Mechanisms of AKI ReviewDocument12 pagesRelevant Equine Renal Anatomy, Physiology and Mechanisms of AKI ReviewMarilú ValdepeñaNo ratings yet
- Textbook of MedicineDocument198 pagesTextbook of MedicineSoumyadip pradhanNo ratings yet
- Ebook Selective Anatomy Vol 2 2Nd Edition PDF Full Chapter PDFDocument67 pagesEbook Selective Anatomy Vol 2 2Nd Edition PDF Full Chapter PDFcharles.brewer536100% (35)
- Atrial Septal Defect With Pulmonary Hypertension: When/how Can We Consider Closure?Document9 pagesAtrial Septal Defect With Pulmonary Hypertension: When/how Can We Consider Closure?Faradiba MaricarNo ratings yet
- الاختصارات الطبية PDFDocument37 pagesالاختصارات الطبية PDFdede jdjNo ratings yet
- Nursing Notes 3Document3 pagesNursing Notes 3karan SinghNo ratings yet
- Drug-Induced Nutrient DepletionDocument4 pagesDrug-Induced Nutrient DepletionVictoria HristovaNo ratings yet
- NRes1 AssignmentDocument2 pagesNRes1 AssignmentAinee MeuvinNo ratings yet
- HES 005 P2 Coverage and Drug Study GuideDocument4 pagesHES 005 P2 Coverage and Drug Study GuideXander Jake Asturias TangcalaganNo ratings yet
- Midodrine For Post-Operative Hypotension - 094 - 2021-02Document3 pagesMidodrine For Post-Operative Hypotension - 094 - 2021-02Miad HabibiNo ratings yet
- Wacker Neuson Crawler Excavator 38z3 Spare Parts List 1000180706Document23 pagesWacker Neuson Crawler Excavator 38z3 Spare Parts List 1000180706thomasyates140693dgp100% (127)
- Unit 5: Implications of Developmental Biology: Teratogenesis: Types and Teratogenic AgentsDocument12 pagesUnit 5: Implications of Developmental Biology: Teratogenesis: Types and Teratogenic AgentsAmar Kant JhaNo ratings yet
- HypertensionDocument57 pagesHypertensionmers puno100% (5)
- Circulation and Gas ExchangeDocument164 pagesCirculation and Gas ExchangeZuliyanto ZakariaNo ratings yet
- The Urinary SystemDocument46 pagesThe Urinary SystemWeb AredomNo ratings yet
- 1193 PDFDocument376 pages1193 PDFAnonymous bsbdWEEKNo ratings yet
- FON Question BankDocument5 pagesFON Question Bankramzan aliNo ratings yet
- Left Bundle Branch Block - UpToDateDocument25 pagesLeft Bundle Branch Block - UpToDateKrull TTTeamNo ratings yet
- General Population (No Diabetes or CKD) Diabetes or CKD PresentDocument2 pagesGeneral Population (No Diabetes or CKD) Diabetes or CKD PresentLalu Ranova100% (1)
ANAPHY WEEK 4 (Notes)
ANAPHY WEEK 4 (Notes)
Uploaded by
Jamie Lynn BecaucoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ANAPHY WEEK 4 (Notes)
ANAPHY WEEK 4 (Notes)
Uploaded by
Jamie Lynn BecaucoCopyright:
Available Formats
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY (ANPH 111) – 4TH WEEK | SEPTEMBER 14, 2022
TOPIC: TISSUES
Tissue – a group of cells that usually have a common origin.
Ectoderm
- gives rise to epidermis and nervous system.
- epidermis, nervous tissue
Endoderm
- produces mucous membrane of respiratory tract, thyroid gland, secretory parts of pancreas.
- lung tissue, thyroid tissue, pancreatic tissue.
Mesoderm
- gives rise to connective and muscle tissue.
- cardiac muscle, skeletal muscle, bone, blood, smooth muscle (gut).
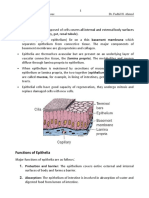
Epithelial
o To found in:
– body coverings
– body linings
– glandular tissues
o To function as:
– protection
– absorption
– filtration
– secretion
o To find as:
– fit close together
– layers has one free surface
– has basement membrane
– avascular
– regenerate easily if well nourished
Cell shape
- Epithelial cells may assume one of three basic shapes:
o Squamous – thin and flat cells
o Cuboidal – cube-shaped cells
o Columnar – tall thin cells
Cell Layers
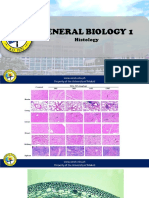
A. Epithelia may appear as single or multiple layers in simple epithelia.
- shape: simple squamous tissues
- consist of a single layer of flat, scale-like cells
- alveoli
B. Simple Cuboidal Tissue
- consist of a single layer of cube-like cells
- secretes and absorbs
- common in glands and their duets
- forms wall of kidney tubules
- covers the ovaries
C. Simple Columnar Epithelial Tissue
- consist of a single layer of tall cells
- absorption often includes goblet cells
- line the digestive tract system
D. Simple Pseudostratified Epithelial Tissue
- consist of a single layer of irregularly shaped columnar cells
- protection and mucus secretion
- sometimes ciliates (respiratory tract)
E. Stratified Squamous
- contains multiple layers (making it stronger)
- found as a protective covering where friction is common
- resist abrasion and penetration of pathogens
- epidermis of skin: mouth and esophagus: vagina/vaginal wall
Two Layer of Cuboidal Cells
- surface cells are columnar cells - stratified cubiodal
- rare in human body - stratified columnar
- found mainly in ducts of large glands - stratified cuboidal and columnar
F. Transitional Epithelium
- multiple cell layer
- shaped depends on amount of stretching
- stretch to allow filling
- line the organs of the urinary system
G. Glandular Epithelium
Endocrine Glands Exocrine Glands
- ductless - ducts to surface
- secretes hormones - oil and sweat
You might also like
- Pediatric ECG Survival Guide - FinalDocument21 pagesPediatric ECG Survival Guide - FinalEmily VlasikNo ratings yet
- Anaphy TissuesDocument4 pagesAnaphy TissuesYo1No ratings yet
- Module 2 TissuesDocument3 pagesModule 2 TissuesRaphael SevillaNo ratings yet
- HistologyDocument16 pagesHistologyHohai ConcepcionNo ratings yet
- MODULE 2.3 Tissue Level of OrganizationDocument12 pagesMODULE 2.3 Tissue Level of OrganizationKate Andrea PanizalesNo ratings yet
- Animal TissuesDocument75 pagesAnimal TissuesFaithlyn Riche YocorNo ratings yet
- TissuesDocument72 pagesTissuesFrelyn Tamba AndresNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissues NEW 1Document54 pagesAnimal Tissues NEW 1Jela AgengaNo ratings yet
- 6 - TissueDocument7 pages6 - TissueJocelyn AtisNo ratings yet
- Topic 4. Cells and Tissues Anatomy and Physiology Autosaved 1Document71 pagesTopic 4. Cells and Tissues Anatomy and Physiology Autosaved 1Janine Jerica JontilanoNo ratings yet
- 4 TissuesDocument124 pages4 TissuesJanette Monica Barrios100% (1)
- Epithelial-Tissues Lect.Document13 pagesEpithelial-Tissues Lect.adelbaneen31No ratings yet
- Vet Histo Notes Chap 2Document10 pagesVet Histo Notes Chap 2Mia Kristhyn Calinawagan SabanalNo ratings yet
- Epithelial Tissue (Compatibility Mode)Document40 pagesEpithelial Tissue (Compatibility Mode)StevenRafaelGarciaManingasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 AnaphyDocument3 pagesChapter 4 AnaphyKate MontenegroNo ratings yet
- BIO2OO - Introduction Tissues, Classification of Living Things & Ecology 1.1.0 Animal TissueDocument19 pagesBIO2OO - Introduction Tissues, Classification of Living Things & Ecology 1.1.0 Animal TissueMark SullivanNo ratings yet
- Tissue and Its ClassificationDocument6 pagesTissue and Its ClassificationPriyanjali Saini100% (1)
- General Biology R Q3Document16 pagesGeneral Biology R Q3Maysheil GalarceNo ratings yet
- BODY TISSUES Reviewer 3Document3 pagesBODY TISSUES Reviewer 3Jaira EmmarinaNo ratings yet
- T I S S U E: 4 Major Types of TissueDocument6 pagesT I S S U E: 4 Major Types of TissueMarla TurquezaNo ratings yet
- Histology Lec 1 & 2Document22 pagesHistology Lec 1 & 2Asma Ghazy100% (1)
- Epithelial TissueDocument71 pagesEpithelial TissueCharlesNo ratings yet
- TissueDocument22 pagesTissueRuhul Qudus NaimNo ratings yet
- Education Notes 2Document6 pagesEducation Notes 2Rwynn MemoryNo ratings yet
- TISSUESDocument28 pagesTISSUESSamuel BordohNo ratings yet
- 03-Epithelial TissuesDocument9 pages03-Epithelial TissuesRehab OmerNo ratings yet
- Animal TissuesDocument46 pagesAnimal TissuesKarthick GovindarajNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Part 2Document10 pagesChapter 3 Part 2Darla FlorendoNo ratings yet
- Skin Body Tissues and MembraneDocument50 pagesSkin Body Tissues and MembraneNaanmatha PuspanathanNo ratings yet
- Tissues ReviewerDocument5 pagesTissues ReviewerJoannah MarieNo ratings yet
- Ep It HeliumDocument24 pagesEp It HeliumKen AkiyamaNo ratings yet
- TissuesDocument91 pagesTissuesSon Ezekiel Gabriel I. BenitezNo ratings yet
- 3.tissue DmaDocument111 pages3.tissue DmaFaisal Mohamad100% (1)
- Epithelial TissueDocument10 pagesEpithelial Tissuememe bolongonNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 4 Tortora TissuesDocument68 pagesCHAPTER 4 Tortora TissuesKenken MijaresNo ratings yet
- Tissues: By: Ruth Abigail C. Valdez BSN, RNDocument62 pagesTissues: By: Ruth Abigail C. Valdez BSN, RNrJNo ratings yet
- Tissue (Notes) (1) 6roDocument4 pagesTissue (Notes) (1) 6romljnura3No ratings yet
- Epithelial TissueDocument5 pagesEpithelial TissueMiss KilmoryNo ratings yet
- Epithelial Tissue - Overview PDFDocument9 pagesEpithelial Tissue - Overview PDFAslak TorgersenNo ratings yet
- Humanhistologyreviewer PDFDocument8 pagesHumanhistologyreviewer PDFDen Angelica DungoNo ratings yet
- Bio HistologyDocument128 pagesBio HistologyYsabelle RamosNo ratings yet
- Animal TissuesDocument20 pagesAnimal TissuesRajesh Kanna A亗No ratings yet
- NothingDocument27 pagesNothingyoussef zareaNo ratings yet
- Tissues, Glands and Membranes: A. FunctionsDocument4 pagesTissues, Glands and Membranes: A. FunctionsRyan Cadorna FontanillaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 General HistologyDocument14 pagesLesson 2 General HistologyDanaNo ratings yet
- Struc. Organization in AnimalsDocument47 pagesStruc. Organization in AnimalsathuNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2Document18 pagesGeneral Biology 2ayah eliviaNo ratings yet
- General HistologyDocument29 pagesGeneral HistologyShalini SinghNo ratings yet
- Human Cell TypesDocument75 pagesHuman Cell Typesmegamemory14No ratings yet
- Tissue ReviewerDocument10 pagesTissue ReviewerDaniela Nicole Manibog Valentino100% (1)
- Microscopical Observation of Epithelial Tissue: Aim of The ExperimentDocument5 pagesMicroscopical Observation of Epithelial Tissue: Aim of The ExperimentCHIRAJIT KUNDUNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Tissue Level of OrganisationDocument66 pagesUnit 1 Tissue Level of Organisationkrystal1994100% (1)
- General Biology IIDocument6 pagesGeneral Biology IIFrederick SantosNo ratings yet
- HistologyDocument6 pagesHistologyMikaela Joy Villaflores CortesNo ratings yet
- lab 9 PDF Epithelial Tissuesم. رشا محمد شاكرDocument12 pageslab 9 PDF Epithelial Tissuesم. رشا محمد شاكرyamanuel25No ratings yet
- Epithelial TissueDocument11 pagesEpithelial TissueFadhil Hussam AhmedNo ratings yet
- Nimal TissueDocument35 pagesNimal TissueJesika GurungNo ratings yet
- Bahasa InggrisDocument5 pagesBahasa Inggrisahmad jamaluddinNo ratings yet
- Epithelial TissuesDocument31 pagesEpithelial Tissuesmuhammad ijazNo ratings yet
- Antecedent and PronounsDocument6 pagesAntecedent and PronounsJamie Lynn BecaucoNo ratings yet
- TFN ReviewerDocument8 pagesTFN ReviewerJamie Lynn BecaucoNo ratings yet
- Moods of The VerbDocument2 pagesMoods of The VerbJamie Lynn BecaucoNo ratings yet
- College EnglishDocument6 pagesCollege EnglishJamie Lynn BecaucoNo ratings yet
- Copernican RevolutionDocument4 pagesCopernican RevolutionJamie Lynn BecaucoNo ratings yet
- Pacemakers Cardiac External Invasive Electrodes TransvenousDocument6 pagesPacemakers Cardiac External Invasive Electrodes TransvenousEduardoNo ratings yet
- Head To Toe Assessment (Sept 12, 2022)Document1 pageHead To Toe Assessment (Sept 12, 2022)Kyle FernandezNo ratings yet
- Intradialytic Hypotension: Arwedi ArwantoDocument17 pagesIntradialytic Hypotension: Arwedi ArwantopiusiNo ratings yet
- Sickle Cell Disease (SCD) - Management Guidelines A5 Booklet A5 Booklet - Final-1Document64 pagesSickle Cell Disease (SCD) - Management Guidelines A5 Booklet A5 Booklet - Final-1Mtwe ZakayoNo ratings yet
- Soal Unstated Detailed QuestionsDocument4 pagesSoal Unstated Detailed QuestionsMaria Delina WijayaNo ratings yet
- Peritoneum 2022Document86 pagesPeritoneum 2022Tayyib KhanNo ratings yet
- Bailey & Love MCQs-EMQs in Surgery-Part - 2Document4 pagesBailey & Love MCQs-EMQs in Surgery-Part - 2JockerNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Cycle & Blood Vessels 2022-1Document8 pagesCardiac Cycle & Blood Vessels 2022-1krrish5906No ratings yet
- Nursing Acronyms Abbreviations TermsDocument5 pagesNursing Acronyms Abbreviations TermsMeyrheana Dorothy GaviolaNo ratings yet
- Medical Auditing Training: CPMA®: Practical Application WorkbookDocument32 pagesMedical Auditing Training: CPMA®: Practical Application WorkbookAnthony El HageNo ratings yet
- Relevant Equine Renal Anatomy, Physiology and Mechanisms of AKI ReviewDocument12 pagesRelevant Equine Renal Anatomy, Physiology and Mechanisms of AKI ReviewMarilú ValdepeñaNo ratings yet
- Textbook of MedicineDocument198 pagesTextbook of MedicineSoumyadip pradhanNo ratings yet
- Ebook Selective Anatomy Vol 2 2Nd Edition PDF Full Chapter PDFDocument67 pagesEbook Selective Anatomy Vol 2 2Nd Edition PDF Full Chapter PDFcharles.brewer536100% (35)
- Atrial Septal Defect With Pulmonary Hypertension: When/how Can We Consider Closure?Document9 pagesAtrial Septal Defect With Pulmonary Hypertension: When/how Can We Consider Closure?Faradiba MaricarNo ratings yet
- الاختصارات الطبية PDFDocument37 pagesالاختصارات الطبية PDFdede jdjNo ratings yet
- Nursing Notes 3Document3 pagesNursing Notes 3karan SinghNo ratings yet
- Drug-Induced Nutrient DepletionDocument4 pagesDrug-Induced Nutrient DepletionVictoria HristovaNo ratings yet
- NRes1 AssignmentDocument2 pagesNRes1 AssignmentAinee MeuvinNo ratings yet
- HES 005 P2 Coverage and Drug Study GuideDocument4 pagesHES 005 P2 Coverage and Drug Study GuideXander Jake Asturias TangcalaganNo ratings yet
- Midodrine For Post-Operative Hypotension - 094 - 2021-02Document3 pagesMidodrine For Post-Operative Hypotension - 094 - 2021-02Miad HabibiNo ratings yet
- Wacker Neuson Crawler Excavator 38z3 Spare Parts List 1000180706Document23 pagesWacker Neuson Crawler Excavator 38z3 Spare Parts List 1000180706thomasyates140693dgp100% (127)
- Unit 5: Implications of Developmental Biology: Teratogenesis: Types and Teratogenic AgentsDocument12 pagesUnit 5: Implications of Developmental Biology: Teratogenesis: Types and Teratogenic AgentsAmar Kant JhaNo ratings yet
- HypertensionDocument57 pagesHypertensionmers puno100% (5)
- Circulation and Gas ExchangeDocument164 pagesCirculation and Gas ExchangeZuliyanto ZakariaNo ratings yet
- The Urinary SystemDocument46 pagesThe Urinary SystemWeb AredomNo ratings yet
- 1193 PDFDocument376 pages1193 PDFAnonymous bsbdWEEKNo ratings yet
- FON Question BankDocument5 pagesFON Question Bankramzan aliNo ratings yet
- Left Bundle Branch Block - UpToDateDocument25 pagesLeft Bundle Branch Block - UpToDateKrull TTTeamNo ratings yet
- General Population (No Diabetes or CKD) Diabetes or CKD PresentDocument2 pagesGeneral Population (No Diabetes or CKD) Diabetes or CKD PresentLalu Ranova100% (1)