Professional Documents
Culture Documents
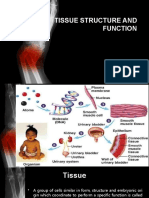
05 Tissue Glands and Membranes
05 Tissue Glands and Membranes
Uploaded by
Kent ClaresterCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Full Download Human Anatomy 9th Edition Martini Solutions ManualDocument35 pagesFull Download Human Anatomy 9th Edition Martini Solutions Manualberthasauflyvski1j100% (30)
- Bobbi Kristina Brown AutopsyDocument10 pagesBobbi Kristina Brown AutopsySyndicated News100% (2)
- Trigger Point Techniques - What Is NAT - Niel Asher HealthcareDocument17 pagesTrigger Point Techniques - What Is NAT - Niel Asher Healthcaresalmazz50% (2)
- Skull RadiographyDocument35 pagesSkull RadiographyHyde Lee Bin HaoNo ratings yet
- 05 Tissue Glands and MembranesDocument6 pages05 Tissue Glands and MembranesRezza PalpallatocNo ratings yet
- Exploring The World of Microscopic AnatomyDocument5 pagesExploring The World of Microscopic AnatomyMark Russel Sean LealNo ratings yet
- Activity No. 4 Module Cell Types and Cell ModificationsDocument7 pagesActivity No. 4 Module Cell Types and Cell ModificationsAryan Jovic DomingoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 - Tissues PDFDocument70 pagesLesson 6 - Tissues PDFVjay Payumo100% (1)
- BIOL 2210L Unit 2: Tissues: Terms To Know For Unit 2Document15 pagesBIOL 2210L Unit 2: Tissues: Terms To Know For Unit 2iuventasNo ratings yet
- Nur112: Anatomy and Physiology ISU Echague - College of NursingDocument14 pagesNur112: Anatomy and Physiology ISU Echague - College of NursingWai KikiNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissues 2023Document70 pagesAnimal Tissues 2023yxcz.rzNo ratings yet
- Module 5 - Body TissuesDocument10 pagesModule 5 - Body Tissues10. Briol AlvinNo ratings yet
- ANPH-M1-CU3. The Tissues and Integumentary SystemDocument33 pagesANPH-M1-CU3. The Tissues and Integumentary Systemajd100% (1)
- Eguia Nsc10Document6 pagesEguia Nsc10AJ EguiaNo ratings yet
- Act05 Animal Histology and Organology DiscussionDocument9 pagesAct05 Animal Histology and Organology DiscussionPaula Nicole AlanoNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy 9th Edition Martini Solutions ManualDocument8 pagesHuman Anatomy 9th Edition Martini Solutions ManualKevinHarrisoncatjn100% (12)
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument13 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyMary Rose Jose GragasinNo ratings yet
- Lab Exercise 1 - Epithelial and Adipose TissuesDocument8 pagesLab Exercise 1 - Epithelial and Adipose TissuesPia CincoNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual - TissuesDocument14 pagesLab Manual - Tissues46bwilson100% (2)
- NRS1102: Anatomy and Physiology (Lecture) 1 Semester 2020-2021 Ejfmania DMD, RN, MANDocument9 pagesNRS1102: Anatomy and Physiology (Lecture) 1 Semester 2020-2021 Ejfmania DMD, RN, MANEllen Mynelle Mabulac100% (1)
- Anaphy ReportingDocument8 pagesAnaphy ReportingRushyl Angela FaeldanNo ratings yet
- LAB EXERCISE4 TISSUES SilveroDocument4 pagesLAB EXERCISE4 TISSUES SilveroGeia Marie SilveroNo ratings yet
- HistologyDocument11 pagesHistologyKeith OmwoyoNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2 Quarter 4 (Week 1-4) : Animals Specialized StructuresDocument18 pagesGeneral Biology 2 Quarter 4 (Week 1-4) : Animals Specialized StructuresHannah CastroNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio 1 Experiment No.2 Animal CellDocument18 pagesGen Bio 1 Experiment No.2 Animal CellIan Karlo NuñezNo ratings yet
- TissuesDocument40 pagesTissuesInsatiable CleeNo ratings yet
- Cells & Tissues: Anatomy & Physiology LaboratoryDocument8 pagesCells & Tissues: Anatomy & Physiology LaboratoryjamielNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Human Anatomy 9th Edition Martini Solutions Manual PDFDocument27 pagesDwnload Full Human Anatomy 9th Edition Martini Solutions Manual PDFcapsicum.imprison0fwm100% (13)
- 1 TISSUES Online Teaching - REVISED 2021 AnaphyDocument38 pages1 TISSUES Online Teaching - REVISED 2021 AnaphySerendipity ParkNo ratings yet
- Bio Presentation Week 2.1Document53 pagesBio Presentation Week 2.1NormanNo ratings yet
- Tissue Structure & FunctionDocument74 pagesTissue Structure & FunctionTaufiqurrahman Sidqi100% (1)
- Cell Types and Cell Modification: LessonDocument6 pagesCell Types and Cell Modification: Lessonjoshiah glennNo ratings yet
- Lab Exercise 4Document4 pagesLab Exercise 4Yeong-Ja KwonNo ratings yet
- Histology Self Quiz Intro and EpitheliumDocument3 pagesHistology Self Quiz Intro and EpitheliumJoonHong An100% (1)
- The Fundamental Unit of Life (Ch-5) : Robert Hooke in 1665Document11 pagesThe Fundamental Unit of Life (Ch-5) : Robert Hooke in 1665Pradeep KhanthNo ratings yet
- Module-4-Tissues, Organs, and Organ SystemsDocument19 pagesModule-4-Tissues, Organs, and Organ SystemsMARIA CORAZON CONTANTENo ratings yet
- 2.human Tissue - For MedicineDocument105 pages2.human Tissue - For Medicineyigermalamanuel32No ratings yet
- Worksheet On TissuesDocument5 pagesWorksheet On TissuesBryan AmoresNo ratings yet
- MODULe 3 AnaphysioDocument9 pagesMODULe 3 Anaphysiojoshua ordenaNo ratings yet
- Module 5. Muscle Tissue17Document7 pagesModule 5. Muscle Tissue17Mark Jay PagaduanNo ratings yet
- Bagian IsiDocument16 pagesBagian IsiKeyla AishaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan: Animal Tissues & CellsDocument7 pagesLesson Plan: Animal Tissues & CellsShailaja MestryNo ratings yet
- A&p Lab Ex 06aDocument6 pagesA&p Lab Ex 06amarycox1989100% (6)
- Connective TissueDocument33 pagesConnective Tissue20227730 PRACHI TOMAR100% (1)
- A221 Module 1 Cell and Tissue PDFDocument10 pagesA221 Module 1 Cell and Tissue PDFAkmal Danish100% (1)
- ENGLISH IN MEDICINE 1 (Y đa khoa) -đã chuyển đổiDocument16 pagesENGLISH IN MEDICINE 1 (Y đa khoa) -đã chuyển đổiNguyễn Thị HiênNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6. HistologyDocument22 pagesChapter 6. Histologymaryelle conejarNo ratings yet
- Cells, Tissues and Membranes-FinaDocument12 pagesCells, Tissues and Membranes-FinaDerrick kinyaNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY Animal Cells ReviewerDocument7 pagesBIOLOGY Animal Cells ReviewerBedecir, Schrister Hynes D.No ratings yet
- Part 3 - Laboratory ManualDocument50 pagesPart 3 - Laboratory ManualBianca AnguloNo ratings yet
- Present 1 - HistologyDocument59 pagesPresent 1 - HistologySultanNo ratings yet
- Mirador Kiana Anaphyact.9Document5 pagesMirador Kiana Anaphyact.9Kiana MiradorNo ratings yet
- 3 Animal Tissues Structure and FunctionDocument16 pages3 Animal Tissues Structure and FunctionIce ShadowNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Tissues, Glands & MembranesDocument10 pagesChapter 4 Tissues, Glands & MembranesMowliid DayibNo ratings yet
- Tissues 1.Document2 pagesTissues 1.Adeaga ElizabethNo ratings yet
- Kristel Joy Bauyon - Lab Activity No.1Document5 pagesKristel Joy Bauyon - Lab Activity No.1tel krisNo ratings yet
- TB3BIOANDGEOUND1Document10 pagesTB3BIOANDGEOUND1Núria Real TortosaNo ratings yet
- Biology Contents - RPSC FSO by Food TecKnowDocument35 pagesBiology Contents - RPSC FSO by Food TecKnowRahul JainNo ratings yet
- Cuizon Lab Act 3Document18 pagesCuizon Lab Act 3Clarizza Joy J. CuizonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document10 pagesChapter 2Deolita BadiangNo ratings yet
- Sri Arliza Febriani TGS 2 No.1Document22 pagesSri Arliza Febriani TGS 2 No.1Sriarliza FebrianiNo ratings yet
- General Histology PDFDocument110 pagesGeneral Histology PDFrudra narayanNo ratings yet
- 09 Nervous System 1 - Human Brain Spinal Cord and NervesDocument4 pages09 Nervous System 1 - Human Brain Spinal Cord and NervesKent ClaresterNo ratings yet
- 08 Muscular System - Muscles and Muscle ContractionDocument6 pages08 Muscular System - Muscles and Muscle ContractionKent Clarester100% (1)
- Structure and Function of CellsDocument6 pagesStructure and Function of CellsKent ClaresterNo ratings yet
- 06 Integumentary SystemDocument4 pages06 Integumentary SystemKent ClaresterNo ratings yet
- 07 Skeletal SystemDocument9 pages07 Skeletal SystemKent ClaresterNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of LifeDocument8 pagesChemistry of LifeKent ClaresterNo ratings yet
- Microscope and MicrosDocument4 pagesMicroscope and MicrosKent ClaresterNo ratings yet
- Physiology and AnatomyDocument5 pagesPhysiology and AnatomyKent ClaresterNo ratings yet
- Cerebral Palsy Assessment Form: History: VisionDocument16 pagesCerebral Palsy Assessment Form: History: VisionRupam KanungoNo ratings yet
- Additional Info of BalletDocument7 pagesAdditional Info of BalletKaren Roldan RosalejosNo ratings yet
- Revisional Asian Blepharoplasty of The High Eyelid Fold - Tarsus-Orbicularis Fixation Combined With Orbital Fat Repositioning TechniqueDocument5 pagesRevisional Asian Blepharoplasty of The High Eyelid Fold - Tarsus-Orbicularis Fixation Combined With Orbital Fat Repositioning TechniqueRaul FonsecaNo ratings yet
- Histology Nutshell - Notespaedia Elite NotesDocument28 pagesHistology Nutshell - Notespaedia Elite NotesShyamPrashadNo ratings yet
- Makhraj Student HandoutsDocument50 pagesMakhraj Student HandoutsZakia Rehman100% (1)
- Subtle Energy Module 01 Materials Color Chakra DiagramDocument1 pageSubtle Energy Module 01 Materials Color Chakra Diagramjoyous leeNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Stretching - Stability - Strength.570239Document2 pagesDynamic Stretching - Stability - Strength.570239Sylvia GraceNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument8 pagesCardiovascular Systemomar farooqNo ratings yet
- PHA618 - Anatomical TermsDocument4 pagesPHA618 - Anatomical TermsGrace Hernandez100% (1)
- Brachial Plexus InjuryDocument39 pagesBrachial Plexus InjurymariaNo ratings yet
- Le Lymphedema Progress SpreadsheetDocument4 pagesLe Lymphedema Progress Spreadsheetapi-486167635No ratings yet
- Relations of Knee Joint: AnteriorlyDocument100 pagesRelations of Knee Joint: AnteriorlysrisakthiNo ratings yet
- 2010 PublicationsLCSPMDDocument6 pages2010 PublicationsLCSPMDEvelyn AsencioNo ratings yet
- Histology of Digestive SystemDocument100 pagesHistology of Digestive SystemFadhila Putri Palupi100% (3)
- Oral Radio Lec 4 FinalDocument11 pagesOral Radio Lec 4 FinalPrince AhmedNo ratings yet
- Trachea (Windpipe)Document21 pagesTrachea (Windpipe)zenith parmarNo ratings yet
- Chap6 Muscular Anaphy NotesDocument13 pagesChap6 Muscular Anaphy NotesAxel Neil VidalNo ratings yet
- D Pharmacy 1st Year B Pharm First Sem - Anatomy & Physiology Notes - Solved Question PaperDocument28 pagesD Pharmacy 1st Year B Pharm First Sem - Anatomy & Physiology Notes - Solved Question Papersham100% (3)
- Neurobiology, Physiology, and BehaviorDocument14 pagesNeurobiology, Physiology, and BehaviorcindyucdNo ratings yet
- Pes 2013 Face FormulasDocument73 pagesPes 2013 Face FormulasCarlos Diaz AcostaNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical (MS) Lecture Respiratory System: Alteration in OxygenationDocument44 pagesMedical Surgical (MS) Lecture Respiratory System: Alteration in OxygenationYman Gio BumanglagNo ratings yet
- Male Physical and Sexual Changes: Happening To An IndividualDocument2 pagesMale Physical and Sexual Changes: Happening To An IndividualMarian Licuasen Ab-aboNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of ConjunctivaDocument22 pagesAnatomy of ConjunctivaDr Sravya M VNo ratings yet
- Thyroid and Antithyroid DrugsDocument2 pagesThyroid and Antithyroid DrugsVidamazing 123No ratings yet
- ReflexesDocument37 pagesReflexesmishky19No ratings yet
- NeuroradiologiDocument76 pagesNeuroradiologiVanessa JuventiaNo ratings yet
- Nbde Part 1 NerveDocument12 pagesNbde Part 1 NerveMrunal DoiphodeNo ratings yet
05 Tissue Glands and Membranes
05 Tissue Glands and Membranes
Uploaded by
Kent ClaresterOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
05 Tissue Glands and Membranes
05 Tissue Glands and Membranes
Uploaded by
Kent ClaresterCopyright:
Available Formats
College of Nursing
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY
LABORATORY
ACTIVITY # 05
TISSUE, GLANDS AND MEMBRANES
I. OBJECTIVES:
1. To observe characteristics common to all epithelial, connective, nervous and muscle tissues
2. To differentiate types f epithelial tissue according to their cellular components
3. To differentiate the types of connective tissue according to their components
4. To cite major differences between connective tissue and epithelial tissue
5. To know different types of glands and membranes.
6. To identify the types of muscles, their morphological characteristics and structural components
7. To identify nervous tissue, their cellular components and structure
II. MATERIALS
1. Compound microscope
2. Prepared slides of X-S of blood vessels, small intestines, kidney, trachea, human skin, urinary
bladder, urethra
3. Prepared slides of dense fibrous connective tissue (tendon), loose fibrous or areola, elastic
reticular and adipose tissue.
4. Slides of skeletal muscles, cardiac muscles and smooth muscles
5. Cross section of myelinated and unmyelinated nerve fiber
III. PROCEDURES
1. Epithelial tissue. Focus each slide under LPO.
Locate the epithelial tissue except for the human skin where the epithelium is on its surface. All
other specimens have the epithelial tissue as their innermost lining. Locate the basement
memories. Shift to MPO or HPO for more detailed study. Observe closely the cellular membrane
arrangement, cell forms, number of cellular layers and the amount of matrix between and among
the cells.
2. Connective tissue. Focus each slide under LPO to get a general view of each specimen. Observe
the:
a. Distribution, abundance, forms and types of cells
b. Amount of intercellular substance of matrix
c. Presence arrangement and types of fibers
Shift to MPO of HPO for detailed study
3. Muscle tissue.
Obtain the slides of a smooth muscle. Study this under MPO and HPO. Study how long spindle
cells are arranged.
Examine a slide containing a section of the heart under LPO. Notice the shape of the cells, how
they are arranged with one another. Take note of the shape of their nucleus and how the nuclei are
distributed. Shift to MPO or HPO “transverse line “maybe seen crossing the cells giving the
muscle fibers a strapped appearance. These are striations. There may also be thicker known as
“intercalated discs”.
Mount slide of the skeletal muscle and observe under LPO. Observe how the fibers are compactly
arranged paralleled to one another. Shift to MPO/HPO and look for the myofibrils, nucleus of the
body (anteriorly and posteriorly)
UC-CON: Anatomy and Physiology Laboratory│ Tissue, Glands and Membranes | 1
4. Nervous tissue. Focus the slide showing the cross section of the myelinated and unmyelinated
nerve fiber under LPO. Look for all the structures of a neuron.
IV. DRAWINGS
Draw the specimen as seen under two observed objectives (LPO, MPO/HPO). Below each,
indicate types of tissue and total magnification.
V. QUESTIONS FOR RESEARCH
EPITHELIAL
1. Enumerate the characteristics common to all epithelial tissues studied in forms of:
a. Arrangement of cells
They form sheets of tightly bound cells or roll into tubes. Epithelial cells lie on the basement membrane.
Epithelial cells have two different “sides”—apical and basolateral.
b. Amount of intercellular substance of matrix
The cells in epithelial tissue are tightly packed together with very little intercellular matrix. Because the
tissues form coverings and linings, the cells have one free surface that is not in contact with other cells.
c. Locate the epithelial tissue
Epithelial tissue or epithelium forms the outer covering of the skin and also lines the body cavity. It forms
the lining of respiratory, digestive, reproductive and excretory tracts.
d. Structure that separates epithelial tissue from other types of tissues
Epithelial cells attach to a specialized kind of extracellular matrix called the basal lamina or basement
membrane that separates epithelial cells from the underlying tissue.
2. How would you distinguish a non-stratified from stratified epithelial tissues?
The fundamental difference between simple and stratified epithelial tissue is that simple epithelial tissue
has only one cell layer. In contrast, stratified epithelial tissue has two or more cell layers piled upon each
other.
3. Classify the specimens used into non-stratified
The stratified epithelium may be categorized based on the type of cells that makes it up.
4. Based on the location and arrangement of the cells of epithelial tissue, give four possible
functions of said tissue. Explain each and cite a specific organ where such is exhibited.
Epithelial tissues are widespread throughout the body. They form the covering of all body
surfaces, line body cavities and hollow organs, and are the major tissue in glands. They perform a variety
of functions that include protection, secretion, absorption, excretion, filtration, diffusion, and sensory
reception.
CONNECTIVE
1. Enumerate characteristics of connective tissues common to the majority of specimens studied.
Connective tissues come in a vast variety of forms, yet they typically have in common three characteristic
components: cells, large amounts of amorphous ground substance, and protein fibers.
2. Identify the pipes of connective tissue fibers in the specimen studied. Describe each as to their
forms or shapes, arrangement location and abundance.
UC-CON: Anatomy and Physiology Laboratory│ Tissue, Glands and Membranes | 2
Connective tissue consists of three main components: cells, protein fibers, and an amorphous ground
substance. Together the fibers and ground substance make up the extracellular matrix. Whereas the other
tissue types (epithelium, muscle, and nervous tissue) are largely made up of cells, the extracellular matrix
is the major component of most connective tissue.
3. List down the types of connective tissues and give a brief description of each as two.
a. Types of cell present of their abundance.
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________________
b. Types of fibers present, if any, their arrangement and abundance.
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________________
c. Amount of intercellular fluid present
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________________
4. Compare the connective tissues with the epithelial tissues. Cite at least four differences.
_________________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________________
_______________
MUSCLE
1. What cellular structures were visibly common to all types and muscle cell?
_________________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________________
_______________
2. In tabulated form, differentiate the skeletal, smooth or cardiac muscles in terms of:
a. Location
b. Functions
c. Types of control
d. Structural features (cell width, cell form, number of nuclei, position of nuclei, presence of
intercalated disc, t-tubules, sarcoplasmic reticulum)
e. Contraction style
NERVOUS
1. Describe the structure of a neuron.
UC-CON: Anatomy and Physiology Laboratory│ Tissue, Glands and Membranes | 3
_________________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________________
_______________
2. What are the differences observed between the myelinated and non-myelinated nerve fibers?
_________________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________________
_______________
GLANDS AND MEMBRANES
a. Enumerate and give the function of the different types of glands (tabulate)
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________________
b. Complete the following table relating to body membranes.
MEMBRANE TISSUE TYPE COMMON FUNCTIONS
LOCATIONS
SEROUS
MUCOUS
CUTANEOUS
SYNOVIAL
c. Why do injuries in adults heal more slowly?
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________________
d. Why would heparin be important to the body?
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________________
Total score: ______________
UC-CON: Anatomy and Physiology Laboratory│ Tissue, Glands and Membranes | 4
Student’s Name Yr & Sec Date Clinical Instructor
UC-CON: Anatomy and Physiology Laboratory│ Tissue, Glands and Membranes | 5
UC-CON: Anatomy and Physiology Laboratory│ Tissue, Glands and Membranes | 6
You might also like
- Full Download Human Anatomy 9th Edition Martini Solutions ManualDocument35 pagesFull Download Human Anatomy 9th Edition Martini Solutions Manualberthasauflyvski1j100% (30)
- Bobbi Kristina Brown AutopsyDocument10 pagesBobbi Kristina Brown AutopsySyndicated News100% (2)
- Trigger Point Techniques - What Is NAT - Niel Asher HealthcareDocument17 pagesTrigger Point Techniques - What Is NAT - Niel Asher Healthcaresalmazz50% (2)
- Skull RadiographyDocument35 pagesSkull RadiographyHyde Lee Bin HaoNo ratings yet
- 05 Tissue Glands and MembranesDocument6 pages05 Tissue Glands and MembranesRezza PalpallatocNo ratings yet
- Exploring The World of Microscopic AnatomyDocument5 pagesExploring The World of Microscopic AnatomyMark Russel Sean LealNo ratings yet
- Activity No. 4 Module Cell Types and Cell ModificationsDocument7 pagesActivity No. 4 Module Cell Types and Cell ModificationsAryan Jovic DomingoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 - Tissues PDFDocument70 pagesLesson 6 - Tissues PDFVjay Payumo100% (1)
- BIOL 2210L Unit 2: Tissues: Terms To Know For Unit 2Document15 pagesBIOL 2210L Unit 2: Tissues: Terms To Know For Unit 2iuventasNo ratings yet
- Nur112: Anatomy and Physiology ISU Echague - College of NursingDocument14 pagesNur112: Anatomy and Physiology ISU Echague - College of NursingWai KikiNo ratings yet
- Animal Tissues 2023Document70 pagesAnimal Tissues 2023yxcz.rzNo ratings yet
- Module 5 - Body TissuesDocument10 pagesModule 5 - Body Tissues10. Briol AlvinNo ratings yet
- ANPH-M1-CU3. The Tissues and Integumentary SystemDocument33 pagesANPH-M1-CU3. The Tissues and Integumentary Systemajd100% (1)
- Eguia Nsc10Document6 pagesEguia Nsc10AJ EguiaNo ratings yet
- Act05 Animal Histology and Organology DiscussionDocument9 pagesAct05 Animal Histology and Organology DiscussionPaula Nicole AlanoNo ratings yet
- Human Anatomy 9th Edition Martini Solutions ManualDocument8 pagesHuman Anatomy 9th Edition Martini Solutions ManualKevinHarrisoncatjn100% (12)
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument13 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyMary Rose Jose GragasinNo ratings yet
- Lab Exercise 1 - Epithelial and Adipose TissuesDocument8 pagesLab Exercise 1 - Epithelial and Adipose TissuesPia CincoNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual - TissuesDocument14 pagesLab Manual - Tissues46bwilson100% (2)
- NRS1102: Anatomy and Physiology (Lecture) 1 Semester 2020-2021 Ejfmania DMD, RN, MANDocument9 pagesNRS1102: Anatomy and Physiology (Lecture) 1 Semester 2020-2021 Ejfmania DMD, RN, MANEllen Mynelle Mabulac100% (1)
- Anaphy ReportingDocument8 pagesAnaphy ReportingRushyl Angela FaeldanNo ratings yet
- LAB EXERCISE4 TISSUES SilveroDocument4 pagesLAB EXERCISE4 TISSUES SilveroGeia Marie SilveroNo ratings yet
- HistologyDocument11 pagesHistologyKeith OmwoyoNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2 Quarter 4 (Week 1-4) : Animals Specialized StructuresDocument18 pagesGeneral Biology 2 Quarter 4 (Week 1-4) : Animals Specialized StructuresHannah CastroNo ratings yet
- Gen Bio 1 Experiment No.2 Animal CellDocument18 pagesGen Bio 1 Experiment No.2 Animal CellIan Karlo NuñezNo ratings yet
- TissuesDocument40 pagesTissuesInsatiable CleeNo ratings yet
- Cells & Tissues: Anatomy & Physiology LaboratoryDocument8 pagesCells & Tissues: Anatomy & Physiology LaboratoryjamielNo ratings yet
- Dwnload Full Human Anatomy 9th Edition Martini Solutions Manual PDFDocument27 pagesDwnload Full Human Anatomy 9th Edition Martini Solutions Manual PDFcapsicum.imprison0fwm100% (13)
- 1 TISSUES Online Teaching - REVISED 2021 AnaphyDocument38 pages1 TISSUES Online Teaching - REVISED 2021 AnaphySerendipity ParkNo ratings yet
- Bio Presentation Week 2.1Document53 pagesBio Presentation Week 2.1NormanNo ratings yet
- Tissue Structure & FunctionDocument74 pagesTissue Structure & FunctionTaufiqurrahman Sidqi100% (1)
- Cell Types and Cell Modification: LessonDocument6 pagesCell Types and Cell Modification: Lessonjoshiah glennNo ratings yet
- Lab Exercise 4Document4 pagesLab Exercise 4Yeong-Ja KwonNo ratings yet
- Histology Self Quiz Intro and EpitheliumDocument3 pagesHistology Self Quiz Intro and EpitheliumJoonHong An100% (1)
- The Fundamental Unit of Life (Ch-5) : Robert Hooke in 1665Document11 pagesThe Fundamental Unit of Life (Ch-5) : Robert Hooke in 1665Pradeep KhanthNo ratings yet
- Module-4-Tissues, Organs, and Organ SystemsDocument19 pagesModule-4-Tissues, Organs, and Organ SystemsMARIA CORAZON CONTANTENo ratings yet
- 2.human Tissue - For MedicineDocument105 pages2.human Tissue - For Medicineyigermalamanuel32No ratings yet
- Worksheet On TissuesDocument5 pagesWorksheet On TissuesBryan AmoresNo ratings yet
- MODULe 3 AnaphysioDocument9 pagesMODULe 3 Anaphysiojoshua ordenaNo ratings yet
- Module 5. Muscle Tissue17Document7 pagesModule 5. Muscle Tissue17Mark Jay PagaduanNo ratings yet
- Bagian IsiDocument16 pagesBagian IsiKeyla AishaNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan: Animal Tissues & CellsDocument7 pagesLesson Plan: Animal Tissues & CellsShailaja MestryNo ratings yet
- A&p Lab Ex 06aDocument6 pagesA&p Lab Ex 06amarycox1989100% (6)
- Connective TissueDocument33 pagesConnective Tissue20227730 PRACHI TOMAR100% (1)
- A221 Module 1 Cell and Tissue PDFDocument10 pagesA221 Module 1 Cell and Tissue PDFAkmal Danish100% (1)
- ENGLISH IN MEDICINE 1 (Y đa khoa) -đã chuyển đổiDocument16 pagesENGLISH IN MEDICINE 1 (Y đa khoa) -đã chuyển đổiNguyễn Thị HiênNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6. HistologyDocument22 pagesChapter 6. Histologymaryelle conejarNo ratings yet
- Cells, Tissues and Membranes-FinaDocument12 pagesCells, Tissues and Membranes-FinaDerrick kinyaNo ratings yet
- BIOLOGY Animal Cells ReviewerDocument7 pagesBIOLOGY Animal Cells ReviewerBedecir, Schrister Hynes D.No ratings yet
- Part 3 - Laboratory ManualDocument50 pagesPart 3 - Laboratory ManualBianca AnguloNo ratings yet
- Present 1 - HistologyDocument59 pagesPresent 1 - HistologySultanNo ratings yet
- Mirador Kiana Anaphyact.9Document5 pagesMirador Kiana Anaphyact.9Kiana MiradorNo ratings yet
- 3 Animal Tissues Structure and FunctionDocument16 pages3 Animal Tissues Structure and FunctionIce ShadowNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Tissues, Glands & MembranesDocument10 pagesChapter 4 Tissues, Glands & MembranesMowliid DayibNo ratings yet
- Tissues 1.Document2 pagesTissues 1.Adeaga ElizabethNo ratings yet
- Kristel Joy Bauyon - Lab Activity No.1Document5 pagesKristel Joy Bauyon - Lab Activity No.1tel krisNo ratings yet
- TB3BIOANDGEOUND1Document10 pagesTB3BIOANDGEOUND1Núria Real TortosaNo ratings yet
- Biology Contents - RPSC FSO by Food TecKnowDocument35 pagesBiology Contents - RPSC FSO by Food TecKnowRahul JainNo ratings yet
- Cuizon Lab Act 3Document18 pagesCuizon Lab Act 3Clarizza Joy J. CuizonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document10 pagesChapter 2Deolita BadiangNo ratings yet
- Sri Arliza Febriani TGS 2 No.1Document22 pagesSri Arliza Febriani TGS 2 No.1Sriarliza FebrianiNo ratings yet
- General Histology PDFDocument110 pagesGeneral Histology PDFrudra narayanNo ratings yet
- 09 Nervous System 1 - Human Brain Spinal Cord and NervesDocument4 pages09 Nervous System 1 - Human Brain Spinal Cord and NervesKent ClaresterNo ratings yet
- 08 Muscular System - Muscles and Muscle ContractionDocument6 pages08 Muscular System - Muscles and Muscle ContractionKent Clarester100% (1)
- Structure and Function of CellsDocument6 pagesStructure and Function of CellsKent ClaresterNo ratings yet
- 06 Integumentary SystemDocument4 pages06 Integumentary SystemKent ClaresterNo ratings yet
- 07 Skeletal SystemDocument9 pages07 Skeletal SystemKent ClaresterNo ratings yet
- Chemistry of LifeDocument8 pagesChemistry of LifeKent ClaresterNo ratings yet
- Microscope and MicrosDocument4 pagesMicroscope and MicrosKent ClaresterNo ratings yet
- Physiology and AnatomyDocument5 pagesPhysiology and AnatomyKent ClaresterNo ratings yet
- Cerebral Palsy Assessment Form: History: VisionDocument16 pagesCerebral Palsy Assessment Form: History: VisionRupam KanungoNo ratings yet
- Additional Info of BalletDocument7 pagesAdditional Info of BalletKaren Roldan RosalejosNo ratings yet
- Revisional Asian Blepharoplasty of The High Eyelid Fold - Tarsus-Orbicularis Fixation Combined With Orbital Fat Repositioning TechniqueDocument5 pagesRevisional Asian Blepharoplasty of The High Eyelid Fold - Tarsus-Orbicularis Fixation Combined With Orbital Fat Repositioning TechniqueRaul FonsecaNo ratings yet
- Histology Nutshell - Notespaedia Elite NotesDocument28 pagesHistology Nutshell - Notespaedia Elite NotesShyamPrashadNo ratings yet
- Makhraj Student HandoutsDocument50 pagesMakhraj Student HandoutsZakia Rehman100% (1)
- Subtle Energy Module 01 Materials Color Chakra DiagramDocument1 pageSubtle Energy Module 01 Materials Color Chakra Diagramjoyous leeNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Stretching - Stability - Strength.570239Document2 pagesDynamic Stretching - Stability - Strength.570239Sylvia GraceNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument8 pagesCardiovascular Systemomar farooqNo ratings yet
- PHA618 - Anatomical TermsDocument4 pagesPHA618 - Anatomical TermsGrace Hernandez100% (1)
- Brachial Plexus InjuryDocument39 pagesBrachial Plexus InjurymariaNo ratings yet
- Le Lymphedema Progress SpreadsheetDocument4 pagesLe Lymphedema Progress Spreadsheetapi-486167635No ratings yet
- Relations of Knee Joint: AnteriorlyDocument100 pagesRelations of Knee Joint: AnteriorlysrisakthiNo ratings yet
- 2010 PublicationsLCSPMDDocument6 pages2010 PublicationsLCSPMDEvelyn AsencioNo ratings yet
- Histology of Digestive SystemDocument100 pagesHistology of Digestive SystemFadhila Putri Palupi100% (3)
- Oral Radio Lec 4 FinalDocument11 pagesOral Radio Lec 4 FinalPrince AhmedNo ratings yet
- Trachea (Windpipe)Document21 pagesTrachea (Windpipe)zenith parmarNo ratings yet
- Chap6 Muscular Anaphy NotesDocument13 pagesChap6 Muscular Anaphy NotesAxel Neil VidalNo ratings yet
- D Pharmacy 1st Year B Pharm First Sem - Anatomy & Physiology Notes - Solved Question PaperDocument28 pagesD Pharmacy 1st Year B Pharm First Sem - Anatomy & Physiology Notes - Solved Question Papersham100% (3)
- Neurobiology, Physiology, and BehaviorDocument14 pagesNeurobiology, Physiology, and BehaviorcindyucdNo ratings yet
- Pes 2013 Face FormulasDocument73 pagesPes 2013 Face FormulasCarlos Diaz AcostaNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical (MS) Lecture Respiratory System: Alteration in OxygenationDocument44 pagesMedical Surgical (MS) Lecture Respiratory System: Alteration in OxygenationYman Gio BumanglagNo ratings yet
- Male Physical and Sexual Changes: Happening To An IndividualDocument2 pagesMale Physical and Sexual Changes: Happening To An IndividualMarian Licuasen Ab-aboNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of ConjunctivaDocument22 pagesAnatomy of ConjunctivaDr Sravya M VNo ratings yet
- Thyroid and Antithyroid DrugsDocument2 pagesThyroid and Antithyroid DrugsVidamazing 123No ratings yet
- ReflexesDocument37 pagesReflexesmishky19No ratings yet
- NeuroradiologiDocument76 pagesNeuroradiologiVanessa JuventiaNo ratings yet
- Nbde Part 1 NerveDocument12 pagesNbde Part 1 NerveMrunal DoiphodeNo ratings yet