Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Waves and Optics 1
Waves and Optics 1
Uploaded by
Genesis PalangiOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Waves and Optics 1
Waves and Optics 1
Uploaded by
Genesis PalangiCopyright:
Available Formats
Divine Word College of Bangued
Bangued, Abra
School of Arts, Sciences and Education
Palangi, Genesis B.
BSED 3 (Major in Science)
Waves and Optics
Research on the following:
1. What are waves?
A wave is a disturbance in a medium that carries energy without a net movement of particles.
It may take the form of elastic deformation, a variation of pressure, electric or magnetic
intensity, electric potential, or temperature.
Source:
https://byjus.com/physics/waves/#:~:text=A%20wave%20is%20a%20disturbance,%2C
%20electric%20potential%2C%20or%20temperature.
2. What is the nature of waves?
A disturbance, in the sense used in this definition, is a change from the current state of a
measurable quantity at some location. For example
a change in a kinematic variable like position, velocity, or acceleration;
a change in an intensive property like pressure, density, or temperature;
a change in field strength like electric field strength, magnetic field strength, or gravitational
field strength.
To propagate, in the sense used in this definition, is to transmit the influence of something in a
particular direction.
Synonyms for propagate include spread, transmit, communicate, and broadcast. The noun
form of the word is propagation.
A medium is the substance through which a wave can propagate. Water is the medium of
ocean waves.
Air is the medium through which we hear sound waves. The electric and magnetic fields are the
medium of light.
People are the medium of a stadium wave.
The Earth is the medium of seismic waves (earthquake waves).
Cell membranes are the medium of nerve impulses.
Transmission lines are the medium of alternating current electric power. Medium is the singuar
form of the noun.
Media is the plural form (although mediums is preferred by some people).
Source:
https://physics.info/waves/
3. What are the types of waves?
Mechanical waves.
Divine Word College of Bangued
Bangued, Abra
School of Arts, Sciences and Education
Electromagnetic waves.
Matter waves.
4. What are the parts of waves in physics?
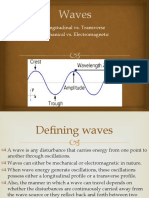
Wave Crest:
The highest part of a wave.
Wave Trough:
The lowest part of a wave.
Wave Height:
The vertical distance between the wave trough and the wave crest.
Wave Length:
The distance between two consecutive wave crests or between two
consecutive wave troughs.
Source:
https://secoora.org/education-outreach/waves/glossary/#:~:text=Wave%20Crest
%3A%20The%20highest%20part,between%20two%20consecutive%20wave
%20troughs.
You might also like
- SPH 103 Waves and Optics - Lecture Notes - January - April 2016Document32 pagesSPH 103 Waves and Optics - Lecture Notes - January - April 2016Vikas TomarNo ratings yet
- Professional English For Students of Logistics PDFDocument187 pagesProfessional English For Students of Logistics PDFbibaNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity Sheet: WavesDocument7 pagesLearning Activity Sheet: WavesKyera LovesNo ratings yet
- Presentation On WavesDocument7 pagesPresentation On Wavesmaqsood ahmadNo ratings yet
- WaveDocument17 pagesWaveJevanthe Miguel ObusanNo ratings yet
- Biophysics 1Document25 pagesBiophysics 1Shadrack SamuelNo ratings yet
- Properties of Waves: o o o oDocument2 pagesProperties of Waves: o o o oJho BugtongNo ratings yet
- Phys101 - Finals Quiz 1Document2 pagesPhys101 - Finals Quiz 1Natasha AcaoNo ratings yet
- Basic Wave PhenomenaDocument43 pagesBasic Wave Phenomena李彊No ratings yet
- Learning Activity Sheet in General Physics 1 Lesson 11: Mechanical Waves and SoundDocument10 pagesLearning Activity Sheet in General Physics 1 Lesson 11: Mechanical Waves and SoundSenica Caydil Jay D.No ratings yet
- P22 1 Sound and ResonanceDocument12 pagesP22 1 Sound and ResonanceSantiago GaliciaNo ratings yet
- The World Communicates James SaraDocument11 pagesThe World Communicates James SaraJames coleNo ratings yet
- General Physics 2 Module 3 My AnswersDocument3 pagesGeneral Physics 2 Module 3 My AnswersMatth N. ErejerNo ratings yet
- " Wave Motion": Ma. Clarissa Cantos - G6 Innah Denyse Almarez - G2 IV - St. Stephen Mrs. Viola AbratiqueDocument12 pages" Wave Motion": Ma. Clarissa Cantos - G6 Innah Denyse Almarez - G2 IV - St. Stephen Mrs. Viola AbratiqueMaria ClarissaNo ratings yet
- Waves: Physics Departement Mathematics and Science Faculty Padang State University 2011Document13 pagesWaves: Physics Departement Mathematics and Science Faculty Padang State University 2011Yuli AriyadiNo ratings yet
- Building Utilities 3: Acoustics and Lighting SystemsDocument5 pagesBuilding Utilities 3: Acoustics and Lighting SystemsDennis Roel T. DulayNo ratings yet
- Different Types of Wave1Document5 pagesDifferent Types of Wave1Patrick Joshua ZacariasNo ratings yet
- 1-Classification of Waves-16-02-2023Document12 pages1-Classification of Waves-16-02-2023efewfwedawasNo ratings yet
- Physics - Peak Science: Three Dimensions Depending On The Nature of The WaveDocument13 pagesPhysics - Peak Science: Three Dimensions Depending On The Nature of The WaveVincent TranNo ratings yet
- 03+G7 WavesDocument26 pages03+G7 WavesRose Ann YamcoNo ratings yet
- Wave HandoutDocument2 pagesWave HandoutBridget CumlatNo ratings yet
- WaveDocument1 pageWaveTrideep BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- A Wave Is A Disturbance in A Medium That Carries Energy Without A Net Movement of ParticlesDocument5 pagesA Wave Is A Disturbance in A Medium That Carries Energy Without A Net Movement of ParticlesMercy PaduaNo ratings yet
- This Article Is About Waves in The Scientific Sense. For Waves On The Surface of The Ocean or Lakes, See - For Other Uses, SeeDocument1 pageThis Article Is About Waves in The Scientific Sense. For Waves On The Surface of The Ocean or Lakes, See - For Other Uses, SeeANMOLNo ratings yet
- Waves, Light Waves, Sound Waves and Ultrasound (The Physics Of)Document15 pagesWaves, Light Waves, Sound Waves and Ultrasound (The Physics Of)ShatiJanzour TicketingNo ratings yet
- Wave C11Document8 pagesWave C11Wajira Sanjaya PereraNo ratings yet
- Different Types of WavesDocument4 pagesDifferent Types of Waveselladionisio01No ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1 - Learning MaterialDocument22 pagesCHAPTER 1 - Learning MaterialRachelle DacuycuyNo ratings yet
- Bse Iii-3 - Sci117 - Module 1Document15 pagesBse Iii-3 - Sci117 - Module 1Ambat mark anthonyNo ratings yet
- Bse III-3 Sci117 Module 1Document15 pagesBse III-3 Sci117 Module 1Ambat mark anthonyNo ratings yet
- Wave Motion PDFDocument23 pagesWave Motion PDFFRANCES VISAYA100% (1)
- Electromagnetic Theory and WavesDocument8 pagesElectromagnetic Theory and WavesLina Maria Medina VelezNo ratings yet
- Las Science 7 w4Document2 pagesLas Science 7 w4Darven CinchezNo ratings yet
- WaveDocument14 pagesWaveLitiaMikoNo ratings yet
- Formative Assessment 5Document1 pageFormative Assessment 5bashadelacruz7No ratings yet
- Physics II - WavesDocument15 pagesPhysics II - WavesVicky Waran RajNo ratings yet
- Waves Homework From The Book:: MechanicalDocument11 pagesWaves Homework From The Book:: MechanicalMaha Letchumy BalakeristananNo ratings yet
- Kottakkal Farook ArtsDocument9 pagesKottakkal Farook Artsvishnuvnair751No ratings yet
- Mechanicalvselectromagneticwaves 121211033256 Phpapp01Document29 pagesMechanicalvselectromagneticwaves 121211033256 Phpapp01almira villarealNo ratings yet
- Wave Theory1Document30 pagesWave Theory1refoyak828No ratings yet
- Waves 2021Document40 pagesWaves 2021Dimas VidiandaruNo ratings yet
- Phych 1Document4 pagesPhych 1bhaveshjoshifirehNo ratings yet
- 01 Introduction To Properties of Waves Text MergedDocument8 pages01 Introduction To Properties of Waves Text MergedkachechiekurosakiNo ratings yet
- Waves 1Document7 pagesWaves 1Fathimath SajahathNo ratings yet
- Oscillation: Online Learning Resources For Malaysia StudentsDocument0 pagesOscillation: Online Learning Resources For Malaysia StudentsJia HuiNo ratings yet
- G7 WavesDocument15 pagesG7 WavesHoney Mae CarvajalNo ratings yet
- Waves, Light Waves, Sound Waves and Ultrasound (The Physics Of)Document15 pagesWaves, Light Waves, Sound Waves and Ultrasound (The Physics Of)Jc C. GomezNo ratings yet
- Acoustics and UltasonicsDocument17 pagesAcoustics and UltasonicsKamalesh KarthiNo ratings yet
- SLHT SCI 7 Q3 WK 4 OKDocument7 pagesSLHT SCI 7 Q3 WK 4 OKpadayaojonsamuelNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To WaveDocument9 pagesAn Introduction To WaveOyeladun IdrisNo ratings yet
- Wave - WikipediaDocument29 pagesWave - WikipediaMark NyamesemNo ratings yet
- Clem Waves Lesson02 Notes As PDFDocument1 pageClem Waves Lesson02 Notes As PDFRusherNo ratings yet
- Subject: Physics AS (Unit 2) Topic: Waves: Made By: Moustafa Mohamed Ahmed Ewis Adham Ibrahim Youssef BedairDocument7 pagesSubject: Physics AS (Unit 2) Topic: Waves: Made By: Moustafa Mohamed Ahmed Ewis Adham Ibrahim Youssef BedairAhmed Mohamed EwisNo ratings yet
- Articulo IeeeDocument5 pagesArticulo IeeeFajardo Acosta Julian CamiloNo ratings yet
- Pintuan Joshua MoisesDocument7 pagesPintuan Joshua MoisesKate Winslet Love Galan FazonNo ratings yet
- WavesDocument27 pagesWavesBrianna MalcolmNo ratings yet
- Paper EnglishDocument18 pagesPaper EnglishShinta Mutiara DewiNo ratings yet
- Waves and ColourDocument10 pagesWaves and ColourEMMANUELNo ratings yet
- SLK G7 Q3wk4 Catubig RevisedDocument12 pagesSLK G7 Q3wk4 Catubig RevisedJen-jen Ybanez BalderasNo ratings yet
- Wave Hi and Goodbye to Energy! An Introduction to Waves - Physics Lessons for Kids | Children's Physics BooksFrom EverandWave Hi and Goodbye to Energy! An Introduction to Waves - Physics Lessons for Kids | Children's Physics BooksNo ratings yet
- ELECTROMAGNETIC FIELDS: Exposure is not optional, no one can avoid itFrom EverandELECTROMAGNETIC FIELDS: Exposure is not optional, no one can avoid itNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3Document2 pagesLesson 3Genesis PalangiNo ratings yet
- Learning Plan Atomic Structure 8Document2 pagesLearning Plan Atomic Structure 8Genesis PalangiNo ratings yet
- LEARNING PLAN WavesDocument7 pagesLEARNING PLAN WavesGenesis PalangiNo ratings yet
- Research TitleDocument1 pageResearch TitleGenesis PalangiNo ratings yet
- LESSON PLAN (Revised Version)Document14 pagesLESSON PLAN (Revised Version)Genesis PalangiNo ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument17 pagesLesson PlanGenesis PalangiNo ratings yet
- To Edit Case Study GladysDocument12 pagesTo Edit Case Study GladysGenesis PalangiNo ratings yet
- EvaluationDocument1 pageEvaluationGenesis PalangiNo ratings yet
- Latest Leeson Plan Week 1Document9 pagesLatest Leeson Plan Week 1Genesis PalangiNo ratings yet
- LaterRomanEducationinAusoniusCapellaandtheTheodosianCode 10067272Document44 pagesLaterRomanEducationinAusoniusCapellaandtheTheodosianCode 10067272Genesis PalangiNo ratings yet
- Lit 2 Lessons 5, 6 and 7 AldrinDocument7 pagesLit 2 Lessons 5, 6 and 7 AldrinGenesis PalangiNo ratings yet
- Dark Green and White Modern Minimalist Thesis Defense PresentationDocument13 pagesDark Green and White Modern Minimalist Thesis Defense PresentationGenesis PalangiNo ratings yet
- 2021 PBB TemplateDocument8 pages2021 PBB TemplateGenesis PalangiNo ratings yet
- NCM 110 LaboratoryDocument3 pagesNCM 110 LaboratoryGenesis PalangiNo ratings yet
- Dar 0ctober La Ba PS and Makingag Es 1Document8 pagesDar 0ctober La Ba PS and Makingag Es 1Genesis PalangiNo ratings yet
- LABADocument2 pagesLABAGenesis PalangiNo ratings yet
- Darjune 2021Document8 pagesDarjune 2021Genesis PalangiNo ratings yet
- EDDITEDDocument6 pagesEDDITEDGenesis PalangiNo ratings yet
- NCM 110 LectureDocument3 pagesNCM 110 LectureGenesis PalangiNo ratings yet
- StoichiometryDocument26 pagesStoichiometryGenesis PalangiNo ratings yet
- DPA February 2021Document2 pagesDPA February 2021Genesis PalangiNo ratings yet
- Brigada Eskwela 2022Document8 pagesBrigada Eskwela 2022Genesis PalangiNo ratings yet
- Earth Science Module 1Document23 pagesEarth Science Module 1Genesis PalangiNo ratings yet
- Final Best PracticeDocument6 pagesFinal Best PracticeGenesis PalangiNo ratings yet
- Teaching As A Profession, As A Vocation and MissionDocument4 pagesTeaching As A Profession, As A Vocation and MissionGenesis PalangiNo ratings yet
- Teaching TechnologyDocument6 pagesTeaching TechnologyGenesis PalangiNo ratings yet
- NCM 108 (Health Care Ethics)Document3 pagesNCM 108 (Health Care Ethics)Genesis PalangiNo ratings yet
- Research The FollowingDocument4 pagesResearch The FollowingGenesis PalangiNo ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesLesson PlanGenesis PalangiNo ratings yet
- Vectors and ScalesDocument4 pagesVectors and ScalesGenesis PalangiNo ratings yet
- Austin Lecture 5Document3 pagesAustin Lecture 5adityatnnlsNo ratings yet
- Bca SyllabusDocument18 pagesBca SyllabusKAUSHIKNo ratings yet
- ISBN Registration 1Document6 pagesISBN Registration 1prncoNo ratings yet
- Tok - 2.2Document3 pagesTok - 2.2Mehar SalmanNo ratings yet
- Kinetics HL - Set 2-MSDocument75 pagesKinetics HL - Set 2-MSN I K K INo ratings yet
- Running Tensorflow Lite On The Raspberry Pi 4Document21 pagesRunning Tensorflow Lite On The Raspberry Pi 411mustafa.mNo ratings yet
- AsciiDocument1 pageAsciiocetazamNo ratings yet
- Saurabh Garg - CVDocument4 pagesSaurabh Garg - CVJEn Narendra Singh DeoraNo ratings yet
- Jesus Invites Us From ConscienceDocument18 pagesJesus Invites Us From Consciencejonalyn obinaNo ratings yet
- What Does The Love SaysDocument4 pagesWhat Does The Love SaysReymond CuisonNo ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument2 pagesSyllabusNaveen GuptaNo ratings yet
- Energy Efficient Home Automation Using Python Programming - V1.8Document21 pagesEnergy Efficient Home Automation Using Python Programming - V1.8Lava KumarNo ratings yet
- BIBLIOGRAPHYDocument12 pagesBIBLIOGRAPHYdingdongjungkookNo ratings yet
- The Power of WordsDocument2 pagesThe Power of WordsWendy WezerNo ratings yet
- Mindanao FinalDocument17 pagesMindanao FinalCharisse Jane PacilanNo ratings yet
- Apmo 2019 ListDocument2 pagesApmo 2019 Listnaresh malikNo ratings yet
- Spanish AQADocument20 pagesSpanish AQAsanhe0803No ratings yet
- LFS LFS LFS LFS LFS: User ManualDocument38 pagesLFS LFS LFS LFS LFS: User ManualRyan Dwi OutsiderNo ratings yet
- 46TH CBF Stall DetailsDocument10 pages46TH CBF Stall Detailsmmurugesh_rajNo ratings yet
- KING, C. Richard. Alter Native Heroes Native Americans, Comic Books, and The Struggle For Self-Definition.Document10 pagesKING, C. Richard. Alter Native Heroes Native Americans, Comic Books, and The Struggle For Self-Definition.IVAN LIMA GOMESNo ratings yet
- Cause and Effect Table PDFDocument3 pagesCause and Effect Table PDFKamal DeshapriyaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To CFX - CEL-chapter 11Document19 pagesIntroduction To CFX - CEL-chapter 11mohmehrNo ratings yet
- 3rd Grade Instructional Module English ProgramDocument118 pages3rd Grade Instructional Module English ProgramRaquel VargasNo ratings yet
- Window To World HistoryDocument22 pagesWindow To World HistoryDAYYAN AHMED BHATT100% (1)
- 100% Work! Ubuntu+Freeradius2+CoovaChilli+DaloradiusDocument9 pages100% Work! Ubuntu+Freeradius2+CoovaChilli+DaloradiusTetsuya Free67% (3)
- Allan S. One Palette, Two Lands. The Myth of The Unification of Egypt by The Narmer Palette PDFDocument128 pagesAllan S. One Palette, Two Lands. The Myth of The Unification of Egypt by The Narmer Palette PDFМихаил ЧегодаевNo ratings yet
- The Official Website of Alshaikh Hafiz Zubair Alizai (MABPWH) IsDocument51 pagesThe Official Website of Alshaikh Hafiz Zubair Alizai (MABPWH) IsishaatulhadithNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Vitae: ShruthiDocument2 pagesCurriculum Vitae: ShruthiSHRUTHI ASODUNo ratings yet
- Ms Excel Test Max Marks-20 Duration - 20minDocument3 pagesMs Excel Test Max Marks-20 Duration - 20minPravin ShindeNo ratings yet