Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Purpose:: Investigation of The Inverse Square Law of Radiation
Purpose:: Investigation of The Inverse Square Law of Radiation
Uploaded by
Ra Yan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views3 pagesThis document investigates the inverse square law of radiation by measuring the radiation (R in mV) from a source at distances (X in cm) ranging from 10 to 90 cm. It records the inverse and inverse square of the distances. The discussion explains that the inverse square law states that a physical quantity like radiation decreases inversely with the square of the distance from the source, because the area of the sphere around the source increases with the square of the radius. The experiment's results support that the radiation measured follows the inverse square relationship with distance predicted by the law.
Original Description:
Original Title
164458392660834 copy copy
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document investigates the inverse square law of radiation by measuring the radiation (R in mV) from a source at distances (X in cm) ranging from 10 to 90 cm. It records the inverse and inverse square of the distances. The discussion explains that the inverse square law states that a physical quantity like radiation decreases inversely with the square of the distance from the source, because the area of the sphere around the source increases with the square of the radius. The experiment's results support that the radiation measured follows the inverse square relationship with distance predicted by the law.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views3 pagesPurpose:: Investigation of The Inverse Square Law of Radiation
Purpose:: Investigation of The Inverse Square Law of Radiation
Uploaded by
Ra YanThis document investigates the inverse square law of radiation by measuring the radiation (R in mV) from a source at distances (X in cm) ranging from 10 to 90 cm. It records the inverse and inverse square of the distances. The discussion explains that the inverse square law states that a physical quantity like radiation decreases inversely with the square of the distance from the source, because the area of the sphere around the source increases with the square of the radius. The experiment's results support that the radiation measured follows the inverse square relationship with distance predicted by the law.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
Purpose:
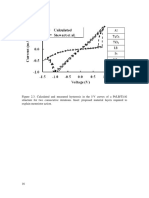
Investigation of the inverse square law of radiation.
Reading:
X (cm) R (mV) 1/ X (cm¿ −1
1/ X
2
(cm¿ −2
∗10
−3
10 4.1 0.1 10
20 3.4 0.05 2.5
30 2.7 0.033 1.1
40 2.1 0.025 0.63
50 1.5 0.020 0.4
60 1 0.016 0.27
70 0.8 0.014 0.2
80 0.6 0.0125 0.15
90 0.5 0.011 0.12
Parameter:
X: is the distance (cm)
R: is the radiation (mV)
Discussion:-
The inverse square law is defined as a physical law that
recognises that a given physical quantity or force is inversely
proportional to the square of the distance to the source of this
physical quantity (1)(2)(3) this law is applicable to many
physical phenomena such as gravity , electricity magnetism ,
light , sound and radiation. Lines represent the flow emitted
from the source . The total number of flux lines depends on the
power of the source , and it is constant as the distance radius .
The higher the density of the flux lines ( flux line ) (unit area ) ,
the greater the field strength. The density of the flux lines is
inversely proportional to the square of the distance from the
source because the area of the sphere is proportional to the
square of the radius hence, the field strength is inversely
proportional to the square of the distance from the source
You might also like
- On The Measurement of The Resistivity of The Material of A WireDocument5 pagesOn The Measurement of The Resistivity of The Material of A Wirebabycryy100% (2)
- Biot Savarts LawDocument13 pagesBiot Savarts Lawubaidnazir45198No ratings yet
- Objectives:: What Does Resistance Depend On?Document4 pagesObjectives:: What Does Resistance Depend On?Rodrigo TavarezNo ratings yet
- 006 solve1DConvectionDiffusionEquationUpwindDocument5 pages006 solve1DConvectionDiffusionEquationUpwindvbkNo ratings yet
- Blackbody Radiation SpectrumDocument3 pagesBlackbody Radiation SpectrumernaNo ratings yet
- Well Draw Down 9758Document7 pagesWell Draw Down 9758Rayhan HafelNo ratings yet
- 2003SP MicrowaveOpticsDocument34 pages2003SP MicrowaveOpticsOmar HraouiNo ratings yet
- Experimental Report 5Document6 pagesExperimental Report 5Minh Huệ TôNo ratings yet
- Frequency Response of A Linear NetworkDocument8 pagesFrequency Response of A Linear NetworkIsaac CefaiNo ratings yet
- Geophysical Techniques Lab Report:: Micro-WaveDocument7 pagesGeophysical Techniques Lab Report:: Micro-WaveDeniz AkoumNo ratings yet
- ELECTRON DIFFRACTION ReportDocument4 pagesELECTRON DIFFRACTION Reportsohaila gaberNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 3 - Edm Calibration: AbstractDocument2 pagesLab Report 3 - Edm Calibration: AbstractAman JainNo ratings yet
- Post TensionDocument8 pagesPost Tensionedc1312No ratings yet
- LAB WORK 5 - Group 4Document5 pagesLAB WORK 5 - Group 4mark50nanotechNo ratings yet
- Xeuss 2 Q Ranges BDocument2 pagesXeuss 2 Q Ranges BGabriel TeobaldoNo ratings yet
- Expt 4 (Aviral Tanwar, 20103094, B4)Document9 pagesExpt 4 (Aviral Tanwar, 20103094, B4)Krishna SaxenaNo ratings yet
- AC Report 1Document5 pagesAC Report 1Ahmed HusseinNo ratings yet
- HW 2 CHAP 2 - YepezDocument9 pagesHW 2 CHAP 2 - YepezElviraNo ratings yet
- Sonometer Report 221LDocument5 pagesSonometer Report 221LNour ShamiNo ratings yet
- Beam 3Document20 pagesBeam 3MARIO MARCELONo ratings yet
- Beam 3Document20 pagesBeam 3MARIO MARCELONo ratings yet
- Structures Lab 2 Report 2 (18AE10003)Document7 pagesStructures Lab 2 Report 2 (18AE10003)Rahul RoyNo ratings yet
- P3D Sol1Document6 pagesP3D Sol1alvaro juro pomaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 Regression analysisDocument35 pagesLecture 6 Regression analysissharontaoNo ratings yet
- PH102 Lab Report 3 (S11172685)Document8 pagesPH102 Lab Report 3 (S11172685)Nitesh ChandNo ratings yet
- Microwave Optics (3) : Sleman Nabeel Sa'adDocument6 pagesMicrowave Optics (3) : Sleman Nabeel Sa'adSleman SaadNo ratings yet
- Eng FileDocument15 pagesEng FileRaghavNo ratings yet
- Enzyme KineticsDocument72 pagesEnzyme Kineticsitokki otoya100% (1)
- Report 2Document4 pagesReport 2Tuan NguyenNo ratings yet
- Kimia Fisik A 440871 Fadhlih Al-Zaki Sitorus PDFDocument7 pagesKimia Fisik A 440871 Fadhlih Al-Zaki Sitorus PDFFadhlih Al-zakiNo ratings yet
- E - M OF ELECTRON LAB PDFDocument9 pagesE - M OF ELECTRON LAB PDFAisha AtkinsonNo ratings yet
- Ship Hydrodynamics 1 Part B Lecture 7Document5 pagesShip Hydrodynamics 1 Part B Lecture 7Mohamed AtefNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 - Rectilinear MotionDocument54 pagesChapter 15 - Rectilinear MotionAbdallah KabalanNo ratings yet
- The Simple Pendulum Experiment and Conclusion LabDocument5 pagesThe Simple Pendulum Experiment and Conclusion LabKing JonesNo ratings yet
- Malte Behrens X-Ray and Neutron Diffraction 081024 PDFDocument43 pagesMalte Behrens X-Ray and Neutron Diffraction 081024 PDFleakarimNo ratings yet
- Malte Behrens X-Ray and Neutron Diffraction 081024Document43 pagesMalte Behrens X-Ray and Neutron Diffraction 081024leakarimNo ratings yet
- Calculo Del Espectro de AceleracionesDocument2 pagesCalculo Del Espectro de AceleracionesLuis Miguel GaviñoNo ratings yet
- Calculo Del Espectro de AceleracionesDocument2 pagesCalculo Del Espectro de AceleracionesLuis Miguel GaviñoNo ratings yet
- Memristors 31 40Document10 pagesMemristors 31 40Tamas ZefferNo ratings yet
- Measurement of Magnetic Field Inside A Solenoid With Finite LengthDocument4 pagesMeasurement of Magnetic Field Inside A Solenoid With Finite LengthNguyễn Đức MạnhNo ratings yet
- HW - 1 - Introduction To Surveying, Mistakes and ErrorsDocument2 pagesHW - 1 - Introduction To Surveying, Mistakes and ErrorsAngel Mae Lastimosa PabonNo ratings yet
- The Crystal Structure of MagnesiumDocument4 pagesThe Crystal Structure of MagnesiumDharmaMaya ChandrahasNo ratings yet
- Measurement of Coefficient of Linear Expansion by Fizeau's Method. ObjectiveDocument4 pagesMeasurement of Coefficient of Linear Expansion by Fizeau's Method. ObjectiveGaurav Kumar Tiwari100% (1)
- Untitled 1Document1 pageUntitled 1Truong Phuoc TriNo ratings yet
- Phys2 Week4 Simple PendulumDocument7 pagesPhys2 Week4 Simple PendulumSahirNo ratings yet
- Measurement of Magnetic Field Inside A Solenoid With Finite LengthDocument4 pagesMeasurement of Magnetic Field Inside A Solenoid With Finite Lengthhuyhoang01bgNo ratings yet
- Physical Experiment 2 ViệtDocument6 pagesPhysical Experiment 2 ViệtLâm NgôNo ratings yet
- Um-Flygbilderintro2image Interpretation 2017 English v3 PDFDocument118 pagesUm-Flygbilderintro2image Interpretation 2017 English v3 PDFpacotao123No ratings yet
- Experimental Validation of The Dynamic InteractionDocument13 pagesExperimental Validation of The Dynamic InteractionNavid SalamiPargooNo ratings yet
- Physics Practical 22-23Document25 pagesPhysics Practical 22-23Arnav100% (1)
- Title of ExperimentDocument12 pagesTitle of ExperimentLi Xian YongNo ratings yet
- Fludi Mechanics Report On Hydraulic BenchDocument6 pagesFludi Mechanics Report On Hydraulic Bencharham rizwanNo ratings yet
- Comparitive Nalysis Work For Free and Forced VibrationsDocument4 pagesComparitive Nalysis Work For Free and Forced VibrationsVAIDEHI SHARMANo ratings yet
- Thi Nghiem Lý 2 02Document6 pagesThi Nghiem Lý 2 02Hoang Anh PhamNo ratings yet
- RESULT and DISCUSSIONDocument5 pagesRESULT and DISCUSSIONnisasoberiNo ratings yet
- 5.soal Load Flow Study..Document9 pages5.soal Load Flow Study..Exa GonalNo ratings yet
- Modeling, Fabrication, and Characterization of - Memristors-81-109Document29 pagesModeling, Fabrication, and Characterization of - Memristors-81-109Tamas ZefferNo ratings yet
- Practical Notes Physics 12Document9 pagesPractical Notes Physics 12FawwazNo ratings yet
- Tugas 4 DinamikaDocument7 pagesTugas 4 DinamikapegaNo ratings yet