Professional Documents
Culture Documents
SSLC Science Chaper 1
SSLC Science Chaper 1
Uploaded by
Rekha DushyanthOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
SSLC Science Chaper 1
SSLC Science Chaper 1
Uploaded by
Rekha DushyanthCopyright:
Available Formats
www.amkresourceinfo.
com
AMK Resource World
SSLC Exam Mentor
CLICK & JOIN
NOW
SCIENCE – CHAPTER 01
Chemical Reactions and Equations
Chemical Reaction:
The transformation of chemical substance into another chemical substance is known
as Chemical Reaction. For example: Rusting of iron, the setting of milk into curd,
digestion of food, respiration, etc
Example: The burning of magnesium in the air to form magnesium oxide is an
example of a chemical reaction
(KNOW IT: Magnesium metal is highly reactive. In stored conditions, it reacts with oxygen
to form magnesium oxide over its outer layer. To remove this layer and to expose the underlying
metal into air, the magnesium ribbon is cleaned by sandpaper)
The substances which take part in a chemical reaction are called reactants.The new
substances produced as a result of a chemical reaction are called products
Changes to determine that the chemical reaction has taken place are
▪ Change in state
▪ Change in colour
▪ Evolution of gas
▪ Change in temperature
Chemical Equation:
A chemical equation is the symbolic representation of a chemical reaction in the form
of symbols and formulae, wherein the reactant entities are given on the left-hand side
and the product entities on the right-hand side.
Example: A + B → C + D
SUBSCRIBE Website www.amkresourceinfo.com by Clicking Bell Icon for latest updates
In this equation, A and B are called reactants and C and D are called the products. The
arrow shows the direction of the chemical reaction. Condition, if any, is written
generally above the arrow.
(KNOW IT - Iron is more reactive than copper. When an iron nail is dipped in copper sulphate
solution, iron forms its sulphate (iron sulphate) solution by displacing copper of copper
sulphate. The colour of iron sulphate is green. So, colour change in solution appears)
A chemical equation can be divided into two types: Balanced Chemical Equation and
Unbalanced Chemical Equation
Balanced Chemical Equation
The chemical equation that shows the chemical reaction needs to be balanced. A
balanced chemical equation occurs when the number of the atoms involved in the
reactants side is equal to the number of atoms in the products side, We must balance
the chemical equation, otherwise it becomes skeletal chemical equation.
(KNOW IT - According to the Law of Conservation of Mass, mass can neither be created nor
destroyed in a chemical reaction. To obey this law, the total mass of elements present in
reactants must be equal to the total mass of elements present in products)
Example
▪ H2(g) + Cl2(g) ➝ 2HCl(g)
▪ 3BaCl2(s) + Al2(SO4)3(s) ➝ 3BaSO4 + 2Al2Cl3(s)
▪ 2Na(s) + 2H2O(l) ➝ 2NaOH(aq) + H2(g)
▪ Zn + H2SO4 → ZnSO4 + H2
▪ 3Fe (s) + 4H2O (g) → Fe3O4 (s) + 4H2 (g)
Unbalanced Chemical Equation
If the number of atoms of each element in reactants is not equal to the number of atoms
of each element present in the product, then the chemical equation is called
Unbalanced Chemical Equation.
Types of chemical reaction
Combination reaction
Such a reaction in which a single product is formed from two or more reactants is
known as a combination reaction. A general combination reaction can be represented
by the chemical equation is A + B → AB
CaO (s) + H2O (l) → Ca(OH)2 (aq)
▪ Burning of coal: C (s) + O2 (g) → CO2 (aq)
▪ Formation of water: H2 (g) + O2 (g) → H2O (aq)
▪ Burning of natural gas (Methane): CH4 (g) + O2 (g) → CO2 (g) + H2O (l)
SUBSCRIBE Website www.amkresourceinfo.com by Clicking Bell Icon for latest updates
Exothermic Chemical Reaction
Reactions in which heat is released along with the formation of products are called
exothermic chemical reactions.
Eg: CH4(g)+2O2(g) ➝ CO2(g) + 2H2O(g)
(KNOW IT - During digestion complex molecules of food are broken into simpler molecule
such as glucose. This glucose combines with oxygen in the cells of our body and provides
energy. Therefore, respiration is considered an exothermic reaction)
Endothermic Chemical Reaction
Reactions in which energy is absorbed are known as endothermic reactions.
Eg - 6CO2 + 6H2O(l) ➝ C6H12O6(aq) + 6O2(g)
Decomposition reaction
When single reactant breaks down to give simpler products. This is a decomposition
reaction, they are the exact opposite of combination reactions in which two or more
substances combine to give a new substance, A general decomposition reaction can be
represented as AB → A + B
▪ ZnCO3(s) → ZnO(s) + CO2(g)
▪ CaCO3(s) −→ CaO(s) + CO2(g)
▪ 2Fe(OH)3(s) → Fe2O3(s) + 3H2O(l)
Displacement reaction
Displacement reaction is a chemical reaction in which a more reactive element
displaces a less reactive element from its compound. Both metals and non-metals take
part in displacement reactions. A general displacement reaction can be represented by
using a chemical equation as A + BC → AC + B
Displacement reaction takes place only when ‘A’ is more reactive than B. If ‘B’ is more
reactive than ‘A’, then ‘A’ will not displace ‘C’ from ‘BC’ and reaction will not be
taking place.
▪ Zn(s) + 2HCl(aq) → ZnCl2(aq) + H2(g)
▪ Zn(s) + CuSO4(aq) → ZnSO4(aq) + Cu(s)
▪ Fe (s) + CuSO4 (aq) → FeSO4 (g) + Cu (s)
▪ Pb (s) + CuCl2 (aq) → PbCl2 (aq) + Cu (s)
Double Displacement reaction
A double displacement reaction, also known as a double replacement reaction or
metathesis, is a type of chemical reaction where two compounds react, and the
positive ions (cation) and the negative ions (anion) of the two reactants switch places,
forming two new compounds or products.
SUBSCRIBE Website www.amkresourceinfo.com by Clicking Bell Icon for latest updates
A general displacement reaction can be represented by using a chemical equation as
AB + CD → AC + BD
▪ Na2(SO)4 (aq) + BaCl2 (aq) → BaSO4 (s) + NaCl (aq)
▪ BaCl2(aq) + Na2SO4(aq) → BaSO4(s) (Precipitate) + 2NaCl(aq)
▪ NaOH(aq) + HCl(aq) → NaCl(aq) + H2O(l)
Precipitation Reaction
The reaction in which precipitate is formed by the mixing of the aqueous solution of
two salts is called Precipitation Reaction
Neutralization Reaction
The reaction in which an acid reacts with a base to form salt and water by an exchange
of ions is called Neutralization Reaction.
Oxidation
Addition of oxygen or non-metallic element or removal of hydrogen or metallic
element from a compound is known as Oxidation.
Elements or compounds in which oxygen or non-metallic element is added or
hydrogen or metallic element is removed are called to be Oxidized.
Reduction
Addition of hydrogen or metallic element or removal of oxygen or non-metallic
element from a compound is called Reduction.
The compound or element which goes under reduction in called to be Reduced
Oxidizing agent:
The substance which gives oxygen for oxidation is called an Oxidizing agent.The
substance which removes hydrogen is also called an Oxidizing agent.
(KNOW IT - Oxidation is the process which involves loss of electrons but reduction is the
process which involves gain of electrons.)
Reducing agent:
The substance which gives hydrogen for reduction is called a Reducing agent. The
substance which removes oxygen is also called a Reducing agent
SUBSCRIBE Website www.amkresourceinfo.com by Clicking Bell Icon for latest updates
Redox Reaction
The reaction in which oxidation and reduction both take place simultaneously is called
Redox reaction (The substance which gets oxidised is the reducing agent / The
substance which gets reduced is the oxidizing agent)
Corrosion
The process of slow conversion of metals into their undesirable compounds due to
their reaction with oxygen, water, acids, gases etc. present in the atmosphere is called
corrosion.
Rusting – Iron when reacts with oxygen and moisture forms red substance called rust.
(KNOW IT - Iron articles are painted to prevent them from rusting. When painted, the contact
of iron articles with atmospheric moisture and the air is cut off. Hence, rusting is prevented)
Methods to Prevent Rusting
▪ By painting.
▪ By greasing and oiling.
▪ By galvanisation.
(KNOW IT - Copper objects lose their lustre and shine after some time because the surface of
these objects acquires a green coating of basic copper carbonate, CuCO3.Cu(OH)2 when
exposed to air / The surface of silver metal gets tarnished (becomes dull) on exposure to air, due
to the formation of a coating of black silver sulphide(Ag2S) on its surface by the action of H2S
gas present in the air)
Rancidity
The taste and odour of food materials containing fat and oil changes when they are
left exposed to air for a long time. This is called Rancidity. It is caused due to the
oxidation of fat and oil present in food materials.
Methods to prevent rancidity
▪ By adding anti-oxidant.
▪ Vacuum packing.
▪ Replacing air by nitrogen.
▪ Refrigeration of foodstuff.
(KNOW IT - Oil and fat containing food items are flushed with nitrogen to prevent the items
from getting oxidised which may result in rancidity of such products. When fats and oils are
oxidised, they become rancid and their smell and taste change. Nitrogen provides an inert
atmosphere for them)
CLICK & JOIN
NOW
SUBSCRIBE Website www.amkresourceinfo.com by Clicking Bell Icon for latest updates
You might also like
- Organic Chemistry 3rd Edition Gorzynski Test BankDocument25 pagesOrganic Chemistry 3rd Edition Gorzynski Test BankKristenJamescrmf100% (46)
- BS en Iso 17892-4-2016Document42 pagesBS en Iso 17892-4-2016Geotechnical Reports100% (2)
- Chemical Reactions and EquationsDocument36 pagesChemical Reactions and EquationsASHRITH RASAKATLANo ratings yet
- Class 10 Chemistry Chemical ReactionsDocument12 pagesClass 10 Chemistry Chemical ReactionsSahil SweNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-1Document9 pagesChapter 1-1nxtpython09No ratings yet
- Chapter - 1 (S - X)Document7 pagesChapter - 1 (S - X)Víshál RánáNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions and EquationsDocument21 pagesChemical Reactions and EquationsEric ArtocilloNo ratings yet
- accurate note Chemical Reactions & EquationsDocument5 pagesaccurate note Chemical Reactions & EquationsCuzco CuckooNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes Class 10 Chapter 1Document8 pagesChemistry Notes Class 10 Chapter 1Sandhya RaniNo ratings yet
- Ch1 - Chemical Equation NotesDocument7 pagesCh1 - Chemical Equation Notesਕੇਸ਼ਵ ਗੁਰਜਰNo ratings yet
- Krish (Notes) : Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and EquationsDocument20 pagesKrish (Notes) : Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and EquationsVivek saklaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and EquationsDocument10 pagesChapter 1 Chemical Reactions and EquationsShabnam GolaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Notes Class 10 Chapter 1Document8 pagesChemistry Notes Class 10 Chapter 1VrindaNo ratings yet
- Points To RememberDocument9 pagesPoints To RememberrisjhiNo ratings yet
- X - Ch.1 NotesDocument5 pagesX - Ch.1 NotesgunjjanchoudharyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and EquationsDocument6 pagesChapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equationsminimata100% (1)
- 10th NotesDocument7 pages10th NotesPratibha GuptaNo ratings yet
- 99998324Document7 pages99998324Ashish Urff ĐãkšhNo ratings yet
- Science Support Material 1Document207 pagesScience Support Material 1yajurv Trivedi officialNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reaction & EquationDocument8 pagesChemical Reaction & EquationMerakiNo ratings yet
- Chemicalreactionandequations Notes&PracticequestionsDocument8 pagesChemicalreactionandequations Notes&PracticequestionsVinod KumarNo ratings yet
- M.E.S Indian School, Doha - Qatar NOTES 2024-2025Document9 pagesM.E.S Indian School, Doha - Qatar NOTES 2024-2025Rafiya95z MynirNo ratings yet
- ChemChapter7 RojasDocument6 pagesChemChapter7 RojasTn F'dzNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reaction and Equations (Class X) : Characteristics of Chemical ReactionsDocument8 pagesChemical Reaction and Equations (Class X) : Characteristics of Chemical ReactionsAngelic ShineNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations CBSE Notes For Class 10 Science Chemistry Download in PDFDocument9 pagesChapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations CBSE Notes For Class 10 Science Chemistry Download in PDFNaved ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Science Revision STUDY MATERIALDocument94 pagesScience Revision STUDY MATERIALYoNo ratings yet
- Chemical EqnsDocument17 pagesChemical Eqnsmacff217No ratings yet
- Introduction To Chemical ReactionsDocument54 pagesIntroduction To Chemical ReactionsGretchen Barut JavierNo ratings yet
- Padhle Akshay 99 Pages ScienceDocument101 pagesPadhle Akshay 99 Pages Scienceviragam359100% (1)
- Chemical Reactions and EquationsDocument9 pagesChemical Reactions and EquationsRaima SharmaNo ratings yet
- Stoichiometry 1Document52 pagesStoichiometry 1Mero Miro100% (1)
- Grade10 L-1 Chemical Reactions and Equations - Notes.2024-25Document9 pagesGrade10 L-1 Chemical Reactions and Equations - Notes.2024-25luqmaanahm2009No ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions O Level NotesDocument22 pagesChemical Reactions O Level Notesveryveryhappyfeet100% (1)
- Paradise Cbse: Join For MoreDocument202 pagesParadise Cbse: Join For MoreDeepak GoyalNo ratings yet
- Introduction: Ch:1 - Chemical Reactions and EquationsDocument6 pagesIntroduction: Ch:1 - Chemical Reactions and EquationsJitendra PatelNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions and EquationsDocument36 pagesChemical Reactions and EquationsAbhyuday SwamiNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Ch. 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations Notes 2020-2021Document4 pagesClass 10 Ch. 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations Notes 2020-2021ramya anil nairNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions and EquationsDocument8 pagesChemical Reactions and Equationsapi-246793885No ratings yet
- Notes - Chemical Rections and EquationsDocument7 pagesNotes - Chemical Rections and EquationsLizannNo ratings yet
- Chm101: Introductory Chemistry 1 MODULE 1: Methods of Science Lecture Four: Types of Chemical ReactionsDocument34 pagesChm101: Introductory Chemistry 1 MODULE 1: Methods of Science Lecture Four: Types of Chemical ReactionsOluwabusolami Akinola100% (1)
- SHS Notes Chemical Equations and ReactionsDocument5 pagesSHS Notes Chemical Equations and ReactionsIMAYOYONo ratings yet
- What Is Chemical Reaction and Its TypeDocument9 pagesWhat Is Chemical Reaction and Its TypekamilbismaNo ratings yet
- 1110 ChemistryDocument6 pages1110 ChemistryPatrickNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions and EquationsDocument7 pagesChemical Reactions and EquationsAmit KumarNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions and Equations What Is A Chemical Reaction?Document5 pagesChemical Reactions and Equations What Is A Chemical Reaction?Sushmitha KrishnamoorthyNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reactions - Shobhit NirwanDocument21 pagesChemical Reactions - Shobhit NirwanBhaskar 8287No ratings yet
- IOC Chemical-ReactionsDocument37 pagesIOC Chemical-ReactionsUwe JasmiraNo ratings yet
- Chemical Equations2Document28 pagesChemical Equations2Saleem BashaNo ratings yet
- Chmical ReactionDocument30 pagesChmical Reactionarshasaraf114No ratings yet
- 1.chemical Reactions and EquationsDocument6 pages1.chemical Reactions and EquationsayanNo ratings yet
- Types of Reactions and Balancing EquationsDocument23 pagesTypes of Reactions and Balancing EquationsALIGARBES, Rhonna May L.No ratings yet
- Introduction To Chemical ReactionsDocument74 pagesIntroduction To Chemical ReactionsJuan Pablo BuitragoNo ratings yet
- Chemical ReactionsDocument61 pagesChemical ReactionsTrudy- Ann CaineNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Chemistry Part 1 of 2Document73 pagesClass 10 Chemistry Part 1 of 2Sudhakar ChollangiNo ratings yet
- Class X - ChemistryDocument135 pagesClass X - Chemistrysvprabhu123100% (1)
- LN - 1 - Chemical Reactions & Equations - by MeDocument8 pagesLN - 1 - Chemical Reactions & Equations - by Mepriyanshu08394No ratings yet
- Made By:-Ruchika NigamDocument11 pagesMade By:-Ruchika NigamRuchika NigamNo ratings yet
- Chemical Reaction and EquationsDocument8 pagesChemical Reaction and Equationsdsarika61No ratings yet
- 10th STD Science Glance Me Once Eng Version 2022-23 by KolarDocument103 pages10th STD Science Glance Me Once Eng Version 2022-23 by Kolarlokesh vNo ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-ReductionRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: Oxidation-Reduction with AnswersNo ratings yet
- Physical and Chemical Reactions : 6th Grade Chemistry Book | Children's Chemistry BooksFrom EverandPhysical and Chemical Reactions : 6th Grade Chemistry Book | Children's Chemistry BooksNo ratings yet
- An Efficient Method For Preparing Gem-Dimethylcyclopropanes From Gem-DibromocyclopropanesDocument4 pagesAn Efficient Method For Preparing Gem-Dimethylcyclopropanes From Gem-DibromocyclopropanesNamrata MaityNo ratings yet
- Calcium Silicate False Ceiling TilesDocument6 pagesCalcium Silicate False Ceiling TilesDeepak ChandolaNo ratings yet
- Hartal (Arsenictrisulphide) A Conceptual StudyDocument10 pagesHartal (Arsenictrisulphide) A Conceptual StudyIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Amber 22Document1,013 pagesAmber 22Igor MarquesNo ratings yet
- Bio PDF 1Document7 pagesBio PDF 1Shin3 KimNo ratings yet
- 2018 Megazyme Procedur K-TSTA AssayDocument24 pages2018 Megazyme Procedur K-TSTA Assayfitri electrikaNo ratings yet
- Design Project On Nitric Acid ProductionDocument152 pagesDesign Project On Nitric Acid Productionحاتم غيدان خلف100% (1)
- International Numbering System For Food Additives - Wikipedia PDFDocument27 pagesInternational Numbering System For Food Additives - Wikipedia PDFGayatri PpNo ratings yet
- MNO Manuale Vuoto IngleseDocument52 pagesMNO Manuale Vuoto Inglesen9bf9vrpg2No ratings yet
- Injection MouldingDocument18 pagesInjection MouldingKishore Steve AustinNo ratings yet
- Midterm Pharm. Inorganic Q#2Document3 pagesMidterm Pharm. Inorganic Q#2Kate MendozaNo ratings yet
- Solutions Mind Map PDFDocument4 pagesSolutions Mind Map PDFvashuy091No ratings yet
- Q2 - Module 1 PDFDocument33 pagesQ2 - Module 1 PDFdem dorothy bosqueNo ratings yet
- 01 STRUCTURAL ISOMERISMDocument34 pages01 STRUCTURAL ISOMERISMArman Kb ArmanNo ratings yet
- Solid Phase Extraction Technique - Trends, Opportunities and ApplicationsDocument15 pagesSolid Phase Extraction Technique - Trends, Opportunities and ApplicationsRohimah NHNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry I: Thomson Sanudi, PHD Basic Sciences Department Tsanudi@Luanar - Ac.MwDocument9 pagesBiochemistry I: Thomson Sanudi, PHD Basic Sciences Department Tsanudi@Luanar - Ac.MwKelz mangNo ratings yet
- ElectrophoresisDocument42 pagesElectrophoresisAnamIlyasNo ratings yet
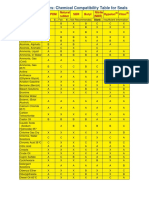
- Chemical Compatibility Table For SealsDocument3 pagesChemical Compatibility Table For SealsThanh Tuyên VõNo ratings yet
- Properties of Food Materials: BCHEM 459Document28 pagesProperties of Food Materials: BCHEM 459Kwaku frimpongNo ratings yet
- Coffe Roasted 1330-2Document1 pageCoffe Roasted 1330-2salamancagrossoNo ratings yet
- 2nd - Puc - Chemistry - Midterm Queston - Paper - 2018-19Document2 pages2nd - Puc - Chemistry - Midterm Queston - Paper - 2018-19Rahil HassanNo ratings yet
- Sars Excise External Policy BiodieselDocument15 pagesSars Excise External Policy BiodieselEnergiebleu ProjectsNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 ChemistryDocument10 pagesLecture 1 Chemistrysamreen khalidNo ratings yet
- Solutions Class 12 Notes Chemistry Chapter 2 - Learn CBSEDocument7 pagesSolutions Class 12 Notes Chemistry Chapter 2 - Learn CBSEpofacoNo ratings yet
- Paint Raw Maerials Hs Codes + Local ManufacturersDocument5 pagesPaint Raw Maerials Hs Codes + Local ManufacturersIfteha Hammad ZaheerNo ratings yet
- 2x5 Template SIP TES Grade 6 LSTDocument1 page2x5 Template SIP TES Grade 6 LSTkristinebarredoNo ratings yet
- 13 LLE NotesDocument10 pages13 LLE NotesayushNo ratings yet
- Ionpure® VNX High Flow Continuous Electrodeionization (CEDI) ModulesDocument2 pagesIonpure® VNX High Flow Continuous Electrodeionization (CEDI) ModulesEdwinNo ratings yet