Professional Documents
Culture Documents
6 Earths Mechanisms Mantle Convection
6 Earths Mechanisms Mantle Convection
Uploaded by
Sile Lu0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views22 pagesThe document summarizes key components of Earth's structure including the mantle, asthenosphere, magma, convection currents, and core. It also describes plate tectonic theory, which states that the lithosphere is broken into plates that move slowly along boundaries, interacting in ways that cause earthquakes, subduction, and the formation of geologic features like mountains and volcanoes.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document summarizes key components of Earth's structure including the mantle, asthenosphere, magma, convection currents, and core. It also describes plate tectonic theory, which states that the lithosphere is broken into plates that move slowly along boundaries, interacting in ways that cause earthquakes, subduction, and the formation of geologic features like mountains and volcanoes.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views22 pages6 Earths Mechanisms Mantle Convection
6 Earths Mechanisms Mantle Convection
Uploaded by
Sile LuThe document summarizes key components of Earth's structure including the mantle, asthenosphere, magma, convection currents, and core. It also describes plate tectonic theory, which states that the lithosphere is broken into plates that move slowly along boundaries, interacting in ways that cause earthquakes, subduction, and the formation of geologic features like mountains and volcanoes.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 22
SCIENCE 10 | EARTH & SPACE
Presentation by | Lyka Berandette T. Versoza
LET’S UNLOCK THE
JUMBLED WORDS
tmnael
A layer beneath where the less
dense hot molten material rises,
and sinks
mantle
A layer beneath where the less
dense hot molten material rises,
and sinks
thprehaeosens
A soft, weak and plastic-like layer,
the upper part of the mantle
where lithospheric plates float
and move.
asthenosphere
A soft, weak and plastic-like layer,
the upper part of the mantle
where lithospheric plates float
and move.
mmgaa
Hot molten rocks formed beneath
the Earth’s surface
magma
Hot molten rocks formed beneath
the Earth’s surface
noitcevnoc ctunrre
Facilitates the movement of the
lithospheric plates.
convection current
Facilitates the movement of the
lithospheric plates.
orce
The innermost layer of the Earth,
which generates heat to the
mantle.
core
The innermost layer of the Earth,
which generates heat to the
mantle.
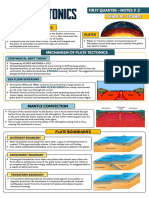
Plate Tectonic Theory was developed in 1960s, stating that
the Earth’s lithosphere-the crust and the upper mantle- is
broken up into several pieces called plates that move slowly.
It explains how the massive plates move along the different
types of plate tectonic boundaries (convergent, divergent,
and transform fault) where they interact, and the geologic
events (earthquakes and subduction) and geologic features
(formation of mountains, volcanoes, and trenches) that
occur at their boundaries.
’
•
•
‘ ’
’
’
√
You might also like
- Introduction To Engineering GeologyDocument84 pagesIntroduction To Engineering GeologyTan U-ShangNo ratings yet
- Lebs ScienceDocument9 pagesLebs ScienceVince Casison Dela PeñaNo ratings yet
- Science g10Document4 pagesScience g10Julia Amor DestuaNo ratings yet
- ReflectionDocument2 pagesReflectionJoy MalibiranNo ratings yet
- G10 Lesson 1 Plate TectonicDocument27 pagesG10 Lesson 1 Plate Tectonicmae ann perochoNo ratings yet
- Notes 2 - Plate TectonicsDocument1 pageNotes 2 - Plate TectonicsSabrina May LabradorNo ratings yet
- ScienceDocument3 pagesScienceMariah Alyssa DuranNo ratings yet
- Sciencestudyguide 3Document3 pagesSciencestudyguide 3api-251436295No ratings yet
- Exam 1 Study Guide GEOL 1014 24534Document6 pagesExam 1 Study Guide GEOL 1014 24534Jason WolfeNo ratings yet
- Science 10Document31 pagesScience 10Joan RituaNo ratings yet
- Dangerous Earth: A Plate Tectonic Story: Learning ObjectivesDocument2 pagesDangerous Earth: A Plate Tectonic Story: Learning ObjectivesKayll SierraNo ratings yet
- Science 10 Quarter 1 Lesson 8Document2 pagesScience 10 Quarter 1 Lesson 8ViaNo ratings yet
- Overview of TNT 201 - Lecture 1Document36 pagesOverview of TNT 201 - Lecture 1kim968714No ratings yet
- Plate TectonicsDocument19 pagesPlate Tectonicsapi-354859496No ratings yet
- Science 10Document1 pageScience 10Glaidylle Jade PagasNo ratings yet
- Grade10 Lesson 4Document21 pagesGrade10 Lesson 4Ka KlasmeytNo ratings yet
- The Dynamic EarthDocument2 pagesThe Dynamic EartharmenianpricessNo ratings yet
- EARTHS-MECHANISM PPTDocument15 pagesEARTHS-MECHANISM PPTLourdes Largado100% (1)
- Group 2: Elements of Seismology: Earthquake Faults Theory of Plate TectonicsDocument3 pagesGroup 2: Elements of Seismology: Earthquake Faults Theory of Plate TectonicsJessa Mae Enciso AustriaNo ratings yet
- LESSON 1-Location of Plate TectonicsDocument16 pagesLESSON 1-Location of Plate TectonicsAndreaNicoleBanzonNo ratings yet
- Science 8 4Document17 pagesScience 8 4Hannah Leigh CoronelNo ratings yet
- l3 Earth's Internal HeatDocument75 pagesl3 Earth's Internal HeatLearni J. EscoteNo ratings yet
- The Anatomy of A Tectonic PlateDocument2 pagesThe Anatomy of A Tectonic PlateIan Vincent CadisalNo ratings yet
- Geologia Trabajo 2Document14 pagesGeologia Trabajo 2MARIA CAMILA PAZ SOLARTENo ratings yet
- What Can You Say About The Ages of The Oceanic Rocks Far From The MidDocument2 pagesWhat Can You Say About The Ages of The Oceanic Rocks Far From The MidBreianah Jare SalesNo ratings yet
- Earth ScienceDocument52 pagesEarth Sciencejazminelesliebunalade.bascNo ratings yet
- Plate TectonicsDocument13 pagesPlate TectonicsKatherine CampillosNo ratings yet
- Science PPTDocument28 pagesScience PPTquencia beth radinNo ratings yet
- Earthquake: CE 231 Engineering Geology & GeomorphologyDocument39 pagesEarthquake: CE 231 Engineering Geology & GeomorphologyMuhammadNo ratings yet
- Earth Continental Drift Plate Tectonics Sea Floor Spreading-0Document59 pagesEarth Continental Drift Plate Tectonics Sea Floor Spreading-0MALOU ELEVERANo ratings yet
- Grade 10 - Science WW2: Dominican College of Tarlac, IncDocument3 pagesGrade 10 - Science WW2: Dominican College of Tarlac, IncKerol Arkie TarrielaNo ratings yet
- The Lithosphere - Written ReportDocument5 pagesThe Lithosphere - Written ReportsnoahjustineNo ratings yet
- Reviewer 8 ScienceDocument16 pagesReviewer 8 ScienceJhanna Gil BuctolanNo ratings yet
- Lecture Plate Tectonic Earth Interior Science 10 q1Document14 pagesLecture Plate Tectonic Earth Interior Science 10 q1echevarrialorainneNo ratings yet
- Lithosphere: Earth StructureDocument43 pagesLithosphere: Earth StructureM Rafiq ullahNo ratings yet
- 4 - Plate Tectonics Part 1 - Ch03 04Document43 pages4 - Plate Tectonics Part 1 - Ch03 04Jordan RixNo ratings yet
- q1 m1 Chinese WhisperqDocument41 pagesq1 m1 Chinese Whisperqrodena sabadoNo ratings yet
- Chemically, The Layers of Earth Are As Follow: Crust, Upper Mantle, LowerDocument8 pagesChemically, The Layers of Earth Are As Follow: Crust, Upper Mantle, LowerMarg EraesNo ratings yet
- Earth Continental Drift Plate Tectonics Sea Floor Spreading-0Document59 pagesEarth Continental Drift Plate Tectonics Sea Floor Spreading-0roziel A.mabitasanNo ratings yet
- Yna's EarthDocument11 pagesYna's EarthYnara VillaunuevaNo ratings yet
- L6 Earths Driving ForcesDocument30 pagesL6 Earths Driving ForcesgabwastedNo ratings yet
- Tectonic Plates GeronimoDocument20 pagesTectonic Plates GeronimoTrexay ReigoNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics Plate Tectonics: Crust Mantle Plate Boundaries Thrust Faults Oceanic Spreading Ridges Transform FaultsDocument3 pagesPlate Tectonics Plate Tectonics: Crust Mantle Plate Boundaries Thrust Faults Oceanic Spreading Ridges Transform FaultsFaye Andrea FranciscoNo ratings yet
- Plates Tectonics 2Document57 pagesPlates Tectonics 2Mark LourenceNo ratings yet
- Assignment 01Document3 pagesAssignment 01Sahir Aly BadarpuraNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics AsssignmentDocument11 pagesPlate Tectonics AsssignmentAdikalie Kholifa KamaraNo ratings yet
- Genesis IntroDocument19 pagesGenesis IntroNeil Villa MepranumNo ratings yet
- Narrator: Insert Visual Map Showing The Major Tectonic PlatesDocument3 pagesNarrator: Insert Visual Map Showing The Major Tectonic Plates5,000 subscribers without video in 1 monthNo ratings yet
- Tattatatata PDFDocument40 pagesTattatatata PDFMark joseph cruzNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics NotesDocument7 pagesPlate Tectonics Notesmahsa tNo ratings yet
- Written Report in Science Group 4Document11 pagesWritten Report in Science Group 4Stephen Tracy TabamoNo ratings yet
- Earth Science ReviewerDocument3 pagesEarth Science ReviewerBenz Nicolf CasadorNo ratings yet
- Science 10 Week 1-3Document14 pagesScience 10 Week 1-3Princess AdanoNo ratings yet
- Semesterproject 2Document62 pagesSemesterproject 2api-281484560No ratings yet
- Earth Science: Journey The EarthDocument5 pagesEarth Science: Journey The EarthElyka Marie LambarteNo ratings yet
- Impact of Geographical Phenomena - Form 6Document139 pagesImpact of Geographical Phenomena - Form 6Conrod Wayne Smith100% (1)
- I. Plate TectonicsDocument16 pagesI. Plate TectonicsChristian GanganNo ratings yet
- Why Do Tectonic Plates Crash and Slip? Geology Book for Kids | Children's Earth Sciences BooksFrom EverandWhy Do Tectonic Plates Crash and Slip? Geology Book for Kids | Children's Earth Sciences BooksNo ratings yet
- The Explosive World of Volcanoes with Max Axiom Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceFrom EverandThe Explosive World of Volcanoes with Max Axiom Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceNo ratings yet