Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chen 6853 - Graduate Che Thermodynamics - Fall 2016 Homework #4
Chen 6853 - Graduate Che Thermodynamics - Fall 2016 Homework #4
Uploaded by
Md Faisal KarimCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Ebook PDF Transnational Management Text and Cases in Cross Border Management 8th Edition PDFDocument41 pagesEbook PDF Transnational Management Text and Cases in Cross Border Management 8th Edition PDFernest.kirschenbaum650100% (40)
- CH Be 3110 ProblemsDocument75 pagesCH Be 3110 ProblemsAnkit DhalNo ratings yet
- CH138P WS 1.2 Geromo HALDocument11 pagesCH138P WS 1.2 Geromo HALLora Bell100% (1)
- Thermodynamics Workshop Problems Model Answers 2010-2011 1Document9 pagesThermodynamics Workshop Problems Model Answers 2010-2011 1djsmilie77No ratings yet
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers EnzymesFrom EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers EnzymesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- 05 Flash CalculationsDocument2 pages05 Flash CalculationsJoseph OrjiNo ratings yet
- Phase Equilibrium WorksheetDocument15 pagesPhase Equilibrium WorksheetJue MayaNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 4Document10 pagesLab Report 4sagarchawlaNo ratings yet
- Gases and VaporsDocument2 pagesGases and VaporsKhristel PenoliarNo ratings yet
- Medicinal PlantsDocument10 pagesMedicinal PlantsAnurag GoelNo ratings yet
- PC2 - Practice Exam WorkedDocument12 pagesPC2 - Practice Exam WorkednomsyNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamic Problem With SolutionDocument3 pagesThermodynamic Problem With SolutionKirika Yumura0% (1)
- Tutorial 1 - Review of ThermodynamicsDocument2 pagesTutorial 1 - Review of ThermodynamicsAdruNo ratings yet
- CH en 6853 - Graduate Che Thermodynamics - Fall 2016 Homework #5Document3 pagesCH en 6853 - Graduate Che Thermodynamics - Fall 2016 Homework #5Md Faisal KarimNo ratings yet
- Chen 6853 - Graduate Che Thermodynamics - Fall 2016 Homework #2Document2 pagesChen 6853 - Graduate Che Thermodynamics - Fall 2016 Homework #2Md Faisal KarimNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 5 Phase EquilibriumDocument3 pagesTutorial 5 Phase EquilibriumezanaNo ratings yet
- CHNG1000 - Sep Processes TutorialDocument3 pagesCHNG1000 - Sep Processes TutorialTamirNo ratings yet
- P Chem Homework 10Document3 pagesP Chem Homework 10Matthew RayNo ratings yet
- Physical Principles 1 - Problem Set 4Document3 pagesPhysical Principles 1 - Problem Set 4Ray ReynoldsNo ratings yet
- Sem1 Unit8 Phase EquilibriaDocument5 pagesSem1 Unit8 Phase EquilibriashehdilanunNo ratings yet
- Distillation Lec 2Document12 pagesDistillation Lec 2Omer IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Mass Transfer II (CH3006D) Assignment 1: T, K X yDocument2 pagesMass Transfer II (CH3006D) Assignment 1: T, K X ykeerthi srijithNo ratings yet
- ChE 101 VLE Practice ProblemsDocument2 pagesChE 101 VLE Practice ProblemsLester Jason T. ChengNo ratings yet
- Numerical Assignment - Chemical Equilibrium-IDocument6 pagesNumerical Assignment - Chemical Equilibrium-ISwastik DasNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document5 pagesAssignment 2SouravNo ratings yet
- PIKEMDocument2 pagesPIKEMDream CakeNo ratings yet
- Extra Exercises Chapter 16: Phase EquilibriumDocument2 pagesExtra Exercises Chapter 16: Phase EquilibriumggNo ratings yet
- Distillation - Self Study QuestionsDocument8 pagesDistillation - Self Study QuestionsEsther MaidenNo ratings yet
- Steam Tables: Determining H, U, V, T, and P UsingDocument7 pagesSteam Tables: Determining H, U, V, T, and P Usingاحمد ماجد زبنNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 DistillationDocument110 pagesChapter 1 DistillationSiti Nurshahira80% (5)
- Tutorial 1 - Part II: Vapour Liquid EquilibriumDocument3 pagesTutorial 1 - Part II: Vapour Liquid EquilibriumIshanSaneNo ratings yet
- Chemical Equilibrium: CHE 195 Process ChemistryDocument25 pagesChemical Equilibrium: CHE 195 Process ChemistryMohd Shahrul Nizam SallehNo ratings yet
- Physical Transformations of Pure Substances: Answers To Discussion QuestionsDocument13 pagesPhysical Transformations of Pure Substances: Answers To Discussion QuestionsLalaNo ratings yet
- Assignment - 6 Chemical Engineering Principles - Ii Self-Assessment Tests (Sats) Section-4.1Document7 pagesAssignment - 6 Chemical Engineering Principles - Ii Self-Assessment Tests (Sats) Section-4.1Ali Hamza ManzoorNo ratings yet
- Menghitung Jumlah Plate PDFDocument12 pagesMenghitung Jumlah Plate PDFUtari NuravifahNo ratings yet
- Distillation - Dr.K.Suresh - NotesDocument63 pagesDistillation - Dr.K.Suresh - NotesRoyalNo ratings yet
- 7 1. Vapor Liquid EquilibriumDocument9 pages7 1. Vapor Liquid Equilibriumwaseemkhan49No ratings yet
- KP 1 - Tutorial - Vapor Gas (AE)Document22 pagesKP 1 - Tutorial - Vapor Gas (AE)Choirima Ulfa RusniaNo ratings yet
- Ctdcha 2Document10 pagesCtdcha 2TKNo ratings yet
- Sample CalculationsDocument3 pagesSample Calculationsjeonjungkook10No ratings yet
- CHM271 - Tutorial 6 - Phase EquilibriumDocument5 pagesCHM271 - Tutorial 6 - Phase Equilibriumfiefy zmrNo ratings yet
- DocxDocument11 pagesDocxNabila PutriNo ratings yet
- Physical Chemistry Reference 2Document33 pagesPhysical Chemistry Reference 2Kuo SarongNo ratings yet
- CHM 471 Tutorial 3 Phase DiagramDocument4 pagesCHM 471 Tutorial 3 Phase DiagramCharlesRolendNo ratings yet
- Outlook: Molar Flowrate of Benzene Heat Transfer RequiredDocument5 pagesOutlook: Molar Flowrate of Benzene Heat Transfer RequiredRenatoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document111 pagesChapter 1Radhi Abdullah100% (1)
- Exercises 6Document1 pageExercises 6ITZEL GUADALUPE CORDERO JASSONo ratings yet
- Experiment 3 Three Component SystemsDocument8 pagesExperiment 3 Three Component Systemsmohammednoor_No ratings yet
- I Pledge On My Honor That I Have Not Given or Received Any Unauthorized Assistance On This ExaminationDocument2 pagesI Pledge On My Honor That I Have Not Given or Received Any Unauthorized Assistance On This ExaminationTosinNo ratings yet
- Distillation 150401163307 Conversion Gate01Document72 pagesDistillation 150401163307 Conversion Gate01Iwuoha Maxrofuzo Chibueze100% (1)
- Practice QuestionsDocument7 pagesPractice QuestionsDIBAKOANE KARABONo ratings yet
- Tgas 1 - VLE - Kelas BDocument2 pagesTgas 1 - VLE - Kelas Bmyxxx5dfjjNo ratings yet
- Liquid Vapor EquilibriumDocument4 pagesLiquid Vapor EquilibriumDoge WoweNo ratings yet
- Set 3 AnsDocument13 pagesSet 3 Ansluis fernando santos narvaezNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Multicomponent DistillationDocument13 pagesIntroduction To Multicomponent DistillationKritagyaNo ratings yet
- Chemengthermo Tutorial 022 K 17Document4 pagesChemengthermo Tutorial 022 K 17AthinaNo ratings yet
- Aquatic ChemistryDocument3 pagesAquatic ChemistrysaivenkatNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4Document3 pagesAssignment 4Saurabh BhimwalNo ratings yet
- Equilibrio de Benceno, CiclohexanoDocument5 pagesEquilibrio de Benceno, CiclohexanoLuiz AzpilcuetaNo ratings yet
- A Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsFrom EverandA Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Chen 6853 - Graduate Che Thermodynamics - Fall 2016 Homework #2Document2 pagesChen 6853 - Graduate Che Thermodynamics - Fall 2016 Homework #2Md Faisal KarimNo ratings yet
- CH en 6853 - Graduate Che Thermodynamics - Fall 2016 Homework #5Document3 pagesCH en 6853 - Graduate Che Thermodynamics - Fall 2016 Homework #5Md Faisal KarimNo ratings yet
- The Student Will Prepare Standard Report Contains: Experiment Name, Introduction, Theory, Experiment Procedures, Results and ConclusionDocument1 pageThe Student Will Prepare Standard Report Contains: Experiment Name, Introduction, Theory, Experiment Procedures, Results and ConclusionMd Faisal KarimNo ratings yet
- Drilling Fluid Preparation ReportDocument4 pagesDrilling Fluid Preparation ReportMd Faisal KarimNo ratings yet
- Report On Visit To Maddhapara Granite Mine & Boropukuria Coal MineDocument28 pagesReport On Visit To Maddhapara Granite Mine & Boropukuria Coal MineMd Faisal Karim100% (1)
- Report On Geological Survey of Bangladesh MFKDocument20 pagesReport On Geological Survey of Bangladesh MFKMd Faisal KarimNo ratings yet
- Recomendation Letter3Document1 pageRecomendation Letter3Ana ClaudiaNo ratings yet
- ADIS - COURSE Information SheetDocument1 pageADIS - COURSE Information SheetPriteshJangamNo ratings yet
- Mechanotechnology N3Document32 pagesMechanotechnology N3Alfred NdlovuNo ratings yet
- iPECS eMG800: Transform Your Business CommunicationDocument2 pagesiPECS eMG800: Transform Your Business CommunicationathNo ratings yet
- A Computer Program For Excess Water Production Diagnosis Case Study - Heglig Oil Field - SudanDocument53 pagesA Computer Program For Excess Water Production Diagnosis Case Study - Heglig Oil Field - SudanOmernour1990100% (1)
- DLP Gen MathDocument1 pageDLP Gen Mathjonnah esparragoNo ratings yet
- AnovaDocument3 pagesAnovaammi890No ratings yet
- Serial Adder Mealy Modelling ProgramDocument22 pagesSerial Adder Mealy Modelling ProgrambcemailidNo ratings yet
- BSBPM505A Skills KitDocument49 pagesBSBPM505A Skills KitLili Pabuena VillarrealNo ratings yet
- Managing The Internal Audit ActivityDocument20 pagesManaging The Internal Audit ActivityLeah May M. FamorNo ratings yet
- Towards Agenda 2030Document23 pagesTowards Agenda 2030Muhammad Syailendra Prima PutraNo ratings yet
- Adchoice S: Meaning of School LifeDocument3 pagesAdchoice S: Meaning of School LifeMariaNo ratings yet
- Finite Element Analysis of A Cantilevered BeamDocument17 pagesFinite Element Analysis of A Cantilevered BeamAnand ShahNo ratings yet
- Practice Paper For XII BDocument6 pagesPractice Paper For XII BvartikaagrawalaNo ratings yet
- Tsla SD GenDocument30 pagesTsla SD GenSimon AlvarezNo ratings yet
- LCGC Eur Burke 2001 - Missing Values, Outliers, Robust Stat and NonParametric PDFDocument6 pagesLCGC Eur Burke 2001 - Missing Values, Outliers, Robust Stat and NonParametric PDFaloediyahNo ratings yet
- Welcome To Our Presentation: Topic: Teacher Role in Group DiscussionDocument18 pagesWelcome To Our Presentation: Topic: Teacher Role in Group DiscussionDuy NguyễnNo ratings yet
- IEEE Conference Flyear 2024Document1 pageIEEE Conference Flyear 2024sundeep siddulaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Philo Module 1 (Intro)Document4 pagesReviewer Philo Module 1 (Intro)JhenryNo ratings yet
- rd-m592 2Document1 pagerd-m592 2faizgpNo ratings yet
- Stanford BinetDocument11 pagesStanford Binetsam0% (1)
- Ecological Systems TheoryDocument17 pagesEcological Systems Theorymk soberanoNo ratings yet
- N45MNT DS P2g04n004u PDFDocument4 pagesN45MNT DS P2g04n004u PDFSecret64No ratings yet
- NepalQR Standardization Framework and GuidelinesDocument26 pagesNepalQR Standardization Framework and GuidelinesRüpësh ẞhäñdårîNo ratings yet
- Amafilter MVDCDDocument3 pagesAmafilter MVDCDFaiz ElninoNo ratings yet
- Course Outline Fourth Quarter Grade FiveDocument2 pagesCourse Outline Fourth Quarter Grade FiveRemer JalbunaNo ratings yet
- IBM Data Science CapstoneDocument51 pagesIBM Data Science CapstonegeorgebhilaiNo ratings yet
- Flyer Euro Rig 450t enDocument2 pagesFlyer Euro Rig 450t enHayLenLeeNo ratings yet
Chen 6853 - Graduate Che Thermodynamics - Fall 2016 Homework #4
Chen 6853 - Graduate Che Thermodynamics - Fall 2016 Homework #4
Uploaded by
Md Faisal KarimOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chen 6853 - Graduate Che Thermodynamics - Fall 2016 Homework #4
Chen 6853 - Graduate Che Thermodynamics - Fall 2016 Homework #4
Uploaded by
Md Faisal KarimCopyright:
Available Formats
CHEN 6853 – Graduate ChE Thermodynamics – Fall 2016
Homework #4
Due: Start of class on Friday, October 21st
1. Derive the following expression for the partial fugacity coefficient of a mixture that adheres to the
Virial equation of state:
! !
! 𝑓! 2𝑃
𝑙𝑛 𝜙! = 𝑙𝑛 = 𝑦! 𝐵!" 𝑇 − 𝑙𝑛 𝑍!"#
𝑦! 𝑃 𝑍!"# 𝑅𝑇
!!!
Where the original equation of state and mixing rules are given below.
𝑃𝑉 𝐵!"# 𝑇, 𝑦
𝑍!"# = =1+ 𝐵!"# 𝑇, 𝑦 = 𝑦! 𝑦! 𝐵!" 𝑇
𝑅𝑇 𝑉
! !
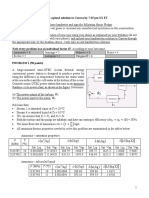
2. A 10 m3 tank stores 1 m3 of liquid benzene at atmospheric pressure and a temperature of 30 ˚C. The
remainder of the volume of the tank is filled with air, and assume there is no air dissolved in the
benzene (i.e., xAir = 0). If the liquid benzene is in vapor-liquid equilibrium with the air, what is the
total mass of benzene in the vapor phase inside the tank? You may assume Raoult’s Law behavior.
This calculation is important to determine the amount of benzene released into the environment
because the air mixture will be released to the atmosphere once the tank is filled to capacity. (A: 4 kg
benzene)
3. Assuming ideal behavior (Raoult’s Law) please perform the follow actions for a n-hexane and n-
heptane mixture:
a. Plot a Pxy diagram (in units of kPa) at 90 ˚C.
b. Plot a Txy diagram (in units of ˚C) at 100 kPa pressure.
c. Plot a xy diagram for P = 100 kPa.
d. Determine how many equilibrium stages in a distillation column at infinite reflux are
required to create a top product consisting of a 95% n-hexane stream at the top and a 95%
n-heptane stream at the bottom? The column is operated isobarically at 100 kPa. (A:
Number of stages between 4 and 9)
e. Why was the pressure fixed in the xy diagram (part d) as opposed to the temperature fixed?
Consider the operation of a distillation column.
4. A 50:50 blend of n-hexane and n-heptane is flashed at T = 60 ˚C and P = 50 kPa.
a. What is the composition of the liquid and vapor phases? (A: xHex = 0.5, yHex = 0.7)
b. What fraction of the feed is in the vapor and liquid phases? (L = 0.8)
5. An Ethanol (1)-Benzene (2) system does not follow Raoult’s Law, and the liquid phase is highly
non-ideal. Use the van Laar equation to model the activity coefficients (alpha = 1.946, beta = 1.610).
You may assume an ideal gas vapor phase.
a. Plot a Pxy diagram (in units of kPa) at T = 70 ˚C.
b. Plot a Txy diagram (in units of ˚C) at P = 100 kPa.
c. Plot an xy diagram at a constant pressure of 100 kPa.
d. What is the azeotrope composition at P = 100 kPa? (A: x = y = 0.5)
B
ln P sat ( in kPa ) = A −
T ( in deg C) + C
Compound A B C
Ethanol 16.8958 3795.17 230.918
Benzene 13.7819 2726.81 217.572
n-Hexane 13.8193 2696.04 224.317
n-Heptane 13.8622 2910.26 216.432
You might also like
- Ebook PDF Transnational Management Text and Cases in Cross Border Management 8th Edition PDFDocument41 pagesEbook PDF Transnational Management Text and Cases in Cross Border Management 8th Edition PDFernest.kirschenbaum650100% (40)
- CH Be 3110 ProblemsDocument75 pagesCH Be 3110 ProblemsAnkit DhalNo ratings yet
- CH138P WS 1.2 Geromo HALDocument11 pagesCH138P WS 1.2 Geromo HALLora Bell100% (1)
- Thermodynamics Workshop Problems Model Answers 2010-2011 1Document9 pagesThermodynamics Workshop Problems Model Answers 2010-2011 1djsmilie77No ratings yet
- O Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers EnzymesFrom EverandO Level Biology Practice Questions And Answers EnzymesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- 05 Flash CalculationsDocument2 pages05 Flash CalculationsJoseph OrjiNo ratings yet
- Phase Equilibrium WorksheetDocument15 pagesPhase Equilibrium WorksheetJue MayaNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 4Document10 pagesLab Report 4sagarchawlaNo ratings yet
- Gases and VaporsDocument2 pagesGases and VaporsKhristel PenoliarNo ratings yet
- Medicinal PlantsDocument10 pagesMedicinal PlantsAnurag GoelNo ratings yet
- PC2 - Practice Exam WorkedDocument12 pagesPC2 - Practice Exam WorkednomsyNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamic Problem With SolutionDocument3 pagesThermodynamic Problem With SolutionKirika Yumura0% (1)
- Tutorial 1 - Review of ThermodynamicsDocument2 pagesTutorial 1 - Review of ThermodynamicsAdruNo ratings yet
- CH en 6853 - Graduate Che Thermodynamics - Fall 2016 Homework #5Document3 pagesCH en 6853 - Graduate Che Thermodynamics - Fall 2016 Homework #5Md Faisal KarimNo ratings yet
- Chen 6853 - Graduate Che Thermodynamics - Fall 2016 Homework #2Document2 pagesChen 6853 - Graduate Che Thermodynamics - Fall 2016 Homework #2Md Faisal KarimNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 5 Phase EquilibriumDocument3 pagesTutorial 5 Phase EquilibriumezanaNo ratings yet
- CHNG1000 - Sep Processes TutorialDocument3 pagesCHNG1000 - Sep Processes TutorialTamirNo ratings yet
- P Chem Homework 10Document3 pagesP Chem Homework 10Matthew RayNo ratings yet
- Physical Principles 1 - Problem Set 4Document3 pagesPhysical Principles 1 - Problem Set 4Ray ReynoldsNo ratings yet
- Sem1 Unit8 Phase EquilibriaDocument5 pagesSem1 Unit8 Phase EquilibriashehdilanunNo ratings yet
- Distillation Lec 2Document12 pagesDistillation Lec 2Omer IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Mass Transfer II (CH3006D) Assignment 1: T, K X yDocument2 pagesMass Transfer II (CH3006D) Assignment 1: T, K X ykeerthi srijithNo ratings yet
- ChE 101 VLE Practice ProblemsDocument2 pagesChE 101 VLE Practice ProblemsLester Jason T. ChengNo ratings yet
- Numerical Assignment - Chemical Equilibrium-IDocument6 pagesNumerical Assignment - Chemical Equilibrium-ISwastik DasNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document5 pagesAssignment 2SouravNo ratings yet
- PIKEMDocument2 pagesPIKEMDream CakeNo ratings yet
- Extra Exercises Chapter 16: Phase EquilibriumDocument2 pagesExtra Exercises Chapter 16: Phase EquilibriumggNo ratings yet
- Distillation - Self Study QuestionsDocument8 pagesDistillation - Self Study QuestionsEsther MaidenNo ratings yet
- Steam Tables: Determining H, U, V, T, and P UsingDocument7 pagesSteam Tables: Determining H, U, V, T, and P Usingاحمد ماجد زبنNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 DistillationDocument110 pagesChapter 1 DistillationSiti Nurshahira80% (5)
- Tutorial 1 - Part II: Vapour Liquid EquilibriumDocument3 pagesTutorial 1 - Part II: Vapour Liquid EquilibriumIshanSaneNo ratings yet
- Chemical Equilibrium: CHE 195 Process ChemistryDocument25 pagesChemical Equilibrium: CHE 195 Process ChemistryMohd Shahrul Nizam SallehNo ratings yet
- Physical Transformations of Pure Substances: Answers To Discussion QuestionsDocument13 pagesPhysical Transformations of Pure Substances: Answers To Discussion QuestionsLalaNo ratings yet
- Assignment - 6 Chemical Engineering Principles - Ii Self-Assessment Tests (Sats) Section-4.1Document7 pagesAssignment - 6 Chemical Engineering Principles - Ii Self-Assessment Tests (Sats) Section-4.1Ali Hamza ManzoorNo ratings yet
- Menghitung Jumlah Plate PDFDocument12 pagesMenghitung Jumlah Plate PDFUtari NuravifahNo ratings yet
- Distillation - Dr.K.Suresh - NotesDocument63 pagesDistillation - Dr.K.Suresh - NotesRoyalNo ratings yet
- 7 1. Vapor Liquid EquilibriumDocument9 pages7 1. Vapor Liquid Equilibriumwaseemkhan49No ratings yet
- KP 1 - Tutorial - Vapor Gas (AE)Document22 pagesKP 1 - Tutorial - Vapor Gas (AE)Choirima Ulfa RusniaNo ratings yet
- Ctdcha 2Document10 pagesCtdcha 2TKNo ratings yet
- Sample CalculationsDocument3 pagesSample Calculationsjeonjungkook10No ratings yet
- CHM271 - Tutorial 6 - Phase EquilibriumDocument5 pagesCHM271 - Tutorial 6 - Phase Equilibriumfiefy zmrNo ratings yet
- DocxDocument11 pagesDocxNabila PutriNo ratings yet
- Physical Chemistry Reference 2Document33 pagesPhysical Chemistry Reference 2Kuo SarongNo ratings yet
- CHM 471 Tutorial 3 Phase DiagramDocument4 pagesCHM 471 Tutorial 3 Phase DiagramCharlesRolendNo ratings yet
- Outlook: Molar Flowrate of Benzene Heat Transfer RequiredDocument5 pagesOutlook: Molar Flowrate of Benzene Heat Transfer RequiredRenatoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document111 pagesChapter 1Radhi Abdullah100% (1)
- Exercises 6Document1 pageExercises 6ITZEL GUADALUPE CORDERO JASSONo ratings yet
- Experiment 3 Three Component SystemsDocument8 pagesExperiment 3 Three Component Systemsmohammednoor_No ratings yet
- I Pledge On My Honor That I Have Not Given or Received Any Unauthorized Assistance On This ExaminationDocument2 pagesI Pledge On My Honor That I Have Not Given or Received Any Unauthorized Assistance On This ExaminationTosinNo ratings yet
- Distillation 150401163307 Conversion Gate01Document72 pagesDistillation 150401163307 Conversion Gate01Iwuoha Maxrofuzo Chibueze100% (1)
- Practice QuestionsDocument7 pagesPractice QuestionsDIBAKOANE KARABONo ratings yet
- Tgas 1 - VLE - Kelas BDocument2 pagesTgas 1 - VLE - Kelas Bmyxxx5dfjjNo ratings yet
- Liquid Vapor EquilibriumDocument4 pagesLiquid Vapor EquilibriumDoge WoweNo ratings yet
- Set 3 AnsDocument13 pagesSet 3 Ansluis fernando santos narvaezNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Multicomponent DistillationDocument13 pagesIntroduction To Multicomponent DistillationKritagyaNo ratings yet
- Chemengthermo Tutorial 022 K 17Document4 pagesChemengthermo Tutorial 022 K 17AthinaNo ratings yet
- Aquatic ChemistryDocument3 pagesAquatic ChemistrysaivenkatNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4Document3 pagesAssignment 4Saurabh BhimwalNo ratings yet
- Equilibrio de Benceno, CiclohexanoDocument5 pagesEquilibrio de Benceno, CiclohexanoLuiz AzpilcuetaNo ratings yet
- A Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsFrom EverandA Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Chen 6853 - Graduate Che Thermodynamics - Fall 2016 Homework #2Document2 pagesChen 6853 - Graduate Che Thermodynamics - Fall 2016 Homework #2Md Faisal KarimNo ratings yet
- CH en 6853 - Graduate Che Thermodynamics - Fall 2016 Homework #5Document3 pagesCH en 6853 - Graduate Che Thermodynamics - Fall 2016 Homework #5Md Faisal KarimNo ratings yet
- The Student Will Prepare Standard Report Contains: Experiment Name, Introduction, Theory, Experiment Procedures, Results and ConclusionDocument1 pageThe Student Will Prepare Standard Report Contains: Experiment Name, Introduction, Theory, Experiment Procedures, Results and ConclusionMd Faisal KarimNo ratings yet
- Drilling Fluid Preparation ReportDocument4 pagesDrilling Fluid Preparation ReportMd Faisal KarimNo ratings yet
- Report On Visit To Maddhapara Granite Mine & Boropukuria Coal MineDocument28 pagesReport On Visit To Maddhapara Granite Mine & Boropukuria Coal MineMd Faisal Karim100% (1)
- Report On Geological Survey of Bangladesh MFKDocument20 pagesReport On Geological Survey of Bangladesh MFKMd Faisal KarimNo ratings yet
- Recomendation Letter3Document1 pageRecomendation Letter3Ana ClaudiaNo ratings yet
- ADIS - COURSE Information SheetDocument1 pageADIS - COURSE Information SheetPriteshJangamNo ratings yet
- Mechanotechnology N3Document32 pagesMechanotechnology N3Alfred NdlovuNo ratings yet
- iPECS eMG800: Transform Your Business CommunicationDocument2 pagesiPECS eMG800: Transform Your Business CommunicationathNo ratings yet
- A Computer Program For Excess Water Production Diagnosis Case Study - Heglig Oil Field - SudanDocument53 pagesA Computer Program For Excess Water Production Diagnosis Case Study - Heglig Oil Field - SudanOmernour1990100% (1)
- DLP Gen MathDocument1 pageDLP Gen Mathjonnah esparragoNo ratings yet
- AnovaDocument3 pagesAnovaammi890No ratings yet
- Serial Adder Mealy Modelling ProgramDocument22 pagesSerial Adder Mealy Modelling ProgrambcemailidNo ratings yet
- BSBPM505A Skills KitDocument49 pagesBSBPM505A Skills KitLili Pabuena VillarrealNo ratings yet
- Managing The Internal Audit ActivityDocument20 pagesManaging The Internal Audit ActivityLeah May M. FamorNo ratings yet
- Towards Agenda 2030Document23 pagesTowards Agenda 2030Muhammad Syailendra Prima PutraNo ratings yet
- Adchoice S: Meaning of School LifeDocument3 pagesAdchoice S: Meaning of School LifeMariaNo ratings yet
- Finite Element Analysis of A Cantilevered BeamDocument17 pagesFinite Element Analysis of A Cantilevered BeamAnand ShahNo ratings yet
- Practice Paper For XII BDocument6 pagesPractice Paper For XII BvartikaagrawalaNo ratings yet
- Tsla SD GenDocument30 pagesTsla SD GenSimon AlvarezNo ratings yet
- LCGC Eur Burke 2001 - Missing Values, Outliers, Robust Stat and NonParametric PDFDocument6 pagesLCGC Eur Burke 2001 - Missing Values, Outliers, Robust Stat and NonParametric PDFaloediyahNo ratings yet
- Welcome To Our Presentation: Topic: Teacher Role in Group DiscussionDocument18 pagesWelcome To Our Presentation: Topic: Teacher Role in Group DiscussionDuy NguyễnNo ratings yet
- IEEE Conference Flyear 2024Document1 pageIEEE Conference Flyear 2024sundeep siddulaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Philo Module 1 (Intro)Document4 pagesReviewer Philo Module 1 (Intro)JhenryNo ratings yet
- rd-m592 2Document1 pagerd-m592 2faizgpNo ratings yet
- Stanford BinetDocument11 pagesStanford Binetsam0% (1)
- Ecological Systems TheoryDocument17 pagesEcological Systems Theorymk soberanoNo ratings yet
- N45MNT DS P2g04n004u PDFDocument4 pagesN45MNT DS P2g04n004u PDFSecret64No ratings yet
- NepalQR Standardization Framework and GuidelinesDocument26 pagesNepalQR Standardization Framework and GuidelinesRüpësh ẞhäñdårîNo ratings yet
- Amafilter MVDCDDocument3 pagesAmafilter MVDCDFaiz ElninoNo ratings yet
- Course Outline Fourth Quarter Grade FiveDocument2 pagesCourse Outline Fourth Quarter Grade FiveRemer JalbunaNo ratings yet
- IBM Data Science CapstoneDocument51 pagesIBM Data Science CapstonegeorgebhilaiNo ratings yet
- Flyer Euro Rig 450t enDocument2 pagesFlyer Euro Rig 450t enHayLenLeeNo ratings yet