Professional Documents
Culture Documents
8 - L-19 (SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)
8 - L-19 (SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)
Uploaded by
Chark0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views1 page1) The document describes a circuit using an SCR, capacitor C, and inductor L to commutate a 25 Amp load current at a 220 V supply voltage.
2) It calculates the required capacitor rating of 2.0 μF to successfully commutate the load over a period of 61.6 μs.
3) It also notes that if the supply voltage is reduced by a factor K, the required capacitor rating increases by the same factor K to commutate the same 25 Amp load current.
Original Description:
Original Title
8_L-19(SSG)(PE) ((EE)NPTEL)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1) The document describes a circuit using an SCR, capacitor C, and inductor L to commutate a 25 Amp load current at a 220 V supply voltage.
2) It calculates the required capacitor rating of 2.0 μF to successfully commutate the load over a period of 61.6 μs.
3) It also notes that if the supply voltage is reduced by a factor K, the required capacitor rating increases by the same factor K to commutate the same 25 Amp load current.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1 views1 page8 - L-19 (SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)
8 - L-19 (SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)
Uploaded by
Chark1) The document describes a circuit using an SCR, capacitor C, and inductor L to commutate a 25 Amp load current at a 220 V supply voltage.
2) It calculates the required capacitor rating of 2.0 μF to successfully commutate the load over a period of 61.6 μs.
3) It also notes that if the supply voltage is reduced by a factor K, the required capacitor rating increases by the same factor K to commutate the same 25 Amp load current.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
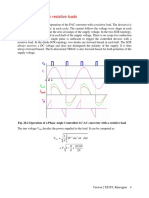
Soln # 2
The capacitor is initially charged to the supply voltage 220 V at the end of the conduction period
of SCRA.
When SCRM is triggered, the 25 Amps load current and the L-C ringing current flows
through it. Peak current through SCR is
i peak = 25 + 220 C Amps
L
Selecting L such that ipeak ~ 1.5 . load current,
25
C = = 0.0568
L 2.220
L = 3.1 mH
Assuming that the capacitor charges to 70% of its original charge because of losses in the
C- SCRM -L-D network, and it charges linearly when SCRA is again triggered,
I load .t q = 10(0.7.220)10 −6 = 1540.10 −6
tq = 1540 / 25 = 61.6 μ sec s
The SCR can therefore be successfully commutated.
The maximum current that can be commutated with the given Capacitor at the 220 V
supply voltage is
I load = 1540 / 12 = 128 Amps
For the 25 Amps load current the capacitor just enough would have a rating of
C = I load .t q /(0.7.220) = (25.12) / 154 = 1.95 ≈ 2.0 μF
If the supply voltage is reduced by a factor K, the required capacitor rating
increases by the same factor K for the same load current.
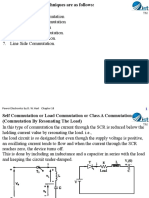
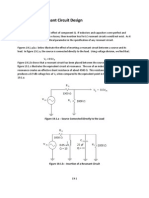
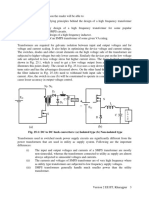
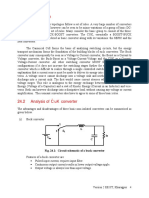
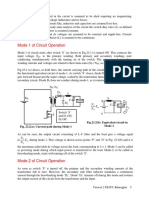
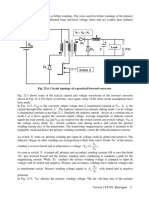
Class E – External pulse source for commutation
The transformer is designed with sufficient iron and air gap so as not to saturate. It is capable of
carrying the load current with a small voltage drop compared with the supply voltage.
When SCR1 is triggered, current flows through the load and pulse transformer. To turn SCR1 off
a positive pulse is applied to the cathode of the SCR from an external pulse generator via the
pulse transformer. The capacitor C is only charged to about 1 volt and for the duration of the
turn-off pulse it can be considered to have zero impedance. Thus the pulse from the transformer
reverses the voltage across the SCR, and it supplies the reverse recovery current and holds the
voltage negative for the required turn-off time.
Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpur 8
You might also like
- Switching Power Supply Design: A Concise Practical HandbookFrom EverandSwitching Power Supply Design: A Concise Practical HandbookNo ratings yet
- MC Murray InverterDocument92 pagesMC Murray InverterGnanaseharan Arunachalam100% (5)
- L-19 (SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document12 pagesL-19 (SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)umi_ktkNo ratings yet
- Parallel Capacitor Inverter With Feedback DiodesDocument9 pagesParallel Capacitor Inverter With Feedback DiodesJayant Kirpekar100% (1)
- Name Ubaid Ur Rehman REG NO FA18-BEE-121-E: in This Lab We LearntDocument3 pagesName Ubaid Ur Rehman REG NO FA18-BEE-121-E: in This Lab We LearntMuhammad DawoodNo ratings yet
- Pe 42 Ee17Document16 pagesPe 42 Ee17Knight knightNo ratings yet
- Commutation Circuits: Technical Manual FORDocument26 pagesCommutation Circuits: Technical Manual FORSoumyadeep NagNo ratings yet
- S.NO. 1 Single Phase Half Wave Rectifier With R & RL Load AimDocument15 pagesS.NO. 1 Single Phase Half Wave Rectifier With R & RL Load AimShailendra KumarNo ratings yet
- Course OutlineDocument28 pagesCourse OutlineIdrisa Mussa ChubwaNo ratings yet
- SCR Power Control CircuitDocument8 pagesSCR Power Control CircuitRyan Joseph BalmacedaNo ratings yet
- Charging and DischargingDocument38 pagesCharging and DischargingUmar M UmarNo ratings yet
- Turn-Off Process of SCRDocument16 pagesTurn-Off Process of SCRDeepika BairagiNo ratings yet
- Overload Protection Switch: Part List C D - D F R R R, R R RDocument2 pagesOverload Protection Switch: Part List C D - D F R R R, R R RFranch Maverick Arellano LorillaNo ratings yet
- 5 - L-19 (SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page5 - L-19 (SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- Jones ChopperDocument12 pagesJones ChopperRudra MishraNo ratings yet
- Power Control.: SCR Can Be Turned-On Phase ControlDocument6 pagesPower Control.: SCR Can Be Turned-On Phase ControlEric BiscochoNo ratings yet
- Astable Multivibrator Using TransistorsDocument10 pagesAstable Multivibrator Using TransistorsGangireddy SanjeevNo ratings yet
- Jones Chopper: Pratik Gupta (Vgec Electrical)Document13 pagesJones Chopper: Pratik Gupta (Vgec Electrical)guptapratik100% (1)
- Quiz 1 IsDocument19 pagesQuiz 1 IsNathan KingNo ratings yet
- CapacitorsDocument4 pagesCapacitorsShern Ren TeeNo ratings yet
- Monostable CircuitsDocument5 pagesMonostable CircuitsJBS SPOBINo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Lab Demo NADocument155 pagesPower Electronics Lab Demo NAsoumyaNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios TransitoriosDocument13 pagesEjercicios TransitoriosCARLOS DANIEL MEJIA BANDANo ratings yet
- Commutation MethodDocument20 pagesCommutation Methodsarikaaborade07No ratings yet
- Clapp OscillatorDocument5 pagesClapp OscillatorHemantha DalugamaNo ratings yet
- Jones ChopperDocument1 pageJones ChoppersuriyasureshNo ratings yet
- InverterDocument93 pagesInverterABCDNo ratings yet
- Commutation of Thyristor-Based Circuits Part-I: DR - Arkan A.Hussein Power Electronics Fourth ClassDocument11 pagesCommutation of Thyristor-Based Circuits Part-I: DR - Arkan A.Hussein Power Electronics Fourth Classmohammed aliNo ratings yet
- Inverter and ChopperDocument92 pagesInverter and ChopperGnanaseharan ArunachalamNo ratings yet
- T3 TugasDocument15 pagesT3 TugasSri rahayuNo ratings yet
- UNIT I - SCR Triggering and CommutationDocument14 pagesUNIT I - SCR Triggering and CommutationmalathynarayaniNo ratings yet
- Commutation of SCRDocument8 pagesCommutation of SCRJPR EEE100% (3)
- 7 - L-19 (SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page7 - L-19 (SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- Commutation Techniques 1Document19 pagesCommutation Techniques 1Nataraju Gandla60% (5)
- Capacitance Is The Ability of A Body To Store An Electrical ChargeDocument6 pagesCapacitance Is The Ability of A Body To Store An Electrical Chargeankita071291No ratings yet
- Project Description October 2011Document7 pagesProject Description October 2011Daniel Norberto DemariaNo ratings yet
- Comparison and Simulation of Full Bridge and LCL-T Buck DC-DC Converter SystemsDocument5 pagesComparison and Simulation of Full Bridge and LCL-T Buck DC-DC Converter SystemsKrishnaveni Subramani SNo ratings yet
- Snubber PDFDocument5 pagesSnubber PDFJ Milk SilvaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 19 Resonant Circuit DesignDocument15 pagesLecture 19 Resonant Circuit DesignG Mi LinNo ratings yet
- RC Circuit and Its ApplicationTerm PaperDocument13 pagesRC Circuit and Its ApplicationTerm PapersummitzNo ratings yet
- 19IE10018 - Differntiator and IntegratorDocument10 pages19IE10018 - Differntiator and IntegratorMitrayosna Mishra100% (1)
- PEL Lab ManualDocument127 pagesPEL Lab Manualmksamy2021No ratings yet
- SCR Trigerring CircuitsDocument11 pagesSCR Trigerring Circuitsprakash srinivasanNo ratings yet
- Kirchoffs Law & RC CircuitsDocument7 pagesKirchoffs Law & RC Circuitsrajput1287No ratings yet
- Dual Transistor Multivariate Circuit.Document3 pagesDual Transistor Multivariate Circuit.sbpatel123No ratings yet
- Power Electronics Lab Practical FileDocument7 pagesPower Electronics Lab Practical FileMathewNo ratings yet
- Half Wave Controlled Rectifier - SusuDocument2 pagesHalf Wave Controlled Rectifier - SusuSHAHAD SHAMEEM V.PNo ratings yet
- EDCM2Document19 pagesEDCM2yanith kumarNo ratings yet
- Power Amplifier Learning Objectives: The Small Signal Amplifiers We Studied Previously Are All Class A AmplifiersDocument9 pagesPower Amplifier Learning Objectives: The Small Signal Amplifiers We Studied Previously Are All Class A AmplifiersPascual Hilario ReNo ratings yet
- Lec 2Document17 pagesLec 2mezo4326No ratings yet
- XLine Modeling - Medium Transmission LineDocument11 pagesXLine Modeling - Medium Transmission LineKyla BelgadoNo ratings yet
- On InverterDocument49 pagesOn InverterSahil ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- 12 - L-20 (SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page12 - L-20 (SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- Astable MultivibratorDocument4 pagesAstable MultivibratorWaldo PulancoNo ratings yet
- EE6503-Power ElectronicsDocument41 pagesEE6503-Power Electronicscwizard60No ratings yet
- Implementation of A Modular Full-Bridge DC/DC Converter: B.R. Lin, Senior Member, IEEE, and Sheng-Zhi ZhangDocument6 pagesImplementation of A Modular Full-Bridge DC/DC Converter: B.R. Lin, Senior Member, IEEE, and Sheng-Zhi ZhangRaja ReddyNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- 3 - L-26 (SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page3 - L-26 (SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 8 - L-26 (SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page8 - L-26 (SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 9 - L-26 (SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page9 - L-26 (SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 4 - L-26 (SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page4 - L-26 (SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 10 - L-25 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page10 - L-25 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 3 - L-25 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page3 - L-25 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 6 - L-25 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page6 - L-25 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 5 - L-26 (SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page5 - L-26 (SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 7 - L-25 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page7 - L-25 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 13 - L-24 (DK&SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page13 - L-24 (DK&SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 12 - L-24 (DK&SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page12 - L-24 (DK&SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 4 - L-25 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page4 - L-25 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 5 - L-25 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page5 - L-25 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 10 - L-23 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page10 - L-23 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 15 - L-24 (DK&SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page15 - L-24 (DK&SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 10 - L-24 (DK&SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page10 - L-24 (DK&SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 5 - L-24 (DK&SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page5 - L-24 (DK&SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 6 - L-23 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page6 - L-23 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 4 - L-24 (DK&SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page4 - L-24 (DK&SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 14 - L-24 (DK&SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page14 - L-24 (DK&SSG) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 5 - L-23 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page5 - L-23 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 9 - L-23 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page9 - L-23 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 13 - L-23 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page13 - L-23 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 11 - L-23 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page11 - L-23 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 8 - L-23 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page8 - L-23 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 3 - L-23 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page3 - L-23 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 4 - L-23 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page4 - L-23 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 12 - L-23 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page12 - L-23 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 7 - L-22 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page7 - L-22 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet
- 12 - L-22 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)Document1 page12 - L-22 (DP) (Pe) ( (Ee) Nptel)CharkNo ratings yet