Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Group 12 Modules
Group 12 Modules
Uploaded by
PETER AARON CASTROMAYORCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Aeration Calculation PDFDocument20 pagesAeration Calculation PDFBrian Thomas100% (1)
- Water Resources Sustainability ReportDocument26 pagesWater Resources Sustainability ReportEmre KaracaNo ratings yet
- Project Report On Prepare A Report On Polluted Natural Resources and Collect Information How To Manage ThemDocument26 pagesProject Report On Prepare A Report On Polluted Natural Resources and Collect Information How To Manage ThemArya KeneNo ratings yet
- NSTP Environmental ProtectionDocument7 pagesNSTP Environmental ProtectionAMPONIN EUNICENo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document37 pagesUnit 3venkateswaran k.sNo ratings yet
- Green and Beige Illustration Climate Change Presentation 2Document21 pagesGreen and Beige Illustration Climate Change Presentation 2Ajay CarandanNo ratings yet
- Nicholas 2023Document16 pagesNicholas 2023Tatenda Alfred KajauNo ratings yet
- Solid_and_Liquid_Waste_ManagementDocument19 pagesSolid_and_Liquid_Waste_ManagementDeva AnandNo ratings yet
- Fact Sheet Unit 3Document5 pagesFact Sheet Unit 3Shinta KusumawardaniNo ratings yet
- Environmental EngineeringDocument8 pagesEnvironmental EngineeringJohn Revin CagatinNo ratings yet
- English Project ALDO CAMILO ANDALUZ GUAMÀN 2DO BGU ADocument17 pagesEnglish Project ALDO CAMILO ANDALUZ GUAMÀN 2DO BGU Acamilo AndaluzNo ratings yet
- Trends, Networks, and Critical Thinking in The 21 Century Quarter 1: Week 6 - Module 6Document16 pagesTrends, Networks, and Critical Thinking in The 21 Century Quarter 1: Week 6 - Module 6Jocel CalugayNo ratings yet
- BEV2036 - EV414 Chpt. 1 Introduction To Env. EngineeringDocument51 pagesBEV2036 - EV414 Chpt. 1 Introduction To Env. EngineeringSam KhorNo ratings yet
- Chapter 23Document13 pagesChapter 23Shelton UamusseNo ratings yet
- New Climate ChangeDocument28 pagesNew Climate ChangeMark EstreraNo ratings yet
- 01 Introduction-Rev02Document33 pages01 Introduction-Rev02GRAZIELLA CZARINA MARIE LABRADORNo ratings yet
- The Reuse of Water From Wastewater Treatment PlantsDocument33 pagesThe Reuse of Water From Wastewater Treatment PlantsLudor EngineeringNo ratings yet
- PCOMM EM1 PSE Castro EsparteroDocument20 pagesPCOMM EM1 PSE Castro Esparterodianecastro618No ratings yet
- Environmental Protection: NSTP 1 - L003-L013 Il MC Coulie Del MundoDocument29 pagesEnvironmental Protection: NSTP 1 - L003-L013 Il MC Coulie Del MundoNeil Matthew AlbiolNo ratings yet
- ASSIGNMENT Environmental ChemistryDocument8 pagesASSIGNMENT Environmental ChemistryAyesha MalikNo ratings yet
- Pollution Control Measures: Environmental Science - Chapter 7Document39 pagesPollution Control Measures: Environmental Science - Chapter 7Elrach MeanneNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document24 pagesLecture 1TahaNo ratings yet
- Ps Eau Wash Services Climate Change Impacts and Responses 2018Document76 pagesPs Eau Wash Services Climate Change Impacts and Responses 2018Hifza JoharNo ratings yet
- Desalination: Keirrstian Roque C. AlvaradoDocument8 pagesDesalination: Keirrstian Roque C. AlvaradoJuvelyn DaculaNo ratings yet
- Desalination: Keirrstian Roque C. AlvaradoDocument8 pagesDesalination: Keirrstian Roque C. AlvaradoJuvelyn DaculaNo ratings yet
- Engineering Environent DocsDocument1 pageEngineering Environent DocsShaaira Riva HamidNo ratings yet
- EmrecchiDocument10 pagesEmrecchiEmre KaracaNo ratings yet
- 03.tjahjanto Et Al. 2012 - FulltextDocument15 pages03.tjahjanto Et Al. 2012 - FulltextMuhamad AskariNo ratings yet
- Recycling of WaterDocument20 pagesRecycling of Water10bcl002No ratings yet
- Environmental Education Project PpyDocument16 pagesEnvironmental Education Project PpyChandana RaoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 30Document30 pagesChapter 30KathiresanMechanicNo ratings yet
- WTPSTP 2017Document13 pagesWTPSTP 2017Shivraj SuryawanshiNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 EeDocument12 pagesAssignment 1 EeAHSAN SHAHBAZNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document14 pagesChapter 1abbyappleNo ratings yet
- English Project ALDO CAMILO ANDALUZ GUAMÀN 2DO BGU ADocument16 pagesEnglish Project ALDO CAMILO ANDALUZ GUAMÀN 2DO BGU Acamilo AndaluzNo ratings yet
- A Technology Portfolio of Nature Based Solutions (PDFDrive)Document139 pagesA Technology Portfolio of Nature Based Solutions (PDFDrive)rajanNo ratings yet
- LESSON 8 Environmental IssuesDocument21 pagesLESSON 8 Environmental IssuesJean DoriaNo ratings yet
- Water Treatment Process Using Conventional and Advanced MethodsDocument14 pagesWater Treatment Process Using Conventional and Advanced MethodsRenaizel MalcredoNo ratings yet
- EE 101 - Hydraulics, Hydrology, Environmental Engineering PDFDocument24 pagesEE 101 - Hydraulics, Hydrology, Environmental Engineering PDFIsrael PopeNo ratings yet
- Environmental Management Implication of Climate Change in NigeriaDocument20 pagesEnvironmental Management Implication of Climate Change in NigeriaJohn PeterNo ratings yet
- Environmental StudiesDocument13 pagesEnvironmental StudiesStuti MathurNo ratings yet
- Join Hands TogetherDocument50 pagesJoin Hands TogetherSahilNo ratings yet
- Dynamics of A CommunityDocument34 pagesDynamics of A CommunityGermie PosionNo ratings yet
- S Announcement 27018Document136 pagesS Announcement 27018patricia piliNo ratings yet
- SEJ441 Project ProposalDocument18 pagesSEJ441 Project ProposalBusiku SilengaNo ratings yet
- 938 Aurora BLVD., Cubao, Quezon City: Technological Institute of The PhilippinesDocument8 pages938 Aurora BLVD., Cubao, Quezon City: Technological Institute of The PhilippinesI'am PhilNo ratings yet
- Chapter3 20160403Document100 pagesChapter3 20160403Kavi MaranNo ratings yet
- Est Assignment No 5Document4 pagesEst Assignment No 5Amritvish ChannelNo ratings yet
- Makbul Final PDFDocument33 pagesMakbul Final PDFLalit raj PurohitNo ratings yet
- Chapter3 2Document92 pagesChapter3 2Mohd ZulhairiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document54 pagesChapter 5Dol SobariNo ratings yet
- Explain Mechanism of Mitigating Environmental DegradationDocument8 pagesExplain Mechanism of Mitigating Environmental DegradationAbdela Aman MtechNo ratings yet
- Restoration of EcosystemDocument6 pagesRestoration of EcosystemSonali Guha RoyNo ratings yet
- Biofilter MasterDocument49 pagesBiofilter MasterVinoth VinoNo ratings yet
- Primary Wastewater Treatment Plant: Abir Hasan ShovonDocument5 pagesPrimary Wastewater Treatment Plant: Abir Hasan ShovonAbir HasanNo ratings yet
- UNIT-4 2 MarksDocument21 pagesUNIT-4 2 MarksSEEKofficial17No ratings yet
- UEMK 3613 Topic1-1Document43 pagesUEMK 3613 Topic1-1igantiNo ratings yet
- Env. Sci AssignmentDocument8 pagesEnv. Sci AssignmentSyed NaqeeNo ratings yet
- Sewage Water TreatmentDocument21 pagesSewage Water TreatmentVelpula NagarajuNo ratings yet
- Reflection and Refraction of LightDocument4 pagesReflection and Refraction of LightMaxNo ratings yet
- Climate Change To Global Warming RealDocument1 pageClimate Change To Global Warming RealHaidarNo ratings yet
- BioCycle Magazine Article OpenRoad CompostingDocument6 pagesBioCycle Magazine Article OpenRoad CompostingPaula Hewitt AmramNo ratings yet
- Common Breathing Air Quality Standards For Scba and AirlinesDocument4 pagesCommon Breathing Air Quality Standards For Scba and AirlinesDaniel RodasNo ratings yet
- ASTM D1607-91 (2005) Standard Test Method For Nitrogen Dioxide Content of The Atmosphere (Griess-Saltzman ReacDocument6 pagesASTM D1607-91 (2005) Standard Test Method For Nitrogen Dioxide Content of The Atmosphere (Griess-Saltzman ReacArif WibisonoNo ratings yet
- MEC701 Pre-Lab Questions W2015Document2 pagesMEC701 Pre-Lab Questions W2015Isra SajjadNo ratings yet
- Managing Waste WaterDocument18 pagesManaging Waste WaterShreyas JaipuirarNo ratings yet
- U3-M4-Lynne (Responding2uncertainties - Changes 061705)Document29 pagesU3-M4-Lynne (Responding2uncertainties - Changes 061705)John Lester Burca MagdaraogNo ratings yet
- 11 Economics Notes ch19 Environment and Sustainable Economic DevelopmentDocument4 pages11 Economics Notes ch19 Environment and Sustainable Economic Developmentrohan chaturvediNo ratings yet
- Review 2 ReadingDocument2 pagesReview 2 ReadingDuongthuy NguyenNo ratings yet
- TQ - Q4 - SCIENCE - 7 - Aster Madalla - Asterio MadallaDocument11 pagesTQ - Q4 - SCIENCE - 7 - Aster Madalla - Asterio MadallaKhim YabesNo ratings yet
- Presnetation of Air PollutionDocument31 pagesPresnetation of Air Pollutionksbbs100% (1)
- Postmortem ChangesDocument23 pagesPostmortem ChangesNisrina NurhikmahNo ratings yet
- 14 Importance of PlantsDocument6 pages14 Importance of PlantsdeepakatoliaNo ratings yet
- Studyguide360: Chapter-2 The Origin and Evolution of The EarthDocument8 pagesStudyguide360: Chapter-2 The Origin and Evolution of The EarthShantanu SarkarNo ratings yet
- Stamicarbon Y2kDocument11 pagesStamicarbon Y2kvariable26100% (1)
- Env. ScienceDocument2 pagesEnv. ScienceHarold BautistaNo ratings yet
- Air Quality AhmedabadDocument15 pagesAir Quality AhmedabadAnurag KandyaNo ratings yet
- Minimax Oxeo Extinguishing Systems With Nitrogen and ArgonDocument12 pagesMinimax Oxeo Extinguishing Systems With Nitrogen and ArgonJuhar MohammedNo ratings yet
- Geography (UG), SEM - VI, Paper - DSC - 4T: Agriculture Geography, Unit - I (3. Factors Affecting Agriculture.)Document16 pagesGeography (UG), SEM - VI, Paper - DSC - 4T: Agriculture Geography, Unit - I (3. Factors Affecting Agriculture.)Vider AscarNo ratings yet
- Sullair Filtration PDFDocument12 pagesSullair Filtration PDFmahmod alrousanNo ratings yet
- Every Day Science PDFDocument115 pagesEvery Day Science PDFmuhammad ihtishamNo ratings yet
- Earth SystemsDocument4 pagesEarth SystemsfvdgffgNo ratings yet
- Ammonia Synthesis Catalyst OperationDocument19 pagesAmmonia Synthesis Catalyst OperationMuhammad Junaid0% (1)
- Aerodynamics 1Document2 pagesAerodynamics 1Kelvin SudaniNo ratings yet
- US Patent 2465498 - Production of Formaldehyde PDFDocument6 pagesUS Patent 2465498 - Production of Formaldehyde PDFAndrika TrepniaNo ratings yet
- ABCD-FE-01-00 Flight Envelope - V1 08.03.16Document21 pagesABCD-FE-01-00 Flight Envelope - V1 08.03.16OmasudNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Climate and Built EnvironmentDocument23 pagesUnit 1 Climate and Built EnvironmentSrilakshmi PriyaNo ratings yet
- Dispersion of Air Pollutants: Depends On Meteorological ConditionsDocument43 pagesDispersion of Air Pollutants: Depends On Meteorological ConditionsSamrat SalikineediNo ratings yet
Group 12 Modules
Group 12 Modules
Uploaded by
PETER AARON CASTROMAYOROriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Group 12 Modules
Group 12 Modules
Uploaded by
PETER AARON CASTROMAYORCopyright:
Available Formats
LEARNING SURIGAO DEL NORTE STATE
MODULE UNIVERSITY
LEARNING MODULE 23
Title Water Waste Management
Topic INTRODUCTION
23.1 Wastewater
23.2 Waterwaste Treatment
Time Frame 15 minutes
Introduction This module discusses how to manage water waste.
Objectives After reading this module ,you should be able to:
23.1 Know how waste water is produced.
23.2 Know the process of water waste management.
Learning Activities
(to include Content/Discussion of the topic)
Water waste management is an important approach to protect water resources and
it is defined as the collection, treatment, and reuse of wastewater. In wastewater
collection network as one of important infrastructures, undesirable performance can
lead to different problems.
23.1 Wastewater
Wastewater refers to any water that is not
clean or is adversely affected in quality by
human-induced activities. Wastewater
originates from a combination of domestic,
industrial, commercial, or agricultural
activities.
ES 246 – Environmental Science and Engineering
Instructor: Analyn S. Morite Page 1 of 13
LEARNING SURIGAO DEL NORTE STATE
MODULE UNIVERSITY
23.2 Waterwaste Treatment
Wastewater treatment or management refers to the processes used to convert
wastewater into an effluent that can be either returned to the water cycle with
negligible environmental impact or can be reused.
The major objective of wastewater
treatment is generally to allow human
and industrial effluents to be
disposed of without danger to human
health or unacceptable damage to
the natural environment.
This picture shows the water
treatment plant in Maynilad.
Wastewater Treatment Process
Phase Separation − It transfers impurities into a non-aqueous phase.
Sedimentation − Sedimentation is a physical water treatment process using gravity
to remove suspended solids from water. Solid particles entrained by the turbulence
of moving water may be removed naturally by sedimentation in the still water of
lakes and oceans.
Filtration − Suspension of fine solids may be removed by filtration through physical
barriers such as coarser screens or sieves.
Oxidation − This process diminishes the biochemical oxygen demand of wastewater
and may reduce the toxicity of some impurities. Advanced Oxidation Processes
(AOPs) are a set of chemical treatment of wastewater purported to remove organic
and also inorganic materials in waste water by oxidation through reaction with
hydroxyl radicals.
Chemical oxidation may remove some persistent organic pollutants and
concentrations remaining after biochemical oxidation.
Wastewater treatment plants are set up for effective treatment of wastewater. They
may be distinguished by the type of wastewater to be treated. They are as follows.
Sewage treatment plants
Industrial wastewater treatment plants
Agricultural wastewater treatment plants
ES 246 – Environmental Science and Engineering
Instructor: Analyn S. Morite Page 2 of 13
LEARNING SURIGAO DEL NORTE STATE
MODULE UNIVERSITY
Self-Evaluation Using your own words, construct sentences below to self-
assess your learning about the lesson. Make your
answer brief but concise. Limit your answer to a
maximum of four (4) sentences only.
Review of Concepts Wastewater is water generated after the use
of freshwater, raw water, drinking water or saline water in
a variety of deliberate applications or processes.
Wastewater treatment or management refers to the
processes used to convert wastewater into an effluent
that can be either returned to the water cycle with
negligible environmental impact or can be reused.
The process of Wastewater Treatment are Phase
Separation, Sedimentation, Filtration and Oxidation
References
Environmental Studies Tutorial “Waterwaste Management”
Retrieved from:
https://www.tutorialspoint.com/environmental_studies/environmental_studies_water_
waste_management.htm
Maynilad Water Treatment Plant photo
Retrieved from:
https://www.google.com/search?q=maynilad+water+treatment+plant&tbm=isch&ved
=2ahUKEwjF4PL617b6AhXJEKYKHdm2DzwQ2-
cCegQIABAA&oq=maynilad+water+trea&gs_lcp=CgNpbWcQARgAMgQIABAYMgQI
ABAYMgQIABAYMgQIABAYOgQIABBDOgcIABCxAxBDOgUIABCABDoECCMQJz
oHCCMQ6gIQJzoLCAAQgAQQsQMQgwE6CAgAEIAEELEDOggIABCxAxCDAToG
CAAQHhAIUP8FWNNTYPNfaAVwAHgEgAG2AYgBmxqSAQQwLjI1mAEAoAEBqg
ELZ3dzLXdpei1pbWewAQXAAQE&sclient=img&ei=itIzY8XzKcmhmAXZ7b7gAw&rlz
=1C1GCEA_enPH961PH961
ES 246 – Environmental Science and Engineering
Instructor: Analyn S. Morite Page 3 of 13
LEARNING SURIGAO DEL NORTE STATE
MODULE UNIVERSITY
LEARNING MODULE 24
Title Global Environmental Problems
Topic INTRODUCTION
24.1 Climate Change
24.2 Crazy Consumers
Time Frame 20 minutes
Introduction This module discusses what are the global environmental
problems.
Objectives After reading this module ,you should be able to:
24.1 Know the cause and impact of climate change.
24.2 Know the reason why there are crazy consumers.
Learning Activities
(to include Content/Discussion of the topic)
Climate refers to the usual weather of a place. Climate differs from season to
season, from region to region. A combination of all the climates of the world is
termed as the Earth‟s climate.
24.1 Climate Change
Climate change refers to a change or changes in the usual weather condition found
in a place or region. Changes could be experienced in the rainfall or snowfall
pattern, temperature, etc. Climate change is also a change in Earth‟s climate.
Climate change is now a much-discussed concept around the globe. It is because it
is now experienced that the world temperature is increasing during these years. The
global average surface temperature is believed to have increased by 0.6° + 0.2° C
over the last century. Globally, 1998 was the warmest year and the 1990s was the
warmest decade on record.
ES 246 – Environmental Science and Engineering
Instructor: Analyn S. Morite Page 4 of 13
LEARNING SURIGAO DEL NORTE STATE
MODULE UNIVERSITY
Many countries have experienced increases in rainfall, particularly in the countries
situated in the mid to high latitudes. In some regions, such as parts of Asia and
Africa, the frequency and intensity of droughts have been observed to increase in
recent decades.
Episodes of El Nino, which
creates great storms, have
been more frequent,
persistent, and intense since
mid-1970s compared with the
previous 100 years. All these
signs show that the earth‟s
climate is changing, making it
more difficult for mankind to
survive.
Causes of Climate Change
Climate changes on its own in nature. Earth‟s distance from the sun, volcanic
eruption at large scale, heavy rainfall for longer period, are the instances of natural
phenomena that influence the Earth‟s climate. These are natural and have nothing to
do with our present concern about climate change.
What concerns us today is the rise in global temperature, especially. Most scientists
say that human activities have caused certain changes in the natural climate of the
earth.
Most scientists agree that the main cause of current global warming is human
expansion of the „greenhouse effect‟. Greenhouse effect is the increase in the
number of certain gases that include, carbon dioxide (CO2), methane, nitrous oxide
(N2O), water vapor, chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), etc.
Greenhouse gases are produced naturally and trap heat in the Earth‟s atmosphere
like a blanket. When there is increased concentration of such gases in the
atmosphere mostly by burning fossil fuels, there is a proportionate increase in the
temperature of the Earth‟s atmosphere. It is called global warming.
ES 246 – Environmental Science and Engineering
Instructor: Analyn S. Morite Page 5 of 13
LEARNING SURIGAO DEL NORTE STATE
MODULE UNIVERSITY
Significant human-led factors responsible for climate change are −
Exponential growth in human population.
Massive and unplanned urbanization and industrialization over the last
century.
Burning of fossil fuels such as coal, petroleum, and natural gas at huge scale
to meet the growing energy needs of the bulging world population.
Change in lifestyle and massive increase in the number of machinery,
gadgets, etc.
Impact of Climate Change on Human Environment
It is now clear that climate change causes unwanted alterations in the natural
systems. The environmental consequences of climate change are extreme heat
waves, rising sea levels, changes in precipitation resulting in flooding and droughts,
intense hurricanes, and degraded air quality.
The above phenomenal changes directly and indirectly affect the physical, social,
and psychological health of human beings.
Frequency in Weather-Related Disasters
Changes in precipitation create changes in the availability and quantity of water and
also results in extreme weather events, such as intense storms, flooding and
droughts. Frequency in all these weather phenomena sometimes lead to human
causality in great proportion apart from huge loss of property, mostly in developing
and underdeveloped countries.
Human Health
Climate change affects the
prerequisites of human health
such as clean air and water,
sufficient and healthy food,
natural constraints to infectious
disease agents and the
adequacy and security of
shelter.
The report of the WHO Commission on Social Determinants of Health points out that
disadvantaged communities are likely to shoulder a disproportionate share of the
burden of climate change because of their increased exposure and vulnerability to
health threats.
Large Scale Displacement of People
Climate change effects such as desertification, rising sea levels and severity of
weatherrelated disasters along with the spread of epidemics can destroy or affect
human habitation causing people to seek shelter elsewhere.
ES 246 – Environmental Science and Engineering
Instructor: Analyn S. Morite Page 6 of 13
LEARNING SURIGAO DEL NORTE STATE
MODULE UNIVERSITY
Deteriorating environment and depleting resources can result in human conflicts at
all levels. The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) has estimated
that there will be over 150 million environmental migrants by 2050 and the number
will be perplexing due to complexity of the issue and lack of data.
Apart from the above, following are some other consequences of climate change −
Change in hydrological cycle and water supply
The Inter-Tropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ) may move northward in the
northern hemisphere causing rapid changes in rainfall pattern
Increase in tropical and temperate cyclones, cloud cover, tornadoes and
storms
Changes in pressure belts and atmospheric circulation
Warming of ocean water may endanger the corals worldwide
Expansion of deserts and more desertification within deserts
Effect on food supply and international trade of grains
National parks, sanctuaries and biosphere reserves may be altered
Countries such as Maldives and greater parts of Netherlands etc. may
submerge under water
Climate change is making food crops less nutritious. Rising carbon dioxide
emissions lead to iron and zinc deficiencies in food crops
Population Explosion & its Pressure on Environment
Finite Resources
Most resources being finite since the very
beginning and natural limit to resource
generation being slow, constant rise in the
number of people on the earth exerts undue
pressure on world resources.
Population growth and the resultant increase
in human habitations in the last couple of
centuries has taken away a considerable
portion of natural vegetation, cultivable lands,
and above all the natural habitats of wild
animals. There has been loss of biodiversity
and resultant ecological imbalance in severity
in the current times.
ES 246 – Environmental Science and Engineering
Instructor: Analyn S. Morite Page 7 of 13
LEARNING SURIGAO DEL NORTE STATE
MODULE UNIVERSITY
More People, More Demand, More Waste
With the advent of science and technology man‟s need for comfort and luxury has
multiplied many times. This has necessitated the production of a great number of
goods and services in the world.
Not only the huge population (7.4 billion in 2016), but also the lifestyle, consumption
patterns in modern time directly affect the environment. More people demand more
resources and generate more waste. Clearly one of the challenges of a growing
population is that the mere presence of so many people sharing a limited number of
resources strain the environment.
Rapid Urbanization and Industrialization
Rapid urbanization and industrialization during the last century in most part of the
world has not only destroyed a substantial part of natural vegetation but also forced
many wild animals on the verge of extinction.
Apart from the pressure on the resources due to high growth in population,
technological and scientific innovations, rapid rise in automobile population,
electronic gadgets, machinery and equipment have added a great number of
pollutants to the environment. As a result, environmental degradation has risen to an
irrecoverable level.
Developed countries where the levels of consumption are high add more to pollution
than other countries. A child born in a country, where the levels of material and
energy use are high, places a greater burden on the earth's resources than a child
born in a poorer country..
24.2 Crazy Consumerism
Consumption, although necessary for the economy,
can be hazardous to the environment.
Consumerism is a social and economic order that
supports and encourages the acquisition of goods
and services in ever increasing amounts.
ES 246 – Environmental Science and Engineering
Instructor: Analyn S. Morite Page 8 of 13
LEARNING SURIGAO DEL NORTE STATE
MODULE UNIVERSITY
Man has developed an unprecedented craze for a mushrooming number of products
and services available in the world market. This has been aggravated by improved
marketing strategies, alluring advertisements, and consumer-friendly services
offered by companies and outlets.
Approximately 2 billion people belonging to the “consumer class” are characterized
by desire for processed food, desire for bigger houses, cars, durables, etc. to
maintain their desired lifestyles.
Consumerism has become more acute in developing countries such as India and
China than that in developed countries due to the rise in population in the former.
Reasons for Crazy Consumerism
Growing materialistic tendencies among the modern man
Easy access to markets due to faster development in transport and
communication
Effective marketing and advertising strategies
Rising income levels in most part of the world
Globalization and liberalization
Rapid rise in income generation ways
Greed to possess more and more
Impact of Crazy Consumerism
Increasing consumerism has led to excessive production of goods and services,
which in turn has led to enormous pressure on natural environment and natural
resources. Resource depletion, environmental degradation, and pollution have
become the order of the day. Mankind has reached the height of environmental
pollution from where it seems very difficult to return. Race for comfort and luxury has
vitiated the environment disproportionately.
Excessive demand for consumer products has created most of the current
environmental imbalances and these imbalances have already caused ecological
disaster in different places all over the world.
Consumerism has resulted in heaps of waste in urban and also in rural areas which
lead to a pollution of environment. Mounting e-waste in the world, especially in
developed countries, is causing more harm to the environment. Popularity of plastic
for various purposes is adding severely to air, water, and land pollution.
Self-Evaluation Using your own words, construct sentences below to self-
assess your learning about the lesson. Make your
answer brief but concise. Limit your answer to a
maximum of four (4) sentences only.
ES 246 – Environmental Science and Engineering
Instructor: Analyn S. Morite Page 9 of 13
LEARNING SURIGAO DEL NORTE STATE
MODULE UNIVERSITY
Review of Concepts Climate change refers to a change or changes in the
usual weather condition found in a place or region.
Climate changes on its own in nature. Earth‟s distance
from the sun, volcanic eruption at large scale, heavy
rainfall for longer period, are the instances of natural
phenomena that influence the Earth‟s climate.
When there is increased concentration of such gases
in the atmosphere mostly by burning fossil fuels, there is
a proportionate increase in the temperature of the Earth‟s
atmosphere. It is called global warming.
References
Environmental Studies Tutorial “Waterwaste Management”
Retrieved from:
https://www.tutorialspoint.com/environmental_studies/environmental_studies_water_
waste_management.htm
ES 246 – Environmental Science and Engineering
Instructor: Analyn S. Morite Page 10 of 13
LEARNING SURIGAO DEL NORTE STATE
MODULE UNIVERSITY
LEARNING MODULE 25
Title Ozone Depletion
Topic INTRODUCTION
25. 1 Ozone Depletion
25. 2 Ozone Depleting Substances
Time Frame 15 minutes
Introduction This module discusses why the ozone layer is depleting.
Objectives After reading this module ,you should be able to:
25.1 Know why the ozone layer is depleting.
25.2 Know what are the substances that causes the
ozone layer to deplete.
Learning Activities
(to include Content/Discussion of the topic)
Ozone is a form of oxygen in which three atoms of
oxygen combine to form a single molecule of ozone.
It normally is not found in the lower atmosphere. It
exists in the stratosphere between 20 and 50
kilometers above the surface.
The presence of ozone is of singular importance
because it filters out the incoming ultraviolet (UV)
radiation and thus acts as a screen against
ultraviolent radiation that can increase the
occurrence of skin cancer, cataracts, and other
diseases of eyes. It also affects the body defense
mechanism, which increases the vulnerability of
infectious diseases.
Increased ultraviolet radiation can seriously affect plant and fish production.
25.1 Ozone Depletion
Ozone depletion refers to the wearing out or reduction of the amount of ozone in
the stratosphere. It was first identified in 1970s due to the advent of supersonic
aircraft, which fly in the lower stratosphere and emit nitrogen oxides.
ES 246 – Environmental Science and Engineering
Instructor: Analyn S. Morite Page 11 of 13
LEARNING SURIGAO DEL NORTE STATE
MODULE UNIVERSITY
25.2 Ozone Depleting Substances
Ozone depleting substances
are those substances which
deplete the ozone layer.
It is found that the major
cause of ozone depletions is
the CFC
(Chlorofluorocarbons) gases.
CFCs are used for a wide
range of applications
including refrigerant, foaming
agents, plastic manufacturing,
fire extinguishing agents,
solvents for freezing food, cleaners for electronic components fine retardant,
solvents, aerosol, propellants, and the production of foamed plastics.
Other ozone depleting substances controlled by Montreal Protocol (discussed in a
subsequent chapter) are −
Halon
Carbon tetrachloride (CCl4), Methyl chloroform (CH3CCl3)
Hydrobromofluorocarbons (HBFCs)
Hydrochlorofluorocarbons (HCFCs)
Methyl bromide (CH3Br)
Bromochloromethane (CH2BrCl)
There are serious consequences of ozone depletion. Following are some of the
significant consequences of ozone depletion.
Plants and animals vary in their tolerance of ultraviolet rays. The ultraviolet
rays damage DNA (the genetic code in every living being). Crops such as
soybean are the worst affected.
Animals and humans also have adapted to UVB radiation. In case of depletion
of the ozone layer, there is danger of melanoma – a type of skin cancer. The
disease is now almost epidemic in the United States.
Self-Evaluation Using your own words, construct sentences below to self-
assess your learning about the lesson. Make your
answer brief but concise. Limit your answer to a
maximum of four (4) sentences only.
ES 246 – Environmental Science and Engineering
Instructor: Analyn S. Morite Page 12 of 13
LEARNING SURIGAO DEL NORTE STATE
MODULE UNIVERSITY
Review of Concepts Ozone is a form of oxygen in which three atoms of
oxygen combine to form a single molecule of ozone. It
normally is not found in the lower atmosphere. Ozoone
depletion refers to the wearing out or the reduction of
the amount of ozone in the stratosphere.
Ozone depleting substances are those substances
which deplete the ozone layer. It is found that the major
cause of ozone depletions is the CFC
(Chlorofluorocarbons) gases.
References
Environmental Studies Tutorial “Waterwaste Management”
Retrieved from:
https://www.tutorialspoint.com/environmental_studies/environmental_studies_water_
waste_management.htm
ES 246 – Environmental Science and Engineering
Instructor: Analyn S. Morite Page 13 of 13
You might also like
- Aeration Calculation PDFDocument20 pagesAeration Calculation PDFBrian Thomas100% (1)
- Water Resources Sustainability ReportDocument26 pagesWater Resources Sustainability ReportEmre KaracaNo ratings yet
- Project Report On Prepare A Report On Polluted Natural Resources and Collect Information How To Manage ThemDocument26 pagesProject Report On Prepare A Report On Polluted Natural Resources and Collect Information How To Manage ThemArya KeneNo ratings yet
- NSTP Environmental ProtectionDocument7 pagesNSTP Environmental ProtectionAMPONIN EUNICENo ratings yet
- Unit 3Document37 pagesUnit 3venkateswaran k.sNo ratings yet
- Green and Beige Illustration Climate Change Presentation 2Document21 pagesGreen and Beige Illustration Climate Change Presentation 2Ajay CarandanNo ratings yet
- Nicholas 2023Document16 pagesNicholas 2023Tatenda Alfred KajauNo ratings yet
- Solid_and_Liquid_Waste_ManagementDocument19 pagesSolid_and_Liquid_Waste_ManagementDeva AnandNo ratings yet
- Fact Sheet Unit 3Document5 pagesFact Sheet Unit 3Shinta KusumawardaniNo ratings yet
- Environmental EngineeringDocument8 pagesEnvironmental EngineeringJohn Revin CagatinNo ratings yet
- English Project ALDO CAMILO ANDALUZ GUAMÀN 2DO BGU ADocument17 pagesEnglish Project ALDO CAMILO ANDALUZ GUAMÀN 2DO BGU Acamilo AndaluzNo ratings yet
- Trends, Networks, and Critical Thinking in The 21 Century Quarter 1: Week 6 - Module 6Document16 pagesTrends, Networks, and Critical Thinking in The 21 Century Quarter 1: Week 6 - Module 6Jocel CalugayNo ratings yet
- BEV2036 - EV414 Chpt. 1 Introduction To Env. EngineeringDocument51 pagesBEV2036 - EV414 Chpt. 1 Introduction To Env. EngineeringSam KhorNo ratings yet
- Chapter 23Document13 pagesChapter 23Shelton UamusseNo ratings yet
- New Climate ChangeDocument28 pagesNew Climate ChangeMark EstreraNo ratings yet
- 01 Introduction-Rev02Document33 pages01 Introduction-Rev02GRAZIELLA CZARINA MARIE LABRADORNo ratings yet
- The Reuse of Water From Wastewater Treatment PlantsDocument33 pagesThe Reuse of Water From Wastewater Treatment PlantsLudor EngineeringNo ratings yet
- PCOMM EM1 PSE Castro EsparteroDocument20 pagesPCOMM EM1 PSE Castro Esparterodianecastro618No ratings yet
- Environmental Protection: NSTP 1 - L003-L013 Il MC Coulie Del MundoDocument29 pagesEnvironmental Protection: NSTP 1 - L003-L013 Il MC Coulie Del MundoNeil Matthew AlbiolNo ratings yet
- ASSIGNMENT Environmental ChemistryDocument8 pagesASSIGNMENT Environmental ChemistryAyesha MalikNo ratings yet
- Pollution Control Measures: Environmental Science - Chapter 7Document39 pagesPollution Control Measures: Environmental Science - Chapter 7Elrach MeanneNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document24 pagesLecture 1TahaNo ratings yet
- Ps Eau Wash Services Climate Change Impacts and Responses 2018Document76 pagesPs Eau Wash Services Climate Change Impacts and Responses 2018Hifza JoharNo ratings yet
- Desalination: Keirrstian Roque C. AlvaradoDocument8 pagesDesalination: Keirrstian Roque C. AlvaradoJuvelyn DaculaNo ratings yet
- Desalination: Keirrstian Roque C. AlvaradoDocument8 pagesDesalination: Keirrstian Roque C. AlvaradoJuvelyn DaculaNo ratings yet
- Engineering Environent DocsDocument1 pageEngineering Environent DocsShaaira Riva HamidNo ratings yet
- EmrecchiDocument10 pagesEmrecchiEmre KaracaNo ratings yet
- 03.tjahjanto Et Al. 2012 - FulltextDocument15 pages03.tjahjanto Et Al. 2012 - FulltextMuhamad AskariNo ratings yet
- Recycling of WaterDocument20 pagesRecycling of Water10bcl002No ratings yet
- Environmental Education Project PpyDocument16 pagesEnvironmental Education Project PpyChandana RaoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 30Document30 pagesChapter 30KathiresanMechanicNo ratings yet
- WTPSTP 2017Document13 pagesWTPSTP 2017Shivraj SuryawanshiNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 EeDocument12 pagesAssignment 1 EeAHSAN SHAHBAZNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document14 pagesChapter 1abbyappleNo ratings yet
- English Project ALDO CAMILO ANDALUZ GUAMÀN 2DO BGU ADocument16 pagesEnglish Project ALDO CAMILO ANDALUZ GUAMÀN 2DO BGU Acamilo AndaluzNo ratings yet
- A Technology Portfolio of Nature Based Solutions (PDFDrive)Document139 pagesA Technology Portfolio of Nature Based Solutions (PDFDrive)rajanNo ratings yet
- LESSON 8 Environmental IssuesDocument21 pagesLESSON 8 Environmental IssuesJean DoriaNo ratings yet
- Water Treatment Process Using Conventional and Advanced MethodsDocument14 pagesWater Treatment Process Using Conventional and Advanced MethodsRenaizel MalcredoNo ratings yet
- EE 101 - Hydraulics, Hydrology, Environmental Engineering PDFDocument24 pagesEE 101 - Hydraulics, Hydrology, Environmental Engineering PDFIsrael PopeNo ratings yet
- Environmental Management Implication of Climate Change in NigeriaDocument20 pagesEnvironmental Management Implication of Climate Change in NigeriaJohn PeterNo ratings yet
- Environmental StudiesDocument13 pagesEnvironmental StudiesStuti MathurNo ratings yet
- Join Hands TogetherDocument50 pagesJoin Hands TogetherSahilNo ratings yet
- Dynamics of A CommunityDocument34 pagesDynamics of A CommunityGermie PosionNo ratings yet
- S Announcement 27018Document136 pagesS Announcement 27018patricia piliNo ratings yet
- SEJ441 Project ProposalDocument18 pagesSEJ441 Project ProposalBusiku SilengaNo ratings yet
- 938 Aurora BLVD., Cubao, Quezon City: Technological Institute of The PhilippinesDocument8 pages938 Aurora BLVD., Cubao, Quezon City: Technological Institute of The PhilippinesI'am PhilNo ratings yet
- Chapter3 20160403Document100 pagesChapter3 20160403Kavi MaranNo ratings yet
- Est Assignment No 5Document4 pagesEst Assignment No 5Amritvish ChannelNo ratings yet
- Makbul Final PDFDocument33 pagesMakbul Final PDFLalit raj PurohitNo ratings yet
- Chapter3 2Document92 pagesChapter3 2Mohd ZulhairiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document54 pagesChapter 5Dol SobariNo ratings yet
- Explain Mechanism of Mitigating Environmental DegradationDocument8 pagesExplain Mechanism of Mitigating Environmental DegradationAbdela Aman MtechNo ratings yet
- Restoration of EcosystemDocument6 pagesRestoration of EcosystemSonali Guha RoyNo ratings yet
- Biofilter MasterDocument49 pagesBiofilter MasterVinoth VinoNo ratings yet
- Primary Wastewater Treatment Plant: Abir Hasan ShovonDocument5 pagesPrimary Wastewater Treatment Plant: Abir Hasan ShovonAbir HasanNo ratings yet
- UNIT-4 2 MarksDocument21 pagesUNIT-4 2 MarksSEEKofficial17No ratings yet
- UEMK 3613 Topic1-1Document43 pagesUEMK 3613 Topic1-1igantiNo ratings yet
- Env. Sci AssignmentDocument8 pagesEnv. Sci AssignmentSyed NaqeeNo ratings yet
- Sewage Water TreatmentDocument21 pagesSewage Water TreatmentVelpula NagarajuNo ratings yet
- Reflection and Refraction of LightDocument4 pagesReflection and Refraction of LightMaxNo ratings yet
- Climate Change To Global Warming RealDocument1 pageClimate Change To Global Warming RealHaidarNo ratings yet
- BioCycle Magazine Article OpenRoad CompostingDocument6 pagesBioCycle Magazine Article OpenRoad CompostingPaula Hewitt AmramNo ratings yet
- Common Breathing Air Quality Standards For Scba and AirlinesDocument4 pagesCommon Breathing Air Quality Standards For Scba and AirlinesDaniel RodasNo ratings yet
- ASTM D1607-91 (2005) Standard Test Method For Nitrogen Dioxide Content of The Atmosphere (Griess-Saltzman ReacDocument6 pagesASTM D1607-91 (2005) Standard Test Method For Nitrogen Dioxide Content of The Atmosphere (Griess-Saltzman ReacArif WibisonoNo ratings yet
- MEC701 Pre-Lab Questions W2015Document2 pagesMEC701 Pre-Lab Questions W2015Isra SajjadNo ratings yet
- Managing Waste WaterDocument18 pagesManaging Waste WaterShreyas JaipuirarNo ratings yet
- U3-M4-Lynne (Responding2uncertainties - Changes 061705)Document29 pagesU3-M4-Lynne (Responding2uncertainties - Changes 061705)John Lester Burca MagdaraogNo ratings yet
- 11 Economics Notes ch19 Environment and Sustainable Economic DevelopmentDocument4 pages11 Economics Notes ch19 Environment and Sustainable Economic Developmentrohan chaturvediNo ratings yet
- Review 2 ReadingDocument2 pagesReview 2 ReadingDuongthuy NguyenNo ratings yet
- TQ - Q4 - SCIENCE - 7 - Aster Madalla - Asterio MadallaDocument11 pagesTQ - Q4 - SCIENCE - 7 - Aster Madalla - Asterio MadallaKhim YabesNo ratings yet
- Presnetation of Air PollutionDocument31 pagesPresnetation of Air Pollutionksbbs100% (1)
- Postmortem ChangesDocument23 pagesPostmortem ChangesNisrina NurhikmahNo ratings yet
- 14 Importance of PlantsDocument6 pages14 Importance of PlantsdeepakatoliaNo ratings yet
- Studyguide360: Chapter-2 The Origin and Evolution of The EarthDocument8 pagesStudyguide360: Chapter-2 The Origin and Evolution of The EarthShantanu SarkarNo ratings yet
- Stamicarbon Y2kDocument11 pagesStamicarbon Y2kvariable26100% (1)
- Env. ScienceDocument2 pagesEnv. ScienceHarold BautistaNo ratings yet
- Air Quality AhmedabadDocument15 pagesAir Quality AhmedabadAnurag KandyaNo ratings yet
- Minimax Oxeo Extinguishing Systems With Nitrogen and ArgonDocument12 pagesMinimax Oxeo Extinguishing Systems With Nitrogen and ArgonJuhar MohammedNo ratings yet
- Geography (UG), SEM - VI, Paper - DSC - 4T: Agriculture Geography, Unit - I (3. Factors Affecting Agriculture.)Document16 pagesGeography (UG), SEM - VI, Paper - DSC - 4T: Agriculture Geography, Unit - I (3. Factors Affecting Agriculture.)Vider AscarNo ratings yet
- Sullair Filtration PDFDocument12 pagesSullair Filtration PDFmahmod alrousanNo ratings yet
- Every Day Science PDFDocument115 pagesEvery Day Science PDFmuhammad ihtishamNo ratings yet
- Earth SystemsDocument4 pagesEarth SystemsfvdgffgNo ratings yet
- Ammonia Synthesis Catalyst OperationDocument19 pagesAmmonia Synthesis Catalyst OperationMuhammad Junaid0% (1)
- Aerodynamics 1Document2 pagesAerodynamics 1Kelvin SudaniNo ratings yet
- US Patent 2465498 - Production of Formaldehyde PDFDocument6 pagesUS Patent 2465498 - Production of Formaldehyde PDFAndrika TrepniaNo ratings yet
- ABCD-FE-01-00 Flight Envelope - V1 08.03.16Document21 pagesABCD-FE-01-00 Flight Envelope - V1 08.03.16OmasudNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Climate and Built EnvironmentDocument23 pagesUnit 1 Climate and Built EnvironmentSrilakshmi PriyaNo ratings yet
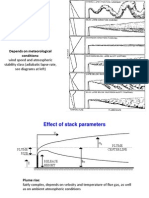
- Dispersion of Air Pollutants: Depends On Meteorological ConditionsDocument43 pagesDispersion of Air Pollutants: Depends On Meteorological ConditionsSamrat SalikineediNo ratings yet