Professional Documents
Culture Documents
El 108 Teaching Grammar
El 108 Teaching Grammar
Uploaded by
Razyl EdioOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
El 108 Teaching Grammar
El 108 Teaching Grammar
Uploaded by
Razyl EdioCopyright:
Available Formats
El 108 Teaching Grammar Structured Input
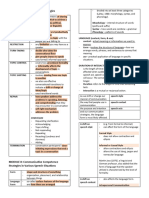
Processing Instruction- based on how learners interpret and process input into meaning. -classroom activities that are used in input-processing instruction are called structured input
-1. Learners provided with information about the target linguistic form or structure. -1. Referential – activities for which there is always right and wrong answer. (true or False)
-2. They are formed of the input processing strategies that may negatively affect their -2. Affective- activities that do not have any right and wrong answer. i.e agreement or
processing of the target structure. opinions
-3. The carry out input-based activities that help them understand and process the form Guidelines in Developing Structured Input activities
during comprehension.
-1. Keep meaning in focus
VanPattern-To assist the learner in making form-meaning connections during IP; it is more
-2. Present One item at a time
appropriate view as it as a type of FoF.
-3. Use oral and written input
Input Processing- strategies that learners use to link grammatical forms to their meaning
and functions. Attempts to explain how learners get form from input and how they parse -4. Move from individual sentences to connected discourse
sentence during the act of comprehension while their primary attention is on meaning.
-5. Keep learners’ processing strategies in mind
Processing- refers to mechanism used in drawing meaning from input.
Perception- refers to the registration of acoustic signals present in utterance that the
learners hear. Focus on Grammar through Textual Enhancement
Noticing- refers to the conscious registration of those forms in memory. -aims to achieve this by highlighting certain aspects of input by means of various
typographic devices.
Intake- refers to that part of the input that the learner has notices and has stored in his or
her working memory for further processing. Input Enhancement
Empirical Evidence for Processing Instruction -the process through which salience of input is enhanced is called input enhancement.
Conscious-raising (Sharwood Smith and Rutherford)
Perceptual Salience- refers to features of the target structure that are easily noticed.
-1. Explicitness- concerns the degree of directness in how the attention is drawn to form.
-2. Elaboration- the duration or intensity with which enhancement procedures take place.
a. Explicit Enhancement- may be overt form-focused intervention in which the teacher
explicitly directs learners’ attention to particular linguistic features
b. Implicit Enhancement- occurs when learners attention is drawn to grammatical forms
while their focus in on meaning.
Focus on Grammar through Discourse Principles and Techniques in English instruction Methods
-considers the meaning and use of forms within the larger discourse context. 1. Grammar/ Translation Method- read and appreciate the foreign language lit.
2. Direct Method- No translation allowed/ use of realia
Discourse- defined as a continuous stretch of language larger than a sentence, often
3. Audio-Lingual Method- expose students to correct from of language
constituting a coherent unit.
4. The Silent Way Method- Gattegno/point or use gestures to modify sounds
Discourse competence- defined as the ability to process and create coherent discourse 5. Desuggestopedia Method- break psychological barrier/cheerful environment
6. Community Language Learning- student to become language counselors
Grammar as Syntax- refers to the ways in which words are arranged in a phrase, a clause, or 7. Total Physical Response- gives importance to listening comprehensions
a sentence and the rules governing these arrangements. 8. Communicative Language Learning- students is expose to promising, declining
Grammar as Language- refers to the ability to understand and use grammar in a Communicative Competence- the ability to understand and use language
communicative discourse. 9.1- Linguistic- Understanding and using language vocab & conventions
9.2- Strategies- using techniques, overcome language gaps/ plan and assess
Corpus Linguistics and Focus in Grammar 9.3- Socio-Linguistics- Awareness or social rules and language/ politeness
-the study of language as expressed in corpora or large bodies of text. 9.4- Discourse- understanding how ideas are connected through patterns of
organizations/ cohesive and Transmitted devices
-the collection of sampled text, written or spoken, in machine readable form which may be a. Content-Based Instruction- academic subject matter/ geographic study
annotated with various forms of linguistic information. b. Task-Based Instruction- aims to provide learners with natural context
c. Participatory Approach- Friere /learner reflecting on their relationship to the world
Essential Characteristics
d. Learning Strategy in Learning- Rubin/Nomonics strategy or memorizations
-1. It is empirical, analyzing the actual patterns of use in natural test e. Cooperative Learning- learning from each other in groups/Cooperation
f. Multiple intelligence – categorize them according to their intelligences type
-2. Utilizes a large and principled collection of natural text, know as “corpus” as the basis for
9. Structural Approach- grammatical rules/mastering structure, building skills
analysis
10. Natural Approach- communication through exposure
-3. Make extensive use of computers for analysis, using both automatic and interactive 11. Functional-Notion Approach- language functions and notions
techniques 12. The Test Teach Test Approach- teacher to observe/focus on gap/maintain accuracy
13. The Series Method- Fracios Gouin-learn German through memorization
-4. Depends on both quantitative and qualitative analytical techniques
Data-Driven Learning (DDL)- the use in the classroom of computer-generated concordances
to get students to explore regularities of patterning in the target languages, and the
development of activities and exercises based in concordance output.
Discourse Analysis (DA)- relationship between language forms and the context in which
they are used. -it aimed for investigating the nature of social interaction.
You might also like
- Induction: Course ObjectivesDocument36 pagesInduction: Course ObjectivesQuyền Huỳnh TuấnNo ratings yet
- AURAL COMPREHENSION INSTRUCTION: Principles and Practices: Remedial Instruction in EnglishDocument10 pagesAURAL COMPREHENSION INSTRUCTION: Principles and Practices: Remedial Instruction in EnglishVandolph Acupido CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Task-based grammar teaching of English: Where cognitive grammar and task-based language teaching meetFrom EverandTask-based grammar teaching of English: Where cognitive grammar and task-based language teaching meetRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (4)
- ENGL022 ReviewerDocument5 pagesENGL022 ReviewerIrelle B.No ratings yet
- UntitledDocument4 pagesUntitledAngelica DL. LerumNo ratings yet
- EL 109 ReviewerDocument7 pagesEL 109 ReviewerCHRISTINE LUMBRENo ratings yet
- E114 ReviewerDocument8 pagesE114 Reviewerdarcyy2003No ratings yet
- Communicative ApproachDocument2 pagesCommunicative ApproachJohn LawrenceNo ratings yet
- Study Guide Representing Procedural KnowledgeDocument14 pagesStudy Guide Representing Procedural KnowledgeSHIELA SAMANTHA SANTOSNo ratings yet
- A Method of Teaching A Language Through Conversation, Discussion, and Reading in The Language Itself Without Translation and Without The Study of Formal GrammarDocument3 pagesA Method of Teaching A Language Through Conversation, Discussion, and Reading in The Language Itself Without Translation and Without The Study of Formal GrammarAnonymous jM7XemNo ratings yet
- Reviewer - EngDocument8 pagesReviewer - EngRegina CarreonNo ratings yet
- Cuadro Comparativo AproachesDocument1 pageCuadro Comparativo AproachesJosé Luis Fernández ReyesNo ratings yet
- Approaches and Methods of English Language Teaching in One LookDocument7 pagesApproaches and Methods of English Language Teaching in One LookNina LynNo ratings yet
- ASSUMPTIONS-approaches - AnswersDocument2 pagesASSUMPTIONS-approaches - AnswersYicheng JNo ratings yet
- APPROACHES (2) NotesDocument2 pagesAPPROACHES (2) NotesLaarnie Blessful SucalNo ratings yet
- At The Beginning Stages of Language Study, Listening ThatDocument14 pagesAt The Beginning Stages of Language Study, Listening ThatJanine BenoliraoNo ratings yet
- Listening Comprehension InstructionDocument9 pagesListening Comprehension InstructionxxxxNo ratings yet
- Listening and SpeakingDocument10 pagesListening and SpeakingSherannie AbaloNo ratings yet
- ORAL COM 2 ReviewerDocument4 pagesORAL COM 2 ReviewerAmani LintangNo ratings yet
- English Teaching MethodsDocument11 pagesEnglish Teaching MethodsMaria BolonkinaNo ratings yet
- Purpose NOTESDocument9 pagesPurpose NOTEScraig tolfreeNo ratings yet
- EDUP211 ReviewerDocument6 pagesEDUP211 ReviewerMico SeritoNo ratings yet
- Lexical Approach - Exe 23bDocument2 pagesLexical Approach - Exe 23bMonse AlbeNo ratings yet
- MODULE 1 - MacroskillsDocument8 pagesMODULE 1 - MacroskillsIze PentecostesNo ratings yet
- The Skill in Eap and EopDocument16 pagesThe Skill in Eap and EopPrilia Dwiher Fitriana67% (3)
- Don Carlos Polytechnic College: Republic of The Philippines Province of Bukidnon Municipality of Don CarlosDocument9 pagesDon Carlos Polytechnic College: Republic of The Philippines Province of Bukidnon Municipality of Don Carlosjade tagabNo ratings yet
- The Lexical ApproachDocument9 pagesThe Lexical ApproachIssam karchouchNo ratings yet
- Curriculum KLMPK 4 On Process 1Document29 pagesCurriculum KLMPK 4 On Process 1reini kurniawati effendiNo ratings yet
- Module 10: Mastery of The Structures of The English/FilipinoDocument3 pagesModule 10: Mastery of The Structures of The English/FilipinoYrrehc CawisNo ratings yet
- SpeakingDocument9 pagesSpeakingJomar MarianoNo ratings yet
- Written-Report 1Document7 pagesWritten-Report 1clarincelouigenotivaNo ratings yet
- Guiding Principles On KDocument25 pagesGuiding Principles On Kitaewon ClassNo ratings yet
- Using Technology To Teach Listening Skills: Technology and Language LearningDocument6 pagesUsing Technology To Teach Listening Skills: Technology and Language LearningWedyan alsadiNo ratings yet
- Rod Ellis Hunt and Beglar: Grammar VocabularyDocument3 pagesRod Ellis Hunt and Beglar: Grammar VocabularyJulieta M UKNo ratings yet
- ORAL COM q2 ReviewerDocument5 pagesORAL COM q2 Reviewer0u4ntumNo ratings yet
- Maria José Chica Lugo Mateo Muñoz Moreno Method Theory Design ProcedureDocument3 pagesMaria José Chica Lugo Mateo Muñoz Moreno Method Theory Design Proceduremaria joseNo ratings yet
- Teaching MacroskillsDocument15 pagesTeaching MacroskillsFCI Isabela SHSNo ratings yet
- Eng 104Document9 pagesEng 104Fiona Medalla AngelesNo ratings yet
- 2ND Achievement Test ReviewerDocument18 pages2ND Achievement Test ReviewerScott'em BergNo ratings yet
- Abigail Assignment TechniquesDocument5 pagesAbigail Assignment TechniquesmilesalforteNo ratings yet
- Unit 5. Using Technology To Teach Listening Skills: Please ReadDocument10 pagesUnit 5. Using Technology To Teach Listening Skills: Please ReadAzzel ArietaNo ratings yet
- T ING 1303047 Chapter3Document18 pagesT ING 1303047 Chapter3araniarani2903No ratings yet
- Approaches NotesDocument2 pagesApproaches NotesLaarnie Blessful SucalNo ratings yet
- Academic Reading.Glossary. ШерстнёваDocument4 pagesAcademic Reading.Glossary. ШерстнёваAnastaciaNo ratings yet
- MODULE 6 Approaches To Language TeachingDocument6 pagesMODULE 6 Approaches To Language TeachingyoraczayengNo ratings yet
- Group 1 Listening PDFDocument5 pagesGroup 1 Listening PDFJHANELLE MAE PALAFOXNo ratings yet
- Oral Com Reviewer 2ND QuarterDocument4 pagesOral Com Reviewer 2ND QuarterChristian Lorence LubayNo ratings yet
- GrammarDocument6 pagesGrammarSophia Micaella HermosoNo ratings yet
- English ReviewerDocument7 pagesEnglish ReviewerBEED 2-E JALANDOON, PAUL DAVID B.No ratings yet
- Student Bandscale and Relevent StratgiesDocument5 pagesStudent Bandscale and Relevent Stratgiesapi-366807311No ratings yet
- From "Approaches and Methods in Language Teaching" by J.C. Richards and T.S. RodgersDocument21 pagesFrom "Approaches and Methods in Language Teaching" by J.C. Richards and T.S. RodgersjoshefNo ratings yet
- What Is Esp?Document5 pagesWhat Is Esp?Danlie BeraquitNo ratings yet
- Task4 COLABORATIVEDocument19 pagesTask4 COLABORATIVELaura Leto MilicevicNo ratings yet
- Task BaseDocument3 pagesTask BaseKhánh TrìnhNo ratings yet
- Teaching Grammar: Students: Guevara Vanessa Rojas JessicaDocument31 pagesTeaching Grammar: Students: Guevara Vanessa Rojas JessicaLigia VillazónNo ratings yet
- 2ND Achievement Test ReviewerDocument18 pages2ND Achievement Test ReviewerNicole VisperasNo ratings yet
- Group Iv: Teaching Productive Skills (Teaching Speaking)Document10 pagesGroup Iv: Teaching Productive Skills (Teaching Speaking)Kwetiaw SeafoodNo ratings yet
- Syllabus BussComm AWing - Hasil Rakor 04022019 - REGULERDocument10 pagesSyllabus BussComm AWing - Hasil Rakor 04022019 - REGULERIndah Dina SalsabilaNo ratings yet
- Lost in Translation? Mastering Languages with Memorable Methods: Memory Improvement Series, #1From EverandLost in Translation? Mastering Languages with Memorable Methods: Memory Improvement Series, #1No ratings yet
- Teaching English to Young Learners: Teacher DevelopmentFrom EverandTeaching English to Young Learners: Teacher DevelopmentRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5)