Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Theories of L1 Acquisition
Theories of L1 Acquisition
Uploaded by
JazminOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Theories of L1 Acquisition
Theories of L1 Acquisition
Uploaded by
JazminCopyright:
Available Formats
Fundamentos de la Enseñanza y Aprendizaje de Inglés I
Assignment: Theories of L1 acquisition
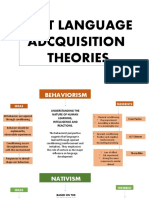
1. How did Chomsky challenge the behaviouristic position?
● Chomsky challenged the behaviouristic position by claiming that children
are biologically programmed for language rather than developing it through
imitation. This special ability, which is referred to as Language Acquisition
Device (LAD), develops in the kid just the same way that other biological
functions develops.
2. What is the role of imitation in language acquisition?
● To behaviourists, language acquisition is the result of imitation, practice,
feedback on success and habit formation. Children imitate the sounds or
patterns which they hear around them and receive positive reinforcement
for doing so. Once encouraged by their environment, they continue to
imitate and practice until they form habits of correct language use.
● What about the position of cognitivism?
3. Define the critical period hypothesis (CPH)
What happens if you start leaning a language after this period?
● The critical period hypothesis is a specific and limited time period for
language acquisition. To Lenneberg, the ability to develop normal
behaviours and knowledge does not continue indefinitely. He argued that
the Language Acquisition Device works successfully when it is stimulated at
the right time. If you start learning a language after this period, the
language won’t be developed successfully. Specify time period
4. In what aspects does Interactionism differ from Innatism?
● Interactionism differs from Innatism in different aspects. First, it differs in
how interactionism gives more importance to the environment (interact in
order to generate language development). Then, interactionists also
emphasize the importance of ‘child directed speech’, this is the language
which is adjusted in ways that make it easier for children to understand.
5. Compare Piaget and Vygotsky’s position about language development.
● Jean Piaget did not see language as based on a separate module of the
mind. To him, it was one of the symbol systems which are developed in
childhood. Piaget believed that cognitive development and the interaction
with the physical world appears before language development. On the
other hand, Vigotsky concluded that language develops entirely from social
interaction. He observed the importance of conversations which children
have with adults and with other children and saw in those conversations
the origins of both language and thought.
1. Complete the following chart.
Behaviourism Innatism Connectionism
What is innate? Children’s minds Children are born The ability to learn
are blank slates to with a special ability is innate.
be filled by to discover for
imitation of themselves the
language. underlying rules of
a language system.
What is the role of Input? The language The language input The input is the
spoken in the is mainly a ‘trigger’ principal source of
environment to activate innate linguistic
functions as the knowledge. knowledge. It is the
input. yes, and it is exposure to
essential. linguistic features.
How do we acquire language according to According to To innatists, After hearing
each theory? behaviourism children are language features
children learn biologically in specific
through imitating programmed for situational or
the language that language. And it linguistic contexts
they hear around develops in children over and over
them. Once
as the same way again, learners
encouraged by their
that other develop stronger
environment
through biological functions and stronger
reinforcement, develop. mental or
children continue to neurological
imitate and practice ‘connections’
until they form between these
habits. elements.
You might also like
- IB Physics D.1 PPT TEACHERDocument36 pagesIB Physics D.1 PPT TEACHERPio100% (2)
- First Language Acquisition TheoriesDocument5 pagesFirst Language Acquisition TheoriesCaroline Line100% (2)
- RAISE Plus WEEKLY PLAN FOR BLENDED LEARNING TleDocument3 pagesRAISE Plus WEEKLY PLAN FOR BLENDED LEARNING TleRomeo jr RamirezNo ratings yet
- JRR 13-2 RabanDocument11 pagesJRR 13-2 RabanDL GirolettiNo ratings yet
- Theories of First and Second Language AcquisitionDocument4 pagesTheories of First and Second Language AcquisitionMa. Elena Abainza - ArambalaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2-Theories of Language DevelopmentDocument42 pagesChapter 2-Theories of Language DevelopmentFAHMIEY BIN ABDULLAH (KB)100% (2)
- Tatoy, Angelica-Mc Elt 1 MidtermDocument5 pagesTatoy, Angelica-Mc Elt 1 MidtermAngel Gomez TatoyNo ratings yet
- Mei Abril MedinacruzDocument3 pagesMei Abril MedinacruzAbril CruzNo ratings yet
- Behaviourism and Mentalism NasirDocument7 pagesBehaviourism and Mentalism Nasiroananisioi100% (2)
- Psycholinguistics and Its Theories PDFDocument8 pagesPsycholinguistics and Its Theories PDFAnonymous yjVfMH100% (4)
- First Language AcquisitionDocument33 pagesFirst Language AcquisitionPauline Karen Macaisa-Concepcion100% (1)
- First Language Acquisition TheoriesDocument19 pagesFirst Language Acquisition TheoriesDARIEL DIAZNo ratings yet
- Activity Nativist Theory ACT 3Document1 pageActivity Nativist Theory ACT 3Blessie Joy LactaotaoNo ratings yet
- Psycholinguistics and Its TheoriesDocument8 pagesPsycholinguistics and Its TheoriesDr-Mubashar AltafNo ratings yet
- Module 3: Theories of First Language AcquisitionDocument19 pagesModule 3: Theories of First Language AcquisitionMINGO, APPLE, GABAYNONo ratings yet
- Classwork 2 First Language Acquisition - JESSICA YANEZDocument3 pagesClasswork 2 First Language Acquisition - JESSICA YANEZJessicaNo ratings yet
- El 204 - Principles and Theories of Language Acquisition and Learning Lesson 8Document3 pagesEl 204 - Principles and Theories of Language Acquisition and Learning Lesson 8Chaé RiNo ratings yet
- Eturma Navarro SumayaDocument3 pagesEturma Navarro SumayaMawee Joy SumayaNo ratings yet
- Psycholinguistics - Part 2Document32 pagesPsycholinguistics - Part 2Sou SouNo ratings yet
- Theory Assignment 2 Julia GleasonDocument3 pagesTheory Assignment 2 Julia Gleasonapi-439614932No ratings yet
- PTLAL Pinahirap Na ReviewerDocument3 pagesPTLAL Pinahirap Na ReviewerandreiapplecahawiganNo ratings yet
- L1 L2 AcquisitionDocument48 pagesL1 L2 AcquisitionHeidi Lee50% (2)
- Lesson1 3Document8 pagesLesson1 3Lea Marie De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- 5701 - grp1 - Outline - First Language and Literacy DevelopmentDocument8 pages5701 - grp1 - Outline - First Language and Literacy DevelopmentRhobie Jean Candinato AgtonNo ratings yet
- Theories of FLA and SLA (Eng. ELT 2)Document52 pagesTheories of FLA and SLA (Eng. ELT 2)Askin D. VillariasNo ratings yet
- Lang 121 W2-4Document60 pagesLang 121 W2-4DaisyADenial100% (2)
- Prelim Week 2 Part 1Document3 pagesPrelim Week 2 Part 1Mariel CarabuenaNo ratings yet
- Behaviourism and MentalismDocument7 pagesBehaviourism and MentalismHesper Abigail83% (6)
- Lecture 2 Theories and Principles of MTB-MLEDocument3 pagesLecture 2 Theories and Principles of MTB-MLEAnne BautistaNo ratings yet
- Language AcquisitionDocument17 pagesLanguage AcquisitionElif Guvendi Yalcin100% (2)
- Group 3 - Approaches On How Children Learn LanguageDocument24 pagesGroup 3 - Approaches On How Children Learn LanguageLaila Nur Hanifah laila7586fbs.2019No ratings yet
- Behaviourism and MentalismDocument6 pagesBehaviourism and MentalismMubarak Khan100% (3)
- Theories of Language LearningDocument24 pagesTheories of Language LearningBayissa BekeleNo ratings yet
- Share PRINCIPLES & THEORIES OF LANGUAGE ACQUISITION - FIRST LANGUAGE ACQUSITION THEORIES & CONSIDERATIONSDocument9 pagesShare PRINCIPLES & THEORIES OF LANGUAGE ACQUISITION - FIRST LANGUAGE ACQUSITION THEORIES & CONSIDERATIONSDaisy joy BeroniaNo ratings yet
- Language DevelopmentDocument3 pagesLanguage DevelopmentRuth MasenguNo ratings yet
- Theories of FLADocument26 pagesTheories of FLAMaite Andueza (Maite Andueza)No ratings yet
- Resume TEYLDocument1 pageResume TEYLHanata HappyNo ratings yet
- LESSON 3 PSYCH of LANGUAGE Empirical or Behavioral Approach EDITDocument3 pagesLESSON 3 PSYCH of LANGUAGE Empirical or Behavioral Approach EDITKENNETH JOSEPH MONROIDNo ratings yet
- PsycholinguisticsDocument7 pagesPsycholinguisticsglorymhone04No ratings yet
- 6 - M30 - S5P2, Applied Linguistics, Pr. OuahidiDocument20 pages6 - M30 - S5P2, Applied Linguistics, Pr. OuahidiCHARROU Mohamed AminENo ratings yet
- Behaviourist Theory of PsycholinguisticsDocument4 pagesBehaviourist Theory of PsycholinguisticsMaryam Butt100% (1)
- Competence and Performance: .-Competence Refers To One's Underlying of A SystemDocument4 pagesCompetence and Performance: .-Competence Refers To One's Underlying of A SystemDane NarzolesNo ratings yet
- ELD 211 - Lecture 2 - 20-02-2023Document14 pagesELD 211 - Lecture 2 - 20-02-2023bradeylinders110No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 2mergedDocument16 pagesChapter 1 2mergedDomi NyxNo ratings yet
- Behaviorism - Integrated ApproachDocument12 pagesBehaviorism - Integrated ApproachAnonymous rDHWR8eBNo ratings yet
- Overview of Theories On Language Study: Behaviorist TheoryDocument4 pagesOverview of Theories On Language Study: Behaviorist TheoryClifford MantleNo ratings yet
- First Language Acquisition - Group 1Document15 pagesFirst Language Acquisition - Group 1arif angga putraNo ratings yet
- Theories of First Language AcquisitionDocument4 pagesTheories of First Language AcquisitionKristine CantileroNo ratings yet
- MODULEEEDocument24 pagesMODULEEEAidie Mendoza100% (1)
- Sir Ahmad Assignmnt 1Document5 pagesSir Ahmad Assignmnt 1Saba HanifNo ratings yet
- Seminar On LinguisticsDocument10 pagesSeminar On LinguisticssuriyachyNo ratings yet
- Natural History of Language DevelopmentDocument36 pagesNatural History of Language DevelopmentJhay GregorioNo ratings yet
- Paper 3 Q2 Child Language Acquisition CLADocument12 pagesPaper 3 Q2 Child Language Acquisition CLAibemad123No ratings yet
- Perkembangan Bahasa Pada Anak Usia Dini Rizki Alfiana, Eko Kuntarto, Andry Wahyu Oktavianto, Ella Putri Julianty EmailDocument6 pagesPerkembangan Bahasa Pada Anak Usia Dini Rizki Alfiana, Eko Kuntarto, Andry Wahyu Oktavianto, Ella Putri Julianty EmailAchmad ZahidNo ratings yet
- A Level English Language S4.4 Theories About Language DevelopmentDocument11 pagesA Level English Language S4.4 Theories About Language Developmentcucumber5621No ratings yet
- Language Theories 5Document19 pagesLanguage Theories 5Rabeeya ArshadNo ratings yet
- Class Notes - Areas of DevelopmentDocument5 pagesClass Notes - Areas of DevelopmentChristine JoyceNo ratings yet
- Behaviorism Vs MentelismDocument22 pagesBehaviorism Vs Mentelismabdul haqNo ratings yet
- Psychology and Language LearningDocument2 pagesPsychology and Language LearningRelax, find yourselfNo ratings yet
- Conceptual Map Theories of Language AcquisitionDocument3 pagesConceptual Map Theories of Language AcquisitionScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Task 3. Empiricism Vs Rationalism-Cabido, Christine Ann C.Document4 pagesTask 3. Empiricism Vs Rationalism-Cabido, Christine Ann C.Christine Ann CabidoNo ratings yet
- The Child and the World: How the Child Acquires Language; How Language Mirrors the WorldFrom EverandThe Child and the World: How the Child Acquires Language; How Language Mirrors the WorldNo ratings yet
- Phonology Workshop Feb 2024Document2 pagesPhonology Workshop Feb 2024JazminNo ratings yet
- Formal Email Paua M.Document1 pageFormal Email Paua M.JazminNo ratings yet
- Phono 2024Document13 pagesPhono 2024JazminNo ratings yet
- Jazmin Velazquez Notthoff - B2 FIRST - VERB PATTERNS - PRACTICE IIIDocument4 pagesJazmin Velazquez Notthoff - B2 FIRST - VERB PATTERNS - PRACTICE IIIJazminNo ratings yet
- The VerbDocument23 pagesThe VerbJazminNo ratings yet
- ActivityDocument2 pagesActivityJazminNo ratings yet
- Estudios Interculturales en Lengua Inglesa - Junio 10Document6 pagesEstudios Interculturales en Lengua Inglesa - Junio 10JazminNo ratings yet
- Can Clase 19Document5 pagesCan Clase 19JazminNo ratings yet
- Role ModelDocument2 pagesRole ModelJazminNo ratings yet
- Theory - Const - Del Trabajo DocenteDocument7 pagesTheory - Const - Del Trabajo DocenteJazminNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Writing.Document3 pagesLesson Plan Writing.JazminNo ratings yet
- Azul MondayDocument11 pagesAzul MondayJazminNo ratings yet
- Construccion Liste + SpeakingDocument4 pagesConstruccion Liste + SpeakingJazminNo ratings yet
- AmbarDocument10 pagesAmbarJazminNo ratings yet
- Civil War and Reconstruction II IscbDocument26 pagesCivil War and Reconstruction II IscbJazminNo ratings yet
- Lesson Planing DescriptionDocument5 pagesLesson Planing DescriptionJazminNo ratings yet
- ASSIGMENT - Development of Skills - MarianiDocument2 pagesASSIGMENT - Development of Skills - MarianiJazminNo ratings yet
- MiniThesis GenderDocument16 pagesMiniThesis GenderRica Pearl ZorillaNo ratings yet
- PERIODIC TEST - Docx (N)Document2 pagesPERIODIC TEST - Docx (N)Sooraj RajmohanNo ratings yet
- Checking of Forms Sample TemplateDocument3 pagesChecking of Forms Sample TemplateMilain NabiaNo ratings yet
- SCZ Salongo Bio 1 2020Document11 pagesSCZ Salongo Bio 1 2020JoanNo ratings yet
- (Template) Sprinkler and Micro Irrigation Systems Manual - PROOF 21072020Document84 pages(Template) Sprinkler and Micro Irrigation Systems Manual - PROOF 21072020Lakum Ravi N.No ratings yet
- Oral Communication Mod2 Week 2Document5 pagesOral Communication Mod2 Week 2Josie EscalaNo ratings yet
- Leviton AppNote RetentionForceTechnologyDocument5 pagesLeviton AppNote RetentionForceTechnologySajeda M. Al-TalafhaNo ratings yet
- Contoh ProposalDocument44 pagesContoh ProposalHendra Umar Al Faruq100% (1)
- Introduction To LinguisticsDocument14 pagesIntroduction To LinguisticsasdfadsNo ratings yet
- Rencana Pelaksanaan Pembelajaran (RPP) : School Identity Course Name Class/Semester Topic Discussion Skill Time AllocationDocument6 pagesRencana Pelaksanaan Pembelajaran (RPP) : School Identity Course Name Class/Semester Topic Discussion Skill Time AllocationNadya Septiani RahmanNo ratings yet
- Unit 0 - Friends Word of Self, Family and Friends Writing SpeakingDocument14 pagesUnit 0 - Friends Word of Self, Family and Friends Writing SpeakinglelaNo ratings yet
- Defence Presentation - Ekaterina NazarenkoDocument44 pagesDefence Presentation - Ekaterina NazarenkoЕкатерина НазаренкоNo ratings yet
- Synopsis On Electromagnetic Car PDFDocument3 pagesSynopsis On Electromagnetic Car PDFyrikkiNo ratings yet
- How To Design An Innovative WorkplaceDocument2 pagesHow To Design An Innovative WorkplacemuskanNo ratings yet
- RD Sharma Jan21 Class 11 Maths Solutions Chapter 7Document25 pagesRD Sharma Jan21 Class 11 Maths Solutions Chapter 7SAIKIRANNo ratings yet
- Yg-1 V7plusa Endmill America YuDocument25 pagesYg-1 V7plusa Endmill America YuLuis CoolNo ratings yet
- ComparisonofAxialLoadonColumn FormattedPaperDocument7 pagesComparisonofAxialLoadonColumn FormattedPaperVictor Omotoriogun100% (1)
- College-Algebra, Take Home Test 2Document3 pagesCollege-Algebra, Take Home Test 2Michelle Morgan LongstrethNo ratings yet
- Translating English Sentences To Mathematical Sentences and Vice-VersaDocument8 pagesTranslating English Sentences To Mathematical Sentences and Vice-VersaDana0% (1)
- Chapter 2 Part 2 - Deflection Unit Load MethodDocument51 pagesChapter 2 Part 2 - Deflection Unit Load MethodAnonymous 8f2veZf100% (2)
- Emf Values of Organic CompoundsDocument34 pagesEmf Values of Organic CompoundsPrabir SahaNo ratings yet
- Sewer Odor Control: Master PlanDocument168 pagesSewer Odor Control: Master PlanVikk SuriyaNo ratings yet
- Jenitri 3Document7 pagesJenitri 3Zaenal MubaroqNo ratings yet
- Bahasa Inggris I: (Teknik Informatika/Sistem Komputer)Document13 pagesBahasa Inggris I: (Teknik Informatika/Sistem Komputer)Kadek DitoNo ratings yet
- Heat of Vaporization and Heat of FusionDocument17 pagesHeat of Vaporization and Heat of FusionJASIS JULIA NOELYN V.No ratings yet
- 2020 - Daily Activity Report - 16.06.2020Document1 page2020 - Daily Activity Report - 16.06.2020Bayu Anugrah FajarNo ratings yet
- Geology For CE Module Ch2 - 2Document12 pagesGeology For CE Module Ch2 - 2Anthony LoñezNo ratings yet
- MKTG 2P52 Chapter 2Document41 pagesMKTG 2P52 Chapter 2Jeffrey O'LearyNo ratings yet