Professional Documents
Culture Documents
JSA - Acoustic Eye
JSA - Acoustic Eye
Uploaded by
Ronel John CustodioCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Risk Assessment - ACS & CCTVDocument3 pagesRisk Assessment - ACS & CCTVUmair Liaqat86% (7)
- Risk Assessment For Kerb Stones, Wheel Stopper and Paving InterlocksDocument4 pagesRisk Assessment For Kerb Stones, Wheel Stopper and Paving Interlockspete chiz92% (24)
- JSA - Fire Proofing WorksDocument5 pagesJSA - Fire Proofing WorksAnis Uddin100% (4)
- JSA Fall ProtectionDocument2 pagesJSA Fall ProtectionAli SadiqinNo ratings yet
- JHA 15-Work at Height Using ScaffoldingDocument3 pagesJHA 15-Work at Height Using ScaffoldingWte SB100% (7)
- Affidavit of Parental Care and CustodyDocument1 pageAffidavit of Parental Care and CustodySJ JianNo ratings yet
- JSA Cable Laying PDFDocument2 pagesJSA Cable Laying PDFManoj WaskelNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment For Resin Injection Via HoseDocument1 pageRisk Assessment For Resin Injection Via HoseKrishna KishoreNo ratings yet
- Fabrication Work Risk AssessmentDocument11 pagesFabrication Work Risk Assessmentstansilous100% (1)
- Risk Assessment - Installation of Cable Trays & DCAC CablesDocument5 pagesRisk Assessment - Installation of Cable Trays & DCAC CablesIbrahim Esmat100% (1)
- JSA For Coating and Raping Activity in TankDocument7 pagesJSA For Coating and Raping Activity in TankEslam lotfy- Eslam elsadatNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment - Ad-456 - Installation and Testing Vav Boxes & Controls in OmbDocument9 pagesRisk Assessment - Ad-456 - Installation and Testing Vav Boxes & Controls in Ombnsadnan100% (1)
- A Guide To Filing A Public Interest Litigation (PIL) - Citizen MattersDocument13 pagesA Guide To Filing A Public Interest Litigation (PIL) - Citizen MattersZaeem KhanNo ratings yet
- Jsa For Work at HeightsDocument4 pagesJsa For Work at Heightsjithin shankar100% (1)
- Risk Assesment For Chamber ConstructionDocument5 pagesRisk Assesment For Chamber ConstructionSasi KumarNo ratings yet
- JSA On LighteningDocument3 pagesJSA On Lighteningsyed baqarNo ratings yet
- Risk Assesment For Chamber ConstructionDocument5 pagesRisk Assesment For Chamber ConstructionSasi KumarNo ratings yet
- JSA 03 Gate Entrance Traffic ProposalDocument10 pagesJSA 03 Gate Entrance Traffic Proposalrahul tkNo ratings yet
- Petrofac: Job Safety AnalysisDocument2 pagesPetrofac: Job Safety AnalysisMon Trang Nguyễn100% (1)
- Work at Height - JSADocument2 pagesWork at Height - JSARanadheer Reddy KanthalaNo ratings yet
- Job Hazard AnalysisDocument2 pagesJob Hazard Analysispanganibanlailanie15No ratings yet
- 50 MW Artistic Wind Power Project: Job Safety Analysis Worksheet (Equipment Lifting)Document3 pages50 MW Artistic Wind Power Project: Job Safety Analysis Worksheet (Equipment Lifting)Raza Muhammad SoomroNo ratings yet
- Rev-00 JsaDocument4 pagesRev-00 Jsam.jawwadNo ratings yet
- 5.19 JSP ScaffoldDocument4 pages5.19 JSP Scaffoldpoorm879No ratings yet
- JSA Hot Work and ModificationDocument19 pagesJSA Hot Work and ModificationBrings MotoVlogNo ratings yet
- Appendix BDocument14 pagesAppendix Bmohsin.meizaNo ratings yet
- 1st Aid Training Siemens ContractorDocument11 pages1st Aid Training Siemens ContractorTigor GurningNo ratings yet
- Jsa For Cable LayingDocument2 pagesJsa For Cable LayingSabari VtNo ratings yet
- Cable Laying - Docx4Document2 pagesCable Laying - Docx4Dhaneswar SwainNo ratings yet
- Daily JSA - Fence Post InstallationDocument5 pagesDaily JSA - Fence Post Installationshoaib akhtarNo ratings yet
- General Works Risk AssessmentDocument15 pagesGeneral Works Risk AssessmentMohammed MustafaNo ratings yet
- Project: Job Title:Suspended Rope Platform S.No Activities Hazard Risk Control MeasuresDocument3 pagesProject: Job Title:Suspended Rope Platform S.No Activities Hazard Risk Control Measureskhaja asifuddin100% (1)
- JSA Mobile CranesDocument2 pagesJSA Mobile CranesAmanya DickallansNo ratings yet
- Job Safety Analysis Work Sheet: Date Prepared D / M / YDocument4 pagesJob Safety Analysis Work Sheet: Date Prepared D / M / Ykkalvi0% (1)
- QRC-RA-001-Construction and Installation of Manhole (Precast)Document10 pagesQRC-RA-001-Construction and Installation of Manhole (Precast)Kallem RajashekarNo ratings yet
- Hot Work Gift Gift / Near Gis SEPCOO III Early Comb: Job Hazard Analysis (Jha) WorksheetDocument4 pagesHot Work Gift Gift / Near Gis SEPCOO III Early Comb: Job Hazard Analysis (Jha) Worksheet王志伟No ratings yet
- JSA Work at Hight - Rev-6Document2 pagesJSA Work at Hight - Rev-6Mahamudul HasanNo ratings yet
- EHS-SWI-037 - 0 Loadbank Testing - DraftDocument2 pagesEHS-SWI-037 - 0 Loadbank Testing - DraftChris Bonnington100% (1)
- JSA For Screeding With MeshDocument4 pagesJSA For Screeding With MeshMohammed Minhaj100% (1)
- JSA Erection StructureDocument11 pagesJSA Erection StructureJAYESH JOSHINo ratings yet
- Qrc-Ra-001-00-Road and Footpath Modification WorksDocument27 pagesQrc-Ra-001-00-Road and Footpath Modification WorksKallem RajashekarNo ratings yet
- New JuneDocument6 pagesNew JuneShovon khanNo ratings yet
- Testing Comissioning of Electrical SystemDocument8 pagesTesting Comissioning of Electrical Systemmo7d aliNo ratings yet
- JSA Column Errection, Shuttering, Casting, Deshuttering Raw Material Ware HouseDocument9 pagesJSA Column Errection, Shuttering, Casting, Deshuttering Raw Material Ware Houseradeep100% (1)
- JSA For Erection and Repair Work of TanksDocument19 pagesJSA For Erection and Repair Work of TanksMohamed Farouk100% (2)
- JSA Mobile Crane Pipe Installation Tandem LiftDocument3 pagesJSA Mobile Crane Pipe Installation Tandem LiftSyed HarisNo ratings yet
- Jsa For Concreate and CivilworksDocument7 pagesJsa For Concreate and CivilworksAnna JisabaNo ratings yet
- 1TB02011 011C49 FFC MTS Me 0012 RaDocument7 pages1TB02011 011C49 FFC MTS Me 0012 RaAijaz AhmedNo ratings yet
- JSA For Scaffolding Erection Dismantling and Modification WorkDocument17 pagesJSA For Scaffolding Erection Dismantling and Modification Workshane.ramirez1980No ratings yet
- 139 Casting ConcretingDocument4 pages139 Casting Concreting王志伟No ratings yet
- 50 MW Artistic Wind Power Project: Job Safety Analysis Worksheet (Equipment Lifting)Document3 pages50 MW Artistic Wind Power Project: Job Safety Analysis Worksheet (Equipment Lifting)Raza Muhammad SoomroNo ratings yet
- JSA For Working at HeightDocument2 pagesJSA For Working at HeightXUE JIANNo ratings yet
- Jsa For Concreate and CivilworksDocument7 pagesJsa For Concreate and CivilworksAnna JisabaNo ratings yet
- JHA 01 Erecting Fixed ScaffoldingDocument4 pagesJHA 01 Erecting Fixed Scaffoldingadil khan100% (1)
- Job Safety Analysis (JSA) : Description Hazard ControlDocument2 pagesJob Safety Analysis (JSA) : Description Hazard ControlRidha BennasrNo ratings yet
- Appendix C - Risk AssessmentDocument2 pagesAppendix C - Risk Assessmentjavedashraf.ptNo ratings yet
- JSA - Working at HeightDocument5 pagesJSA - Working at HeightSampath Kumar KandasamyNo ratings yet
- SL Work Activity Potential Hazards Preventive Measures/Action TakenDocument28 pagesSL Work Activity Potential Hazards Preventive Measures/Action TakenDarius DsouzaNo ratings yet
- Wet Area Water Proofing WorkDocument8 pagesWet Area Water Proofing Worksarath SNo ratings yet
- Answer Keys Ut MPT PTDocument5 pagesAnswer Keys Ut MPT PTRonel John CustodioNo ratings yet
- Binder 1Document15 pagesBinder 1Ronel John CustodioNo ratings yet
- Course & Examination Enrolment Form (BINDT-PCN)Document2 pagesCourse & Examination Enrolment Form (BINDT-PCN)Ronel John CustodioNo ratings yet
- PSL-44 - Vision RequirementsDocument5 pagesPSL-44 - Vision RequirementsRonel John CustodioNo ratings yet
- 45MG Upgrade Instructions Using Upgrade 2010Document3 pages45MG Upgrade Instructions Using Upgrade 2010Ronel John CustodioNo ratings yet
- A-1101c Paut Cracks ScreenshotsDocument6 pagesA-1101c Paut Cracks ScreenshotsRonel John CustodioNo ratings yet
- SOAD9110 - Marking Guide - Assessment 3 - Case Study Assessment and InterventionDocument2 pagesSOAD9110 - Marking Guide - Assessment 3 - Case Study Assessment and InterventionJoseph NdibaNo ratings yet
- NammaKPSC GP2018 GS 2Document4 pagesNammaKPSC GP2018 GS 2rohtihr2611No ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Axiology of ValuesDocument19 pagesLesson 1 Axiology of ValuesJennifer OriolaNo ratings yet
- Auditing 1Document9 pagesAuditing 1Vanessa BatallaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Strategic ManagementDocument28 pagesIntroduction To Strategic Managementroyaltravelsofficial777No ratings yet
- Self-Learning Module in Practical Research I Lesson:: III 1&2 Day and Time: Learning CompetenciesDocument11 pagesSelf-Learning Module in Practical Research I Lesson:: III 1&2 Day and Time: Learning CompetenciesGhaniella B. JulianNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10: Nature and Scope of PhilosophyDocument6 pagesChapter 10: Nature and Scope of PhilosophyKim GiananNo ratings yet
- Case Study HomelessnessDocument14 pagesCase Study Homelessnessapi-608106291No ratings yet
- Module 2 LESSON 2Document3 pagesModule 2 LESSON 2Mitzi Portia VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- BMBA-410 - Final Assignment - Leadership InterviewDocument5 pagesBMBA-410 - Final Assignment - Leadership InterviewWeslley FortunatoNo ratings yet
- Form 78 Statutory Declaration As To Proof of Debt - Employees Group FormDocument1 pageForm 78 Statutory Declaration As To Proof of Debt - Employees Group FormolingirlNo ratings yet
- Ethics and Moral Philosophy - General Introduction - 2020 - Lecture 5aDocument3 pagesEthics and Moral Philosophy - General Introduction - 2020 - Lecture 5aBlueBladeNo ratings yet
- NSTPDocument3 pagesNSTPfreya alejoNo ratings yet
- OB 1 Historical Evolution of Organisational BehaviourDocument76 pagesOB 1 Historical Evolution of Organisational Behaviourjayamohan100% (1)
- P.ed. 2 Prelim Module MonicaDocument43 pagesP.ed. 2 Prelim Module MonicaMonica BedijaNo ratings yet
- Colonial Reports N 186 - Basutoland 1895-96Document50 pagesColonial Reports N 186 - Basutoland 1895-96EmmanuelleLizéNo ratings yet
- Of Studies Reflection PaperDocument4 pagesOf Studies Reflection PaperGONZALES, ASHLEY MARIE G.No ratings yet
- Day6 Activity Aptitude C TwistorsDocument12 pagesDay6 Activity Aptitude C TwistorsHota bNo ratings yet
- Film Making Registration FormDocument2 pagesFilm Making Registration FormRavi PrakashNo ratings yet
- Beauty Unmasked-A Haunting Journey Through The Picture of Dorian GrayDocument3 pagesBeauty Unmasked-A Haunting Journey Through The Picture of Dorian GrayJhonnel TizonNo ratings yet
- NSTP Ass2 DoneDocument5 pagesNSTP Ass2 DoneMikaela Francesca EchaluceNo ratings yet
- Easement MCQDocument7 pagesEasement MCQTshewang Dema67% (3)
- Lead Me Lord Sheet Music - CurrentDocument2 pagesLead Me Lord Sheet Music - CurrentAdedayo MichaelNo ratings yet
- Campus Journalism Is Public ServiceDocument2 pagesCampus Journalism Is Public ServiceAnn RoseNo ratings yet
- DIFFERENT Types of WillDocument6 pagesDIFFERENT Types of WillShivani TelangeNo ratings yet
- Organizational Theory, Design, and Change, 7e (Jones) : Chapter 2 Stakeholders, Managers, and EthicsDocument63 pagesOrganizational Theory, Design, and Change, 7e (Jones) : Chapter 2 Stakeholders, Managers, and EthicsNisreen EmadNo ratings yet
- Reflection Paper About Anti-BULLYDocument2 pagesReflection Paper About Anti-BULLYSherman AdralesNo ratings yet
- 4 Rules For Being A Good BandmateDocument3 pages4 Rules For Being A Good BandmateMarjorie Joy MartirNalupa AninoNo ratings yet
JSA - Acoustic Eye
JSA - Acoustic Eye
Uploaded by
Ronel John CustodioOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
JSA - Acoustic Eye
JSA - Acoustic Eye
Uploaded by
Ronel John CustodioCopyright:
Available Formats
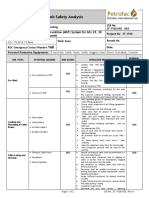
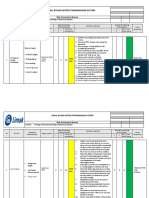
JOB SAFETY ANALYSIS – WORKSHEET
SABIC
JOB DESCRIPTION: Acoustic Eye DATE: March 28, 2016 JSA number: P620-009
NEW REVISED
JOB SAFETY ANALYSIS WP No:009
JOB LOCATION (Plant): Sabic (IBNSINA) MEOH PLANT AREA: MEOH PLANT
Risk Level
No BASIC STEP POTENTIAL HAZARDS MITIGATION PLAN RESPONSIBILITY Significant (S)/Moderate (M)/
Low (L)
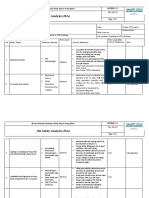
Scaffolding not adaptable to guard rails shall
require the use of safety harnesses with
double shock absorbing lanyard attached to
a secure substantial object.
Scaffold supervisor to ensure all scaffolds
are inspected and tagged safe for use prior LOW
to the use thereof and weekly thereafter by
1. Working at height climbing on scaffolding Fall of personnel due to incomplete working platform. TCR Site In - Charge
a competent scaffold inspector.
A proper scaffold inspection and tagging
system, which is consistent with OSHA and
universally recognized industry standards,
shall be utilized and maintained.
Unsafe scaffolds will be tagged unsafe and
rectified immediately.
A safe means of entry and exit shall be
provided and used whenever the elevated
work area is .6 meters above or below LOW
Unavailability of access to working platform. TCR Site In - Charge
working surface.
Means of exit shall be provided at least every
100 ft. or 30 meters.
Toe board shall be installed around the
working platform to prevent the tools or
materials from falling. LOW
Falling materials, tools. TCR Site In - Charge
Barricade the area below into which objects
can fall and not permitting workers to enter
the hazard area.
Personnel shall not be on any elevated
working platform if the wind is more than 65
High wind. TCR Site In - Charge
KHP unless working area is indoor or not LOW
affected by high winds.
All personnel working at high elevation must
2. Using appropriate PPE Improper use PPE. be trained in the use, inspection, and TCR Site In - Charge LOW
maintenance of fall arrest systems.
REQUIRED AND/OR RECOMMENDED P.P.E. 1. Safety Shoes, Helmet, Safety glass, Cotton Hand gloves, Full body Harness.
______________________________________________________________________________________________________
All recommendations suggested in JSA have been implemented at site: (Maintenance Supervisor)
Prepared by: JSA Team Leader Acknowledged by: Manager/Shift Supervisor
Name:______________ Signature:__________ Badge#: __________
Name: Reviewed and acknowledged by Operation Sr. Manager In case of Major / Significant Risk (Critical
Activity).
JSA Team Members
Name ID # Department Signature Date Name:______________ Signature:__________ Badge#: __________
Comment: …………………………………………………………………………………………………
Approved by Maintenance Manager / Supervisor …………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Name:_____________________ Signature:__________ Badge #:________
……………………………………………………………………………………………………………
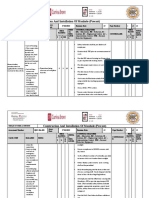
INSTRUCTIONS FOR COMPLETING THE JOB SAFETY ANALYSIS FORM
Job Safety Analysis (JSA) is an important incident prevention tool that works by finding hazards and eliminating or Select a job to be analyzed. Before filling out this from, consider the following:
minimizing them before the job is preformed, and before they have a chance to become accidents. Use JSA for job The purpose of the job-What has to be done? Who has to do it?. The activities involved: How is it done? When is it done? Where is it
clarification and hazard awareness, as a guide in new employees training, for periodic contacts and for retraining of senior done?
employees, as a refresher on jobs which run infrequently, as an incident investigation tool, and for informing employees of
specific job hazards and protective measures. In summary, to complete this form you should consider the purpose of the job, the activities it involves, and the hazards its presents. If
you are not familiar with a particular job or operation, interview an employee who is. In addition, observing an employee performing
Set priorities for doing JSA’s: jobs that have a history or many accidents, jobs that have produced disabling injuries, jobs the job, or “walking through” the operation step may give additional insight into potential hazards. You may also videotape the job and
with high potential for disabling injury of death, and new jobs with no accident history. analyze it. Here’s how to do each of the three parts of Job Safety Analysis
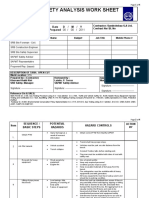
RESPONSIBLE
SEQUENCE OF BASIC JOB STEPS POTENTIAL HAZARDS RECOMMENDED ACTION OR PROCEDURE
PERSON
Examining a specific job by breaking it down into a series of A hazard is a potential danger. The purpose of the Job Safety Analysis is Using the first two columns as a guide, decide what actions or procedures Who is responsible? Write the person
steps of tasks, will enable you to discover potential hazards to identify all hazards, both those produced by the environment or are necessary to eliminate or minimize the hazards that could lead to an (receiver) responsible (Supervisor/Work
employees may encounter. conditions and those connected with the job procedure. accident, injury, or occupational illness. Permit Issuer receiver/contractor) to
implement the control measures
Each job operation will consists of a set of steps or tasks. To identify hazards, ask yourself these questions about each step: Begin by trying: identified.
1. Engineer the hazard out: 2. provide guards, safety devices, etc.; 3.
For example: 1. Is the danger of the employee striking against, being struck by, or provide personal protective equipment; 4. provide job instruction training;
otherwise making injurious contact with an object? 5. maintain good housekeeping; 6. insure good ergonomics (positioning
The job might be to move a box from conveyor in the receiving
the person in relation to the machine or other elements in such a way as
area to a shelf in the storage area. To determine where a steps 2. Can the employee be caught in, by or between objects?
to improve safely).
begins or ends, look for a change of activity, change in direction
or movement. 3. Is there potential for slipping, tripping, or falling?
List the recommended safe operating procedures. Begin with an action
4. Could the employee suffers strains from pushing, pulling, lifting, word. Say exactly what needs to be done to correct the hazard, such as,
Picking up the box from the conveyor and placing it on a hand
bending, or twisting? “lift using your leg muscles”. Avoid general statements such as “be
truck is one step. The next step might be to push the loaded
careful”.
hand truck to the storage area (a change in activity). Moving the
5. Is the environment hazardous to safety and/or health (toxic gas,
boxes from the truck and placing them on the shelf is another List the required or recommended personal protective equipment
vapor, mist, fumes, dust, heat, or radiation)?.
step. The final step might be returning the hand truck to the necessary to perform each step of the job.
receiving area. Close observations and knowledge of the job is important. Examine
each step carefully to find and identify hazards; the actions, conditions Give a recommended action or procedure for each hazard.
Be sure to list all the steps needed to perform the job. Some
and possibilities that could lead to an accident. Compiling an accurate
steps may not be performed each time; an example could be Serious hazards should be corrected immediately. The JSA should then be
and complete list of potential hazards will allow you to develop the
checking the casters on the hand truck. However, if the step is changed to reflect the new conditions.
recommended safe job procedures needed to prevent accidents.
generally part of the job it should be listed.
Finally, review your input on all three columns for accuracy and
completeness. Determine if the recommended actions or procedures have
been put in place. Re-evaluate the job safety analysis as necessary.
You might also like
- Risk Assessment - ACS & CCTVDocument3 pagesRisk Assessment - ACS & CCTVUmair Liaqat86% (7)
- Risk Assessment For Kerb Stones, Wheel Stopper and Paving InterlocksDocument4 pagesRisk Assessment For Kerb Stones, Wheel Stopper and Paving Interlockspete chiz92% (24)
- JSA - Fire Proofing WorksDocument5 pagesJSA - Fire Proofing WorksAnis Uddin100% (4)
- JSA Fall ProtectionDocument2 pagesJSA Fall ProtectionAli SadiqinNo ratings yet
- JHA 15-Work at Height Using ScaffoldingDocument3 pagesJHA 15-Work at Height Using ScaffoldingWte SB100% (7)
- Affidavit of Parental Care and CustodyDocument1 pageAffidavit of Parental Care and CustodySJ JianNo ratings yet
- JSA Cable Laying PDFDocument2 pagesJSA Cable Laying PDFManoj WaskelNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment For Resin Injection Via HoseDocument1 pageRisk Assessment For Resin Injection Via HoseKrishna KishoreNo ratings yet
- Fabrication Work Risk AssessmentDocument11 pagesFabrication Work Risk Assessmentstansilous100% (1)
- Risk Assessment - Installation of Cable Trays & DCAC CablesDocument5 pagesRisk Assessment - Installation of Cable Trays & DCAC CablesIbrahim Esmat100% (1)
- JSA For Coating and Raping Activity in TankDocument7 pagesJSA For Coating and Raping Activity in TankEslam lotfy- Eslam elsadatNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment - Ad-456 - Installation and Testing Vav Boxes & Controls in OmbDocument9 pagesRisk Assessment - Ad-456 - Installation and Testing Vav Boxes & Controls in Ombnsadnan100% (1)
- A Guide To Filing A Public Interest Litigation (PIL) - Citizen MattersDocument13 pagesA Guide To Filing A Public Interest Litigation (PIL) - Citizen MattersZaeem KhanNo ratings yet
- Jsa For Work at HeightsDocument4 pagesJsa For Work at Heightsjithin shankar100% (1)
- Risk Assesment For Chamber ConstructionDocument5 pagesRisk Assesment For Chamber ConstructionSasi KumarNo ratings yet
- JSA On LighteningDocument3 pagesJSA On Lighteningsyed baqarNo ratings yet
- Risk Assesment For Chamber ConstructionDocument5 pagesRisk Assesment For Chamber ConstructionSasi KumarNo ratings yet
- JSA 03 Gate Entrance Traffic ProposalDocument10 pagesJSA 03 Gate Entrance Traffic Proposalrahul tkNo ratings yet
- Petrofac: Job Safety AnalysisDocument2 pagesPetrofac: Job Safety AnalysisMon Trang Nguyễn100% (1)
- Work at Height - JSADocument2 pagesWork at Height - JSARanadheer Reddy KanthalaNo ratings yet
- Job Hazard AnalysisDocument2 pagesJob Hazard Analysispanganibanlailanie15No ratings yet
- 50 MW Artistic Wind Power Project: Job Safety Analysis Worksheet (Equipment Lifting)Document3 pages50 MW Artistic Wind Power Project: Job Safety Analysis Worksheet (Equipment Lifting)Raza Muhammad SoomroNo ratings yet
- Rev-00 JsaDocument4 pagesRev-00 Jsam.jawwadNo ratings yet
- 5.19 JSP ScaffoldDocument4 pages5.19 JSP Scaffoldpoorm879No ratings yet
- JSA Hot Work and ModificationDocument19 pagesJSA Hot Work and ModificationBrings MotoVlogNo ratings yet
- Appendix BDocument14 pagesAppendix Bmohsin.meizaNo ratings yet
- 1st Aid Training Siemens ContractorDocument11 pages1st Aid Training Siemens ContractorTigor GurningNo ratings yet
- Jsa For Cable LayingDocument2 pagesJsa For Cable LayingSabari VtNo ratings yet
- Cable Laying - Docx4Document2 pagesCable Laying - Docx4Dhaneswar SwainNo ratings yet
- Daily JSA - Fence Post InstallationDocument5 pagesDaily JSA - Fence Post Installationshoaib akhtarNo ratings yet
- General Works Risk AssessmentDocument15 pagesGeneral Works Risk AssessmentMohammed MustafaNo ratings yet
- Project: Job Title:Suspended Rope Platform S.No Activities Hazard Risk Control MeasuresDocument3 pagesProject: Job Title:Suspended Rope Platform S.No Activities Hazard Risk Control Measureskhaja asifuddin100% (1)
- JSA Mobile CranesDocument2 pagesJSA Mobile CranesAmanya DickallansNo ratings yet
- Job Safety Analysis Work Sheet: Date Prepared D / M / YDocument4 pagesJob Safety Analysis Work Sheet: Date Prepared D / M / Ykkalvi0% (1)
- QRC-RA-001-Construction and Installation of Manhole (Precast)Document10 pagesQRC-RA-001-Construction and Installation of Manhole (Precast)Kallem RajashekarNo ratings yet
- Hot Work Gift Gift / Near Gis SEPCOO III Early Comb: Job Hazard Analysis (Jha) WorksheetDocument4 pagesHot Work Gift Gift / Near Gis SEPCOO III Early Comb: Job Hazard Analysis (Jha) Worksheet王志伟No ratings yet
- JSA Work at Hight - Rev-6Document2 pagesJSA Work at Hight - Rev-6Mahamudul HasanNo ratings yet
- EHS-SWI-037 - 0 Loadbank Testing - DraftDocument2 pagesEHS-SWI-037 - 0 Loadbank Testing - DraftChris Bonnington100% (1)
- JSA For Screeding With MeshDocument4 pagesJSA For Screeding With MeshMohammed Minhaj100% (1)
- JSA Erection StructureDocument11 pagesJSA Erection StructureJAYESH JOSHINo ratings yet
- Qrc-Ra-001-00-Road and Footpath Modification WorksDocument27 pagesQrc-Ra-001-00-Road and Footpath Modification WorksKallem RajashekarNo ratings yet
- New JuneDocument6 pagesNew JuneShovon khanNo ratings yet
- Testing Comissioning of Electrical SystemDocument8 pagesTesting Comissioning of Electrical Systemmo7d aliNo ratings yet
- JSA Column Errection, Shuttering, Casting, Deshuttering Raw Material Ware HouseDocument9 pagesJSA Column Errection, Shuttering, Casting, Deshuttering Raw Material Ware Houseradeep100% (1)
- JSA For Erection and Repair Work of TanksDocument19 pagesJSA For Erection and Repair Work of TanksMohamed Farouk100% (2)
- JSA Mobile Crane Pipe Installation Tandem LiftDocument3 pagesJSA Mobile Crane Pipe Installation Tandem LiftSyed HarisNo ratings yet
- Jsa For Concreate and CivilworksDocument7 pagesJsa For Concreate and CivilworksAnna JisabaNo ratings yet
- 1TB02011 011C49 FFC MTS Me 0012 RaDocument7 pages1TB02011 011C49 FFC MTS Me 0012 RaAijaz AhmedNo ratings yet
- JSA For Scaffolding Erection Dismantling and Modification WorkDocument17 pagesJSA For Scaffolding Erection Dismantling and Modification Workshane.ramirez1980No ratings yet
- 139 Casting ConcretingDocument4 pages139 Casting Concreting王志伟No ratings yet
- 50 MW Artistic Wind Power Project: Job Safety Analysis Worksheet (Equipment Lifting)Document3 pages50 MW Artistic Wind Power Project: Job Safety Analysis Worksheet (Equipment Lifting)Raza Muhammad SoomroNo ratings yet
- JSA For Working at HeightDocument2 pagesJSA For Working at HeightXUE JIANNo ratings yet
- Jsa For Concreate and CivilworksDocument7 pagesJsa For Concreate and CivilworksAnna JisabaNo ratings yet
- JHA 01 Erecting Fixed ScaffoldingDocument4 pagesJHA 01 Erecting Fixed Scaffoldingadil khan100% (1)
- Job Safety Analysis (JSA) : Description Hazard ControlDocument2 pagesJob Safety Analysis (JSA) : Description Hazard ControlRidha BennasrNo ratings yet
- Appendix C - Risk AssessmentDocument2 pagesAppendix C - Risk Assessmentjavedashraf.ptNo ratings yet
- JSA - Working at HeightDocument5 pagesJSA - Working at HeightSampath Kumar KandasamyNo ratings yet
- SL Work Activity Potential Hazards Preventive Measures/Action TakenDocument28 pagesSL Work Activity Potential Hazards Preventive Measures/Action TakenDarius DsouzaNo ratings yet
- Wet Area Water Proofing WorkDocument8 pagesWet Area Water Proofing Worksarath SNo ratings yet
- Answer Keys Ut MPT PTDocument5 pagesAnswer Keys Ut MPT PTRonel John CustodioNo ratings yet
- Binder 1Document15 pagesBinder 1Ronel John CustodioNo ratings yet
- Course & Examination Enrolment Form (BINDT-PCN)Document2 pagesCourse & Examination Enrolment Form (BINDT-PCN)Ronel John CustodioNo ratings yet
- PSL-44 - Vision RequirementsDocument5 pagesPSL-44 - Vision RequirementsRonel John CustodioNo ratings yet
- 45MG Upgrade Instructions Using Upgrade 2010Document3 pages45MG Upgrade Instructions Using Upgrade 2010Ronel John CustodioNo ratings yet
- A-1101c Paut Cracks ScreenshotsDocument6 pagesA-1101c Paut Cracks ScreenshotsRonel John CustodioNo ratings yet
- SOAD9110 - Marking Guide - Assessment 3 - Case Study Assessment and InterventionDocument2 pagesSOAD9110 - Marking Guide - Assessment 3 - Case Study Assessment and InterventionJoseph NdibaNo ratings yet
- NammaKPSC GP2018 GS 2Document4 pagesNammaKPSC GP2018 GS 2rohtihr2611No ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Axiology of ValuesDocument19 pagesLesson 1 Axiology of ValuesJennifer OriolaNo ratings yet
- Auditing 1Document9 pagesAuditing 1Vanessa BatallaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Strategic ManagementDocument28 pagesIntroduction To Strategic Managementroyaltravelsofficial777No ratings yet
- Self-Learning Module in Practical Research I Lesson:: III 1&2 Day and Time: Learning CompetenciesDocument11 pagesSelf-Learning Module in Practical Research I Lesson:: III 1&2 Day and Time: Learning CompetenciesGhaniella B. JulianNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10: Nature and Scope of PhilosophyDocument6 pagesChapter 10: Nature and Scope of PhilosophyKim GiananNo ratings yet
- Case Study HomelessnessDocument14 pagesCase Study Homelessnessapi-608106291No ratings yet
- Module 2 LESSON 2Document3 pagesModule 2 LESSON 2Mitzi Portia VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- BMBA-410 - Final Assignment - Leadership InterviewDocument5 pagesBMBA-410 - Final Assignment - Leadership InterviewWeslley FortunatoNo ratings yet
- Form 78 Statutory Declaration As To Proof of Debt - Employees Group FormDocument1 pageForm 78 Statutory Declaration As To Proof of Debt - Employees Group FormolingirlNo ratings yet
- Ethics and Moral Philosophy - General Introduction - 2020 - Lecture 5aDocument3 pagesEthics and Moral Philosophy - General Introduction - 2020 - Lecture 5aBlueBladeNo ratings yet
- NSTPDocument3 pagesNSTPfreya alejoNo ratings yet
- OB 1 Historical Evolution of Organisational BehaviourDocument76 pagesOB 1 Historical Evolution of Organisational Behaviourjayamohan100% (1)
- P.ed. 2 Prelim Module MonicaDocument43 pagesP.ed. 2 Prelim Module MonicaMonica BedijaNo ratings yet
- Colonial Reports N 186 - Basutoland 1895-96Document50 pagesColonial Reports N 186 - Basutoland 1895-96EmmanuelleLizéNo ratings yet
- Of Studies Reflection PaperDocument4 pagesOf Studies Reflection PaperGONZALES, ASHLEY MARIE G.No ratings yet
- Day6 Activity Aptitude C TwistorsDocument12 pagesDay6 Activity Aptitude C TwistorsHota bNo ratings yet
- Film Making Registration FormDocument2 pagesFilm Making Registration FormRavi PrakashNo ratings yet
- Beauty Unmasked-A Haunting Journey Through The Picture of Dorian GrayDocument3 pagesBeauty Unmasked-A Haunting Journey Through The Picture of Dorian GrayJhonnel TizonNo ratings yet
- NSTP Ass2 DoneDocument5 pagesNSTP Ass2 DoneMikaela Francesca EchaluceNo ratings yet
- Easement MCQDocument7 pagesEasement MCQTshewang Dema67% (3)
- Lead Me Lord Sheet Music - CurrentDocument2 pagesLead Me Lord Sheet Music - CurrentAdedayo MichaelNo ratings yet
- Campus Journalism Is Public ServiceDocument2 pagesCampus Journalism Is Public ServiceAnn RoseNo ratings yet
- DIFFERENT Types of WillDocument6 pagesDIFFERENT Types of WillShivani TelangeNo ratings yet
- Organizational Theory, Design, and Change, 7e (Jones) : Chapter 2 Stakeholders, Managers, and EthicsDocument63 pagesOrganizational Theory, Design, and Change, 7e (Jones) : Chapter 2 Stakeholders, Managers, and EthicsNisreen EmadNo ratings yet
- Reflection Paper About Anti-BULLYDocument2 pagesReflection Paper About Anti-BULLYSherman AdralesNo ratings yet
- 4 Rules For Being A Good BandmateDocument3 pages4 Rules For Being A Good BandmateMarjorie Joy MartirNalupa AninoNo ratings yet