Professional Documents
Culture Documents
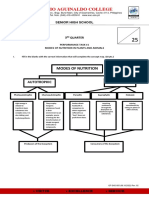
Melc G9 Q1 Week 6 DLL
Melc G9 Q1 Week 6 DLL
Uploaded by
philip galizaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Kami Export - Maxwell Modeste - Photosynthesis Case Study - Killing ChloroplastsDocument7 pagesKami Export - Maxwell Modeste - Photosynthesis Case Study - Killing ChloroplastsMaxwell Modeste0% (2)
- Cape Biology Unit 2 CompleteDocument92 pagesCape Biology Unit 2 CompleteBisham Siew75% (4)
- LP Biological MacromoleculesDocument5 pagesLP Biological MacromoleculesDexter Jess Dag-uman100% (7)
- Cot-1 Lesson Plan (Grade 9)Document9 pagesCot-1 Lesson Plan (Grade 9)Marlon S. Baranggan100% (3)
- Photosynthesis Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesPhotosynthesis Lesson PlanEldie Ocariza100% (2)
- ELS Q2 M3 Introduction To Life ScienceDocument20 pagesELS Q2 M3 Introduction To Life ScienceKath Tan Alcantara86% (7)
- QUESTIONAIRE Basic ResaerchDocument4 pagesQUESTIONAIRE Basic Resaerchphilip galiza100% (5)
- Interrelationship Between Carbohydrate Protein Fat MetabolismDocument12 pagesInterrelationship Between Carbohydrate Protein Fat MetabolismShailaja Neaupane100% (5)
- Semi-Detailed Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesSemi-Detailed Lesson Planjoselyn bergonia100% (1)
- DLP - August 2, 2018Document3 pagesDLP - August 2, 2018Vee Jay BlanciaNo ratings yet
- 1st QT - PhotosynthesisDocument4 pages1st QT - PhotosynthesisTEREMIE JOSEPH OBADONo ratings yet
- SCIENCE-9 Q1 W6-W7 Mod5 ADM-1-photosythesisDocument42 pagesSCIENCE-9 Q1 W6-W7 Mod5 ADM-1-photosythesisJB Dar100% (1)
- DLL TemplateDocument8 pagesDLL TemplateCristelle EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Final Demo Teaching Lesson Plan NemenzoDocument13 pagesFinal Demo Teaching Lesson Plan Nemenzoapi-652151038No ratings yet
- General Biology 1 Q2 Week 2 - 075858Document11 pagesGeneral Biology 1 Q2 Week 2 - 075858raymondreyremandaban2007No ratings yet
- PT1 GuevarraDocument3 pagesPT1 GuevarraAkeelah EstacioNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 9 (1) - MELC 5 - Reviewed by CommitteeDocument14 pagesSCIENCE 9 (1) - MELC 5 - Reviewed by CommitteeBayani VicencioNo ratings yet
- General Biology-Q2-Week 2Document15 pagesGeneral Biology-Q2-Week 2ALFREDO CALEDANo ratings yet
- Science 8 - 6.1Document5 pagesScience 8 - 6.1Sherine Marianne IgnacioNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan SampleDocument7 pagesLesson Plan SampleVILLA 2 ANACITA LOCIONNo ratings yet
- Technical Assistance Lesson PlanDocument8 pagesTechnical Assistance Lesson PlanJaybie TejadaNo ratings yet
- Barba Lesson-Exemplar Cot1Document6 pagesBarba Lesson-Exemplar Cot1Rodney BarbaNo ratings yet
- DLL-Cellular RespirationDocument4 pagesDLL-Cellular RespirationCyril Alba ConstantinoNo ratings yet
- Science 8 SLM16Document15 pagesScience 8 SLM16Cristian ErfeNo ratings yet
- Research Vinegar MakingDocument7 pagesResearch Vinegar MakingJosef EscobarNo ratings yet
- Science 9 Q1 W8Document5 pagesScience 9 Q1 W8Abram BaranganNo ratings yet
- Bixby Knolls Preparatory Academy - San Antonio, Quezon: Science and Technology 8Document3 pagesBixby Knolls Preparatory Academy - San Antonio, Quezon: Science and Technology 8Oliver VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- AUREEN ICBAN Pedagogically Designed LP, - EARTH AND LIFE SCIENCEDocument4 pagesAUREEN ICBAN Pedagogically Designed LP, - EARTH AND LIFE SCIENCEJonathan OlegarioNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: (Ngaran Han Leksyon)Document5 pagesDepartment of Education: (Ngaran Han Leksyon)Teacher MitzeNo ratings yet
- Science 9 Q1 W9Document4 pagesScience 9 Q1 W9Abram BaranganNo ratings yet
- DLL Biotechnology - July 15 - 19Document3 pagesDLL Biotechnology - July 15 - 19MichaelAbdonDomingoFavoNo ratings yet
- Senior High LP - Energy FlowDocument3 pagesSenior High LP - Energy Flowking devesfrutoNo ratings yet
- DLL Science 8Document7 pagesDLL Science 8Paradillo Regatuna LesterNo ratings yet
- Nuguid, Rochelle D - Assessment InstrumentDocument16 pagesNuguid, Rochelle D - Assessment InstrumentRochelle NuguidNo ratings yet
- Senior High LP - BioenergeticsDocument2 pagesSenior High LP - Bioenergeticsking devesfruto100% (2)
- Lesson Exemplar in Science 9 - MELC 5Document18 pagesLesson Exemplar in Science 9 - MELC 5Michael SocuajeNo ratings yet
- DLL SHS STEM Grade 12 - General Biology1 Quarter1 Week2 (Palawan Division)Document17 pagesDLL SHS STEM Grade 12 - General Biology1 Quarter1 Week2 (Palawan Division)Ann Quirante100% (3)
- Science 8 - Q4 - Week 6Document23 pagesScience 8 - Q4 - Week 6EyphRhylle100% (1)
- General Biology - Q2 - Week 2Document23 pagesGeneral Biology - Q2 - Week 2Renard JaenNo ratings yet
- LESSON PLAN Practice Teaching - AFT - Putri Dyah AstariDocument9 pagesLESSON PLAN Practice Teaching - AFT - Putri Dyah AstariAfnestya100% (1)
- Revised Q1 WHLP in ConChemDocument4 pagesRevised Q1 WHLP in ConChemChianlee CarreonNo ratings yet
- Classes of AntropodsDocument3 pagesClasses of AntropodsArchemedes BarrocaNo ratings yet
- Cot Lesson JanDocument7 pagesCot Lesson JanSittie Asyah Solaiman EdrisNo ratings yet
- DLL 9Document5 pagesDLL 9Jonathan TabbunNo ratings yet
- Aldin LP FinalDocument13 pagesAldin LP FinalMelvin Cabonegro100% (1)
- Daily Lesson Log Earth and Life Science For CotDocument2 pagesDaily Lesson Log Earth and Life Science For CotMARY JOSEPH OCONo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Science 7Document4 pagesLesson Plan in Science 7Alegna Bajado50% (2)
- Lesson Plan On NutritionDocument4 pagesLesson Plan On NutritionJENNY MAY SUDAY100% (1)
- School Grade Level Teacher Learning Area Time & Dates Quarter I. ObjectivesDocument6 pagesSchool Grade Level Teacher Learning Area Time & Dates Quarter I. ObjectivesPatrick Jerome SilvanoNo ratings yet
- Cot 2 - 2024 - Energy TransferDocument4 pagesCot 2 - 2024 - Energy TransferFatima Abacan ReyesNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science Quarter 2 Mod 2Document11 pagesEarth and Life Science Quarter 2 Mod 2Lovely Rose Jardin OzoNo ratings yet
- Bio1 Q2 M2 Revised RemovedDocument13 pagesBio1 Q2 M2 Revised RemovedClaries HeyrosaNo ratings yet
- AntropodsDocument3 pagesAntropodsArchemedes BarrocaNo ratings yet
- DLP April 11 GenBio2Document2 pagesDLP April 11 GenBio2Elaiza marie VenusNo ratings yet
- COT 1 (2nd Sem - 3rd Q - PHYS)Document10 pagesCOT 1 (2nd Sem - 3rd Q - PHYS)Helen Grace SentinaNo ratings yet
- School Grade Level Teacher Quarter Learning Area Teaching Dates &durationDocument3 pagesSchool Grade Level Teacher Quarter Learning Area Teaching Dates &durationmaryjoy cacaldoNo ratings yet
- ELS Q2 M3 Intro-to-Life-Science 16pDocument16 pagesELS Q2 M3 Intro-to-Life-Science 16pYella SerranoNo ratings yet
- A SemiDocument4 pagesA SemiJhEng Cao Manansala100% (1)
- Lesson Plan in Physical Science COT 1 2022 2023Document4 pagesLesson Plan in Physical Science COT 1 2022 2023Taten Balmes100% (2)
- Content Standard Performance Standard Learning Competency I. Learning ObjectivesDocument10 pagesContent Standard Performance Standard Learning Competency I. Learning ObjectivesNur ShaNo ratings yet
- Cot DLP For A Video LessonDocument4 pagesCot DLP For A Video LessonLhea Joy T. CiprianoNo ratings yet
- April 14-27 DLLL GB2Document3 pagesApril 14-27 DLLL GB2Race De VillaNo ratings yet
- Science Melc g9 q1 Week 4 DLLDocument35 pagesScience Melc g9 q1 Week 4 DLLphilip galizaNo ratings yet
- Science MELC-G9-Q1-WEEK-5-DLLDocument39 pagesScience MELC-G9-Q1-WEEK-5-DLLphilip galizaNo ratings yet
- Thesis Physical ActivityDocument46 pagesThesis Physical Activityphilip galizaNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 2 Quantitative ResearchDocument25 pagesPractical Research 2 Quantitative Researchphilip galizaNo ratings yet
- Community-Service PBGDocument9 pagesCommunity-Service PBGphilip galizaNo ratings yet
- Advances in PhotosynthesisDocument305 pagesAdvances in PhotosynthesisVidyasagar DeshpandeNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry For CLDocument5 pagesBiochemistry For CLGashaw TilahunNo ratings yet
- Biology M5 Cellular RespirationDocument30 pagesBiology M5 Cellular RespirationjtNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Module 2Document3 pagesBiochemistry Module 2Sanee ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Norme SangeDocument2 pagesNorme SangePS NINo ratings yet
- Acid-Base Balance Study GuideDocument2 pagesAcid-Base Balance Study GuideNoah ClevengerNo ratings yet
- Energy Zones in SwimmingDocument12 pagesEnergy Zones in SwimmingShean landrei labalanNo ratings yet
- Bioenergetics and Oxidative PhosphorylationDocument32 pagesBioenergetics and Oxidative PhosphorylationShimmering MoonNo ratings yet
- Autotrophic NutritionDocument22 pagesAutotrophic NutritionBWAMBALE HARISONNo ratings yet
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Fermentation and Aerobic RespirationDocument10 pagesAdvantages and Disadvantages of Fermentation and Aerobic RespirationIan Gabriel MayoNo ratings yet
- Topic 5 - Energy Transfers in and Between Organisms: Definitions and Concepts For AQA Biology A-LevelDocument5 pagesTopic 5 - Energy Transfers in and Between Organisms: Definitions and Concepts For AQA Biology A-LevelsamNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Biology The Unity and Diversity of Life 12th EditionDocument11 pagesTest Bank For Biology The Unity and Diversity of Life 12th Editionandrewduffydckjxfspnq100% (37)
- Back To Basics Critical Care Transport Review Course Simple Rules For Arterial Blood Gas InterpretationDocument12 pagesBack To Basics Critical Care Transport Review Course Simple Rules For Arterial Blood Gas Interpretationedderj2585No ratings yet
- BMSC 230 Noted Chapter 2Document3 pagesBMSC 230 Noted Chapter 2shakshi dhruvNo ratings yet
- Fermentation Processes and Their Application PDFDocument8 pagesFermentation Processes and Their Application PDFninasabelita100% (9)
- 8.2 Cell Respiration - WSDocument16 pages8.2 Cell Respiration - WS한서현No ratings yet
- Amino AcidsDocument32 pagesAmino AcidsWakjira GemedaNo ratings yet
- 8 3 PhotosynthesisDocument39 pages8 3 PhotosynthesisKhin (Darin) Hnin PhyuNo ratings yet
- Nitrogen Fixation and Nitrogen Cycle JNV PapumpareDocument5 pagesNitrogen Fixation and Nitrogen Cycle JNV PapumpareJyotiNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Biology Respiration Chapter Video 3Document14 pagesClass 10 Biology Respiration Chapter Video 3Dadi SindhuNo ratings yet
- Citric Acid ConversionDocument1 pageCitric Acid ConversionWendy TekikoNo ratings yet
- COFACTORSDocument12 pagesCOFACTORSНаталья СтилсонNo ratings yet
- Ketonuria 1Document10 pagesKetonuria 1Habib UllahNo ratings yet
- Drishya Krishnakumar 1Msc BiotechnologyDocument20 pagesDrishya Krishnakumar 1Msc BiotechnologyKarthika GokulanNo ratings yet
- Chap 12 Energy and RespirationDocument34 pagesChap 12 Energy and RespirationGeorge ApidiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9, Biols300Document31 pagesChapter 9, Biols300mariamNo ratings yet
- THE TEN REACTIONS OF GLYCOLYSIS - AND THE FATES OF PYRUVATEdocxDocument6 pagesTHE TEN REACTIONS OF GLYCOLYSIS - AND THE FATES OF PYRUVATEdocxRubylyn VillanuevaNo ratings yet
Melc G9 Q1 Week 6 DLL
Melc G9 Q1 Week 6 DLL
Uploaded by
philip galizaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Melc G9 Q1 Week 6 DLL
Melc G9 Q1 Week 6 DLL
Uploaded by
philip galizaCopyright:
Available Formats
Republic of the Philippines
Department of Education
REGION III – CENTRAL LUZON
SCHOOLS DIVISION OF TARLAC PROVINCE
DAILY LESSON LOG IN SCIENCE GRADE 9
Name of Teacher:PHILIP B. GALIZA Quarter: First Date/Day: Oct. 12 -
13, 2022
I. OBJECTIVES
A. Content Standards The learners demonstrate understanding of
a. The structure and function of plant parts and organelle
involved in photosynthesis
B. Performance Standards: The learners should be able to design and conduct an
investigation to provide evidence that plants can
manufacture their own food.
C. Learner’s Competencies Differentiate basic features and importance of
/ Code: photosynthesis and respiration ( S9LT – Ig – j – 31)
1. Cognitive* Explain the process of food making.
2. Psychomotor* Label the internal structure of a leaf and chloroplast.
3. Affective* Recognize and show appreciation of the importance of
photosynthesis in daily living.
II. CONTENT
Topic ECOSYSTEM: LIFE ENERGY
Sub Topic PHOTOSYNTHESIS
III. LEARNING RESOURCES
A. REFERENCES
1. Teacher’s Guide 2. Learner’s Material 3. Textbook Pages
Pages 3 - 7 Pages 74 – 77 Functional Biology
( Modular Approach)
Joaquin, Crescencia C.
Pages 212 - 214
4. Additional Materials from LR Portal
Other Learning Resources: courses.lumenlearning.com/boundless-biology/chapter/overview-
of-photosynthesis/
http://www.youtybe.com/watch?v=C1_uez5WX1o(as of October 13)
http://earthguide.ucsd.edu/earthguide/diagrams/photosynthesis/ photosynthesis.html
biology-igce.weebly.com/the-equation-for-photosynthesis.html
http://www.youtybe.com/watch?v=C1_uez5WX1o(as of October 13)
http://earthguide.ucsd.edu/earthguide/diagrams/photosynthesis/ photosynthesis.html
http://dendro.cnre.vt.edu/forestbiology/photosynthesis
http://dendro.cnre.vt.edu/forestbiology/photosynthesis.swf
enchantedlearning.com/subjects/plants/leaf
Address: Macabulos Drive, San Roque, Tarlac City
Telephone No.: (045) 982-0374
Email Address: tarlac @deped.gov.ph
Republic of the Philippines
Department of Education
REGION III – CENTRAL LUZON
SCHOOLS DIVISION OF TARLAC PROVINCE
IV. PROCEDURES
A. Reviewing previous Picture Analysis:
lesson (or) presenting The teacher will show the following photos of organisms.
the new lesson Ask the students to name and describe them.
SOURCE:courses.lumenlearning.com/boundless-
biology/chapter/overview-of-photosynthesis/
Answers:
Photosynthetic and Chemosynthetic Organisms:
1. Photoautotrophs ( a. plants, b. algae, c.
cyanobacteria) synthesize their organic compounds
via photosynthesis using sunlight as an energy
source
2. Chemoautotrophs ( d. deep sea vent
chemoautotrophs e. thermophilic
bacteria) capture energy from inorganic compounds
to produce organic compounds
B. Establishing a purpose Based from the pictures, the teacher will ask the following
to the lesson questions?
1. What are photoautotrophs?
2. What are chemoautotrophs?
3. What are heterotrophs?
4. How autotrophs differ from heterotrophs?
Answers:
Address: Macabulos Drive, San Roque, Tarlac City
Telephone No.: (045) 982-0374
Email Address: tarlac @deped.gov.ph
Republic of the Philippines
Department of Education
REGION III – CENTRAL LUZON
SCHOOLS DIVISION OF TARLAC PROVINCE
1. photoautotroph - an organism that can synthesize
its own food by using light as a source of energy
2. chemoautotroph - a simple organism, such as a
protozoan, that derives its energy from chemical
processes rather than photosynthesis
3. heterotrophs - organisms that are unable to produce
their own food, rely on the carbohydrates produced
by photosynthetic organisms for their energy needs.
4. Autotrophs or the self - feeders are organisms that
can produce their own food while heterotrophs
(other-feeder) are organisms that feed on autotrophs
or other heterotrophs to obtain the energy they
need
C. Presenting examples/ PICTURE ANALYSIS:
instances of the lesson Let the students study the picture below and ask them to
describe the photosynthetic process.
SOURCE:courses.lumenlearning.com/boundless-
biology/chapter/overview-of-photosynthesis/
Answer:
Photosynthesis uses solar energy, carbon dioxide and water
to produce energy-storing carbohydrates. Oxygen is
generated as a waste product of photosynthesis.
Address: Macabulos Drive, San Roque, Tarlac City
Telephone No.: (045) 982-0374
Email Address: tarlac @deped.gov.ph
Republic of the Philippines
Department of Education
REGION III – CENTRAL LUZON
SCHOOLS DIVISION OF TARLAC PROVINCE
D. Discussing new EQUATION INTERPRETATION:
concepts and practicing Present the equation of photosynthesis. Analyze the
new skills #1. chemical reaction then answer the following questions.
SOURCE: biology-igce.weebly.com/the-equation-for-
photosynthesis.html
Guide Questions:
1. Explain the photosynthesis equation.
2. Complete the table below.
TABLE 1. Raw Materials and Products of
Photosynthesis
Complete the table below. Write the raw materials and
products of photosynthesis.
Raw Materials Products
Address: Macabulos Drive, San Roque, Tarlac City
Telephone No.: (045) 982-0374
Email Address: tarlac @deped.gov.ph
Republic of the Philippines
Department of Education
REGION III – CENTRAL LUZON
SCHOOLS DIVISION OF TARLAC PROVINCE
Answers:
1. The energy from sunlight drives the reaction of
carbon dioxide and water molecules to produce
sugar and oxygen, as seen in the chemical equation
for photosynthesis.
2.
Products
Raw Materials
carbon dioxide Sugar (glucose)
Water Oxygen
Sunlight
Chlorophyll
SOURCES:
http://www.youtybe.com/watch?v=C1_uez5WX1o(as of
October 13)
http://earthguide.ucsd.edu/earthguide/diagrams/
photosynthesis/ photosynthesis.html
E. Discussing new concepts How are plants structurally adapted to perform the
and practicing new skill function of photosynthesis?
#2.
Let the students study the diagrams and perform the
activities that follow.
Address: Macabulos Drive, San Roque, Tarlac City
Telephone No.: (045) 982-0374
Email Address: tarlac @deped.gov.ph
Republic of the Philippines
Department of Education
REGION III – CENTRAL LUZON
SCHOOLS DIVISION OF TARLAC PROVINCE
Structure of a leaf (cross-section): Photosynthesis
takes place in the mesophyll. The palisade layer
contains most of the chloroplast and principal
region in which photosynthesis is carried out. The
airy spongy layer is the region of storage and gas
exchange. The stomata regulate carbon dioxide and
water balance.
Address: Macabulos Drive, San Roque, Tarlac City
Telephone No.: (045) 982-0374
Email Address: tarlac @deped.gov.ph
Republic of the Philippines
Department of Education
REGION III – CENTRAL LUZON
SCHOOLS DIVISION OF TARLAC PROVINCE
Structure of the Chloroplast: Photosynthesis
takes place in chloroplasts, which have an outer
membrane and an inner membrane. Stacks of
thylakoids called grana form a third membrane
layer.
SOURCES:
http://dendro.cnre.vt.edu/forestbiology/photosynthesis
courses.lumenlearning.com/boundless-biology/chapter/
overview-of-photosynthesis/
enchantedlearning.com/subjects/plants/leaf
ACTIVITY 1 – What are the structures involved in the
food making process in plants?
I A. Plant Structure for Photosynthesis
1.Label the parts of a chloroplast and the internal structure
Address: Macabulos Drive, San Roque, Tarlac City
Telephone No.: (045) 982-0374
Email Address: tarlac @deped.gov.ph
Republic of the Philippines
Department of Education
REGION III – CENTRAL LUZON
SCHOOLS DIVISION OF TARLAC PROVINCE
of a leaf ( Science Learner’s Module, page 76 )
SOURCE:
http://dendro.cnre.vt.edu/forestbiology/photosynthesis.swf
F. Discussing new concepts The learners will be asked to discuss the importance of
and practicing new photosynthesis.
skills #3.
Guide Question:
Why is it very refreshing to stay in area with a lot of plants
during hot period of the day?
Answer:
1. Plants release oxygen in the atmosphere. Plants absorb
carbon dioxide from the air, which in turn can help reduce
global warming.
G. Developing Mastery Let the students answer the Self- Check below:
SELF-CHECK*
1. What do plants need for photosynthesis?
2. Explain how plants are structurally designed so they can
obtain their needs.
3. Write the summary equation of photosynthesis. From
this, point out the products that are of great importance to
an ecosystem.
Answers:
1. Plants create their own energy food, called glucose,
through a process called photosynthesis. To carry
out photosynthesis, plants need four things:
chloroplasts, light, water and carbon dioxide.
2. Plants are provided with chlorophyll –containing
leaves that harness light energy, veins containing
transport vessels that distribute water and stomata
on the lower epidermis for the uptake of carbon
dioxide.
Address: Macabulos Drive, San Roque, Tarlac City
Telephone No.: (045) 982-0374
Email Address: tarlac @deped.gov.ph
Republic of the Philippines
Department of Education
REGION III – CENTRAL LUZON
SCHOOLS DIVISION OF TARLAC PROVINCE
A. Glucose is a sugar that many plants, animals and
fungi use for energy. Glucose is also required for
the process of cellular respiration, in which plants
convert carbon dioxide from the air into oxygen.
B. Oxygen provides the most energy to plants and
animals and microbes during respiration
H. Finding practical APPLICATION QUESTIONS:
application of concepts
and skills in daily living Photosynthesis requires a lot of work. However, cells are so
How can you make organized that organelles responsible for specific
sense of the concept of mechanisms are able to do their responsibility.
the lesson in your real- How will you relate division of labor and
life context? * responsibility done by cells to your everyday tasks?
Are you as organized as the cells in our body?
Do we perform our tasks well?
(Students’ responses may vary)
I. Making Generalization Let the students answer the following questions:
and Abstraction about
the lesson: (Sequence of 1. How autotrophs differ from heterotrophs?
Questions) 2. What is photosynthesis?
3. What are the raw materials of photosynthesis?
4. What are the products of photosynthesis?
5. Where does photosynthesis occur?
6. What happens to the glucose molecule?
7. What are the roles played by the following structures in
the photosynthetic process?
a. chloroplast
Address: Macabulos Drive, San Roque, Tarlac City
Telephone No.: (045) 982-0374
Email Address: tarlac @deped.gov.ph
Republic of the Philippines
Department of Education
REGION III – CENTRAL LUZON
SCHOOLS DIVISION OF TARLAC PROVINCE
b. mesophyll
c. stomata
8. What is the significance of photosynthesis?
Answers:
1. Autotrophs are organisms that can produce their
own food either by
photosynthesis( photoautotrophs ) or
chemosynthesis ( chemoautotrophs )
2. Photosynthesis is the process wherein producers
trap the light energy from the sun and transforms it
into food
3. The raw materials of photosynthesis are carbon
dioxide, water and sunlight
4. The products of photosynthesis are glucose and
oxygen
5. Photosynthesis takes place in the chloroplasts
6. Glucose may be utilized for cellular respiration. It
is essentially the major source of energy for various
life processes
7. chloroplast – an organelle found in the cells of
green
plants and photosynthetic algae where
photosynthesis takes place
mesophyll – a layer of cells that comprise most of
the interior of the leaf between the upper and lower
layers of epidermis
stoma – a pore in the leaf and stem epidermis that
is used for gas exchange
8. During photosynthesis, oxygen gas is liberated out
into the environment and is utilized by humans,
animals, and other living species during the process
of respiration.
J. Evaluating Learning Supply the missing words to complete the sentences.
Choose your answers from the pool or words inside the
box.
photosynthesis photoautotrophs
Address: Macabulos Drive, San Roque, Tarlac City
Telephone No.: (045) 982-0374
Email Address: tarlac @deped.gov.ph
Republic of the Philippines
Department of Education
REGION III – CENTRAL LUZON
SCHOOLS DIVISION OF TARLAC PROVINCE
glucose epidermis
chlorophyll heterotrophs
stomata spongy mesophyll
chloroplast palisade
mesophyll
1.___________are small openings where carbon dioxide
enters and water and oxygen leave.( stomata )
2. __________is the process by which green plants harness
light energy from the sun to convert it to the chemical
energy of sugar. ( photosynthesis )
3. The product of photosynthesis that stores chemical
energy is called_____________.( glucose )
4. ______________is an example of photosynthetic
pigment that absorbs light energy.( chlorophyll )
5. Plants, algae, and cyanobacteria manufacture food
through a process called photosynthesis, wherein energy
from the sun is converted to chemical energy found in the
biomolecules of organisms are called________________.
(photoautotrophs )
6. _______________ is a protective layer of cells covering
the entire leaf which is coated with a waterproof, waxy
material called cutin. (epidermis)
7. The organisms that depend on other organisms for food
are called_____________. ( heterotrophs )
8.______________is the site of photosynthesis.
(chloroplast)
9. The_______________ is made up of compactly arrange
d cells usually located near the upper surface that performs
the bulk of photosynthesis.(palisade mesophyll )
10. The ______________is made up of loosely arranged,
irregularly shaped cells that are provided with large
intercellular spaces and fewer chloroplasts.( spongy
mesophyll )
K. Additional activities for You are a researcher in the Department of Agriculture, and
Application or you have been tasked by your Science Leader/ Teacher to
Remediation research on farming practices which use the concept of
photosynthesis to increase yield of certain crops.
Address: Macabulos Drive, San Roque, Tarlac City
Telephone No.: (045) 982-0374
Email Address: tarlac @deped.gov.ph
Republic of the Philippines
Department of Education
REGION III – CENTRAL LUZON
SCHOOLS DIVISION OF TARLAC PROVINCE
Research on these practices and present a report based on
these practices. Your research will serve as reference for
students who wish to understand how science concepts are
strongly linked to applied science such as agriculture.
Your Science Leader/Teacher will evaluate your report
based on the following criteria:
accuracy of information
comprehensiveness
organization and
grammar
V. REMARKS
VI. REFLECTION
A. No. of learners who
earned 80% in the
Evaluation:
B. No. of learners who
require additional
activities for
remediation who scored
below 80%:
C. Did the remedial work?
No. of learners who
have caught up with the
lesson:
D. No. of learners who
continue to require
remediation:
E. Which of my teaching
strategies worked well?
Why did this work?
F. What difficulties did I
encounter which my
principal or superior can
help me solve?
G. What innovations or
localized materials did
I use/ discover which I
Address: Macabulos Drive, San Roque, Tarlac City
Telephone No.: (045) 982-0374
Email Address: tarlac @deped.gov.ph
Republic of the Philippines
Department of Education
REGION III – CENTRAL LUZON
SCHOOLS DIVISION OF TARLAC PROVINCE
wish to share with other
teachers
Prepared by:
PHILIP B. GALIZA
Teacher III
Checked by:
MARITA F. GARILLES
OIC – HT
Noted:
VILMA B. AGUAS,EDD
Principal III
DAILY LESSON LOG IN SCIENCE GRADE 9
PRO e of Teacher:PHILIP B. GALIZA Quarter: First Date/Day: Oct. 17,
2022
I. OBJECTIVES
A. Content Standards The learners demonstrate understanding of
a. The structure and function of plant parts and organelle
involved in photosynthesis
Address: Macabulos Drive, San Roque, Tarlac City
Telephone No.: (045) 982-0374
Email Address: tarlac @deped.gov.ph
Republic of the Philippines
Department of Education
REGION III – CENTRAL LUZON
SCHOOLS DIVISION OF TARLAC PROVINCE
B. Performance Standards: The learners should be able to design and conduct an
investigation to provide evidence that plants can
manufacture their own food.
C. Learner’s Competencies / Differentiate basic features and importance of
Code: photosynthesis and respiration ( S9LT – Ig – j – 31)
*Specific Objectives (3 Skills a Day)
1.Cognitive* Describe the stomata.
2.Psychomotor* Draw and label the stomata as viewed from the microscope.
3Affective* Recognize and show appreciation of the significance of
these plant structures in the food making process.
II. CONTENT
Topic ECOSYSTEM: LIFE ENERGY
Sub Topic PHOTOSYNTHESIS
III. LEARNING RESOURCES
A. REFERENCES
1. Teacher’s Guide 2. Learner’s Material 3. Textbook Pages
Page 9 Pages 78 - 79
4. Additional Materials from LR Portal
B. Other Learning Resources: qsstudy.com/biology/structure-functions-
stomata-plants
byjus.com/biology/stomata/
IV. PROCEDURES
A. Reviewing previous lesson Let the learners recall the structures involved in food
(or) presenting the new lesson making process in plants.
Emphasize the structures responsible for gas exchange in
plants.
B. Establishing a purpose to the Let the learners compare the mechanisms of gas exchange
lesson in plants and animals.
C. Presenting examples/ Ask the learners: How plants 'breathe' through their leaves?
instances of the lesson
Answer:
Tiny openings called stomata allow plants to exchange
gases necessary for cellular processes, such as
photosynthesis.
D. Discussing new concepts and Study the diagram. Then, the learners will be asked to
practicing new skills #1. answer the questions below.
Address: Macabulos Drive, San Roque, Tarlac City
Telephone No.: (045) 982-0374
Email Address: tarlac @deped.gov.ph
Republic of the Philippines
Department of Education
REGION III – CENTRAL LUZON
SCHOOLS DIVISION OF TARLAC PROVINCE
Guide Questions:
1. Describe the stomata.
2. What are the functions of stomata?
3. Why do stomata close at night?
Answers:
1. The stomatal pores are very minute and are covered with
crescent-shaped guard cells.
The outer wall of guard cells are thin and the inner wall is
thick. Each guard cell contains cytoplasm, a nucleus and
plenty of chloroplast.t
2. Stomata allow the ingress of carbon dioxide and release
of oxygen i.e. gaseous exchange takes place through
stomata. These gas molecules are really the source of the
carbon atoms used by plants to create sugars, proteins, and
other vital materials for life.
3. At night, stomata close because, in the absence of
sunlight, carbon dioxide is not required for photosynthesis.
At this time, their only objective is to prevent water loss.
Address: Macabulos Drive, San Roque, Tarlac City
Telephone No.: (045) 982-0374
Email Address: tarlac @deped.gov.ph
Republic of the Philippines
Department of Education
REGION III – CENTRAL LUZON
SCHOOLS DIVISION OF TARLAC PROVINCE
E. Discussing new concepts Let the learners examine the structure that enables the
and practicing new skill
#2. entrance and exit of gases in the leaf.
ACTIVITY 2 - Investigating the Stomata
Objectives:
identify the stomata
describe the function of the stomata
Materials:
leaf of rheo discolor (boat lily)
glass slide
microscope
clear nail polish
clear tape
Procedure:
1. Paint a thick patch of clear nail polish on the lower
surface of the leaf.
2. Allow the nail polish to dry completely.
3. Put a clear tape on the dried nail polished patch.
4. Gently peel the nail polished patch by pulling the corner
of the clear tape. This will serve your leaf impression for
microscopic observation.
5. Tape your leaf impression on a clean glass slide.
6. Observe the leaf impression under low power objective
of the microscope. Have you seen similar structures as
shown in Figure 1? (see Science Learner’s Module, page
79)
Guide Questions:
1. Draw and label the stomata as seen under the
microscope. Which do you think are the stomata?
2. What are the functions of stomata?
Answers:
1. Drawing as seen from the microscope.
Address: Macabulos Drive, San Roque, Tarlac City
Telephone No.: (045) 982-0374
Email Address: tarlac @deped.gov.ph
Republic of the Philippines
Department of Education
REGION III – CENTRAL LUZON
SCHOOLS DIVISION OF TARLAC PROVINCE
2. Stomata are found on the lower surface of the leaf that
allows the entrance of carbon dioxide needed for
photosynthesis. They also serve as exit point for the oxygen
produced during photosynthesis
F. Discussing new concepts Let the learners discuss the significant role/s of stomata in
and practicing new photosynthetic process.
skills #3.
Answer:
The gas exchange that occurs when stomata are
open facilitates photosynthesis. Photosynthesis is
the procedure by which plants change sunlight into
utilizable energy. During photosynthesis, carbon
dioxide is taken in from the environment through
the stomata and oxygen is released as a waste
product. Both photosynthesis and the gas exchange
that powers it is vital to the plant’s survival.
G. Developing Mastery Let the students answer the Self- Check below:
SELF – CHECK*
1. What are stomata?
2. Where are stomata found?
3. Why are stomata important?
Answers:
1. Stomata are tiny openings or pores in plant tissue that
allow for gas exchange.
2. Stomata are typically found in plant leaves but can also
be found in some stems.
3. The stomata are also important for
photosynthesis because they allow carbon dioxide into the
plant cells, and release oxygen from the plant into the
atmosphere.
H. Finding practical APPPLICATION QUESTIONS:
application of concepts
and skills in daily living 1 .Gas exchange is necessary for survival.
How can you make Cite other things that you cannot live without. How does it
Address: Macabulos Drive, San Roque, Tarlac City
Telephone No.: (045) 982-0374
Email Address: tarlac @deped.gov.ph
Republic of the Philippines
Department of Education
REGION III – CENTRAL LUZON
SCHOOLS DIVISION OF TARLAC PROVINCE
sense of the concept of affect your daily living?
the lesson in your real-
life context? * 2. How you will be able to respond and adapt to
environmental changes?
I. Making Generalization Let the students answer the following questions.
and Abstraction about
the lesson: (Sequence of Guide Questions:
Questions)
1. Where are stomata found in the plant cells?
2. Why do plants need stomata?
3. What are guard cells?
4. Explain the structure of stomata.
Answers:
1. Stomata are found in the epidermis of leaves, stems, and
other organs.
2. Stomata are the specialized pores or openings present in
the epidermis of plant cells, which play a crucial role in
gaseous exchange during the process of photosynthesis
3. Two bean-shaped cells surrounding a stoma are called
guard cells. They are also known as the epidermal cells and
play a crucial role during the process of photosynthesis.
4. Stomata are the tiny, kidney, or bean-shaped pores or
openings present in the epidermis of the cell and are
surrounded by the specialized guard cells.
J. Evaluating Learning 1. Draw the stomata. Label the parts
2. Describe the stomata.
3. Cite the functions of stomata.
K. Additional activities for Conduct a research on the various factors affecting opening
Application or and closing of stomata.
Remediation
VII. REMARKS
Address: Macabulos Drive, San Roque, Tarlac City
Telephone No.: (045) 982-0374
Email Address: tarlac @deped.gov.ph
Republic of the Philippines
Department of Education
REGION III – CENTRAL LUZON
SCHOOLS DIVISION OF TARLAC PROVINCE
VIII. REFLECTION
A. No. of learners who
earned 80% in the
Evaluation:
B. No. of learners who
require additional
activities for
remediation who scored
below 80%:
C. Did the remedial work?
No. of learners who
have caught up with the
lesson:
D. No. of learners who
continue to require
remediation:
E. Which of my teaching
strategies worked well?
Why did this work?
F. What difficulties did I
encounter which my
principal or superior can
help me solve?
G. What innovations or
localized materials did
I use/ discover which I
wish to share with other
teachers
Prepared by:
PHILIP B. GALIZA
Teacher III
Address: Macabulos Drive, San Roque, Tarlac City
Telephone No.: (045) 982-0374
Email Address: tarlac @deped.gov.ph
Republic of the Philippines
Department of Education
REGION III – CENTRAL LUZON
SCHOOLS DIVISION OF TARLAC PROVINCE
Checked by:
MARITA F. GARILLES
OIC – HT
Noted:
VILMA B. AGUAS,EDD
Principal III
DAILY LESSON LOG IN SCIENCE GRADE 9
Name of Teacher:PHILIP B. GALIZA Quarter: First Date/Day: Oct. 18,
2022
I.OBJECTIVES
A. Content Standards The learners demonstrate understanding of the structure and
function of plant parts and organelle involved in
photosynthesis
B. Performance Standards: The learners should be able to design and conduct an
investigation to provide evidence that plants can
manufacture their own food.
C. Learner’s Competencies / Differentiate basic features and importance of
Code: photosynthesis and respiration ( S9LT – Ig – j – 31)
*Specific Objectives (3 Skills a Day)
1. Cognitive* Differentiate the light-dependent and light-independent
reactions of photosynthesis
2.Psychomotor* construct a concept map showing the key events of the
light-dependent and light-independent reactions
3.Affective* recognize and appreciate the significant role of plants in
supplying energy to an ecosystem
II.CONTENT
Address: Macabulos Drive, San Roque, Tarlac City
Telephone No.: (045) 982-0374
Email Address: tarlac @deped.gov.ph
Republic of the Philippines
Department of Education
REGION III – CENTRAL LUZON
SCHOOLS DIVISION OF TARLAC PROVINCE
Topic ECOSYSTEM: LIFE ENERGY
Sub Topic PHOTOSYSNTHESIS
III.LEARNING RESOURCES
A. REFERENCES
1.Teacher’s Guide Page 7 2.Learner’s Material 3. Textbook Pages
Page 77 Functional Biology
( Modular Approach )
Joaquin, Crescencia C.
Pages 216 – 218
4. Additional Materials from LR Portal
B. Other Learning Resources: https://www.ck12.org>section
(ck12.org/book/ck-biology)
http://www.sites.ext.vt.edu/virtualforest/modules/phot.html
https://www.blogarama.com/education-blogs/305039-science-concepts-questions-blog/
1047819-photosynthesis-cellular-respiration-activities
pslides.com/templates/oxygen-cycle-powerpoint-diagram/
IV.PROCEDURES
A. Reviewing previous lesson VIDEO PRESENTATION:
(or) presenting the new lesson Recall the process of photosynthesis by watching a simple
video presentation ( Photosynthesis Song )
SOURCE: https://www.ck12.org>section
(ck12.org/book/ck-biology)
B. Establishing a purpose to the Let the students summarize the chemical reactions involved
lesson
in photosynthesis. After writing the equation, let the
students answer these questions:
1. What is a chemical reaction?
2. What are reactants?
3. What are products?
4. How chemical reactions take place?
5. In the equation, identify the reactants and products
of photosynthesis.
Address: Macabulos Drive, San Roque, Tarlac City
Telephone No.: (045) 982-0374
Email Address: tarlac @deped.gov.ph
Republic of the Philippines
Department of Education
REGION III – CENTRAL LUZON
SCHOOLS DIVISION OF TARLAC PROVINCE
Answers:
1. Chemical reaction is a process in which one or
more substances, the reactants, are converted to one
or more different substances, the products
2. Reactants are substances undergoing chemical
reactions
3. Products are the substances produced from a
chemical reaction
4. Chemical reaction occurs when two or more
molecules interact and the molecules change
5. In photosynthesis, the reactants are carbon dioxide,
water and sunlight while the products are glucose
and oxygen
C. Presenting examples/
instances of the lesson
Let the students look closely at the equation of
photosynthesis. Emphasize that the equation is simple but
the exact mechanism by which photosynthesis occurs is
complicated because the process may be divided into two
Address: Macabulos Drive, San Roque, Tarlac City
Telephone No.: (045) 982-0374
Email Address: tarlac @deped.gov.ph
Republic of the Philippines
Department of Education
REGION III – CENTRAL LUZON
SCHOOLS DIVISION OF TARLAC PROVINCE
phases.
Light –dependent phase/reaction – take place in the
thylakoids and requires the presence of light energy
to occur
Light-independent phase/reaction ( Dark Reaction/
Calvin Cycle) – occurs in the stroma with or
without light
Ask the learners: How the two stages of photosynthesis are
related?
Answer:
The products of the light-dependent phase are used as
reactants in the light-independent phase. Hence, the light-
dependent phase is a prerequisite to the light-independent
phase.
D. Discussing new concepts and Study and analyze the diagram below.
practicing new skills #1. Ask the students to distinguish the two phases of
photosynthesis.
Address: Macabulos Drive, San Roque, Tarlac City
Telephone No.: (045) 982-0374
Email Address: tarlac @deped.gov.ph
Republic of the Philippines
Department of Education
REGION III – CENTRAL LUZON
SCHOOLS DIVISION OF TARLAC PROVINCE
Light Reaction of Photosynthesis (or) Light-dependent
Reaction
Photosynthesis begins with the light reaction which
is carried out only during the day in the presence of
sunlight. In plants, the light-dependent reaction
takes place in the thylakoid membranes of
chloroplasts.
The grana, membrane-bound sacs like structures
present inside the thylakoid functions by gathering
light and is called photosystems.
These photosystems have large complexes of
pigment and proteins molecules present within the
plant cells which plays the primary role during the
process of light reactions of photosynthesis.
There are two types of photosystems: photosystem
I and photosystem II.
Under the light-dependent reactions, the light
energy is converted to ATP and NADPH which are
used in the second phase of photosynthesis.
During the light reactions, ATP and NADPH are
Address: Macabulos Drive, San Roque, Tarlac City
Telephone No.: (045) 982-0374
Email Address: tarlac @deped.gov.ph
Republic of the Philippines
Department of Education
REGION III – CENTRAL LUZON
SCHOOLS DIVISION OF TARLAC PROVINCE
generated by two electron-transport chains, water is
used and oxygen is produced.
Dark Reaction of Photosynthesis (or) Light-independent
Reaction
Dark reaction is also called carbon-fixing reaction.
It is a light-independent process in which sugar
molecules are formed from the water and carbon
dioxide molecules.
The dark reaction occurs in the stroma of the
chloroplast where they utilize the NADPH and
ATP products of the light reaction.
Plants capture the carbon dioxide from the
atmosphere through stomata and proceed to the
Calvin photosynthesis cycle.
In the Calvin cycle, the ATP and NADPH formed
during light reaction drive the reaction and convert
6 molecules of carbon dioxide into one sugar
molecule or glucose.
SELF-CHECK*
TABLE 2. Light and Dark Reactions of Photosynthesis
Complete the table: Write the location, raw materials and
products of light and dark reactions of photosynthesis.
Light reaction Dark reaction
Location
Raw Materials
Products
E. Discussing new concepts Let the students Perform Activity 3– Understanding the
and practicing new skill Process of Food- Making
Address: Macabulos Drive, San Roque, Tarlac City
Telephone No.: (045) 982-0374
Email Address: tarlac @deped.gov.ph
Republic of the Philippines
Department of Education
REGION III – CENTRAL LUZON
SCHOOLS DIVISION OF TARLAC PROVINCE
#2.
A. VIDEO PRESENTATION:
After watching the video clip on photosynthesis, make a
concept map of the entire process by filling up the
processes involved, raw materials used, and end products of
the entire process of food making. ( see Science Learner’s
Module, page 77)
Guide Questions:
1. Where do the light reactions of photosynthesis take
place?
2. Where do the light- independent reactions take place?
3. Explain why light-dependent reactions are called as such.
4. Explain why light-independent reactions are called as
such.
Answers:
1. Light reactions occur in the thylakoids
2. Light-independent reactions occur in the stroma
3.The reaction is called light-dependent because it requires
the presence of light
4. The reaction is said to be light-independent because it
occurs with or without light
F. Discussing new concepts How are the materials and energy flow in the ecosystem?
and practicing new
skills #3. Study the figure and answer the following questions:
SOURCE:pslides.com/templates/oxygen-cycle-
powerpoint-diagram/
Address: Macabulos Drive, San Roque, Tarlac City
Telephone No.: (045) 982-0374
Email Address: tarlac @deped.gov.ph
Republic of the Philippines
Department of Education
REGION III – CENTRAL LUZON
SCHOOLS DIVISION OF TARLAC PROVINCE
1. How are photosynthesis and aerobic respiration related?
2. How do the two processes maintain ecological balance?
Answers:
1. Photosynthesis and aerobic respiration are related in that
the products of photosynthesis are used as reactants in
respiration and vice versa.
2. The two processes, photosynthesis and aerobic
respiration, maintain ecological balance by keeping the
relative concentrations of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the
atmosphere constant. Whatever carbon dioxide is produced
during respiration is used up in photosynthesis. Likewise,
the oxygen used up by respiration is replenished during
photosynthesis.
G. Developing Mastery Answer the Self- Check below.
SELF-CHECK*
1. Explain the process of photosynthesis.
2. What are the different stages of photosynthesis?
3. What are the substances produced during the light-
dependent
phase? Explain how they are formed.
4. What are the products of the light-dependent reaction that
are
important to the fixation of carbon dioxide?
5. What is the Calvin Cycle?
Answers:
1. Photosynthesis is a biological process utilized by
all green plants to synthesize their own
nutrients. The process of photosynthesis
requires solar energy, water and carbon dioxide.
The by-product of this process is oxygen.
2. Photosynthesis takes place in two stages, namely
light-dependent reactions and light-independent
reactions. Light-dependent reactions are also called
Address: Macabulos Drive, San Roque, Tarlac City
Telephone No.: (045) 982-0374
Email Address: tarlac @deped.gov.ph
Republic of the Philippines
Department of Education
REGION III – CENTRAL LUZON
SCHOOLS DIVISION OF TARLAC PROVINCE
light reactions and occur during the day time.
Light-independent reaction is also called the dark
reaction or the Calvin cycle.
3. The following are produced during the light-
dependent phase:
a. Oxygen gas (O2) from water and released
as a gaseous by-product of photosynthesis
b. NADPH, from NADP+, a hydrogen ion
from water and two electrons from
chlorophyll
c. ATP, from ADP and inorganic phosphate
combined in the presence of energy
harnessed by chlorophyll from the sun
4. NADPH and ATP
5. The Calvin cycle is also called the light-
independent reaction. The complete process of the
Calvin cycle takes place in the stroma of the
chloroplasts.
H. Finding practical APPLICATION QUESTIONS:
application of concepts
and skills in daily living Plants apply a chemical reaction called photosynthesis to
How can you make convert carbon dioxide and water into food (glucose) and
sense of the concept of oxygen.
the lesson in your real- Chemical reactions are common to everyday life.
life context? * Cite examples of chemical reactions you encounter
in your daily life.
What are the benefits derived from these chemical
reactions?
I. Making Generalization INTERACTIVE DISCUSSION:
and Abstraction about
the lesson: (Sequence of 1.From the summary equation of photosynthesis,
Questions)
a. describe how each is involved in the light and dark
reactions.
b .point out the products that are of great importance to an
ecosystem.
2. Explain why the light reaction of photosynthesis is
Address: Macabulos Drive, San Roque, Tarlac City
Telephone No.: (045) 982-0374
Email Address: tarlac @deped.gov.ph
Republic of the Philippines
Department of Education
REGION III – CENTRAL LUZON
SCHOOLS DIVISION OF TARLAC PROVINCE
essential before the dark reaction can proceed.
3. What is the importance of photosynthesis to both plants
and animals?
4. How do energy transformations help maintain balance in
the ecosystem?
Answers:
1a.
Light reactions
Light is captured by chlorophyll that results in the
release of energized electrons
Water splits into hydrogen ions and oxygen gas in
the presence of energized electrons
Oxygen gas from water is released as a gaseous by-
product of photosynthesis
Dark reactions/ Calvin cycle
Carbon dioxide is converted into carbohydrates
using the ATP and NADPH produced in the light
reactions
2. The products of the light-dependent phase are used as
reactants in the light-independent phase. Hence, the light –
dependent phase is a perquisite to the light-independent
phase.
3. The process of photosynthesis makes it possible for
herbivores and omnivores to feed on plants. The by-product
of photosynthesis is glucose and oxygen. The oxygen
produced is needed by animals for respiration.
4. The chemical reactions of photosynthesis and respiration
illustrate life functions that make it possible the cycling of
materials, like oxygen and carbon dioxide. Energy is
transformed as it is used by organisms in chemical
reactions.
J. Evaluating Learning IDENTIFICATION: Choose the correct answer from the
words in the box below. Write your answer on the space
Address: Macabulos Drive, San Roque, Tarlac City
Telephone No.: (045) 982-0374
Email Address: tarlac @deped.gov.ph
Republic of the Philippines
Department of Education
REGION III – CENTRAL LUZON
SCHOOLS DIVISION OF TARLAC PROVINCE
before each number.
stroma light reaction
glucose dark reaction
thylakoids chloroplasts
chlorophyll water
ATP and NADPH carbon dioxide
_____________1. The green, light trapping
pigment(chlorophyll)
_____________2. High energy organic molecule formed
during dark reaction(glucose)
_____________3. The part in the chloroplasts where
synthesis of glucose takes place(stroma)
_____________4. Compound involved in the production of
oxygen during photosynthesis(water)
_____________5.Specific site for light dependent
reactions(thylakoids)
_____________6. Organelle for photosynthesis
(chloroplast)
_____________7.product/s of light reactions that are used
in the dark reactions of photosynthesis(ATP and NADPH)
_____________8. Utilizes ATP and NADPH to build
carbohydrates(dark reaction)
_____________9.The photo- part of photosynthesis(light
reaction)
_____________10. The source of carbon for making
biomolecules(carbon dioxide)
K. Additional activities for Create a song or a rap that explains what happens during
Application or a. Light reaction of photosynthesis
Remediation b. Dark reaction of photosynthesis
The product/performance will be assessed based on the
following criteria:
Accuracy of content and explanation
Organization and coherence of idea
Clarity of message
Creativity
IX. REMARKS
Address: Macabulos Drive, San Roque, Tarlac City
Telephone No.: (045) 982-0374
Email Address: tarlac @deped.gov.ph
Republic of the Philippines
Department of Education
REGION III – CENTRAL LUZON
SCHOOLS DIVISION OF TARLAC PROVINCE
X. REFLECTION
A. No. of learners who
earned 80% in the
Evaluation:
B. No. of learners who
require additional
activities for
remediation who scored
below 80%:
C. Did the remedial work?
No. of learners who
have caught up with the
lesson:
D. No. of learners who
continue to require
remediation:
E. Which of my teaching
strategies worked well?
Why did this work?
F. What difficulties did I
encounter which my
principal or superior can
help me solve?
G. What innovations or
localized materials did
I use/ discover which I
wish to share with other
teachers
Prepared by:
PHILIP B. GALIZA
Teacher III
Checked by:
MARITA F. GARILLES
OIC – HT
Address: Macabulos Drive, San Roque, Tarlac City
Telephone No.: (045) 982-0374
Email Address: tarlac @deped.gov.ph
Republic of the Philippines
Department of Education
REGION III – CENTRAL LUZON
SCHOOLS DIVISION OF TARLAC PROVINCE
Noted:
VILMA B. AGUAS,EDD
Principal III
DAILY LESSON LOG IN SCIENCE GRADE 9
Name of Teacher:PHILIP B. GALIZA Quarter: First Date/Day: Oct. 19,
2022
I .OBJECTIVES
A. Content Standards The learners demonstrate understanding of
a. The structure and function of plant parts and organelle
involved in photosynthesis
B. Performance Standards: The learners should be able to design and conduct an
investigation to provide evidence that plants can
manufacture their own food.
C. Learner’s Competencies / Differentiate basic features and importance of
Code: photosynthesis and respiration ( S9LT – Ig – j – 31)
*Specific Objectives (3 Skills a Day)
1. Cognitive* Cite an indication that oxygen is produced in
photosynthesis.
2.Psychomotor* Conduct an investigation to provide evidence that plants
can manufacture their own food.
3. Affective* Show appreciation of the significance of photosynthesis in
food and energy production.
II. CONTENT
Topic ECOSYSTEM: LIFE ENERGY
Sub Topic PHOTOSYSNTHESIS
III. LEARNING RESOURCES
A. REFERENCES
1.Teacher’s Guide 2.Learner’s Material Pages 1. Textbook Pages
Page 10 79 – 80
Address: Macabulos Drive, San Roque, Tarlac City
Telephone No.: (045) 982-0374
Email Address: tarlac @deped.gov.ph
Republic of the Philippines
Department of Education
REGION III – CENTRAL LUZON
SCHOOLS DIVISION OF TARLAC PROVINCE
2. Additional Materials from LR Portal
B. Other Learning Resources: passnow.com/classwork-exercise-and-series-
biology-ss1-evidence-of-photosynthesis-in-plant/
5. PROCEDURES
A. Reviewing previous lesson Recall the summary equation of photosynthesis.
(or) presenting the new lesson
1. What requirements in the environment are needed to
undergo photosynthetic process?
2. What are the products of photosynthetic activity?
B. Establishing a purpose to the Ask the learners:
lesson How do you know that plants really manufacture their own
food?
(Students’ responses will be based from their prior
understanding).
C. Presenting examples/ The teacher will discuss and explain evidence/s showing
instances of the lesson that plants are really capable of making food.
Concepts:
Photosynthesis is the process by which green plants
convert carbon dioxide and water, in the presence
of sunlight, to glucose and oxygen. The glucose
that is produced is used as an energy source or
converted to starch for storage.
The presence of starch in a leaf is a direct evidence
that photosynthesis has taken place.
Starch can be detected by the iodine test. In this
test, leaf is boiled in water and then boiled in
ethanol until it decolorizes. The decolorized leaf is
then washed with water and a few drops of iodine
solution are placed on it. If the leaf turns blue-
black, starch is present in it.
D. Discussing new concepts and Let the students perform activities that will show pieces of
practicing new skills #1. evidence that plants are really capable of making food.
ACTIVITY 4A - Oxygen and Photosynthesis
Address: Macabulos Drive, San Roque, Tarlac City
Telephone No.: (045) 982-0374
Email Address: tarlac @deped.gov.ph
Republic of the Philippines
Department of Education
REGION III – CENTRAL LUZON
SCHOOLS DIVISION OF TARLAC PROVINCE
Objective:
To show that oxygen is produced by photosynthesis( Santan
leaf can be used if Elodea or Hydrilla is not available)
Materials:
test tube
water
available plant sample
Procedure:
1. Place fresh mature Santan leaf or Elodea or Hydrilla
inside a test tube. Add water to the test tube to cover the
leaf or plant.
2. Leave the setup for about 3 to 5 minutes at room
temperature (29 0C).
3. Observe the set up.
Guide Questions:
1 .What did you see on the leaf/plant?
2. Did you see any bubbles in the setup?
3. What do these bubbles indicate?
Answers:
1. Bubbles were seen on the surface of the leaf.
2. Yes, there are bubbles seen in the setup.
3. These bubbles indicate that the leaf releases gas (O 2)
E. Discussing new concepts ACTIVITY 4B – Presence of Starch in a Leaf
and practicing new skill
#2. Objective:
To show that sugar is produced by photosynthesis
Materials:
tincture of iodine
denatured alcohol
water bath
alcohol lamp
medicine dropper
beaker
Address: Macabulos Drive, San Roque, Tarlac City
Telephone No.: (045) 982-0374
Email Address: tarlac @deped.gov.ph
Republic of the Philippines
Department of Education
REGION III – CENTRAL LUZON
SCHOOLS DIVISION OF TARLAC PROVINCE
petri dish
tripod
wire gauze
box of matches
fresh leaf of mayana
Procedure:
1.Get a coleus leaf (mayana)
Remove the leaf color by boiling it in alcohol. To do this,
follow the steps below:
A. Fill the beaker (¾ of its capacity) with water. Let it
boil. See Figure 3 for the sample setup (Science
Learner’s Module, page 80).
B. While waiting for the water to boil, get a leaf
sample and place it in a test tube. Pour denatured
alcohol into the test tube until the leaf has been
submerged. See Figure 3 for the sample setup.
C. When the water in the beaker boils, place the test
tube with leaf and alcohol in it. Let the water boil
for another three minutes or until all the color of
the leaf has been extracted. See Figure 4 for the
sample setup (Science Learner’s Module, page 80).
Remove the test tube from the beaker. Then get, the
leaf out of the test tube.
3. Rinse the leaf with water, and then place it on a petri
dish.
4. Put drops of iodine, until the leaf has been soaked.
5. Observe the leaf
If the color of the leaf turns to bluish black, it indicates the
presence of starch. No change in color indicates absence of
starch.
Guide Question:
1. What can you infer from your observation?
Possible Answers:
The leaf can perform photosynthesis.
The leaf contains starch.
The leaf can produce sugar or starch.
Green parts of the plant can produce sugar.
Address: Macabulos Drive, San Roque, Tarlac City
Telephone No.: (045) 982-0374
Email Address: tarlac @deped.gov.ph
Republic of the Philippines
Department of Education
REGION III – CENTRAL LUZON
SCHOOLS DIVISION OF TARLAC PROVINCE
Conclusion:
Since the leaf in the real experiment turned blue-black with
iodine solution, it shows that photosynthesis has taken place
or starch is formed by the leaf.
F. Discussing new concepts Let the learners discuss the importance of photosynthesis in
and practicing new food and energy production.
skills #3.
(Students’ responses may vary)
G. Developing Mastery SELF-CHECK*
1. How do we know that oxygen is produced during
photosynthesis?
2. How are leaves tested for starch?
Answers:
1.The bubbles produced in the setup indicate that the leaf
releases gas (O2)
2. We test the leaf with iodine solution. Iodine solution
turns blue-black when starch is present.
H. Finding practical APPLICATION QUESTIONS:
application of concepts
and skills in daily living 1. Cite evidence that you’ve really work hard in the
How can you make achievement of your goal/s in life.
sense of the concept of 2. In life, we encounter problems/challenges every day.
the lesson in your real- Where do we get our ENERGY in facing these
life context? * challenges?
What/Who motivates us to strive and go on with
our lives?
(Students’ responses may vary)
I. Making Generalization INTERACTIVE DISCUSSION:
and Abstraction about
the lesson: (Sequence of 1. Cite an evidence that plants can manufacture food.
Questions) 2. How will you prove that starch is formed during
Address: Macabulos Drive, San Roque, Tarlac City
Telephone No.: (045) 982-0374
Email Address: tarlac @deped.gov.ph
Republic of the Philippines
Department of Education
REGION III – CENTRAL LUZON
SCHOOLS DIVISION OF TARLAC PROVINCE
photosynthesis?
Answers:
1. We can use the presence of starch in a leaf as a proof of
photosynthesis.
2. Starch can be detected by the iodine test. Iodine solution
turns blue-black when starch is present
J. Evaluating Learning ESSAY:
1. How to prove that photosynthesis has taken place?
Answer:
1. The presence of starch in a leaf is direct evidence that
photosynthesis has taken place. Starch can be detected by
the iodine test.
K. Additional activities for PAMPHLET/BROCHURE MAKING:
Application or Create a pamphlet/brochure containing the following:
Remediation a. The significance of eating food
b. Ways of improving photosynthesis
Your product will be assessed based on the following
criteria:
1.Accuracy of content and explanation
2.Organization and coherence of ideas
3.Clarity of message
4.Creativity
6. REMARKS
7. REFLECTION
A. No. of learners who
earned 80% in the
Evaluation:
B. No. of learners who
require additional
activities for
remediation who scored
below 80%:
C. Did the remedial work?
Address: Macabulos Drive, San Roque, Tarlac City
Telephone No.: (045) 982-0374
Email Address: tarlac @deped.gov.ph
Republic of the Philippines
Department of Education
REGION III – CENTRAL LUZON
SCHOOLS DIVISION OF TARLAC PROVINCE
No. of learners who
have caught up with the
lesson:
D. No. of learners who
continue to require
remediation:
E. Which of my teaching
strategies worked well?
Why did this work?
F. What difficulties did I
encounter which my
principal or superior can
help me solve?
G. What innovations or
localized materials did
I use/ discover which I
wish to share with other
teachers
Prepared by:
PHILIP B. GALIZA
Teacher III
Checked by:
MARITA F. GARILLES
OIC – HT
Noted:
VILMA B. AGUAS,EDD
Principal III
DAILY LESSON LOG IN SCIENCE GRADE 9
Address: Macabulos Drive, San Roque, Tarlac City
Telephone No.: (045) 982-0374
Email Address: tarlac @deped.gov.ph
Republic of the Philippines
Department of Education
REGION III – CENTRAL LUZON
SCHOOLS DIVISION OF TARLAC PROVINCE
PROPO Name of Teacher:PHILIP B. GALIZA Quarter: First Date/Day:
Oct. 20, 2022
I.OBJECTIVES
A. Content Standards The learners demonstrate understanding of
a. The structure and function of plant parts and organelle
involved in photosynthesis
B. Performance Standards: The learners should be able to design and conduct an
investigation to provide evidence that plants can
manufacture their own food.
C. Learner’s Competencies / Differentiate basic features and importance of
Code: photosynthesis and respiration ( S9LT – Ig – j – 31)
*Specific Objectives (3 Skills a Day)
1. Cognitive* Describe the key factors affecting the rate of
photosynthesis.
2. Psychomotor* Conduct an investigation showing the effect of light on the
rate of photosynthesis.
3. Affective* Recognize and show appreciation of the importance of
photosynthesis on the quality and quantity of harvest.
II.CONTENT
Topic ECOSYSTEM: LIFE ENERGY
Sub Topic PHOTOSYNTHESIS
III.LEARNING RESOURCES
D. REFERENCES
1.Teacher’s Guide Page 2.Learner’s 3. Textbook Pages
12 Material
Pages 81 - 85
4. Additional Materials from LR Portal
Other Learning Resources: sites.google.com/site/plantsmake food/discussion/factors-
affecting-the-rate-of-photosynthesis
youtube.com/watch?v=J0KxRX3fol
IV. PROCEDURES
A. Reviewing previous lesson The teacher will introduce the question of what happens to
(or) presenting the new lesson the rate of photosynthesis if various environmental factors
are varied.
Ideas from the class may be solicited in order to set the
lesson.
Address: Macabulos Drive, San Roque, Tarlac City
Telephone No.: (045) 982-0374
Email Address: tarlac @deped.gov.ph
Republic of the Philippines
Department of Education
REGION III – CENTRAL LUZON
SCHOOLS DIVISION OF TARLAC PROVINCE
(Students’ responses may vary)
B. Establishing a purpose to the THINK/PAIR/SHARE:
lesson
Can you think with an environmental factor which will
affect the rate of photosynthesis?
Share and discuss with your partner and the other groups in
the class.
Possible Answers:
Factors affecting the Rate of Photosynthesis are:
1. Light
2. Temperature
3. Carbon dioxide
4. Chlorophyll
C. Presenting examples/ Study the figures. Familiarize yourselves on how each
instances of the lesson factor affects the rate of photosynthesis.
Factors Affecting the Rate of Photosynthesis
1. Light
Figure 1.
The rate of photosynthesis increases as the light gets
brighter.
The rate of photosynthesis increases linearly with
Address: Macabulos Drive, San Roque, Tarlac City
Telephone No.: (045) 982-0374
Email Address: tarlac @deped.gov.ph
Republic of the Philippines
Department of Education
REGION III – CENTRAL LUZON
SCHOOLS DIVISION OF TARLAC PROVINCE
increasing light intensity (from point A to point B
on the graph). Gradually the rate falls and at a
certain light intensity, the rate of
photosynthesis remain constant (from point B to
point C on the graph).
Too much light at a high intensity can damage
chloroplasts.
2. Temperature
Figure 2.
The higher the temperature then typically the
greater the rate of photosynthesis, photosynthesis is
a chemical reaction and the rate of most chemical
reactions increases with temperature.
For photosynthesis at temperatures above 40°C the
rate slows down. This is because the enzymes
involved in the chemical reactions of
photosynthesis are temperature sensitive and
destroyed at higher temperatures.
3.Carbon dioxide
Figure 3
Address: Macabulos Drive, San Roque, Tarlac City
Telephone No.: (045) 982-0374
Email Address: tarlac @deped.gov.ph
Republic of the Philippines
Department of Education
REGION III – CENTRAL LUZON
SCHOOLS DIVISION OF TARLAC PROVINCE
An increase in concentration of carbon dioxide gives an
increase in the rate of photosynthesis.
The rate of photosynthesis increases linearly with
increasing carbon dioxide concentration (from
point A to point B on the graph).At a certain carbon
dioxide concentration, the rate of photosynthesis
remain constant (from point B to point C on the
graph). Hence, a rise in carbon dioxide levels has
no effect on the rate of photosynthesis as the other
factors such as light intensity and temperature
become limiting.
4.Chlorophyll
Leaves with more chlorophyll are better able to absorb the
light required for photosynthesis.
Chlorophyll absorbs the light required to convert
carbon dioxide and water into glucose.
Chlorophyll is green - so absorbs the red and blue
parts of the electromagnetic spectrum and reflects
the green part of the spectrum
SOURCES:
sites.google.com/site/plantsmake food/discussion/factors-
Address: Macabulos Drive, San Roque, Tarlac City
Telephone No.: (045) 982-0374
Email Address: tarlac @deped.gov.ph
Republic of the Philippines
Department of Education
REGION III – CENTRAL LUZON
SCHOOLS DIVISION OF TARLAC PROVINCE
affecting-the-rate-of-photosynthesis
youtube.com/watch?v=J0KxRX3fol
D. Discussing new concepts and After analyzing and interpreting the various figures
practicing new skills #1. illustrating how the key factors affect the rate of
photosynthesis, students will be asked the following
questions:
Checking of Ideas:
1. What is the relationship of light intensity and
photosynthesis?
2. What will happen to the chloroplast in the presence
of too much light at a high intensity?
3. How temperature and photosynthesis are related?
4. What happens to the rate of photosynthesis as the
temperature exceeds 40 C? Explain.
5. How carbon dioxide concentration affects the rate of
photosynthetic activity?
6. How chlorophyll affects the photosynthetic process?
Answers:
1. The rate of photosynthesis increases when the light gets
better.
2. Too much light at a high intensity can damage the
chloroplasts.
3. The higher the temperature, the greater the rate of
photosynthesis.
4. The rate of photosynthesis slows down because the
enzymes involved in the chemical reactions of
photosynthesis are temperature sensitive and destroyed at
higher temperatures.
5. An increase in the concentration of carbon dioxide gives
an increase in the rate of photosynthesis.
6. Leaves with more chlorophyll are better able to absorb
the light required for photosynthesis.
E. Discussing new concepts Investigating the Effect of Light on the Rate of
and practicing new skill Photosynthesis
Address: Macabulos Drive, San Roque, Tarlac City
Telephone No.: (045) 982-0374
Email Address: tarlac @deped.gov.ph
Republic of the Philippines
Department of Education
REGION III – CENTRAL LUZON
SCHOOLS DIVISION OF TARLAC PROVINCE
#2.
ACTIVITY 5A - Light Intensity and Photosynthesis
Objective:
To show the effect of light on the rate of photosynthesis
Materials:
2 – 250 ml beakers
2 funnels
500 ml water
scotch tape
2 test tubes
2 santan leaf or twigs of hydrilla or elodea
used carbon paper
Procedure:
1. Make two setups similar to Figure 5.( See Science
Learner’s Module, page 81 )
2. Take 2-3 pcs of small mature Santan leaves or sprigs of
healthy hydrilla and place them in a glass funnel.
3. Insert the funnel in a beaker of water.
4. Invert a test tube full of water over the stem of the
funnel.
5. Leave one of the setup in sunlight for three minutes. At
the same time, cover the other setup with a carbon paper in
a shaded area or cabinet.
6. Count the number of bubbles every 30 seconds and
record it in the observation table.
CAUTION:
Do not insert the glowing splinter without the teacher’s
supervision.
OPTIONAL: Remove the test tube carefully and insert a
glowing splinter deep into it. The splinter burns brightly. It
indicates that oxygen is the gas collected in the test tube.
OBSERVATION TABLE
Time ( seconds ) No. of Bubbles Produced
Exposed leaf Covered leaf
Address: Macabulos Drive, San Roque, Tarlac City
Telephone No.: (045) 982-0374
Email Address: tarlac @deped.gov.ph
Republic of the Philippines
Department of Education
REGION III – CENTRAL LUZON
SCHOOLS DIVISION OF TARLAC PROVINCE
30
60
90
120
150
180
210
Guide Questions:
1. Which setup produced more bubbles?
2. What do the bubbles indicate?
3. What happens to the number of bubbles as time passed?
4. How did you know that photosynthesis has taken place?
5. How does the amount of light affect the rate of
photosynthesis?
Answers:
1.The setup that is exposed to sunlight
2.The bubbles indicate that there is photosynthesis
3.The number of bubbles also increases
4.Production of bubbles indicates that photosynthesis takes
place
5. As the intensity of light increases, the rate of
photosynthesis also increases.
F. Discussing new concepts GROUP SHARING:
and practicing new
skills #3. Let the students discuss the following:
1. The importance of photosynthesis in relation to the
quality and quantity of harvest/yield.
2. Various ways to enhance photosynthesis resulting in
better harvest.
Address: Macabulos Drive, San Roque, Tarlac City
Telephone No.: (045) 982-0374
Email Address: tarlac @deped.gov.ph
Republic of the Philippines
Department of Education
REGION III – CENTRAL LUZON
SCHOOLS DIVISION OF TARLAC PROVINCE
(Students’ responses may vary)
G. Developing Mastery
Answer the Self-Check below
SELF – CHECK*
Given the following situations, discuss and explain the
factors affecting the rate of photosynthesis. Justify why you
agree or disagree. Share your answers with the class.
Question 1
Plant A is placed in a room by the window and plant B is
placed on the open field. Assuming all other factors remain
constant (same amount of carbon dioxide and water), which
plant will have a high rate of photosynthesis? Why?
Explain your answer.
Question 2
The higher the temperature, the greater the rate of
photosynthesis. Is this statement always true? Give reasons
to support your answer.
Question 3
Plant A and plant B are placed in a room with direct
sunlight. However, plant A is placed in an enclosed glass
box. Will plant A have the same rate of photosynthesis as
plant B Why? Explain your answer.
(Students’ responses may vary)
H. Finding practical APPLICATION QUESTIONS:
application of concepts
Address: Macabulos Drive, San Roque, Tarlac City
Telephone No.: (045) 982-0374
Email Address: tarlac @deped.gov.ph
Republic of the Philippines
Department of Education
REGION III – CENTRAL LUZON
SCHOOLS DIVISION OF TARLAC PROVINCE
and skills in daily living 1. Imagine that you are a carbon atom, You have just
How can you make undergone photosynthesis. How will you describe your
sense of the concept of chemical journey?
the lesson in your real-
life context? 2. What are the key factors that must be considered in the
achievement of your dreams?
(Students’ responses may vary)
I. Making Generalization INTERACTIVE DISCUSSION:
and Abstraction about
the lesson: (Sequence of What are the factors affecting the rate of photosynthesis?
Questions) Explain how each factor affects the rate of photosynthetic
activity.
J. Evaluating Learning Worksheet: Limiting Factors of Photosynthesis
In this worksheet, we will practice describing and
explaining the effects of temperature, light intensity and
carbon dioxide concentration on the rate of
photosynthesis.
1. Why will an increase in carbon dioxide concentration
result in an increase in the rate of photosynthesis?
a. Carbon dioxide provides the energy needed for
photosynthesis.
b. Carbon dioxide is a reactant and a raw material needed
for photosynthesis.
c. Carbon dioxide acts as a catalyst to speed up the rate of
reaction. d. Carbon dioxide is a product of photosynthesis
2. Complete the following statements with “increase,”
“decrease,” or “have no effect on.”
An increase in the amount of chlorophyll in the leaf
will_____the rate of photosynthesis.
a. increase
b. decrease
c. have no effect on
Address: Macabulos Drive, San Roque, Tarlac City
Telephone No.: (045) 982-0374
Email Address: tarlac @deped.gov.ph
Republic of the Philippines
Department of Education
REGION III – CENTRAL LUZON
SCHOOLS DIVISION OF TARLAC PROVINCE
A decrease in carbon dioxide availability
will_____ the rate of photosynthesis.
a. decrease
b. increase
c. have no effect on
3. Which of the following is not a major limiting factor for
the rate of photosynthesis?
a. carbon dioxide concentration
b. temperature
c. light intensity
d. oxygen concentration
4. Why will a decrease in light intensity result in a decrease
in the rate of photosynthesis?
a. A decrease in light intensity means a decrease in the
energy required for photosynthesis to take place.
b. A decrease in light intensity means the enzymes that
control photosynthesis may denature.
c. A decrease in light intensity means an increase in the
energy required for photosynthesis to take place.
d. A decrease in light intensity means a decrease in the
available reactants needed for photosynthesis.
5. When investigating biological reactions, which of the
following best explains the term “limiting factor”?
a. A factor that must be removed before a reaction can take
place
b. A factor that must have its impact limited before a
reaction can take place
c. A factor that speeds up the rate of reaction without being
used up
d. A factor that restricts the rate of a reaction
Address: Macabulos Drive, San Roque, Tarlac City
Telephone No.: (045) 982-0374
Email Address: tarlac @deped.gov.ph
Republic of the Philippines
Department of Education
REGION III – CENTRAL LUZON
SCHOOLS DIVISION OF TARLAC PROVINCE
Answers:
1. B
2. A
A
3. D
4. B
5. D
K. Additional activities for CONDUCTING AN INTERVIEW:
Application or
Remediation Interview a farmer who grows a different crop from rice.
Write down his or her farming practices.
Explain how each activity enhances photosynthesis.
B. Put up a Home Vegetable Garden.” Apply the various
strategies/activities practiced to enhance photosynthesis and
food production.
V. REMARKS
VI. REFLECTION
A. No. of learners who
earned 80% in the
Evaluation:
B. No. of learners who
require additional
activities for
remediation who scored
below 80%:
C. Did the remedial work?
No. of learners who
have caught up with the
lesson:
D. No. of learners who
continue to require
remediation:
E. Which of my teaching
strategies worked well?
Why did this work?
F. What difficulties did I
encounter which my
Address: Macabulos Drive, San Roque, Tarlac City
Telephone No.: (045) 982-0374
Email Address: tarlac @deped.gov.ph
Republic of the Philippines
Department of Education
REGION III – CENTRAL LUZON
SCHOOLS DIVISION OF TARLAC PROVINCE
principal or superior can
help me solve?
G. What innovations or
localized materials did
I use/ discover which I
wish to share with other
teachers
Prepared by:
PHILIP B. GALIZA
Teacher III
Checked by:
MARITA F. GARILLES
OIC – HT
Noted:
VILMA B. AGUAS,EDD
Principal III
Address: Macabulos Drive, San Roque, Tarlac City
Telephone No.: (045) 982-0374
Email Address: tarlac @deped.gov.ph
You might also like
- Kami Export - Maxwell Modeste - Photosynthesis Case Study - Killing ChloroplastsDocument7 pagesKami Export - Maxwell Modeste - Photosynthesis Case Study - Killing ChloroplastsMaxwell Modeste0% (2)
- Cape Biology Unit 2 CompleteDocument92 pagesCape Biology Unit 2 CompleteBisham Siew75% (4)
- LP Biological MacromoleculesDocument5 pagesLP Biological MacromoleculesDexter Jess Dag-uman100% (7)
- Cot-1 Lesson Plan (Grade 9)Document9 pagesCot-1 Lesson Plan (Grade 9)Marlon S. Baranggan100% (3)
- Photosynthesis Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesPhotosynthesis Lesson PlanEldie Ocariza100% (2)
- ELS Q2 M3 Introduction To Life ScienceDocument20 pagesELS Q2 M3 Introduction To Life ScienceKath Tan Alcantara86% (7)
- QUESTIONAIRE Basic ResaerchDocument4 pagesQUESTIONAIRE Basic Resaerchphilip galiza100% (5)
- Interrelationship Between Carbohydrate Protein Fat MetabolismDocument12 pagesInterrelationship Between Carbohydrate Protein Fat MetabolismShailaja Neaupane100% (5)
- Semi-Detailed Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesSemi-Detailed Lesson Planjoselyn bergonia100% (1)
- DLP - August 2, 2018Document3 pagesDLP - August 2, 2018Vee Jay BlanciaNo ratings yet
- 1st QT - PhotosynthesisDocument4 pages1st QT - PhotosynthesisTEREMIE JOSEPH OBADONo ratings yet
- SCIENCE-9 Q1 W6-W7 Mod5 ADM-1-photosythesisDocument42 pagesSCIENCE-9 Q1 W6-W7 Mod5 ADM-1-photosythesisJB Dar100% (1)
- DLL TemplateDocument8 pagesDLL TemplateCristelle EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Final Demo Teaching Lesson Plan NemenzoDocument13 pagesFinal Demo Teaching Lesson Plan Nemenzoapi-652151038No ratings yet
- General Biology 1 Q2 Week 2 - 075858Document11 pagesGeneral Biology 1 Q2 Week 2 - 075858raymondreyremandaban2007No ratings yet
- PT1 GuevarraDocument3 pagesPT1 GuevarraAkeelah EstacioNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 9 (1) - MELC 5 - Reviewed by CommitteeDocument14 pagesSCIENCE 9 (1) - MELC 5 - Reviewed by CommitteeBayani VicencioNo ratings yet
- General Biology-Q2-Week 2Document15 pagesGeneral Biology-Q2-Week 2ALFREDO CALEDANo ratings yet
- Science 8 - 6.1Document5 pagesScience 8 - 6.1Sherine Marianne IgnacioNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan SampleDocument7 pagesLesson Plan SampleVILLA 2 ANACITA LOCIONNo ratings yet
- Technical Assistance Lesson PlanDocument8 pagesTechnical Assistance Lesson PlanJaybie TejadaNo ratings yet
- Barba Lesson-Exemplar Cot1Document6 pagesBarba Lesson-Exemplar Cot1Rodney BarbaNo ratings yet
- DLL-Cellular RespirationDocument4 pagesDLL-Cellular RespirationCyril Alba ConstantinoNo ratings yet
- Science 8 SLM16Document15 pagesScience 8 SLM16Cristian ErfeNo ratings yet
- Research Vinegar MakingDocument7 pagesResearch Vinegar MakingJosef EscobarNo ratings yet
- Science 9 Q1 W8Document5 pagesScience 9 Q1 W8Abram BaranganNo ratings yet
- Bixby Knolls Preparatory Academy - San Antonio, Quezon: Science and Technology 8Document3 pagesBixby Knolls Preparatory Academy - San Antonio, Quezon: Science and Technology 8Oliver VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- AUREEN ICBAN Pedagogically Designed LP, - EARTH AND LIFE SCIENCEDocument4 pagesAUREEN ICBAN Pedagogically Designed LP, - EARTH AND LIFE SCIENCEJonathan OlegarioNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: (Ngaran Han Leksyon)Document5 pagesDepartment of Education: (Ngaran Han Leksyon)Teacher MitzeNo ratings yet
- Science 9 Q1 W9Document4 pagesScience 9 Q1 W9Abram BaranganNo ratings yet
- DLL Biotechnology - July 15 - 19Document3 pagesDLL Biotechnology - July 15 - 19MichaelAbdonDomingoFavoNo ratings yet
- Senior High LP - Energy FlowDocument3 pagesSenior High LP - Energy Flowking devesfrutoNo ratings yet
- DLL Science 8Document7 pagesDLL Science 8Paradillo Regatuna LesterNo ratings yet
- Nuguid, Rochelle D - Assessment InstrumentDocument16 pagesNuguid, Rochelle D - Assessment InstrumentRochelle NuguidNo ratings yet
- Senior High LP - BioenergeticsDocument2 pagesSenior High LP - Bioenergeticsking devesfruto100% (2)
- Lesson Exemplar in Science 9 - MELC 5Document18 pagesLesson Exemplar in Science 9 - MELC 5Michael SocuajeNo ratings yet
- DLL SHS STEM Grade 12 - General Biology1 Quarter1 Week2 (Palawan Division)Document17 pagesDLL SHS STEM Grade 12 - General Biology1 Quarter1 Week2 (Palawan Division)Ann Quirante100% (3)
- Science 8 - Q4 - Week 6Document23 pagesScience 8 - Q4 - Week 6EyphRhylle100% (1)
- General Biology - Q2 - Week 2Document23 pagesGeneral Biology - Q2 - Week 2Renard JaenNo ratings yet
- LESSON PLAN Practice Teaching - AFT - Putri Dyah AstariDocument9 pagesLESSON PLAN Practice Teaching - AFT - Putri Dyah AstariAfnestya100% (1)
- Revised Q1 WHLP in ConChemDocument4 pagesRevised Q1 WHLP in ConChemChianlee CarreonNo ratings yet
- Classes of AntropodsDocument3 pagesClasses of AntropodsArchemedes BarrocaNo ratings yet
- Cot Lesson JanDocument7 pagesCot Lesson JanSittie Asyah Solaiman EdrisNo ratings yet
- DLL 9Document5 pagesDLL 9Jonathan TabbunNo ratings yet
- Aldin LP FinalDocument13 pagesAldin LP FinalMelvin Cabonegro100% (1)
- Daily Lesson Log Earth and Life Science For CotDocument2 pagesDaily Lesson Log Earth and Life Science For CotMARY JOSEPH OCONo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan in Science 7Document4 pagesLesson Plan in Science 7Alegna Bajado50% (2)
- Lesson Plan On NutritionDocument4 pagesLesson Plan On NutritionJENNY MAY SUDAY100% (1)
- School Grade Level Teacher Learning Area Time & Dates Quarter I. ObjectivesDocument6 pagesSchool Grade Level Teacher Learning Area Time & Dates Quarter I. ObjectivesPatrick Jerome SilvanoNo ratings yet
- Cot 2 - 2024 - Energy TransferDocument4 pagesCot 2 - 2024 - Energy TransferFatima Abacan ReyesNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science Quarter 2 Mod 2Document11 pagesEarth and Life Science Quarter 2 Mod 2Lovely Rose Jardin OzoNo ratings yet
- Bio1 Q2 M2 Revised RemovedDocument13 pagesBio1 Q2 M2 Revised RemovedClaries HeyrosaNo ratings yet
- AntropodsDocument3 pagesAntropodsArchemedes BarrocaNo ratings yet
- DLP April 11 GenBio2Document2 pagesDLP April 11 GenBio2Elaiza marie VenusNo ratings yet
- COT 1 (2nd Sem - 3rd Q - PHYS)Document10 pagesCOT 1 (2nd Sem - 3rd Q - PHYS)Helen Grace SentinaNo ratings yet
- School Grade Level Teacher Quarter Learning Area Teaching Dates &durationDocument3 pagesSchool Grade Level Teacher Quarter Learning Area Teaching Dates &durationmaryjoy cacaldoNo ratings yet
- ELS Q2 M3 Intro-to-Life-Science 16pDocument16 pagesELS Q2 M3 Intro-to-Life-Science 16pYella SerranoNo ratings yet
- A SemiDocument4 pagesA SemiJhEng Cao Manansala100% (1)
- Lesson Plan in Physical Science COT 1 2022 2023Document4 pagesLesson Plan in Physical Science COT 1 2022 2023Taten Balmes100% (2)
- Content Standard Performance Standard Learning Competency I. Learning ObjectivesDocument10 pagesContent Standard Performance Standard Learning Competency I. Learning ObjectivesNur ShaNo ratings yet
- Cot DLP For A Video LessonDocument4 pagesCot DLP For A Video LessonLhea Joy T. CiprianoNo ratings yet
- April 14-27 DLLL GB2Document3 pagesApril 14-27 DLLL GB2Race De VillaNo ratings yet
- Science Melc g9 q1 Week 4 DLLDocument35 pagesScience Melc g9 q1 Week 4 DLLphilip galizaNo ratings yet
- Science MELC-G9-Q1-WEEK-5-DLLDocument39 pagesScience MELC-G9-Q1-WEEK-5-DLLphilip galizaNo ratings yet
- Thesis Physical ActivityDocument46 pagesThesis Physical Activityphilip galizaNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 2 Quantitative ResearchDocument25 pagesPractical Research 2 Quantitative Researchphilip galizaNo ratings yet
- Community-Service PBGDocument9 pagesCommunity-Service PBGphilip galizaNo ratings yet
- Advances in PhotosynthesisDocument305 pagesAdvances in PhotosynthesisVidyasagar DeshpandeNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry For CLDocument5 pagesBiochemistry For CLGashaw TilahunNo ratings yet
- Biology M5 Cellular RespirationDocument30 pagesBiology M5 Cellular RespirationjtNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Module 2Document3 pagesBiochemistry Module 2Sanee ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Norme SangeDocument2 pagesNorme SangePS NINo ratings yet
- Acid-Base Balance Study GuideDocument2 pagesAcid-Base Balance Study GuideNoah ClevengerNo ratings yet
- Energy Zones in SwimmingDocument12 pagesEnergy Zones in SwimmingShean landrei labalanNo ratings yet
- Bioenergetics and Oxidative PhosphorylationDocument32 pagesBioenergetics and Oxidative PhosphorylationShimmering MoonNo ratings yet
- Autotrophic NutritionDocument22 pagesAutotrophic NutritionBWAMBALE HARISONNo ratings yet
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Fermentation and Aerobic RespirationDocument10 pagesAdvantages and Disadvantages of Fermentation and Aerobic RespirationIan Gabriel MayoNo ratings yet
- Topic 5 - Energy Transfers in and Between Organisms: Definitions and Concepts For AQA Biology A-LevelDocument5 pagesTopic 5 - Energy Transfers in and Between Organisms: Definitions and Concepts For AQA Biology A-LevelsamNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Biology The Unity and Diversity of Life 12th EditionDocument11 pagesTest Bank For Biology The Unity and Diversity of Life 12th Editionandrewduffydckjxfspnq100% (37)
- Back To Basics Critical Care Transport Review Course Simple Rules For Arterial Blood Gas InterpretationDocument12 pagesBack To Basics Critical Care Transport Review Course Simple Rules For Arterial Blood Gas Interpretationedderj2585No ratings yet
- BMSC 230 Noted Chapter 2Document3 pagesBMSC 230 Noted Chapter 2shakshi dhruvNo ratings yet
- Fermentation Processes and Their Application PDFDocument8 pagesFermentation Processes and Their Application PDFninasabelita100% (9)
- 8.2 Cell Respiration - WSDocument16 pages8.2 Cell Respiration - WS한서현No ratings yet
- Amino AcidsDocument32 pagesAmino AcidsWakjira GemedaNo ratings yet
- 8 3 PhotosynthesisDocument39 pages8 3 PhotosynthesisKhin (Darin) Hnin PhyuNo ratings yet
- Nitrogen Fixation and Nitrogen Cycle JNV PapumpareDocument5 pagesNitrogen Fixation and Nitrogen Cycle JNV PapumpareJyotiNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Biology Respiration Chapter Video 3Document14 pagesClass 10 Biology Respiration Chapter Video 3Dadi SindhuNo ratings yet
- Citric Acid ConversionDocument1 pageCitric Acid ConversionWendy TekikoNo ratings yet
- COFACTORSDocument12 pagesCOFACTORSНаталья СтилсонNo ratings yet
- Ketonuria 1Document10 pagesKetonuria 1Habib UllahNo ratings yet
- Drishya Krishnakumar 1Msc BiotechnologyDocument20 pagesDrishya Krishnakumar 1Msc BiotechnologyKarthika GokulanNo ratings yet
- Chap 12 Energy and RespirationDocument34 pagesChap 12 Energy and RespirationGeorge ApidiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9, Biols300Document31 pagesChapter 9, Biols300mariamNo ratings yet
- THE TEN REACTIONS OF GLYCOLYSIS - AND THE FATES OF PYRUVATEdocxDocument6 pagesTHE TEN REACTIONS OF GLYCOLYSIS - AND THE FATES OF PYRUVATEdocxRubylyn VillanuevaNo ratings yet