Professional Documents
Culture Documents
NIFEDIPINE
NIFEDIPINE
Uploaded by
Jv Jore VillahermosaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Drug NeurontinDocument1 pageDrug NeurontinSrkocher100% (2)
- Hydrochlorothiazide ThiazideDocument1 pageHydrochlorothiazide ThiazideE100% (1)
- Encyclopedia of Korean Folk BeliefsDocument167 pagesEncyclopedia of Korean Folk BeliefsAria7No ratings yet
- Norvasc Drug CardDocument1 pageNorvasc Drug CardSheri490No ratings yet
- RisperdalDocument2 pagesRisperdalAdrianne Bazo100% (1)
- Drug Card ToradolDocument2 pagesDrug Card ToradolAdrianne Bazo100% (1)
- Pregabalin LYricaDocument2 pagesPregabalin LYricaKristine Young100% (3)
- Naplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesFrom EverandNaplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Stress - The Different Kinds of StressDocument4 pagesStress - The Different Kinds of StressbogdanNo ratings yet
- PhenerganDocument2 pagesPhenerganKatie McPeekNo ratings yet
- Sertraline Generic Name: Sertraline Hydrochloride Brand Name: Zoloft Classification: SSRI Antidepressant Mode of ActionDocument11 pagesSertraline Generic Name: Sertraline Hydrochloride Brand Name: Zoloft Classification: SSRI Antidepressant Mode of Actionkarl montanoNo ratings yet
- Promethazine (Phenergan)Document1 pagePromethazine (Phenergan)Adrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- Drug PhenerganDocument1 pageDrug PhenerganSrkocherNo ratings yet
- Drug Study RivastigmineDocument6 pagesDrug Study RivastigmineRaijenne VersolaNo ratings yet
- Padilla-Drug StudyDocument5 pagesPadilla-Drug Studybunso padillaNo ratings yet
- Lopressor (Metoprolol) 100mgDocument2 pagesLopressor (Metoprolol) 100mgAdrianne Bazo100% (2)
- ParaDocument2 pagesParaMary Kate ClarosNo ratings yet
- Catapres (Clonidine)Document2 pagesCatapres (Clonidine)Adrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- Quetiapine - Drug StudyDocument3 pagesQuetiapine - Drug StudyJeran Henrich BusobusoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyArnel MacabalitaoNo ratings yet
- Generic Name Indication (S) Action Adverse Reaction Interaction Contraindication Patient Teaching Nursing ImplicationsDocument2 pagesGeneric Name Indication (S) Action Adverse Reaction Interaction Contraindication Patient Teaching Nursing ImplicationsJake Yvan DizonNo ratings yet
- Avapro (Irbesartan)Document2 pagesAvapro (Irbesartan)ENo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument41 pagesDrug StudyCatherine PradoNo ratings yet
- Prinivil LisinoprilDocument3 pagesPrinivil LisinoprilENo ratings yet
- AtropineDocument3 pagesAtropinegovind_soni_15No ratings yet
- Drug DigoxinDocument1 pageDrug DigoxinSrkocherNo ratings yet
- C C C Vertigo,: Electrolyte and Water Balance AgentDocument12 pagesC C C Vertigo,: Electrolyte and Water Balance AgentEarl Tony TrinidadNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument23 pagesDrug StudyJoyce Anne SupnetNo ratings yet
- SeroquelDocument1 pageSeroquelE100% (1)
- PropanolDocument8 pagesPropanolStacey CamilleNo ratings yet
- Re Me RonDocument2 pagesRe Me RonKatie McPeekNo ratings yet
- NifedipineDocument2 pagesNifedipineapi-3797941100% (3)
- Coreg (Carvedilol)Document3 pagesCoreg (Carvedilol)ENo ratings yet
- Name of Drug/ Therapeutic Class Action Indications Side Effect Nursing Considerations ParacetamolDocument7 pagesName of Drug/ Therapeutic Class Action Indications Side Effect Nursing Considerations ParacetamolAnne Monique Moran OngjocoNo ratings yet
- Dexamethasone DrugStudyDocument8 pagesDexamethasone DrugStudySophia IbuyanNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument14 pagesDrug StudyjackSNMMCNo ratings yet
- Drug DilantinDocument1 pageDrug DilantinSrkocherNo ratings yet
- Prozac (Fluoxetine) 40mgDocument1 pageProzac (Fluoxetine) 40mgENo ratings yet
- Prescribed Medication: Information Leaflet PriorDocument4 pagesPrescribed Medication: Information Leaflet PriorHavier EsparagueraNo ratings yet
- Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme (ACE)Document5 pagesAngiotensin-Converting Enzyme (ACE)Isabella SamsonNo ratings yet
- Drug LopressorDocument1 pageDrug LopressorSrkocherNo ratings yet
- Hydralazine.1 3Document1 pageHydralazine.1 3SNo ratings yet
- Bulandos BSN3-1 Duty Drug StudyDocument5 pagesBulandos BSN3-1 Duty Drug StudyRolan BulandosNo ratings yet
- PhenobarbitalDocument5 pagesPhenobarbitalapi-3797941100% (1)
- DiltiazemDocument2 pagesDiltiazemE100% (1)
- NCP DS NCM114 RleDocument12 pagesNCP DS NCM114 RleAllysa Kyle AlfonsoNo ratings yet
- Escaran - Drug Study - Set ADocument4 pagesEscaran - Drug Study - Set AFrancis Alfred EscaranNo ratings yet
- Avapro (Irbesartan)Document1 pageAvapro (Irbesartan)Adrianne Bazo100% (1)
- Medical Encyclopedia XXL: Prof. J.P. Schadé, M.D., Ph.D. D.Sc.hcFrom EverandMedical Encyclopedia XXL: Prof. J.P. Schadé, M.D., Ph.D. D.Sc.hcNo ratings yet
- Critical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsFrom EverandCritical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsNo ratings yet
- Diabetes: Complications of Diabetes: The most important information you need to improve your healthFrom EverandDiabetes: Complications of Diabetes: The most important information you need to improve your healthNo ratings yet
- Fast Facts: Optimización del tratamiento de las fluctuaciones motoras en la enfermedad de Parkinson: Adaptando el tratamiento al pacienteFrom EverandFast Facts: Optimización del tratamiento de las fluctuaciones motoras en la enfermedad de Parkinson: Adaptando el tratamiento al pacienteNo ratings yet
- Reversing Chronic Hypertension Naturally : The Healthy way to Prevent the Silent KillerFrom EverandReversing Chronic Hypertension Naturally : The Healthy way to Prevent the Silent KillerNo ratings yet
- Prediabetes Diet: A Beginner's Step-by-Step Guide to Reversing Prediabetes: Includes Curated Recipes and a Meal PlanFrom EverandPrediabetes Diet: A Beginner's Step-by-Step Guide to Reversing Prediabetes: Includes Curated Recipes and a Meal PlanNo ratings yet
- Migraines: Migraine Treatment and Prevention Options: The most important information you need to improve your healthFrom EverandMigraines: Migraine Treatment and Prevention Options: The most important information you need to improve your healthNo ratings yet
- The Diabetic Neuropathy Mastery Bible: Your Blueprint for Complete Diabetic Neuropathy ManagementFrom EverandThe Diabetic Neuropathy Mastery Bible: Your Blueprint for Complete Diabetic Neuropathy ManagementNo ratings yet
- VILLAHERMOSA Tetanus ToxoidDocument6 pagesVILLAHERMOSA Tetanus ToxoidJv Jore VillahermosaNo ratings yet
- VILLAHERMOSA - Anorexia NCPDocument9 pagesVILLAHERMOSA - Anorexia NCPJv Jore VillahermosaNo ratings yet
- Villahermosa - GDM NCPDocument9 pagesVillahermosa - GDM NCPJv Jore VillahermosaNo ratings yet
- NCP - Villahermosa - Risk For InfectionDocument5 pagesNCP - Villahermosa - Risk For InfectionJv Jore VillahermosaNo ratings yet
- Reading Villahermosa CTSDocument9 pagesReading Villahermosa CTSJv Jore VillahermosaNo ratings yet
- NCP Villahermosa CTSDocument6 pagesNCP Villahermosa CTSJv Jore VillahermosaNo ratings yet
- NCP - Villahermosa - BreastcancerDocument5 pagesNCP - Villahermosa - BreastcancerJv Jore VillahermosaNo ratings yet
- Prepared by - Snehal ChintalaDocument78 pagesPrepared by - Snehal ChintalaSnehal ChintalaNo ratings yet
- Cable HDMI 10 MetrosDocument3 pagesCable HDMI 10 Metroschristian eduardoNo ratings yet
- The Myth of PlutoDocument6 pagesThe Myth of PlutoZsuzsanna ZöldNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic WavesDocument173 pagesElectromagnetic WavesatiqdhepNo ratings yet
- Magic TutorialDocument3 pagesMagic TutorialGaurav SainiNo ratings yet
- Manual Spare Parts DB540!72!07Document124 pagesManual Spare Parts DB540!72!07Gustavo CarvalhoNo ratings yet
- SwitchwordsDocument8 pagesSwitchwordssonali100% (1)
- 6 Biomechanical Basis of Extraction Space Closure - Pocket DentistryDocument5 pages6 Biomechanical Basis of Extraction Space Closure - Pocket DentistryParameswaran ManiNo ratings yet
- Hypomorphic Mutations in PRF1, MUNC13-4, and STXBP2 Are Associated With Adult-Onset Familial HLHDocument6 pagesHypomorphic Mutations in PRF1, MUNC13-4, and STXBP2 Are Associated With Adult-Onset Familial HLHLeyla SaabNo ratings yet
- Hotpoint Washing Machine Wmf740Document16 pagesHotpoint Washing Machine Wmf740furheavensakeNo ratings yet
- Logic Pro X Cheat Sheet (Atajos)Document14 pagesLogic Pro X Cheat Sheet (Atajos)Nazareno AltamiranoNo ratings yet
- Revelation I Excerpt PDFDocument10 pagesRevelation I Excerpt PDFMikhael ChangNo ratings yet
- The Estimation of Drying-Flux Profiles in Continuously Worked DryersDocument3 pagesThe Estimation of Drying-Flux Profiles in Continuously Worked DryerslorencorumbaNo ratings yet
- Unexplained Mysteries - Mona Lisa's Eyes Reveal CodeDocument33 pagesUnexplained Mysteries - Mona Lisa's Eyes Reveal CodeFirst LastNo ratings yet
- Méthodes de Dissolution FDADocument129 pagesMéthodes de Dissolution FDACH NarimaneNo ratings yet
- Lesson 02 PDFDocument13 pagesLesson 02 PDFJeremy TohNo ratings yet
- C21 - Curriculum Diploma in Mechanical EngineeringDocument118 pagesC21 - Curriculum Diploma in Mechanical EngineeringsathishkandulaNo ratings yet
- Construction Method (PICC)Document2 pagesConstruction Method (PICC)rheymar diwaNo ratings yet
- LDPDocument46 pagesLDPSoundradevi ArumugamNo ratings yet
- Biochar-Supported Reduced Graphene Oxide Composite For Adsorption and Coadsorption of Atrazine and Lead IonsDocument9 pagesBiochar-Supported Reduced Graphene Oxide Composite For Adsorption and Coadsorption of Atrazine and Lead IonsJuliana LuconiNo ratings yet
- State Feedback Controller Design Using MATLABDocument19 pagesState Feedback Controller Design Using MATLABhariNo ratings yet
- Edible PackagingDocument7 pagesEdible Packagingyouthsafetyinitiative244No ratings yet
- Percussion Laser DrillingDocument1 pagePercussion Laser DrillingBefzzNo ratings yet
- Zeiss Erosion ModuleDocument13 pagesZeiss Erosion ModulepakhiddeyasNo ratings yet
- The Secrets of Ancient Rome's Buildings - History - Smithsonian Magazine PDFDocument2 pagesThe Secrets of Ancient Rome's Buildings - History - Smithsonian Magazine PDFMarlui Faith MaglambayanNo ratings yet
- Forensic Syllabus@Document6 pagesForensic Syllabus@YocobSamandrewsNo ratings yet
- The Bird CageDocument1 pageThe Bird CageNick BlueNo ratings yet
- The Ultimate Guide To Arduino LibraryDocument76 pagesThe Ultimate Guide To Arduino LibraryNguyễn Hòa75% (4)
NIFEDIPINE
NIFEDIPINE
Uploaded by
Jv Jore VillahermosaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
NIFEDIPINE
NIFEDIPINE
Uploaded by
Jv Jore VillahermosaCopyright:
Available Formats
A Drug Study on
NIFEDIPINE
In Partial Fulfillment to the
Requirements in NCM 209 – RLE
PEDIATRIC ROTATION
Submitted to:
MARIA CATHERINE M. BELARMA, RN, MN
Clinical Instructor
Submitted by:
JV J. VILLAHERMOSA
BSN-2L – Group 5
March 24, 2021
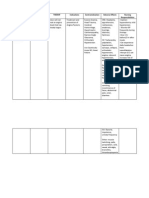
Generic name: Nifedipine
Brand Name: Procardia, Procardia XL, Adalat CC, Nifedical XL, Adalat, Afeditab
CR, and Nifediac CC
Classification: - Calcium- channel blocker; antianginal; antihypertensive
Mode of Action: Calcium-channel blocker that interferes with signals to the heart
and blood vessels. It dilates blood vessels by relaxing the muscle
layer in the vessel walls thereby allowing more blood to be pumped
and reducing the strain on the heart,
Dose & Route:
Hypertension
Adult dosage (ages 18–64 years)
The starting dose is 30 mg or 60 mg by mouth once per day. The
dosage can be increased every 7 to 14 days until the maximum
dosage of 90–120 mg per day is reached.
Senior dosage (ages 65 years and older)
The kidneys of older adults may not work as well as they used to.
This can cause your body to process drugs more slowly. As a result,
more of a drug stays in your body for a longer time. This increases
your risk of side effects. Your doctor may start you on a lowered
dose or a different medication schedule. This can help keep levels
of this drug from building up too much in your body.
Vasospastic angina
Adult dosage (ages 18–64 years)
The starting dose is 30 mg or 60 mg by mouth once per day. The
dosage can be increased every 7 to 14 days until the maximum
dosage of 180 mg per day is reached.
Senior dosage (ages 65 years and older)
The kidneys of older adults may not work as well as they used to.
This can cause your body to process drugs more slowly. As a result,
more of a drug stays in your body for a longer time. This increases
your risk of side effects. Your doctor may start you on a lowered
dose or a different medication schedule. This can help keep levels
of this drug from building up too much in your body.
Chronic stable angina
Adult dosage (ages 18–64 years)
The starting dose is 30 mg or 60 mg by mouth once per day. The
dosage can be increased every 7 to 14 days until the maximum
dosage of 90–120 mg per day is reached.
Senior dosage (ages 65 years and older)
The kidneys of older adults may not work as well as they used to.
This can cause your body to process drugs more slowly. As a result,
more of a drug stays in your body for a longer time. This increases
your risk of side effects. Your doctor may start you on a lowered
dose or a different medication schedule. This can help keep levels
of this drug from building up too much in your body.
Prophylaxis of angina; hypertension; Raynaud’s
Indication:
phenomenon
Contraindicated in patients with cardiogenic shock;
Contraindication: advanced aortic stenosis; acute angina; within a month of
myocardial infarction
Drug Interaction: Can increase the effects of antihypertensive medication,
phenytoin, toxicity of digoxin
Effects of nifedipine will be reduced when taken with
rifampicin
Side/ Adverse Effect: Headache
Flushing
Palpitations
Dizziness
Lethargy
Gravitational oedema
Tachycardia
Pruritis
Rashes
Urticaria
Increased urine output
Constipation/ diarrhea
Eye Pain
Visual disturbances
Gum hyperplasia
Asthenia
Paraesthesia
Myalgia
Tremor
Impotence
Gynaecomastia
Depression
Telangiectasia
Cholestasis
Nursing Responsibilities: Assess for angina pain, including location, intensity, duration,
and alleviating and aggravating factors.
Assess the cardiac status with BP, pulse, respiration and
ECG
Monitor potassium and liver function tests throughout
treatment with Nifedipine
Teaching points
Avoid dangerous activities until stabilized on the medicine or
dizziness is not present.
Limit caffeine
Avoid alcohol
Patients should change position carefully as orthostatic
hypotension can occur
REFERENCES:
Arnarson, A. (2018, November 19). Nifedipine, Oral Tablet. Healthline.
https://www.healthline.com/health/nifedipine-oral-tablet?fbclid=IwAR10aGqvp_vQjmo-
4XjS55OnOvK8Dwg4B2awzWzDaalTKhjfJLnYkz4uBO8#about
Ford, S. (2019, August 1). Nifedipine. Nursing Times. https://www.nursingtimes.net/clinical-
archive/medicine-management/nifedipine-03-06-2004/?fbclid=IwAR2f6-
7FjHuduXNfXnLL7BEQ39SJJ6gJAb9RwBVrtHMTK7lD5x327OZpyYs
You might also like
- Drug NeurontinDocument1 pageDrug NeurontinSrkocher100% (2)
- Hydrochlorothiazide ThiazideDocument1 pageHydrochlorothiazide ThiazideE100% (1)
- Encyclopedia of Korean Folk BeliefsDocument167 pagesEncyclopedia of Korean Folk BeliefsAria7No ratings yet
- Norvasc Drug CardDocument1 pageNorvasc Drug CardSheri490No ratings yet
- RisperdalDocument2 pagesRisperdalAdrianne Bazo100% (1)
- Drug Card ToradolDocument2 pagesDrug Card ToradolAdrianne Bazo100% (1)
- Pregabalin LYricaDocument2 pagesPregabalin LYricaKristine Young100% (3)
- Naplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesFrom EverandNaplex Complete Study Outline A Topic-Wise Approach DiabetesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Stress - The Different Kinds of StressDocument4 pagesStress - The Different Kinds of StressbogdanNo ratings yet
- PhenerganDocument2 pagesPhenerganKatie McPeekNo ratings yet
- Sertraline Generic Name: Sertraline Hydrochloride Brand Name: Zoloft Classification: SSRI Antidepressant Mode of ActionDocument11 pagesSertraline Generic Name: Sertraline Hydrochloride Brand Name: Zoloft Classification: SSRI Antidepressant Mode of Actionkarl montanoNo ratings yet
- Promethazine (Phenergan)Document1 pagePromethazine (Phenergan)Adrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- Drug PhenerganDocument1 pageDrug PhenerganSrkocherNo ratings yet
- Drug Study RivastigmineDocument6 pagesDrug Study RivastigmineRaijenne VersolaNo ratings yet
- Padilla-Drug StudyDocument5 pagesPadilla-Drug Studybunso padillaNo ratings yet
- Lopressor (Metoprolol) 100mgDocument2 pagesLopressor (Metoprolol) 100mgAdrianne Bazo100% (2)
- ParaDocument2 pagesParaMary Kate ClarosNo ratings yet
- Catapres (Clonidine)Document2 pagesCatapres (Clonidine)Adrianne BazoNo ratings yet
- Quetiapine - Drug StudyDocument3 pagesQuetiapine - Drug StudyJeran Henrich BusobusoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyArnel MacabalitaoNo ratings yet
- Generic Name Indication (S) Action Adverse Reaction Interaction Contraindication Patient Teaching Nursing ImplicationsDocument2 pagesGeneric Name Indication (S) Action Adverse Reaction Interaction Contraindication Patient Teaching Nursing ImplicationsJake Yvan DizonNo ratings yet
- Avapro (Irbesartan)Document2 pagesAvapro (Irbesartan)ENo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument41 pagesDrug StudyCatherine PradoNo ratings yet
- Prinivil LisinoprilDocument3 pagesPrinivil LisinoprilENo ratings yet
- AtropineDocument3 pagesAtropinegovind_soni_15No ratings yet
- Drug DigoxinDocument1 pageDrug DigoxinSrkocherNo ratings yet
- C C C Vertigo,: Electrolyte and Water Balance AgentDocument12 pagesC C C Vertigo,: Electrolyte and Water Balance AgentEarl Tony TrinidadNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument23 pagesDrug StudyJoyce Anne SupnetNo ratings yet
- SeroquelDocument1 pageSeroquelE100% (1)
- PropanolDocument8 pagesPropanolStacey CamilleNo ratings yet
- Re Me RonDocument2 pagesRe Me RonKatie McPeekNo ratings yet
- NifedipineDocument2 pagesNifedipineapi-3797941100% (3)
- Coreg (Carvedilol)Document3 pagesCoreg (Carvedilol)ENo ratings yet
- Name of Drug/ Therapeutic Class Action Indications Side Effect Nursing Considerations ParacetamolDocument7 pagesName of Drug/ Therapeutic Class Action Indications Side Effect Nursing Considerations ParacetamolAnne Monique Moran OngjocoNo ratings yet
- Dexamethasone DrugStudyDocument8 pagesDexamethasone DrugStudySophia IbuyanNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument14 pagesDrug StudyjackSNMMCNo ratings yet
- Drug DilantinDocument1 pageDrug DilantinSrkocherNo ratings yet
- Prozac (Fluoxetine) 40mgDocument1 pageProzac (Fluoxetine) 40mgENo ratings yet
- Prescribed Medication: Information Leaflet PriorDocument4 pagesPrescribed Medication: Information Leaflet PriorHavier EsparagueraNo ratings yet
- Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme (ACE)Document5 pagesAngiotensin-Converting Enzyme (ACE)Isabella SamsonNo ratings yet
- Drug LopressorDocument1 pageDrug LopressorSrkocherNo ratings yet
- Hydralazine.1 3Document1 pageHydralazine.1 3SNo ratings yet
- Bulandos BSN3-1 Duty Drug StudyDocument5 pagesBulandos BSN3-1 Duty Drug StudyRolan BulandosNo ratings yet
- PhenobarbitalDocument5 pagesPhenobarbitalapi-3797941100% (1)
- DiltiazemDocument2 pagesDiltiazemE100% (1)
- NCP DS NCM114 RleDocument12 pagesNCP DS NCM114 RleAllysa Kyle AlfonsoNo ratings yet
- Escaran - Drug Study - Set ADocument4 pagesEscaran - Drug Study - Set AFrancis Alfred EscaranNo ratings yet
- Avapro (Irbesartan)Document1 pageAvapro (Irbesartan)Adrianne Bazo100% (1)
- Medical Encyclopedia XXL: Prof. J.P. Schadé, M.D., Ph.D. D.Sc.hcFrom EverandMedical Encyclopedia XXL: Prof. J.P. Schadé, M.D., Ph.D. D.Sc.hcNo ratings yet
- Critical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsFrom EverandCritical Care Medications: Anti-Arrhythmics Study Guide: Critical Care EssentialsNo ratings yet
- Diabetes: Complications of Diabetes: The most important information you need to improve your healthFrom EverandDiabetes: Complications of Diabetes: The most important information you need to improve your healthNo ratings yet
- Fast Facts: Optimización del tratamiento de las fluctuaciones motoras en la enfermedad de Parkinson: Adaptando el tratamiento al pacienteFrom EverandFast Facts: Optimización del tratamiento de las fluctuaciones motoras en la enfermedad de Parkinson: Adaptando el tratamiento al pacienteNo ratings yet
- Reversing Chronic Hypertension Naturally : The Healthy way to Prevent the Silent KillerFrom EverandReversing Chronic Hypertension Naturally : The Healthy way to Prevent the Silent KillerNo ratings yet
- Prediabetes Diet: A Beginner's Step-by-Step Guide to Reversing Prediabetes: Includes Curated Recipes and a Meal PlanFrom EverandPrediabetes Diet: A Beginner's Step-by-Step Guide to Reversing Prediabetes: Includes Curated Recipes and a Meal PlanNo ratings yet
- Migraines: Migraine Treatment and Prevention Options: The most important information you need to improve your healthFrom EverandMigraines: Migraine Treatment and Prevention Options: The most important information you need to improve your healthNo ratings yet
- The Diabetic Neuropathy Mastery Bible: Your Blueprint for Complete Diabetic Neuropathy ManagementFrom EverandThe Diabetic Neuropathy Mastery Bible: Your Blueprint for Complete Diabetic Neuropathy ManagementNo ratings yet
- VILLAHERMOSA Tetanus ToxoidDocument6 pagesVILLAHERMOSA Tetanus ToxoidJv Jore VillahermosaNo ratings yet
- VILLAHERMOSA - Anorexia NCPDocument9 pagesVILLAHERMOSA - Anorexia NCPJv Jore VillahermosaNo ratings yet
- Villahermosa - GDM NCPDocument9 pagesVillahermosa - GDM NCPJv Jore VillahermosaNo ratings yet
- NCP - Villahermosa - Risk For InfectionDocument5 pagesNCP - Villahermosa - Risk For InfectionJv Jore VillahermosaNo ratings yet
- Reading Villahermosa CTSDocument9 pagesReading Villahermosa CTSJv Jore VillahermosaNo ratings yet
- NCP Villahermosa CTSDocument6 pagesNCP Villahermosa CTSJv Jore VillahermosaNo ratings yet
- NCP - Villahermosa - BreastcancerDocument5 pagesNCP - Villahermosa - BreastcancerJv Jore VillahermosaNo ratings yet
- Prepared by - Snehal ChintalaDocument78 pagesPrepared by - Snehal ChintalaSnehal ChintalaNo ratings yet
- Cable HDMI 10 MetrosDocument3 pagesCable HDMI 10 Metroschristian eduardoNo ratings yet
- The Myth of PlutoDocument6 pagesThe Myth of PlutoZsuzsanna ZöldNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic WavesDocument173 pagesElectromagnetic WavesatiqdhepNo ratings yet
- Magic TutorialDocument3 pagesMagic TutorialGaurav SainiNo ratings yet
- Manual Spare Parts DB540!72!07Document124 pagesManual Spare Parts DB540!72!07Gustavo CarvalhoNo ratings yet
- SwitchwordsDocument8 pagesSwitchwordssonali100% (1)
- 6 Biomechanical Basis of Extraction Space Closure - Pocket DentistryDocument5 pages6 Biomechanical Basis of Extraction Space Closure - Pocket DentistryParameswaran ManiNo ratings yet
- Hypomorphic Mutations in PRF1, MUNC13-4, and STXBP2 Are Associated With Adult-Onset Familial HLHDocument6 pagesHypomorphic Mutations in PRF1, MUNC13-4, and STXBP2 Are Associated With Adult-Onset Familial HLHLeyla SaabNo ratings yet
- Hotpoint Washing Machine Wmf740Document16 pagesHotpoint Washing Machine Wmf740furheavensakeNo ratings yet
- Logic Pro X Cheat Sheet (Atajos)Document14 pagesLogic Pro X Cheat Sheet (Atajos)Nazareno AltamiranoNo ratings yet
- Revelation I Excerpt PDFDocument10 pagesRevelation I Excerpt PDFMikhael ChangNo ratings yet
- The Estimation of Drying-Flux Profiles in Continuously Worked DryersDocument3 pagesThe Estimation of Drying-Flux Profiles in Continuously Worked DryerslorencorumbaNo ratings yet
- Unexplained Mysteries - Mona Lisa's Eyes Reveal CodeDocument33 pagesUnexplained Mysteries - Mona Lisa's Eyes Reveal CodeFirst LastNo ratings yet
- Méthodes de Dissolution FDADocument129 pagesMéthodes de Dissolution FDACH NarimaneNo ratings yet
- Lesson 02 PDFDocument13 pagesLesson 02 PDFJeremy TohNo ratings yet
- C21 - Curriculum Diploma in Mechanical EngineeringDocument118 pagesC21 - Curriculum Diploma in Mechanical EngineeringsathishkandulaNo ratings yet
- Construction Method (PICC)Document2 pagesConstruction Method (PICC)rheymar diwaNo ratings yet
- LDPDocument46 pagesLDPSoundradevi ArumugamNo ratings yet
- Biochar-Supported Reduced Graphene Oxide Composite For Adsorption and Coadsorption of Atrazine and Lead IonsDocument9 pagesBiochar-Supported Reduced Graphene Oxide Composite For Adsorption and Coadsorption of Atrazine and Lead IonsJuliana LuconiNo ratings yet
- State Feedback Controller Design Using MATLABDocument19 pagesState Feedback Controller Design Using MATLABhariNo ratings yet
- Edible PackagingDocument7 pagesEdible Packagingyouthsafetyinitiative244No ratings yet
- Percussion Laser DrillingDocument1 pagePercussion Laser DrillingBefzzNo ratings yet
- Zeiss Erosion ModuleDocument13 pagesZeiss Erosion ModulepakhiddeyasNo ratings yet
- The Secrets of Ancient Rome's Buildings - History - Smithsonian Magazine PDFDocument2 pagesThe Secrets of Ancient Rome's Buildings - History - Smithsonian Magazine PDFMarlui Faith MaglambayanNo ratings yet
- Forensic Syllabus@Document6 pagesForensic Syllabus@YocobSamandrewsNo ratings yet
- The Bird CageDocument1 pageThe Bird CageNick BlueNo ratings yet
- The Ultimate Guide To Arduino LibraryDocument76 pagesThe Ultimate Guide To Arduino LibraryNguyễn Hòa75% (4)