Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Porfolio Blood and Blood Vessels
Porfolio Blood and Blood Vessels
Uploaded by
Dianne Colmo0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views2 pagesThe document summarizes the structure and function of the heart and blood vessels. It identifies the four chambers of the heart as two atria and two ventricles, and explains their roles in receiving and pumping blood. It also outlines the principal structures of blood vessels as arteries, capillaries, and veins, and describes their roles in transporting oxygenated and deoxygenated blood throughout the body. Finally, it explains that blood vessels function to transport blood, nutrients, oxygen, waste, and carbon dioxide between tissues and the heart.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document summarizes the structure and function of the heart and blood vessels. It identifies the four chambers of the heart as two atria and two ventricles, and explains their roles in receiving and pumping blood. It also outlines the principal structures of blood vessels as arteries, capillaries, and veins, and describes their roles in transporting oxygenated and deoxygenated blood throughout the body. Finally, it explains that blood vessels function to transport blood, nutrients, oxygen, waste, and carbon dioxide between tissues and the heart.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views2 pagesPorfolio Blood and Blood Vessels
Porfolio Blood and Blood Vessels
Uploaded by
Dianne ColmoThe document summarizes the structure and function of the heart and blood vessels. It identifies the four chambers of the heart as two atria and two ventricles, and explains their roles in receiving and pumping blood. It also outlines the principal structures of blood vessels as arteries, capillaries, and veins, and describes their roles in transporting oxygenated and deoxygenated blood throughout the body. Finally, it explains that blood vessels function to transport blood, nutrients, oxygen, waste, and carbon dioxide between tissues and the heart.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
EMILIO AGUINALDO COLLEGE
Gov. D. Mangubat St., Brgy. Burol Main, City of Dasmariñas, Cavite 4114, Philippines
Tel. Nos. (046) 416-4341-42www.eac.edu.ph
ISO 9001:2015 CERTIFIED
SCHOOL OF NURSING QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS
COLLABORATIVE MODULE FOR OUTCOMES-BASED AND FLEXIBLE LEARNING
IN Human Anatomy and Physiology - Lab
Student: Dianne R. Colmo Student Number: 20-1-03191
Name of Professor: Leila deVilla-Masajo Year Level/Section: BSN 1-5
INTENDED LEARNING OUTCOME
1. Identify the principal structure of the heart.
In humans, the heart is about the size of a clenched fist. It is divided into four
chambers: two atria and two ventricles. The heart is divided into four chambers
consisting of two atria and two ventricles the atria receive blood, while the
ventricles pump blood. The right atrium receives blood from the superior and
inferior vena cava’s and the coronary sinus; blood then moves to the right
ventricle where it is pumped to the lungs.
2. Explain how heart structure function.
heart is an organ made of clastic tissues cardiac muscles, performs volunteer
reflex actions, simultaneously accumulate blood. And do pumping of blood
throughout the body through blood vessels by creating vacuum pressure. And
these are the heart structure with their functions. The vena cava that carries
deoxygenated blood from the body to heart, the semilunar valve that flaps that
prevent backflow of blood, left atrium that receives oxygenated blood from the
lungs, left ventricle the region of the heart that pumps blood to the body,
pulmonary artery that carries blood to the lungs, right ventricle the region of the
heart that pumps blood to the lungs, pulmonary vein the responsible in carrying
blood from the lungs, the right atrium that segment of the heart that receives
deoxygenated blood, and lastly the aorta the main artery carrying blood to all
parts of the body.
INTENDED LEARNING OUTCOME
1. Identify the principal structure of the blood vessels.
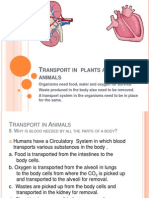
Blood vessels have a range of different sizes and structures, depending on their
role in the body. And the principal structure of the blood vessels are arteries that
responsible for oxygenated blood is pumped from the heart along arteries, which
are muscular. Arteries divide like tree branches until they are slender. The largest
artery is the aorta, which connects to the heart and picks up oxygenated blood
from the left ventricle. The only artery that picks up deoxygenated blood is the
pulmonary artery, which runs between the heart and lungs. And the next is
capillaries that is the arteries eventually divide down into the smallest blood
vessel, the capillary. Capillaries are so small that blood cells can only move
through them one at a time. Oxygen and food nutrients pass from these
capillaries to the cells. Capillaries are also connected to veins, so wastes from
the cells can be transferred to the blood. And lastly veins that have one-way
valves instead of muscles, to stop blood from running back the wrong way.
Generally, veins carry deoxygenated blood from the body to the heart, where it
can be sent to the lungs. The exception is the network of pulmonary veins, which
take oxygenated blood from the lungs to the heart.
• VIRTUE • EXCELLENCE • SERVICE
EMILIO AGUINALDO COLLEGE
Gov. D. Mangubat St., Brgy. Burol Main, City of Dasmariñas, Cavite 4114, Philippines
Tel. Nos. (046) 416-4341-42www.eac.edu.ph
ISO 9001:2015 CERTIFIED
SCHOOL OF NURSING QUALITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS
2. Explain how blood vessels function.
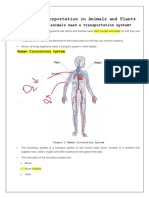
The blood vessels are the components of the circulatory system that transport
blood throughout the human body. These vessels transport blood cells, nutrients,
and oxygen to the tissues of the body. They also take waste and carbon dioxide
away from the tissues. The vessels that carry blood away from the heart are
called arteries, and their very small branches are arterioles. Very small branches
that collect the blood from the various organs and parts are called venules, and
they unite to form veins, which return the blood to the heart. Capillaries are
minute thin-walled vessels that connect the arterioles and venules; it is through
the capillaries that nutrients and wastes are exchanged between the blood and
body tissues.
• VIRTUE • EXCELLENCE • SERVICE
You might also like
- GCC - Ykone 2023Document50 pagesGCC - Ykone 2023JeanThomasNo ratings yet
- VanGogh EbookDocument288 pagesVanGogh EbookDragan Cvetkovic88% (8)
- Section 13 of HMADocument11 pagesSection 13 of HMAria rajeevNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System: A Tutorial Study GuideFrom EverandCirculatory System: A Tutorial Study GuideRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- The Oxford Dictionary of Pronunciation For Current EnglishDocument1,232 pagesThe Oxford Dictionary of Pronunciation For Current EnglishAndry Alexander90% (10)
- Respiratory and Circulatory SystemDocument59 pagesRespiratory and Circulatory SystemTrisha OxalesNo ratings yet
- Alwadi International School Grade 9 Biology 9. Transport in Animals NotesDocument62 pagesAlwadi International School Grade 9 Biology 9. Transport in Animals NotesMohammed HelmyNo ratings yet
- Pralay Mondal BBA (HM) - 201 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEMDocument13 pagesPralay Mondal BBA (HM) - 201 CARDIOVASCULAR SYSTEMPralay MondalNo ratings yet
- Candon City, Ilocos Sur Grade 9 Reviewer School Year 2021 - 2022Document7 pagesCandon City, Ilocos Sur Grade 9 Reviewer School Year 2021 - 2022Aleah TungbabanNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory SystemDocument4 pagesThe Circulatory Systemnoemi feblesNo ratings yet
- Science-Grade 9 Learner Activity Sheets Quarter 1-Week 1: Respiratory and Circulatory System: Parts and Functions First Edition, 2021Document11 pagesScience-Grade 9 Learner Activity Sheets Quarter 1-Week 1: Respiratory and Circulatory System: Parts and Functions First Edition, 2021MA EDYLYN NOGUERRANo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument9 pagesCirculatory SystemKyla Mae JinonNo ratings yet
- Transportation in Humans - Handout Class-XDocument4 pagesTransportation in Humans - Handout Class-Xkiran2000tripathiNo ratings yet
- Handouts in Circulatory SystemDocument4 pagesHandouts in Circulatory Systemcabarles quemeNo ratings yet
- Summary Unit 3. Systems of The Nutrition FunctionDocument29 pagesSummary Unit 3. Systems of The Nutrition FunctionwendyNo ratings yet
- Assignment-Ch 11-Ans SheetDocument6 pagesAssignment-Ch 11-Ans Sheetrachna sharmaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument9 pagesAnatomy and PhysiologyHamza IshtiaqNo ratings yet
- General Biology - Q4 - W4 - M4 - LDS - Plants-and-Animals-Transport-and-Circulation - RTPDocument7 pagesGeneral Biology - Q4 - W4 - M4 - LDS - Plants-and-Animals-Transport-and-Circulation - RTPElsa BiswelanNo ratings yet
- Life Processes - Transportation QB 2019-20 PDFDocument5 pagesLife Processes - Transportation QB 2019-20 PDFRatheesh HrishikeshNo ratings yet
- As Biology NotesDocument48 pagesAs Biology Notesella100% (1)
- Life Processes - Transportation in Human Beings 1Document24 pagesLife Processes - Transportation in Human Beings 1raghavrungtambwaNo ratings yet
- Circulatory Pt. 1Document10 pagesCirculatory Pt. 1Melvin Razon Espinola Jr.No ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument10 pagesCirculatory SystemMahamad BakrNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 Life Processes Part IIDocument9 pagesLesson 6 Life Processes Part IIjokerbladed19No ratings yet
- I. Clinical Discusion of The Disease 1. Anatomy and Physiology KidneysDocument4 pagesI. Clinical Discusion of The Disease 1. Anatomy and Physiology KidneysLemuel GuevarraNo ratings yet
- Life Processes NotesDocument10 pagesLife Processes NotesKarishmm KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Science - 020121 - TRANSPORTATION IN PLANTS AND ANIMALSDocument9 pagesScience - 020121 - TRANSPORTATION IN PLANTS AND ANIMALSDeepak KansalNo ratings yet
- IV Therapy HandoutsDocument32 pagesIV Therapy HandoutsMichael Antimano BascosNo ratings yet
- Nha and Funda ReviewerDocument18 pagesNha and Funda ReviewerNatasha ParasNo ratings yet
- Vascular SystemDocument20 pagesVascular SystemHama HamidNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 9 - Module 1Document7 pagesSCIENCE 9 - Module 1cherish calachanNo ratings yet
- Circulation and Gas ExchangeDocument164 pagesCirculation and Gas ExchangeZuliyanto ZakariaNo ratings yet
- Ch#2 Working of Human BodyDocument14 pagesCh#2 Working of Human BodyShaikhamirfaheemNo ratings yet
- Cow HeartDocument7 pagesCow HeartArun RajNo ratings yet
- Guess The PictureDocument26 pagesGuess The PictureRolland MoraNo ratings yet
- CirculationDocument9 pagesCirculationakkaranniNo ratings yet
- Asm 8300Document2 pagesAsm 8300Taranpreet KaurNo ratings yet
- KS3 Science Year 9 The Circulatory System-2Document15 pagesKS3 Science Year 9 The Circulatory System-2f72ktyd78nNo ratings yet
- CH-11 Transportation in Animals and PlantsDocument12 pagesCH-11 Transportation in Animals and PlantsNaitik MeenaNo ratings yet
- Cardio Anapyhy Session1Document24 pagesCardio Anapyhy Session1Louise Anne Agnazata GayoNo ratings yet
- Transportation of Materials in Plants and Animals Question and AnswersDocument5 pagesTransportation of Materials in Plants and Animals Question and AnswersKunal SumukNo ratings yet
- Notes - Life Processes - Transportation - C-X - PART-IIIDocument4 pagesNotes - Life Processes - Transportation - C-X - PART-IIIApoorv ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Biology C - Lesson 1 - Circulatory SystemDocument58 pagesBiology C - Lesson 1 - Circulatory SystemmemmotilalNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System - Chapter 9Document4 pagesCirculatory System - Chapter 9Viviana PlacentinoNo ratings yet
- Body Systems RevisionDocument11 pagesBody Systems Revisionamie122auNo ratings yet
- Cardio Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesCardio Lesson PlanAmiel Francisco Reyes100% (1)
- VRS BIOLOGY 7th Class 2nd TermDocument129 pagesVRS BIOLOGY 7th Class 2nd TermpullapakasamathaNo ratings yet
- Sci Tracks8 CH 08Document38 pagesSci Tracks8 CH 08Fúul 'O' ReagrettNo ratings yet
- Circulatory System Cardiovascular and LymphaticDocument60 pagesCirculatory System Cardiovascular and LymphaticJJ AlmagroNo ratings yet
- LRDP 1 InglesDocument15 pagesLRDP 1 Inglesdelacruzkim618No ratings yet
- Module 3 The Circulatory SystemDocument11 pagesModule 3 The Circulatory SystemAndriya JoshyNo ratings yet
- Transportation in Plants and AnimalsDocument12 pagesTransportation in Plants and AnimalsRaman -No ratings yet
- Now The Question Arises How Autotrophic Nutrition Occurs in Plants Using Photosynthesis?Document9 pagesNow The Question Arises How Autotrophic Nutrition Occurs in Plants Using Photosynthesis?Bhaskar SharmaNo ratings yet
- Urinary SystemDocument77 pagesUrinary SystemJushelle Anne Tigoy PilareNo ratings yet
- TransportDocument26 pagesTransportBhaskar MajumdarNo ratings yet
- Normal AnatomyDocument4 pagesNormal AnatomyDoneva Lyn MedinaNo ratings yet
- Life Processes Part - 3Document22 pagesLife Processes Part - 3Nripendra TiwaryNo ratings yet
- Biology - Unit 3: Dissolved SubstancesDocument11 pagesBiology - Unit 3: Dissolved SubstancesTahirNo ratings yet
- Chapter 42 Reading GuideDocument5 pagesChapter 42 Reading GuideCaleb SchantzNo ratings yet
- The Circulatory SystemDocument6 pagesThe Circulatory SystemShamel BebitaNo ratings yet
- Gr9 q1 Mod1 Respiratory-And-circulatory-systemDocument5 pagesGr9 q1 Mod1 Respiratory-And-circulatory-systemCristinekate VinasNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 NotesDocument18 pagesTopic 1 NotesKesithan AnandarashNo ratings yet
- Lesson on Blood Circulation - Biology 4th Grade | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandLesson on Blood Circulation - Biology 4th Grade | Children's Biology BooksRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- S Setting Value, C Check Value) OT Outside Tolerance (X Is Set)Document3 pagesS Setting Value, C Check Value) OT Outside Tolerance (X Is Set)Agus WijayadiNo ratings yet
- Sinope Inscription Roman Period CatalogueDocument2 pagesSinope Inscription Roman Period CatalogueC.y. WuNo ratings yet
- Panaguiton, Jr. Vs DOJ - G.R. No. 167571 - Nov 25, 2008Document9 pagesPanaguiton, Jr. Vs DOJ - G.R. No. 167571 - Nov 25, 2008Boogie San JuanNo ratings yet
- 1Document11 pages1SonnyNo ratings yet
- LED Lighting Design & Specifi Cation Guide: Considerations For Harsh and Hazardous Area ApplicationsDocument20 pagesLED Lighting Design & Specifi Cation Guide: Considerations For Harsh and Hazardous Area ApplicationsSarvesh AhluwaliaNo ratings yet
- Group 7 Selecting Channel PartnersDocument24 pagesGroup 7 Selecting Channel PartnersJillian Salipande AbulenciaNo ratings yet
- Climate Change Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesClimate Change Lesson PlanMbagnick Diop100% (1)
- GMS 691 Week 2Document23 pagesGMS 691 Week 2Mit DaveNo ratings yet
- University Management SystemDocument4 pagesUniversity Management Systemnavayuga83% (6)
- Chapter 1 TVTDocument14 pagesChapter 1 TVTtemedebereNo ratings yet
- Heirs of Christina Ayuste vs. Court of Appeals and Viena MalabongaDocument6 pagesHeirs of Christina Ayuste vs. Court of Appeals and Viena Malabongatalla aldoverNo ratings yet
- Project Management Day of Service: PmdosDocument20 pagesProject Management Day of Service: PmdosAlexis JulianoNo ratings yet
- Health Optimizing Physical Education 3: Philippine Folk DanceDocument15 pagesHealth Optimizing Physical Education 3: Philippine Folk DanceYenthel BanguangaNo ratings yet
- At The HotelDocument38 pagesAt The HotelДіана БатраковаNo ratings yet
- A.C. No. 7054 - Que Vs Atty. Revilla - Case DigestDocument3 pagesA.C. No. 7054 - Que Vs Atty. Revilla - Case DigestSarah Jade Layug100% (2)
- Intermediate Accounting - Kieso - Chapter 1Document46 pagesIntermediate Accounting - Kieso - Chapter 1Steffy AmoryNo ratings yet
- ReynalD Ocampo ResumeDocument1 pageReynalD Ocampo Resumerawlens studioNo ratings yet
- Manila Standard Today - Friday (November 23, 2012) IssueDocument28 pagesManila Standard Today - Friday (November 23, 2012) IssueManila Standard TodayNo ratings yet
- CumiDocument56 pagesCumiRahul NairNo ratings yet
- PP9 Biodiversity of PlantsDocument93 pagesPP9 Biodiversity of PlantsRorisang MotsamaiNo ratings yet
- PSS2020 345Document11 pagesPSS2020 345Fergus BurnsNo ratings yet
- 4.3 TRANSFER MECHANISMS - CuikSuiqbad RekaDayaUpayaDocument4 pages4.3 TRANSFER MECHANISMS - CuikSuiqbad RekaDayaUpayasri7877No ratings yet
- The A To Z List of Reflexology Research3Document110 pagesThe A To Z List of Reflexology Research3Ahmad Saiful Ridzwan JaharuddinNo ratings yet
- Ineffective But Reasonable - Why Do European Airlines Operate Short-Haul Flights?Document9 pagesIneffective But Reasonable - Why Do European Airlines Operate Short-Haul Flights?tanvir ehsanNo ratings yet
- Discourse AnalysisDocument3 pagesDiscourse AnalysisPrashant KushwahNo ratings yet
- Bajaj Allianz General Insurance CompanyDocument12 pagesBajaj Allianz General Insurance CompanymkbhimaniNo ratings yet