Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 viewsPerformance Management and Appraisal
Performance Management and Appraisal
Uploaded by
Pricil HanovThis document discusses performance appraisal and various methods for conducting appraisals. It begins by defining performance appraisal as evaluating an employee's current or past performance relative to standards. It then outlines the typical appraisal process of setting standards, assessing performance, and providing feedback. Several reasons for conducting appraisals are given, including for pay/promotion decisions, linking performance to goals, correcting deficiencies, and identifying training needs. The document concludes by describing various techniques for appraising performance such as rating scales, rankings, critical incidents, and management by objectives.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Human Resource Management 15Th Edition Dessler Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument35 pagesHuman Resource Management 15Th Edition Dessler Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFEricHowardftzs100% (8)
- Consultants List-ADCEDocument6 pagesConsultants List-ADCEJaveed Taji100% (3)
- Unit 5 - Performace Evaluation and Control ProcessDocument17 pagesUnit 5 - Performace Evaluation and Control Processapi-1975380893% (14)
- My SMART Goal UK - Big Life JournalDocument6 pagesMy SMART Goal UK - Big Life Journalacmc100% (2)
- Performance Management & Appraisal: Presented By: FSZDocument32 pagesPerformance Management & Appraisal: Presented By: FSZRashedul IslamNo ratings yet
- Chap 9-HrlecDocument3 pagesChap 9-Hrlecjana leeNo ratings yet
- CH 9 - HR Performance Management and AppraisalDocument10 pagesCH 9 - HR Performance Management and AppraisalfirasNo ratings yet
- Performance Appraisal: Unit 3Document49 pagesPerformance Appraisal: Unit 3jerlinjoseNo ratings yet
- Performance Appraisal: Unit 3Document37 pagesPerformance Appraisal: Unit 3Bobby GeorgeNo ratings yet
- L6 Performance AppraisalDocument35 pagesL6 Performance Appraisaltruong.hd4358No ratings yet
- Perf Appraisal 1Document21 pagesPerf Appraisal 1OceanifyNo ratings yet
- HRM PRESENTATIONDocument16 pagesHRM PRESENTATIONAlfe Sani FahimNo ratings yet
- Indus Psych NotesDocument8 pagesIndus Psych NotesMinagaFathmaSonnayaNo ratings yet
- Performance Management VS Performance Appraisal: Presented by Alen Mathew GeorgeDocument28 pagesPerformance Management VS Performance Appraisal: Presented by Alen Mathew GeorgeAlen Mathew GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Management 15th Edition Dessler Solutions ManualDocument14 pagesHuman Resource Management 15th Edition Dessler Solutions Manualmagdalavicemanocgp100% (23)
- HRM - Management of Performance Appraisal SystemDocument2 pagesHRM - Management of Performance Appraisal Systemitsmebridgeth100% (1)
- 9 Performance Management and AppraisalDocument26 pages9 Performance Management and Appraisalaahilchourasia873No ratings yet
- Human Resource Management 13Th Edition Gary Dessler Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument33 pagesHuman Resource Management 13Th Edition Gary Dessler Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFumbarasanayab100% (12)
- Human Resource Management 13th Edition Gary Dessler Solutions ManualDocument12 pagesHuman Resource Management 13th Edition Gary Dessler Solutions Manualmagdalavicemanocgp100% (30)
- Performance Management and AppraisalDocument6 pagesPerformance Management and Appraisalvnilla.lattNo ratings yet
- Performanceappraisal-160117065718Document31 pagesPerformanceappraisal-160117065718atiqur192122No ratings yet
- 09A Performance ManagementDocument49 pages09A Performance ManagementvarunNo ratings yet
- Process and Techniques For Appraising PerformaneDocument32 pagesProcess and Techniques For Appraising PerformaneĐào Minh Quân TrầnNo ratings yet
- Performance ManagementDocument7 pagesPerformance ManagementMARC URRUTIA MIRÓNo ratings yet
- Performance Management: Robert L. Mathis John H. JacksonDocument40 pagesPerformance Management: Robert L. Mathis John H. JacksonpritiNo ratings yet
- COM RDS 3 SEMHONS CC V Unit 4Document30 pagesCOM RDS 3 SEMHONS CC V Unit 4Anwesha KarmakarNo ratings yet
- 5 Performance Appraisal Methods-1Document4 pages5 Performance Appraisal Methods-1Khizer PashaNo ratings yet
- Project 1-Performance Appraisal Methods The Methods of Performance Appraisal Are As Follows A. Traditional MethodsDocument4 pagesProject 1-Performance Appraisal Methods The Methods of Performance Appraisal Are As Follows A. Traditional Methodsmanoj kumar DasNo ratings yet
- In-Class Activity 7Document3 pagesIn-Class Activity 7shajij321No ratings yet
- Setting Work Standards Assessing Employee Actual Performance Providing FeedbackDocument6 pagesSetting Work Standards Assessing Employee Actual Performance Providing FeedbackvinamramittalNo ratings yet
- Performance Management and Appraisal: T NineDocument12 pagesPerformance Management and Appraisal: T NineNouman AhmadNo ratings yet
- Performance Appraisal: - A Formal System of PERIODIC (Not Sporadic)Document12 pagesPerformance Appraisal: - A Formal System of PERIODIC (Not Sporadic)Ankita SharmaNo ratings yet
- Ch7 PSY16Document2 pagesCh7 PSY16Rain TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Dessler Ch9Document12 pagesDessler Ch9Muhammad Aditya TMNo ratings yet
- Unit 5Document15 pagesUnit 5vaishsrinivasNo ratings yet
- Performance Appraisal MethodsDocument18 pagesPerformance Appraisal MethodsMonique RamosNo ratings yet
- MSDM (Performance Appraisal)Document24 pagesMSDM (Performance Appraisal)Giovany AlvanoNo ratings yet
- 7.performance Appraisal (9-11E)Document39 pages7.performance Appraisal (9-11E)Fareed ShahwaniNo ratings yet
- MGT-351 Human Resource Management Chapter-9 Performance Management and AppraisalDocument22 pagesMGT-351 Human Resource Management Chapter-9 Performance Management and AppraisalNazmul Islam Joy 2031255630No ratings yet
- HRM Performance AppraisalDocument25 pagesHRM Performance AppraisalSuraj KumarNo ratings yet
- Babor - PERFORMANCE APPRAISALDocument6 pagesBabor - PERFORMANCE APPRAISALRica DonezaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 AppraisalDocument43 pagesChapter 7 AppraisalCường Nguyễn TháiNo ratings yet
- HRM AssignmentDocument15 pagesHRM AssignmentKhondaker Fahad JohnyNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Management: Performance Management and AppraisalDocument24 pagesHuman Resource Management: Performance Management and AppraisalHammad AliNo ratings yet
- Essentials of An Effective Performance Appraisal SystemDocument10 pagesEssentials of An Effective Performance Appraisal SystemSourav MickeyNo ratings yet
- Job Performance Employee Evaluated Manager Supervisor Career DevelopmentDocument6 pagesJob Performance Employee Evaluated Manager Supervisor Career DevelopmentKunal RajputNo ratings yet
- Performance AppraisalDocument3 pagesPerformance Appraisalfunelasjcg.cbpaNo ratings yet
- Erformance Anagement and Ppraisal: B P - J V CimpDocument25 pagesErformance Anagement and Ppraisal: B P - J V CimpSuraj KumarNo ratings yet
- Erformance Anagement and Ppraisal: B P - J V CimpDocument25 pagesErformance Anagement and Ppraisal: B P - J V CimpSuraj KumarNo ratings yet
- HRM PresentationDocument10 pagesHRM Presentationprashantbhati0440No ratings yet
- Chapter - 4Document48 pagesChapter - 4Ankitha KavyaNo ratings yet
- Presentation Human ResourceDocument17 pagesPresentation Human ResourceSamiira Abdukadir AdanNo ratings yet
- Performance AppraisalDocument73 pagesPerformance AppraisalPravat SatpathyNo ratings yet
- Performance Appraisal PERFORMANCE APPRAISALDocument61 pagesPerformance Appraisal PERFORMANCE APPRAISALAnkit SalujaNo ratings yet
- Institute of Business Administration University of Dhaka H601: Compensation Management Fall Semester, 2019Document42 pagesInstitute of Business Administration University of Dhaka H601: Compensation Management Fall Semester, 2019Tamim HossainNo ratings yet
- Performance Management and AppraisalDocument2 pagesPerformance Management and AppraisalkhanNo ratings yet
- Performance AppraisalDocument37 pagesPerformance AppraisalSaptrsi BanrjiNo ratings yet
- 20100814092649886Document12 pages20100814092649886Muhammad Irsyad33% (3)
- HRM Performance AppraisalDocument35 pagesHRM Performance AppraisalHARIS ZAFARNo ratings yet
- Performance AppraisalDocument32 pagesPerformance AppraisalParamesh WaranNo ratings yet
- Critical Incident Method Weighted ChecklistDocument6 pagesCritical Incident Method Weighted ChecklistsonammattooNo ratings yet
- How to Make the Most of Your Performance Appraisal: Adopt a winning attitude and reap the benefitsFrom EverandHow to Make the Most of Your Performance Appraisal: Adopt a winning attitude and reap the benefitsNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes Session 23 & 24Document7 pagesLecture Notes Session 23 & 24Pricil HanovNo ratings yet
- Building Positive Employee Relations - Session 13&14Document8 pagesBuilding Positive Employee Relations - Session 13&14Pricil HanovNo ratings yet
- HR SeparationDocument2 pagesHR SeparationPricil HanovNo ratings yet
- 19 - Managing Careers and RetentionsDocument6 pages19 - Managing Careers and RetentionsPricil HanovNo ratings yet
- Crusader Communicator: "Safer at Home" Edition #5: Sheboygan Lutheran High SchoolDocument7 pagesCrusader Communicator: "Safer at Home" Edition #5: Sheboygan Lutheran High SchoolMatt ThielNo ratings yet
- Atheism and Radical Skepticism Ibn Taymiyyahs Epistemic CritiqueDocument52 pagesAtheism and Radical Skepticism Ibn Taymiyyahs Epistemic CritiqueZaky MuzaffarNo ratings yet
- 0173NF2016 Fo2c PDFDocument26 pages0173NF2016 Fo2c PDFRadhakrishna MadabhushiNo ratings yet
- Standard Specification: LPG Loading / Unloading ArmDocument19 pagesStandard Specification: LPG Loading / Unloading ArmANIL KUMAR100% (1)
- Information Management Systems, ObstetricalDocument12 pagesInformation Management Systems, ObstetricalLee ThoongNo ratings yet
- Src419X 192-Khz Stereo Asynchronous Sample-Rate Converters: 1 Features 3 DescriptionDocument45 pagesSrc419X 192-Khz Stereo Asynchronous Sample-Rate Converters: 1 Features 3 DescriptionNguyễn QuangNo ratings yet
- Crossing The Jordan River 08-06-20Document37 pagesCrossing The Jordan River 08-06-20elmerdlpNo ratings yet
- SWE2007 - Fundamentals of Operating SystemsDocument6 pagesSWE2007 - Fundamentals of Operating SystemsmaneeshmogallpuNo ratings yet
- SOME and ANYDocument3 pagesSOME and ANYMikeNo ratings yet
- ZH 6000-10000 MK 4 İnst BookDocument90 pagesZH 6000-10000 MK 4 İnst BookESRANo ratings yet
- Chapter One The Problem and Its Setting 1.1 Background of The StudyDocument10 pagesChapter One The Problem and Its Setting 1.1 Background of The StudyJholo BuctonNo ratings yet
- English MCB - L-2Document3 pagesEnglish MCB - L-2Priya SinghNo ratings yet
- MPI GTU Study Material E-Notes Introduction-To-Microprocessor 13052022114954AMDocument4 pagesMPI GTU Study Material E-Notes Introduction-To-Microprocessor 13052022114954AMKartik RamchandaniNo ratings yet
- Dogmatism, Religion, and Psychological Type.Document16 pagesDogmatism, Religion, and Psychological Type.ciprilisticusNo ratings yet
- Experimentalstudies On The Effects of Reduction in Gear Tooth Stiffness Lubricant Film Thicknessina Spur Geared SystemDocument13 pagesExperimentalstudies On The Effects of Reduction in Gear Tooth Stiffness Lubricant Film Thicknessina Spur Geared SystemBurak TuncerNo ratings yet
- Ahb Example Amba System: Technical Reference ManualDocument222 pagesAhb Example Amba System: Technical Reference ManualJinsNo ratings yet
- Flame ArresterDocument2 pagesFlame ArresterNicholas RiveraNo ratings yet
- MTP44001Document63 pagesMTP44001Dong-seob ParkNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Information & Communications Technology Introduction ToDocument37 pagesIntroduction To Information & Communications Technology Introduction ToKathleen BorjaNo ratings yet
- Standards For Mobile Health-Related AppsDocument9 pagesStandards For Mobile Health-Related Appsharsono harsonoNo ratings yet
- What Is Intranet?: Document & Content ManagementDocument4 pagesWhat Is Intranet?: Document & Content Managementali muhdorNo ratings yet
- Quick Charge Device ListDocument16 pagesQuick Charge Device Listlimited0% (1)
- Microwave Oven: User'S ManualDocument20 pagesMicrowave Oven: User'S ManualRuiPereiraNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4Document39 pagesLesson 4Anne FloresNo ratings yet
- You Are Anointed For Good's Works PDFDocument2 pagesYou Are Anointed For Good's Works PDFJohn Nzinahora0% (1)
- Mata PadmavatiDocument2 pagesMata Padmavatinkhera.hecateNo ratings yet
- Angel CVDocument2 pagesAngel CValexandraNo ratings yet
- Organizational Behavior: Robbins & JudgeDocument18 pagesOrganizational Behavior: Robbins & JudgeYandex PrithuNo ratings yet
Performance Management and Appraisal
Performance Management and Appraisal
Uploaded by
Pricil Hanov0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views7 pagesThis document discusses performance appraisal and various methods for conducting appraisals. It begins by defining performance appraisal as evaluating an employee's current or past performance relative to standards. It then outlines the typical appraisal process of setting standards, assessing performance, and providing feedback. Several reasons for conducting appraisals are given, including for pay/promotion decisions, linking performance to goals, correcting deficiencies, and identifying training needs. The document concludes by describing various techniques for appraising performance such as rating scales, rankings, critical incidents, and management by objectives.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses performance appraisal and various methods for conducting appraisals. It begins by defining performance appraisal as evaluating an employee's current or past performance relative to standards. It then outlines the typical appraisal process of setting standards, assessing performance, and providing feedback. Several reasons for conducting appraisals are given, including for pay/promotion decisions, linking performance to goals, correcting deficiencies, and identifying training needs. The document concludes by describing various techniques for appraising performance such as rating scales, rankings, critical incidents, and management by objectives.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views7 pagesPerformance Management and Appraisal
Performance Management and Appraisal
Uploaded by
Pricil HanovThis document discusses performance appraisal and various methods for conducting appraisals. It begins by defining performance appraisal as evaluating an employee's current or past performance relative to standards. It then outlines the typical appraisal process of setting standards, assessing performance, and providing feedback. Several reasons for conducting appraisals are given, including for pay/promotion decisions, linking performance to goals, correcting deficiencies, and identifying training needs. The document concludes by describing various techniques for appraising performance such as rating scales, rankings, critical incidents, and management by objectives.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 7
Human Resources Management
Saturday, December 4, 2021
Performance Management and Appraisal
(Session 15&16)
What is Performance Appraisal?
Performance appraisal means evaluating an employee’s current and/or past performance
relative to his or her performance standards.
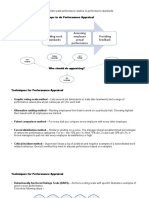
Performance Appraisal Process
1. Setting work standards
2. Assessing the employee’s actual performance relative to those standards
Usually involve some rating form
3. Providing feedback to the employee
Five Reasons Why We Need to Appraise Performance
1. Used for paying, promotion, and retention decisions
2. Link performance management to company goals
3. The manager can correct deficiencies and reinforce strengths
4. With appraisals, employees can review career plans
5. Training needs are identified
Who Should do the Appraising?
1. The supervisor
2. The peers (in peer appraisals)
3. Rating committees
4. The employee themselves (self-ratings)
5. Subordinates
6. Internal and external customers
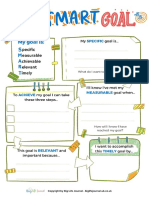
The Goals Importance
Effective appraisal goals should be SMART
- Specific
- Measurable
Human Resources Management
Saturday, December 4, 2021
- Attainable
- Relevant
- Timely
Techniques for Appraising Performance
Graphic rating scale method
- Using scale to list a number of traits and a range of performance for each.
- Next the employee is rated by identifying the score that best describes his/her
performance level for each trait.
- Managers must decide which job performance aspect to measure.
- Some options include generic dimensions, actual job duties, or behaviorally
recognizable competencies.
Alternative ranking method
- Employees are ranked from the best to worst on a particular trait, choosing highest,
then lowest, until all the employees ranked.
Human Resources Management
Saturday, December 4, 2021
Paired comparison method
- This method involves ranking employees by making a chart of all possible pairs of
employees for each trait and indicating which one is the better employee of the pair.
Forced distribution method
- Predetermined percentages of rates are placed in various performance categories,
which is similar to grading on a curve.
Human Resources Management
Saturday, December 4, 2021
Critical incident method
- A supervisor keeps a record of positive and negative examples of a subordinate’s
work-related behavior and reviews the record with the employee at predetermined
times.
Narrative forms
- The method involves rating the employee’s performance for each performance factor,
writing down examples and an improvement plan, aiding the employee in
understanding where his/her performance was good or bad, and summarizing with a
focus on problem solving.
Computerized and web-based method
- Using computer and web to appraise.
Electronic performance monitoring
Human Resources Management
Saturday, December 4, 2021
- Using electronic devices to monitor all the employees’ performances.
Behaviorally anchored rating scales (BARS)
- Method that combines the benefits of narratives, critical incidents, and quantified
scales by anchoring a scale with specific behavioral examples of good or poor
performance.
- Step of (BARS):
1. Generate critical incidents
2. Develop performance dimensions
3. Reallocate incidents
4. Scale the incidents
5. Develop a final instrument
Mixed standard scale
Human Resources Management
Saturday, December 4, 2021
- The employer ‘mixes’ together sequentially the good and poor behavioral example
statements when listing them.
- The aim is to reduce rating errors by making it less obvious to appraiser what
performance dimensions he or she is rating and whether the behavioral example
statements represent high, medium, or low performance.
Management by objectives (MBO)
- Multistep company wide goal setting and appraisal program.
- In MBO, the manager sets specific measurable goals with each employee and then
periodically discusses the employee’s progress toward these goals.
- Steps of MBO:
1. Set the organization’s goals
2. Set departmental goals
3. Discuss departmental goals
4. Define expected results (set individual goals)
5. Conduct performance reviews
6. Provide feedbacks
Comparison of each method
Human Resources Management
Saturday, December 4, 2021
You might also like
- Human Resource Management 15Th Edition Dessler Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument35 pagesHuman Resource Management 15Th Edition Dessler Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFEricHowardftzs100% (8)
- Consultants List-ADCEDocument6 pagesConsultants List-ADCEJaveed Taji100% (3)
- Unit 5 - Performace Evaluation and Control ProcessDocument17 pagesUnit 5 - Performace Evaluation and Control Processapi-1975380893% (14)
- My SMART Goal UK - Big Life JournalDocument6 pagesMy SMART Goal UK - Big Life Journalacmc100% (2)
- Performance Management & Appraisal: Presented By: FSZDocument32 pagesPerformance Management & Appraisal: Presented By: FSZRashedul IslamNo ratings yet
- Chap 9-HrlecDocument3 pagesChap 9-Hrlecjana leeNo ratings yet
- CH 9 - HR Performance Management and AppraisalDocument10 pagesCH 9 - HR Performance Management and AppraisalfirasNo ratings yet
- Performance Appraisal: Unit 3Document49 pagesPerformance Appraisal: Unit 3jerlinjoseNo ratings yet
- Performance Appraisal: Unit 3Document37 pagesPerformance Appraisal: Unit 3Bobby GeorgeNo ratings yet
- L6 Performance AppraisalDocument35 pagesL6 Performance Appraisaltruong.hd4358No ratings yet
- Perf Appraisal 1Document21 pagesPerf Appraisal 1OceanifyNo ratings yet
- HRM PRESENTATIONDocument16 pagesHRM PRESENTATIONAlfe Sani FahimNo ratings yet
- Indus Psych NotesDocument8 pagesIndus Psych NotesMinagaFathmaSonnayaNo ratings yet
- Performance Management VS Performance Appraisal: Presented by Alen Mathew GeorgeDocument28 pagesPerformance Management VS Performance Appraisal: Presented by Alen Mathew GeorgeAlen Mathew GeorgeNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Management 15th Edition Dessler Solutions ManualDocument14 pagesHuman Resource Management 15th Edition Dessler Solutions Manualmagdalavicemanocgp100% (23)
- HRM - Management of Performance Appraisal SystemDocument2 pagesHRM - Management of Performance Appraisal Systemitsmebridgeth100% (1)
- 9 Performance Management and AppraisalDocument26 pages9 Performance Management and Appraisalaahilchourasia873No ratings yet
- Human Resource Management 13Th Edition Gary Dessler Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument33 pagesHuman Resource Management 13Th Edition Gary Dessler Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFumbarasanayab100% (12)
- Human Resource Management 13th Edition Gary Dessler Solutions ManualDocument12 pagesHuman Resource Management 13th Edition Gary Dessler Solutions Manualmagdalavicemanocgp100% (30)
- Performance Management and AppraisalDocument6 pagesPerformance Management and Appraisalvnilla.lattNo ratings yet
- Performanceappraisal-160117065718Document31 pagesPerformanceappraisal-160117065718atiqur192122No ratings yet
- 09A Performance ManagementDocument49 pages09A Performance ManagementvarunNo ratings yet
- Process and Techniques For Appraising PerformaneDocument32 pagesProcess and Techniques For Appraising PerformaneĐào Minh Quân TrầnNo ratings yet
- Performance ManagementDocument7 pagesPerformance ManagementMARC URRUTIA MIRÓNo ratings yet
- Performance Management: Robert L. Mathis John H. JacksonDocument40 pagesPerformance Management: Robert L. Mathis John H. JacksonpritiNo ratings yet
- COM RDS 3 SEMHONS CC V Unit 4Document30 pagesCOM RDS 3 SEMHONS CC V Unit 4Anwesha KarmakarNo ratings yet
- 5 Performance Appraisal Methods-1Document4 pages5 Performance Appraisal Methods-1Khizer PashaNo ratings yet
- Project 1-Performance Appraisal Methods The Methods of Performance Appraisal Are As Follows A. Traditional MethodsDocument4 pagesProject 1-Performance Appraisal Methods The Methods of Performance Appraisal Are As Follows A. Traditional Methodsmanoj kumar DasNo ratings yet
- In-Class Activity 7Document3 pagesIn-Class Activity 7shajij321No ratings yet
- Setting Work Standards Assessing Employee Actual Performance Providing FeedbackDocument6 pagesSetting Work Standards Assessing Employee Actual Performance Providing FeedbackvinamramittalNo ratings yet
- Performance Management and Appraisal: T NineDocument12 pagesPerformance Management and Appraisal: T NineNouman AhmadNo ratings yet
- Performance Appraisal: - A Formal System of PERIODIC (Not Sporadic)Document12 pagesPerformance Appraisal: - A Formal System of PERIODIC (Not Sporadic)Ankita SharmaNo ratings yet
- Ch7 PSY16Document2 pagesCh7 PSY16Rain TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Dessler Ch9Document12 pagesDessler Ch9Muhammad Aditya TMNo ratings yet
- Unit 5Document15 pagesUnit 5vaishsrinivasNo ratings yet
- Performance Appraisal MethodsDocument18 pagesPerformance Appraisal MethodsMonique RamosNo ratings yet
- MSDM (Performance Appraisal)Document24 pagesMSDM (Performance Appraisal)Giovany AlvanoNo ratings yet
- 7.performance Appraisal (9-11E)Document39 pages7.performance Appraisal (9-11E)Fareed ShahwaniNo ratings yet
- MGT-351 Human Resource Management Chapter-9 Performance Management and AppraisalDocument22 pagesMGT-351 Human Resource Management Chapter-9 Performance Management and AppraisalNazmul Islam Joy 2031255630No ratings yet
- HRM Performance AppraisalDocument25 pagesHRM Performance AppraisalSuraj KumarNo ratings yet
- Babor - PERFORMANCE APPRAISALDocument6 pagesBabor - PERFORMANCE APPRAISALRica DonezaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 AppraisalDocument43 pagesChapter 7 AppraisalCường Nguyễn TháiNo ratings yet
- HRM AssignmentDocument15 pagesHRM AssignmentKhondaker Fahad JohnyNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Management: Performance Management and AppraisalDocument24 pagesHuman Resource Management: Performance Management and AppraisalHammad AliNo ratings yet
- Essentials of An Effective Performance Appraisal SystemDocument10 pagesEssentials of An Effective Performance Appraisal SystemSourav MickeyNo ratings yet
- Job Performance Employee Evaluated Manager Supervisor Career DevelopmentDocument6 pagesJob Performance Employee Evaluated Manager Supervisor Career DevelopmentKunal RajputNo ratings yet
- Performance AppraisalDocument3 pagesPerformance Appraisalfunelasjcg.cbpaNo ratings yet
- Erformance Anagement and Ppraisal: B P - J V CimpDocument25 pagesErformance Anagement and Ppraisal: B P - J V CimpSuraj KumarNo ratings yet
- Erformance Anagement and Ppraisal: B P - J V CimpDocument25 pagesErformance Anagement and Ppraisal: B P - J V CimpSuraj KumarNo ratings yet
- HRM PresentationDocument10 pagesHRM Presentationprashantbhati0440No ratings yet
- Chapter - 4Document48 pagesChapter - 4Ankitha KavyaNo ratings yet
- Presentation Human ResourceDocument17 pagesPresentation Human ResourceSamiira Abdukadir AdanNo ratings yet
- Performance AppraisalDocument73 pagesPerformance AppraisalPravat SatpathyNo ratings yet
- Performance Appraisal PERFORMANCE APPRAISALDocument61 pagesPerformance Appraisal PERFORMANCE APPRAISALAnkit SalujaNo ratings yet
- Institute of Business Administration University of Dhaka H601: Compensation Management Fall Semester, 2019Document42 pagesInstitute of Business Administration University of Dhaka H601: Compensation Management Fall Semester, 2019Tamim HossainNo ratings yet
- Performance Management and AppraisalDocument2 pagesPerformance Management and AppraisalkhanNo ratings yet
- Performance AppraisalDocument37 pagesPerformance AppraisalSaptrsi BanrjiNo ratings yet
- 20100814092649886Document12 pages20100814092649886Muhammad Irsyad33% (3)
- HRM Performance AppraisalDocument35 pagesHRM Performance AppraisalHARIS ZAFARNo ratings yet
- Performance AppraisalDocument32 pagesPerformance AppraisalParamesh WaranNo ratings yet
- Critical Incident Method Weighted ChecklistDocument6 pagesCritical Incident Method Weighted ChecklistsonammattooNo ratings yet
- How to Make the Most of Your Performance Appraisal: Adopt a winning attitude and reap the benefitsFrom EverandHow to Make the Most of Your Performance Appraisal: Adopt a winning attitude and reap the benefitsNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes Session 23 & 24Document7 pagesLecture Notes Session 23 & 24Pricil HanovNo ratings yet
- Building Positive Employee Relations - Session 13&14Document8 pagesBuilding Positive Employee Relations - Session 13&14Pricil HanovNo ratings yet
- HR SeparationDocument2 pagesHR SeparationPricil HanovNo ratings yet
- 19 - Managing Careers and RetentionsDocument6 pages19 - Managing Careers and RetentionsPricil HanovNo ratings yet
- Crusader Communicator: "Safer at Home" Edition #5: Sheboygan Lutheran High SchoolDocument7 pagesCrusader Communicator: "Safer at Home" Edition #5: Sheboygan Lutheran High SchoolMatt ThielNo ratings yet
- Atheism and Radical Skepticism Ibn Taymiyyahs Epistemic CritiqueDocument52 pagesAtheism and Radical Skepticism Ibn Taymiyyahs Epistemic CritiqueZaky MuzaffarNo ratings yet
- 0173NF2016 Fo2c PDFDocument26 pages0173NF2016 Fo2c PDFRadhakrishna MadabhushiNo ratings yet
- Standard Specification: LPG Loading / Unloading ArmDocument19 pagesStandard Specification: LPG Loading / Unloading ArmANIL KUMAR100% (1)
- Information Management Systems, ObstetricalDocument12 pagesInformation Management Systems, ObstetricalLee ThoongNo ratings yet
- Src419X 192-Khz Stereo Asynchronous Sample-Rate Converters: 1 Features 3 DescriptionDocument45 pagesSrc419X 192-Khz Stereo Asynchronous Sample-Rate Converters: 1 Features 3 DescriptionNguyễn QuangNo ratings yet
- Crossing The Jordan River 08-06-20Document37 pagesCrossing The Jordan River 08-06-20elmerdlpNo ratings yet
- SWE2007 - Fundamentals of Operating SystemsDocument6 pagesSWE2007 - Fundamentals of Operating SystemsmaneeshmogallpuNo ratings yet
- SOME and ANYDocument3 pagesSOME and ANYMikeNo ratings yet
- ZH 6000-10000 MK 4 İnst BookDocument90 pagesZH 6000-10000 MK 4 İnst BookESRANo ratings yet
- Chapter One The Problem and Its Setting 1.1 Background of The StudyDocument10 pagesChapter One The Problem and Its Setting 1.1 Background of The StudyJholo BuctonNo ratings yet
- English MCB - L-2Document3 pagesEnglish MCB - L-2Priya SinghNo ratings yet
- MPI GTU Study Material E-Notes Introduction-To-Microprocessor 13052022114954AMDocument4 pagesMPI GTU Study Material E-Notes Introduction-To-Microprocessor 13052022114954AMKartik RamchandaniNo ratings yet
- Dogmatism, Religion, and Psychological Type.Document16 pagesDogmatism, Religion, and Psychological Type.ciprilisticusNo ratings yet
- Experimentalstudies On The Effects of Reduction in Gear Tooth Stiffness Lubricant Film Thicknessina Spur Geared SystemDocument13 pagesExperimentalstudies On The Effects of Reduction in Gear Tooth Stiffness Lubricant Film Thicknessina Spur Geared SystemBurak TuncerNo ratings yet
- Ahb Example Amba System: Technical Reference ManualDocument222 pagesAhb Example Amba System: Technical Reference ManualJinsNo ratings yet
- Flame ArresterDocument2 pagesFlame ArresterNicholas RiveraNo ratings yet
- MTP44001Document63 pagesMTP44001Dong-seob ParkNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Information & Communications Technology Introduction ToDocument37 pagesIntroduction To Information & Communications Technology Introduction ToKathleen BorjaNo ratings yet
- Standards For Mobile Health-Related AppsDocument9 pagesStandards For Mobile Health-Related Appsharsono harsonoNo ratings yet
- What Is Intranet?: Document & Content ManagementDocument4 pagesWhat Is Intranet?: Document & Content Managementali muhdorNo ratings yet
- Quick Charge Device ListDocument16 pagesQuick Charge Device Listlimited0% (1)
- Microwave Oven: User'S ManualDocument20 pagesMicrowave Oven: User'S ManualRuiPereiraNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4Document39 pagesLesson 4Anne FloresNo ratings yet
- You Are Anointed For Good's Works PDFDocument2 pagesYou Are Anointed For Good's Works PDFJohn Nzinahora0% (1)
- Mata PadmavatiDocument2 pagesMata Padmavatinkhera.hecateNo ratings yet
- Angel CVDocument2 pagesAngel CValexandraNo ratings yet
- Organizational Behavior: Robbins & JudgeDocument18 pagesOrganizational Behavior: Robbins & JudgeYandex PrithuNo ratings yet