Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Digestive System Summary
Digestive System Summary
Uploaded by
Apple Bottom Jeans0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
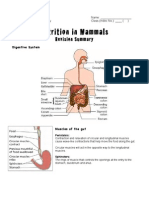
25 views2 pagesThe digestive system breaks down food through a multi-step process. Food enters the mouth where it is chewed by teeth and moistened by saliva. It then moves to the esophagus and is propelled to the stomach through peristalsis. In the stomach, protein digestion begins. The partially digested food moves to the small intestine, where the majority of digestion and absorption of nutrients occurs through enzymes from the pancreas, liver and intestine. The leftover waste then moves to the large intestine where water is absorbed before elimination of feces through the anus.
Original Description:
Original Title
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM SUMMARY
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe digestive system breaks down food through a multi-step process. Food enters the mouth where it is chewed by teeth and moistened by saliva. It then moves to the esophagus and is propelled to the stomach through peristalsis. In the stomach, protein digestion begins. The partially digested food moves to the small intestine, where the majority of digestion and absorption of nutrients occurs through enzymes from the pancreas, liver and intestine. The leftover waste then moves to the large intestine where water is absorbed before elimination of feces through the anus.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
25 views2 pagesDigestive System Summary
Digestive System Summary
Uploaded by
Apple Bottom JeansThe digestive system breaks down food through a multi-step process. Food enters the mouth where it is chewed by teeth and moistened by saliva. It then moves to the esophagus and is propelled to the stomach through peristalsis. In the stomach, protein digestion begins. The partially digested food moves to the small intestine, where the majority of digestion and absorption of nutrients occurs through enzymes from the pancreas, liver and intestine. The leftover waste then moves to the large intestine where water is absorbed before elimination of feces through the anus.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
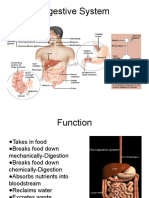
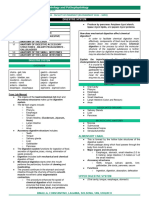
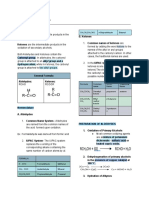
MAIN AND ACCESSORY ORGANS OF THE some of its most important proteins,
Sucrase (sugar) Glucose
DIGESTIVE SYSTEM excretion of waste products into bile,
● Oral Cavity - to serve as the entrance of carbohydrate metabolism, lipid metabolism, Lactase Lactose and
food and to initiate the digestive process by protein metabolism, filtering and cleansing Maltase (milk sugar) fructose
salivation and propulsion of the alimentary blood from poisonous substance
Maltose Glucose
bolus into the pharynx. ★ Gallbladder-store and recycle excess bile
● Pharynx - contains sensory receptors from the small intestine so that it can be and
around the fauces that activate when food reused for the digestion of subsequent galactose
enters the opening, triggering an instinctive meals
Glucose
swallowing response ★ Pancreas - secrete the hormones insulin
● Esophagus - serves as a passageway and glucagon into the blood [endocrine],
between the pharynx and stomach. Its secrete digestive enzymes into tiny ducts Bile from the liver Fats Fat
primary function is to empty food materials interwoven between the cells [exocrine] Bile salts globules droplets
into the stomach via peristalsis (waves of
contraction of its longitudinal and circular MAJOR SECRETIONS OF THE DIGESTIVE
muscle known as peristalsis). SYSTEM Intestinal Peptides Amino acids
● Stomach- located in the upper left quadrant
enzymes Sucrose Glucose
of the abdomen, receives food from the
esophagus. It is divided into the fundic, DIGESTIVE JUICE SUBSTAN PRODUC Peptidases (sugar) and fructose
cardiac, body, and pyloric regions. AND ENZYME CE T Sucrase Lactose Glucose
● Small Intestine - finishes the process of
Saliva DIGESTED Maltose Lactase (milk and
digestion, absorbs the nutrients, and
passes the residue on to the large intestine. Amylase Starch Maltase sugar) galactose
● Large Intestine - Absorption (water, salts, Maltose Glucose
vitamins), STorage (holds feces), Mixing Gastric juice Proteins Partly
and Propulsion, Lubrication
Protease (pepsin) and digested
● Rectum - collect feces from the colon,
notify that stool has to be released, and hydrochloric acid proteins The major secretions in the digestive system are:
keep the stool until it is expelled. In the mouth: saliva, salivary amylase, and
● Anus - where stools go out Pancreatic juice Proteins Peptides
lysozyme.
Proteases (trypsin) Fats and
★ Teeth - grinding food Stomach secretions from the gastric glands:
★ Tongue - manipulation to assist in chewing Lipases emulsified amino
hydrochloric acid, pepsin, mucus, and intrinsic factor.
and preparing material for swallowing, Amylase by bile acids
In the small intestine & associated glands -
secretion of mucins and lingual lipase, taste Chymotrypsin Starch Fatty
food ofc bile, bicarbonate ions, proteolytic, pancreatic
Carboxypeptidase acids and
★ Salivary Glands - produce saliva to enzymes, pancreatic amylase, pancreatic lipase,
moisten food glycerol
nucleases, mucus, peptidases, enterokinase,
★ Liver - production and secretion of bile into Maltose
the small intestine, synthesis of bile salts, sucrase, lactase, maltase, and isomaltase.
storage of excess glucose as glycogen,
Intestinal enzymes Peptides Amino
detoxification by converting toxins into
DIGESTIVE TRACK EVENTS
waste products and metabolizing nutrients Peptidases Sucrose acids
and medications to provide the body with
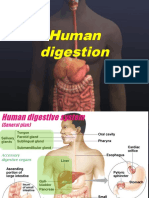
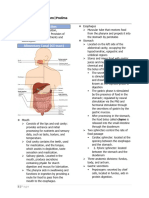
First, the food is taken into the mouth, and the food is
being chewed there by the teeth. Now, the food that
was broken down in the mouth is pushed into the
pharynx or the throat by the tongue, and further into
the esophagus, which produces mucus for
lubrication, but no digestive enzymes are present
here. Then to the stomach in which a large part of
protein digestion occurs. And then the chyme moves
from the stomach to the small intestine. The small
intestine is the organ where the digestion of proteins,
fats, nucleic acid, minerals, vitamins, carbohydrates,
and water is completed. And moves then to the large
intestine where it reabsorbs the water from
indigestible food material and processes the waste
material. The undigested food then will enter your
colon where the water will be reabsorbed into the
body and the excess waste is eliminated through your
anus.
You might also like
- NCM 116 Prelims ReviewerDocument28 pagesNCM 116 Prelims ReviewerMary Cruz100% (2)
- PEM4 Fuel Configuration and SelectionDocument3 pagesPEM4 Fuel Configuration and SelectionSergei GovorkoNo ratings yet
- Human PhysiologyDocument257 pagesHuman PhysiologyAyushNo ratings yet
- Enzyme: DigestionDocument5 pagesEnzyme: Digestion24 LOONG BAO XINl龙宝鈊No ratings yet
- Digestion and AbsorptionDocument10 pagesDigestion and Absorptionvivek kumarNo ratings yet
- Digestion-Food Is BrokenDocument32 pagesDigestion-Food Is Brokenaerell manuelNo ratings yet
- Digestion and Absorption By-Dr. Suntia Saxena Part 2Document41 pagesDigestion and Absorption By-Dr. Suntia Saxena Part 2Divya AgarawalNo ratings yet
- Digestion WiwiDocument23 pagesDigestion WiwiSCE1-0622 Amni Insyirah Binti Mohd NasarudinNo ratings yet
- Biology DigestionDocument14 pagesBiology DigestionhhhhhhhhhhhhhhNo ratings yet
- The Alimentary CanalDocument10 pagesThe Alimentary CanalJade J.No ratings yet
- Digestive System OverviewDocument40 pagesDigestive System OverviewJOHN PAUL B. ENOPIANo ratings yet
- Presentation 05 Human DigestionDocument45 pagesPresentation 05 Human DigestionCarl (Carl)No ratings yet
- Presentation 05 Human DigestionDocument40 pagesPresentation 05 Human DigestionCarl (Carl)No ratings yet
- Animal NutritionDocument48 pagesAnimal Nutritionalkirstenlexie.galvezNo ratings yet
- 06 Nutrition in Humans NoteDocument12 pages06 Nutrition in Humans Notetarankaur401No ratings yet
- Human Digestive SystemDocument8 pagesHuman Digestive SystemBlister CountNo ratings yet
- Biology Piratical 2024Document21 pagesBiology Piratical 2024roddybrainiacNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in AnimalsDocument46 pagesNutrition in AnimalsFreshNo ratings yet
- Digestion, Absorption and TransportDocument48 pagesDigestion, Absorption and TransportAJ VizmanosNo ratings yet
- Nutrition and Diet Theraphy PDF 2Document1 pageNutrition and Diet Theraphy PDF 29xc2fc8hnqNo ratings yet
- The Digestive System - Physical & ChemicalDocument19 pagesThe Digestive System - Physical & ChemicalTrinity BenjaminNo ratings yet
- 9 Nutrition-and-dietetics-IntroDocument51 pages9 Nutrition-and-dietetics-IntroPratiksha JhareeNo ratings yet
- Human Digestive PDFDocument1 pageHuman Digestive PDFsiyin limNo ratings yet
- Food Classes: FAT Water Vitamins, Minerals, & Roughage ProteinDocument25 pagesFood Classes: FAT Water Vitamins, Minerals, & Roughage Proteinuminoriah80% (5)
- DigestionenzymesDocument3 pagesDigestionenzymesapi-358681703No ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal SystemDocument33 pagesGastrointestinal Systemngocnguyen033No ratings yet
- Digestion of Food (PS)Document12 pagesDigestion of Food (PS)Pragya SahooNo ratings yet
- 3 - Alimentary CanalDocument18 pages3 - Alimentary CanalPuji AnastasiaNo ratings yet
- The Digestive Enzyme of The BodyDocument12 pagesThe Digestive Enzyme of The BodyClarisse WongNo ratings yet
- 2nd AssignmentDocument4 pages2nd AssignmentpakayaNo ratings yet
- Rev Sci Summary DigestionDocument2 pagesRev Sci Summary Digestionprameeta100% (1)
- PDF 1686404856729 7747998126007773086Document45 pagesPDF 1686404856729 7747998126007773086Pratiksha JhareeNo ratings yet
- Gastro highlightCHAPTER1Document12 pagesGastro highlightCHAPTER1Lovely CruzxNo ratings yet
- 618lab DigestiveDocument16 pages618lab DigestiveKirsten Shayne ManingasNo ratings yet
- GASTROSYSP1Document11 pagesGASTROSYSP1merlinalra.lucero.mnlNo ratings yet
- DigestionDocument7 pagesDigestionAbubakar Sunusi IshakNo ratings yet
- Week 14: Digestion Chemistry: Intrinsic FactorDocument4 pagesWeek 14: Digestion Chemistry: Intrinsic FactorLore Anne Mhae SantosNo ratings yet
- (BIO) Chapter 4 - Nutrition in HumanDocument21 pages(BIO) Chapter 4 - Nutrition in Humantaco ghoulNo ratings yet
- The Small IntestineDocument16 pagesThe Small IntestineMichael NyaongoNo ratings yet
- Digestion and AbsorptionDocument11 pagesDigestion and Absorption2023541012tnauNo ratings yet
- Digestive Form 4Document43 pagesDigestive Form 4miraazizNo ratings yet
- Digestive System: Overview of The Digestive System Physiology of Digestion and AbsorptionDocument26 pagesDigestive System: Overview of The Digestive System Physiology of Digestion and AbsorptionTemz HlubyNo ratings yet
- Digestion and Absorption of Carbohydrate Lecture For 1st Yr MBBS by DR WaseemDocument33 pagesDigestion and Absorption of Carbohydrate Lecture For 1st Yr MBBS by DR WaseemIMDCBiochem100% (2)
- 3.3 Human Digestive SystemDocument17 pages3.3 Human Digestive SystemCASSENDREA CHAI CHEN YI MoeNo ratings yet
- The Digestive System BrochureDocument2 pagesThe Digestive System BrochureWasna Osama Al SaifNo ratings yet
- A&P: The Digestive SystemDocument79 pagesA&P: The Digestive SystemxiaoNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument24 pagesDigestive SystemDainalissa SaddlerNo ratings yet
- Digestive SystemDocument49 pagesDigestive SystemDaniel WakaWakaNo ratings yet
- Small Intestine and PancreasDocument52 pagesSmall Intestine and PancreasLutfi AuliaNo ratings yet
- 2 - Carbohydrates (Part 2)Document25 pages2 - Carbohydrates (Part 2)Sean Polo MallariNo ratings yet
- Principle of Digestion, Digestive Juices - Composition, Phases of Secretion, Regulations and FunctionsDocument31 pagesPrinciple of Digestion, Digestive Juices - Composition, Phases of Secretion, Regulations and FunctionsRaju NiraulaNo ratings yet
- Digestion of Carbohydrate Enzyme Produced BY Site of Action Substrate Acting On End ProductsDocument3 pagesDigestion of Carbohydrate Enzyme Produced BY Site of Action Substrate Acting On End ProductsNepomuceno, Sanny Jr. T.No ratings yet
- PDF Digestion and Absorption of Carbohydrate and ProteinDocument5 pagesPDF Digestion and Absorption of Carbohydrate and ProteinHhh HhhNo ratings yet
- Science First Quarter Grade 9Document10 pagesScience First Quarter Grade 9Hikinwind GamerNo ratings yet
- Digestive System Educational Video in Red Pink Illustrative StyleDocument15 pagesDigestive System Educational Video in Red Pink Illustrative Stylefarrahfahad72No ratings yet
- 5 & 6. Fisiologi Digestif-BSDocument56 pages5 & 6. Fisiologi Digestif-BSNingrum JayantiNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in HumansDocument4 pagesNutrition in Humanselise limNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in MammalsDocument4 pagesNutrition in MammalsAhmed OmarNo ratings yet
- Digestive ReviewerDocument1 pageDigestive ReviewerJay Ivan Milen GamboaNo ratings yet
- Name: (Class: 3EB Chapter 5: Nutrition in AnimalsDocument10 pagesName: (Class: 3EB Chapter 5: Nutrition in Animalsjanling82No ratings yet
- NCM 103 - CommunicationDocument7 pagesNCM 103 - CommunicationApple Bottom JeansNo ratings yet
- Biochemlab (Lipids)Document18 pagesBiochemlab (Lipids)Apple Bottom JeansNo ratings yet
- Perinatal PeriodDocument3 pagesPerinatal PeriodApple Bottom JeansNo ratings yet
- Voting and PatternsDocument12 pagesVoting and PatternsApple Bottom JeansNo ratings yet
- NCM 101 - Assessmental of Mental StatusDocument3 pagesNCM 101 - Assessmental of Mental StatusApple Bottom JeansNo ratings yet
- Family CHNDocument10 pagesFamily CHNApple Bottom JeansNo ratings yet
- Important Legal Matters For MarriageDocument3 pagesImportant Legal Matters For MarriageApple Bottom JeansNo ratings yet
- Maglaya Nursing ProcessDocument4 pagesMaglaya Nursing ProcessApple Bottom JeansNo ratings yet
- Philosophers - Locke, Churchland, FreudDocument2 pagesPhilosophers - Locke, Churchland, FreudApple Bottom JeansNo ratings yet
- Unit Iii (Bioethics)Document3 pagesUnit Iii (Bioethics)Apple Bottom JeansNo ratings yet
- Aldehydes and KetonesDocument8 pagesAldehydes and KetonesApple Bottom JeansNo ratings yet
- Voting SystemsDocument4 pagesVoting SystemsApple Bottom JeansNo ratings yet
- ETHERSDocument2 pagesETHERSApple Bottom JeansNo ratings yet
- General Physics IntroductionDocument2 pagesGeneral Physics IntroductionApple Bottom JeansNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Balancing EquationsDocument3 pagesChemistry Balancing EquationsApple Bottom JeansNo ratings yet
- Product Description RailPipe System With EBA CertificationDocument16 pagesProduct Description RailPipe System With EBA Certificationjpantazis1975No ratings yet
- Components of Time SeriesDocument4 pagesComponents of Time SeriesSumit BainNo ratings yet
- JJJ ThursdayDocument47 pagesJJJ ThursdayhozhabrNo ratings yet
- EquipguideDocument8 pagesEquipguideNilton Bruno Salazar MartinezNo ratings yet
- Stretch Your ImaginationDocument3 pagesStretch Your ImaginationJilliene IsaacsNo ratings yet
- MixxxDocument29 pagesMixxxAixita sanhuezaNo ratings yet
- Rendering Trees From Precomputed Z-Buffer ViewsDocument10 pagesRendering Trees From Precomputed Z-Buffer ViewsLuis Enrique PulidoNo ratings yet
- Approximate Integration: Dr. Lê Xuân Đ IDocument34 pagesApproximate Integration: Dr. Lê Xuân Đ ITran Nguyen KhangNo ratings yet
- Spot Report LisondraDocument3 pagesSpot Report LisondraKim MoritNo ratings yet
- He Who Is Possessed of Supreme Knowledge by Concentration of MindDocument46 pagesHe Who Is Possessed of Supreme Knowledge by Concentration of MindGaurav PratikNo ratings yet
- Old MACDONALD Had A Farm LyricsDocument1 pageOld MACDONALD Had A Farm Lyricsanna zmNo ratings yet
- Man Industrial Gas Engines e 2876 Te 302 Repair ManualDocument10 pagesMan Industrial Gas Engines e 2876 Te 302 Repair ManualMichael100% (58)
- Melatonin Agonists A Brief Clinical ReviewDocument6 pagesMelatonin Agonists A Brief Clinical ReviewgeoaislaNo ratings yet
- Psych Case StudyDocument94 pagesPsych Case Studyrhia casinillo100% (4)
- Learning Through StoriesDocument21 pagesLearning Through Storiesjeff talk talksNo ratings yet
- IFP 2021 Oct 18 STM Based Automation and Energy Management SystemDocument11 pagesIFP 2021 Oct 18 STM Based Automation and Energy Management Systemleo rajuNo ratings yet
- Theoretical Overview of Surge AnalysesDocument14 pagesTheoretical Overview of Surge AnalysesdNo ratings yet
- Rear Final Drive 0BC 0BD 0BE 0BFDocument177 pagesRear Final Drive 0BC 0BD 0BE 0BFergdegNo ratings yet
- Rule of Procedure For Environmental CasesDocument84 pagesRule of Procedure For Environmental CasesjelyneptNo ratings yet
- 13 013 Design PDFDocument6 pages13 013 Design PDFMayur RaundalNo ratings yet
- 12 PAPYEX Flexible Graphite Mersen - 09 PDFDocument14 pages12 PAPYEX Flexible Graphite Mersen - 09 PDFarizagameroNo ratings yet
- 2014 Fokke GBS Brighton Brain 2014Document36 pages2014 Fokke GBS Brighton Brain 2014putriNo ratings yet
- PG ENGLISH-Q-BOOK CompressedDocument424 pagesPG ENGLISH-Q-BOOK CompressedPOOJA RSNo ratings yet
- DE Question BankDocument5 pagesDE Question BankKaree MullahNo ratings yet
- VMC Advance 1 Paper 1Document11 pagesVMC Advance 1 Paper 1amogh kumarNo ratings yet
- CAE Listening Practice Test 20 Printable v2Document8 pagesCAE Listening Practice Test 20 Printable v2Trang NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Assignment #3: Due April 11, 2016Document6 pagesAssignment #3: Due April 11, 2016Ahmed HamoudaNo ratings yet
- Inulin PDFDocument14 pagesInulin PDFNani HardiantiNo ratings yet
- FortiGate 600CDocument2 pagesFortiGate 600CImam Adhita ViryaNo ratings yet