Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Third Space Learning Quadratic Graphs GCSE Worksheet
Third Space Learning Quadratic Graphs GCSE Worksheet
Uploaded by
ZoonieFRCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Third Space Learning Quadratic Graphs GCSE Worksheet
Third Space Learning Quadratic Graphs GCSE Worksheet
Uploaded by
ZoonieFRCopyright:
Available Formats
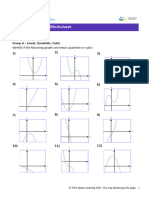
GCSE Maths Revision | Algebra
Quadratic Graphs - Worksheet
Skill
Group A - Graphs of simple quadratic functions
Plot the graphs of these functions, using the x values given.
1) 𝑦 2
= 𝑥 + 1, − 3 ≤ 𝑥 ≤ 3 2) 𝑦 2
= 𝑥 + 3, − 3 ≤ 𝑥 ≤ 3 3) 𝑦 2
= 𝑥 − 3, − 3 ≤ 𝑥 ≤ 3
4) 𝑦 2
= 𝑥 + 3𝑥, − 5 ≤ 𝑥 ≤ 2 5) 𝑦 2
= 𝑥 + 4𝑥, − 6 ≤ 𝑥 ≤ 2 6) 𝑦 2
= 𝑥 − 2𝑥, − 2 ≤ 𝑥 ≤ 4
7) 𝑦 2
= 𝑥 + 3𝑥 + 1, − 5 ≤ 𝑥 ≤ 3 8) 𝑦 2
= 𝑥 + 2𝑥 + 1, − 5 ≤ 𝑥 ≤ 3 9) 𝑦 2
= 𝑥 − 3𝑥 + 1, − 2 ≤ 𝑥 ≤ 5
Group B - Graphs of more tricky quadratic functions
Plot the graphs of these functions, using the x values given.
1) 𝑦 2
= 𝑥 − 2𝑥, − 3 ≤ 𝑥 ≤ 5 2) 𝑦 2
= 𝑥 + 2𝑥 + 5, − 4 ≤ 𝑥 ≤ 2 3) 𝑦 2
= 𝑥 − 2𝑥 + 5, − 2 ≤ 𝑥 ≤ 4
4) 𝑦 2
=3 − 𝑥 , − 3 ≤ 𝑥 ≤ 3 5) 𝑦 2
= 3𝑥 − 𝑥 , − 3 ≤ 𝑥 ≤ 5 6) 𝑦 2
= 3 + 2𝑥 − 𝑥 ,− 2 ≤ 𝑥 ≤ 4
7) 𝑦 = 2𝑥
2
+ 4𝑥, − 4 ≤ 𝑥 ≤ 2 8) 𝑦 2
= 4𝑥 + 2𝑥 + 3, − 4 ≤ 𝑥 ≤ 2 9) 𝑦 2
= 4𝑥 − 2𝑥 , − 1 ≤ 𝑥 ≤ 3
Group C - Finding key points and sketching quadratic graphs
Find the turning points and y-intercepts of these quadratic functions, then sketch their graphs.
2 2 2
1) 𝑦 = 𝑥 + 6𝑥 + 8 2) 𝑦 = 𝑥 + 8𝑥 + 12 3) 𝑦 = 𝑥 − 2𝑥 − 8
2 2 2
4) 𝑦 = 𝑥 + 3𝑥 5) 𝑦 = 𝑥 − 3𝑥 6) 𝑦 = 2𝑥 + 3𝑥
2 2 2
7) 𝑦 = 4𝑥 − 2𝑥 8) 𝑦 = 4𝑥 + 2𝑥 + 3 9) 𝑦 = 4𝑥 + 2𝑥
© Third Space Learning 2021. You may photocopy this page. 1
GCSE Maths Revision | Algebra
Quadratic Graphs - Worksheet
Applied
1) a) 2
Draw the graph of the function 𝑦 = 𝑥 + 2𝑥 + 4, − 4 ≤ 𝑥 ≤ 2
b) Use your graph to write down the coordinates of the turning point. Is it a
maximum or a minimum?
c) 2
What happens when you try to solve the equation 𝑥 + 2𝑥 + 4 = 0? Use your
graph to explain why this happens.
2) a) 2
Draw the graph of the function 𝑦 = 𝑥 − 5𝑥 + 6, − 1 ≤ 𝑥 ≤ 6
b) 2
Solve the equation 𝑥 − 5𝑥 + 6 = 0. Where can you see these solutions on
the graph?
c) Use your graph to estimate the coordinates of the turning point. Check your
2
answer algebraically by completing the square on the expression 𝑥 − 5𝑥 + 6.
3) a) 2
Draw the graph of the function 𝑦 = 2𝑥 + 8 − 𝑥 , − 3 ≤ 𝑥 ≤ 5.
b) Write down the coordinates of the vertex and roots.
c) 2
Using the graph, estimate the solutions to the equation 2𝑥 + 8 − 𝑥 = 4.
d) 2
Using the graph, find the solutions to the equation 2𝑥 + 8 = 𝑥 .
e) 2
Using the graph, find the solutions to the equation 2𝑥 + 8 − 𝑥 = 2𝑥 + 4.
Check your answer algebraically.
© Third Space Learning 2021. You may photocopy this page. 2
GCSE Maths Revision | Algebra
Quadratic Graphs - Exam Questions
1) (a) 2
Complete the table of values for 𝑦 = 𝑥 − 5𝑥 − 2 (2)
(b) On the grid draw the graph of (2)
2
𝑦 = 𝑥 − 5𝑥 − 2 for values of x from -1 to 6
(c) Use the graph to find estimates of the solutions to the equation ….……………
2
− 4 = 𝑥 − 5𝑥 − 2 (2)
(6 marks)
© Third Space Learning 2021. You may photocopy this page. 3
2) (a) 2
Here is the graph of 𝑦 = 𝑥 + 4𝑥 − 2 ….……………
(1)
2
Write down the turning point of the graph 𝑦 = 𝑥 + 4𝑥 − 2
(b) Use the graph to find approximate roots of the equation ….……………
2
𝑥 + 4𝑥 + 3 = 5 (2)
(c) Use the graph to find approximate solutions of the equation ….……………
2
5 = 𝑥 + 4𝑥 − 2 (2)
(5 marks)
© Third Space Learning 2021. You may photocopy this page. 4
3) (a) Complete the table of values for 𝑦 = 3 − 2𝑥 − 𝑥
2 ….……………
(2)
(b) 2
Draw the graph of 𝑦 = 3 − 2𝑥 − 𝑥 for values of x from -4 to ….……………
2. (2)
(c) Use the graph to find estimates of the solutions to the equation ….……………
3 − 2𝑥 = 𝑥
2 (2)
(d) Use the graph to find the coordinates of the turning point of the ….……………
graph 𝑦 = 3 − 2𝑥 − 𝑥 .
2 (1)
(7 marks)
© Third Space Learning 2021. You may photocopy this page. 5
GCSE Maths Revision | Algebra
Quadratic Graphs - Answers
Question Answer
Group A Skill Questions
Plot the graphs of these functions, using
the x values given. 1-3)
You can plot each set of three graphs on
one set of axes to speed things up.
2
1) 𝑦 = 𝑥 + 1, − 3 ≤ 𝑥 ≤ 3
2
2) 𝑦 = 𝑥 + 3, − 3 ≤ 𝑥 ≤ 3
2
3) 𝑦 = 𝑥 − 3, − 3 ≤ 𝑥 ≤ 3
2
4) 𝑦 = 𝑥 + 3𝑥, − 5 ≤ 𝑥 ≤ 2 4-6)
2
5) 𝑦 = 𝑥 + 4𝑥, − 6 ≤ 𝑥 ≤ 2
2
6) 𝑦 = 𝑥 − 2𝑥, − 2 ≤ 𝑥 ≤ 4
© Third Space Learning 2021. You may photocopy this page. 6
2
7) 𝑦 = 𝑥 + 3𝑥 + 1, − 5 ≤ 𝑥 ≤ 3 7-9)
2
8) 𝑦 = 𝑥 + 2𝑥 + 1, − 5 ≤ 𝑥 ≤ 3
2
9) 𝑦 = 𝑥 − 3𝑥 + 1, − 2 ≤ 𝑥 ≤ 5
Group B Plot the graphs of these functions, using
the x values given.
You can plot each set of three graphs on
one set of axes to speed things up. 1-3)
2
1) 𝑦 = 𝑥 − 2𝑥, − 3 ≤ 𝑥 ≤ 5
2
2) 𝑦 = 𝑥 + 2𝑥 + 5, − 4 ≤ 𝑥 ≤ 2
2
3) 𝑦 = 𝑥 − 2𝑥 + 5, − 2 ≤ 𝑥 ≤ 4
4-6)
2
4) 𝑦 = 3 − 𝑥 , − 3 ≤ 𝑥 ≤ 3
2
5) 𝑦 = 3𝑥 − 𝑥 , − 3 ≤ 𝑥 ≤ 5
2
6) 𝑦 = 3 + 2𝑥 − 𝑥 ,− 2 ≤ 𝑥 ≤ 4
7) 𝑦 = 2𝑥
2
+ 4𝑥, − 4 ≤ 𝑥 ≤ 2 7-9)
2
8) 𝑦 = 4𝑥 + 2𝑥 + 3, − 4 ≤ 𝑥 ≤ 2
2
9) 𝑦 = 4𝑥 − 2𝑥 , − 1 ≤ 𝑥 ≤ 3
© Third Space Learning 2021. You may photocopy this page. 7
GCSE Maths Revision | Algebra
Quadratic Graphs - Answers
Question Answer
Group C Skill Questions
Find the key points of these quadratic 1-3)
functions algebraically, then sketch their
graphs.
You can sketch each set of three graphs on
one set of axes to speed things up.
2
1) 𝑦 = 𝑥 + 6𝑥 + 8
2 2
2) 𝑦 = 𝑥 + 8𝑥 + 12 𝑦 = 𝑥 + 6𝑥 + 8
2 Roots (-4,0) and (-2,0)
3) 𝑦 = 𝑥 − 2𝑥 − 8 Vertex (-3,-1)
y-intercept (0,8)
2
𝑦 = 𝑥 + 8𝑥 + 12
Roots (-6,0) and (-2,0)
Vertex (-4,-4)
y-intercept (0,-8)
2
𝑦 = 𝑥 − 2𝑥 − 8
Roots (-2,0) and (4,0)
Vertex (1,-9)
y-intercept (0,12)
2
4) 𝑦 = 𝑥 + 6𝑥 + 8 4-6)
2
5) 𝑦 = 𝑥 + 8𝑥 + 12
2
6) 𝑦 = 𝑥 − 2𝑥 − 8
2
𝑦 = 𝑥 + 3𝑥
Roots (0,0) and (-3,0)
© Third Space Learning 2021. You may photocopy this page. 8
3 9
Vertex (- 2 ,- 4 )
y-intercept (0,0)
2
𝑦 = 𝑥 − 3𝑥
Roots (0,0) and (3,0)
3 9
Vertex ( 2 ,- 4 )
y-intercept (0,0)
2
𝑦 = 2𝑥 + 3𝑥
3
Roots (0,0) and (- 2 ,0)
3 9
Vertex (- 4 ,- 8 )
y-intercept (0,0)
2
7) 𝑦 = 4 − 𝑥 7-9)
2
8) 𝑦 = 4 + 3𝑥 − 𝑥
2
9) 𝑦 = 𝑥 + 4
2
𝑦 = 4 −𝑥
Roots (2,0) and (-2,0)
Vertex (0,4)
y-intercept (0,4)
2
𝑦 = 4 + 3𝑥 − 𝑥
Roots (-1,0) and (4,0)
3 25
Vertex ( 2 , 4 )
y-intercept (0,4)
2
𝑦 =𝑥 + 4
No real roots
Vertex (0,4)
y-intercept (0,4)
© Third Space Learning 2021. You may photocopy this page. 9
GCSE Maths Revision | Algebra
Quadratic Graphs - Answers
Question Answer
Applied Questions
1) a) Draw the graph of the function a)
2
𝑦 = 𝑥 + 2𝑥 + 4, − 4 ≤ 𝑥 ≤ 2
b) (− 1, 3)
b)
Use your graph to write down the
coordinates of the turning point. Is it a Minimum.
maximum or a minimum?
c)
There are no (real) solutions -
c) What happens when you try to solve the
2 the quadratic formula doesn’t
equation 𝑥 + 2𝑥 + 4 = 0? Use your graph
work because you have to
to explain why this happens.
square root a negative
number. The graph has no
x-intercepts so we can tell
there are no real roots.
© Third Space Learning 2021. You may photocopy this page. 10
2) a) Draw the graph of the function
2
𝑦 = 𝑥 − 5𝑥 + 6, − 1 ≤ 𝑥 ≤ 6
a)
2
(𝑥 − 3)(𝑥 − 2) = 0
b) Solve the equation 𝑥 − 5𝑥 + 6 = 0.
b) gives solutions 𝑥 = 3, 𝑥 = 2.
Where can you see these solutions on the
These solutions are the
graph?
roots/x-intercepts.
c)
Use your graph to estimate the coordinates
of the turning point. If you know how to,
check your answer algebraically by 5 −1
c)
(2, )
completing the square on the expression 4
5 2 1
2 (𝑥 − ) −
𝑥 − 5𝑥 + 6. 2 4
© Third Space Learning 2021. You may photocopy this page. 11
3) a) Draw the graph of the function
a)
2
𝑦 = 2𝑥 + 8 − 𝑥 , − 3 ≤ 𝑥 ≤ 5
b)
b) Write down the coordinates of the vertex
Vertex (1, 9)
and roots. Roots 𝑥 = 4, 𝑥 =− 2
c)
c) Using the graph, estimate the solutions to
2 𝑥 =− 1. 2, 𝑥 = 3. 2
the equation 2𝑥 + 8 − 𝑥 = 4.
d) Using the graph, find the solutions to the
d) 𝑥 = 4, 𝑥 =− 2
2
equation 2𝑥 + 8 = 𝑥 .
e) Using the graph, find the solutions to the
e)
2
equation 2𝑥 + 8 − 𝑥 = 2𝑥 + 4. Check
your answer algebraically.
© Third Space Learning 2021. You may photocopy this page. 12
GCSE Maths Revision | Algebra
Quadratic Graphs - Mark Scheme
Question Answer
Exam Questions
1) (a) Complete the table of values for (a) (2)
2
𝑦 = 𝑥 − 5𝑥 − 2
(1) 4-5 correct values
(1) All correct values
(b) On the grid draw the graph of (b) (2)
2
𝑦 = 𝑥 − 5𝑥 − 2 for values of x
from -1 to 6
(1) Points plotted correctly ft. pt (a)
(1) Points joined with a smooth curve
(c) Use the graph to find estimates of the 𝑥 = 0. 4, 𝑥 = 4. 6 (2)
solutions to the equation
2 (1) Line 𝑦 =− 4 drawn on graph
− 4 = 𝑥 − 5𝑥 − 2 (1) Solutions ± 0. 1
© Third Space Learning 2021. You may photocopy this page. 13
2) (a) Write down the turning point of the (a) (− 2, − 6) (1)
2
graph 𝑦 = 𝑥 + 4𝑥 − 2
(1) Correct coordinates
(b) Use the graph to find approximate (b) 𝑥 = 0. 4, 𝑥 =− 4. 4 (2)
roots of the equation
2 2
𝑥 + 4𝑥 + 3 = 5 (1) Rearrangement to 𝑥 + 4𝑥 + 3 = 5
and indication of reading x-intercept values
(1) Correct answers
(c) Use the graph to find approximate (c) 𝑥 = 1. 3, 𝑥 =− 5. 3 (2)
solutions of the equation (1) Line 𝑦 = 5 drawn on graph
2
5 = 𝑥 + 4𝑥 − 2 (1) Solutions ± 0. 1
3) (a) Complete the table of values for (a) (2)
2
𝑦 = 3 − 2𝑥 − 𝑥
(1) 4-5 correct values
(1) All correct values
(b) Draw the graph of (b) (2)
2
𝑦 = 3 − 2𝑥 − 𝑥 for values of x
from -4 to 2.
(1) Points plotted correctly ft. pt (a)
(1) Points joined with a smooth curve
Use the graph to find estimates of the (c) 𝑥 =− 3, 𝑥 = 1 (2)
solutions to the equation
2 (1) Rearrangement to 3 − 2𝑥 − 𝑥 = 0 and
3 − 2𝑥 = 𝑥
indication of reading x-intercept values
(1) Correct answers
© Third Space Learning 2021. You may photocopy this page. 14
Use the graph to find the coordinates (− 1, 4) (1)
of the turning point of the graph
2 (1) Correct coordinates
𝑦 = 3 − 2𝑥 − 𝑥
Do you have KS4 students who need additional support in maths?
Our specialist tutors will help them develop the skills they need to succeed at GCSE in weekly one to one online
revision lessons. Trusted by secondary schools across the UK.
Visit thirdspacelearning.com to find out more.
© Third Space Learning 2021. You may photocopy this page. 15
You might also like
- 4ph1 1pr Que 20230525Document26 pages4ph1 1pr Que 20230525ZoonieFR0% (1)
- A - 1 DANGER OF A SINGLE STORY Edexcel Igcse English Language A Anthology Free Study NotesDocument18 pagesA - 1 DANGER OF A SINGLE STORY Edexcel Igcse English Language A Anthology Free Study NotesZoonieFRNo ratings yet
- Unseen-Poems (1) Edexcel Igcse English Language A Free Exam PracticeDocument10 pagesUnseen-Poems (1) Edexcel Igcse English Language A Free Exam PracticeZoonieFRNo ratings yet
- MATH 2412 Precalculus Prerequisite ReviewDocument4 pagesMATH 2412 Precalculus Prerequisite ReviewAnaNo ratings yet
- Millard HouseDocument20 pagesMillard HouseMadiha Rehmath100% (1)
- Informatica FunctionsDocument46 pagesInformatica FunctionsManoj Krishna100% (1)
- Third Space Learning Completing The Square GCSE WorksheetDocument11 pagesThird Space Learning Completing The Square GCSE Worksheetisaaceden24No ratings yet
- Third Space Learning Solving Equations GCSE WorksheetDocument6 pagesThird Space Learning Solving Equations GCSE WorksheetZoonieFRNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Equations - Worksheet: Skill Group A - Factorising Quadratics 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 2 6) 2 7) 2 8) 3 9) 2Document10 pagesQuadratic Equations - Worksheet: Skill Group A - Factorising Quadratics 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 2 6) 2 7) 2 8) 3 9) 2erin zietsmanNo ratings yet
- Third Space Learning Quadratic Simultaneous Equations GCSE Worksheet 1Document9 pagesThird Space Learning Quadratic Simultaneous Equations GCSE Worksheet 1Sabrin AhmedNo ratings yet
- Equations and Subject of The Formula Worksheet With SolutionsDocument11 pagesEquations and Subject of The Formula Worksheet With SolutionsCamille ComasNo ratings yet
- Third Space Learning Factorising Quadratics Double 230821 025952Document7 pagesThird Space Learning Factorising Quadratics Double 230821 025952Chelsea ChikafuNo ratings yet
- Third Space Learning Factorising Quadratics Double Brackets GCSE WorksheetDocument6 pagesThird Space Learning Factorising Quadratics Double Brackets GCSE Worksheetaliza khanNo ratings yet
- Essential Skills Whole BookletDocument44 pagesEssential Skills Whole BookletJo PatrickNo ratings yet
- Specimen of Admission Test Bachelor S Degree Programme - Academic Year 2021/22 - MathematicsDocument4 pagesSpecimen of Admission Test Bachelor S Degree Programme - Academic Year 2021/22 - MathematicsRami Jamal AldinNo ratings yet
- Third Space Learning Solving Linear Equations GCSE Worksheet 1Document8 pagesThird Space Learning Solving Linear Equations GCSE Worksheet 1erin zietsmanNo ratings yet
- Algebric Expressions WorksheetDocument3 pagesAlgebric Expressions WorksheetNidhi MehtaNo ratings yet
- ESci 11 - Mid Term Exam ADocument1 pageESci 11 - Mid Term Exam Aje solarteNo ratings yet
- Quadratic EquationsDocument2 pagesQuadratic EquationsNidhi MehtaNo ratings yet
- Curve Sketching Questions Marks 1. 1Document3 pagesCurve Sketching Questions Marks 1. 1Kelvin ChenNo ratings yet
- Pure Mathematics Revision Worksheet Month 5Document4 pagesPure Mathematics Revision Worksheet Month 5Le Jeu LifeNo ratings yet
- DPP Qs 2.0 DE & AUTC (New Syllabus)Document5 pagesDPP Qs 2.0 DE & AUTC (New Syllabus)akash.c.2005No ratings yet
- 2 6B-HomeworkDocument2 pages2 6B-Homeworkkkareena.1999No ratings yet
- Topical Guidance of SPM MathematicsDocument39 pagesTopical Guidance of SPM MathematicsSEOW INN LEENo ratings yet
- Chapter 18 QuizDocument6 pagesChapter 18 QuizBruce ZhouNo ratings yet
- Assignment IPL (Itc)Document2 pagesAssignment IPL (Itc)Anjali SinhaNo ratings yet
- Algebraic FractionsDocument11 pagesAlgebraic FractionsSafiya Shiraz ImamudeenNo ratings yet
- Mat 1033 FinalreviewDocument9 pagesMat 1033 FinalreviewMarvin RubiaNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Equations and Inequalities Presentation TeacherDocument59 pagesQuadratic Equations and Inequalities Presentation TeacherAhmad Al-ShormanNo ratings yet
- Makeup Assignment CH 2 AnswersDocument3 pagesMakeup Assignment CH 2 AnswersMs YousufNo ratings yet
- p4 May Batch (Upto CH 4)Document2 pagesp4 May Batch (Upto CH 4)Bibi Marium SiddiqueNo ratings yet
- P4 MAY BATCH (Upto CH 4)Document2 pagesP4 MAY BATCH (Upto CH 4)Bibi Marium SiddiqueNo ratings yet
- TCCL - Share - 160 Study Guide For Final Exam Updated 4-26-22Document5 pagesTCCL - Share - 160 Study Guide For Final Exam Updated 4-26-22BrentNo ratings yet
- REVISIONDocument1 pageREVISIONantonela.karacic2008No ratings yet
- FactorisationDocument6 pagesFactorisationSafiya Shiraz ImamudeenNo ratings yet
- VIII-Algebra-Revision WorksheetDocument5 pagesVIII-Algebra-Revision Worksheetanousha1488No ratings yet
- Pure Mathematic Revision Worksheet Month 3Document2 pagesPure Mathematic Revision Worksheet Month 3Le Jeu LifeNo ratings yet
- 2022 Prelim P1 MemoDocument22 pages2022 Prelim P1 Memokaleb12345No ratings yet
- Completing The SquareDocument2 pagesCompleting The Squarenunonascimento4No ratings yet
- CH 4 Quadratic EquationsDocument2 pagesCH 4 Quadratic EquationsRaisa SagarNo ratings yet
- Calculus 12 - Unit 2 Derivatives AssignmentDocument13 pagesCalculus 12 - Unit 2 Derivatives AssignmenttucakovsashaNo ratings yet
- Midterm-Math 211fall 2023Document7 pagesMidterm-Math 211fall 2023aalrjl08No ratings yet
- Y11 2U Algebra QuizDocument9 pagesY11 2U Algebra QuizmisoandcheeseNo ratings yet
- GE1359 Problem Set 3 (Part 1)Document2 pagesGE1359 Problem Set 3 (Part 1)liangjiajuneasonNo ratings yet
- Equations. Workbook. 2º ESO. MathematicsDocument12 pagesEquations. Workbook. 2º ESO. MathematicsJOSHUA MACIASNo ratings yet
- P3 JAN 21 Revision Worksheet All ChaptersDocument3 pagesP3 JAN 21 Revision Worksheet All ChaptersSheikh HassanNo ratings yet
- GENMATH - Week 6&7Document6 pagesGENMATH - Week 6&7Crizza LoraineNo ratings yet
- 1718 QS015 - 2 SolutionDocument22 pages1718 QS015 - 2 SolutionVeshal RameshNo ratings yet
- Types of Graphs GCSE WorksheetDocument20 pagesTypes of Graphs GCSE WorksheetMr dogeNo ratings yet
- Integration (Ans)Document9 pagesIntegration (Ans)Naim RahmanNo ratings yet
- AK - Mathematics - Class 11 - UT1 - 2022-23Document5 pagesAK - Mathematics - Class 11 - UT1 - 2022-23Aditya jainNo ratings yet
- AK - Mathematics - Class 11 - UT1 - 2022-23Document5 pagesAK - Mathematics - Class 11 - UT1 - 2022-23Aditya jainNo ratings yet
- Sheet 12 - MTH90x - Fall - 2023Document1 pageSheet 12 - MTH90x - Fall - 2023Reem HaithamNo ratings yet
- Algebra WorksheetDocument2 pagesAlgebra WorksheetnkoziNo ratings yet
- Review For Quadratic Factoring Math CareDocument3 pagesReview For Quadratic Factoring Math Careanas_tiyamaulaniNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 Maths Test 1 Term 1Document1 pageGrade 11 Maths Test 1 Term 1Karla LeemansNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3 Answer Scheme TutorialDocument17 pagesTutorial 3 Answer Scheme Tutorialfiqah BatrisyiaNo ratings yet
- MHF 4U Rational Functions Practice TestDocument24 pagesMHF 4U Rational Functions Practice TestMateo LobatoNo ratings yet
- MathsDocument5 pagesMathsThorNo ratings yet
- BYJU'S Home Learning Program: Daily Practice ProblemsDocument5 pagesBYJU'S Home Learning Program: Daily Practice ProblemsSomesh GhoshNo ratings yet
- MathsDocument5 pagesMathsThorNo ratings yet
- Fracci One Algebraic AsDocument3 pagesFracci One Algebraic Asvictor olivaNo ratings yet
- AQA IGCSE Further Maths Predicted PaperDocument8 pagesAQA IGCSE Further Maths Predicted PapermrudulaNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Analytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageFrom EverandAnalytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageNo ratings yet
- Plant Hormones Handout WJMDocument3 pagesPlant Hormones Handout WJMZoonieFRNo ratings yet
- New Quick Wits Higher 1Document2 pagesNew Quick Wits Higher 1ZoonieFRNo ratings yet
- Ict Practical Examination Schedule May 2023Document2 pagesIct Practical Examination Schedule May 2023ZoonieFRNo ratings yet
- Year 10 - Chemistry - Monthly Test - October 2021Document8 pagesYear 10 - Chemistry - Monthly Test - October 2021ZoonieFRNo ratings yet
- Revision Mat1Document1 pageRevision Mat1ZoonieFRNo ratings yet
- Third Space Learning Angle Rules GCSE WorksheetDocument15 pagesThird Space Learning Angle Rules GCSE WorksheetZoonieFRNo ratings yet
- Contamination and Irradiation Worksheet999Document1 pageContamination and Irradiation Worksheet999ZoonieFRNo ratings yet
- Workbook - Gasexchangehumans - AL & OLDocument23 pagesWorkbook - Gasexchangehumans - AL & OLZoonieFRNo ratings yet
- Edexcel IGCSE Biology Specification Questions Part 2 Section 1Document53 pagesEdexcel IGCSE Biology Specification Questions Part 2 Section 1ZoonieFRNo ratings yet
- Kelvin Scale Pressure Temperature Relationship Edexcel IgcseDocument2 pagesKelvin Scale Pressure Temperature Relationship Edexcel IgcseZoonieFRNo ratings yet
- Atomic Structure For SeparatesDocument4 pagesAtomic Structure For SeparatesZoonieFRNo ratings yet
- Separate Physics Paper 1 Revision Sheet54644Document4 pagesSeparate Physics Paper 1 Revision Sheet54644ZoonieFRNo ratings yet
- Special Revision For 1 Month Holiday - Mathematics - Year 10Document64 pagesSpecial Revision For 1 Month Holiday - Mathematics - Year 10ZoonieFRNo ratings yet
- Paper 1 Physics Knowledge AssessmentDocument6 pagesPaper 1 Physics Knowledge AssessmentZoonieFRNo ratings yet
- Intro To Conservation of MomentumDocument1 pageIntro To Conservation of MomentumZoonieFRNo ratings yet
- Paper 1 Multi Step Questionsddme,,e, E,,eeeDocument4 pagesPaper 1 Multi Step Questionsddme,,e, E,,eeeZoonieFRNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Year 11-Mock 2021-2022Document51 pagesMathematics Year 11-Mock 2021-2022ZoonieFRNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 4HR 2017 2018Document19 pagesGrade 11 4HR 2017 2018ZoonieFRNo ratings yet
- Set 1 Cell Biology Grades 1 3Document22 pagesSet 1 Cell Biology Grades 1 3ZoonieFRNo ratings yet
- Pearson Edexcel International Gcse Sciences Support OverviewDocument1 pagePearson Edexcel International Gcse Sciences Support OverviewZoonieFRNo ratings yet
- Third Space Learning - Fluent in Five - Spring Term 2 Week 5Document11 pagesThird Space Learning - Fluent in Five - Spring Term 2 Week 5ZoonieFRNo ratings yet
- Third Space Learning - Fluent in Five GCSE - Progress Tracker GCSE FoundationDocument44 pagesThird Space Learning - Fluent in Five GCSE - Progress Tracker GCSE FoundationZoonieFRNo ratings yet
- Third Space Learning Powers and Roots GCSE WorksheetDocument7 pagesThird Space Learning Powers and Roots GCSE WorksheetZoonieFRNo ratings yet
- Circle Theorems Third Space Learning GCSE WorksheetDocument18 pagesCircle Theorems Third Space Learning GCSE WorksheetZoonieFR0% (1)
- Third Space Learning Solving Equations GCSE WorksheetDocument6 pagesThird Space Learning Solving Equations GCSE WorksheetZoonieFRNo ratings yet
- Third Space Learning Simultaneous Equations GCSE WorksheetDocument11 pagesThird Space Learning Simultaneous Equations GCSE WorksheetZoonieFRNo ratings yet
- 4A. IntroductionDocument20 pages4A. IntroductionZoonieFRNo ratings yet
- AUTOMOBILE ENGI-WPS Office-1Document14 pagesAUTOMOBILE ENGI-WPS Office-1GaneshNo ratings yet
- Appserver Job - LogDocument1,225 pagesAppserver Job - LogThiago Ximenes LopesNo ratings yet
- 3 Day Course On Project ManagementDocument196 pages3 Day Course On Project ManagementPeyman MznNo ratings yet
- Tle Freezing and Defrosting MeatDocument17 pagesTle Freezing and Defrosting MeatEnna PaulaNo ratings yet
- Sarvan Racism and The Heart of DarknessDocument5 pagesSarvan Racism and The Heart of Darknesspriya royNo ratings yet
- Bank Funds Management: by Dr. Suhardi, S.E., M.MDocument17 pagesBank Funds Management: by Dr. Suhardi, S.E., M.MLiviantiNo ratings yet
- Class 10 Science Revision NotesDocument76 pagesClass 10 Science Revision Notessharmarajankumar822No ratings yet
- Hygiene - Nutrition Grade 3 Term 2-2Document6 pagesHygiene - Nutrition Grade 3 Term 2-2Willy AddijahNo ratings yet
- Lec 9Document19 pagesLec 9Aqsa gulNo ratings yet
- Delta Function and So OnDocument20 pagesDelta Function and So OnLionel TopperNo ratings yet
- CompTIA Security+ (SY0-701)Document405 pagesCompTIA Security+ (SY0-701)Calisto Junior100% (1)
- Codelco Guia Graduado 2018Document120 pagesCodelco Guia Graduado 2018Wilson Campos RojasNo ratings yet
- History of ShamsabadDocument6 pagesHistory of Shamsabadtaqiiftikhar0% (1)
- 50.20-nm1 Long Term Storage Requirements GeneralDocument4 pages50.20-nm1 Long Term Storage Requirements GeneralJoe YoungNo ratings yet
- CT3Document7 pagesCT3Vishy BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Foreign Technology DivisionDocument467 pagesForeign Technology DivisionArashNo ratings yet
- Schematic/Electrical Parts: 36021V5J, V7J 36026V5J, V7J 42026 & 42030V6J With "H" ControlsDocument55 pagesSchematic/Electrical Parts: 36021V5J, V7J 36026V5J, V7J 42026 & 42030V6J With "H" ControlsJose Moreno TorbiscoNo ratings yet
- ExamplesDocument1 pageExamplesSwordhamza KyatNo ratings yet
- Plu Grid-No.19Document1 pagePlu Grid-No.19BrijeshgevariyaNo ratings yet
- Teaching Assistant: Roi YehoshuaDocument17 pagesTeaching Assistant: Roi YehoshuaKarthik RaoNo ratings yet
- Module #1 - Introduction To Community Development - PPT DownloadDocument18 pagesModule #1 - Introduction To Community Development - PPT DownloadRoland CepedaNo ratings yet
- ACP1withsolution 16303 16301873391Document23 pagesACP1withsolution 16303 16301873391Arman DehuriNo ratings yet
- Sexual Orientation Sexuality Wiki Fandom PDFDocument1 pageSexual Orientation Sexuality Wiki Fandom PDFAngus FieldingNo ratings yet
- Literature Review Ending Violence Against Women and GirlsDocument93 pagesLiterature Review Ending Violence Against Women and GirlsKyteNo ratings yet
- Imam Ash Shafi'EeDocument3 pagesImam Ash Shafi'EeAmalia AmiraNo ratings yet
- Concept NoteDocument4 pagesConcept NoteAfanie Mae Romero EstepaNo ratings yet
- Advanced View Arduino Projects List - Use Arduino For Projects-2Document53 pagesAdvanced View Arduino Projects List - Use Arduino For Projects-2Bilal AfzalNo ratings yet
- Petronas Technical Standards: Site Preparation and EarthworksDocument29 pagesPetronas Technical Standards: Site Preparation and EarthworksFirdausi FauziNo ratings yet