Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 viewsUnit2 7
Unit2 7
Uploaded by
Ngô Việtt AnnhUnit 7 discusses character strings in C. Character strings are arrays of characters that end with a null character. Strings are accessed using pointers to the first character. Common string functions include strlen() to get the length, strcpy() to copy strings, and strcmp() to compare strings. Other functions process strings, such as strcat() to concatenate strings and strchr() to find the first occurrence of a character in a string.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Quizzes Official ISC Certified in Cybersecurity CC PDFDocument48 pagesQuizzes Official ISC Certified in Cybersecurity CC PDFraspberries1100% (2)
- Unit 11Document14 pagesUnit 11Nguyễn Nam AnhNo ratings yet
- CP StringDocument13 pagesCP StringLakshay BishtNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document21 pagesChapter 5vishal kumar oadNo ratings yet
- PPS Unit-3 StringsDocument20 pagesPPS Unit-3 StringsVickey MylcatNo ratings yet
- Character String in C, String OperationsDocument13 pagesCharacter String in C, String OperationsAmit JhaNo ratings yet
- Character Array StringsDocument34 pagesCharacter Array StringsHariom JadonNo ratings yet
- Array and StringsDocument4 pagesArray and StringstovilasNo ratings yet
- StringDocument7 pagesStringRitik Rajput dhanaNo ratings yet
- M3 S7 StringsDocument26 pagesM3 S7 StringskarunaNo ratings yet
- CLang Lect12Document22 pagesCLang Lect12ThànhNo ratings yet
- Lab Material For Practice On StringDocument3 pagesLab Material For Practice On Stringashiqurrahmankhan120No ratings yet
- String 21Document19 pagesString 21Ozan AKYOLNo ratings yet
- String and String Handling INCDocument31 pagesString and String Handling INCtalhaskNo ratings yet
- CStringsDocument30 pagesCStringstpvv sreenivasaraoNo ratings yet
- Poornima College of Engineering: Sting, String FunctionsDocument22 pagesPoornima College of Engineering: Sting, String FunctionsVishal ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- StringDocument48 pagesStringHerpNo ratings yet
- Bpops103 Module4Document47 pagesBpops103 Module4shivabnNo ratings yet
- C Programming String, Array & Pointer (Cont.)Document15 pagesC Programming String, Array & Pointer (Cont.)Xuân Khương Trần LêNo ratings yet
- StringsDocument17 pagesStringsCharu AjayNo ratings yet
- Strings: - A String Is A Sequence of Characters Treated As A Group - We Have Already Used Some String LiteralsDocument48 pagesStrings: - A String Is A Sequence of Characters Treated As A Group - We Have Already Used Some String LiteralsJNUNo ratings yet
- C Programming StringsDocument9 pagesC Programming StringsKartheeban KamatchiNo ratings yet
- StringDocument33 pagesStringadarsh rajNo ratings yet
- String Using ArraysDocument38 pagesString Using Arraysmookes ombaniNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Characters and StringsDocument19 pagesFundamentals of Characters and StringsMir Fida NadeemNo ratings yet
- C-Programming-Class 9Document47 pagesC-Programming-Class 9jack_harishNo ratings yet
- StringsDocument32 pagesStringsSuresh Reddy PolinatiNo ratings yet
- Fall 23-24lecture 6 StringDocument13 pagesFall 23-24lecture 6 Stringfardinmojumdar123No ratings yet
- StringsDocument8 pagesStringssri vallideviNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5b - Built in FunctionsDocument12 pagesChapter 5b - Built in FunctionsSamantha MorinNo ratings yet
- L2 StringsDocument21 pagesL2 Strings910.ngochauthanhvyNo ratings yet
- Strings C ProgramingDocument23 pagesStrings C ProgramingNandiniAgarwalNo ratings yet
- Modern Programming Tools and Techniques-I: StringDocument26 pagesModern Programming Tools and Techniques-I: StringKuldeep SinghNo ratings yet
- 12 StringsDocument13 pages12 StringsKarthikeyaNo ratings yet
- StringsDocument21 pagesStringsAtharv GuptaNo ratings yet
- Lect StringsDocument30 pagesLect StringsRohit YadavNo ratings yet
- C - Strings: Declaration of Strings: Declaring A String Is As Simple As Declaring A One Dimensional ArrayDocument18 pagesC - Strings: Declaration of Strings: Declaring A String Is As Simple As Declaring A One Dimensional ArrayShahed HossainNo ratings yet
- Strings ConceptsDocument32 pagesStrings ConceptsBala AnandNo ratings yet
- StringDocument8 pagesStringTanmay VashishthNo ratings yet
- Computer Programming BasicsDocument25 pagesComputer Programming BasicsAytul GullNo ratings yet
- Lec-11 (Strings)Document11 pagesLec-11 (Strings)heye3775No ratings yet
- DS Unit1 StringsDocument17 pagesDS Unit1 Stringsnamansehgal3006No ratings yet
- C Programming UNIT 4.2 StringDocument12 pagesC Programming UNIT 4.2 StringrishikaNo ratings yet
- StringDocument12 pagesStringrohitggothiNo ratings yet
- Week 07 ProgrammingDocument8 pagesWeek 07 ProgrammingShivam YadavNo ratings yet
- Arrays and StringsDocument19 pagesArrays and StringsPoonam VaswaniNo ratings yet
- StringDocument35 pagesStringDaniel PioquintoNo ratings yet
- StringDocument26 pagesStringsridhargoudgeetaNo ratings yet
- Strings: CSE115: Computing ConceptsDocument20 pagesStrings: CSE115: Computing ConceptsMd. YeasinNo ratings yet
- L2 StringsDocument23 pagesL2 Stringslongngo1234560No ratings yet
- Module4 NotesDocument10 pagesModule4 Notessoumyaks81No ratings yet
- Unit-1 (Strings in C)Document22 pagesUnit-1 (Strings in C)Vinay RawatNo ratings yet
- StringDocument12 pagesStringsatyaNo ratings yet
- Strings in C: Selvakumar SDocument16 pagesStrings in C: Selvakumar SSu DeepthiNo ratings yet
- Strings Methods in JavaDocument3 pagesStrings Methods in JavabanaganapallimunidhanushNo ratings yet
- Strings in CDocument17 pagesStrings in CRaminder CheemaNo ratings yet
- Strings PDFDocument21 pagesStrings PDFGoutham Mukkera123No ratings yet
- C++ String FuctionsDocument15 pagesC++ String FuctionsJay SmithNo ratings yet
- StringsDocument22 pagesStringsNishant AroraNo ratings yet
- StringsDocument22 pagesStringsNishant AroraNo ratings yet
- Unit2 4Document38 pagesUnit2 4Ngô Việtt AnnhNo ratings yet
- Unit2 6Document17 pagesUnit2 6Ngô Việtt AnnhNo ratings yet
- Unit2 5Document57 pagesUnit2 5Ngô Việtt AnnhNo ratings yet
- Unit2 3Document19 pagesUnit2 3Ngô Việtt AnnhNo ratings yet
- Unit2 1Document33 pagesUnit2 1Ngô Việtt AnnhNo ratings yet
- Unit2 2Document74 pagesUnit2 2Ngô Việtt AnnhNo ratings yet
- Unit2 8Document11 pagesUnit2 8Ngô Việtt AnnhNo ratings yet
- TextbookDocument138 pagesTextbookNgô Việtt AnnhNo ratings yet
- Unit 0Document11 pagesUnit 0Ngô Việtt AnnhNo ratings yet
- Unit1 5Document76 pagesUnit1 5Ngô Việtt AnnhNo ratings yet
- Unit1 4Document52 pagesUnit1 4Ngô Việtt AnnhNo ratings yet
- Unit1 3Document51 pagesUnit1 3Ngô Việtt AnnhNo ratings yet
- Unit1 1Document32 pagesUnit1 1Ngô Việtt AnnhNo ratings yet
- Unit1 2Document64 pagesUnit1 2Ngô Việtt AnnhNo ratings yet
- MS Excel Assignment Mycslab 01Document11 pagesMS Excel Assignment Mycslab 01raihanrobin2002No ratings yet
- Boston Dynamics Spot Robot Answers: 1. Which Domains of AI Are Used in This RobotDocument3 pagesBoston Dynamics Spot Robot Answers: 1. Which Domains of AI Are Used in This RobotSagar chaudhariNo ratings yet
- CCC MarchDocument24 pagesCCC MarchRitesh RaiNo ratings yet
- BacktraceDocument5 pagesBacktraceGod LevelNo ratings yet
- Iveri Client Developers Guide 4Document170 pagesIveri Client Developers Guide 4HerbertNo ratings yet
- Aws Engineer: Resume Examples & SamplesDocument4 pagesAws Engineer: Resume Examples & SamplesmadhubaddapuriNo ratings yet
- 6.4 Security Analyst Guide For Multi-TenantDocument323 pages6.4 Security Analyst Guide For Multi-TenantClaudio LuizNo ratings yet
- As 65109Document9 pagesAs 65109Fábio FariasNo ratings yet
- Major Project File SumitDocument27 pagesMajor Project File Sumitdineshmahor9669553872No ratings yet
- Best Practices For ImplementingDocument119 pagesBest Practices For Implementingsalesforce.com100% (10)
- Using The AVCS ENC ServiceDocument19 pagesUsing The AVCS ENC ServiceMohamed El SayyadNo ratings yet
- Enquiry LetterDocument11 pagesEnquiry LetterDileswar NayakNo ratings yet
- Elb ClassicDocument129 pagesElb Classicbaby kaliniNo ratings yet
- 05 Sync Basics PDFDocument28 pages05 Sync Basics PDFRaJu SinGhNo ratings yet
- Model Question Paper Programming in C and Data Structures (14PCD13/14PCD23)Document4 pagesModel Question Paper Programming in C and Data Structures (14PCD13/14PCD23)Bruce WayneNo ratings yet
- Lab 6: Ciphers and Digital CertificatesDocument9 pagesLab 6: Ciphers and Digital CertificatesmNo ratings yet
- Unit-IV System DesignDocument60 pagesUnit-IV System DesignHargun Yashkumar AshwinbhaiNo ratings yet
- AWS+SAA C03+Exam+Guide+Mapped+to+VideosDocument29 pagesAWS+SAA C03+Exam+Guide+Mapped+to+VideosAmit KumarNo ratings yet
- Migrating 32bit Applications To 64bit v2021Document18 pagesMigrating 32bit Applications To 64bit v2021BGS IITBNo ratings yet
- ps7pck B PDFDocument168 pagesps7pck B PDFSohail AhmedNo ratings yet
- Erdas Imagine Student Instructions - 2015Document10 pagesErdas Imagine Student Instructions - 2015Samuel YufraNo ratings yet
- 08 Laboratory Exercise 1Document5 pages08 Laboratory Exercise 1Christian LeonesNo ratings yet
- Real SQL Queries 50 Challenges - Brian CohenDocument1 pageReal SQL Queries 50 Challenges - Brian Cohenxterminal01No ratings yet
- Network File SystemDocument29 pagesNetwork File SystemYosef TayeNo ratings yet
- Sharepoint STSADM CommandsDocument14 pagesSharepoint STSADM CommandsDarksManNo ratings yet
- The Designing of Android-Based Smart RT-RW Information System Perumahan Permata Depok Regency, Kelurahan Ratu Jaya, Depok, IndonesiaDocument6 pagesThe Designing of Android-Based Smart RT-RW Information System Perumahan Permata Depok Regency, Kelurahan Ratu Jaya, Depok, IndonesiaIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Network Design Proposal: Feasibility StudyDocument2 pagesNetwork Design Proposal: Feasibility StudyJaweria JaweriaNo ratings yet
- Minitab Tips and TricksDocument54 pagesMinitab Tips and TricksRicardo Oliveros100% (1)
- Input, Output and StorageDocument4 pagesInput, Output and StorageEnimsaj CastroNo ratings yet
Unit2 7
Unit2 7
Uploaded by
Ngô Việtt Annh0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views14 pagesUnit 7 discusses character strings in C. Character strings are arrays of characters that end with a null character. Strings are accessed using pointers to the first character. Common string functions include strlen() to get the length, strcpy() to copy strings, and strcmp() to compare strings. Other functions process strings, such as strcat() to concatenate strings and strchr() to find the first occurrence of a character in a string.
Original Description:
Original Title
Unit2_7
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentUnit 7 discusses character strings in C. Character strings are arrays of characters that end with a null character. Strings are accessed using pointers to the first character. Common string functions include strlen() to get the length, strcpy() to copy strings, and strcmp() to compare strings. Other functions process strings, such as strcat() to concatenate strings and strchr() to find the first occurrence of a character in a string.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
8 views14 pagesUnit2 7
Unit2 7
Uploaded by
Ngô Việtt AnnhUnit 7 discusses character strings in C. Character strings are arrays of characters that end with a null character. Strings are accessed using pointers to the first character. Common string functions include strlen() to get the length, strcpy() to copy strings, and strcmp() to compare strings. Other functions process strings, such as strcat() to concatenate strings and strchr() to find the first occurrence of a character in a string.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 14
Unit 7: Strings
Character Strings
• A variable of type char may hold a single character
• Example: char onechar = 'z' ;
• Character strings are arrays of simple characters with a
special character inserted into the string at the very end: null
character ( '\0' ).
• They are assigned values with a pair of double quotes:
• Example:char arraychar[6] = "abcde" ;
Character Strings
• Strings are normally accessed by a pointer to
the first character in the string.
• This means that the value of a string pointer
is the address of it's first character.
Character Strings
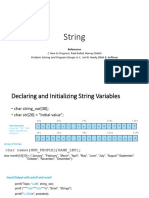
• Declaration and initialization:
char color [ ] = "scarlet" ;
or
char color [8] = {'s', 'c', 'a', 'r', 'l', 'e', 't', '\0'} ;
• NOTE: Allowance must always be made for the
terminating null character.
String I/O Library Routines
#include <stdio.h>
/* The following are function prototypes for some of
the String I/O and Handling Library Routines */
/* Input next character as an integer */
int getchar (void) ;
(Don’t confuse with getch() of conio.h)
/* Input string into array s until newline */
char *gets (char *s) ;
String I/O Library Routines
• #include <stdio.h>
/* Print character stored in character variable c */
int putchar (int c) ;
//Don’t confuse with putch() of conio.h)
/* Print character string s followed by \n */
int puts (const char *s) ;
Character classification functions
String-processing functions
String-processing functions
• size_t strlen(char[] s)
• Get length of string s
• printf("%d ",strlen("Hello world")); 11
• char[] strcpy(char[] str1, char[] str2)
• Copy string string str2 to string str1
• printf("%s ",strcpy(Str,"Hello")); Hello
• printf("%s", Str); Hello
• int strcmp(char[] str1, char[] str2)
• Compare str1 to str2
• Return 0 if they are equal to each other;
• Return a value < 0: str1 < str2
• Return a value >0: str1 > str2
String-processing functions
• char[] strcat(char[] str1, char[] str2)
• Appends a copy of the string str2 to the end
of the string str1. ...
• The strcat function returns a pointer to str1
• Example
char Str[20];
strcpy(Str,"Hello ");
printf("%s ",strcat(Str,"world"));
Helloworld
printf("\n%s",Str); Helloworld
String-processing functions
• char * strchr (char * s, int c)
• Searches for the first occurrence of the
character c (an unsigned char) in the string
pointed to by the argument s
• . strcpy(Str,"Hello world");
printf("%s ",strchr(Str,‘o')); o world
• char* strstr(char * str1, char * str2)
• Return a pointer to the first occurrence
in str2 of the entire sequence of characters
specified in str1, or a null pointer if the
sequence is not present in str1.
printf("%s ",strstr(Str,”llo”)); llo world
Searching using function strstr
1. #include<stdio.h>
2. #include<conio.h>
3. #include<string.h>
4. main()
5. {char s[20],u[20];
6. int m,i, n;
7. puts("Enter your string");gets(s);
8. fflush(stdin);
9. puts("Enter string you want to
search");gets(u);
10.if(strstr(s,u)==NULL)puts("False");
else puts("True");
11.}
Searching
Enter two strings s and u and an integer number n The program prints the position of the first occurrence
of u within a substring of s. n is the position where the substring begins. If t is not found in the substring of
s, the program prints zero
1. #include<stdio.h>
2. #include<conio.h>
3. #include<string.h>
4. main()
5. {char s[20],t[20],u[20];
6. int m,i, n;
7. puts("Enter your string");gets(s);
8. puts("n=");scanf("%d",&n);
9. m=strlen(s);
10. for(i=n;i<=m;i++) t[i-n]=s[i];
11. fflush(stdin);
12. puts("Enter string you want to search");gets(u);
13. if(strstr(t,u)==NULL)puts(“0");else
14. {printf("\nPosition of the first occurence of string %s in a substring
of %s",u,s);
15. printf("\nstart from %dth character is %d",n, strstr(t,u)-&t[0]+n);}
16. }
Classical example: convert a
number from decimal to binary
1. #include<stdio.h>
2. #include<conio.h>
3. #include<string.h>
4. main()
5. {char s[100]="",t[100];
6. int i, n;
7. puts("n="); scanf("%d",&n);
8. i=n;
9. while (i>0)
10.{if(i%2==0) strcpy(t,"0");else strcpy(t,"1");
11.strcat(t,s);
12.strcpy(s,t);
13.i/=2;}
14.printf("\n");
15.puts(s);
16.}
You might also like
- Quizzes Official ISC Certified in Cybersecurity CC PDFDocument48 pagesQuizzes Official ISC Certified in Cybersecurity CC PDFraspberries1100% (2)
- Unit 11Document14 pagesUnit 11Nguyễn Nam AnhNo ratings yet
- CP StringDocument13 pagesCP StringLakshay BishtNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document21 pagesChapter 5vishal kumar oadNo ratings yet
- PPS Unit-3 StringsDocument20 pagesPPS Unit-3 StringsVickey MylcatNo ratings yet
- Character String in C, String OperationsDocument13 pagesCharacter String in C, String OperationsAmit JhaNo ratings yet
- Character Array StringsDocument34 pagesCharacter Array StringsHariom JadonNo ratings yet
- Array and StringsDocument4 pagesArray and StringstovilasNo ratings yet
- StringDocument7 pagesStringRitik Rajput dhanaNo ratings yet
- M3 S7 StringsDocument26 pagesM3 S7 StringskarunaNo ratings yet
- CLang Lect12Document22 pagesCLang Lect12ThànhNo ratings yet
- Lab Material For Practice On StringDocument3 pagesLab Material For Practice On Stringashiqurrahmankhan120No ratings yet
- String 21Document19 pagesString 21Ozan AKYOLNo ratings yet
- String and String Handling INCDocument31 pagesString and String Handling INCtalhaskNo ratings yet
- CStringsDocument30 pagesCStringstpvv sreenivasaraoNo ratings yet
- Poornima College of Engineering: Sting, String FunctionsDocument22 pagesPoornima College of Engineering: Sting, String FunctionsVishal ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- StringDocument48 pagesStringHerpNo ratings yet
- Bpops103 Module4Document47 pagesBpops103 Module4shivabnNo ratings yet
- C Programming String, Array & Pointer (Cont.)Document15 pagesC Programming String, Array & Pointer (Cont.)Xuân Khương Trần LêNo ratings yet
- StringsDocument17 pagesStringsCharu AjayNo ratings yet
- Strings: - A String Is A Sequence of Characters Treated As A Group - We Have Already Used Some String LiteralsDocument48 pagesStrings: - A String Is A Sequence of Characters Treated As A Group - We Have Already Used Some String LiteralsJNUNo ratings yet
- C Programming StringsDocument9 pagesC Programming StringsKartheeban KamatchiNo ratings yet
- StringDocument33 pagesStringadarsh rajNo ratings yet
- String Using ArraysDocument38 pagesString Using Arraysmookes ombaniNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Characters and StringsDocument19 pagesFundamentals of Characters and StringsMir Fida NadeemNo ratings yet
- C-Programming-Class 9Document47 pagesC-Programming-Class 9jack_harishNo ratings yet
- StringsDocument32 pagesStringsSuresh Reddy PolinatiNo ratings yet
- Fall 23-24lecture 6 StringDocument13 pagesFall 23-24lecture 6 Stringfardinmojumdar123No ratings yet
- StringsDocument8 pagesStringssri vallideviNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5b - Built in FunctionsDocument12 pagesChapter 5b - Built in FunctionsSamantha MorinNo ratings yet
- L2 StringsDocument21 pagesL2 Strings910.ngochauthanhvyNo ratings yet
- Strings C ProgramingDocument23 pagesStrings C ProgramingNandiniAgarwalNo ratings yet
- Modern Programming Tools and Techniques-I: StringDocument26 pagesModern Programming Tools and Techniques-I: StringKuldeep SinghNo ratings yet
- 12 StringsDocument13 pages12 StringsKarthikeyaNo ratings yet
- StringsDocument21 pagesStringsAtharv GuptaNo ratings yet
- Lect StringsDocument30 pagesLect StringsRohit YadavNo ratings yet
- C - Strings: Declaration of Strings: Declaring A String Is As Simple As Declaring A One Dimensional ArrayDocument18 pagesC - Strings: Declaration of Strings: Declaring A String Is As Simple As Declaring A One Dimensional ArrayShahed HossainNo ratings yet
- Strings ConceptsDocument32 pagesStrings ConceptsBala AnandNo ratings yet
- StringDocument8 pagesStringTanmay VashishthNo ratings yet
- Computer Programming BasicsDocument25 pagesComputer Programming BasicsAytul GullNo ratings yet
- Lec-11 (Strings)Document11 pagesLec-11 (Strings)heye3775No ratings yet
- DS Unit1 StringsDocument17 pagesDS Unit1 Stringsnamansehgal3006No ratings yet
- C Programming UNIT 4.2 StringDocument12 pagesC Programming UNIT 4.2 StringrishikaNo ratings yet
- StringDocument12 pagesStringrohitggothiNo ratings yet
- Week 07 ProgrammingDocument8 pagesWeek 07 ProgrammingShivam YadavNo ratings yet
- Arrays and StringsDocument19 pagesArrays and StringsPoonam VaswaniNo ratings yet
- StringDocument35 pagesStringDaniel PioquintoNo ratings yet
- StringDocument26 pagesStringsridhargoudgeetaNo ratings yet
- Strings: CSE115: Computing ConceptsDocument20 pagesStrings: CSE115: Computing ConceptsMd. YeasinNo ratings yet
- L2 StringsDocument23 pagesL2 Stringslongngo1234560No ratings yet
- Module4 NotesDocument10 pagesModule4 Notessoumyaks81No ratings yet
- Unit-1 (Strings in C)Document22 pagesUnit-1 (Strings in C)Vinay RawatNo ratings yet
- StringDocument12 pagesStringsatyaNo ratings yet
- Strings in C: Selvakumar SDocument16 pagesStrings in C: Selvakumar SSu DeepthiNo ratings yet
- Strings Methods in JavaDocument3 pagesStrings Methods in JavabanaganapallimunidhanushNo ratings yet
- Strings in CDocument17 pagesStrings in CRaminder CheemaNo ratings yet
- Strings PDFDocument21 pagesStrings PDFGoutham Mukkera123No ratings yet
- C++ String FuctionsDocument15 pagesC++ String FuctionsJay SmithNo ratings yet
- StringsDocument22 pagesStringsNishant AroraNo ratings yet
- StringsDocument22 pagesStringsNishant AroraNo ratings yet
- Unit2 4Document38 pagesUnit2 4Ngô Việtt AnnhNo ratings yet
- Unit2 6Document17 pagesUnit2 6Ngô Việtt AnnhNo ratings yet
- Unit2 5Document57 pagesUnit2 5Ngô Việtt AnnhNo ratings yet
- Unit2 3Document19 pagesUnit2 3Ngô Việtt AnnhNo ratings yet
- Unit2 1Document33 pagesUnit2 1Ngô Việtt AnnhNo ratings yet
- Unit2 2Document74 pagesUnit2 2Ngô Việtt AnnhNo ratings yet
- Unit2 8Document11 pagesUnit2 8Ngô Việtt AnnhNo ratings yet
- TextbookDocument138 pagesTextbookNgô Việtt AnnhNo ratings yet
- Unit 0Document11 pagesUnit 0Ngô Việtt AnnhNo ratings yet
- Unit1 5Document76 pagesUnit1 5Ngô Việtt AnnhNo ratings yet
- Unit1 4Document52 pagesUnit1 4Ngô Việtt AnnhNo ratings yet
- Unit1 3Document51 pagesUnit1 3Ngô Việtt AnnhNo ratings yet
- Unit1 1Document32 pagesUnit1 1Ngô Việtt AnnhNo ratings yet
- Unit1 2Document64 pagesUnit1 2Ngô Việtt AnnhNo ratings yet
- MS Excel Assignment Mycslab 01Document11 pagesMS Excel Assignment Mycslab 01raihanrobin2002No ratings yet
- Boston Dynamics Spot Robot Answers: 1. Which Domains of AI Are Used in This RobotDocument3 pagesBoston Dynamics Spot Robot Answers: 1. Which Domains of AI Are Used in This RobotSagar chaudhariNo ratings yet
- CCC MarchDocument24 pagesCCC MarchRitesh RaiNo ratings yet
- BacktraceDocument5 pagesBacktraceGod LevelNo ratings yet
- Iveri Client Developers Guide 4Document170 pagesIveri Client Developers Guide 4HerbertNo ratings yet
- Aws Engineer: Resume Examples & SamplesDocument4 pagesAws Engineer: Resume Examples & SamplesmadhubaddapuriNo ratings yet
- 6.4 Security Analyst Guide For Multi-TenantDocument323 pages6.4 Security Analyst Guide For Multi-TenantClaudio LuizNo ratings yet
- As 65109Document9 pagesAs 65109Fábio FariasNo ratings yet
- Major Project File SumitDocument27 pagesMajor Project File Sumitdineshmahor9669553872No ratings yet
- Best Practices For ImplementingDocument119 pagesBest Practices For Implementingsalesforce.com100% (10)
- Using The AVCS ENC ServiceDocument19 pagesUsing The AVCS ENC ServiceMohamed El SayyadNo ratings yet
- Enquiry LetterDocument11 pagesEnquiry LetterDileswar NayakNo ratings yet
- Elb ClassicDocument129 pagesElb Classicbaby kaliniNo ratings yet
- 05 Sync Basics PDFDocument28 pages05 Sync Basics PDFRaJu SinGhNo ratings yet
- Model Question Paper Programming in C and Data Structures (14PCD13/14PCD23)Document4 pagesModel Question Paper Programming in C and Data Structures (14PCD13/14PCD23)Bruce WayneNo ratings yet
- Lab 6: Ciphers and Digital CertificatesDocument9 pagesLab 6: Ciphers and Digital CertificatesmNo ratings yet
- Unit-IV System DesignDocument60 pagesUnit-IV System DesignHargun Yashkumar AshwinbhaiNo ratings yet
- AWS+SAA C03+Exam+Guide+Mapped+to+VideosDocument29 pagesAWS+SAA C03+Exam+Guide+Mapped+to+VideosAmit KumarNo ratings yet
- Migrating 32bit Applications To 64bit v2021Document18 pagesMigrating 32bit Applications To 64bit v2021BGS IITBNo ratings yet
- ps7pck B PDFDocument168 pagesps7pck B PDFSohail AhmedNo ratings yet
- Erdas Imagine Student Instructions - 2015Document10 pagesErdas Imagine Student Instructions - 2015Samuel YufraNo ratings yet
- 08 Laboratory Exercise 1Document5 pages08 Laboratory Exercise 1Christian LeonesNo ratings yet
- Real SQL Queries 50 Challenges - Brian CohenDocument1 pageReal SQL Queries 50 Challenges - Brian Cohenxterminal01No ratings yet
- Network File SystemDocument29 pagesNetwork File SystemYosef TayeNo ratings yet
- Sharepoint STSADM CommandsDocument14 pagesSharepoint STSADM CommandsDarksManNo ratings yet
- The Designing of Android-Based Smart RT-RW Information System Perumahan Permata Depok Regency, Kelurahan Ratu Jaya, Depok, IndonesiaDocument6 pagesThe Designing of Android-Based Smart RT-RW Information System Perumahan Permata Depok Regency, Kelurahan Ratu Jaya, Depok, IndonesiaIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Network Design Proposal: Feasibility StudyDocument2 pagesNetwork Design Proposal: Feasibility StudyJaweria JaweriaNo ratings yet
- Minitab Tips and TricksDocument54 pagesMinitab Tips and TricksRicardo Oliveros100% (1)
- Input, Output and StorageDocument4 pagesInput, Output and StorageEnimsaj CastroNo ratings yet