Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Quizni Annie
Quizni Annie
Uploaded by
Jake Cormanes PeraltaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Quizni Annie
Quizni Annie
Uploaded by
Jake Cormanes PeraltaCopyright:
Available Formats
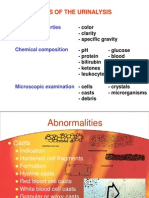
**MANNERS OF REPORTING**
RCSs WBCs - ave / number HPF
Casts - ave / number LPF
Crystals - rare few mod plenty HPF
Squamous EC - rare few mod plenty LPF
Bacteria - rare few mod plenty HPF
Transitional - rare few mod plenty HPF
Renal EC - ave/number HPF
ABNORMAL CRYSTALS - may be reported ave/ LPF
Squamous Epith cells / LPF
- None : 0
- Rare : 0-5
- Few : 5-20
- Moderate 20-100
- Many : > 100
Casts / LPF
- 0 /lpf
- 0-5 /lpf
- -10 /lpf
- >10/lpf
RBCs/WBCs / HPF
- None 25-50
- 0-2 50-100
- 2-5 >100 (TNTC)
- 5 -10
- 10- 25
Crystals / HPF
- None: 0
- Rare: 0-2
- Few: 2-5
- Moderate: 5-20
- Many: >20
- ABNORMAL CRYSTALS ave/ LPF
Bacteria / HPF
- None: 0
- Rare: 0-10
- Few: 10-50
- Moderate: 50-20
URINE SEDIMENT PREPARATION
10 to 15 mL of Urine (ave. of 12mL)
V
Spin at 400 RCF for 5 minutes
V
Decant urine (0.5 or 1mL remains)
V
Transfer uL (0.02mL) sediment to glass slide with 22x22 coverslip
V
Examine microscopically 10 LPF, 10 HPF under reduced light
RBCs (Hematuria) - NV: 0-2 to 0-3/HPF
> Smooth, anucleated, biconcave
• HYPERTONIC =
• HYPOTONIC =
• GLOMERULAR DAMAGE =
SOURCES OF ERROR:
Yeasts Air Bubbles
Oil Droplets CaOx
REMDY: 2% AcetOH (RBC lysis)
SEQUENCE OF CAST FORMATION
Hyaline > Cellular > Coarse Gran > Fine Gran > Waxy
Cen-slide - closed system for performing fast, clean, accurate, microscopic urine
analysis.
- provides a specially designed tube that permits direct reading of the urine
sediment.
ADDIS COUNT - quantitative measure of formed elements of urine using
hemacytometer.
- Specimen: 12-hour urine
- Preservative: Formalin
Normal Values:
- RBC = 0 to 500,000/12hr
- WBC = 0 to 1,200,000/12hr
- Hyaline Casts = 0 to 5,000/12 hr
Phase-Contrast - Enhanced visualization of highly refractile elements
Polarizing - ID of chole in oval fat bodies, fatty casts and crystals
(maltese cross)
Dark-Field - ID of T. pallidum
Fluorescence - Visualization of fluorescent organism/substances
Interference
a.Normarsky
b. Hoffman
- 3D microscopy. And layer-by-layer imaging
- Differential/Bright field
- Modulation/Birght field
WBCs (Pyelonephritis) - NV: 0-5 to 0-8/HPF > Larger than RBCs
- NEUTROPHILS (Predominant) - Granulated and multilobes
- Hypotonic: Granules swell and undergo BROWNIAN MOVEMENT (Glitter Cells)
- EOSINOPHILS (<1% of Urine WBCs) - Significant if >1%
- Primarily associated with interstitial nephritis.
- Monouclear Cells (Lympho, Mono, Macro and Histiocytes)
SQUAMOUS EPITHELIAL CELLS
- LARGEST cell in the urine. Irregular cytoplasm.
- Form the lining of vagina, urethra of male and female.
VARIANT: CLUE CELLS – squamous epith cell
covered G. vaginalis. à assoc with Bacterial vaginosis.
TRANSITIONAL EPITHELIAL CELLS (UROTHELIAL)
- Spherical, polyhedral or caudate
- Centrally located tubules
- Derived from the linings of pelvis, ureter, urinary bladder and upper
portion of male urethra
RENAL TUBULAR CELLS
- Most clinically significant epithelial cells
- Originates for the NEPHRON
- Rectangular, polyhedral cuboidal or columnar
- Eccentric nucleus
- > 2 RTE/hpf à tubular injury
RTE CELL VARIANTS:
- OVAL FAT BODIES – lipid conraining RTEC. Seen in Lipiduria (ex. Nephrotic
syndrome)
- ID: Lipid stains and Polarizing Microscope.
- BUBBLE CELLS – RTEC with non-lipid vacuoles (Acute Tubular Necrosis)
BACTERIA : UTI = Bacteria + WBCs
- Not significant unless there is increased WBCs
YEAST – true infection in presence of WBCs
- May or not seen with mycelia
- Commonly mistaken as RBC
PARASITES
Trichomonas vaginalis
- Most frequent parasite encountered in urine.
- Pear-shaped flagellate with jerky motility.
- Agent of PING PREPARED & COMPILED BY: -PONG JAMES PATRICK PICAR, RMT
DISEASE
Schistosoma haematobium
- With terminal spine
- Hematuria and bladder cancer
- SPX: 24 hr UNPRESERVED urine Enterobius vermicularis
- Most common fecal contaminant
SPERMATOZOA – seen post-coitus/post#ejaculation
URINE SEDIMENTS: CASTS
CASTS (Cylindruria) – unique to the kidney
- Formed in the DCT and Collecting Ducts
- MAJOR CONSTITUENTS: Tamm-Horsfall Protein or UROMODULIN.
- Performed along the EDGES of the COVERSLIP with subdued light
FORMATION OF CASTS:
- Aggregation of Tamm-Horsfall CHON into individual protein fibrils attached
to the RTE cells.
- Interweaving of CHON fibrils to form a loose fibrillary network.
- Further CHON fibril interweaving to form a solid structure.
- Possible attachment of urinary constituents to the solid matrix
- Detachment of CHON fibrils from the epithelial cells
- Excretion of the cast
HYALINE CASTS – prototype cast
- NV: 0 to 2/LPF
- CLINICAL SIGNIFICANCE:
- Physiologic: Stress, Strenuous Exercise, Dehydration and Heat exposre
- Pathologic: Glomerulo and Pyelonephritis, Congestive Heart failure and
Chronic Renal conditions.
RBC CASTS – indicative of bleeding in nephron.
- Glomerulonephritis and Strenous exercise.
WBC CASTS – inflammation in the nephron. May be mistake as EPITHELIAL CELLS casts.
To differentiate: Phase Microscopy and Supravital stain.
- Pyelonephritis and Acute Interstitial Nephritis (elevated urine
Eosinophils)
EPITHELIAL CAST – indicative of advanced tubular destruction. (RTE cell casts)
BACTERIAL CAST – indicative of pyelonephritis
GRANULAR CAST – granules are derived from lysosomes of RTE cells during normal
metabolism (non-pathologic)
- Glomerulonephritis, Pyelonephritis, Stress and Strenuous exercise
FATTY CASTS – not stained by Sternheimer-Malbin. For to identify:
- TG and Neutral Fats: Lipid Stains
- Cholesterol: Polarizing Microscope
- Nephrotic syndrome
WAXY CASTS – degenerative form of all types of casts.
- Urine flow stasis and Chronic renal failure.
BROAD CASTS – RENAL FAILURE CAST
- Indicates widening of the tubular walls. ANY TYPE OF
CASTS MAY BE BROAD.
- Extreme URINE STASIS
- Renal PREPARED & COMPILED BY: Failure
You might also like
- Black's Medical DictionaryDocument849 pagesBlack's Medical Dictionaryanon-97048197% (30)
- Clinical Microscopy: Standard Operating Procedures FORDocument8 pagesClinical Microscopy: Standard Operating Procedures FORRochell OcampoNo ratings yet
- Topnotch Lab Interpretation For MoonlightersDocument41 pagesTopnotch Lab Interpretation For Moonlightersmefav7778520No ratings yet
- 6 Microscopic Examination of UrineDocument116 pages6 Microscopic Examination of Urineaddine061421No ratings yet
- 1.clinicolab Diagnosis PleuPeritEFFUSIONS016Document23 pages1.clinicolab Diagnosis PleuPeritEFFUSIONS016Elena CărăvanNo ratings yet
- AUB - Microscopic Analysis of UrineDocument4 pagesAUB - Microscopic Analysis of UrineJeanne Rodiño100% (1)
- Chapter FiveDocument155 pagesChapter Fivetadele10No ratings yet
- Microscopic Examination of Urine CompressedDocument75 pagesMicroscopic Examination of Urine CompressedJheshari VinaNo ratings yet
- TMH PBS PresentationDocument61 pagesTMH PBS PresentationcandiddreamsNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Interpretation Made Easy: Diana Tamondong-Lachica, MD, FPCPDocument41 pagesLaboratory Interpretation Made Easy: Diana Tamondong-Lachica, MD, FPCPmarieNo ratings yet
- Microscopic Examination of UrineDocument41 pagesMicroscopic Examination of UrineSuman ChaturvediNo ratings yet
- CDE Series-2-Body-Fluids-Routine-Analysis-AutomationDocument38 pagesCDE Series-2-Body-Fluids-Routine-Analysis-AutomationAfrasiab KhanNo ratings yet
- Serous Fluid: FormationDocument4 pagesSerous Fluid: FormationemmanuelNo ratings yet
- Spleno - DR MOKHTARDocument57 pagesSpleno - DR MOKHTARAbdelrahman MokhtarNo ratings yet
- Human Blood s2Document46 pagesHuman Blood s2Nita SaragihNo ratings yet
- Patho SpottersDocument86 pagesPatho Spottersarishbharadwaj192No ratings yet
- 20 CSFDocument53 pages20 CSFnivetha26082000No ratings yet
- Analysis of Urine and Other Body FluidsDocument9 pagesAnalysis of Urine and Other Body FluidsPajarillaga Franz Erick QuintoNo ratings yet
- Interpretation of HistogramDocument92 pagesInterpretation of HistogramJagu ShahNo ratings yet
- CKD + Kejang SuyonoDocument15 pagesCKD + Kejang Suyonodevi_pramulawatiNo ratings yet
- RD THDocument5 pagesRD THKLIPPNo ratings yet
- Hemograma Buna 2023 BunaDocument71 pagesHemograma Buna 2023 BunaMirelDabuleanuNo ratings yet
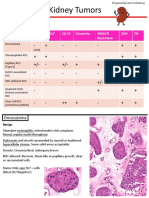
- Kidney Tumors: EosinophilicDocument11 pagesKidney Tumors: EosinophilicPankaj DubeyNo ratings yet
- Urinary System: Kidneys Ureters Urinary Bladder UrethraDocument46 pagesUrinary System: Kidneys Ureters Urinary Bladder UrethraSandley Majan SabangNo ratings yet
- Microscopic Examination of Urine Part 1Document3 pagesMicroscopic Examination of Urine Part 1Sareene Joyce Pepito100% (1)
- Chapter 1 - An Overview of Clinical Laboratory HematologyDocument3 pagesChapter 1 - An Overview of Clinical Laboratory HematologyAira UsiNo ratings yet
- Adjuncts Quiz 1: Study Online atDocument5 pagesAdjuncts Quiz 1: Study Online atcrystalsheNo ratings yet
- Hematology Lecture Lesson 1&2Document3 pagesHematology Lecture Lesson 1&2puhtaytoeNo ratings yet
- Clinical Microscopy ProcedureDocument2 pagesClinical Microscopy ProcedureSamanthaCadaDevillaNo ratings yet
- Cerebrospinal Fluid CSFDocument60 pagesCerebrospinal Fluid CSFpikachuNo ratings yet
- Aubf Lab Microscopic Examination Part 1Document2 pagesAubf Lab Microscopic Examination Part 1Hannah KateNo ratings yet
- презентація, картинкиDocument59 pagesпрезентація, картинкиБогдана ВацебаNo ratings yet
- Rarwrdqrmicroscopic Examination of Urine: RCF 1.118 X 10 XR CMXRPMDocument13 pagesRarwrdqrmicroscopic Examination of Urine: RCF 1.118 X 10 XR CMXRPMpixiedustNo ratings yet
- Cytology of Body FluidDocument68 pagesCytology of Body FluidZeeshan YousufNo ratings yet
- Anaphysio Module 10 Hematologic SystemDocument39 pagesAnaphysio Module 10 Hematologic SystemJoshua UveroNo ratings yet
- Rarwrdrmicroscopic Examination of Urine: RCF 1.118 X 10 XR CMXRPMDocument13 pagesRarwrdrmicroscopic Examination of Urine: RCF 1.118 X 10 XR CMXRPMpixiedustNo ratings yet
- Rarwardqaarmicroscopic Examination of Urine: RCF 1.118 X 10 XR CMXRPMDocument13 pagesRarwardqaarmicroscopic Examination of Urine: RCF 1.118 X 10 XR CMXRPMpixiedust100% (1)
- Rarwrrmicroscopic Examination of Urine: RCF 1.118 X 10 XR CMXRPMDocument13 pagesRarwrrmicroscopic Examination of Urine: RCF 1.118 X 10 XR CMXRPMpixiedustNo ratings yet
- Meningitis MicrobiologyDocument74 pagesMeningitis MicrobiologyJyoti YadavNo ratings yet
- Rarwrmicroscopic Examination of Urine: RCF 1.118 X 10 XR CMXRPMDocument13 pagesRarwrmicroscopic Examination of Urine: RCF 1.118 X 10 XR CMXRPMpixiedustNo ratings yet
- Rarwrdqaarmicroscopic Examination of Urine: RCF 1.118 X 10 XR CMXRPMDocument13 pagesRarwrdqaarmicroscopic Examination of Urine: RCF 1.118 X 10 XR CMXRPMpixiedustNo ratings yet
- Hematologic DiseasesDocument11 pagesHematologic DiseasesPerrilyn Perey100% (2)
- Serous Fluid: FunctionDocument23 pagesSerous Fluid: FunctionMarl EstradaNo ratings yet
- AUBF - MidtermsDocument14 pagesAUBF - MidtermsRomie Solacito100% (1)
- Studytwt Quicknotes and MnemonicsDocument16 pagesStudytwt Quicknotes and MnemonicsLiz LasNo ratings yet
- Approach To SplenomegalyDocument37 pagesApproach To SplenomegalySarath Menon R100% (1)
- AUBFDocument10 pagesAUBFnillascadivinevan.rNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular SystemDocument127 pagesCardiovascular Systembreanna coyneNo ratings yet
- Hematologic DiseasesDocument2 pagesHematologic Diseasessun shineNo ratings yet
- Abnormalities of Haematopoiesis and Blood DisordersDocument51 pagesAbnormalities of Haematopoiesis and Blood DisordersRenad AlharbiNo ratings yet
- HD B Braun For CNN TakersDocument6 pagesHD B Braun For CNN TakersWhimsey CipresNo ratings yet
- Hema Lesson 1Document64 pagesHema Lesson 1fleur harrisonNo ratings yet
- Urine Cast ดิวDocument40 pagesUrine Cast ดิวVeerapong Vattanavanit100% (1)
- Laboratory Evaluation of PlateletsDocument4 pagesLaboratory Evaluation of Plateletscherry nokiaNo ratings yet
- L23 Panceatic ProblemsDocument14 pagesL23 Panceatic ProblemsBint Islam HDNo ratings yet
- HEMA LAB Reticulocyte Study ESR OFT RBC CountDocument17 pagesHEMA LAB Reticulocyte Study ESR OFT RBC CountJam RamosNo ratings yet
- Other Body Fluid Cerebrospinal FluidDocument16 pagesOther Body Fluid Cerebrospinal Fluidrona hilarioNo ratings yet
- AUBF Microscopic Exam Part 2&3Document13 pagesAUBF Microscopic Exam Part 2&3Anya IgnacioNo ratings yet
- AUBF2Document132 pagesAUBF2Trina Fay QuicoNo ratings yet
- Microscopic Examination - Renal Diseases-1Document12 pagesMicroscopic Examination - Renal Diseases-1Jorraine Anne EscañaNo ratings yet
- Figure 1: Inferior View of The Brain and Brain Stem Showing Cranial NervesDocument40 pagesFigure 1: Inferior View of The Brain and Brain Stem Showing Cranial NervesVishnu Karunakaran0% (1)
- Cell Structure Function and PropertiesDocument10 pagesCell Structure Function and PropertiesWanda JohnNo ratings yet
- Lee Endocrine SystemDocument3 pagesLee Endocrine SystemLouise Mica LeeNo ratings yet
- The Endoctrine GlandDocument28 pagesThe Endoctrine GlandKizyanah Palanas Bentic100% (1)
- Partial Extraction Therapies (PET) Part - Maintaining Alveolar Ridge Contour at Pontic and Immediate Implant SitesDocument8 pagesPartial Extraction Therapies (PET) Part - Maintaining Alveolar Ridge Contour at Pontic and Immediate Implant SitesCristina EneNo ratings yet
- Collège de La Salle (Frères) Amman - Jordan: Biology / Cells: Cell SpecialisationDocument3 pagesCollège de La Salle (Frères) Amman - Jordan: Biology / Cells: Cell Specialisationwafa eliasNo ratings yet
- Hormones and The Endocrine System: BiologyDocument78 pagesHormones and The Endocrine System: Biologytricia tghNo ratings yet
- MCQ 23 Physio AnswersDocument8 pagesMCQ 23 Physio AnswersJulyhathul Kuraishi100% (1)
- Maternal Lec Week 1 3Document4 pagesMaternal Lec Week 1 3Althea ManarpiisNo ratings yet
- University Journal of Medicine and Medical SpecialitiesDocument4 pagesUniversity Journal of Medicine and Medical SpecialitiesVivek ShankarNo ratings yet
- A. Background: Truncus and Cauda. The Caput Part Is Relatively Small, Consist of A Beak Made FromDocument9 pagesA. Background: Truncus and Cauda. The Caput Part Is Relatively Small, Consist of A Beak Made FromDaisy KavinskyNo ratings yet
- Fufen Bl-41: Bladder Channel 1Document1 pageFufen Bl-41: Bladder Channel 1BDI92No ratings yet
- Techniques of Mandibular AnesthesiaDocument46 pagesTechniques of Mandibular AnesthesiaashishNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER17 Anatomy and Physiology of OcularMotor SystemsDocument78 pagesCHAPTER17 Anatomy and Physiology of OcularMotor Systemsbenjumear_719607598No ratings yet
- Assesment of Hearing in Infants & ChildrenDocument36 pagesAssesment of Hearing in Infants & ChildrenDr.PriyanjalNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Deep Vein Thrombosis (Thrombophlebitis)Document7 pagesPathophysiology of Deep Vein Thrombosis (Thrombophlebitis)resty tacataNo ratings yet
- 2nd Quarter - WK 3-4 2nd SUMMATIVE TEST SCIENCE - ASIONGDocument2 pages2nd Quarter - WK 3-4 2nd SUMMATIVE TEST SCIENCE - ASIONGVirgie Calderon AbestadoNo ratings yet
- TXB Anomali RadenDocument10 pagesTXB Anomali Radenayu waodeNo ratings yet
- 26 PDFDocument13 pages26 PDFMonica TrifitrianaNo ratings yet
- LP IcuDocument15 pagesLP IcuMario Kape100% (1)
- Slide Lecture - Identifying and Etiology of A MalocclusionDocument8 pagesSlide Lecture - Identifying and Etiology of A MalocclusionZupe SyachbaniahNo ratings yet
- Lab ManualDocument19 pagesLab ManualShafin FinaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of The HeartDocument8 pagesAnatomy of The HeartAbigail BrillantesNo ratings yet
- Smile Analysis: A Review Part IDocument3 pagesSmile Analysis: A Review Part IGustavoAndresGarciaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Meridians and CollateralsDocument27 pagesChapter 4 - Meridians and CollateralsAudrygodwyn50% (2)
- Kuliah Patofisiologi Trauma - DR Raden Ajeng Sri WulandariDocument22 pagesKuliah Patofisiologi Trauma - DR Raden Ajeng Sri WulandariAgung Budi SuristioNo ratings yet
- Head InjuryDocument39 pagesHead InjuryDr. Jayesh Patidar100% (1)
- Blood: Presented By: Jomar P. Ronquillo, RNDocument65 pagesBlood: Presented By: Jomar P. Ronquillo, RNHypothalamus1No ratings yet
- Endocrine DrugsDocument50 pagesEndocrine DrugsJohney DoeNo ratings yet