Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 viewsRespiration in Organisms
Respiration in Organisms
Uploaded by
Saurabh kumarRespiration is the process by which organisms convert food into energy. There are two types of respiration - aerobic respiration which uses oxygen to fully break down glucose, producing carbon dioxide and water, and anaerobic respiration which breaks down glucose without oxygen, producing less energy. In humans and most animals, aerobic respiration takes place in cells. Anaerobic respiration occurs briefly during intense exercise when oxygen demand exceeds supply. Plants also respire to produce energy, taking in oxygen and releasing carbon dioxide through stomata in their leaves.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Ray PeatDocument10 pagesRay PeatCosti Sorescu100% (3)
- Integrative Human Biochemistry PDF - A Textbook For Medical Biochemistry PDFDocument433 pagesIntegrative Human Biochemistry PDF - A Textbook For Medical Biochemistry PDFJuan100% (5)
- Screenshot 2024-03-06 at 2.59.00 AMDocument34 pagesScreenshot 2024-03-06 at 2.59.00 AMbgarg9079No ratings yet
- Cells of Animals: Glucose + Oxygen Carbon Dioxide + Water + EnergyDocument3 pagesCells of Animals: Glucose + Oxygen Carbon Dioxide + Water + EnergyHONLETH ROMBLONNo ratings yet
- RespirationDocument35 pagesRespirationnabeeha malhiNo ratings yet
- B7-CBSE-Respiration in OrganismDocument29 pagesB7-CBSE-Respiration in OrganismSwyamjeet PradhanNo ratings yet
- RESPIRATIONDocument11 pagesRESPIRATIONCREATIVING TAMILANNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 - Respiration in Organisms - Class 7 Biology NotesDocument5 pagesChapter 10 - Respiration in Organisms - Class 7 Biology Notessriniram_2002No ratings yet
- Respiration Science AssessmentDocument19 pagesRespiration Science Assessmentmarta.amsNo ratings yet
- Respiration Is The Process of Breaking Down of Glucose To Produce EnergyDocument5 pagesRespiration Is The Process of Breaking Down of Glucose To Produce EnergyTechnical AyushNo ratings yet
- Life Process RespirationDocument51 pagesLife Process RespirationJatin Kalra 10 DNo ratings yet
- Respiration in OrganismsDocument9 pagesRespiration in Organismsshreya kashyapNo ratings yet
- Animal Physiology and Physiological Chemistry Paper Mzo503 Paper Mzo503Document19 pagesAnimal Physiology and Physiological Chemistry Paper Mzo503 Paper Mzo503Abhishek Singh ChandelNo ratings yet
- Class 7 RespirationDocument5 pagesClass 7 RespirationGopi SNo ratings yet
- Week 7 (A) Human and Social BiologyDocument4 pagesWeek 7 (A) Human and Social BiologyBeyonce SkekelNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System of Frog: External RespirationDocument3 pagesRespiratory System of Frog: External RespirationShaira CogollodoNo ratings yet
- Notes Life Processes (Repiration)Document2 pagesNotes Life Processes (Repiration)07.joycharlieNo ratings yet
- Respiration: Biology GCE Study BuddyDocument45 pagesRespiration: Biology GCE Study BuddyMaleeha HumayunNo ratings yet
- 7T Respiration in Plants and AnimalsDocument22 pages7T Respiration in Plants and AnimalsPOONAM SHARMANo ratings yet
- Document 5Document5 pagesDocument 5kauthar hassanNo ratings yet
- Respiration NotesDocument7 pagesRespiration NotesTamisha JacobsNo ratings yet
- Respiration and Gas Exchange 2Document35 pagesRespiration and Gas Exchange 2Nabil SinukrotNo ratings yet
- Bio Project - Respiration and Gas Exchange .Document21 pagesBio Project - Respiration and Gas Exchange .naazim mohamedNo ratings yet
- Respiration in OrganismDocument67 pagesRespiration in Organismsangeetha alurNo ratings yet
- Notebook Work Respiration in OrganismsDocument4 pagesNotebook Work Respiration in OrganismsachlaNo ratings yet
- Respiration and Gas ExchangeDocument29 pagesRespiration and Gas Exchangemiriam odonkorNo ratings yet
- G Jxcyp 9 LRR Wo ESRMna M3Document14 pagesG Jxcyp 9 LRR Wo ESRMna M3jhaorpratyushNo ratings yet
- 4 A - RespirationDocument15 pages4 A - Respirationsalishfan1289No ratings yet
- The Respiratory System and RespirationDocument7 pagesThe Respiratory System and RespirationAntonateNo ratings yet
- Respiration and Gas ExchangeDocument48 pagesRespiration and Gas ExchangeIbrahim NOORZADNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument14 pagesRespiratory SystemTedi FetoNo ratings yet
- Notes RespirationDocument6 pagesNotes Respirationakheel7353No ratings yet
- RespirationDocument5 pagesRespirationDivyansh SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Respiration 2Document23 pagesRespiration 2api-233649346No ratings yet
- MLP HLP Class VII Respiration in OrganismsDocument4 pagesMLP HLP Class VII Respiration in OrganismsDivyanshi BansalNo ratings yet
- Respiration in PlantsDocument9 pagesRespiration in PlantsnolaNo ratings yet
- S2 - Bio - RevisionNotes 1.1 To 1.4 - PreMidDocument7 pagesS2 - Bio - RevisionNotes 1.1 To 1.4 - PreMidKaung ThihaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Bio NotesDocument4 pagesChapter 11 Bio NotesArabella ShepherdNo ratings yet
- CLASS 10th RESPIRATIONDocument3 pagesCLASS 10th RESPIRATIONNavkaran SinghNo ratings yet
- Respiration NotesDocument7 pagesRespiration NotesKrishna SharmaNo ratings yet
- Respiration in OrganismsDocument6 pagesRespiration in OrganismsAdityaNo ratings yet
- What Is Respiration?Document8 pagesWhat Is Respiration?Waleed Bin KhalidNo ratings yet
- Introduction To RespirationDocument14 pagesIntroduction To RespirationAzneezal Ar-RashidNo ratings yet
- Respiration in OrganismsDocument7 pagesRespiration in Organismschristopher thomasNo ratings yet
- Spyros Filippas A4 Biology Term ProjectDocument12 pagesSpyros Filippas A4 Biology Term Projectpipis pipasNo ratings yet
- RESPIRATIONDocument36 pagesRESPIRATIONnyemarichardssvgNo ratings yet
- Term 2 - Unit 1 - ADocument26 pagesTerm 2 - Unit 1 - Amusa shahidNo ratings yet
- Grade - 7 Biology: Chapter-10 Respiration in OrganismsDocument22 pagesGrade - 7 Biology: Chapter-10 Respiration in OrganismsJanardhanNo ratings yet
- 10S2 .Group 3-Human Gas ExchangeDocument33 pages10S2 .Group 3-Human Gas ExchangeEmy AnkrahNo ratings yet
- Respiration and Gas ExchangeDocument24 pagesRespiration and Gas ExchangeEizelle100% (2)
- Biology ScienceDocument9 pagesBiology SciencetalaNo ratings yet
- Respiration and The Respiratory SystemDocument41 pagesRespiration and The Respiratory Systemfrancis iduruNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in PlantsDocument15 pagesNutrition in PlantspranayaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 - Respiration and Gas ExchangeDocument64 pagesChapter 11 - Respiration and Gas ExchangeKareem DmourNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory SystemDocument18 pagesThe Respiratory SystemTamilore WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Dieaseas and ImmunityDocument30 pagesDieaseas and Immunityadvikabhavar4No ratings yet
- Respiration in Organisms Class 7 NotesDocument37 pagesRespiration in Organisms Class 7 Notestrisha.sharma2347No ratings yet
- Science Notes WITH CHEMDocument11 pagesScience Notes WITH CHEMAlfredNo ratings yet
- Gas Exchange in AnimalsDocument20 pagesGas Exchange in AnimalsMaria Theresa HerreroNo ratings yet
- Q2 Respiration L3Document49 pagesQ2 Respiration L3aranjuezjohnlloydNo ratings yet
- Biology U2Document10 pagesBiology U2Alima IqbalNo ratings yet
- How Do Humans Breathe? Science Book Age 8 | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandHow Do Humans Breathe? Science Book Age 8 | Children's Biology BooksNo ratings yet
- Class VIIIDocument7 pagesClass VIIISaurabh kumarNo ratings yet
- 9TH Math Advanced Assignment-1 With KeyDocument1 page9TH Math Advanced Assignment-1 With KeySaurabh kumarNo ratings yet
- Physics (5) SampleDocument4 pagesPhysics (5) SampleSaurabh kumarNo ratings yet
- 9th Advanced Trigonometry Assignment-1Document1 page9th Advanced Trigonometry Assignment-1Saurabh kumarNo ratings yet
- ChromosomeDocument28 pagesChromosomeSaurabh kumarNo ratings yet
- Cell ConceptDocument21 pagesCell ConceptSaurabh kumarNo ratings yet
- PHOTOSYNTHESISDocument24 pagesPHOTOSYNTHESISSaurabh kumarNo ratings yet
- Stability of PH, Blood Gas Partial Pressure, Hemoglobin Oxygen Saturation Fraction, and Lactate ConcentrationDocument9 pagesStability of PH, Blood Gas Partial Pressure, Hemoglobin Oxygen Saturation Fraction, and Lactate ConcentrationJavier DeinecaNo ratings yet
- 5 Food Production eDocument20 pages5 Food Production eIG LibraryNo ratings yet
- Grade Twelve Biology Model QuestionsDocument9 pagesGrade Twelve Biology Model Questionsmmree yyttNo ratings yet
- MCQ RespirationDocument28 pagesMCQ RespirationBonifacius Budi Nugroho100% (1)
- 407) Science Ctet Paper - 2 (Content English Medium)Document116 pages407) Science Ctet Paper - 2 (Content English Medium)Atul ThakurNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument11 pagesCellular RespirationNiña Jennifer Potter Vergara100% (2)
- Chapter 9Document32 pagesChapter 9DivineGloryMalbuyoNo ratings yet
- MC Chapter 10 TestDocument12 pagesMC Chapter 10 TestMohammed AlMujainiNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1: Quarter 2 - Module 3: When Cells BreatheDocument26 pagesGeneral Biology 1: Quarter 2 - Module 3: When Cells BreathePLS help me get 1k subsNo ratings yet
- Biodegradation of HydrocarbonDocument5 pagesBiodegradation of HydrocarbonNITI SHAHNo ratings yet
- Endosymbiotic TheoryDocument9 pagesEndosymbiotic TheoryFrancisco CañonNo ratings yet
- Practice Chapter TestDocument4 pagesPractice Chapter Testhossam mohamedNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 2.3: Flows of Energy and MatterDocument11 pagesLab Report 2.3: Flows of Energy and MatterMiranda Olimpia Morante ReinosoNo ratings yet
- Resporation WorksheetDocument6 pagesResporation WorksheetRosty Ann GrabilloNo ratings yet
- Answer Key NAFS Science Worksheet 1Document9 pagesAnswer Key NAFS Science Worksheet 1ManaalNo ratings yet
- Suprarasional Camp Kelas 8: Pembahasan Soal Web Sesi 1Document7 pagesSuprarasional Camp Kelas 8: Pembahasan Soal Web Sesi 1Yumna Sa'diyyahNo ratings yet
- Fixed Soal Pat Bingg XiDocument7 pagesFixed Soal Pat Bingg XidilahNo ratings yet
- Oxidative Phosphorylation - Biology (Article) - Khan AcademyDocument16 pagesOxidative Phosphorylation - Biology (Article) - Khan Academydeepali_nih9585No ratings yet
- Cellular Metabolism Overview of MetabolismDocument17 pagesCellular Metabolism Overview of MetabolismNathan Louis PalacioNo ratings yet
- ATP SynthesisDocument3 pagesATP SynthesisAmanyNo ratings yet
- Anaerobic Respiration in YeastDocument10 pagesAnaerobic Respiration in Yeastmaya hawaniNo ratings yet
- New Doc Feb 20, 2022 9.34 PMDocument13 pagesNew Doc Feb 20, 2022 9.34 PMsomnathmannaxx3No ratings yet
- 2020 Specimen Paper 1 PDFDocument16 pages2020 Specimen Paper 1 PDFThapelo JeremiahNo ratings yet
- Latihan Chap 7 f4Document3 pagesLatihan Chap 7 f4Faizal PejerNo ratings yet
- Lecture8 Homework BIO1401 Sp23Document7 pagesLecture8 Homework BIO1401 Sp23wafae moutanaNo ratings yet
- Muscular System NotesDocument40 pagesMuscular System NotesWindhy Dzakiyyah Aurora100% (1)
- IB Biology - Revision Workbook - Roxanne Russo - Anthem Press 2020Document199 pagesIB Biology - Revision Workbook - Roxanne Russo - Anthem Press 2020Renju Kuriakose100% (1)
- Mark Scheme (Results) : Summer 2017Document12 pagesMark Scheme (Results) : Summer 2017Ege Arda AkyürekNo ratings yet
Respiration in Organisms
Respiration in Organisms
Uploaded by
Saurabh kumar0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views17 pagesRespiration is the process by which organisms convert food into energy. There are two types of respiration - aerobic respiration which uses oxygen to fully break down glucose, producing carbon dioxide and water, and anaerobic respiration which breaks down glucose without oxygen, producing less energy. In humans and most animals, aerobic respiration takes place in cells. Anaerobic respiration occurs briefly during intense exercise when oxygen demand exceeds supply. Plants also respire to produce energy, taking in oxygen and releasing carbon dioxide through stomata in their leaves.
Original Description:
Respiration
Original Title
RESPIRATION IN ORGANISMS-converted - Copy
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentRespiration is the process by which organisms convert food into energy. There are two types of respiration - aerobic respiration which uses oxygen to fully break down glucose, producing carbon dioxide and water, and anaerobic respiration which breaks down glucose without oxygen, producing less energy. In humans and most animals, aerobic respiration takes place in cells. Anaerobic respiration occurs briefly during intense exercise when oxygen demand exceeds supply. Plants also respire to produce energy, taking in oxygen and releasing carbon dioxide through stomata in their leaves.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views17 pagesRespiration in Organisms
Respiration in Organisms
Uploaded by
Saurabh kumarRespiration is the process by which organisms convert food into energy. There are two types of respiration - aerobic respiration which uses oxygen to fully break down glucose, producing carbon dioxide and water, and anaerobic respiration which breaks down glucose without oxygen, producing less energy. In humans and most animals, aerobic respiration takes place in cells. Anaerobic respiration occurs briefly during intense exercise when oxygen demand exceeds supply. Plants also respire to produce energy, taking in oxygen and releasing carbon dioxide through stomata in their leaves.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 17
RESPIRATION IN By: Teyas Chakraborty
ORGANISMS Date: 18/08/2021
INTRODUCTION
• All living organisms need energy to do work.
• Energy is required to perform various functions of life such as nutrition, excretion,
growth, movement, transportation and reproduction. Without energy, organisms
cannot do any work.
• The energy, comes from the food we eat.
• Respiration is the process which converts energy stored in food into a form which the
body can use.
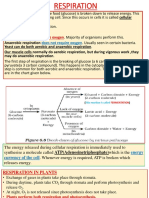
RESPIRATION
The process of oxidation of food into carbon dioxide and water to produce energy is called
respiration.
On the basis of presence of oxygen respiration is of two types :
✓ Aerobic respiration : When break-down of glucose occurs with the use of O2 , it is called
aerobic respiration. In this process there is complete breakdown of food, so maximum
production of energy.
Glucose →Carbon-dioxide + water + energy. (in presence of oxygen)
✓Anaerobic respiration :When breakdown of glucose occurs in lack or limited supply of O2 is
called anaerobic respiration.
Glucose → Alcohol + CO2 + energy. (in absence of oxygen)
During heavy exercise, when the supply of oxygen to our muscle cell is insufficient, food
breakdown occurs by anaerobic respiration.
Glucose → Lactic acid + energy ( in absence of oxygen)
TYPES OF RESPIRATION
There are two types of respiration – aerobic and anaerobic respiration.
✓Aerobic Respiration :When the breakdown of food substances (like glucose) takes place in the
presence of oxygen with the release of a large amount of energy, it is called aerobic respiration.
In this process, carbon dioxide and water are released as waste products. The overall equation for
aerobic respiration is:
Food + Oxygen → Energy + Carbon dioxide + Water
Most animals including humans and green plants respire aerobically.
✓Anaerobic Respiration : Anaerobic respiration is the breakdown of food substances with the release of
a small amount of energy in the absence of oxygen. It occurs in certain organisms like yeast and some
bacteria. These organisms are called anaerobes.
In the absence of oxygen, glucose breaks down into alcohol and carbon dioxide with the release of
comparatively less energy.
The equation for anaerobic respiration is:
Food (glucose) → Energy +Alcohol + Carbon dioxide (occurs in absence of oxygen.)
AEROBIC RESPIRATION IN HUMAN
BEING
• Aerobic respiration is more efficient than anaerobic one, as more energy is produced during aerobic
respiration.
• Anaerobic respiration in humans can take place only for a short time. It takes place in our muscles when
our body undergoes vigorous muscular activity during heavy exercise or fast running.
Muscular cramps may develop as a result of heavy exercise or fast running.
• When muscle cells respire anaerobically, there is a partial breakdown of glucose and lactic acid is
produced, accumulation of lactic acid causes muscle cramps.
Food (glucose)→ Lactic Acid + Energy ( in muscle cell in the absence of oxygen)
• Relief from muscle cramps can be obtained bay hot water bath or a massage.
• Circulation of blood in the body is improved by these acts. As a result, the supply of oxygen to the
muscles increases.
• Increase in supply of oxygen brings about complete breakdown of lactic acid into carbon dioxide and
water.
DIFFERENCES BETWEEN AEROBIC AND
ANAEROBIC RESPIRATION
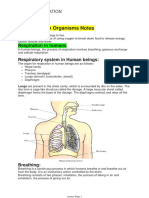
BREATHING
• Exchange of gases or taking in oxygen and giving out carbon dioxide with the help of
respiratory organs is called breathing.
The taking in of air rich in oxygen is called inhalation and giving out CO2 rich air is called
exhalation.
• It is a continuous process which goes on all the time and throughout the life of an organism.
• The number of times a person breathes in a minute is called the breathing rate.
• Normal breathing of adult human beings at rest is about 15-18 per min. But it can change
according to requirement of O2 by the body.
During heavy exercise, the breathing rate can increase up to 25 times per minute and also we
take deep breaths to inhale more oxygen.
•As a result more oxygen is supplied to our cells.So speeds up the breakdown of food and
more energy is released.
That is the cause we feel hungry after a physical activity
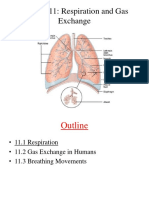
HUMAN RESPIRATION SYSTEM
In humans, several organs take part in the process of respiration. These different
organs together form the respiratory system.
Organs of the Respiratory System:
-Nostrils
- Nasal cavity or passage
- Windpipe (trachea)
- Bronchi (singular bronchus)
- Lungs
Continue…
Air enters our body through the nostrils.
From the nostrils, the air containing oxygen is taken into the nasal cavity.
From here it goes down the windpipe or trachea, from trachea it goes to two smaller tubes
called bronchi(Singular bronchus). One bronchus enters each lung.
Inside the lungs, each bronchus divides repeatedly into a large number of small branches
called the bronchioles.
Each bronchiole ends in a number of air sacs known as alveoli (singular alveolus).
The walls of the alveoli have a large number of very thin blood capillaries.
Lungs are present in the chest cavity. This cavity is surrounded by ribs on the sides.
Ribs form a cage-like structure called the rib cage.
A large muscular sheet called diaphragm forms the floor of the chest cavity. Breathing
involves the movement of the diaphragm and the rib cage.
MECHANISM OF BREATHING IN HUMANS
BEINGS
During inhalation:
-Ribs move up and outwards and diaphragm moves
down.
-Its movement increases space in our chest cavity and air
rushes into the lungs.
-The lungs get filled with air and exchange of gases take
place by the process of difference in alveoli.
During exhalation:
-Ribs move down and inwards, while diaphragm moves
up to its former position.
-This reduces the size of the chest cavity and air is pushed
out of the lungs.
TO SHOW THAT CARBON DIOXIDE IS
GIVEN OUT DURING BREATHING:
To show that carbon dioxide is given out during breathing:
- Take a test tube with freshly prepared lime water [Ca(OH)2 ].
- With the help of a plastic straw dipped in the lime water,
breathe out into the test tube a few times.
- The lime water turns milky (due to the formation of CaCO3 ) .
- This shows that carbon dioxide is present in the exhaled air.
TO SHOW THAT EXHALED AIR
CONTAINS WATER VAPOUR
- Stand in front of a clean mirror.
- Breathe out some air from your mouth on the mirror.
- The mirror becomes cloudy.
- Sometimes even water droplets maybe seen on the mirror.
- This activity shows that exhaled air contains water vapour.
RESPIRATION IN INSECTS
•A cockroach has small openings on the sides of its
body. Other insects also have similar openings.
These openings are called spiracles.
•Insects have a network of air tubes called
tracheae for gas exchange. This type of respiration
is called tracheal respiration.
•Oxygen rich air rushes through spiracles into the
tracheal tubes, diffuses into the body tissue, and
reaches every cell of the body.
Similarly, carbon dioxide from the cells goes into
the tracheal tubes and moves out through
spiracles.
RESPIRATION IN EARTHWORM
•Earthworms breathe through their skin. This is called
cutaneous respiration.
•The skin of an earthworm feels moist and slimy on
touching.
•Gases can easily pass through them.
•Though frogs have pair of lungs like human beings,
they can also breathe through their skin, which is
moist and slippery by the process of diffusion.
BREATHING UNDER WATER
•Gills in fish help them to use oxygen dissolved in
water.
•Gills are projections of the skin.
•Gills help in breathing.
•Gills are well supplied with blood vessels for
exchange of gases.
• But breathing in water is quite difficult as water is
dense and having less dissolved oxygen than air.
DO PLANTSALSO RESPIRE?
Plants take in oxygen from the air and give out carbon
dioxide.
In the cells oxygen is used to break down glucose into
carbon dioxide and water as in other organisms.
• In plants each part can independently take in oxygen
from the air and give out carbon dioxide.
• The leaves of the plants have tiny pores called stomata
for exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide.
• Like all other living cells of the plants, the root cells also
need oxygen to generate energy.
• Roots take up air from the air spaces present between
the soil particles with the help of root hairs.
Lenticels in old stems and general surface of roots help in
respiration.
THE END
You might also like
- Ray PeatDocument10 pagesRay PeatCosti Sorescu100% (3)
- Integrative Human Biochemistry PDF - A Textbook For Medical Biochemistry PDFDocument433 pagesIntegrative Human Biochemistry PDF - A Textbook For Medical Biochemistry PDFJuan100% (5)
- Screenshot 2024-03-06 at 2.59.00 AMDocument34 pagesScreenshot 2024-03-06 at 2.59.00 AMbgarg9079No ratings yet
- Cells of Animals: Glucose + Oxygen Carbon Dioxide + Water + EnergyDocument3 pagesCells of Animals: Glucose + Oxygen Carbon Dioxide + Water + EnergyHONLETH ROMBLONNo ratings yet
- RespirationDocument35 pagesRespirationnabeeha malhiNo ratings yet
- B7-CBSE-Respiration in OrganismDocument29 pagesB7-CBSE-Respiration in OrganismSwyamjeet PradhanNo ratings yet
- RESPIRATIONDocument11 pagesRESPIRATIONCREATIVING TAMILANNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 - Respiration in Organisms - Class 7 Biology NotesDocument5 pagesChapter 10 - Respiration in Organisms - Class 7 Biology Notessriniram_2002No ratings yet
- Respiration Science AssessmentDocument19 pagesRespiration Science Assessmentmarta.amsNo ratings yet
- Respiration Is The Process of Breaking Down of Glucose To Produce EnergyDocument5 pagesRespiration Is The Process of Breaking Down of Glucose To Produce EnergyTechnical AyushNo ratings yet
- Life Process RespirationDocument51 pagesLife Process RespirationJatin Kalra 10 DNo ratings yet
- Respiration in OrganismsDocument9 pagesRespiration in Organismsshreya kashyapNo ratings yet
- Animal Physiology and Physiological Chemistry Paper Mzo503 Paper Mzo503Document19 pagesAnimal Physiology and Physiological Chemistry Paper Mzo503 Paper Mzo503Abhishek Singh ChandelNo ratings yet
- Class 7 RespirationDocument5 pagesClass 7 RespirationGopi SNo ratings yet
- Week 7 (A) Human and Social BiologyDocument4 pagesWeek 7 (A) Human and Social BiologyBeyonce SkekelNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System of Frog: External RespirationDocument3 pagesRespiratory System of Frog: External RespirationShaira CogollodoNo ratings yet
- Notes Life Processes (Repiration)Document2 pagesNotes Life Processes (Repiration)07.joycharlieNo ratings yet
- Respiration: Biology GCE Study BuddyDocument45 pagesRespiration: Biology GCE Study BuddyMaleeha HumayunNo ratings yet
- 7T Respiration in Plants and AnimalsDocument22 pages7T Respiration in Plants and AnimalsPOONAM SHARMANo ratings yet
- Document 5Document5 pagesDocument 5kauthar hassanNo ratings yet
- Respiration NotesDocument7 pagesRespiration NotesTamisha JacobsNo ratings yet
- Respiration and Gas Exchange 2Document35 pagesRespiration and Gas Exchange 2Nabil SinukrotNo ratings yet
- Bio Project - Respiration and Gas Exchange .Document21 pagesBio Project - Respiration and Gas Exchange .naazim mohamedNo ratings yet
- Respiration in OrganismDocument67 pagesRespiration in Organismsangeetha alurNo ratings yet
- Notebook Work Respiration in OrganismsDocument4 pagesNotebook Work Respiration in OrganismsachlaNo ratings yet
- Respiration and Gas ExchangeDocument29 pagesRespiration and Gas Exchangemiriam odonkorNo ratings yet
- G Jxcyp 9 LRR Wo ESRMna M3Document14 pagesG Jxcyp 9 LRR Wo ESRMna M3jhaorpratyushNo ratings yet
- 4 A - RespirationDocument15 pages4 A - Respirationsalishfan1289No ratings yet
- The Respiratory System and RespirationDocument7 pagesThe Respiratory System and RespirationAntonateNo ratings yet
- Respiration and Gas ExchangeDocument48 pagesRespiration and Gas ExchangeIbrahim NOORZADNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument14 pagesRespiratory SystemTedi FetoNo ratings yet
- Notes RespirationDocument6 pagesNotes Respirationakheel7353No ratings yet
- RespirationDocument5 pagesRespirationDivyansh SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Respiration 2Document23 pagesRespiration 2api-233649346No ratings yet
- MLP HLP Class VII Respiration in OrganismsDocument4 pagesMLP HLP Class VII Respiration in OrganismsDivyanshi BansalNo ratings yet
- Respiration in PlantsDocument9 pagesRespiration in PlantsnolaNo ratings yet
- S2 - Bio - RevisionNotes 1.1 To 1.4 - PreMidDocument7 pagesS2 - Bio - RevisionNotes 1.1 To 1.4 - PreMidKaung ThihaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Bio NotesDocument4 pagesChapter 11 Bio NotesArabella ShepherdNo ratings yet
- CLASS 10th RESPIRATIONDocument3 pagesCLASS 10th RESPIRATIONNavkaran SinghNo ratings yet
- Respiration NotesDocument7 pagesRespiration NotesKrishna SharmaNo ratings yet
- Respiration in OrganismsDocument6 pagesRespiration in OrganismsAdityaNo ratings yet
- What Is Respiration?Document8 pagesWhat Is Respiration?Waleed Bin KhalidNo ratings yet
- Introduction To RespirationDocument14 pagesIntroduction To RespirationAzneezal Ar-RashidNo ratings yet
- Respiration in OrganismsDocument7 pagesRespiration in Organismschristopher thomasNo ratings yet
- Spyros Filippas A4 Biology Term ProjectDocument12 pagesSpyros Filippas A4 Biology Term Projectpipis pipasNo ratings yet
- RESPIRATIONDocument36 pagesRESPIRATIONnyemarichardssvgNo ratings yet
- Term 2 - Unit 1 - ADocument26 pagesTerm 2 - Unit 1 - Amusa shahidNo ratings yet
- Grade - 7 Biology: Chapter-10 Respiration in OrganismsDocument22 pagesGrade - 7 Biology: Chapter-10 Respiration in OrganismsJanardhanNo ratings yet
- 10S2 .Group 3-Human Gas ExchangeDocument33 pages10S2 .Group 3-Human Gas ExchangeEmy AnkrahNo ratings yet
- Respiration and Gas ExchangeDocument24 pagesRespiration and Gas ExchangeEizelle100% (2)
- Biology ScienceDocument9 pagesBiology SciencetalaNo ratings yet
- Respiration and The Respiratory SystemDocument41 pagesRespiration and The Respiratory Systemfrancis iduruNo ratings yet
- Nutrition in PlantsDocument15 pagesNutrition in PlantspranayaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 - Respiration and Gas ExchangeDocument64 pagesChapter 11 - Respiration and Gas ExchangeKareem DmourNo ratings yet
- The Respiratory SystemDocument18 pagesThe Respiratory SystemTamilore WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Dieaseas and ImmunityDocument30 pagesDieaseas and Immunityadvikabhavar4No ratings yet
- Respiration in Organisms Class 7 NotesDocument37 pagesRespiration in Organisms Class 7 Notestrisha.sharma2347No ratings yet
- Science Notes WITH CHEMDocument11 pagesScience Notes WITH CHEMAlfredNo ratings yet
- Gas Exchange in AnimalsDocument20 pagesGas Exchange in AnimalsMaria Theresa HerreroNo ratings yet
- Q2 Respiration L3Document49 pagesQ2 Respiration L3aranjuezjohnlloydNo ratings yet
- Biology U2Document10 pagesBiology U2Alima IqbalNo ratings yet
- How Do Humans Breathe? Science Book Age 8 | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandHow Do Humans Breathe? Science Book Age 8 | Children's Biology BooksNo ratings yet
- Class VIIIDocument7 pagesClass VIIISaurabh kumarNo ratings yet
- 9TH Math Advanced Assignment-1 With KeyDocument1 page9TH Math Advanced Assignment-1 With KeySaurabh kumarNo ratings yet
- Physics (5) SampleDocument4 pagesPhysics (5) SampleSaurabh kumarNo ratings yet
- 9th Advanced Trigonometry Assignment-1Document1 page9th Advanced Trigonometry Assignment-1Saurabh kumarNo ratings yet
- ChromosomeDocument28 pagesChromosomeSaurabh kumarNo ratings yet
- Cell ConceptDocument21 pagesCell ConceptSaurabh kumarNo ratings yet
- PHOTOSYNTHESISDocument24 pagesPHOTOSYNTHESISSaurabh kumarNo ratings yet
- Stability of PH, Blood Gas Partial Pressure, Hemoglobin Oxygen Saturation Fraction, and Lactate ConcentrationDocument9 pagesStability of PH, Blood Gas Partial Pressure, Hemoglobin Oxygen Saturation Fraction, and Lactate ConcentrationJavier DeinecaNo ratings yet
- 5 Food Production eDocument20 pages5 Food Production eIG LibraryNo ratings yet
- Grade Twelve Biology Model QuestionsDocument9 pagesGrade Twelve Biology Model Questionsmmree yyttNo ratings yet
- MCQ RespirationDocument28 pagesMCQ RespirationBonifacius Budi Nugroho100% (1)
- 407) Science Ctet Paper - 2 (Content English Medium)Document116 pages407) Science Ctet Paper - 2 (Content English Medium)Atul ThakurNo ratings yet
- Cellular RespirationDocument11 pagesCellular RespirationNiña Jennifer Potter Vergara100% (2)
- Chapter 9Document32 pagesChapter 9DivineGloryMalbuyoNo ratings yet
- MC Chapter 10 TestDocument12 pagesMC Chapter 10 TestMohammed AlMujainiNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1: Quarter 2 - Module 3: When Cells BreatheDocument26 pagesGeneral Biology 1: Quarter 2 - Module 3: When Cells BreathePLS help me get 1k subsNo ratings yet
- Biodegradation of HydrocarbonDocument5 pagesBiodegradation of HydrocarbonNITI SHAHNo ratings yet
- Endosymbiotic TheoryDocument9 pagesEndosymbiotic TheoryFrancisco CañonNo ratings yet
- Practice Chapter TestDocument4 pagesPractice Chapter Testhossam mohamedNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 2.3: Flows of Energy and MatterDocument11 pagesLab Report 2.3: Flows of Energy and MatterMiranda Olimpia Morante ReinosoNo ratings yet
- Resporation WorksheetDocument6 pagesResporation WorksheetRosty Ann GrabilloNo ratings yet
- Answer Key NAFS Science Worksheet 1Document9 pagesAnswer Key NAFS Science Worksheet 1ManaalNo ratings yet
- Suprarasional Camp Kelas 8: Pembahasan Soal Web Sesi 1Document7 pagesSuprarasional Camp Kelas 8: Pembahasan Soal Web Sesi 1Yumna Sa'diyyahNo ratings yet
- Fixed Soal Pat Bingg XiDocument7 pagesFixed Soal Pat Bingg XidilahNo ratings yet
- Oxidative Phosphorylation - Biology (Article) - Khan AcademyDocument16 pagesOxidative Phosphorylation - Biology (Article) - Khan Academydeepali_nih9585No ratings yet
- Cellular Metabolism Overview of MetabolismDocument17 pagesCellular Metabolism Overview of MetabolismNathan Louis PalacioNo ratings yet
- ATP SynthesisDocument3 pagesATP SynthesisAmanyNo ratings yet
- Anaerobic Respiration in YeastDocument10 pagesAnaerobic Respiration in Yeastmaya hawaniNo ratings yet
- New Doc Feb 20, 2022 9.34 PMDocument13 pagesNew Doc Feb 20, 2022 9.34 PMsomnathmannaxx3No ratings yet
- 2020 Specimen Paper 1 PDFDocument16 pages2020 Specimen Paper 1 PDFThapelo JeremiahNo ratings yet
- Latihan Chap 7 f4Document3 pagesLatihan Chap 7 f4Faizal PejerNo ratings yet
- Lecture8 Homework BIO1401 Sp23Document7 pagesLecture8 Homework BIO1401 Sp23wafae moutanaNo ratings yet
- Muscular System NotesDocument40 pagesMuscular System NotesWindhy Dzakiyyah Aurora100% (1)
- IB Biology - Revision Workbook - Roxanne Russo - Anthem Press 2020Document199 pagesIB Biology - Revision Workbook - Roxanne Russo - Anthem Press 2020Renju Kuriakose100% (1)
- Mark Scheme (Results) : Summer 2017Document12 pagesMark Scheme (Results) : Summer 2017Ege Arda AkyürekNo ratings yet