Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1-Horizon Scanning
1-Horizon Scanning
Uploaded by
Vishal ShivaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
1-Horizon Scanning
1-Horizon Scanning
Uploaded by
Vishal ShivaCopyright:
Available Formats
Advanced strategic toolkit 04/10/2022
MSc Global Management
Dr. Valery Michaux – Neoma BS
Industry and Corporate Foresight :
4 distinct phases -> 4 reports
PHASE 1 PHASE 2 PHASE 3 PHASE 4
Industry Industry future Industry Company
horizon exploration scenarios strategic
Scanning building reflection
(strategic options)
Msc Global Management 2022-2023
Advanced Strategic Toolkit
Industry and Corporate
Foresight : Phase 1
INDUSTRY COMPANY
“Horizon scanning” : analyzing
of the current industry dynamic
1 2
Today Agenda
Courses
PHASE 1 PHASE 2 PHASE 3 PHASE 4 plateform
Industry Industry future Industry Company
horizon exploration scenarios strategic
Scanning building reflection
(strategic options)
Instructions
1
Guidance
INDUSTRY COMPANY
3 4
Horizon scanning
How to spot emerging signals of change
Collection of a large amount of information
Introduction :
Broaden
your view
Main Goal of the
Horizon Scanning
Diverse scenarios about changes that might phase
occur in the future
5 6
DR. Valery Michaux, Neoma Business School
1
Advanced strategic toolkit 04/10/2022
MSc Global Management
What is currently changing ? What is currently changing ?
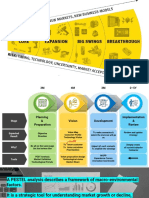
DYNAMICS ? PESTEL = collect
7 8
GROUPING -> Avoid the “PESTEL syndrome”
What is currently changing ?
Main axes of transformation ?
9 10
Systemic thinking
What is currently changing ?
GOAL : 6 to 7 major Step 1 - Collect data
transformational axis
Adopt a
systemic
mode
11 12
DR. Valery Michaux, Neoma Business School
2
Advanced strategic toolkit 04/10/2022
MSc Global Management
Systemic thinking Systemic thinking
Step 2 – Qualify data Step 2 – Qualify data
Qualification Qualification
Qualification Qualification
Qualification Qualification
Change drivers Transformations Change drivers Industry transformations
Environmental sensibility Recycling & second life products
13 14
Industry Horizon scanning
Systemic view : understand the dynamics of
the sector/industry -> change drivers
Distinguish between Step 3 – Group
– Change drivers & change actors data
– Profound transformations induced
Accelerators Deep Several
transformations distinct major
Inhibitors – What do they
change? axes of
transformation
15 16
-A-
Qualification of
Data qualification guidance
the Data
17 18
DR. Valery Michaux, Neoma Business School
3
Advanced strategic toolkit 04/10/2022
MSc Global Management
Which one ? Trends ?
Now
Now Inflection points ?
1 - Notion of trends
Weak signals ?
Green
19 20
Characteristics of trends Characteristics of trends
Long-term axis of Dramatic impacts on Long-term axis of Dramatic impacts on
transformations sectors/industries transformations sectors/industries
21 22
E-commerce in France
Trends characteristics
Trends : long & slow
Billions Euros
Trends : long Billon euros France
21 years
23 24
DR. Valery Michaux, Neoma Business School
4
Advanced strategic toolkit 04/10/2022
MSc Global Management
E-commerce in France ? Trends : long & slow
Disrupted but not stopped
COVID
Trends : long & slow
14 %
20 years
25 26 26
Characteristics of trends Characteristics of trends
Long-term axis of Long-term axis of Dramatic impacts on
transformations transformations sectors/industries
Slow
Robust
Landscape for the future
27 28
E-commerce in France ? Drive different changes throughout the
time
14 %
2000-2010 : E-commerce emergence
– Impacts
2010-2015 : multi-channel
– Impacts
2015 & + : omnichannel
20 years – Impacts
Over the last 20 years, has e-commerce had 2010-
2000-2010 2015
2015
the same impact?
29 30
DR. Valery Michaux, Neoma Business School
5
Advanced strategic toolkit 04/10/2022
MSc Global Management
Characteristics of trends Trends -> goal -> landmark for scenarios
14 %
Long-term axis of Dramatic impacts on Static
transformations sectors/industries
– Profound
– Transformative
– Evolutive/Not static
20 years
31 32
Impacts Transformative/evolutive
Trends
Trends -> Short term, medium term, High
long term impacts
Green Long term
Medium
Medium term
Short term
Time
33 34
Impacts Transformative/evolutive Impacts Transformative/evolutive
Trends Trends
High High
+++++
+++
Long term Long term
Medium Medium
+
Medium term Medium term
Short term Short term
Low
Time Time
35 36
DR. Valery Michaux, Neoma Business School
6
Advanced strategic toolkit 04/10/2022
MSc Global Management
Trends : long & slow
Helps to project into the future Characteristics of trends
14 %
Future
transformations
induced ? Long-term axis of Dramatic impacts on
transformations sectors/industries
Pace ?
Slow – Profound
Robust – Transformative
– Evolutive/Not static
– Future pace and impacts
37 38
Megatrends :
Types of trends structural forces
of change
Powerful forces of
social,
demographic,
Megatrends Industry trends environmental and
technological
changes that are
transforming the
world we live in
Trans-industry
39 40
Industrial/sectorial Trends : structural 2 - The notion of inflection point
forces of changes at the industry level -> current brutal changes
Slow long-term axis of transformations
Dramatic impacts on the sector/industry
Current
Brown
changes
– Signal that is
changing
currently ->
IMPACTS+
41 42
DR. Valery Michaux, Neoma Business School
7
Advanced strategic toolkit 04/10/2022
MSc Global Management
Impacts Impacts
Inflection points -> current brutal changes COVID
High High
Now
Now
Medium Medium
Inflexion point =
Signal of a brutal
acceleration
Inflexion point =
signal of an
emergent trend Time Time
43 44
Impacts
3 – The notion of Weak signals ->
not sure about the future development
High
and potential impacts
Now
Weak signal
– Early signs of currently
small changes ->
potentially IMPACTS+
Medium
Inflexion point = Orange
Signal of a brutal
slowdown
Time
45 46
Future impacts Future impacts
Mega & Industry
trends
Long term transformations
Inflection Weak signals
Early signal of changes
Points
Current Changes
More certain ? More uncertain ? More certain More uncertain
Uncertainty Uncertainty
47 48
DR. Valery Michaux, Neoma Business School
8
Advanced strategic toolkit 04/10/2022
MSc Global Management
What is currently changing ?
Future impacts Horizon scanning
Horizon scanning may explore
Trends
Emerging trends – novel and unexpected issues
– as well as persistent problems or trends
Accelerations Weak signals Horizon scanning is
Early signal of changes – the systematic examination
Slowdowns
– of potential threats, opportunities and likely future
developments
– including – but not restricted to – those that are
at the margins of current thinking
or that challenge past assumptions
More certain More uncertain
Uncertainty 49 50
-B-
Data collection
guidance Nature of the data
Which type of information?
Nature, Gradularity,…?
What type of analysis?
Where ?
51 52
Qualitative X Quantitative
Exploration
Future ? Past & Present
2 years in the past + today
Present Present
Past Future Past Future
53 54
DR. Valery Michaux, Neoma Business School
9
Advanced strategic toolkit 04/10/2022
MSc Global Management
Where can you find information about
industry dynamics?
Consulting firms websites
– Surveys and studies
Neoma Library
– Industry Profiles
Economic, business and financial press -> Europress and
Factiva
– Industry economic news and events
– Companies behaviors
Specialized journals and specialized websites
– Magazines
Organisation of the data
Congress
– Reports
collection
Expert interviews
– Internet - Youtube
55 56
4 or 5 angles of data collection -> 4 or 5 angles of data collection ->
each group member each member
2
1 - Overall industry changes identification and
impacts
2 - Consumer/customer evolution and megatrends
that can influence its behavior in the future Industry
3 – Technologies/new usages & innovations, start- transformations
ups, and new entrants
4 – Current strategic behavior of each industry
actors: focus on incumbent companies and new Overlap 4 5
leading entrants
5 – Identify Main change drivers (accelerators and
inhibitors) and understand the whole dynamics of
the industry
57 58
5 angles of data collection -> each
Group work Project manager
member
1 - Overall industry changes identification and
2
impacts
2 - Consumer/customer evolution and megatrends
that can influence its behavior in the future
Industry
transformations 3 – Technologies/new usages & innovations, start-
ups, and new entrants
4 5 4 – Current strategic behavior of each industry
actors: focus on incumbent companies and new
leading entrants
5 – Identify Main change drivers (accelerators and
inhibitors) and understand the whole dynamics of
59
the industry
59 60
DR. Valery Michaux, Neoma Business School
10
Advanced strategic toolkit 04/10/2022
MSc Global Management
1 - Overall industry description - Middle view
Objectives Automotive
industry
Understand the overall structure
– What is the value chain of the sector from the most upstream to
the most downstream?
– Big players : supply, manufacturing, distribution?
Understand the dynamics of the sector Wholesalers
Suppliers Suppliers Manufacturers Final consumer
– What are the transformations underway? Distributors
Wholesalers
Suppliers Suppliers Manufacturers Final consumer
Distributors
The most structuring phenomena ?
Industry/sector value Chain
61 62
The most structuring phenomena : EV
Systemic view : understand the dynamics of
Qualification today ? the sector/industry -> change drivers
Distinguish between
– Change drivers & change actors
– Profound transformations induced
Accelerators Deep
transformations
Inhibitors – What do they
change?
Qualification in 2010 ?
63 64
2020
European
policy :
Change driver
65 66
DR. Valery Michaux, Neoma Business School
11
Advanced strategic toolkit 04/10/2022
MSc Global Management
2022 Local big municipalities
London ahead
20 % plug-in Hybrids by 2035
35 % by 2026
68 % by 2030
Phase out
combustion-
GB – 2030 ! engine
vehicles
official
planning
2030
on average
Londres : 2025 -> Se sont positionnés sur
l’interdiction de l’hybride aussi
67 68
August 2021 – “Loi Climat et Resilience”
Systemic view : understand the dynamics of
2030 the sector/industry -> change drivers
Distinguish between
– Change drivers & change actors
– Profound transformations induced
Accelerators
40 towns
69 70
Systemic view : understand the dynamics of
the sector/industry -> change drivers The rise of
Hydrogen
Distinguish between
– Change drivers & change actors
– Profound transformations induced BFEV: Battery full
electric vehicle
HEV: hybrid electric
vehicle Qualification ?
Accelerators Deep
PHEV: plug-in hybrid
transformations electric vehicle
Inhibitors – What do they
change?
71 72
DR. Valery Michaux, Neoma Business School
12
Advanced strategic toolkit 04/10/2022
MSc Global Management
Synthetic fuels Qualification ? Upstream
Automotive view
industry
Wholesalers
Suppliers Suppliers Manufacturers Final consumer
Distributors
For fuel
engines that
continue to be
on roads
73 74
Wholesale
Upstream
view
Supplier Manufactur rs Final
Suppliers
s ers Distributor consumer
s
By the end of
Qualification ? the decade,
more than 30
Battery gigafactories
Drill down into
deeper analysis
75 Qualification today ? 76 76
Where is the expertise? -> alliances
Consequences ?
Qualification today ?
Drill down into
deeper analysis
77 77 78
DR. Valery Michaux, Neoma Business School
13
Advanced strategic toolkit 04/10/2022
MSc Global Management
Qualification in
2017 ?
Awarness -> Geopolitic dependency Environmental side
Lithium-Ion
2017 battery
Price of Lithium
• 6.000 dollars/tonne en 2015
• 25.000 dollars/tonnes en janvier
2018
Qualification in
2016-2017 ?
80 %
Geopolitical side
79 80
Qualification today ? Incumbent companies behaviors
Wholesale
Upstream
view
Supplier Manufactur rs Final
Suppliers
s ers Distributor consumer
s
Battery
Qualification ?
2020
81 82
Qualification ?
Emerging industries
Qualification ?
Emerging industries
83 84
DR. Valery Michaux, Neoma Business School
14
Advanced strategic toolkit 04/10/2022
MSc Global Management
Upstream
Supplier
s
Suppliers
Manufactur
ers
Wholesale
rs
Distributor
s
Final
consumer
view
Change drivers ?
Drill down into Anti-waste public policies
deeper analysis Customer sensibility
Battery Energy crisis
Diversification in
battery
Etc…
New avenues of
research
Battery recycling
Battery second Make sense of
used diversification
Rare metals war the information Suppliers Suppliers
Manufacturer
s
Wholesalers
Distributors
Final
consumer
Etc.
85 86
DELPHI
Downstream
Automotive view “The number of
physical retail
industry outlets as we know
them today will be
dramatically
reduced by 2025”
Wholesalers Final
Suppliers Suppliers Manufacturers
Distributors consumer
KPMG
2018
Qualification in 2018 ?
87 88
Choose, configure and
virtually test your future
car
The challenge that can
May 2021
represent CRM and data
Qualification ?
Why ? The dealership
role ?
« Agency model"
89 89 90
DR. Valery Michaux, Neoma Business School
15
Advanced strategic toolkit 04/10/2022
MSc Global Management
Insights 5 angles of data collection -> each
member
The industry value chain -> useful guide
What are all the transformations and changes
underway along the value-chain? 1 - Overall industry changes identification and
What are the impacts of these changes? impacts
Qualify the data 2 - Consumer/customer evolution and megatrends
– Megatrends and Industry trends -> long that can influence its behavior in the future
transformations that have already an impact -> 3 – Technologies/new usages & innovations, start-
strong impact on a medium term
ups, and new entrants
– Inflection point -> current changes -> May transform
into megatrends 4 – Current strategic behavior of each industry
– Weak signal -> little changes -> may have impacts actors: focus on incumbent companies and new
10 years leading entrants
– Change drivers -> transformations 5 – Identify Main change drivers (accelerators and
inhibitors) and understand the whole dynamics of
the industry
91 92
Large issues Understand the dynamics of the
sector/industry
Intentions to buy Beyond the trends, inflection points and weak
Sales signals
Consumption evolution
– Nature
Customer behaviours
– Changes
Accelerators Consumption
Etc. Inhibitors
93 94
Connected car Accelerators Consumption
Inhibitors
Accelerators Consumption
Inhibitors
Qualification ?
Data concerns
and security
concerns
95 Qualification ? Inhibitors 96
DR. Valery Michaux, Neoma Business School
16
Advanced strategic toolkit 04/10/2022
MSc Global Management
No pre-specified pick-up and drop-off locations
Accelerators Consumption
Inhibitors
Accelerators
Qualification ?
Consumption
Inhibitors
Change drivers
Activists
“anti-
Free-floating rental car
discourses”
Qualification : Inhibitors 97 98
Alternatives to the individual cars No pre-specified pick-up and drop-off locations
Qualification ? Qualification ?
Accelerators Consumption
Inhibitors
VTC or PHV
Free-floating rental car
Accelerators Consumption
Private Hire Inhibitors
Vehicles
Price increase
Shortage
VTC or PHV
Private Hire Vehicles Etc.
99 100
Qualification ? Insights ->
the customer view
Do not stay at the surface
– Understand the structural transformations
Adopt a broad societal and technological view
Qualify the data -> long term transformations,
current changes and early signals
When possible… distinguish the difference
between
– change drivers
– and their impacts
101 102
DR. Valery Michaux, Neoma Business School
17
Advanced strategic toolkit 04/10/2022
MSc Global Management
5 angles of data collection -> each
member
1 - Overall industry changes identification and
impacts Suppliers Suppliers Manufacturers
Wholesalers
Final consumer
Distributors
2 - Consumer/customer evolution and megatrends
that can influence its behavior in the future
3 – Technologies/new usages & innovations, start- Industry/sector value Chain
ups, and new entrants
4 – Current strategic behavior of each industry
actors: focus on incumbent companies and new
leading entrants
5 – Identify Main change drivers (accelerators and
inhibitors) and understand the whole dynamics of
the industry
103 104
2 aspects 2 aspects
Technologies, new Start-ups, and new Technologies, new Start-ups, and new
usages and entrants usages and entrants
innovations innovations
105 106
Technologies, new usages and
innovations Technological roadmap -> battery
List all the technologies/usages that are impacting
the sector today
– Speed of adoption? blocking and inertia factors that could
lock in the spread of these technologies/innovations ?
– Impacts?
What are the other innovation areas
– Product innovations – Digital innovations (services) -
Organizational innovation (Industry 4.0) - Business model
innovation
– Impacts?
Nature of the innovation? Incremental versus
radical innovation?
– In which part of the value chain?
Where ?
– Innovation and finance - Areas of investments ?
107 108
DR. Valery Michaux, Neoma Business School
18
Advanced strategic toolkit 04/10/2022
MSc Global Management
Qualification?
Michigan - Detroit
2022
Qualification?
109 109 110 110
Qualification?
Qualification?
Car Infotainment : new services
2021
-> What kinds ?
GAFAM
Alibaba
111 112
2020
Toward Qualification?
“augmented
vehicle” ->
Autopilot
Advanced
Qualification ?
driving
assistance
Parking
assistance
Voice
recognition
Heated seats
Extra cameras
Etc.
113 113 114
DR. Valery Michaux, Neoma Business School
19
Advanced strategic toolkit 04/10/2022
MSc Global Management
Insights
Behind the technologies
– New usages : what do they change for the
industry players and the customers ?
– What are the emerging business models?
– “Think transformations”
Different coopetition behaviors -> GAFAM
– Fierce competition
Qualification ?
– Cooperation
Juin 2019 – Differentiation
115 116
2 aspects
Technologies, new Start-ups, and new
usages and entrants
innovations
117 118
Changes in the Business Model
Battery : 30% Who ?
Engine :
to 40% of the
2000 pieces 37% of
value
the value
Collapse
of entry
barriers
119 120
DR. Valery Michaux, Neoma Business School
20
Advanced strategic toolkit 04/10/2022
MSc Global Management
China will
play an
important
role
New electric
automakers
emerging for
several
years
121 122
2020
100 000
electric
delivery vans
2021
2020
Ford and Amazon : biggest
investors
Achieve net-zero CO2 emissions by
2040
123 124
Las Vegas – 2020 Consumer Electronic
Show - The 2022 FISKER OCEAN EV France
(investment company + start-up)
Announced its IPO
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=m0JoWQ
SWdKM
125 126
DR. Valery Michaux, Neoma Business School
21
Advanced strategic toolkit 04/10/2022
MSc Global Management
Start-ups, and new entrants Insights
Barriers to entry
Rely on fact
Start-ups
– Look for some startups that are in nearby
– What is emerging?
ecosystems or in the area. Do not stay at the surface
– What could be their impact on the sector? – Drill down into deeper analysis
– In which part of the value chain?
Who are the new entrants?
– What novelties do they bring to the sector/industry?
– Be interested in new entrants in every part of the
value chain in the sector, including players from other
sectors who are about to enter or are entering certain
parts of the value chain.
127 128
5 angles of data collection -> each
member
1 - Overall industry changes identification and
impacts
2 - Consumer/customer evolution and megatrends
that can influence its behavior in the future
3 – Technologies/new usages & innovations, start-
ups, and new entrants
4 – Current strategic behavior of each industry
actors: focus on incumbent companies and new
leading entrants
5 – Identify Main change drivers (accelerators and
inhibitors) and understand the whole dynamics of
the industry
129 130
The importance of incumbent companies' Car operating system : dependency
behavior and leading new entrants in versus differentiation
exploring the sector/industry dynamic
Economic,
business and
financial press
Europress and
Factiva
131 132
DR. Valery Michaux, Neoma Business School
22
Advanced strategic toolkit 04/10/2022
MSc Global Management
Car operating system: 3 strategies Car operating system: 3 strategies
133 134
Car operating system: 3 strategies Insights
Rely on facts
– Who are the main players ?
Who is leading the changes? Who is
disrupted?
What exactly are the players doing? Deepen
their strategies to face the new challenges
– What are the current strategies of actors in order
to face new challenges (diversification in which
areas, alliance for what kind of purpose, mergers,
acquisitions, etc.?) Are these strategies
successful?
135 136
5 angles of data collection -> each Understand the dynamics of the
member sector/industry
The change
1 - Overall industry changes identification and drivers
– Accelerators
impacts – Inhibitors
2 - Consumer/customer evolution and The
megatrends that can influence its behavior in Understand the transformations
the future “change actors” – What do they
– Companies (new change?
3 – Technologies/new usages & innovations,
entrants, etc.)
start-ups, and new entrants
– State, Public
4 – Current strategic behavior of each industry authorities
actors: focus on incumbent companies and – Activists
new leading entrants – GAFAM
5 – Identify Main change drivers (accelerators and – Etc.
inhibitors) and understand the whole dynamics of
the industry 137 138
DR. Valery Michaux, Neoma Business School
23
Advanced strategic toolkit 04/10/2022
MSc Global Management
Understand the dynamics of the “Internal
combustion engine”
Electric Vehicle
engine made of
sector/industry (ICE) made of
The change
drivers
– Accelerators
– Inhibitors
The
Understand the transformations
“change actors” – What do they
– Companies (new change?
entrants, etc.)
– State, Public
authorities
– Activists
– GAFAM
– Etc.
139 140
Public policies
The addition of 4 problems
– Less maintenance -> loss of Accelerator
revenue
– Less production stages -> major
industrial transformations E.V. transformation + decline fossil fuel cars
– Loss of know how, value and
leadership
– New entrants surge Accelerator
Revenue loss and expensive industrial
transformations
Accelerator
Dramatic impacts
Search for new source of revenue
IMPACTS ++++
141 142
Insights
Understand the dynamics of the
sector/industry
Acceleration in
software Distinguish between
differentiation – Change drivers & change actors
– Profound transformations induced
Accelerators Deep
transformations
Inhibitors – What do they
change?
143 144
DR. Valery Michaux, Neoma Business School
24
Advanced strategic toolkit 04/10/2022
MSc Global Management
Insights
Do not stay at the surface
– Understand the structural underlying
transformations
What are the main change drivers for this -C-
industry?
– Technological changes, societal changes, etc.. Assignments
What are the change actors?
What are the main changes/transformations
in this industry?
145 146
Dates Course Work assignment
Individual work Phase 1 Between 5/6th Oct. ->
5/6th “horizon scanning” : scanning of the Traditional course 2rd/3th Nov.
October current industry dynamic data collection
Phase 1 Asynchronous Project manager 1
1 - Overall industry changes identification and 2rd/3th “horizon scanning” : scanning of the class Report 1
impacts November current industry dynamic
2 - Consumer/customer evolution and megatrends Individual work
8/10th Phase 2 – Distance Half traditional Project manager 2
that can influence its behavior in the future Choose
November “Futureone angle
exploration” (one angle
through per student)
course Report 2
3 – Technologies/new usages & innovations, start- assumptions about future potential Half group work
DATA COLLECTION -> Data identification
evolutions
ups, and new entrants th DATA QUALIFICATION
16/17 Phase 3 - Distance Half traditional Project manager 3
4 – Current strategic behavior of each industry
actors: focus on incumbent companies and new
November– Change driver versus
“Industry scenarios” : buildingtransformation
and course Report 3
scripting 3 industry scenarios Half group work
leading entrants – Trend versus inflection point (emergence and
23/24th Phase 4 - Distance Half traditional Project manager 4
5 – Identify Main change drivers (accelerators and November
acceleration/slow down) versus
“Company strategic reflexion” : course
weak signalReport 4
inhibitors) and understand the whole dynamics of Findstrategic
20 data clusters
options or structuring
in the 4 industry Half group workphenomena
the industry 7/8th ->propose
Phase 5 to the group Project manager 5
December Final report and presentation with Students’
advices to identify horizon scanning presentations
147 148
targets
Dates Course Work assignment
Phase 1 Between 5/6th Oct. ->
Each student -> his/her proposition
5/6th “horizon scanning” : scanning of the Traditional course 2rd/3th Nov.
October current industry dynamic data collection
20 “clusters” or Accelerators Transformations
Phase 1 Asynchronous Project manager 1
2rd/3th “horizon scanning” : scanning of the class Report 1 structuring Inhibitors
November current industry dynamic
phenomena
8/10th Phase 2 – Distance Half traditional Project manager 2 Accelerators Transformations
November “Future exploration” through course Report 2 Inhibitors
assumptions about future potential Half group work
evolutions
16/17th Phase 3 - Distance Half traditional Project manager 3 Changes drivers Accelerators Transformations
November “Industry scenarios” : building and course Report 3 & Inhibitors
scripting 3 industry scenarios Half group work transformations
23/24th
November
Phase 4 - Distance
“Company strategic reflexion” :
Half traditional
course
Project manager 4
Report 4
induced +
related actors Etc…
strategic options in the 4 industry Half group work
7/8th Phase 5 Project manager 5
December Final report and presentation with Students’
advices to identify horizon scanning presentations
149 150
targets
DR. Valery Michaux, Neoma Business School
25
Advanced strategic toolkit 04/10/2022
MSc Global Management
Accelerators Transformations Accelerators
Dates Course Work assignment Inhibitors Inhibitors
Transformations
Accelerators Transformations
Inhibitors
Phase 1 Between 5/6th Oct. -> Accelerators
Inhibitors
Transformations
5/6th “horizon scanning” : scanning of the Traditional course 2rd/3th Nov.
Accelerators Transformations
October current industry dynamic data collection Isolated data
Accelerators Transformations Inhibitors
Inhibitors
Phase 1 Asynchronous Project manager 1
Accelerators
2rd/3th “horizon scanning” : scanning of the class Report 1 Inhibitors
Transformations Accelerators Transformations
Inhibitors
November current industry dynamic
Isolated data Isolated data
Isolated data
8/10th Phase 2 – Distance Half traditional Project manager 2 Accelerators Transformations
Team work
Inhibitors
November “Future exploration” through course Report 2
assumptions about future potential Half group work Accelerators Transformations
evolutions A time to Accelerators Transformations Inhibitors
Project manager discuss Inhibitors
16/17th Phase 3 - Distance Half traditional Project manager 3 Accelerators Transformations Accelerators Transformations
Inhibitors Inhibitors
November “Industry scenarios” : building and course Report 3
scripting 3 industry scenarios Half group work Isolated data Isolated data
Accelerators Transformations
23/24th Phase 4 - Distance Half traditional Project manager 4 Inhibitors
Accelerators
November “Company strategic reflexion” : course Report 4 Transformations
Around 50-70 Inhibitors
strategic options in the 4 industry Half group work
clusters or Accelerators Transformations
7/8th Phase 5 Project manager 5
structuring Inhibitors Isolated data
December Final report and presentation with Students’ phenomena
advices to identify horizon scanning presentations
151 152
targets
Accelerators Transformations Accelerators
Dates Course Work assignment Inhibitors Inhibitors
Transformations
Accelerators Transformations
Inhibitors
Phase 1 Between 5/6th Oct. -> Accelerators
Inhibitors
Transformations
5/6th “horizon scanning” : scanning of the Traditional course 2rd/3th Nov.
Accelerators Transformations
October current industry dynamic data collection Isolated data
Accelerators Transformations Inhibitors
Inhibitors
Phase 1 Asynchronous Project manager 1
Accelerators
2rd/3th “horizon scanning” : scanning of the class Report 1 Inhibitors
Transformations Accelerators Transformations
Inhibitors
November current industry dynamic
Isolated data Isolated data
Isolated data
8/10th Phase 2 – Distance Half traditional Project manager 2 Accelerators Transformations
Team work
Inhibitors
November “Future exploration” through course Report 2
assumptions about future potential Half group work Accelerators Transformations
evolutions A time to Accelerators Transformations Inhibitors
Project manager discuss Inhibitors
16/17th Phase 3 - Distance Half traditional Project manager 3 Accelerators Transformations Accelerators Transformations
Inhibitors Inhibitors
November “Industry scenarios” : building and course Report 3
scripting 3 industry scenarios Half group work Isolated data Isolated data
Accelerators Transformations
23/24th Phase 4 - Distance Half traditional Project manager 4 Inhibitors
Accelerators
November “Company strategic reflexion” : course Report 4 Inhibitors
Transformations
strategic options in the 4 industry Half group work Grouping
Accelerators Transformations
7/8th Phase 5 Project manager 5 Inhibitors Isolated data
December Final report and presentation with Students’
advices to identify horizon scanning presentations
153 154
targets
Industry Horizon scanning
Avoid the
“PESTEL 5 or 6 main
syndrome” LONG TERM
axes of
transformation
Think transversal transformations > Each axe
DYNAMICS causes to effects relationships – 8/10 related structural
phenomena or clusters
– Changes drivers &
6 to 7 major transformations induced +
transformational related actors
axis
155 156
DR. Valery Michaux, Neoma Business School
26
Advanced strategic toolkit 04/10/2022
MSc Global Management
Industry Horizon scanning
6 long-term transformations
5 or 6 main Electric mobility and the progressive mix of
LONG TERM alternative fuels and powertrain technologies
axes of New digital services and features
New models of car consumption and business
transformation models (subscription)
Augmented car and functional transformation of
Independent enough vehicles
– Even if the change
drivers can be the same Tension between individual cars versus shared
– The nature of the collective urban mobility
transformations is Disintermediation and reintermediation within
distinct
– As less overlap as the automotive value chain (omnicanal)
possible in the
transformations
157 158
Tension between individual cars versus shared collective urban mobility
A tip…. 2
1
In order to verify -> industry transformation or
a change driver that may vary 3
“… More or less rapid…”
“… More or less important…” 5
6
4
8
159
9 160
Tension between individual cars versus shared collective urban mobility Digital services and features digital model
2
1
6
4 7
161
9162
DR. Valery Michaux, Neoma Business School
27
Advanced strategic toolkit 04/10/2022
MSc Global Management
Digital services and features digital model New models of car consumption and new business models (subscription)
163 164
First REPORT
PHASE 1 PHASE 2 PHASE 3 PHASE 4
Industry Industry future Industry Company
horizon exploration scenarios strategic
Scanning building reflection
(strategic options)
1
Conclusion
INDUSTRY COMPANY
165 166
Systemic thinking Systemic thinking Individual task -> until 2rd/3th November
Step 1 - Collect data Step 2 – Qualify data
Weak signals – early signals
Inflection points – current changes
Individual task -> until 2rd/3th November
Trends – long-lasting
Change drivers
Transformations
167 168
DR. Valery Michaux, Neoma Business School
28
Advanced strategic toolkit 04/10/2022
MSc Global Management
Industry Horizon scanning Industry Horizon scanning
Collective task -> 2d/3th November
Collective task -> 2d/3th November
Step 4 - Step 5 –
Change
drivers Grouping Naming +
can be
common
synthesis
Several
distinct major
axes of
transformation
169 170
Report 1
2rd November
PHASE 1
Industry Name of the project manager
horizon
Scanning Work of each member -> name
– Data collection and qualification
– Clusters/ structural phenomena
1
propositions
Collective work : 5-6 main axes
of transformation
– Name
– Synthesis -> quality
171
DR. Valery Michaux, Neoma Business School
29
You might also like
- Solution Manual For Financial Accounting 11th Edition Jerry J Weygandt Paul D Kimmel Donald e Kieso 2Document45 pagesSolution Manual For Financial Accounting 11th Edition Jerry J Weygandt Paul D Kimmel Donald e Kieso 2James Parker100% (40)
- MYH Case StudyDocument62 pagesMYH Case Studyassignmentlink75% (16)
- Retail Banking Transformation Story Post Liberalized IndiaDocument41 pagesRetail Banking Transformation Story Post Liberalized IndiaPallavi Pallu80% (5)
- Bantay KorapsyonDocument18 pagesBantay KorapsyonRheinhart PahilaNo ratings yet
- Corp Strategy SyllabusDocument2 pagesCorp Strategy SyllabusRandomNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 & 3: The Strategy Development Process & The External Environment AnalysisDocument70 pagesLecture 2 & 3: The Strategy Development Process & The External Environment AnalysisApostol Boujev100% (1)
- Post Covid Project Management: Today'S WebinarDocument24 pagesPost Covid Project Management: Today'S Webinarmerry andaniNo ratings yet
- Chap 006Document18 pagesChap 006Abhi KumarNo ratings yet
- Kemal - Industry 4.0 Pain PointsDocument27 pagesKemal - Industry 4.0 Pain PointsM Humaam AlNo ratings yet
- Robert S. Kaplan, David P. Norton - Balanced Scorecard Report - The Strategy Execution Source - Volume 11 Number 4 - Jul-Aug 2009Document16 pagesRobert S. Kaplan, David P. Norton - Balanced Scorecard Report - The Strategy Execution Source - Volume 11 Number 4 - Jul-Aug 2009Javier de ramonNo ratings yet
- Project Report On Business IntelligenceDocument64 pagesProject Report On Business IntelligenceeswarannihilNo ratings yet
- ITONICS Foresight and Strategy Capabilities PlaybookDocument31 pagesITONICS Foresight and Strategy Capabilities PlaybookSASI KUMAR SUNDARA RAJANNo ratings yet
- Les Facteurs Clés de Succés Des SturtupsDocument120 pagesLes Facteurs Clés de Succés Des SturtupsZakaria LABYADNo ratings yet
- Industry 4.oDocument20 pagesIndustry 4.oakshayNo ratings yet
- Business Innovation Unit: Osamu Fujikawa, Senior Vice PresidentDocument10 pagesBusiness Innovation Unit: Osamu Fujikawa, Senior Vice PresidentTanmoy IimcNo ratings yet
- Managing The Applications Portfolio: Strategic Information Systems Series ByapshemiDocument18 pagesManaging The Applications Portfolio: Strategic Information Systems Series ByapshemiRalph Wajah ZwenaNo ratings yet
- Understanding Business Architecture: V3.7 April 2016Document22 pagesUnderstanding Business Architecture: V3.7 April 2016thatsvikalp9328No ratings yet
- Topic 5 - Stategy Formulation - Business Strategy and Strategic Choice - UpdatedDocument50 pagesTopic 5 - Stategy Formulation - Business Strategy and Strategic Choice - UpdatedHồng PhúcNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To The Wallace Innovation NetworkDocument28 pagesAn Introduction To The Wallace Innovation NetworkjoseramonperezNo ratings yet
- Session 17 - Functional StrategyDocument26 pagesSession 17 - Functional StrategyANKIT AGARWALNo ratings yet
- Advanced Strategic Toolkit - IntroductionDocument7 pagesAdvanced Strategic Toolkit - IntroductionVishal ShivaNo ratings yet
- PMBOKDocument8 pagesPMBOKpratto.nicole96No ratings yet
- Technology Chapter 7Document29 pagesTechnology Chapter 7Uzma NaumanNo ratings yet
- Scenario Management-An Approach For Strategic Foresight: Alexander Fink and Oliver SchlakeDocument9 pagesScenario Management-An Approach For Strategic Foresight: Alexander Fink and Oliver SchlakeSteeltonNo ratings yet
- Innovation Space and Marketplace Report - 6.8.2017Document77 pagesInnovation Space and Marketplace Report - 6.8.2017Rubén Cruz100% (2)
- Business FundamentalsDocument72 pagesBusiness FundamentalsHoelboucNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Mgt657 Okt 2022 - Feb 2023Document4 pagesLesson Plan Mgt657 Okt 2022 - Feb 2023shan EzazNo ratings yet
- Plan Value PropositionDocument12 pagesPlan Value PropositioncreynamNo ratings yet
- University of Santo Tomas: Araneta Center, IncDocument90 pagesUniversity of Santo Tomas: Araneta Center, IncloombandNo ratings yet
- Scenario Impact Roadmapping: Edit This Sub-Headline by Clicking HereDocument15 pagesScenario Impact Roadmapping: Edit This Sub-Headline by Clicking HereSASI KUMAR SUNDARA RAJANNo ratings yet
- Strategic Managementfinal PDFDocument125 pagesStrategic Managementfinal PDFAgha AliNo ratings yet
- MPP Unit Guide - T1 2024Document6 pagesMPP Unit Guide - T1 202431221020295No ratings yet
- Prachi AgarwalDocument109 pagesPrachi AgarwalDeepak SinghalNo ratings yet
- EDoc SAF Guide Read OnlypdfDocument92 pagesEDoc SAF Guide Read OnlypdfRue J Nyangulu-MungofaNo ratings yet
- Rencana Strategi Bisnis Pelayanan Laundry Di Rs - Ibu SusyDocument39 pagesRencana Strategi Bisnis Pelayanan Laundry Di Rs - Ibu Susyrsud okutimurNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 RevisedDocument25 pagesUnit 1 RevisedPooja AngiraNo ratings yet
- TKC Think Tank SessionDocument27 pagesTKC Think Tank SessionKuldeep ΜauryaNo ratings yet
- 6-7 Strategic CoorporateDocument50 pages6-7 Strategic CoorporateMoh SabilNo ratings yet
- X03 (1) .StrategicManagement - Capstone.group6 v1Document36 pagesX03 (1) .StrategicManagement - Capstone.group6 v1namanh99No ratings yet
- Ap9 ACTIVITYDocument16 pagesAp9 ACTIVITYFerdinand NabloNo ratings yet
- Business Plan: Institute of Management Sciences University of Lucknow (New Campus) LucknowDocument52 pagesBusiness Plan: Institute of Management Sciences University of Lucknow (New Campus) Lucknowvishal kasaudhanNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Exam Answer (Structure - Model) 2Document8 pagesComprehensive Exam Answer (Structure - Model) 2nash kentNo ratings yet
- A Performance Measurement Systems Design Framework: R. Duarte, F. Deschamps, E. Pinheiro de LimaDocument6 pagesA Performance Measurement Systems Design Framework: R. Duarte, F. Deschamps, E. Pinheiro de Limaموليد خالمNo ratings yet
- IMUNISASIDocument18 pagesIMUNISASIPTM PKL CawangNo ratings yet
- Marketing and Sales Part 2 - Decker MoodleDocument178 pagesMarketing and Sales Part 2 - Decker Moodlegabi freitasNo ratings yet
- REPORT AND PRESENTATION ON INTERVENTION 21 April 2021Document37 pagesREPORT AND PRESENTATION ON INTERVENTION 21 April 2021abdullahsaleem91No ratings yet
- Business Plan StoreIT 120514Document37 pagesBusiness Plan StoreIT 120514Amanda Bonita PersaudNo ratings yet
- BSC Report 2010-Strategy ExecutionDocument6 pagesBSC Report 2010-Strategy ExecutionDavidNo ratings yet
- MEDICI Innovation Framewok For Financial InstitutionsDocument29 pagesMEDICI Innovation Framewok For Financial InstitutionsAkshay PrasathNo ratings yet
- Lumea PlantelorDocument15 pagesLumea PlantelorSmerea AndreeaNo ratings yet
- The New Influence PlaybookDocument32 pagesThe New Influence PlaybookThiago MotaNo ratings yet
- Materi Section 6 Marking Dangerous GoodsDocument19 pagesMateri Section 6 Marking Dangerous GoodsFebi Faza RumaisahNo ratings yet
- Fungi and PlantsDocument15 pagesFungi and PlantsAhmed RahimNo ratings yet
- Summative AssessmentDocument17 pagesSummative AssessmentElis NidalianaNo ratings yet
- Comparative Analysis of SMC With Other Stock Broking Firms: Summer Project Report OnDocument94 pagesComparative Analysis of SMC With Other Stock Broking Firms: Summer Project Report OnSaurav KumarNo ratings yet
- Business Plan: Uddipta SanyalDocument18 pagesBusiness Plan: Uddipta SanyalGAVIN LEWISNo ratings yet
- Manajemen Stratejik (Umar Said)Document70 pagesManajemen Stratejik (Umar Said)Donny Rahman KhalikNo ratings yet
- Beye+Business+Plan+V0 11Document58 pagesBeye+Business+Plan+V0 11Raymond SmithNo ratings yet
- Week 1 RMBDocument16 pagesWeek 1 RMBNabilNo ratings yet
- SAP WIKI Europe: Feasibility Study - Final DeliverableDocument174 pagesSAP WIKI Europe: Feasibility Study - Final DeliverableChristophe MarinoNo ratings yet
- 5-QEM-Six SigmaDocument9 pages5-QEM-Six Sigmabt20mec125No ratings yet
- Business Model and Profitability in the Banking Strategic Process: Focus on DigitalizationFrom EverandBusiness Model and Profitability in the Banking Strategic Process: Focus on DigitalizationNo ratings yet
- Dissertation Vishal ShivaDocument16 pagesDissertation Vishal ShivaVishal ShivaNo ratings yet
- FORM Details of The Missions Maj2022.3045272086Document3 pagesFORM Details of The Missions Maj2022.3045272086Vishal ShivaNo ratings yet
- Advanced Strategic Toolkit - IntroductionDocument7 pagesAdvanced Strategic Toolkit - IntroductionVishal ShivaNo ratings yet
- 2 STR Advanced Toolkit External Analysis 2022Document36 pages2 STR Advanced Toolkit External Analysis 2022Vishal ShivaNo ratings yet
- 1 STR Advanced Toolkit Introduction & Purpose 2022Document38 pages1 STR Advanced Toolkit Introduction & Purpose 2022Vishal ShivaNo ratings yet
- FTMBA Curriculum FlyerDocument3 pagesFTMBA Curriculum FlyerVăn ChươngNo ratings yet
- Tapping Into The Globally Competitive Indian Manufacturing OpportunityDocument58 pagesTapping Into The Globally Competitive Indian Manufacturing OpportunityVishalNo ratings yet
- Brochure RMSL INVERSIONES S.A.S.Document2 pagesBrochure RMSL INVERSIONES S.A.S.juanNo ratings yet
- Legal Notice To Isro BuilderDocument3 pagesLegal Notice To Isro BuilderSHIVENDRA YADAVNo ratings yet
- Influencer MarketingDocument54 pagesInfluencer Marketingtdkhoa92No ratings yet
- Mumbai Europe ImportersDocument120 pagesMumbai Europe ImportersFarookh BaigNo ratings yet
- Partnership Deed: H.No: #80 Annapuran Colony, Uppal MedchalDocument4 pagesPartnership Deed: H.No: #80 Annapuran Colony, Uppal MedchalHarish DevathotiNo ratings yet
- A Report On Organization StudyDocument63 pagesA Report On Organization StudyGowtham KSNo ratings yet
- Azure Sentinel Deployment and Migration ServicesDocument2 pagesAzure Sentinel Deployment and Migration ServicesGerman MarinoNo ratings yet
- Global Village-OBassignmentDocument10 pagesGlobal Village-OBassignmentMOJAHID HASAN Fall 19No ratings yet
- Robinhood Lawsuit SDNYDocument9 pagesRobinhood Lawsuit SDNYLaw&Crime100% (2)
- Method Statement 03g-Placing of CC BlockDocument5 pagesMethod Statement 03g-Placing of CC BlockAbdullah Al MarufNo ratings yet
- Screening Process - Digital Marketing - 9thapril2020Document4 pagesScreening Process - Digital Marketing - 9thapril2020SAURABH SINGHNo ratings yet
- Full Download Financial Statement Analysis 10th Edition Subramanyam Test BankDocument18 pagesFull Download Financial Statement Analysis 10th Edition Subramanyam Test Bankjulianwellsueiy100% (50)
- Materials Letters: Keisuke Azuma, Koichi Sakajiri, Hidetoshi Matsumoto, Sungmin Kang, Junji Watanabe, Masatoshi TokitaDocument3 pagesMaterials Letters: Keisuke Azuma, Koichi Sakajiri, Hidetoshi Matsumoto, Sungmin Kang, Junji Watanabe, Masatoshi TokitaBunga sekarNo ratings yet
- PSA 580 Focus NotesDocument1 pagePSA 580 Focus Noteskristel-marie-pitogo-4419No ratings yet
- Introduction To ICTDocument11 pagesIntroduction To ICTJohanita Juliana ManaluNo ratings yet
- Bank Reconciliation Statement (BRS)Document15 pagesBank Reconciliation Statement (BRS)TheerthuNo ratings yet
- Just ExampleDocument15 pagesJust ExampleIjlal Uddin KarimNo ratings yet
- Marchall Vs AntholzDocument2 pagesMarchall Vs AntholzArthur Kenneth lavapizNo ratings yet
- PBI-WI 005 Dimensional Control Procedure Rev.0Document5 pagesPBI-WI 005 Dimensional Control Procedure Rev.0Tadaya KasaharaNo ratings yet
- Simon-Kucher SPI LCE SC2 DraftDocument68 pagesSimon-Kucher SPI LCE SC2 DraftHugo CaviedesNo ratings yet
- TENSAE ASHEBIR Paper PDFDocument69 pagesTENSAE ASHEBIR Paper PDFanon_308300101No ratings yet
- Level III - Cadastral Surveying and Mapping ServiceDocument267 pagesLevel III - Cadastral Surveying and Mapping Servicekenna abdetenNo ratings yet
- Apple+Case+Study 1294 AkjeDocument3 pagesApple+Case+Study 1294 AkjeInstallment4u PakistanNo ratings yet
- QXC210407-L1048 Crusher XC-GD20HP (Columbia+Ever Edinson Monsalve Salcedo)Document4 pagesQXC210407-L1048 Crusher XC-GD20HP (Columbia+Ever Edinson Monsalve Salcedo)Ever Edinson Monsalve SalcedoNo ratings yet
- Honest Work A Business Ethics Reader 2Nd Edition Joanne B Ciulla Full ChapterDocument67 pagesHonest Work A Business Ethics Reader 2Nd Edition Joanne B Ciulla Full Chapterjon.giusti757100% (19)