Professional Documents
Culture Documents
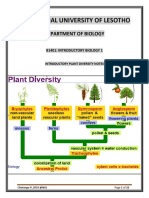
Flower Structure and Reproduction
Flower Structure and Reproduction
Uploaded by
Anand Philip PrasadCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Pollination: Flower To Fruit: Answer KeyDocument5 pagesPollination: Flower To Fruit: Answer KeyPDX Frost40% (5)
- SCIENCE-5-Q2-Module 4Document16 pagesSCIENCE-5-Q2-Module 4Mary Ann Gabion100% (11)
- Plant Breeding As A HobbyDocument20 pagesPlant Breeding As A HobbyJirobuchon100% (1)
- 2Q 2.6C Flower ComparisonDocument3 pages2Q 2.6C Flower ComparisonJenver MarananNo ratings yet
- Flower Structure and Reproduction Reading and QuestionsDocument5 pagesFlower Structure and Reproduction Reading and QuestionsbiffinNo ratings yet
- Flower Structure and ReproductionDocument6 pagesFlower Structure and ReproductionNiraj SethiNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in PlantsDocument8 pagesReproduction in Plantsdwi rahmaNo ratings yet
- Flower Structure and ReproductionDocument6 pagesFlower Structure and ReproductionajithNo ratings yet
- Plant Diversity Lecture 8-AngiospermsDocument22 pagesPlant Diversity Lecture 8-AngiospermsLebohang MakhanyaNo ratings yet
- Flowers and Fruits: An Edible Lab!: ObjectivesDocument7 pagesFlowers and Fruits: An Edible Lab!: ObjectivesMarcos AquinoNo ratings yet
- Flower: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDocument5 pagesFlower: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchAlmira ĆosićNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument16 pagesReproduction in Flowering PlantsShan PMCNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in PlantsDocument26 pagesReproduction in PlantsaddaestewartNo ratings yet
- Flower - EncartaDocument1 pageFlower - Encartaxxxbilly1986xxxNo ratings yet
- Biology Sem 3Document13 pagesBiology Sem 3yondaimeredzuan0% (1)
- Chapter 8Document10 pagesChapter 8Lebanan Aprille MarieNo ratings yet
- LESSON 3 Perpetuation of LifeDocument7 pagesLESSON 3 Perpetuation of LifebrionesmaryshantelNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Plant Science Flower and Inflorescence StructureDocument17 pagesIntroduction To Plant Science Flower and Inflorescence StructureAlan ReidNo ratings yet
- Sexual ReproductionDocument36 pagesSexual ReproductionMasrat AmirNo ratings yet
- Parts of A FlowerDocument3 pagesParts of A FlowerShubham SinghNo ratings yet
- Flower Anatomy 1Document36 pagesFlower Anatomy 1Iram Tahir100% (1)
- Struktur Anatomi Bunga: Kelompok ViiDocument13 pagesStruktur Anatomi Bunga: Kelompok ViiAssalamualaikumZheenNo ratings yet
- Inflorescence, Pollination and FertilizationDocument16 pagesInflorescence, Pollination and Fertilizationniswati zahroNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System in Plants SS2Document7 pagesReproductive System in Plants SS2Ezeh PrincessNo ratings yet
- Perpetuation of LifeDocument22 pagesPerpetuation of Lifemarizel salcedoNo ratings yet
- Flower - Definition, Parts, Anatomy, Types,& Facts - BritannicaDocument18 pagesFlower - Definition, Parts, Anatomy, Types,& Facts - Britannica4g9mz26r8rNo ratings yet
- Parts of A FlowerDocument10 pagesParts of A FlowerAnaly CNo ratings yet
- Pollination NotesDocument6 pagesPollination Notesketki kamatNo ratings yet
- Q2 - W5 Science 5Document48 pagesQ2 - W5 Science 5Mac RamNo ratings yet
- Sexual Rep RodDocument1 pageSexual Rep RodDimple JangirNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System of Flowering, Non-Flowering, and Spore-BearingDocument34 pagesReproductive System of Flowering, Non-Flowering, and Spore-BearingJulie BalogoNo ratings yet
- 03 Reproductive Morphology VegetalDocument25 pages03 Reproductive Morphology VegetalbordinessrineNo ratings yet
- Science 5Document37 pagesScience 5Mariel Anne AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Flowers and FruitsDocument52 pagesFlowers and FruitsKleng Delos Santos BernardoNo ratings yet
- 03 Reproduction in PlantsDocument39 pages03 Reproduction in PlantsseakaneoNo ratings yet
- Module 4 Sexual Reproduction in PlantsDocument6 pagesModule 4 Sexual Reproduction in PlantsRomarie GallanoNo ratings yet
- Plants and People: FlowersDocument28 pagesPlants and People: FlowersYuan ShengNo ratings yet
- Plants and People: FlowersDocument28 pagesPlants and People: FlowersSabrina Naila DastianaNo ratings yet
- Genetics of Development in Plants - NOTESDocument40 pagesGenetics of Development in Plants - NOTESSanthoshNo ratings yet
- Perpetuation OF LifeDocument9 pagesPerpetuation OF LifeEsther YesuNo ratings yet
- Parts of A Flower! Flower Dissection L. IntroductionDocument3 pagesParts of A Flower! Flower Dissection L. IntroductionDaryl Boldios LoterteNo ratings yet
- SS2 3rd Term BiologyDocument16 pagesSS2 3rd Term BiologyabursooterNo ratings yet
- Allaboutplants 151024155216 Lva1 App6891Document14 pagesAllaboutplants 151024155216 Lva1 App6891Nerea MongeNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document7 pagesPresentation 1rex lasurusNo ratings yet
- Flower Structure and FunctionDocument4 pagesFlower Structure and FunctionPrasannaKamathNo ratings yet
- Plant Parts - Flowers: PistilDocument8 pagesPlant Parts - Flowers: PistilDiana Marie MendozaNo ratings yet
- Flowering vs. Non-Flowering Plants : Knowing the Difference - Biology 3rd Grade | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandFlowering vs. Non-Flowering Plants : Knowing the Difference - Biology 3rd Grade | Children's Biology BooksNo ratings yet
- Tracheophyte NotesDocument11 pagesTracheophyte NotesTracy Lou FranciscoNo ratings yet
- (Flower Anatomy) : Kurdistan Regional Government-Iraq College of Education/shaqlawa Biology Department Second StageDocument12 pages(Flower Anatomy) : Kurdistan Regional Government-Iraq College of Education/shaqlawa Biology Department Second StageShalaw LatifNo ratings yet
- Flower GrowthDocument21 pagesFlower Growthtrue livingNo ratings yet
- FlowerDocument22 pagesFlowerGrety IancuNo ratings yet
- Flower - Definition, Parts, Anatomy, Types,& Facts - Britannica 2Document16 pagesFlower - Definition, Parts, Anatomy, Types,& Facts - Britannica 24g9mz26r8rNo ratings yet
- Flower: Blossom, Is The Reproductive Structure Found inDocument29 pagesFlower: Blossom, Is The Reproductive Structure Found inMaya AlessiaNo ratings yet
- Flower: Navigation Search Flower (Disambiguation) Floral (Disambiguation)Document18 pagesFlower: Navigation Search Flower (Disambiguation) Floral (Disambiguation)devakikris1985No ratings yet
- Spider Plant Reproduction-Neo and EmilyDocument9 pagesSpider Plant Reproduction-Neo and EmilyWorkout PrietoNo ratings yet
- 12.2. Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument6 pages12.2. Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsIsaac SiameNo ratings yet
- Flowering Plants: Life-Cycle of A Flowering PlantDocument5 pagesFlowering Plants: Life-Cycle of A Flowering Plantraunak sarafNo ratings yet
- Each Part of The Flower Has Its Own FunctionDocument6 pagesEach Part of The Flower Has Its Own FunctionhonfaNo ratings yet
- Quiver Trees, Phantom Orchids & Rock Splitters: The Remarkable Survival Strategies of PlantsFrom EverandQuiver Trees, Phantom Orchids & Rock Splitters: The Remarkable Survival Strategies of PlantsRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (2)
- Reproduction in PlantsDocument12 pagesReproduction in PlantsAnand Philip PrasadNo ratings yet
- Yr 9 Unit 1 - Health and IllnessDocument15 pagesYr 9 Unit 1 - Health and IllnessAnand Philip PrasadNo ratings yet
- Sates of MatterDocument4 pagesSates of MatterAnand Philip PrasadNo ratings yet
- Ac Bas Assessm MYP3Document6 pagesAc Bas Assessm MYP3Anand Philip PrasadNo ratings yet
- Chemistry The Study of MatterDocument25 pagesChemistry The Study of MatterAnand Philip PrasadNo ratings yet
- On Killing A TreeDocument6 pagesOn Killing A TreeMukesh sahaniNo ratings yet
- Rosentreter Field Oriented Keys To The Florida Lichens Dec 2015Document73 pagesRosentreter Field Oriented Keys To The Florida Lichens Dec 2015robertdcurrierNo ratings yet
- Decoding The Controversies Surrounding The Source Plant of Murva: A ReviewDocument5 pagesDecoding The Controversies Surrounding The Source Plant of Murva: A ReviewIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- IB Biology Plant ScienceDocument26 pagesIB Biology Plant Sciencealekzi67% (3)
- Addition and Subtraction Word ProblemsDocument4 pagesAddition and Subtraction Word ProblemskookyinNo ratings yet
- Types and Features of EndospermDocument3 pagesTypes and Features of EndospermJemson KhundongbamNo ratings yet
- Grade 6-Classifying LifeDocument49 pagesGrade 6-Classifying LifenamrataNo ratings yet
- Study of Phytochemical Composition On Kaempferia Parviflora Wall Ex BakerDocument9 pagesStudy of Phytochemical Composition On Kaempferia Parviflora Wall Ex BakerKumaresh PalNo ratings yet
- Tugas Portofolio Bahasa InggrisDocument5 pagesTugas Portofolio Bahasa InggrisFariz Ahmad YaniNo ratings yet
- 3 Aquatic PlantsDocument43 pages3 Aquatic PlantsMhyna klauNo ratings yet
- Sas Bahasa Inggris Kelas 2Document3 pagesSas Bahasa Inggris Kelas 2Yutaka putriNo ratings yet
- Economic Botany MCQDocument14 pagesEconomic Botany MCQMalaika Javed0% (2)
- Botany: U.G.C. Choice Based Credit System (CBCS) Annual Pattern UG Courses Model CurriculumDocument37 pagesBotany: U.G.C. Choice Based Credit System (CBCS) Annual Pattern UG Courses Model CurriculumRasel parvezNo ratings yet
- InvertDocument4 pagesInvertAditya AroraNo ratings yet
- 2019 P6 FSC Mendaki PSLE (Full)Document22 pages2019 P6 FSC Mendaki PSLE (Full)Aaron HeeNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 PDFDocument22 pagesUnit 7 PDFAdesh RaoNo ratings yet
- Gymnospermous Plants - GYMNOSPERMS: Kordaitorasty LyginodendrorastyDocument14 pagesGymnospermous Plants - GYMNOSPERMS: Kordaitorasty LyginodendrorastyIvana MajovskáNo ratings yet
- DarwishDocument3 pagesDarwishmusharratt44No ratings yet
- Note-Chapter 8 Plant TransportDocument4 pagesNote-Chapter 8 Plant Transportzhenrong zhaoNo ratings yet
- High Yield Test #10 (Level 1)Document22 pagesHigh Yield Test #10 (Level 1)DvishaNo ratings yet
- Look For Fibonacci Numbers in FruitsDocument3 pagesLook For Fibonacci Numbers in FruitsmelonygacerNo ratings yet
- Bio11th Ncert Solutions MergedDocument175 pagesBio11th Ncert Solutions MergedRameshwer KambleNo ratings yet
- Biology Diagram QuestionsDocument3 pagesBiology Diagram QuestionsNasla AbdulsalamNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Variasi SomaklonalDocument8 pagesJurnal Variasi SomaklonalN. Beauregard이진기No ratings yet
- Biology Worksheet X - Plants Anatomy and FunctionalityDocument5 pagesBiology Worksheet X - Plants Anatomy and FunctionalityEmily TsaiNo ratings yet
- Plants 11 03040Document25 pagesPlants 11 03040ZeNo ratings yet
- Juglans Regia (Akhrot) Extracts SupplierDocument2 pagesJuglans Regia (Akhrot) Extracts Supplierherbl3926No ratings yet
- But 1 PDFDocument45 pagesBut 1 PDFHunny SehrawatNo ratings yet
- L-2 Evaluation of Crude DrugsDocument6 pagesL-2 Evaluation of Crude DrugsteraboxofficalNo ratings yet
- Flora Patagonica - Correa, Maevia N. Cabrera, Angel L. - Taxon, #5 - 6, 21, Pages 705-706, 1972 Nov - International Association For Plant Taxonomy - 10.2307 - 1219190 - Anna's ADocument3 pagesFlora Patagonica - Correa, Maevia N. Cabrera, Angel L. - Taxon, #5 - 6, 21, Pages 705-706, 1972 Nov - International Association For Plant Taxonomy - 10.2307 - 1219190 - Anna's AVitro PlantNo ratings yet
Flower Structure and Reproduction
Flower Structure and Reproduction
Uploaded by
Anand Philip PrasadOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Flower Structure and Reproduction
Flower Structure and Reproduction
Uploaded by
Anand Philip PrasadCopyright:
Available Formats
Flower Structure and Reproduction
biologycorner.com /worksheets/f lower_coloring.html
Biologycorner.com
Name: ___________________________________
Flowers are the plant's reproductive structures. Angiosperms are types of plants that bear fruits and flowers. Flowers
are usually both male and female, and are brightly colored to attract insects to help them carry pollen used for
sexual reproduction. Not all flowers are colorful, though. These flowers usually use the wind for pollination.
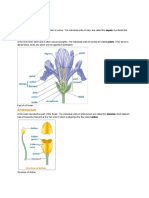
Part s of t he Flower
The receptacle is the part of the branch on which a flower forms. Color the receptacle (B) brown. Sepals are leaf like
structures that surround and protect the flower before it blooms. Color the sepals (C) green. Petals are the colorful
part of the flower that attracts insects and even other small animals, such as mice, birds, and bats. Color the petals
(D) a bright color of your choice. All flowering plants have flowers, but some are not brightly colored. The petals of
these flowers are reduced or absent and the plant relies on the wind or water for pollination.
The flower has both male and female reproductive parts. The female reproductive structures are called carpels. In
most flowers, the carpels are fused together to form a pistil. Color the pistil (P) pink. The pistil has three parts, which
can be seen, in the box labeled "pistil". The stigma at the top is often sticky and is where the pollen attaches. Color
the stigma (J) purple. The style is the long tube that attaches the stigma to the ovary. Sperm from the pollen will
travel down this tube to the ovules. The ovules, or eggs, are stored in the ovary until they are fertiliz ed. Plants can
only fertiliz e eggs of the same species. Special chemicals prevent sperm from fertiliz ing the eggs of flowers that are
not the same kind. Color the style (K) red, and the ovary (L) pink. Color the ovules (O) black.
The male reproductive structures are called the stamens. Color the stamens (H) blue. Each stamen consists of an
anther (A), which produces pollen, and a filament (F), which supports the anther. In the box labeled "stamen" color
the anther dark blue, and the filament light blue. Pollen produced by the anther is carried by insects or other animals
to the pistil of another flower where it may fertiliz e the eggs.
The other flowers in the picture follow the same plan, although they come in many different colors and styles. Color
each of the flowers according to the colors above (blue for stamen, pink for pistil, bright colors for the petals. etc.).
Note that in some of the flowers, not all the structures are visible.
Plant Reproduct ion
Sexual reproduction in plants occurs when the pollen from an anther is transferred to the stigma. Plants can fertiliz e
themselves: called self- fertiliz ation. Self- fertiliz ation occurs when the pollen from an anther fertiliz es the eggs on the
same flower. Cross- fertiliz ation occurs when the pollen is transferred to the stigma of an entirely different plant.
When the ovules are fertiliz ed, they will develop into seeds. The petals of the flower fall off leaving only the ovary
behind, which will develop into a fruit. There are many different kinds of fruits, including apples and oranges and
peaches. A fruit is any structure that encloses and protects a seed, so fruits are also "helicopters" and acorns, and
bean pods. When you eat a fruit, you are actually eating the ovary of the flower.
Quest ions
1. What is an angiosperm?
2. The flower attaches to what part of the plant?
3. Why are flowers brightly colored?
4. Name two mammals that might pollinate a plant.
5. If the petals of a flower are reduced or absent, how is the plant pollinated?
6. The female reproductive structures are called the:
7. Name the three parts of the pistil:
8. Where are the ovules stored?
9. Name the two parts of the stamen:
10. Describe sexual reproduction in plants.
11. The ovary develops into what structure?
12. Define fruit.
13. Some flowers are not brightly colored at all, but have a very pungent odor that smells like rotting meat. How do
you think these flowers are pollinated?
14. In many flowers, the pistils and stamens reach maturity at different times. Considering what you know about
pollination, why would this be an advantage to the plant?
You might also like
- Pollination: Flower To Fruit: Answer KeyDocument5 pagesPollination: Flower To Fruit: Answer KeyPDX Frost40% (5)
- SCIENCE-5-Q2-Module 4Document16 pagesSCIENCE-5-Q2-Module 4Mary Ann Gabion100% (11)
- Plant Breeding As A HobbyDocument20 pagesPlant Breeding As A HobbyJirobuchon100% (1)
- 2Q 2.6C Flower ComparisonDocument3 pages2Q 2.6C Flower ComparisonJenver MarananNo ratings yet
- Flower Structure and Reproduction Reading and QuestionsDocument5 pagesFlower Structure and Reproduction Reading and QuestionsbiffinNo ratings yet
- Flower Structure and ReproductionDocument6 pagesFlower Structure and ReproductionNiraj SethiNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in PlantsDocument8 pagesReproduction in Plantsdwi rahmaNo ratings yet
- Flower Structure and ReproductionDocument6 pagesFlower Structure and ReproductionajithNo ratings yet
- Plant Diversity Lecture 8-AngiospermsDocument22 pagesPlant Diversity Lecture 8-AngiospermsLebohang MakhanyaNo ratings yet
- Flowers and Fruits: An Edible Lab!: ObjectivesDocument7 pagesFlowers and Fruits: An Edible Lab!: ObjectivesMarcos AquinoNo ratings yet
- Flower: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDocument5 pagesFlower: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchAlmira ĆosićNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument16 pagesReproduction in Flowering PlantsShan PMCNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in PlantsDocument26 pagesReproduction in PlantsaddaestewartNo ratings yet
- Flower - EncartaDocument1 pageFlower - Encartaxxxbilly1986xxxNo ratings yet
- Biology Sem 3Document13 pagesBiology Sem 3yondaimeredzuan0% (1)
- Chapter 8Document10 pagesChapter 8Lebanan Aprille MarieNo ratings yet
- LESSON 3 Perpetuation of LifeDocument7 pagesLESSON 3 Perpetuation of LifebrionesmaryshantelNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Plant Science Flower and Inflorescence StructureDocument17 pagesIntroduction To Plant Science Flower and Inflorescence StructureAlan ReidNo ratings yet
- Sexual ReproductionDocument36 pagesSexual ReproductionMasrat AmirNo ratings yet
- Parts of A FlowerDocument3 pagesParts of A FlowerShubham SinghNo ratings yet
- Flower Anatomy 1Document36 pagesFlower Anatomy 1Iram Tahir100% (1)
- Struktur Anatomi Bunga: Kelompok ViiDocument13 pagesStruktur Anatomi Bunga: Kelompok ViiAssalamualaikumZheenNo ratings yet
- Inflorescence, Pollination and FertilizationDocument16 pagesInflorescence, Pollination and Fertilizationniswati zahroNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System in Plants SS2Document7 pagesReproductive System in Plants SS2Ezeh PrincessNo ratings yet
- Perpetuation of LifeDocument22 pagesPerpetuation of Lifemarizel salcedoNo ratings yet
- Flower - Definition, Parts, Anatomy, Types,& Facts - BritannicaDocument18 pagesFlower - Definition, Parts, Anatomy, Types,& Facts - Britannica4g9mz26r8rNo ratings yet
- Parts of A FlowerDocument10 pagesParts of A FlowerAnaly CNo ratings yet
- Pollination NotesDocument6 pagesPollination Notesketki kamatNo ratings yet
- Q2 - W5 Science 5Document48 pagesQ2 - W5 Science 5Mac RamNo ratings yet
- Sexual Rep RodDocument1 pageSexual Rep RodDimple JangirNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System of Flowering, Non-Flowering, and Spore-BearingDocument34 pagesReproductive System of Flowering, Non-Flowering, and Spore-BearingJulie BalogoNo ratings yet
- 03 Reproductive Morphology VegetalDocument25 pages03 Reproductive Morphology VegetalbordinessrineNo ratings yet
- Science 5Document37 pagesScience 5Mariel Anne AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Flowers and FruitsDocument52 pagesFlowers and FruitsKleng Delos Santos BernardoNo ratings yet
- 03 Reproduction in PlantsDocument39 pages03 Reproduction in PlantsseakaneoNo ratings yet
- Module 4 Sexual Reproduction in PlantsDocument6 pagesModule 4 Sexual Reproduction in PlantsRomarie GallanoNo ratings yet
- Plants and People: FlowersDocument28 pagesPlants and People: FlowersYuan ShengNo ratings yet
- Plants and People: FlowersDocument28 pagesPlants and People: FlowersSabrina Naila DastianaNo ratings yet
- Genetics of Development in Plants - NOTESDocument40 pagesGenetics of Development in Plants - NOTESSanthoshNo ratings yet
- Perpetuation OF LifeDocument9 pagesPerpetuation OF LifeEsther YesuNo ratings yet
- Parts of A Flower! Flower Dissection L. IntroductionDocument3 pagesParts of A Flower! Flower Dissection L. IntroductionDaryl Boldios LoterteNo ratings yet
- SS2 3rd Term BiologyDocument16 pagesSS2 3rd Term BiologyabursooterNo ratings yet
- Allaboutplants 151024155216 Lva1 App6891Document14 pagesAllaboutplants 151024155216 Lva1 App6891Nerea MongeNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document7 pagesPresentation 1rex lasurusNo ratings yet
- Flower Structure and FunctionDocument4 pagesFlower Structure and FunctionPrasannaKamathNo ratings yet
- Plant Parts - Flowers: PistilDocument8 pagesPlant Parts - Flowers: PistilDiana Marie MendozaNo ratings yet
- Flowering vs. Non-Flowering Plants : Knowing the Difference - Biology 3rd Grade | Children's Biology BooksFrom EverandFlowering vs. Non-Flowering Plants : Knowing the Difference - Biology 3rd Grade | Children's Biology BooksNo ratings yet
- Tracheophyte NotesDocument11 pagesTracheophyte NotesTracy Lou FranciscoNo ratings yet
- (Flower Anatomy) : Kurdistan Regional Government-Iraq College of Education/shaqlawa Biology Department Second StageDocument12 pages(Flower Anatomy) : Kurdistan Regional Government-Iraq College of Education/shaqlawa Biology Department Second StageShalaw LatifNo ratings yet
- Flower GrowthDocument21 pagesFlower Growthtrue livingNo ratings yet
- FlowerDocument22 pagesFlowerGrety IancuNo ratings yet
- Flower - Definition, Parts, Anatomy, Types,& Facts - Britannica 2Document16 pagesFlower - Definition, Parts, Anatomy, Types,& Facts - Britannica 24g9mz26r8rNo ratings yet
- Flower: Blossom, Is The Reproductive Structure Found inDocument29 pagesFlower: Blossom, Is The Reproductive Structure Found inMaya AlessiaNo ratings yet
- Flower: Navigation Search Flower (Disambiguation) Floral (Disambiguation)Document18 pagesFlower: Navigation Search Flower (Disambiguation) Floral (Disambiguation)devakikris1985No ratings yet
- Spider Plant Reproduction-Neo and EmilyDocument9 pagesSpider Plant Reproduction-Neo and EmilyWorkout PrietoNo ratings yet
- 12.2. Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsDocument6 pages12.2. Sexual Reproduction in Flowering PlantsIsaac SiameNo ratings yet
- Flowering Plants: Life-Cycle of A Flowering PlantDocument5 pagesFlowering Plants: Life-Cycle of A Flowering Plantraunak sarafNo ratings yet
- Each Part of The Flower Has Its Own FunctionDocument6 pagesEach Part of The Flower Has Its Own FunctionhonfaNo ratings yet
- Quiver Trees, Phantom Orchids & Rock Splitters: The Remarkable Survival Strategies of PlantsFrom EverandQuiver Trees, Phantom Orchids & Rock Splitters: The Remarkable Survival Strategies of PlantsRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (2)
- Reproduction in PlantsDocument12 pagesReproduction in PlantsAnand Philip PrasadNo ratings yet
- Yr 9 Unit 1 - Health and IllnessDocument15 pagesYr 9 Unit 1 - Health and IllnessAnand Philip PrasadNo ratings yet
- Sates of MatterDocument4 pagesSates of MatterAnand Philip PrasadNo ratings yet
- Ac Bas Assessm MYP3Document6 pagesAc Bas Assessm MYP3Anand Philip PrasadNo ratings yet
- Chemistry The Study of MatterDocument25 pagesChemistry The Study of MatterAnand Philip PrasadNo ratings yet
- On Killing A TreeDocument6 pagesOn Killing A TreeMukesh sahaniNo ratings yet
- Rosentreter Field Oriented Keys To The Florida Lichens Dec 2015Document73 pagesRosentreter Field Oriented Keys To The Florida Lichens Dec 2015robertdcurrierNo ratings yet
- Decoding The Controversies Surrounding The Source Plant of Murva: A ReviewDocument5 pagesDecoding The Controversies Surrounding The Source Plant of Murva: A ReviewIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- IB Biology Plant ScienceDocument26 pagesIB Biology Plant Sciencealekzi67% (3)
- Addition and Subtraction Word ProblemsDocument4 pagesAddition and Subtraction Word ProblemskookyinNo ratings yet
- Types and Features of EndospermDocument3 pagesTypes and Features of EndospermJemson KhundongbamNo ratings yet
- Grade 6-Classifying LifeDocument49 pagesGrade 6-Classifying LifenamrataNo ratings yet
- Study of Phytochemical Composition On Kaempferia Parviflora Wall Ex BakerDocument9 pagesStudy of Phytochemical Composition On Kaempferia Parviflora Wall Ex BakerKumaresh PalNo ratings yet
- Tugas Portofolio Bahasa InggrisDocument5 pagesTugas Portofolio Bahasa InggrisFariz Ahmad YaniNo ratings yet
- 3 Aquatic PlantsDocument43 pages3 Aquatic PlantsMhyna klauNo ratings yet
- Sas Bahasa Inggris Kelas 2Document3 pagesSas Bahasa Inggris Kelas 2Yutaka putriNo ratings yet
- Economic Botany MCQDocument14 pagesEconomic Botany MCQMalaika Javed0% (2)
- Botany: U.G.C. Choice Based Credit System (CBCS) Annual Pattern UG Courses Model CurriculumDocument37 pagesBotany: U.G.C. Choice Based Credit System (CBCS) Annual Pattern UG Courses Model CurriculumRasel parvezNo ratings yet
- InvertDocument4 pagesInvertAditya AroraNo ratings yet
- 2019 P6 FSC Mendaki PSLE (Full)Document22 pages2019 P6 FSC Mendaki PSLE (Full)Aaron HeeNo ratings yet
- Unit 7 PDFDocument22 pagesUnit 7 PDFAdesh RaoNo ratings yet
- Gymnospermous Plants - GYMNOSPERMS: Kordaitorasty LyginodendrorastyDocument14 pagesGymnospermous Plants - GYMNOSPERMS: Kordaitorasty LyginodendrorastyIvana MajovskáNo ratings yet
- DarwishDocument3 pagesDarwishmusharratt44No ratings yet
- Note-Chapter 8 Plant TransportDocument4 pagesNote-Chapter 8 Plant Transportzhenrong zhaoNo ratings yet
- High Yield Test #10 (Level 1)Document22 pagesHigh Yield Test #10 (Level 1)DvishaNo ratings yet
- Look For Fibonacci Numbers in FruitsDocument3 pagesLook For Fibonacci Numbers in FruitsmelonygacerNo ratings yet
- Bio11th Ncert Solutions MergedDocument175 pagesBio11th Ncert Solutions MergedRameshwer KambleNo ratings yet
- Biology Diagram QuestionsDocument3 pagesBiology Diagram QuestionsNasla AbdulsalamNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Variasi SomaklonalDocument8 pagesJurnal Variasi SomaklonalN. Beauregard이진기No ratings yet
- Biology Worksheet X - Plants Anatomy and FunctionalityDocument5 pagesBiology Worksheet X - Plants Anatomy and FunctionalityEmily TsaiNo ratings yet
- Plants 11 03040Document25 pagesPlants 11 03040ZeNo ratings yet
- Juglans Regia (Akhrot) Extracts SupplierDocument2 pagesJuglans Regia (Akhrot) Extracts Supplierherbl3926No ratings yet
- But 1 PDFDocument45 pagesBut 1 PDFHunny SehrawatNo ratings yet
- L-2 Evaluation of Crude DrugsDocument6 pagesL-2 Evaluation of Crude DrugsteraboxofficalNo ratings yet
- Flora Patagonica - Correa, Maevia N. Cabrera, Angel L. - Taxon, #5 - 6, 21, Pages 705-706, 1972 Nov - International Association For Plant Taxonomy - 10.2307 - 1219190 - Anna's ADocument3 pagesFlora Patagonica - Correa, Maevia N. Cabrera, Angel L. - Taxon, #5 - 6, 21, Pages 705-706, 1972 Nov - International Association For Plant Taxonomy - 10.2307 - 1219190 - Anna's AVitro PlantNo ratings yet