Professional Documents
Culture Documents
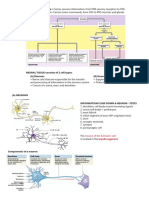
Neuroglial or Glial Cells
Neuroglial or Glial Cells
Uploaded by
Oddysa Estorque100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
27 views2 pagesThis document discusses the different types of neuroglial or glial cells in the central and peripheral nervous systems. It describes the functions of ependymal cells, astrocytes, microglia, oligodendrocytes, satellite cells, Schwann cells, and their roles in forming myelin sheaths, insulating neurons, clearing cellular debris, and supporting nerve fibers. The central topics covered are the four main divisions of the central nervous system, the roles of astrocytes and microglia in the brain, and the functions of satellite cells and Schwann cells in the peripheral nervous system.
Original Description:
Original Title
NEUROGLIAL OR GLIAL CELLS
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses the different types of neuroglial or glial cells in the central and peripheral nervous systems. It describes the functions of ependymal cells, astrocytes, microglia, oligodendrocytes, satellite cells, Schwann cells, and their roles in forming myelin sheaths, insulating neurons, clearing cellular debris, and supporting nerve fibers. The central topics covered are the four main divisions of the central nervous system, the roles of astrocytes and microglia in the brain, and the functions of satellite cells and Schwann cells in the peripheral nervous system.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
100%(1)100% found this document useful (1 vote)
27 views2 pagesNeuroglial or Glial Cells
Neuroglial or Glial Cells
Uploaded by
Oddysa EstorqueThis document discusses the different types of neuroglial or glial cells in the central and peripheral nervous systems. It describes the functions of ependymal cells, astrocytes, microglia, oligodendrocytes, satellite cells, Schwann cells, and their roles in forming myelin sheaths, insulating neurons, clearing cellular debris, and supporting nerve fibers. The central topics covered are the four main divisions of the central nervous system, the roles of astrocytes and microglia in the brain, and the functions of satellite cells and Schwann cells in the peripheral nervous system.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
NEUROGLIAL OR GLIAL CELLS.
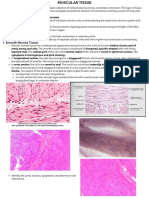
FUNCTION OF ASTROCYTES
A. Central nervous system
a. Ependymal cells – forms in epithelial lining
of ventricles (cavities) in the brain and cental
canal of the spinal chord
-Give rise to the epithelial laye surrounds the
choroid plexus, a network of blood vessels
located in the walls of lateral ventricles (the two
largest ventricles, which occur as a pair in the
cerebral hemispheres).
Choroid Plexus – forms the cerebrospinal fluid
or the CSF.
4 Division – Cerebrum, Cerebellum,
Diencephalon, Brain stem. C. Microglia/Microcytes-are smallest of all
neuroglial
B. Astrocytes / Astroglia – Star shaped found
in nervous system in both intervertebrates and -Their nuclei are oval shaped and projecting out
vertebrates from their cell bodies are slender elongated
processes that enable the cells to move via
-subdivide into two fibrous and protoplasmic
chemotaxis (movement along a chemical
Fibrous astrocytes – Prevalent in myelinated gradient)
nerve fibers in the white matter of the CNS.
-Know as mediate Immune responses in the
-The organelles are seen in neurons also seen CNS by acting as macrophages, clearing cellular
in astrocytes, but they appear to be much debris and dead neurons from nervous tissue
sparser. through the process of phagocytosis (cell eating
-Characterized by the presence of numerous
fibrils in their cytoplasm.
D. Oligodendrocytes/Oligodendoglis (Cells
-Main process exit the cell in radial direction with a few branches)
(hence the name astocyte, meaning ‘star
-Main function are provide support and
shaped cell’), forming expansions and end feet
insulation to axons in the CNS.
at the surface of vascular capillaries.
-Schwann cells in PNS.
Protoplasmic astrocytes – cells occur in gray
matter of CNS. -Create the myelin sheath, which in 80% lipid
and 20% protein.
-Fewer fibril within their cytoplasm, and
cytoplasmic organelles are sparse, that the PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM
soma or the body are shaped by surrounding
neurons and fibers A. SATELLITE CELLS OR MYOSATELLITE
CELLS -small flattened cells found in ganglia of
-Process are making contact with capillaries PNS
Ganglion – collection of cell bodies
-Dorsal root of ganglia located on either side os
spinal cord contain the most prominent satellite
cells.
-It also knows as muscle stem cells, are small
multipotent cells with verry little cytoplasm found
in mature muscle
-The oldest known adult stem cells niche, are
involved in the normal growth of muscle, as well
as regeneration following injury disease.
SCHWANN CELLS/ NEURILEMMA CELLS –
In PNS that produce myelin sheath around
neuronal axons.
-The most important supporting cells found in
PNS which insulate nerve fibers
-Equivalent to a type of oligodendrocytes CNS
-The most important fuction is myelinated the
axons of PNS.
MYELIN- a fatty layer that insulates the axons,
helps to increase the saltatory conduction of the
neuron.
MYELINATING SCHWANN CELLS WRAP
AROUND A SINGLE AXON.
AN OVERVIEW OF THE HUMAN BODY
You might also like
- BLUM, Charles L. Chiropractic Manipulative Reflex Technique (CMRT) - Sacro Occipital TechniqueDocument3 pagesBLUM, Charles L. Chiropractic Manipulative Reflex Technique (CMRT) - Sacro Occipital TechniqueJOSÉ MARIA SÁ FREIRE JRNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis Disturbed Sleep PatternDocument8 pagesNursing Diagnosis Disturbed Sleep Patternmaimai324263100% (2)
- General Histology: Hawler Medical University College of Medicine Department: Anatomy & HistologyDocument29 pagesGeneral Histology: Hawler Medical University College of Medicine Department: Anatomy & HistologyAnonymous gh5UWZJSNo ratings yet
- NeurogliaDocument2 pagesNeurogliaAzia TwylaNo ratings yet
- Nervous System HistologyDocument4 pagesNervous System HistologyShelly Stephanie Bintoro100% (1)
- Physiology U-3 Excitable Nervous TissueDocument122 pagesPhysiology U-3 Excitable Nervous Tissuesinte beyuNo ratings yet
- Macroglia+Neuron ASG 16-01-2023 PDFDocument9 pagesMacroglia+Neuron ASG 16-01-2023 PDFRajat AgrawalNo ratings yet
- 24. Histology of nervous systemDocument100 pages24. Histology of nervous systemAldood Al NatarNo ratings yet
- CNS Histology 1Document60 pagesCNS Histology 1naderipourkianaNo ratings yet
- Wk6 Nervous SystemDocument4 pagesWk6 Nervous SystemLindenScholesNo ratings yet
- 1 Cns HistoDocument54 pages1 Cns HistoNaveed AkhterNo ratings yet
- Nervous TissueDocument9 pagesNervous TissueAlexNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Nervous TissueDocument54 pagesAnatomy of Nervous TissueNand PrakashNo ratings yet
- Nervous Tissue PDFDocument4 pagesNervous Tissue PDFFadhil Hussam AhmedNo ratings yet
- NERVOUS TISSUE HandoutDocument6 pagesNERVOUS TISSUE HandoutAkemi100% (1)
- BioPsychology Chapter 34Document10 pagesBioPsychology Chapter 34Johnreih BanggaNo ratings yet
- Nervous TissueDocument14 pagesNervous Tissueyigermalamanuel32No ratings yet
- K1-Nerve Tissue & Nervous System (Histologi)Document40 pagesK1-Nerve Tissue & Nervous System (Histologi)Perisha Veera100% (1)
- Nerve TissueDocument5 pagesNerve TissueSuccessfactors TrainerNo ratings yet
- NEUROANATOMY IntroductionDocument10 pagesNEUROANATOMY IntroductionIshant SinghNo ratings yet
- Sem 1 - 机能解剖学 (Chapter 2 - Histology of nervous tissue) 笔记Document6 pagesSem 1 - 机能解剖学 (Chapter 2 - Histology of nervous tissue) 笔记Cah YeeNo ratings yet
- Nervous Tissue Cells::: Neurons NeurogliaDocument7 pagesNervous Tissue Cells::: Neurons NeurogliaSonakshi KumarNo ratings yet
- 3 NeurophysiologyDocument35 pages3 NeurophysiologyZerefuNo ratings yet
- Neuroanatomy: NeurogliaDocument4 pagesNeuroanatomy: Neurogliasamiran dekaNo ratings yet
- Histology of Nervous TissueDocument35 pagesHistology of Nervous TissueGlenn Rey D. AninoNo ratings yet
- Ns1 Assignment 1 Neuroembryology and NeurohistologyDocument4 pagesNs1 Assignment 1 Neuroembryology and NeurohistologyMark AbrazaldoNo ratings yet
- Genetics Lab Dent 1Document6 pagesGenetics Lab Dent 1FRANCHEZKA ANGELICA TANIEGRANo ratings yet
- Nervous Tissue 'Document9 pagesNervous Tissue 'ahmedelkaranshawy123456789No ratings yet
- Histology Nervous TissueDocument27 pagesHistology Nervous Tissueaimi BatrisyiaNo ratings yet
- HistologyDocument28 pagesHistologyzoomies homiesNo ratings yet
- Table of Content: Seria L No Page NoDocument48 pagesTable of Content: Seria L No Page NoHadia NoorNo ratings yet
- Nervous Tissue 4th Year 2020-2021 DR Mona1Document40 pagesNervous Tissue 4th Year 2020-2021 DR Mona1Atheer AltowairqiNo ratings yet
- Assignment 5: Nervous Tissue: Neural PlateDocument7 pagesAssignment 5: Nervous Tissue: Neural PlateGauri SulekhaNo ratings yet
- Astrocyte: Structure & FunctionDocument7 pagesAstrocyte: Structure & Functionمحمود الموسويNo ratings yet
- N 4Document85 pagesN 4Riya ThakkarNo ratings yet
- Nerve-Part 1Document30 pagesNerve-Part 1GiftNo ratings yet
- 1 Nervous System OutlinesDocument45 pages1 Nervous System OutlinesTestingAccNo ratings yet
- Neuron Structural UnitDocument113 pagesNeuron Structural Unitathena villaNo ratings yet
- Nervous System: Alianza Paras Casue Darjani Fojas Tan Zebaradami MassoudiDocument76 pagesNervous System: Alianza Paras Casue Darjani Fojas Tan Zebaradami MassoudiLionell CastilloNo ratings yet
- Histology of Nervous Tissue 2010Document39 pagesHistology of Nervous Tissue 2010Ramesh KumarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document18 pagesLecture 2Laveeza KhurramNo ratings yet
- Histology of The CNSDocument7 pagesHistology of The CNStiiandiNo ratings yet
- Cranial Nerves Carry Impulses To and From The: The Central Nervous SystemDocument3 pagesCranial Nerves Carry Impulses To and From The: The Central Nervous SystemLuiciaNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument6 pagesNervous SystemJessica Febrina WuisanNo ratings yet
- Textbook NotesDocument2 pagesTextbook NotesRobiaNo ratings yet
- Nervous Tissue System-92618Document151 pagesNervous Tissue System-92618gokulkrishnayadhavNo ratings yet
- Nervous Tissue: Nervous System Neuron - The Only Cell Type Capable of Generating and PropagatingDocument5 pagesNervous Tissue: Nervous System Neuron - The Only Cell Type Capable of Generating and PropagatingAlyssa AlferezNo ratings yet
- NervusDocument8 pagesNervusAndika Anjani AgustinNo ratings yet
- Neurophysiology August 16 2022 Cns....Document406 pagesNeurophysiology August 16 2022 Cns....stephenotibu03No ratings yet
- Neural Conduction and Synaptic TransmissionDocument23 pagesNeural Conduction and Synaptic TransmissionElysa Sasi EsquivelNo ratings yet
- Neuroglia: Presentation By: Joe Wang and Shelly XuDocument10 pagesNeuroglia: Presentation By: Joe Wang and Shelly XuJose AlonsoNo ratings yet
- LO 1 (Week 2) Cell Structure and Organisation (Cheng)Document4 pagesLO 1 (Week 2) Cell Structure and Organisation (Cheng)nit33vNo ratings yet
- 04 Nervous TissueDocument7 pages04 Nervous Tissuemd faiyazNo ratings yet
- 12 HisDocument83 pages12 HisRIMI SALOUMNo ratings yet
- Table of Content: Serial No Page NoDocument33 pagesTable of Content: Serial No Page NoSID RAJPOOTNo ratings yet
- NERVE SsDocument59 pagesNERVE SsNovianaHartikasariNo ratings yet
- Nerve & MuscleDocument82 pagesNerve & MusclebookaccountNo ratings yet
- Itzar - Neurohistology PDFDocument186 pagesItzar - Neurohistology PDFahmad aqilNo ratings yet
- Nervous Tissue 1Document30 pagesNervous Tissue 1OtencianoNo ratings yet
- The Basics of Cell Life with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceFrom EverandThe Basics of Cell Life with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceNo ratings yet
- Chad Kessler MD FACEP FAAEM-Alterations of Consciousness in The Emergency Department, An Issue of Emergency Medicine Clinics (The Clinics - Internal Medicine) - Saunders (2010) PDFDocument273 pagesChad Kessler MD FACEP FAAEM-Alterations of Consciousness in The Emergency Department, An Issue of Emergency Medicine Clinics (The Clinics - Internal Medicine) - Saunders (2010) PDFSaifullah RachmanNo ratings yet
- Language Disorders - 5Document27 pagesLanguage Disorders - 5Marta Sampedro GonzalezNo ratings yet
- A Case Study of Multiple Sclerosis (MS)Document31 pagesA Case Study of Multiple Sclerosis (MS)william2young-136543No ratings yet
- Screen For Child Anxiety Related Disorders (SCARED) Youth VersionDocument4 pagesScreen For Child Anxiety Related Disorders (SCARED) Youth VersionHambrich BogdanNo ratings yet
- The Alarming Effects of Microwave Apparatus On Food and HumansDocument3 pagesThe Alarming Effects of Microwave Apparatus On Food and HumansMori EntesNo ratings yet
- Film Lorenzos OilDocument4 pagesFilm Lorenzos OilGina ValverdeNo ratings yet
- My Courses: Home Baed-Pdev2111-2012S Week 7: The Powers of The Mind Performancetask2Document4 pagesMy Courses: Home Baed-Pdev2111-2012S Week 7: The Powers of The Mind Performancetask2Daniel John D. Velasco67% (3)
- Toward A Research Practice Frederick Kie PDFDocument31 pagesToward A Research Practice Frederick Kie PDFLeOn Wzz 众No ratings yet
- Long-Acting Injectable Antipsychotics Shall The Last Be First 2014Document3 pagesLong-Acting Injectable Antipsychotics Shall The Last Be First 2014Fan TomasNo ratings yet
- Understanding Disabilities: Sensory Processing Disorder: Introduction & DefinitionDocument4 pagesUnderstanding Disabilities: Sensory Processing Disorder: Introduction & DefinitionSueNo ratings yet
- HeadacheDocument12 pagesHeadacheNaseeb UllahNo ratings yet
- Ischemic StrokeDocument7 pagesIschemic StrokeAlly Juaneza100% (1)
- Sensory Diet: SampleDocument14 pagesSensory Diet: SampleAyra MagpiliNo ratings yet
- Sensation and Perception HandoutsDocument3 pagesSensation and Perception HandoutsMariaMirandaJrNo ratings yet
- K 1 2 Formatio Reticularis & Sistem LimbikDocument39 pagesK 1 2 Formatio Reticularis & Sistem LimbikfelixNo ratings yet
- Per Dev Lesson For 1 WeekDocument2 pagesPer Dev Lesson For 1 WeekEjay Balils IINo ratings yet
- 39-Article Text-131-1-10-20191111Document9 pages39-Article Text-131-1-10-20191111berlian gurningNo ratings yet
- Humor, Laughter, and Those Aha MomentsDocument8 pagesHumor, Laughter, and Those Aha MomentsInês SousaNo ratings yet
- Biological Basis of BehaviorDocument8 pagesBiological Basis of BehaviorLaine DerainNo ratings yet
- Coordination Igcse BiologyDocument108 pagesCoordination Igcse BiologyEllie HousenNo ratings yet
- Neurociencia AdiccionesDocument18 pagesNeurociencia AdiccionesAlejandro GuevaraNo ratings yet
- MIT 2012 - Rest Is Not Idleness Implications of The Brain S Default Mode For Human Development and EducationDocument13 pagesMIT 2012 - Rest Is Not Idleness Implications of The Brain S Default Mode For Human Development and EducationJoão Felipe DavidNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For The World of Psychology Eighth Canadian EditionDocument24 pagesTest Bank For The World of Psychology Eighth Canadian EditionSheilaClarktofa100% (44)
- LAWCN v6Document26 pagesLAWCN v6J Andrés SalasNo ratings yet
- Psychiatric InterviewDocument4 pagesPsychiatric Interviewmarina_shawky100% (1)
- Sensory ExamDocument24 pagesSensory Examsarguss14100% (2)
- Intracerebral HemorrhageDocument12 pagesIntracerebral HemorrhagevizzieNo ratings yet
- Psychoneuroimmunology: From Philosophy, Intuition, and Folklore To A Recognized ScienceDocument6 pagesPsychoneuroimmunology: From Philosophy, Intuition, and Folklore To A Recognized ScienceMita MiftaNo ratings yet