Professional Documents
Culture Documents
F2F Lesson Plan Format 2022 September 5-9, 2022 ELS, ITHP
F2F Lesson Plan Format 2022 September 5-9, 2022 ELS, ITHP
Uploaded by
Cherry Marie Oyo-aOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
F2F Lesson Plan Format 2022 September 5-9, 2022 ELS, ITHP
F2F Lesson Plan Format 2022 September 5-9, 2022 ELS, ITHP
Uploaded by
Cherry Marie Oyo-aCopyright:
Available Formats
Republic of the Philippines
Department of Education
REGION VIII
Schools Division of Calbayog City
SAN POLICARPO NATIONAL HIGH SCHOOL
Calbayog City
LESSON PLAN IN
PROGRESSIVE EXPANSION OF LIMITED FACE TO FACE CLASSES
School: San Policarpo NHS Grade Level: Grade 11 LP on Modular
GRADE
EARTH AND LIFE SCIENCE Instruction Using
12 Teacher: CHERRY MARIE OYO-A MONTES Learning Area: 1:00-2:00, 2:00-3:00, 4:00-5:00 Learning Activity
LESSON Face to Face
Sheets + Video
PLAN Teaching Date: September 5-9, 2022 Quarter: 1st QUARTER Lesson
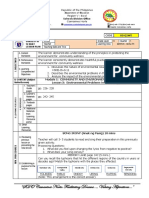
I.OBJECTIVES At the end of the lesson, the learners will be able to
1. Demonstrate understanding about physical and chemical
properties of minerals
2. Identify some common rock-forming minerals
3. Classify minerals based on chemical affinity
Learning Identify common rock-formation minerals using their physical and
Competencies/Objectives chemical properties. (S11/12ES-Ia-9)
II.CONTENT IDENTIFYING ROCK FORMING MINERALS USING THEIR
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
A. References
1.Teacher’s Guide pages TG in Earth and Life Science TG in Earth and Life Science
pages 46-55 pages 46-55
2.Learners’s Materials pages Quarter 1, Week 1 Quarter 1, Week 1
Handouts and Worksheets Handouts and Worksheets
B. Other Learning Resource
IV.PROCEDURES Sep 5, 2022 Sep 6, 2022 Sep 7, 2022 Sep 8, 2022 Sep 9, 2022
Preparatory Activity SICK LEAVE WITH FORM 6 Interfaith Prayer Interfaith Prayer
Checking of Attendance Checking of Attendance
Reminder of IATF Protocol Reminder of IATF Protocol
A. Reviewing previous lesson Enumerate the five important properties Review the concepts
or presenting new lesson which define a mineral. discussed during the previous
Cherry Marie A. Montes
Earth & Life Science Grade 11
Republic of the Philippines
Department of Education
REGION VIII
Schools Division of Calbayog City
SAN POLICARPO NATIONAL HIGH SCHOOL
Calbayog City
LESSON PLAN IN
PROGRESSIVE EXPANSION OF LIMITED FACE TO FACE CLASSES
A. Mineral — a naturally occurring (not discussion
man-made or machine generated),
inorganic (not a byproduct of living things)
solid with an orderly crystalline structure
and a definite chemical composition
B. Minerals are the basic building blocks
of rocks.
B. Establishing a purpose for Introduce the following learning objectives Introduce the following learning
the lesson using the suggested protocols (Verbatim, objectives using the suggested
Own Words, Read-aloud) protocols (Verbatim, Own Words,
A. I can identify and describe the different Read-aloud)
properties of minerals. B. I can group the minerals based on
B. I can group the minerals based on chemical composition.
chemical composition. C. I can identify several common
C. I can identify several common rock- rock-forming minerals.
forming minerals.
C. Presenting SICK LEAVE WITH FORM 6 Questions for the learners
examples/instances of the 1. Do you consider water a mineral?
new lesson Answer: No. It is not solid and crystalline.
2. How about snowflake, or tube ice? Are
these minerals?
Answer: Tube ice is not a mineral,
because it is not naturally occurring. But a
snowflake possesses all the properties
under the definition of a mineral.
D. Discussing new concepts MINERAL PROPERTIES MINERAL GROUPS Read and
and practicing new skills #1 1. Use table salt or halite to demonstrate Minerals, like many other things, can answer Learning
the different mineral properties. also be categorized. Activity Sheets
Cherry Marie A. Montes
Earth & Life Science Grade 11
Republic of the Philippines
Department of Education
REGION VIII
Schools Division of Calbayog City
SAN POLICARPO NATIONAL HIGH SCHOOL
Calbayog City
LESSON PLAN IN
PROGRESSIVE EXPANSION OF LIMITED FACE TO FACE CLASSES
2. Tabulate the answers on the board The most stable and least in Earth and Life
using the template below. ambiguous basis for classification of Science Week 1
minerals is based pages 14-16
on their chemical compositions.
1. Silicates
1. Luster 2. Oxides
a. Metallic 3. Sulfates
b. Non-metallic 4. Sulfides
2. Hardness 5. Carbonates
3. Crystal Form/Habit 6. Native Elements
4. Color and streak a. Metals and Intermetals
5. Cleavage b. Semi-metals
6. Specific Gravity c. Nonmetals
7. Others – magnetism, odor, taste, 7. Halides
tenacity, reaction to acid, etc.
E. Discussing new concepts The elements listed below comprise
and practicing new skills #2 almost 99% of the minerals making
up the Earth’s crust.
Cherry Marie A. Montes
Earth & Life Science Grade 11
Republic of the Philippines
Department of Education
REGION VIII
Schools Division of Calbayog City
SAN POLICARPO NATIONAL HIGH SCHOOL
Calbayog City
LESSON PLAN IN
PROGRESSIVE EXPANSION OF LIMITED FACE TO FACE CLASSES
F. Developing mastery (Leads List five minerals and their Activity: How to identify minerals.
to Formative Assessment) common uses. Identify the Present the Mineral Decision Tree to
specific property/properties that the class, as a visual guide in
makes the mineral suitable for explaining the methods used by
those uses. For example, geologists to identify minerals..
graphite, having a black streak 1. Show a mineral sample (or picture)
and hardness of 1-2, is used in that the class will try to identify.
pencils due to its ability to leave 2. Use the diagram below to narrow
marks on paper and other objects. down the mineral choices into groups
A to F. Then refer to the provided
mineral chart for the list of possible
minerals.
3. Test the other properties provided
in the chart to identify the mineral.
G. Finding practical The identification of the physical and
applications of concepts and chemical properties of a particular mineral
Cherry Marie A. Montes
Earth & Life Science Grade 11
Republic of the Philippines
Department of Education
REGION VIII
Schools Division of Calbayog City
SAN POLICARPO NATIONAL HIGH SCHOOL
Calbayog City
LESSON PLAN IN
PROGRESSIVE EXPANSION OF LIMITED FACE TO FACE CLASSES
skills in daily living will help us identify to what activity or by-
product it will be most suitable to use.
H. Making generalizations and How can we say that a material is a mineral? What are its 5 properties?
abstractions What are the physical properties of a mineral? Chemical properties?
I. Evaluating Learning Refer to Page 55 of ELS TG
Assignment
J. Additional activities for
application or remediation
Prepared by: Inspected by: Approved:
CHERRY MARIE OYO-A MONTES ELEANOR C. CATAMPO MILANER R. OYO-A
SST II STEM Dept. Head, MT-I Science School Principal II
Cherry Marie A. Montes
Earth & Life Science Grade 11
You might also like
- NRG Conservation of Energy - Maximize The Mechanical Energy of A Rollercoaster Lab Manual EnglishDocument7 pagesNRG Conservation of Energy - Maximize The Mechanical Energy of A Rollercoaster Lab Manual EnglishDISTOR, JOSH GABRIELNo ratings yet
- En 16432-1 - EN - Ballastless Track Systems - General RequirementsDocument35 pagesEn 16432-1 - EN - Ballastless Track Systems - General RequirementsBaptiste RochetteNo ratings yet
- How Representative Animals ReproduceDocument57 pagesHow Representative Animals ReproduceCherry Marie Oyo-a100% (2)
- F2F Lesson Plan Format 2022 September 26-30, 2022 ELS, ITHPDocument6 pagesF2F Lesson Plan Format 2022 September 26-30, 2022 ELS, ITHPCherry Marie Oyo-aNo ratings yet
- F2F Lesson Plan Format 2022 September 19-23, 2022 ELS, ITHPDocument7 pagesF2F Lesson Plan Format 2022 September 19-23, 2022 ELS, ITHPCherry Marie Oyo-aNo ratings yet
- F2F Lesson Plan Format 2022 September 12-16, 2022 ELS, ITHPDocument6 pagesF2F Lesson Plan Format 2022 September 12-16, 2022 ELS, ITHPCherry Marie Oyo-aNo ratings yet
- F2F Lesson Plan Format 2022 October 24-28, 2022 ELS, ITHPDocument5 pagesF2F Lesson Plan Format 2022 October 24-28, 2022 ELS, ITHPCherry Marie Oyo-aNo ratings yet
- Science q1 w1Document12 pagesScience q1 w1Milagros ReyesNo ratings yet
- DLL Sci 7 Q2Document35 pagesDLL Sci 7 Q2Carmina DuldulaoNo ratings yet
- Final Polygon LPDocument9 pagesFinal Polygon LPKristine BuñaNo ratings yet
- SDO Camarines Norte: Facilitating Dreams, Valuing AspirationsDocument5 pagesSDO Camarines Norte: Facilitating Dreams, Valuing AspirationsJi YaNo ratings yet
- February 19-23, 2024Document20 pagesFebruary 19-23, 2024Jovilyn JardielNo ratings yet
- DLP-INTRO TO PHILO Q2 Week 1Document6 pagesDLP-INTRO TO PHILO Q2 Week 1Ann Maureen ConcepcionNo ratings yet
- Abmae12 Iw5d1Document6 pagesAbmae12 Iw5d1Arlene Caceres GacheNo ratings yet
- Weekly-Learning-Plan 4Document4 pagesWeekly-Learning-Plan 4RONALYN BERNADASNo ratings yet
- Stem C.chico DLL Genbio 0926-302022Document5 pagesStem C.chico DLL Genbio 0926-302022Celsa ChicoNo ratings yet
- Scie DLL q2 m6 CARBON COMPOUNDSDocument3 pagesScie DLL q2 m6 CARBON COMPOUNDSRoxanne Alcaide OrdoñezNo ratings yet
- Scie DLL q2 m5 CArbon Hybridization Part 2Document4 pagesScie DLL q2 m5 CArbon Hybridization Part 2Roxanne Alcaide OrdoñezNo ratings yet
- Scie DLL q2 m5 CArbon HybridizationDocument4 pagesScie DLL q2 m5 CArbon HybridizationRoxanne Alcaide OrdoñezNo ratings yet
- DLL For SHS 7e's EALS 2nd w7Document6 pagesDLL For SHS 7e's EALS 2nd w7Joseph GutierrezNo ratings yet
- q4 w1 ScienceDocument7 pagesq4 w1 ScienceErika Marie DimayugaNo ratings yet
- DLL-Food Fish Processing 9-Q2-W6Document4 pagesDLL-Food Fish Processing 9-Q2-W6IlY-MyraTorresDeJesusNo ratings yet
- DLL For SHS 7e's EALS w6Document8 pagesDLL For SHS 7e's EALS w6Joseph GutierrezNo ratings yet
- DLL Science 7, Q1W7Document7 pagesDLL Science 7, Q1W7angel pranadaNo ratings yet
- Eng DLL Q1 Week 9Document4 pagesEng DLL Q1 Week 9Roxanne Alcaide OrdoñezNo ratings yet
- DLP-INTRO TO PHILO Week 1Document6 pagesDLP-INTRO TO PHILO Week 1Ann Maureen Concepcion100% (1)
- DLP-INTRO TO PHILO Week 2Document6 pagesDLP-INTRO TO PHILO Week 2Ann Maureen ConcepcionNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument2 pagesDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesKenjie SobrevegaNo ratings yet
- COLISAO Rodante B. Semi DLP Day 10 For PrintDocument5 pagesCOLISAO Rodante B. Semi DLP Day 10 For PrintDan ColisaoNo ratings yet
- SDO Camarines Norte: Facilitating Dreams, Valuing AspirationsDocument5 pagesSDO Camarines Norte: Facilitating Dreams, Valuing AspirationsJi YaNo ratings yet
- Weekly Learning Plan Science 10 (Q4-W2)Document1 pageWeekly Learning Plan Science 10 (Q4-W2)Vhin CruzNo ratings yet
- DLL For SHS 7e's EALS 2nd w5Document9 pagesDLL For SHS 7e's EALS 2nd w5Joseph GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Division of Pangasinan Ii: Subject Allocation Per Grading PeriodDocument4 pagesDivision of Pangasinan Ii: Subject Allocation Per Grading Periodharold carbonelNo ratings yet
- Shs-Daily-Lesson-in-physical Science JMG Q3W1Document14 pagesShs-Daily-Lesson-in-physical Science JMG Q3W1Joseph GutierrezNo ratings yet
- g12 P.E. and Health WHLP Week5 and Week6 March 22 2022Document4 pagesg12 P.E. and Health WHLP Week5 and Week6 March 22 2022DarkDimensionZNo ratings yet
- DLL Week 1-Q4 Science 5Document8 pagesDLL Week 1-Q4 Science 5Ma CkNo ratings yet
- Science DLL Week 4 November 28 29, December 1 2Document9 pagesScience DLL Week 4 November 28 29, December 1 2Ma. Joan Mae MagnoNo ratings yet
- Closing Program Inset 2022Document2 pagesClosing Program Inset 2022Cathy APNo ratings yet
- DLL Oct 17-21 ELSDocument9 pagesDLL Oct 17-21 ELSJerick Jeff Adriano ManiponNo ratings yet
- WEEKLY-LEARNING-PLAN - Earth and Life Science Week 5 and 6-GC Q2Document2 pagesWEEKLY-LEARNING-PLAN - Earth and Life Science Week 5 and 6-GC Q2JAY ANDRESNo ratings yet
- WHLP q2wk1Document6 pagesWHLP q2wk1May CabarrubiasNo ratings yet
- Toaz - Info 4th Quarter DLL Grade 7 Science PRDocument4 pagesToaz - Info 4th Quarter DLL Grade 7 Science PRnorhanifah matanogNo ratings yet
- SDO Camarines Norte: Facilitating Dreams, Valuing AspirationsDocument6 pagesSDO Camarines Norte: Facilitating Dreams, Valuing Aspirationsshuckss taloNo ratings yet
- Grade 10-Observing Correct Grammar in Making DefinitionsDocument8 pagesGrade 10-Observing Correct Grammar in Making DefinitionsLeah MatiasNo ratings yet
- DLL Nov 11Document4 pagesDLL Nov 11Koc EsNo ratings yet
- Passed 114-08-19 Mountain Province Interaction Among Living ThingsDocument19 pagesPassed 114-08-19 Mountain Province Interaction Among Living ThingsKelvinNo ratings yet
- DLP - Q1 - Week 4Document11 pagesDLP - Q1 - Week 4IVY MALENo ratings yet
- NEW DLL Week 2Document10 pagesNEW DLL Week 2kimbeerlyn doromasNo ratings yet
- Intro Aug. 29 - Sept 2, 2022Document6 pagesIntro Aug. 29 - Sept 2, 2022Editha RobillosNo ratings yet
- Schools Division of Legazpi City School: Food & Beverage ServicesDocument2 pagesSchools Division of Legazpi City School: Food & Beverage ServicesJohn Joseph ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- DLL 3rd QuarterDocument8 pagesDLL 3rd QuarterAbigail PanaliganNo ratings yet
- DLL - Mapeh 6 - Q1 - W1Document4 pagesDLL - Mapeh 6 - Q1 - W1Laine Agustin SalemNo ratings yet
- 11 06 10 23 W2Document3 pages11 06 10 23 W2KrizzleNo ratings yet
- Grade 10-GIVING EXPANDED DEFINITIONS OF WORDSDocument7 pagesGrade 10-GIVING EXPANDED DEFINITIONS OF WORDSLeah MatiasNo ratings yet
- DLL ElsDocument3 pagesDLL ElsAldrin SahurdaNo ratings yet
- English 7 DLL Q2 Week 8Document6 pagesEnglish 7 DLL Q2 Week 8Anecito Jr. NeriNo ratings yet
- Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Thursday and Friday (Matthiola) and (Marigold)Document8 pagesTuesday Wednesday Thursday Thursday and Friday (Matthiola) and (Marigold)Jan Joseph UgkiengNo ratings yet
- Eng DLL Q2 Week 1Document4 pagesEng DLL Q2 Week 1Roxanne Alcaide OrdoñezNo ratings yet
- Weekly Home Learning Plan: Day & Time Learning Area Learning Competency Learning Tasks Mode of DeliveryDocument2 pagesWeekly Home Learning Plan: Day & Time Learning Area Learning Competency Learning Tasks Mode of DeliveryAylene GersanibNo ratings yet
- Science 9 Q1 W8Document5 pagesScience 9 Q1 W8Abram BaranganNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan. Jimboy Lumaban Ka Sa Buhay!Document6 pagesLesson Plan. Jimboy Lumaban Ka Sa Buhay!fries riveraNo ratings yet
- g12 P.E. and Health WHLP Week7 and Week8 Scuba DivingDocument2 pagesg12 P.E. and Health WHLP Week7 and Week8 Scuba DivingDarkDimensionZNo ratings yet
- F2F Lesson Plan Format 2022 October 24-28, 2022 ELS, ITHPDocument5 pagesF2F Lesson Plan Format 2022 October 24-28, 2022 ELS, ITHPCherry Marie Oyo-aNo ratings yet
- F2F Lesson Plan Format 2022 September 19-23, 2022 ELS, ITHPDocument7 pagesF2F Lesson Plan Format 2022 September 19-23, 2022 ELS, ITHPCherry Marie Oyo-aNo ratings yet
- F2F Lesson Plan Format 2022 September 26-30, 2022 ELS, ITHPDocument6 pagesF2F Lesson Plan Format 2022 September 26-30, 2022 ELS, ITHPCherry Marie Oyo-aNo ratings yet
- F2F Lesson Plan Format 2022 September 12-16, 2022 ELS, ITHPDocument6 pagesF2F Lesson Plan Format 2022 September 12-16, 2022 ELS, ITHPCherry Marie Oyo-aNo ratings yet
- Guia 11GHz 103468-P360-F090lms3-ExternalDocument2 pagesGuia 11GHz 103468-P360-F090lms3-ExternalGabriel MontenegroNo ratings yet
- English 4 BAC: Nassime El MaataouiDocument52 pagesEnglish 4 BAC: Nassime El Maataouiayoub rhNo ratings yet
- 20-42863-1 M&I Mid Term AssignmentDocument14 pages20-42863-1 M&I Mid Term AssignmentIA DipsNo ratings yet
- 8 DMT Mix MN - Ryan (10!1!24) Ratio N ProportionDocument1 page8 DMT Mix MN - Ryan (10!1!24) Ratio N ProportionRohan MehtaNo ratings yet
- Wire Rope LubricatorDocument8 pagesWire Rope LubricatorvlmiltonNo ratings yet
- Architecture Thesis Topics Ideas PhilippinesDocument4 pagesArchitecture Thesis Topics Ideas Philippinesmichellealexanderminneapolis100% (2)
- Chemical Engineering: Jump To Navigation Jump To SearchDocument12 pagesChemical Engineering: Jump To Navigation Jump To Searchahmad muazNo ratings yet
- Rouse (1974) - MONITORING VEGETATION SYSTEMS IN THE GREAT PLAINS WITH ERTSDocument9 pagesRouse (1974) - MONITORING VEGETATION SYSTEMS IN THE GREAT PLAINS WITH ERTSAndre LanzerNo ratings yet
- Statistical Process Control: True/False QuestionsDocument23 pagesStatistical Process Control: True/False QuestionsBo RaeNo ratings yet
- ELEMENTS of WEATHER and CLIMATEDocument71 pagesELEMENTS of WEATHER and CLIMATEMel DridNo ratings yet
- Mercadal Sanico Cabuslay Thesis TurnitinDocument19 pagesMercadal Sanico Cabuslay Thesis TurnitinLucy CabuslayNo ratings yet
- Day 3 SBL Practice To PassDocument20 pagesDay 3 SBL Practice To PassRaqib MalikNo ratings yet
- GradesDocument1 pageGradesdc9q8ycbvcNo ratings yet
- Essay On Floods in PakistanDocument7 pagesEssay On Floods in Pakistanezke4pq2100% (2)
- Avitera® Blue Se: Safety Data SheetDocument16 pagesAvitera® Blue Se: Safety Data SheetNguyễn Huy Cường100% (1)
- Accumulation of Heavy Metals in SpinaciaDocument12 pagesAccumulation of Heavy Metals in SpinaciaSachin SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3.2 Distinguished Personalities in The LocalityDocument5 pagesLesson 3.2 Distinguished Personalities in The LocalityCharlie PuthNo ratings yet
- La Escalera de Wittgenstein, David LehmanDocument6 pagesLa Escalera de Wittgenstein, David Lehmanwilbert_tapia_1No ratings yet
- The Historical Roots of The Visual ExaminationDocument10 pagesThe Historical Roots of The Visual ExaminationrecolenciNo ratings yet
- Eigen Values of A Matrix by PowerDocument9 pagesEigen Values of A Matrix by PowerVarnika SinghNo ratings yet
- Technology in The Ancient WorldDocument66 pagesTechnology in The Ancient WorldAngela Danielle Tan100% (1)
- SABILE, JOHN REYSTER E - POST-INTERNSHIP PERFORMANCE EVALUATION FORM - INTERNSHIP Final 2Document3 pagesSABILE, JOHN REYSTER E - POST-INTERNSHIP PERFORMANCE EVALUATION FORM - INTERNSHIP Final 2Mary Dee RozalNo ratings yet
- Chapter9 Lecture29 Performance Analysis V Manoeuvres 2Document12 pagesChapter9 Lecture29 Performance Analysis V Manoeuvres 2Chegrani AhmedNo ratings yet
- MIT18 05S14 Class5slides PDFDocument17 pagesMIT18 05S14 Class5slides PDFAftab SaadNo ratings yet
- Score SheetsDocument6 pagesScore SheetsErika Bose CantoriaNo ratings yet
- Frank ISC Mathematics Model Test Paper 20Document3 pagesFrank ISC Mathematics Model Test Paper 20Rohan Chakraborty100% (3)
- Basic Mathematics-A3 PDFDocument3 pagesBasic Mathematics-A3 PDFJatin SinglaNo ratings yet
- Revised Bloom's TaxonomyDocument29 pagesRevised Bloom's Taxonomymariel floresNo ratings yet