Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 viewsM9 Religion Notes
M9 Religion Notes
Uploaded by
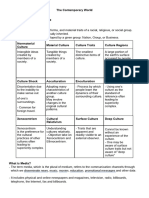
Lisa NgGlobalization has accelerated the spread of religions through increased travel, information sharing, and cultural exchange. Religions have adapted to new communication technologies and face pressures from both cultural globalization and rising nationalism. The ease of traveling and accessing religious information online has led to both increased fundamentalism as cultures feel threatened, and also more liberalization as social values spread across borders.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- The Contemporary World Class (Lesson 9) Activity 9.1Document5 pagesThe Contemporary World Class (Lesson 9) Activity 9.1Jhon dave Surbano100% (4)
- Affidavit of Discrepancy Date of BirthDocument1 pageAffidavit of Discrepancy Date of Birthdempearl2315100% (1)
- Eclipse - Edwards Perspective P.O.VDocument4 pagesEclipse - Edwards Perspective P.O.VSheridan100% (5)
- Negative Averment AffidavitDocument3 pagesNegative Averment Affidavitamenelbey80% (5)
- Chapter 1 Lesson 1Document23 pagesChapter 1 Lesson 1hi qtieeNo ratings yet
- GE 3 Chapter IVDocument8 pagesGE 3 Chapter IVRyan SalipsipNo ratings yet
- Global Culutre ChuchuchuchDocument2 pagesGlobal Culutre ChuchuchuchRalph Elvin MacanlalayNo ratings yet
- Contemporary ReportDocument30 pagesContemporary ReportbalansagjannisemaeNo ratings yet
- Contempo Reviewer in FinalsDocument6 pagesContempo Reviewer in FinalsNicole P. PascualNo ratings yet
- Diasanta, Jirahmae M. - Module 1Document6 pagesDiasanta, Jirahmae M. - Module 1JIrahmae DiasantaNo ratings yet
- CONTEMPORARY Midterm ReviewerDocument2 pagesCONTEMPORARY Midterm ReviewerbdsutingcoNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Unit I: Introduction To GlobalizationDocument9 pagesReviewer Unit I: Introduction To Globalizationkaryma paloNo ratings yet
- Ado Ethics Finals CroduaDocument24 pagesAdo Ethics Finals CroduaJuvy ManejaNo ratings yet
- Contemp Reviewer 2Document6 pagesContemp Reviewer 2Lei IrishNo ratings yet
- CW FinalsDocument8 pagesCW Finalskhen5902No ratings yet
- This Study Resource WasDocument2 pagesThis Study Resource Wasjennifer roslinNo ratings yet
- The Global Interstate System: Christine B. Tenorio, MPADocument15 pagesThe Global Interstate System: Christine B. Tenorio, MPAMoguri OwowNo ratings yet
- Contemporary OutputDocument28 pagesContemporary OutputCriszialyne MaeNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Global Culture and MediaDocument29 pagesLesson 1 Global Culture and Medianeilssen111No ratings yet
- Gcworld Chapt 1 RevwrDocument4 pagesGcworld Chapt 1 RevwrnymousleeNo ratings yet
- York - 2001 - New Age Commodification and Appropriation of SpiritualityDocument14 pagesYork - 2001 - New Age Commodification and Appropriation of SpiritualityAnkur GargNo ratings yet
- CW-Activity-1-4-of-Unit-4 - Cruz, Ma. Pauline Therese - BSP-1-2Document4 pagesCW-Activity-1-4-of-Unit-4 - Cruz, Ma. Pauline Therese - BSP-1-2mariamagadia7No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 A World of Ideas CompressedDocument49 pagesChapter 4 A World of Ideas CompressedEMMANUEL CHARLES ADRIAN BAUTISTANo ratings yet
- ContempoDocument49 pagesContempoDrunkk BaestarrdNo ratings yet
- Globalization: The Contemporary World Preliminaries Page - 1Document6 pagesGlobalization: The Contemporary World Preliminaries Page - 1Jerica Mae GabitoNo ratings yet
- TCW ReviewerDocument3 pagesTCW ReviewerFRANCESCA ALEXANDRIA PAREDESNo ratings yet
- Nation State CountryDocument6 pagesNation State CountryNasrueuNo ratings yet
- Final Module in Contemporary WorldDocument15 pagesFinal Module in Contemporary WorldJohn Henry TampoyNo ratings yet
- Lesson-9-Module-Globalization of ReligionDocument10 pagesLesson-9-Module-Globalization of Religiondeather abuntoNo ratings yet
- SS 113 Module 4 LESSON 9 13 2Document15 pagesSS 113 Module 4 LESSON 9 13 2Izzy Dale Cagas SilangaNo ratings yet
- Religion Globalization SendingDocument20 pagesReligion Globalization SendingDesiree MayugaNo ratings yet
- IEBDocument5 pagesIEBMj NuarinNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Defining GlobalizationDocument3 pagesLesson 1 Defining GlobalizationRosemarie BacallanNo ratings yet
- Engl 101Document4 pagesEngl 101Aira Grace SaragaNo ratings yet
- Contemporary World - Module 12Document4 pagesContemporary World - Module 12Grande, Daniella A.No ratings yet
- Secularism in RetreatDocument11 pagesSecularism in RetreatGiorgi SakhelashviliNo ratings yet
- Globalization of ReligionDocument10 pagesGlobalization of Religionadsaster201No ratings yet
- Q2 Module 5Document5 pagesQ2 Module 5Leo BasNo ratings yet
- ActivitiesDocument2 pagesActivitiesGlaiza FloresNo ratings yet
- Soc Sci: World of RegionsDocument12 pagesSoc Sci: World of RegionsAuroraNo ratings yet
- Contemporary World 123 - Final Term Group Task 1: Chapter 5 - World of Regions Chapter 6 - Globalization of ReligionsDocument2 pagesContemporary World 123 - Final Term Group Task 1: Chapter 5 - World of Regions Chapter 6 - Globalization of ReligionsMaria Desserie S. BohiyanNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Activities GEC103 The Contemporary World (MDO Porras)Document4 pagesModule 1 Activities GEC103 The Contemporary World (MDO Porras)Chamelli RobinNo ratings yet
- THE Contemporary WorldDocument7 pagesTHE Contemporary WorldGerald CorneliaNo ratings yet
- Top 5 Features of Post ModernityDocument1 pageTop 5 Features of Post ModernityahmeduuonfireNo ratings yet
- Unit I Introduction To Globalization: ExamplesDocument11 pagesUnit I Introduction To Globalization: ExamplesPRINCES ANGEL FAMARANGLASNo ratings yet
- The Contemporary World Module 2 Lesson 2Document8 pagesThe Contemporary World Module 2 Lesson 2jgbunaoNo ratings yet
- COworld Lesson1Document3 pagesCOworld Lesson1Joyce VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Con WorldDocument10 pagesCon WorldLaxamana Jacer Clent LNo ratings yet
- World Finals ReviewerDocument2 pagesWorld Finals ReviewerCharlene HernandezNo ratings yet
- Inosr Es 61 43 482020.Document6 pagesInosr Es 61 43 482020.vanessasalinas002No ratings yet
- Gec 103 ReportingDocument4 pagesGec 103 ReportingIanNo ratings yet
- Research Paper Globalization A Cause of Filipinos Cultural Loss GROUP 5 7Document25 pagesResearch Paper Globalization A Cause of Filipinos Cultural Loss GROUP 5 7Merhylle Jade JalopNo ratings yet
- Global Media CulturesDocument11 pagesGlobal Media CulturesNicole Genzeinne GumaraoNo ratings yet
- CW ReviewerDocument3 pagesCW ReviewerlavetorianicholeNo ratings yet
- CW ReportDocument23 pagesCW ReportEllyrose AzarconNo ratings yet
- Contempo ReviewerDocument9 pagesContempo Reviewerlucerocatapanggwen.03No ratings yet
- GEd 104 MIDTERMS REVIEWERDocument12 pagesGEd 104 MIDTERMS REVIEWERYasmin Digal0% (1)
- Contemporary World OutlineDocument5 pagesContemporary World OutlineJeffrey CabarrubiasNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 - Introduction To Globalization - ReviewerDocument9 pagesTopic 1 - Introduction To Globalization - Reviewer2022-201417No ratings yet
- IntroDocument4 pagesIntroRee-Jane Bautista MacaraegNo ratings yet
- Globalization On Citizenship, Culture & Religion: Module 4-Lesson 3Document9 pagesGlobalization On Citizenship, Culture & Religion: Module 4-Lesson 3Alemar LimbingNo ratings yet
- Midterm TemplateDocument3 pagesMidterm TemplateJhon Klier BalesNo ratings yet
- Cultural Resonance: Ancient Beliefs in a Globalized WorldFrom EverandCultural Resonance: Ancient Beliefs in a Globalized WorldNo ratings yet
- M8 Media NotesDocument2 pagesM8 Media NotesLisa NgNo ratings yet
- M7 ASEAN NotesDocument1 pageM7 ASEAN NotesLisa NgNo ratings yet
- M5 UN NotesDocument3 pagesM5 UN NotesLisa NgNo ratings yet
- M5 Global GovernanceDocument24 pagesM5 Global GovernanceLisa NgNo ratings yet
- M6 Global North and South NotesDocument1 pageM6 Global North and South NotesLisa NgNo ratings yet
- Tailieuchung Boi Duong Hoc Sinh Gioi Luong Giac NXB Dai Hoc Quoc Gia 2014-2-8519Document116 pagesTailieuchung Boi Duong Hoc Sinh Gioi Luong Giac NXB Dai Hoc Quoc Gia 2014-2-8519Vincent TuấnNo ratings yet
- LC Jumpers Fap 203 Web PDFDocument3 pagesLC Jumpers Fap 203 Web PDFAlejandro Humberto García QuisbertNo ratings yet
- Cost Accounting Name: - ActivitiesDocument2 pagesCost Accounting Name: - ActivitiesJosh AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Sikamelt 700Document2 pagesSikamelt 700Ionut StoicaNo ratings yet
- Populorum ProgressioDocument4 pagesPopulorum ProgressioSugar JumuadNo ratings yet
- Balfour V Balfour: (1919) 2 KB 571, (1918-19) All ER860 (Court of Appeal)Document5 pagesBalfour V Balfour: (1919) 2 KB 571, (1918-19) All ER860 (Court of Appeal)Kelvin YapNo ratings yet
- User's Guide: W Ing FTP Server HelpDocument174 pagesUser's Guide: W Ing FTP Server HelpIvan Mac Gregor OviedoNo ratings yet
- Fazendo Dinheiro Com A FotografiaDocument132 pagesFazendo Dinheiro Com A FotografiaGiuseppe DecaroNo ratings yet
- Range CoderDocument11 pagesRange CoderftwilliamNo ratings yet
- LSMW - WSQ - GL Master TextDocument7 pagesLSMW - WSQ - GL Master Textpatankar.vaibhav08No ratings yet
- Zhang Ear Accupuncture Rhinititis Cold PDFDocument391 pagesZhang Ear Accupuncture Rhinititis Cold PDFanimeshNo ratings yet
- Meridian Therapy Extra Vessels 2-12-EVDocument22 pagesMeridian Therapy Extra Vessels 2-12-EVDontcho Lissiyski100% (14)
- Bloodborne Rulebook FinalDocument28 pagesBloodborne Rulebook FinalDan L'étron TurconNo ratings yet
- C. Ra 6969 - Engr. Czes BongcoDocument87 pagesC. Ra 6969 - Engr. Czes Bongcorandell vasquezNo ratings yet
- Running Times 2014-01-02.bakDocument72 pagesRunning Times 2014-01-02.bakJsueNo ratings yet
- Leonard Peltier Open Letter - Feb. 6, 2024Document3 pagesLeonard Peltier Open Letter - Feb. 6, 2024jen_benderyNo ratings yet
- Fellowes Powershred P-57Cs Paper Shredder - 3205701Document2 pagesFellowes Powershred P-57Cs Paper Shredder - 3205701papershredders100% (3)
- Ritesh M 06122022Document11 pagesRitesh M 06122022arpit yadavNo ratings yet
- Past Year Ebusiness - Pdf.crdownloadDocument5 pagesPast Year Ebusiness - Pdf.crdownloadFatin IzzahNo ratings yet
- Grupe III 2016 20171Document10 pagesGrupe III 2016 20171No RulesNo ratings yet
- Avernment of Jurisdiction Quo WarrantoDocument7 pagesAvernment of Jurisdiction Quo WarrantoBilal Yusef El Abdullah BeyNo ratings yet
- 2024 03 06 Introduction Lecture Series Climate Protection SS2024Document45 pages2024 03 06 Introduction Lecture Series Climate Protection SS2024Abdullah Khan QadriNo ratings yet
- Lymph Node PathologyDocument4 pagesLymph Node PathologyGerardLum0% (1)
- Baby Food in India AnalysisDocument4 pagesBaby Food in India AnalysisRaheetha AhmedNo ratings yet
- Tingkat Kepatuhan Minum Obat Pada Penderita Penyakit Hipertensi Di Puskesmas Kedaung Wetan Kota Tangerang Bulan Juni - Juli Tahun 2021Document6 pagesTingkat Kepatuhan Minum Obat Pada Penderita Penyakit Hipertensi Di Puskesmas Kedaung Wetan Kota Tangerang Bulan Juni - Juli Tahun 2021Ninin KepoNo ratings yet
- Preparation of Ink FinalDocument16 pagesPreparation of Ink FinalRishabh Kumud40% (5)
- International E-Marketing: Opportunities and IssuesDocument13 pagesInternational E-Marketing: Opportunities and IssuesRaluca SmarandacheNo ratings yet
M9 Religion Notes
M9 Religion Notes
Uploaded by
Lisa Ng0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views1 pageGlobalization has accelerated the spread of religions through increased travel, information sharing, and cultural exchange. Religions have adapted to new communication technologies and face pressures from both cultural globalization and rising nationalism. The ease of traveling and accessing religious information online has led to both increased fundamentalism as cultures feel threatened, and also more liberalization as social values spread across borders.
Original Description:
Religion
Original Title
M9 Religion notes
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentGlobalization has accelerated the spread of religions through increased travel, information sharing, and cultural exchange. Religions have adapted to new communication technologies and face pressures from both cultural globalization and rising nationalism. The ease of traveling and accessing religious information online has led to both increased fundamentalism as cultures feel threatened, and also more liberalization as social values spread across borders.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views1 pageM9 Religion Notes
M9 Religion Notes
Uploaded by
Lisa NgGlobalization has accelerated the spread of religions through increased travel, information sharing, and cultural exchange. Religions have adapted to new communication technologies and face pressures from both cultural globalization and rising nationalism. The ease of traveling and accessing religious information online has led to both increased fundamentalism as cultures feel threatened, and also more liberalization as social values spread across borders.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
MODULE 9 traditions include both private and with public policy changes and
public worship and practice communications technology
Religion has entered the information age some spiritual practices do not innovations cited as the two main
and has globalized at accelerating rates in involve worshipping a god or gods but driving factors.
the methods religion use for teaching and are introspective and draw on the China and India are among the
in belief system. practitioner's own ability to be foremost examples of nations that
responsible for his/her spiritual path have benefited from globalization.
1. Increasing ease to travel long distances, One clear result of globalization is
people are able to travel to religious sites. Globalization that an economic downturn in one
2. Printing press and the internet has Globalization is the spread of products, country can create a domino effect
made it easier for people to read about technology, information, and jobs across through its trade partners.
religions. national borders and cultures. In economic
3. In the past people have little knowledge terms, it describes an interdependence of The effects on religion of globalization can
about religious traditions and views , now nations around the globe fostered through be seen in the following areas:
globalization has led to global religion free trade. Rising religious fundamentalism as
market. people feel culturally threatened by
On the upside, it can raise the standard of an influx of ‘strange’ cultural
Religion living in poor and less developed countries factors resulting from the
a way of explaining the mysteries of by providing job opportunity, increasingly multicultural societies
life modernization, and improved access to triggered by globalization.
how the world was created goods and services. On the downside, it can Conversely, the movement of people
why it was created destroy job opportunities in more and information across national
why there is life and death developed and high-wage countries as the borders increases the rate of social
what happens when people die production of goods moves across and cultural liberalization resulting in
why there is suffering borders. potential loosening of traditional
a way of explaining a supreme power religious strictures.
or absolute power, whether Globalization motives are idealistic, as well The rise of nationalism as a counter
impersonal or personal, nameable or as opportunistic, but the development of a pressure to globalization may put
not global free market has benefited large pressure on ethnic/religious diversity
a way of explaining who or what corporations based in the Western world. in some countries. Particularly,
created the world and all the living Its impact remains mixed for workers, countries that do not have long
beings cultures, and small businesses around the histories of multiculturalism or
a way of describing a dimension globe, in both developed and emerging where there has been historical
beyond the physical world -- the nations. conflict between ethnic/religious
spiritual world groups that had been suppressed due
a way of explaining how to lead a Corporations gain a competitive to the rise of globalization
good life on Earth and in an afterlife advantage on multiple fronts through Same cause as #2 above, but,
these codes of behavior are often globalization. They can reduce operating different effect. The ease of
written in sacred documents or costs by manufacturing abroad. They can information flow also allows the
passed down through oral tradition buy raw materials more cheaply because rapid movement of religious
a way of worshiping the creator(s) of the reduction or removal of tariffs. proselytizing across the world. So,
or spiritual beings who are believed Most of all, they gain access to millions of the converts to regionally
to have power over the world and new consumers. non-traditional religions i.e
people's lives and/or a way of paying Mormonism and Fundamentalist
respects and drawing inspiration Globalization is a social, cultural, Christianity in Latin America, have
from spiritual leaders political, and legal phenomenon. increased dramatically.
Socially, it leads to greater
Worship often includes interaction among various
prayers of thanks, prayers of hopes, populations.
prayers of supplication Culturally, globalization represents
people often worship a god or gods the exchange of ideas, values, and
worship often happens in sacred artistic expression among cultures.
places and spaces Globalization also represents a trend
worship often includes ceremonies toward the development of single
and rituals conducted by spiritual world culture.
guides Politically, globalization has shifted
worship often involves sacred attention to intergovernmental
objects and images A way of joining organizations like the United
with others as a spiritual community Nations (UN) and the World Trade
religions and other spiritual Organization(WTO).
traditions often celebrate festivals Legally, globalization has altered how
or holy days and have special international law is created and
calendars that mark the important enforced.
historical events in the evolution of Globalization has sped up to an
thesource
This study religion
wasreligions andbyspiritual
downloaded unprecedentedonpace
100000850916192 from CourseHero.com since the03:03:51
10-26-2022 1990s, GMT -05:00
https://www.coursehero.com/file/83662190/CONTEMP-MODULE12pdf/
Powered by TCPDF (www.tcpdf.org)
You might also like
- The Contemporary World Class (Lesson 9) Activity 9.1Document5 pagesThe Contemporary World Class (Lesson 9) Activity 9.1Jhon dave Surbano100% (4)
- Affidavit of Discrepancy Date of BirthDocument1 pageAffidavit of Discrepancy Date of Birthdempearl2315100% (1)
- Eclipse - Edwards Perspective P.O.VDocument4 pagesEclipse - Edwards Perspective P.O.VSheridan100% (5)
- Negative Averment AffidavitDocument3 pagesNegative Averment Affidavitamenelbey80% (5)
- Chapter 1 Lesson 1Document23 pagesChapter 1 Lesson 1hi qtieeNo ratings yet
- GE 3 Chapter IVDocument8 pagesGE 3 Chapter IVRyan SalipsipNo ratings yet
- Global Culutre ChuchuchuchDocument2 pagesGlobal Culutre ChuchuchuchRalph Elvin MacanlalayNo ratings yet
- Contemporary ReportDocument30 pagesContemporary ReportbalansagjannisemaeNo ratings yet
- Contempo Reviewer in FinalsDocument6 pagesContempo Reviewer in FinalsNicole P. PascualNo ratings yet
- Diasanta, Jirahmae M. - Module 1Document6 pagesDiasanta, Jirahmae M. - Module 1JIrahmae DiasantaNo ratings yet
- CONTEMPORARY Midterm ReviewerDocument2 pagesCONTEMPORARY Midterm ReviewerbdsutingcoNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Unit I: Introduction To GlobalizationDocument9 pagesReviewer Unit I: Introduction To Globalizationkaryma paloNo ratings yet
- Ado Ethics Finals CroduaDocument24 pagesAdo Ethics Finals CroduaJuvy ManejaNo ratings yet
- Contemp Reviewer 2Document6 pagesContemp Reviewer 2Lei IrishNo ratings yet
- CW FinalsDocument8 pagesCW Finalskhen5902No ratings yet
- This Study Resource WasDocument2 pagesThis Study Resource Wasjennifer roslinNo ratings yet
- The Global Interstate System: Christine B. Tenorio, MPADocument15 pagesThe Global Interstate System: Christine B. Tenorio, MPAMoguri OwowNo ratings yet
- Contemporary OutputDocument28 pagesContemporary OutputCriszialyne MaeNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Global Culture and MediaDocument29 pagesLesson 1 Global Culture and Medianeilssen111No ratings yet
- Gcworld Chapt 1 RevwrDocument4 pagesGcworld Chapt 1 RevwrnymousleeNo ratings yet
- York - 2001 - New Age Commodification and Appropriation of SpiritualityDocument14 pagesYork - 2001 - New Age Commodification and Appropriation of SpiritualityAnkur GargNo ratings yet
- CW-Activity-1-4-of-Unit-4 - Cruz, Ma. Pauline Therese - BSP-1-2Document4 pagesCW-Activity-1-4-of-Unit-4 - Cruz, Ma. Pauline Therese - BSP-1-2mariamagadia7No ratings yet
- Chapter 4 A World of Ideas CompressedDocument49 pagesChapter 4 A World of Ideas CompressedEMMANUEL CHARLES ADRIAN BAUTISTANo ratings yet
- ContempoDocument49 pagesContempoDrunkk BaestarrdNo ratings yet
- Globalization: The Contemporary World Preliminaries Page - 1Document6 pagesGlobalization: The Contemporary World Preliminaries Page - 1Jerica Mae GabitoNo ratings yet
- TCW ReviewerDocument3 pagesTCW ReviewerFRANCESCA ALEXANDRIA PAREDESNo ratings yet
- Nation State CountryDocument6 pagesNation State CountryNasrueuNo ratings yet
- Final Module in Contemporary WorldDocument15 pagesFinal Module in Contemporary WorldJohn Henry TampoyNo ratings yet
- Lesson-9-Module-Globalization of ReligionDocument10 pagesLesson-9-Module-Globalization of Religiondeather abuntoNo ratings yet
- SS 113 Module 4 LESSON 9 13 2Document15 pagesSS 113 Module 4 LESSON 9 13 2Izzy Dale Cagas SilangaNo ratings yet
- Religion Globalization SendingDocument20 pagesReligion Globalization SendingDesiree MayugaNo ratings yet
- IEBDocument5 pagesIEBMj NuarinNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Defining GlobalizationDocument3 pagesLesson 1 Defining GlobalizationRosemarie BacallanNo ratings yet
- Engl 101Document4 pagesEngl 101Aira Grace SaragaNo ratings yet
- Contemporary World - Module 12Document4 pagesContemporary World - Module 12Grande, Daniella A.No ratings yet
- Secularism in RetreatDocument11 pagesSecularism in RetreatGiorgi SakhelashviliNo ratings yet
- Globalization of ReligionDocument10 pagesGlobalization of Religionadsaster201No ratings yet
- Q2 Module 5Document5 pagesQ2 Module 5Leo BasNo ratings yet
- ActivitiesDocument2 pagesActivitiesGlaiza FloresNo ratings yet
- Soc Sci: World of RegionsDocument12 pagesSoc Sci: World of RegionsAuroraNo ratings yet
- Contemporary World 123 - Final Term Group Task 1: Chapter 5 - World of Regions Chapter 6 - Globalization of ReligionsDocument2 pagesContemporary World 123 - Final Term Group Task 1: Chapter 5 - World of Regions Chapter 6 - Globalization of ReligionsMaria Desserie S. BohiyanNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Activities GEC103 The Contemporary World (MDO Porras)Document4 pagesModule 1 Activities GEC103 The Contemporary World (MDO Porras)Chamelli RobinNo ratings yet
- THE Contemporary WorldDocument7 pagesTHE Contemporary WorldGerald CorneliaNo ratings yet
- Top 5 Features of Post ModernityDocument1 pageTop 5 Features of Post ModernityahmeduuonfireNo ratings yet
- Unit I Introduction To Globalization: ExamplesDocument11 pagesUnit I Introduction To Globalization: ExamplesPRINCES ANGEL FAMARANGLASNo ratings yet
- The Contemporary World Module 2 Lesson 2Document8 pagesThe Contemporary World Module 2 Lesson 2jgbunaoNo ratings yet
- COworld Lesson1Document3 pagesCOworld Lesson1Joyce VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Con WorldDocument10 pagesCon WorldLaxamana Jacer Clent LNo ratings yet
- World Finals ReviewerDocument2 pagesWorld Finals ReviewerCharlene HernandezNo ratings yet
- Inosr Es 61 43 482020.Document6 pagesInosr Es 61 43 482020.vanessasalinas002No ratings yet
- Gec 103 ReportingDocument4 pagesGec 103 ReportingIanNo ratings yet
- Research Paper Globalization A Cause of Filipinos Cultural Loss GROUP 5 7Document25 pagesResearch Paper Globalization A Cause of Filipinos Cultural Loss GROUP 5 7Merhylle Jade JalopNo ratings yet
- Global Media CulturesDocument11 pagesGlobal Media CulturesNicole Genzeinne GumaraoNo ratings yet
- CW ReviewerDocument3 pagesCW ReviewerlavetorianicholeNo ratings yet
- CW ReportDocument23 pagesCW ReportEllyrose AzarconNo ratings yet
- Contempo ReviewerDocument9 pagesContempo Reviewerlucerocatapanggwen.03No ratings yet
- GEd 104 MIDTERMS REVIEWERDocument12 pagesGEd 104 MIDTERMS REVIEWERYasmin Digal0% (1)
- Contemporary World OutlineDocument5 pagesContemporary World OutlineJeffrey CabarrubiasNo ratings yet
- Topic 1 - Introduction To Globalization - ReviewerDocument9 pagesTopic 1 - Introduction To Globalization - Reviewer2022-201417No ratings yet
- IntroDocument4 pagesIntroRee-Jane Bautista MacaraegNo ratings yet
- Globalization On Citizenship, Culture & Religion: Module 4-Lesson 3Document9 pagesGlobalization On Citizenship, Culture & Religion: Module 4-Lesson 3Alemar LimbingNo ratings yet
- Midterm TemplateDocument3 pagesMidterm TemplateJhon Klier BalesNo ratings yet
- Cultural Resonance: Ancient Beliefs in a Globalized WorldFrom EverandCultural Resonance: Ancient Beliefs in a Globalized WorldNo ratings yet
- M8 Media NotesDocument2 pagesM8 Media NotesLisa NgNo ratings yet
- M7 ASEAN NotesDocument1 pageM7 ASEAN NotesLisa NgNo ratings yet
- M5 UN NotesDocument3 pagesM5 UN NotesLisa NgNo ratings yet
- M5 Global GovernanceDocument24 pagesM5 Global GovernanceLisa NgNo ratings yet
- M6 Global North and South NotesDocument1 pageM6 Global North and South NotesLisa NgNo ratings yet
- Tailieuchung Boi Duong Hoc Sinh Gioi Luong Giac NXB Dai Hoc Quoc Gia 2014-2-8519Document116 pagesTailieuchung Boi Duong Hoc Sinh Gioi Luong Giac NXB Dai Hoc Quoc Gia 2014-2-8519Vincent TuấnNo ratings yet
- LC Jumpers Fap 203 Web PDFDocument3 pagesLC Jumpers Fap 203 Web PDFAlejandro Humberto García QuisbertNo ratings yet
- Cost Accounting Name: - ActivitiesDocument2 pagesCost Accounting Name: - ActivitiesJosh AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Sikamelt 700Document2 pagesSikamelt 700Ionut StoicaNo ratings yet
- Populorum ProgressioDocument4 pagesPopulorum ProgressioSugar JumuadNo ratings yet
- Balfour V Balfour: (1919) 2 KB 571, (1918-19) All ER860 (Court of Appeal)Document5 pagesBalfour V Balfour: (1919) 2 KB 571, (1918-19) All ER860 (Court of Appeal)Kelvin YapNo ratings yet
- User's Guide: W Ing FTP Server HelpDocument174 pagesUser's Guide: W Ing FTP Server HelpIvan Mac Gregor OviedoNo ratings yet
- Fazendo Dinheiro Com A FotografiaDocument132 pagesFazendo Dinheiro Com A FotografiaGiuseppe DecaroNo ratings yet
- Range CoderDocument11 pagesRange CoderftwilliamNo ratings yet
- LSMW - WSQ - GL Master TextDocument7 pagesLSMW - WSQ - GL Master Textpatankar.vaibhav08No ratings yet
- Zhang Ear Accupuncture Rhinititis Cold PDFDocument391 pagesZhang Ear Accupuncture Rhinititis Cold PDFanimeshNo ratings yet
- Meridian Therapy Extra Vessels 2-12-EVDocument22 pagesMeridian Therapy Extra Vessels 2-12-EVDontcho Lissiyski100% (14)
- Bloodborne Rulebook FinalDocument28 pagesBloodborne Rulebook FinalDan L'étron TurconNo ratings yet
- C. Ra 6969 - Engr. Czes BongcoDocument87 pagesC. Ra 6969 - Engr. Czes Bongcorandell vasquezNo ratings yet
- Running Times 2014-01-02.bakDocument72 pagesRunning Times 2014-01-02.bakJsueNo ratings yet
- Leonard Peltier Open Letter - Feb. 6, 2024Document3 pagesLeonard Peltier Open Letter - Feb. 6, 2024jen_benderyNo ratings yet
- Fellowes Powershred P-57Cs Paper Shredder - 3205701Document2 pagesFellowes Powershred P-57Cs Paper Shredder - 3205701papershredders100% (3)
- Ritesh M 06122022Document11 pagesRitesh M 06122022arpit yadavNo ratings yet
- Past Year Ebusiness - Pdf.crdownloadDocument5 pagesPast Year Ebusiness - Pdf.crdownloadFatin IzzahNo ratings yet
- Grupe III 2016 20171Document10 pagesGrupe III 2016 20171No RulesNo ratings yet
- Avernment of Jurisdiction Quo WarrantoDocument7 pagesAvernment of Jurisdiction Quo WarrantoBilal Yusef El Abdullah BeyNo ratings yet
- 2024 03 06 Introduction Lecture Series Climate Protection SS2024Document45 pages2024 03 06 Introduction Lecture Series Climate Protection SS2024Abdullah Khan QadriNo ratings yet
- Lymph Node PathologyDocument4 pagesLymph Node PathologyGerardLum0% (1)
- Baby Food in India AnalysisDocument4 pagesBaby Food in India AnalysisRaheetha AhmedNo ratings yet
- Tingkat Kepatuhan Minum Obat Pada Penderita Penyakit Hipertensi Di Puskesmas Kedaung Wetan Kota Tangerang Bulan Juni - Juli Tahun 2021Document6 pagesTingkat Kepatuhan Minum Obat Pada Penderita Penyakit Hipertensi Di Puskesmas Kedaung Wetan Kota Tangerang Bulan Juni - Juli Tahun 2021Ninin KepoNo ratings yet
- Preparation of Ink FinalDocument16 pagesPreparation of Ink FinalRishabh Kumud40% (5)
- International E-Marketing: Opportunities and IssuesDocument13 pagesInternational E-Marketing: Opportunities and IssuesRaluca SmarandacheNo ratings yet