Professional Documents
Culture Documents
5.2 Neutralization and Precipitation Titrimetry
5.2 Neutralization and Precipitation Titrimetry
Uploaded by
Sister RislyOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
5.2 Neutralization and Precipitation Titrimetry
5.2 Neutralization and Precipitation Titrimetry
Uploaded by
Sister RislyCopyright:
Available Formats
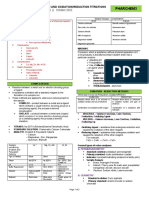
5.
2 NEUTRALIZATION AND PRECIPITATION TITRIMETRY
Ms. Melissa Calambro || October 2022 PHARCHEM3
Transcribers: Navarro
Editors: Montepio
Analytes are too weak to be titrated with water
Type of volumetric analysis based on the type of chemical reaction The limit of Moisture should be less than 0.05%
involved
1. Neutralization
Aqueous Neutralization Sample procedure:
○ Acidimetry Transfer to a conical flask about 400 mg of Methacholine
○ Alkalimetry Chloride, previously dried and accurately weighed, dissolve it in
Non-Aqueous Neutralization 50 mL of glacial acetic acid, add 10 mL of mercuric acetate TS
○ Non-aqueous Acidimetry and 1 drop of crystal violet TS, and titrate with 0.1N perchloric
○ Non-aqueous Alkalimetry acid to a blue green endpoint
2. Precipitation
Gay-Lussac's NON-AQUEOUS ACIDIMETRY
Leibig ANALYTE TIRANT / “VS” 1° INDICATOR
Standar
Mohr d
Fajan's Amines, amines Perchloric Potassium Crystal
Volhard's Salt Acid VS in Biphthalat violet
Heterocyclic Glacial e a-naphthol
3. Complexation Acetic Acid
Nitrogen benzoin
Ca, Mg, Zn, Mn, Al, Bi Compounds (or Quinaldine
3. RedOx Reaction Alkali salts of Dioxane) red
organic and Hydrogen Malachite
Permanganometry bromide
inorganic acids green
Iodine methods Amio acids
○ Iodimetry Example: Assay of
○ Iodometry Diazepam, Assay of
Metacholine Chloride
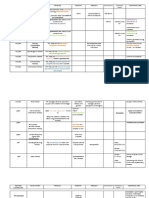
NON-AQUEOUS ACIDIMETRY
Neutralization NON-AQUEOUS NON- NON- NON-
It is a reaction between an acid and base to form water and a ACIDIMETRY AQUEOUS AQUEO AQUEOUS
salt. ACIDIMETRY US ACIDIMETRY
ACIDIM
Acidimetry ETRY
○ It is the measurement of a base of a given sample by Acid halide; acid Sodium or Lithium Benzoic Azo violet
titration with a standard solution of an acid. anhydride Methoxide in Acid Thymol
○ Analyte: Basic Amino acids; Methanol Blue
○ Carboxylic acid Thymolpht
Titrant: Acidic ; sulfuric acid or hydrochloric acid VS
Barbiturates; halein
○ Primary Standard: sodium carbonate Xanthine
○ Sample assays: Penol;
○ Direct : Sodium bicarbonate, sodium hydroxide Sulfunamide
Example: Assay of
○ Residual: Beef extract, Methenamine, Zinc
Phenyton
oxide, Rochelle salt, Milk of Magnesia (MOM)
Alkalimetry Non-aqueous solvent
○ It is the measurement of an acid of a given sample by 1. PROTOGENIC SOLVENT – proton-giving e.g. formic acid,
titration with a standard solution of a base. glacial acetic acid
○ Analyte: Acidic 2. PROTOPHILIC SOLVENT – proton-receiving e.g. ether,
○ Titrant: Basic ; sodium hydroxide VS acetic anhydride
○ Primary standard: potassium biphthalate 3. APROTIC SOLVENT – neither gives or receives e.g.
○ Sample assays: chloroform, hydrocarbon, benzene
○ Direct: hydrochloric acid, diluted phosphoric
acid, boric acid
Precipitation
○ Residual: Aspirin capsules
Also known as saturation method or precipitimetry
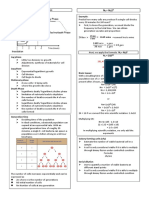
INDICATORS used in Acidimetry and Alkalimetry Reactions that involve the formation of an insoluble
SA + SB (T) → Neutral Salt - Use phenolphthalein substance.
SA (T) + SB → Neutral Salt - Use Methyl Red A substance is titrated by precipitating it with a standard
SA(T) + WB → Acidic Salt - Use Methyl Red solution of a precipitating agent.
○ It may be direct or indirect; that is the precipitating
WA + SB (T) → Basic Salt - Use phenolphthalein
agent may be added to a direct endpoint; or an
excess may be added and the excess determined by
NOTE:
titration
if the TITRANT is ACID - Use Methyl Red
if the TITRANT is BASIC - Use phenolphthalein Sample procedure:
Assay of sodium Lauryl Sulfate for sodium chloride content
Nonaqueous Neutralization Dissolve about 5g of sodium lauryl sulfate, accurately weighed
Performed when the analyte is water insoluble. in about 50 mL of water. Neutralize the solution with dilute nitric
Reactants and products react with water acid (1 in 20), using litmus paper as the indicator.
Ex. Acetic anhydride
Page 1 of 2
[PHARCHEM3] 5.2 NEUTRALIZATION AND PRECIPITATION TITRIMETRY – Ms. Melissa Calambro
Add 2 mL of potassium chromate TS, and titrate with 0.1 N
silver nitrate. Each milliliter of 0.1 N silver nitrate is equivalent to
5.844 mg of NaCl.
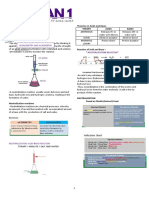
mL x N x mEq
% P or %NaCl =
g
x 100
P= percentage of the precipitate that will be formed
Where:
mL is the volume of Titrant
N is the normality of Titrant
mEq of the Analyte or substance being identified
g is the weight in grams of the Analyte
Types of Precipitimetry
Fajan (Direct Titration)
○ Involves the change of color on the surface of the
precipitate
○ Standard solution: Silver nitrate
○ Indicators: eosin, tetrabromophenolphthalein ethyl
ester (TEE) dichlorofluorescein (DCF)
○ Sample assay:
– Phenylephrine HCl
– Tubocurarine HCl
– Meperidine HCl
Volhard (Residual Titration)
○ Involves the formation of a soluble red colored
complex
○ Standard solution: potassium thiocyanate
○ Indicator: Ferric ammonium sulfate (FAS)
○ Sample assay:
– Aminophylline for theophylline
– Sodium chloride
– Dextrose and Sodium chloride injection
Mohr (Direct Titration)
○ Formation of a second precipitate which is of a
different color from the primary precipitate – It forms
a red precipitate of silver chromate which is seen
against the background of white silver chloride
○ Standard solution: silver nitrate
○ Indicator: potassium chromate
○ Sample assay:
Sodium Lauryl Sulfate for sodium chloride
content
Liebig (Direct Titration)
○ Formation of a blue colored complex
○ Standard solution: sodium tetraphenyl boron
○ Indicator: Bromophenol blue
○ Sample assay:
– Assay of organic nitrogen compounds
Gay-Lussac (Direct Titration)
○ Otherwise known as Equal turbidity method
○ Cessation of precipitate or turbidity
○ This makes use of a technique where the liquid was
drawn off from the reaction mixture and it is placed in
a spot plate. A drop of titrant is added. If turbidity of
precipitate is formed, the process is continued.
○ Standard solution: silver nitrate \No indicator is
used.
○ Sample assay: assay of sodium chloride
Page 2 of 2
You might also like
- Chem31.1 ATQ12 Santos PDFDocument3 pagesChem31.1 ATQ12 Santos PDFClaire SantosNo ratings yet
- Sims 1969Document16 pagesSims 1969Brrr BrrrNo ratings yet
- Final Coverage: Titrimetric Techniques, Gravimetric Analysis and Special MethodsDocument4 pagesFinal Coverage: Titrimetric Techniques, Gravimetric Analysis and Special MethodsKrisza LeiNo ratings yet
- Aqueous and Non-Aqueous Titrimetric AnalysisDocument3 pagesAqueous and Non-Aqueous Titrimetric AnalysisBea TorrecampoNo ratings yet
- Sodium Starch Glycolate MonographDocument2 pagesSodium Starch Glycolate MonographRGIP MagzinNo ratings yet
- Prelims HacksDocument1 pagePrelims HacksBEA FRANCINE DELOS SANTOSNo ratings yet
- 15 DetermindatioOfTheSodium PDFDocument2 pages15 DetermindatioOfTheSodium PDFRogerio CannoniNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Lab Short Procedure_240624_170626Document7 pagesChemistry Lab Short Procedure_240624_170626yogeshprasanna313No ratings yet
- AlbendazoleDocument13 pagesAlbendazoleShankar SoniNo ratings yet
- Haken 1987Document8 pagesHaken 1987Dewala KutaNo ratings yet
- Fyp Project IdeasDocument16 pagesFyp Project IdeasYusuke AyameNo ratings yet
- Principles of Neutralization TitrationDocument3 pagesPrinciples of Neutralization TitrationKeith Celine BaccayNo ratings yet
- Missing Page From - Determining Unknown Organic Compound Lab ReportDocument1 pageMissing Page From - Determining Unknown Organic Compound Lab ReportMark RileyNo ratings yet
- Wiley1931 Gravimetric and Direct Volumetric DeterminationDocument2 pagesWiley1931 Gravimetric and Direct Volumetric DeterminationLeinner José Motta TrujilloNo ratings yet
- Pharmaceutical Analysis (Module 2)Document4 pagesPharmaceutical Analysis (Module 2)Bea TorrecampoNo ratings yet
- ExperDocument2 pagesExperm.sobhy201No ratings yet
- Received 20th August, 1968: and Dilute To 1 Litre With Distilled WaterDocument5 pagesReceived 20th August, 1968: and Dilute To 1 Litre With Distilled WaterRichard MelgarejoNo ratings yet
- 5.3 Complexation and Oxidation or Reduction TitrationsDocument2 pages5.3 Complexation and Oxidation or Reduction TitrationsSister RislyNo ratings yet
- Alkalimetry - Concept MapDocument1 pageAlkalimetry - Concept MapSiegNo ratings yet
- Activity No. 9 - PHAN111 Assay of NaCl Injection Post-LabDocument15 pagesActivity No. 9 - PHAN111 Assay of NaCl Injection Post-LabAyille Dorado ArcigalNo ratings yet
- Post Lab Qc1 2019Document42 pagesPost Lab Qc1 2019Frances SaludNo ratings yet
- Acs ReagentDocument3 pagesAcs ReagentjycortesNo ratings yet
- Wad Cyanide OIA1677Document13 pagesWad Cyanide OIA1677wcenttiNo ratings yet
- UPS Mg Hydroxide pasteDocument2 pagesUPS Mg Hydroxide pasteEmil MitevNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual Synthesis of Aspirin WebDocument8 pagesLab Manual Synthesis of Aspirin WebUjwal VNo ratings yet
- Phan 5Document6 pagesPhan 5esther samonteNo ratings yet
- Basic Chemistry (Amrullah Fatahuddin)Document32 pagesBasic Chemistry (Amrullah Fatahuddin)Ferdik 69No ratings yet
- Types of Titrimetric AnalysisDocument62 pagesTypes of Titrimetric AnalysisJacqueline BaquiranNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Determination of Thiourea & Some of Its Derivatives With Nbsa Reagentquantitative Determination of Thiourea & Some of Its Derivatives With Nbsa ReagentDocument3 pagesQuantitative Determination of Thiourea & Some of Its Derivatives With Nbsa Reagentquantitative Determination of Thiourea & Some of Its Derivatives With Nbsa Reagenttieuca08No ratings yet
- Identification of Unknown Organic CompoundsDocument10 pagesIdentification of Unknown Organic CompoundsabhinickyNo ratings yet
- Titrations in Nonaqueous Solvents Model 1: Definition of Acids and Bases and General Rules in Nonaqueous TitrimetryDocument3 pagesTitrations in Nonaqueous Solvents Model 1: Definition of Acids and Bases and General Rules in Nonaqueous TitrimetryAliza EsplanadaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document9 pagesChapter 7alibel caballeroNo ratings yet
- (Calcium) Dibasic Calcium Phosphate Dihydrate(1)Document2 pages(Calcium) Dibasic Calcium Phosphate Dihydrate(1)Fiona ValenciaNo ratings yet
- Acid ValueDocument7 pagesAcid ValueQuality ProductNo ratings yet
- 10 1021@acsreagents 4012Document3 pages10 1021@acsreagents 4012Quercus AlbaNo ratings yet
- AcetazolamideDocument2 pagesAcetazolamideHage NdoNo ratings yet
- Colorimetric Test That Utilizes: Lactate+ NADDocument4 pagesColorimetric Test That Utilizes: Lactate+ NADPurple basketNo ratings yet
- Dissolution of Solids in Process Waste Streams: Queensland Alumina Limited, Gladstone, QLD, AustraliaDocument3 pagesDissolution of Solids in Process Waste Streams: Queensland Alumina Limited, Gladstone, QLD, AustraliaRogerio CannoniNo ratings yet
- Basics of Nitrite TitrationDocument19 pagesBasics of Nitrite TitrationvipulNo ratings yet
- Volumetric AnalysisDocument15 pagesVolumetric AnalysisSaraNo ratings yet
- Eb d17523 Da Gallery Nutrient Water Ebd17523 en PDFDocument32 pagesEb d17523 Da Gallery Nutrient Water Ebd17523 en PDFmarta sinagaNo ratings yet
- Determination of Nitrogen in Steel: by John Hague, Rolf A. Paulson, and Harry A. BrightDocument7 pagesDetermination of Nitrogen in Steel: by John Hague, Rolf A. Paulson, and Harry A. BrightDang Thi Kim NganNo ratings yet
- IodometryDocument24 pagesIodometrywildan jrNo ratings yet
- Zinc CarbonateDocument2 pagesZinc CarbonateKasidit SornchaiNo ratings yet
- Dispersion Polymerization of Anionic Polyacrylamide in An Aqueous Salt MediumDocument6 pagesDispersion Polymerization of Anionic Polyacrylamide in An Aqueous Salt MediumArslan ArshadNo ratings yet
- Sodium Acetate, AnhydrousDocument3 pagesSodium Acetate, AnhydrousjycortesNo ratings yet
- 4.2. Reactions of AcidsDocument1 page4.2. Reactions of AcidsAnais BegueNo ratings yet
- Usp39 - 3416 Pages 1 2Document2 pagesUsp39 - 3416 Pages 1 2Jersa Mae MaravillaNo ratings yet
- Troubleshooting Chrome PlatingDocument14 pagesTroubleshooting Chrome PlatingAditi YerudkarNo ratings yet
- NORMALDocument1 pageNORMAL1G- MAPA, KARLA MAYSONNo ratings yet
- Experiment 9 SolubilityDocument4 pagesExperiment 9 SolubilityJames GigaquitNo ratings yet
- Ethanol Estimation by Potassium Dichromate Method PDFDocument2 pagesEthanol Estimation by Potassium Dichromate Method PDFJohn33% (3)
- Determination of Ascorbic Acid (Vitamin C) and Its Compounds Bi-Voltammetric Determination With IodineDocument9 pagesDetermination of Ascorbic Acid (Vitamin C) and Its Compounds Bi-Voltammetric Determination With IodineTorkhani RachelNo ratings yet
- Determination of Ascorbic Acid (Vitamin C) and Its Compounds Bi-Voltammetric Determination With IodineDocument9 pagesDetermination of Ascorbic Acid (Vitamin C) and Its Compounds Bi-Voltammetric Determination With IodineAriana FraticelliNo ratings yet
- Ab-098 5 en PDFDocument9 pagesAb-098 5 en PDFAriana FraticelliNo ratings yet
- Determination of Ascorbic Acid (Vitamin C) and Its CompoundsDocument9 pagesDetermination of Ascorbic Acid (Vitamin C) and Its CompoundsTi MaNo ratings yet
- Ab-098 5 en PDFDocument9 pagesAb-098 5 en PDFAriana FraticelliNo ratings yet
- Determination of Ascorbic Acid (Vitamin C) and Its Compounds Bi-Voltammetric Determination With IodineDocument9 pagesDetermination of Ascorbic Acid (Vitamin C) and Its Compounds Bi-Voltammetric Determination With IodineMaria MosqueraNo ratings yet
- Kinetics and Mechanism of Reduction of Silver (I) by Ascorbic AcidDocument3 pagesKinetics and Mechanism of Reduction of Silver (I) by Ascorbic AcidPhú VõNo ratings yet
- Chapter 51Document17 pagesChapter 51Getu TolossaNo ratings yet
- Advanced Pharmaceutical analysisFrom EverandAdvanced Pharmaceutical analysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Clinical Pharmacology Reviewer. RespiDocument4 pagesClinical Pharmacology Reviewer. RespiSister RislyNo ratings yet
- Juris PDFDocument4 pagesJuris PDFSister RislyNo ratings yet
- Clinical Pharmacology ReviewerDocument12 pagesClinical Pharmacology ReviewerSister RislyNo ratings yet
- Ra 9165 - Comprehensive Dangrous Drug Act 2002Document3 pagesRa 9165 - Comprehensive Dangrous Drug Act 2002Sister RislyNo ratings yet
- Management Applications in Specific Pharmacy Practice SettingsDocument6 pagesManagement Applications in Specific Pharmacy Practice SettingsSister RislyNo ratings yet
- Report 221126 021412Document12 pagesReport 221126 021412Sister RislyNo ratings yet
- Ra 8423 - Traditional and Alternative Medicine Act of 1997Document2 pagesRa 8423 - Traditional and Alternative Medicine Act of 1997Sister RislyNo ratings yet
- Summary of Philippine AO EO MC BC PDFDocument34 pagesSummary of Philippine AO EO MC BC PDFSister RislyNo ratings yet
- Module 6 Stress Management and WellbeingDocument55 pagesModule 6 Stress Management and WellbeingSister RislyNo ratings yet
- 2.2 The Titration CurveDocument5 pages2.2 The Titration CurveSister RislyNo ratings yet
- Sampung Halamang GamotDocument5 pagesSampung Halamang GamotSister RislyNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3 Bacterial Growth CurveDocument2 pagesExperiment 3 Bacterial Growth CurveSister RislyNo ratings yet
- Gram Staining StainingDocument3 pagesGram Staining StainingSister RislyNo ratings yet
- Functions of BacteriaDocument4 pagesFunctions of BacteriaSister RislyNo ratings yet
- Aseptic and Sterilization TechniquesDocument5 pagesAseptic and Sterilization TechniquesSister RislyNo ratings yet
- 6.0 Gavimetric AnalysisDocument1 page6.0 Gavimetric AnalysisSister RislyNo ratings yet
- 5.1 Titremetric Analysis - Direct, Indirect and Residual TitrationDocument2 pages5.1 Titremetric Analysis - Direct, Indirect and Residual TitrationSister RislyNo ratings yet
- 5.3 Complexation and Oxidation or Reduction TitrationsDocument2 pages5.3 Complexation and Oxidation or Reduction TitrationsSister RislyNo ratings yet
- 7.0 Special Methods of Analysis of Crude DrugsDocument3 pages7.0 Special Methods of Analysis of Crude DrugsSister RislyNo ratings yet
- Ministry of Education Secondary Engagement Programme Grade 10 Chemistry Week 6 Lesson 2 Topic: Sub-Topic: ObjectivesDocument3 pagesMinistry of Education Secondary Engagement Programme Grade 10 Chemistry Week 6 Lesson 2 Topic: Sub-Topic: ObjectivesDaniel DowdingNo ratings yet
- Ores and Metallurgy-01 - (Theory)Document20 pagesOres and Metallurgy-01 - (Theory)Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- Unit IV - Abrasive Process and Broaching PDFDocument80 pagesUnit IV - Abrasive Process and Broaching PDFKanda SamyNo ratings yet
- Rickers Et Al-2001-Journal of Metamorphic GeologyDocument20 pagesRickers Et Al-2001-Journal of Metamorphic GeologyAmitava SahaNo ratings yet
- Molecular Control of Bioactivity in Sol-Gel GlassesDocument6 pagesMolecular Control of Bioactivity in Sol-Gel GlassesLcdaora TererelNo ratings yet
- Class IX Chapter Cell WorksheetDocument1 pageClass IX Chapter Cell WorksheetInfinity InfinityNo ratings yet
- q1l3 - 2nd Sem Physical ScienceDocument12 pagesq1l3 - 2nd Sem Physical ScienceBilly Jasper DomingoNo ratings yet
- Topics: Introduction of Printing: Tariqul Islam Wet Processing-II (WPE-343) Lecturer (TECN)Document3 pagesTopics: Introduction of Printing: Tariqul Islam Wet Processing-II (WPE-343) Lecturer (TECN)ইমরানুল শহীদ আলভীNo ratings yet
- ISO - ISO - TC 34 - SC 11 - Animal and Vegetable Fats and OilsDocument10 pagesISO - ISO - TC 34 - SC 11 - Animal and Vegetable Fats and OilsZahid Mahmood0% (1)
- Natural Polysaccharides in Drug Delivery and Biomedical Applications Hasnain Download PDF ChapterDocument51 pagesNatural Polysaccharides in Drug Delivery and Biomedical Applications Hasnain Download PDF Chapterscott.street885100% (7)
- Reference Electrode: ConstructionDocument15 pagesReference Electrode: ConstructionMeghana PNo ratings yet
- Acetic Acid MSDS: Section 1: Chemical Product and Company IdentificationDocument7 pagesAcetic Acid MSDS: Section 1: Chemical Product and Company Identificationthu hoaiNo ratings yet
- 37 MolaritywebDocument10 pages37 MolaritywebpenisNo ratings yet
- Effect of Using Potassium Bisulfate As Food Preservative Under Various ConditionsDocument15 pagesEffect of Using Potassium Bisulfate As Food Preservative Under Various Conditionsmihir khabiyaNo ratings yet
- General Guidelines For Distillation Column PDFDocument23 pagesGeneral Guidelines For Distillation Column PDFAhmed HassanNo ratings yet
- Opticlean V Liquid Alkali-V002Document6 pagesOpticlean V Liquid Alkali-V002Anonymous 5PsGXCNo ratings yet
- Natural PolymersDocument16 pagesNatural PolymersjunaidiqbalsialNo ratings yet
- Corrosion of Different Metalsalloys in Soil EnvironmentDocument29 pagesCorrosion of Different Metalsalloys in Soil Environmentsatvik shekharNo ratings yet
- Neopor - Brochure and Mix DesignDocument5 pagesNeopor - Brochure and Mix DesignYahya SalemNo ratings yet
- ChemDocument19 pagesChembrendz murNo ratings yet
- Standard Silicone HoseDocument8 pagesStandard Silicone HoseDana guNo ratings yet
- 5231 The Synthesis of N Substituted Ureas I The N Alkylation of Ureas8647Document8 pages5231 The Synthesis of N Substituted Ureas I The N Alkylation of Ureas8647Chandra ShekharNo ratings yet
- Closing The Carbon Loop in A Circular Plastics EconomyDocument37 pagesClosing The Carbon Loop in A Circular Plastics Economynganssc.119dbpNo ratings yet
- Zumdahl Chapter 13Document32 pagesZumdahl Chapter 13Master NistroNo ratings yet
- Procedures in Chemical AnalysisDocument1 pageProcedures in Chemical AnalysisMary Louwelyn GurreaNo ratings yet
- Melc No. 3: Explain How Ions Are Formed (S9Mt-Iie-F-16) : Alkaline Earth Metals Non-Metals ActinidesDocument11 pagesMelc No. 3: Explain How Ions Are Formed (S9Mt-Iie-F-16) : Alkaline Earth Metals Non-Metals ActinidesAira RamirezNo ratings yet
- Boosting Electrosynthesis of Urea From N2 and CO2 by Defective Cu-BiDocument15 pagesBoosting Electrosynthesis of Urea From N2 and CO2 by Defective Cu-BiCB Dong SuwonNo ratings yet
- DOSSIER-LE-ONE TAB (Levofloxacin 500mg)Document79 pagesDOSSIER-LE-ONE TAB (Levofloxacin 500mg)Mohammed Zubair50% (2)
- Antara Berikut, Yang Manakah Merupakan Garam?Document11 pagesAntara Berikut, Yang Manakah Merupakan Garam?Samsul ArbainNo ratings yet