Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lecture 4&5 - Measures of Central Tendency
Lecture 4&5 - Measures of Central Tendency
Uploaded by
Rae WorksCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- 11 Economics - Measures of Central Tendency - NotesDocument16 pages11 Economics - Measures of Central Tendency - NotesHimanshu Pandey100% (4)
- Module 6 Lesson 2Document16 pagesModule 6 Lesson 2Idvon CardinezNo ratings yet
- Augmented Passive Radiator Loudspeaker Systems, Part 1 PDFDocument11 pagesAugmented Passive Radiator Loudspeaker Systems, Part 1 PDFMajo Jaimes100% (1)
- Stats Lesson 4 and 5Document4 pagesStats Lesson 4 and 5VITAL, Jay Ann S.No ratings yet
- For The Students - MODULE 3 - Week 5-7 - Numerical Techniques in Describing DataDocument24 pagesFor The Students - MODULE 3 - Week 5-7 - Numerical Techniques in Describing DataAgravante LourdesNo ratings yet
- Measures of Central Tendency: Mean, Mode, Median: Soumendra RoyDocument34 pagesMeasures of Central Tendency: Mean, Mode, Median: Soumendra Roybapparoy100% (1)
- Notes 6Document6 pagesNotes 6Kyrene DizonNo ratings yet
- Measures of Central TendencyDocument13 pagesMeasures of Central TendencytheaNo ratings yet
- MATH 6200 Lesson 2 PDFDocument31 pagesMATH 6200 Lesson 2 PDFAldrien S. AllanigueNo ratings yet
- Centrall - Tendency - IVDocument53 pagesCentrall - Tendency - IVRadhika MohataNo ratings yet
- Measure of Central Tendency Grouped Data 1Document4 pagesMeasure of Central Tendency Grouped Data 1Rona Marie Bulaong100% (1)
- Chapter 4 Measures of DispersionDocument45 pagesChapter 4 Measures of Dispersionmonicabalamurugan27No ratings yet
- Module 6 Lesson 2Document15 pagesModule 6 Lesson 2Jan JanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 StatAnaDocument6 pagesLesson 2 StatAnaIya GarciaNo ratings yet
- Given The Learning Materials and Activities of This Chapter, They Will Be Able ToDocument14 pagesGiven The Learning Materials and Activities of This Chapter, They Will Be Able Toedniel maratasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3-4 Basic Stat MaterialDocument21 pagesChapter 3-4 Basic Stat Materialamanuelfitsum589No ratings yet
- Research 8 Grade 8 Melc 1 q4 Week1Document26 pagesResearch 8 Grade 8 Melc 1 q4 Week1iancyrillvillamer10No ratings yet
- Stats 3Document12 pagesStats 3Marianne Christie RagayNo ratings yet
- 1 Unnamed 04 01 2024Document66 pages1 Unnamed 04 01 2024vanchagargNo ratings yet
- Final Measures of Dispersion DR LotfiDocument54 pagesFinal Measures of Dispersion DR Lotfi1givemesome1No ratings yet
- LESSON 2 Statistical Theory-1Document22 pagesLESSON 2 Statistical Theory-1Milanie lihaylihayNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Variance (Anova)Document15 pagesAnalysis of Variance (Anova)SrijanNo ratings yet
- MMW Mod#4 StatisticsDocument6 pagesMMW Mod#4 StatisticsAldrich FelixNo ratings yet
- MCT Biost FuoDocument10 pagesMCT Biost Fuofelixebikonbowei2022No ratings yet
- Probability MC3020Document28 pagesProbability MC3020S Dinuka MadhushanNo ratings yet
- Stat Prof Ed Nov. 25 2023 MCTDocument8 pagesStat Prof Ed Nov. 25 2023 MCTLhoixhie BernardNo ratings yet
- Lesson2 1450Document43 pagesLesson2 1450gm hashNo ratings yet
- Week1-2 Chap 3 Descri DataDocument44 pagesWeek1-2 Chap 3 Descri DataPurnima KadarasenNo ratings yet
- 11 EcoDocument4 pages11 EcoSÚSHÀÍÑ M PÀLNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2b - Describing Data-NumericalDocument47 pagesLecture 2b - Describing Data-NumericalGeorge MandaNo ratings yet
- MODULE IN STATISTICS Measures Tendency VariabilityDocument23 pagesMODULE IN STATISTICS Measures Tendency VariabilityFarah Mae Mosquite-GonzagaNo ratings yet
- First Stage: Lecture ThreeDocument14 pagesFirst Stage: Lecture Three翻訳すると、40秒後に死にますOMGITZTWINZNo ratings yet
- Measures of Central TendencyDocument51 pagesMeasures of Central TendencyJeff YamsNo ratings yet
- Handnote On B-Stat.-I-chapter-3Document57 pagesHandnote On B-Stat.-I-chapter-3Kim NamjoonneNo ratings yet
- Analysis Interpretation and Use of Test DataDocument50 pagesAnalysis Interpretation and Use of Test DataJayson EsperanzaNo ratings yet
- RN6 - BEEA StatPro RN - Student's T-Distribution - SJ - MP - FINALDocument15 pagesRN6 - BEEA StatPro RN - Student's T-Distribution - SJ - MP - FINALkopii utoyyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Summarizing Numerical DataDocument8 pagesChapter 4 - Summarizing Numerical DataeviroyerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Measures of Central Tendency 21 1Document42 pagesChapter 4 - Measures of Central Tendency 21 1tantanbo222No ratings yet
- Central Tendency - Fall 20Document38 pagesCentral Tendency - Fall 20RupalNo ratings yet
- Measures of Central Tendency: (Ungrouped Data)Document24 pagesMeasures of Central Tendency: (Ungrouped Data)Alice KrodeNo ratings yet
- 3 Dispersion Skewness Kurtosis PDFDocument42 pages3 Dispersion Skewness Kurtosis PDFKelvin Kayode OlukojuNo ratings yet
- Gec004 - Module 4 - Normal Distribution and RegressionDocument84 pagesGec004 - Module 4 - Normal Distribution and RegressionDan TañoNo ratings yet
- CH 3 Describing Data: Numerical MeasuresDocument45 pagesCH 3 Describing Data: Numerical MeasuresAnnisa 'Asti' RachmawatiNo ratings yet
- Part-I Central Tendency and Dispersion: Unit-3 Basic StatisticsDocument32 pagesPart-I Central Tendency and Dispersion: Unit-3 Basic StatisticsSandip MouryaNo ratings yet
- Statistics Midterm ReviewDocument21 pagesStatistics Midterm ReviewMai NguyenNo ratings yet
- Measures of Central TendencyDocument13 pagesMeasures of Central TendencyDanica LopezNo ratings yet
- N N (1 + Ne ) : 286 Frequency DistributionDocument4 pagesN N (1 + Ne ) : 286 Frequency DistributionCyrille CastroNo ratings yet
- Q4-Math 7-M3Document6 pagesQ4-Math 7-M3Roella Mae Tudias AlodNo ratings yet
- Tech Seminar Sem 2Document35 pagesTech Seminar Sem 2Athira SajeevNo ratings yet
- Statistics Part IDocument38 pagesStatistics Part IMichelle AlejandrinoNo ratings yet
- Math 1Document7 pagesMath 1Niezel TarifeNo ratings yet
- Review On Descriptive Statistics LESSON 2 - Measures of Central TendencyDocument4 pagesReview On Descriptive Statistics LESSON 2 - Measures of Central TendencyEllora Austria RodelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 ReviewDocument12 pagesChapter 3 Reviewapi-3829767100% (1)
- Three: Mcgraw-Hill/Irwin © 2005 The Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., All Rights ReservedDocument37 pagesThree: Mcgraw-Hill/Irwin © 2005 The Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., All Rights ReservedFrazana12No ratings yet
- Lesson 6c, 7, 8Document46 pagesLesson 6c, 7, 8Fevee Joy BalberonaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Episode 3 - Measure of DispersionDocument10 pagesChapter 1 Episode 3 - Measure of DispersionAngel Ruby NovioNo ratings yet
- Probability and Statistics Lecture NotesDocument9 pagesProbability and Statistics Lecture NotesKristine Almarez100% (1)
- Chapter 1 Episode 2 - Measure of Central TendencyDocument8 pagesChapter 1 Episode 2 - Measure of Central TendencyAngel Ruby NovioNo ratings yet
- Measures of Relative StandingDocument59 pagesMeasures of Relative StandingGracean MaslogNo ratings yet
- Chapter-3ni Kamote ChuaDocument29 pagesChapter-3ni Kamote ChuaBryan GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Mansci - Chapter 3Document2 pagesMansci - Chapter 3Rae WorksNo ratings yet
- TAX Withholding TaxesDocument6 pagesTAX Withholding TaxesRae WorksNo ratings yet
- STRACOSMAN - Chapter 3Document2 pagesSTRACOSMAN - Chapter 3Rae WorksNo ratings yet
- STRACOSMAN - Chapter 5Document1 pageSTRACOSMAN - Chapter 5Rae WorksNo ratings yet
- Tax - Percentage Tax ProblemsDocument17 pagesTax - Percentage Tax ProblemsRae WorksNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Introduction To StatisticsDocument3 pagesLecture 1 - Introduction To StatisticsRae WorksNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 - Measures of VariabilityDocument3 pagesLecture 6 - Measures of VariabilityRae WorksNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Statistical Methods and Sampling TechniquesDocument2 pagesLecture 2 - Statistical Methods and Sampling TechniquesRae WorksNo ratings yet
- Research Methods For Commerce Lab Practical File "BRM Lab" BBA (M1) - BBA 213Document67 pagesResearch Methods For Commerce Lab Practical File "BRM Lab" BBA (M1) - BBA 213Mankeerat Singh ChannaNo ratings yet
- Cell City IntroDocument6 pagesCell City Intromayah12No ratings yet
- Physics Investigatory Project: Made by - Abhishek Choudhary Roll No. - 1 Class - 12 ADocument21 pagesPhysics Investigatory Project: Made by - Abhishek Choudhary Roll No. - 1 Class - 12 AShubham BaghelNo ratings yet
- ABC - Suggested Answer - 0Document8 pagesABC - Suggested Answer - 0pam pamNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Performance AppraisalDocument15 pagesReviewer Performance AppraisaljarelleNo ratings yet
- Lean Six Sigma Black Belt - BrochureDocument3 pagesLean Six Sigma Black Belt - BrochureDevraj NagarajraoNo ratings yet
- NMKV - WikipediaDocument17 pagesNMKV - WikipediaNUTHI SIVA SANTHANNo ratings yet
- Confronting The Storm: Regenerating Leadership and Hope in The Age of UncertaintyDocument38 pagesConfronting The Storm: Regenerating Leadership and Hope in The Age of UncertaintyCharlene Kronstedt100% (1)
- 0809 KarlsenDocument5 pages0809 KarlsenprateekbaldwaNo ratings yet
- Group E, F and G - Labsheet Mastercam DJJ40142Document4 pagesGroup E, F and G - Labsheet Mastercam DJJ40142Nur HaslinahNo ratings yet
- Standard CVDocument3 pagesStandard CVSurzo Chandra DasNo ratings yet
- Math WD Solns PDFDocument13 pagesMath WD Solns PDFVinceNo ratings yet
- 5 ABB Cigre Jornadas Tecnicas FCLDocument35 pages5 ABB Cigre Jornadas Tecnicas FCLmayalasan1No ratings yet
- Decisión de La FCCDocument20 pagesDecisión de La FCCEl Nuevo DíaNo ratings yet
- Fee Payment Method: Bank Islam Malaysia BerhadDocument1 pageFee Payment Method: Bank Islam Malaysia BerhadmerlinNo ratings yet
- PFW - Vol. 23, Issue 08 (August 18, 2008) Escape To New YorkDocument0 pagesPFW - Vol. 23, Issue 08 (August 18, 2008) Escape To New YorkskanzeniNo ratings yet
- Comparing Low RPM Juicers by John KohlerDocument12 pagesComparing Low RPM Juicers by John Kohlerandra_panaitNo ratings yet
- Summer Holiday Homework IdeasDocument5 pagesSummer Holiday Homework Ideasafeungtae100% (1)
- Gass Et Al v. Schlotfeldt Et Al - Document No. 4Document2 pagesGass Et Al v. Schlotfeldt Et Al - Document No. 4Justia.comNo ratings yet
- Suraj Estate Developers Limited RHPDocument532 pagesSuraj Estate Developers Limited RHPJerry SinghNo ratings yet
- 1998 McCurdy KenmareDocument8 pages1998 McCurdy Kenmarerodrigues_luisalbertoNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Anfar 2Document15 pagesJurnal Anfar 2Yulia YunaraNo ratings yet
- Computational Intelligence and Financial Markets - A Survey and Future DirectionsDocument18 pagesComputational Intelligence and Financial Markets - A Survey and Future DirectionsMarcus ViniciusNo ratings yet
- Near Source Fault Effects On The Performance of Base-Isolated Hospital Building vs. A BRBF Hospital BuildingDocument6 pagesNear Source Fault Effects On The Performance of Base-Isolated Hospital Building vs. A BRBF Hospital BuildingJosé Antonio Alarcón LeónNo ratings yet
- Corporations: Organization and Capital Stock Transaction: Corporation Second GradeDocument113 pagesCorporations: Organization and Capital Stock Transaction: Corporation Second GradePeter WagdyNo ratings yet
- SSP Assignment Problems - FinalDocument2 pagesSSP Assignment Problems - FinalVadivelan AdaikkappanNo ratings yet
- Peter Welz - ADocument4 pagesPeter Welz - AkrishfabicoipadNo ratings yet
- American Heart Association PPT - AIHA Webinar - FinalDocument49 pagesAmerican Heart Association PPT - AIHA Webinar - FinalVina WineNo ratings yet
- Manual de Instalación - Tableros Centro de Carga - Marca GEDocument4 pagesManual de Instalación - Tableros Centro de Carga - Marca GEmariana0% (1)
Lecture 4&5 - Measures of Central Tendency
Lecture 4&5 - Measures of Central Tendency
Uploaded by
Rae WorksOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Lecture 4&5 - Measures of Central Tendency
Lecture 4&5 - Measures of Central Tendency
Uploaded by
Rae WorksCopyright:
Available Formats
STATAPP: STATISTICAL ANALYSIS WITH SOFTWARE APPLICATION
CHAPTER 4 & 5: Measures of Central Tendency
MX. LEOPOLDO A. LIANGCO JR – DHVSU COLLEGE OF BUSINESS STUDIES
BS ACCOUNTANCY | 1ST SEMESTER A.Y. 2022-2023
MEASURES OF CENTRAL TENDENCY Problem:
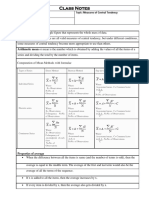
• The measure of central tendency refers to ◼ Compute the average grade of a certain student
measures, which describes the middle or the for a particular semester given his grades as
center of the distribution. It is a central reference follows:
value which is usually close to the point of greater Number of Units Course Code Final Grade
3 units Stat App 1.25
concentration of the measurements and may in 6 units Chem 1 1.50
some sense be thought to typify the whole set. 3 units Literature 1.75
• It is also a value used to represent a set of 3 units Sociology 1.75
observations or frequencies. Solution:
x W (Weight) WX
1.25 3 3.75
MEAN 1.50 6 9
◼ Arithmetic average or arithmetic mean is defined 1.75 3 5.25
as the sum of the values in the data group 1.75 3 5.25
∑ 𝑿𝒘 ∑ 𝟐𝟑.𝟐𝟓
divided by the number of values. WX = = = 1.55
∑𝐰 𝟏𝟓
◼ It is also a value used to represent a set of
observations or frequencies.
Find the weighted mean of the three groups of means
Mean for Ungrouped Data
below:
Formula: Group 1 Group 2 Group 3
◼ X = ∑𝑋 X1 = 60 X1 = 50 X1 = 70
n W1= 10 W1= 60 W1= 30
Where: x = the mean
n = is the sample data ∑Xw = X1w1 + X2w2 + X3w3
∑ 𝑥 = the sum of all measures = (60)(10) + (50)(60) + (70)(30)
= 5700
Example A.
Find the mean of the following set of observations: ∑w = N = 10 + 60 + 30
1) 14, 16, 18, 20, 22 – Answer: 18 = 100
2) 21, 26, 25, 28, 35, 36, 37, 38, 29 – Answer 30.56
5700
3) Scores Of 30 Students in Midterm Examination Wx = = 57
100
88 86 90 92 75
89 79 97 87 79
78 88 73 83 99 THE MEDIAN
74 98 79 76 91 • It is the value of the middle observation in an
90 83 99 84 92 ordered distribution.
75 77 100 86 76 • It is the value or score that divides the ranked
Formula: distribution into two equal parts.
◼ X = ∑𝑋 • The score or class in a distribution below the
N median is where 50% of the scores fall and
= 2563 above where the other 50% lies.
30 • Appropriate to use as measure of average for
distribution containing open-ended class
The Weighted Mean intervals.
• The given groups of data are the average of • Used when the data are ordinal.
means of all the groups.
• Sometimes, some values are given more • To find the median for ungrouped data, we
importance than others. In such cases, the arrange the data first from the highest value to
weighted mean is computed. the lowest or vice versa. The middle value is
Weighted Mean Formula: the median in the distribution.
∑ 𝑿𝒘 ∑𝐗𝐰 a. If there is odd number of observations,
WX = ∑𝐰 = 𝑵
the middle value is the median.
Where: b. If there is an even number of
WX = the weighted mean observations, the median is the sum of
w = the weight of X the middle two scores divided by 2.
∑Xw = the sum of the weight of X’s
∑w = the sum of the weight of W or (N) / total
number of weights
Mind over matter.
STATAPP: STATISTICAL ANALYSIS WITH SOFTWARE APPLICATION
CHAPTER 4 & 5: Measures of Central Tendency
MX. LEOPOLDO A. LIANGCO JR – DHVSU COLLEGE OF BUSINESS STUDIES
BS ACCOUNTANCY | 1ST SEMESTER A.Y. 2022-2023
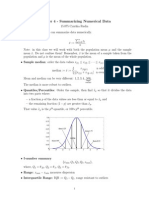
Example: Other Measures of Locations (Quantiles)
1. Find the median of the following numbers: • Quartiles, Deciles, Percentiles
15, 11, 14, 3, 21, 17, 22, 16, 19, 16, 5, 7, 19, 8, 9, 20, 4 • To understand the concept of quartiles, let us take
Answer to (1) Arrange data from lowest to highest the percentile or centiles. A percentile is a point in
3, 4, 5, 7, 8, 9, 11, 14, 15, 16, 16, 17, 19, 19, 20, 21, 22 a distribution below which a given percent of
cases lie.
n = 17, since it is odd, middle value is (n+1)/2 • For example, the 60th percentile or P60 is the
n = (17+1)/2 point or score in a distribution below which 60% of
= 18/2 the cases lie.
= 9th data which is 15. • If the 60th percentile is equal to 75, that is P60 in
2. Find the median of the set of observations if a distribution of scores given to freshmen
observation 22 is deleted. entrance in a certain college, a student who got 75
3, 4, 5, 7, 8, 9, 11, 14, 15, 16, 16, 17, 19, 19, 20, 21 in the admission examination surpassed 60% of
To determine the middle values, first determine the cases with only 40% examinees higher than
𝒏 𝟏𝟔 his grade.
= = 𝟖𝒕𝒉
𝟐 𝟐
The median: (8th data + 9th data)/2 Formula:
14+15
= 2 • Location of Percentile (Note: arrange data from
= 14.5 lowest to highest to locate percentile)
𝑃
𝑷𝒏 = (𝒏 + 𝟏) 100
Find the median of these quiz scores: Where:
5, 10, 8, 6, 4, 8, 2, 5, 7, 7 P = percentile point
n = sample size
SOLUTION:
We start by listing the data in order: Example:
2, 4, 5, 5, 6, 7, 7, 8, 8, 10 a. Find the 20th percentile or P20 of the following
Since there are 10 data values, an even number, there is scores
no one middle number. Raw Data 17 20 6 8 22 16 5 25 12
So, we find the mean of the two middle numbers, 6 and 7, Array 5 6 8 12 16 17 20 22 25
and get (6+7)/2 = 6.5. b. Find the 60th percentile or P60 of the following
The median quiz score was 6.5. scores
Array 60 70 75 80 95 99
Answers:
The Mode
• The mode is the value or item in a distribution with 20
the highest frequency, denoted by Mo. a. To locate: P20 = (𝒏 + 𝟏) 100, n = 9
• When there are two values with the same 20
P20 = (9 + 𝟏) 100 = 2nd (location)
frequency and they are the highest in the
distribution, each value may be considered as the Array 5 6 8 12 16 17 20 22 25
mode, and the distribution is bimodal.
• For ungrouped data, it requires no calculation b. To locate: P60 = (𝒏 + 𝟏) 100, n = 6
60
only counting. 60
• Some distributions have one or more modes, but P20 = (6 + 𝟏) 100 = 4.2 (location)
some have none. To find the value corresponding to the 60 th
percentile, you would locate the 4th value and 5th
Example. Determine the Mode for the following value and determine the distance between the two
Ungrouped Data values. Next, multiply this difference by 0.8 and
a. 16, 28, 28, 28, 17, 16, 22, 19 add the result of the smaller value. The result
Ans. Mo = 28 (unimodal) would be the 60th percentile.
b. 5, 8, 24, 24, 24, 17, 17, 17, 36, Array 60 70 75 80 95 99
Ans. Mo= 24, 17 (bimodal)
c. 39, 39, 12, 18, 18, 27, 13, 44, 45, 45 Therefore, P60 = 80 + .2(95-80)
Ans. Mo=39, 18, 45 (trimodal) 60th percentile or P60 = 83
d. 4, 5, 8, 9, 12, 15, 19, 20
Ans. No mode
Mind over matter.
STATAPP: STATISTICAL ANALYSIS WITH SOFTWARE APPLICATION
CHAPTER 4 & 5: Measures of Central Tendency
MX. LEOPOLDO A. LIANGCO JR – DHVSU COLLEGE OF BUSINESS STUDIES
BS ACCOUNTANCY | 1ST SEMESTER A.Y. 2022-2023
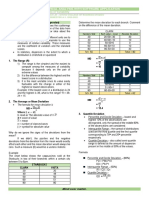
Location of the Quartiles – data is divided into 4 parts. Example 02:
Quartile points (First, Second, Third) FINACC ACCTG Frequency Midpoint fM
SCORES (f) (M)
First Quartile Second Quartile is Third Quartile 40-49 5 44.5 222.5
1 3
Q1 = (𝒏 + 𝟏) 4 also the median Q3 = (𝒏 + 𝟏) 4 50-59 5 54.5 272.5
60-69 11 64.5 709.5
Location of the Deciles – data is divided into 10 parts (D1, 70-79 14 74.5 1043
D2,… D9) 80-89 8 84.5 676
Let’s say: Locate 90-99 7 94.5 661.5
Second Decile Point 7th Decile Point N = 50 ∑ = 3585
2 7
D2 = (𝒏 + 𝟏) 10 D7 = (𝒏 + 𝟏) 10
Solution:
∑𝑓𝑀
◼ X = 𝑁
Note: Procedure for determining quartile and decile points 3585
from the data is the same as Percentiles. ◼ = = 71.70
50
MEASURES OF CENTRAL TENDENCY 02 MEDIAN for Grouped Data
MEAN for Grouped Data Formula:
𝑁−𝐹
Formula: Mdn = L + 2
(i)
𝑓𝑀
◼ X = ∑𝑋
N Where:
Where: X = the mean L = exact lower limit/ boundary of interval containing
Fm = product of each midpoint and the median class
the corresponding frequency F = the sum of frequencies or CF below median class
N = number of class Fm = frequency of interval containing the
median class
Problem 01: N = total number of cases
◼ The Umasa Pero Di Pinaglaban Management i = interval size
* Median class is the class interval where N/2 interval
Class took an online examination in Cost is found
Accounting subject. The 40 students have tallied
their scores via frequency distribution. Find the
Class Interval f M fM <Cf
mean using the grouped data formula.
25-29 1 27 27 1
30-34 0 32 0 1
Example: Find the Mean using grouped data
35-39 3 37 111 4
Class Interval f M fM 40-44 6 42 252 10
25-29 1 27 27 45-49 6 47 282 16
30-34 0 32 0 50-54 6 52 312 22
55-59 7 57 399 29
35-39 3 37 111
60-64 4 62 248 33
40-44 6 42 252
65-69 4 67 268 37
45-49 6 47 282
70-74 1 72 72 38
50-54 6 52 312
75-79 1 77 77 39
55-59 7 57 399
80-84 1 82 82 40
60-64 4 62 248 ∑ = 2130
65-69 4 67 268 N = 40
70-74 1 72 72 𝑁−𝐹 fM F
75-79 1 77 77 Mdn =L+ 2
(i)
80-84 1 82 82 𝑓𝑀 Median Class
(20−16)
N = 40 ∑ = 2130 = 49.5 + 6 (5)
Solution: = 49.5 + 3.33
◼ X = 𝑁
∑𝑓𝑀 = 52.83
2130
◼ = = 53.25
40
Mind over matter.
STATAPP: STATISTICAL ANALYSIS WITH SOFTWARE APPLICATION
CHAPTER 4 & 5: Measures of Central Tendency
MX. LEOPOLDO A. LIANGCO JR – DHVSU COLLEGE OF BUSINESS STUDIES
BS ACCOUNTANCY | 1ST SEMESTER A.Y. 2022-2023
Compute the Median of the test scores:
Class Interval f M <Cf
16-20 2 18 2
21-25 7 23 9
26-30 14 28 23
31-35 8 33 31
36-40 8 38 39
41-45 1 43 40
𝑁−𝐹
Mdn =L+ 2
(i)
𝑓𝑀
(20−9)
= 25.5 + 14 (5)
= 25.5 + 3.93
= 29.43
MODE for Grouped Data
Formula:
𝑑1
Md =L+ (i)
𝑑1+𝑑2
Where:
L = exact lowest limit/boundary of interval containing the
modal class
d1 = difference between the frequency in the modal class
and the frequency in the preceding class interval
d2 = difference between the frequency in the modal class
and the frequency in the succeeding class interval
i = interval size
Compute the mode of the test scores.
Class Interval f <Cf
16-20 2 2
21-25 7 9
26-30 14 23
31-35 8 31
36-40 8 39
41-45 1 40
Modal class: 26-30
L = (26-25)/2 = 25.5
D1 = 14 – 7 = 7
D2 = 14 – 8 = 6
I=5
Formula:
7
Md = 25.5 + (5)
7+6
7
= 25.5 + 13 (5)
= 25.5 + (.538) (5)
= 25.5 + 2.69
Md = 28.19
Mind over matter.
You might also like
- 11 Economics - Measures of Central Tendency - NotesDocument16 pages11 Economics - Measures of Central Tendency - NotesHimanshu Pandey100% (4)
- Module 6 Lesson 2Document16 pagesModule 6 Lesson 2Idvon CardinezNo ratings yet
- Augmented Passive Radiator Loudspeaker Systems, Part 1 PDFDocument11 pagesAugmented Passive Radiator Loudspeaker Systems, Part 1 PDFMajo Jaimes100% (1)
- Stats Lesson 4 and 5Document4 pagesStats Lesson 4 and 5VITAL, Jay Ann S.No ratings yet
- For The Students - MODULE 3 - Week 5-7 - Numerical Techniques in Describing DataDocument24 pagesFor The Students - MODULE 3 - Week 5-7 - Numerical Techniques in Describing DataAgravante LourdesNo ratings yet
- Measures of Central Tendency: Mean, Mode, Median: Soumendra RoyDocument34 pagesMeasures of Central Tendency: Mean, Mode, Median: Soumendra Roybapparoy100% (1)
- Notes 6Document6 pagesNotes 6Kyrene DizonNo ratings yet
- Measures of Central TendencyDocument13 pagesMeasures of Central TendencytheaNo ratings yet
- MATH 6200 Lesson 2 PDFDocument31 pagesMATH 6200 Lesson 2 PDFAldrien S. AllanigueNo ratings yet
- Centrall - Tendency - IVDocument53 pagesCentrall - Tendency - IVRadhika MohataNo ratings yet
- Measure of Central Tendency Grouped Data 1Document4 pagesMeasure of Central Tendency Grouped Data 1Rona Marie Bulaong100% (1)
- Chapter 4 Measures of DispersionDocument45 pagesChapter 4 Measures of Dispersionmonicabalamurugan27No ratings yet
- Module 6 Lesson 2Document15 pagesModule 6 Lesson 2Jan JanNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 StatAnaDocument6 pagesLesson 2 StatAnaIya GarciaNo ratings yet
- Given The Learning Materials and Activities of This Chapter, They Will Be Able ToDocument14 pagesGiven The Learning Materials and Activities of This Chapter, They Will Be Able Toedniel maratasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3-4 Basic Stat MaterialDocument21 pagesChapter 3-4 Basic Stat Materialamanuelfitsum589No ratings yet
- Research 8 Grade 8 Melc 1 q4 Week1Document26 pagesResearch 8 Grade 8 Melc 1 q4 Week1iancyrillvillamer10No ratings yet
- Stats 3Document12 pagesStats 3Marianne Christie RagayNo ratings yet
- 1 Unnamed 04 01 2024Document66 pages1 Unnamed 04 01 2024vanchagargNo ratings yet
- Final Measures of Dispersion DR LotfiDocument54 pagesFinal Measures of Dispersion DR Lotfi1givemesome1No ratings yet
- LESSON 2 Statistical Theory-1Document22 pagesLESSON 2 Statistical Theory-1Milanie lihaylihayNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Variance (Anova)Document15 pagesAnalysis of Variance (Anova)SrijanNo ratings yet
- MMW Mod#4 StatisticsDocument6 pagesMMW Mod#4 StatisticsAldrich FelixNo ratings yet
- MCT Biost FuoDocument10 pagesMCT Biost Fuofelixebikonbowei2022No ratings yet
- Probability MC3020Document28 pagesProbability MC3020S Dinuka MadhushanNo ratings yet
- Stat Prof Ed Nov. 25 2023 MCTDocument8 pagesStat Prof Ed Nov. 25 2023 MCTLhoixhie BernardNo ratings yet
- Lesson2 1450Document43 pagesLesson2 1450gm hashNo ratings yet
- Week1-2 Chap 3 Descri DataDocument44 pagesWeek1-2 Chap 3 Descri DataPurnima KadarasenNo ratings yet
- 11 EcoDocument4 pages11 EcoSÚSHÀÍÑ M PÀLNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2b - Describing Data-NumericalDocument47 pagesLecture 2b - Describing Data-NumericalGeorge MandaNo ratings yet
- MODULE IN STATISTICS Measures Tendency VariabilityDocument23 pagesMODULE IN STATISTICS Measures Tendency VariabilityFarah Mae Mosquite-GonzagaNo ratings yet
- First Stage: Lecture ThreeDocument14 pagesFirst Stage: Lecture Three翻訳すると、40秒後に死にますOMGITZTWINZNo ratings yet
- Measures of Central TendencyDocument51 pagesMeasures of Central TendencyJeff YamsNo ratings yet
- Handnote On B-Stat.-I-chapter-3Document57 pagesHandnote On B-Stat.-I-chapter-3Kim NamjoonneNo ratings yet
- Analysis Interpretation and Use of Test DataDocument50 pagesAnalysis Interpretation and Use of Test DataJayson EsperanzaNo ratings yet
- RN6 - BEEA StatPro RN - Student's T-Distribution - SJ - MP - FINALDocument15 pagesRN6 - BEEA StatPro RN - Student's T-Distribution - SJ - MP - FINALkopii utoyyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Summarizing Numerical DataDocument8 pagesChapter 4 - Summarizing Numerical DataeviroyerNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Measures of Central Tendency 21 1Document42 pagesChapter 4 - Measures of Central Tendency 21 1tantanbo222No ratings yet
- Central Tendency - Fall 20Document38 pagesCentral Tendency - Fall 20RupalNo ratings yet
- Measures of Central Tendency: (Ungrouped Data)Document24 pagesMeasures of Central Tendency: (Ungrouped Data)Alice KrodeNo ratings yet
- 3 Dispersion Skewness Kurtosis PDFDocument42 pages3 Dispersion Skewness Kurtosis PDFKelvin Kayode OlukojuNo ratings yet
- Gec004 - Module 4 - Normal Distribution and RegressionDocument84 pagesGec004 - Module 4 - Normal Distribution and RegressionDan TañoNo ratings yet
- CH 3 Describing Data: Numerical MeasuresDocument45 pagesCH 3 Describing Data: Numerical MeasuresAnnisa 'Asti' RachmawatiNo ratings yet
- Part-I Central Tendency and Dispersion: Unit-3 Basic StatisticsDocument32 pagesPart-I Central Tendency and Dispersion: Unit-3 Basic StatisticsSandip MouryaNo ratings yet
- Statistics Midterm ReviewDocument21 pagesStatistics Midterm ReviewMai NguyenNo ratings yet
- Measures of Central TendencyDocument13 pagesMeasures of Central TendencyDanica LopezNo ratings yet
- N N (1 + Ne ) : 286 Frequency DistributionDocument4 pagesN N (1 + Ne ) : 286 Frequency DistributionCyrille CastroNo ratings yet
- Q4-Math 7-M3Document6 pagesQ4-Math 7-M3Roella Mae Tudias AlodNo ratings yet
- Tech Seminar Sem 2Document35 pagesTech Seminar Sem 2Athira SajeevNo ratings yet
- Statistics Part IDocument38 pagesStatistics Part IMichelle AlejandrinoNo ratings yet
- Math 1Document7 pagesMath 1Niezel TarifeNo ratings yet
- Review On Descriptive Statistics LESSON 2 - Measures of Central TendencyDocument4 pagesReview On Descriptive Statistics LESSON 2 - Measures of Central TendencyEllora Austria RodelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 ReviewDocument12 pagesChapter 3 Reviewapi-3829767100% (1)
- Three: Mcgraw-Hill/Irwin © 2005 The Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., All Rights ReservedDocument37 pagesThree: Mcgraw-Hill/Irwin © 2005 The Mcgraw-Hill Companies, Inc., All Rights ReservedFrazana12No ratings yet
- Lesson 6c, 7, 8Document46 pagesLesson 6c, 7, 8Fevee Joy BalberonaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Episode 3 - Measure of DispersionDocument10 pagesChapter 1 Episode 3 - Measure of DispersionAngel Ruby NovioNo ratings yet
- Probability and Statistics Lecture NotesDocument9 pagesProbability and Statistics Lecture NotesKristine Almarez100% (1)
- Chapter 1 Episode 2 - Measure of Central TendencyDocument8 pagesChapter 1 Episode 2 - Measure of Central TendencyAngel Ruby NovioNo ratings yet
- Measures of Relative StandingDocument59 pagesMeasures of Relative StandingGracean MaslogNo ratings yet
- Chapter-3ni Kamote ChuaDocument29 pagesChapter-3ni Kamote ChuaBryan GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Mansci - Chapter 3Document2 pagesMansci - Chapter 3Rae WorksNo ratings yet
- TAX Withholding TaxesDocument6 pagesTAX Withholding TaxesRae WorksNo ratings yet
- STRACOSMAN - Chapter 3Document2 pagesSTRACOSMAN - Chapter 3Rae WorksNo ratings yet
- STRACOSMAN - Chapter 5Document1 pageSTRACOSMAN - Chapter 5Rae WorksNo ratings yet
- Tax - Percentage Tax ProblemsDocument17 pagesTax - Percentage Tax ProblemsRae WorksNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Introduction To StatisticsDocument3 pagesLecture 1 - Introduction To StatisticsRae WorksNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 - Measures of VariabilityDocument3 pagesLecture 6 - Measures of VariabilityRae WorksNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Statistical Methods and Sampling TechniquesDocument2 pagesLecture 2 - Statistical Methods and Sampling TechniquesRae WorksNo ratings yet
- Research Methods For Commerce Lab Practical File "BRM Lab" BBA (M1) - BBA 213Document67 pagesResearch Methods For Commerce Lab Practical File "BRM Lab" BBA (M1) - BBA 213Mankeerat Singh ChannaNo ratings yet
- Cell City IntroDocument6 pagesCell City Intromayah12No ratings yet
- Physics Investigatory Project: Made by - Abhishek Choudhary Roll No. - 1 Class - 12 ADocument21 pagesPhysics Investigatory Project: Made by - Abhishek Choudhary Roll No. - 1 Class - 12 AShubham BaghelNo ratings yet
- ABC - Suggested Answer - 0Document8 pagesABC - Suggested Answer - 0pam pamNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Performance AppraisalDocument15 pagesReviewer Performance AppraisaljarelleNo ratings yet
- Lean Six Sigma Black Belt - BrochureDocument3 pagesLean Six Sigma Black Belt - BrochureDevraj NagarajraoNo ratings yet
- NMKV - WikipediaDocument17 pagesNMKV - WikipediaNUTHI SIVA SANTHANNo ratings yet
- Confronting The Storm: Regenerating Leadership and Hope in The Age of UncertaintyDocument38 pagesConfronting The Storm: Regenerating Leadership and Hope in The Age of UncertaintyCharlene Kronstedt100% (1)
- 0809 KarlsenDocument5 pages0809 KarlsenprateekbaldwaNo ratings yet
- Group E, F and G - Labsheet Mastercam DJJ40142Document4 pagesGroup E, F and G - Labsheet Mastercam DJJ40142Nur HaslinahNo ratings yet
- Standard CVDocument3 pagesStandard CVSurzo Chandra DasNo ratings yet
- Math WD Solns PDFDocument13 pagesMath WD Solns PDFVinceNo ratings yet
- 5 ABB Cigre Jornadas Tecnicas FCLDocument35 pages5 ABB Cigre Jornadas Tecnicas FCLmayalasan1No ratings yet
- Decisión de La FCCDocument20 pagesDecisión de La FCCEl Nuevo DíaNo ratings yet
- Fee Payment Method: Bank Islam Malaysia BerhadDocument1 pageFee Payment Method: Bank Islam Malaysia BerhadmerlinNo ratings yet
- PFW - Vol. 23, Issue 08 (August 18, 2008) Escape To New YorkDocument0 pagesPFW - Vol. 23, Issue 08 (August 18, 2008) Escape To New YorkskanzeniNo ratings yet
- Comparing Low RPM Juicers by John KohlerDocument12 pagesComparing Low RPM Juicers by John Kohlerandra_panaitNo ratings yet
- Summer Holiday Homework IdeasDocument5 pagesSummer Holiday Homework Ideasafeungtae100% (1)
- Gass Et Al v. Schlotfeldt Et Al - Document No. 4Document2 pagesGass Et Al v. Schlotfeldt Et Al - Document No. 4Justia.comNo ratings yet
- Suraj Estate Developers Limited RHPDocument532 pagesSuraj Estate Developers Limited RHPJerry SinghNo ratings yet
- 1998 McCurdy KenmareDocument8 pages1998 McCurdy Kenmarerodrigues_luisalbertoNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Anfar 2Document15 pagesJurnal Anfar 2Yulia YunaraNo ratings yet
- Computational Intelligence and Financial Markets - A Survey and Future DirectionsDocument18 pagesComputational Intelligence and Financial Markets - A Survey and Future DirectionsMarcus ViniciusNo ratings yet
- Near Source Fault Effects On The Performance of Base-Isolated Hospital Building vs. A BRBF Hospital BuildingDocument6 pagesNear Source Fault Effects On The Performance of Base-Isolated Hospital Building vs. A BRBF Hospital BuildingJosé Antonio Alarcón LeónNo ratings yet
- Corporations: Organization and Capital Stock Transaction: Corporation Second GradeDocument113 pagesCorporations: Organization and Capital Stock Transaction: Corporation Second GradePeter WagdyNo ratings yet
- SSP Assignment Problems - FinalDocument2 pagesSSP Assignment Problems - FinalVadivelan AdaikkappanNo ratings yet
- Peter Welz - ADocument4 pagesPeter Welz - AkrishfabicoipadNo ratings yet
- American Heart Association PPT - AIHA Webinar - FinalDocument49 pagesAmerican Heart Association PPT - AIHA Webinar - FinalVina WineNo ratings yet
- Manual de Instalación - Tableros Centro de Carga - Marca GEDocument4 pagesManual de Instalación - Tableros Centro de Carga - Marca GEmariana0% (1)