Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Asm 8671
Asm 8671
Uploaded by
Taranpreet KaurOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Asm 8671
Asm 8671
Uploaded by
Taranpreet KaurCopyright:
Available Formats
TERM-II
DATE: January 25, 2021
CLASS-7
SCIENCE
CH-15: LIGHT
WORKSHEET-14
SUB-TOPIC: Important Notes + Back Exercises
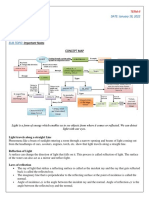
Lenses
Refraction
The bending of the path of light when it moves from one medium to another is known as refraction.
The object we see after refraction is called the apparent object.
There exists some displacement between the apparent and actual object.
To know more about Refraction of Light, visit here.
Image formation by lenses
Convex lens forms a real, inverted and diminished image. When the object is placed very close the lens
the image formed is erect, virtual and magnified. They are also called as converging lens. This type of
lens is also used as a magnifying glass.
Concave lens always forms a virtual, erect and diminished image. They are also called as diverging lens.
They are used as camera lenses and binoculars.
To know more about Image Formation by Lenses, visit here.
Dispersion of white light through prism
Sunlight may appear as white but in fact, is made up of seven component colours. This can be observed
when a beam of sunlight is passed through a triangular prism or when light falls on a compact disk (CD).
The seven colours that appear are violet, indigo, blue, green, yellow, orange and red. These are also the
colours of a rainbow we see after a rainfall.
The splitting of white light into its component colours is called dispersion.
Back Exercises
Q.1.Fill in the blanks:
(a) An image that cannot be obtained on a screen is called ___________ .
(b) Image formed by a convex is __________ always virtual and smaller in size.
(c) An image formed by a __________ mirror is always of the same size as that of the object.
(d) An image which can be obtained on a screen is called a __________ image.
(e) An image formed by a concave __________ cannot be obtained on a screen.
Ans.(a) virtual image (b) mirror (c) plane (d) real (e) lens
Q.2.Mark ‘T’ if the statement is true and ‘F’ if it is false:
(a) We can obtain an enlarged and erect image by a convex mirror. (T/F)
(b) A concave lens always form a virtual image. (T/F)
(c) We can obtain a real, enlarged and inverted image by a concave mirror. (T/F)
(d) A real image cannot be obtained on a screen. (T/F)
(e) A concave mirror always form a real image. (T/F)
Ans. a) F (b) T (c) T (d) F (e) F
Q.3. Match the items given in Column I with one or more items of Column II
Ans.
Q.4.State the characteristics of the image formed by a plane mirror.
Ans. (i) Plane mirror forms an erect image.
(ii) It forms a virtual image.
(iii) Size of the image is same as that of the object.
(iv)Image is formed at the same distance behind the mirror as the object stands in front of it.
(v) Image formed is a laterally inverted image i.e., right hand side of the object seems to be the left hand side
and vice-versa.
Q.5.Find out the letters of English alphabet or any other language known to you in which the image
formed in a plane mirror appears exactly like the letter itself. Discuss your findings.
Ans. Letters like A, H, I, M, O, T, U, V, W etc. appear same when seen through a plane mirror
Q.6.What is a virtual image? Give one situation where a virtual image is formed.
Ans. The image which cannot be taken on a screen is called virtual image. When some object is placed very
close to the concave mirror we don’t get any image on the white screen placed behind the mirror. Such image is
called virtual image.
Q.7. State two differences between a convex and a concave lens.
Q.8. Give one use each of a concave and a convex mirror.
Ans. Use of concave mirror: Concave mirror is used by dentists to examine the teeth.
Use of convex mirror: Convex mirror is used as side view mirror in vehicles.
Q.9. Which type of mirror can form a real image?
Ans. Concave mirror can form a real image.
Q.10. Which type of lens forms always a virtual image?
Ans. Concave lens always forms a virtual image.
Q.11. A virtual image larger than the object can be produced by a
(i) concave lens (ii) concave mirror (iii) convex mirror (iv) plane mirror
Ans. (ii) concave mirror
Q.12. David is observing his image in a plane mirror. Die distance between the mirror and his image is 4
m. If he moves 1 m towards the mirror, then the distance between David and his image will be
(i) 3 m (ii) 5 m (iii) 6 m (iv) 8 m
Ans. (iii) 6 m
Q.13. The rear view mirror of a car is a plane mirror. A driver is reversing his car at a speed of 2 m/s.
The driver sees in his rear mew mirror the image of a truck parked behind his car. The speed at which
the image of the truck appears to approach the driver will be
(i) 1 m/s (ii) 2 m/s (iii) 4 m/s {iv) 8 m/s
Ans. (ii) 4 m/s
You might also like
- Detailed Lesson PLan - Image Formation by LensesDocument9 pagesDetailed Lesson PLan - Image Formation by LensesCyril Cauilan100% (1)
- Questions On Mirrors and LensesDocument29 pagesQuestions On Mirrors and LensesKamal Naser100% (2)
- NCERT Solutions Class 7 Science Chapter 15 LightDocument5 pagesNCERT Solutions Class 7 Science Chapter 15 LightJAI PRAJEN PRO HACKERNo ratings yet
- Light Class 7Document4 pagesLight Class 7Shaurya ManiktalaNo ratings yet
- NCERT Solutions For Class 7 April 3 Science Chapter 15 LightDocument4 pagesNCERT Solutions For Class 7 April 3 Science Chapter 15 LightEsha GuptaNo ratings yet
- CH 15Document5 pagesCH 15devarajramadoss78No ratings yet
- NCERT G7 BOC Physics Ch-15-LightDocument6 pagesNCERT G7 BOC Physics Ch-15-LightTapan Kumar NayakNo ratings yet
- Chapter Light Class 7 Chapter Q and ADocument9 pagesChapter Light Class 7 Chapter Q and ADaiwik GuptaNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Answers - Vii - Light (Part 2)Document6 pagesWorksheet Answers - Vii - Light (Part 2)Suvam Dasgupta100% (1)
- 15 - Science - LightDocument5 pages15 - Science - LightRENJITH PAINo ratings yet
- 08 Science Light 01Document5 pages08 Science Light 01Ranjan RoyNo ratings yet
- NCERT Exemplar Solution Class 7 Science Chapter 15Document7 pagesNCERT Exemplar Solution Class 7 Science Chapter 15deepak.idea84No ratings yet
- Light Case Study QuestionDocument5 pagesLight Case Study Questionkrishavsurya259No ratings yet
- LIGHTDocument3 pagesLIGHTlearnershubbeenaNo ratings yet
- GR 7 - LIGHT - ANSWER KEYDocument3 pagesGR 7 - LIGHT - ANSWER KEYJoseph JayakanthanNo ratings yet
- 10 Science NcertSolutions Chapter 10 ExercisesDocument9 pages10 Science NcertSolutions Chapter 10 Exercisesvikas9saraswatNo ratings yet
- Module 6Document9 pagesModule 6chef curryNo ratings yet
- Science 10 Module 2 Week 6-8 - MabiniDocument27 pagesScience 10 Module 2 Week 6-8 - MabiniChristine Joy EngoNo ratings yet
- Worksheet - Answers - VII - LIGHT (PART 1)Document9 pagesWorksheet - Answers - VII - LIGHT (PART 1)Suvam DasguptaNo ratings yet
- Science10 Q2 E7 SLMDocument5 pagesScience10 Q2 E7 SLMCaryll BaylonNo ratings yet
- Module in Grade 10 (Plane Mirrors)Document13 pagesModule in Grade 10 (Plane Mirrors)Jenalyn NacasabugNo ratings yet
- 7th ch-16 Light and Its Reflaction Solution Living ScienceDocument3 pages7th ch-16 Light and Its Reflaction Solution Living SciencesabletarsingNo ratings yet
- Physics Revision Worksheet Grade X ChlightDocument3 pagesPhysics Revision Worksheet Grade X ChlightKhushi AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Class 7 Chapter 12 LightDocument12 pagesClass 7 Chapter 12 Lightsiddharthsg37No ratings yet
- Kuuw H8 Ajn ZMN4 OOhiatit 0 X 11 LYs 2 VNVDocument2 pagesKuuw H8 Ajn ZMN4 OOhiatit 0 X 11 LYs 2 VNVFarzanaNo ratings yet
- Kiit World School Class-7 Subject: Science, Chapter: Light Assignment Choose The Correct OptionDocument2 pagesKiit World School Class-7 Subject: Science, Chapter: Light Assignment Choose The Correct Optionkirti rupelaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 LIGHTDocument4 pagesChapter 15 LIGHTshravanvk35No ratings yet
- Science 10 - Q2 - Wk6 SLHT 6 (No Answer Key)Document8 pagesScience 10 - Q2 - Wk6 SLHT 6 (No Answer Key)Joy Valerie AricayosNo ratings yet
- 7 IG Light QBDocument3 pages7 IG Light QBsparton xNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 7 Science Chapter 15 WorksheetsDocument3 pagesCBSE Class 7 Science Chapter 15 Worksheetskevinmehta21No ratings yet
- Notebook Work CH - 16 (Light)Document9 pagesNotebook Work CH - 16 (Light)Adhya MisraNo ratings yet
- Lens TestDocument2 pagesLens TestPhilip MooreNo ratings yet
- Chapter-10 - Light: Reflection and RefractionDocument15 pagesChapter-10 - Light: Reflection and RefractionVineet SierraNo ratings yet
- CH 7 Light Colour SightDocument27 pagesCH 7 Light Colour SightTan AylinNo ratings yet
- X April Physics LightDocument2 pagesX April Physics Lightprasidh2021No ratings yet
- Please Remember To Photocopy 4 Pages Onto One Sheet by Going A3 A4 and Using Back To Back On The PhotocopierDocument13 pagesPlease Remember To Photocopy 4 Pages Onto One Sheet by Going A3 A4 and Using Back To Back On The PhotocopierXhenel Vincent LirioNo ratings yet
- MCQs - LightDocument9 pagesMCQs - Lightdeepak.idea84No ratings yet
- Physics 2Document11 pagesPhysics 2bort kortNo ratings yet
- Ch.10 - Light (Reflection)Document35 pagesCh.10 - Light (Reflection)Urmila GNo ratings yet
- Optics10 PhysicsDocument16 pagesOptics10 PhysicsTapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- SUm Test 3 2nd QDocument1 pageSUm Test 3 2nd QJamaica MamburaoNo ratings yet
- Light - AnswersDocument3 pagesLight - AnswersSanyam 1 BNo ratings yet
- Light NoteDocument6 pagesLight NoteGaming ApocalypseNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 7 Science Worksheet (6) - 0Document2 pagesCBSE Class 7 Science Worksheet (6) - 0Yatish TiwariNo ratings yet
- Physics AssignmentDocument5 pagesPhysics AssignmentNabeel KhanNo ratings yet
- Physics Worksheet Light: Reflection and Refraction Name of The Student: Grade - XDocument4 pagesPhysics Worksheet Light: Reflection and Refraction Name of The Student: Grade - XSyed Ahmed AdeelNo ratings yet
- Short Answer Type Questions - I (2 Marks)Document5 pagesShort Answer Type Questions - I (2 Marks)hardikvimal52No ratings yet
- M.E.S Indian School, Doha - Qatar Notes 2024 - 2025Document10 pagesM.E.S Indian School, Doha - Qatar Notes 2024 - 2025Rafiya95z MynirNo ratings yet
- Performance: Physics Light 01Document4 pagesPerformance: Physics Light 01Vijay kumar LokanadamNo ratings yet
- Performance: Physics Light 01Document4 pagesPerformance: Physics Light 01Vijay kumar LokanadamNo ratings yet
- Light NcertDocument55 pagesLight NcertDani MathewNo ratings yet
- MCQ Type QuestionsDocument2 pagesMCQ Type QuestionsAnonymous rn5Te9MwkNo ratings yet
- Q2 Science 10 M3ST3Document3 pagesQ2 Science 10 M3ST3Leother Yee SosmenaNo ratings yet
- Quarter 1 - Module 4 Reflection of Light in Mirrors Week 6Document20 pagesQuarter 1 - Module 4 Reflection of Light in Mirrors Week 6Anjelo Marick AvilesNo ratings yet
- Question Bank - Light - Grade VIIIDocument5 pagesQuestion Bank - Light - Grade VIIIpk197679No ratings yet
- Amity International School, Noida Science Class - 7 Light Worksheet (2023-24)Document3 pagesAmity International School, Noida Science Class - 7 Light Worksheet (2023-24)alatexgamingNo ratings yet
- Cylindrical Perspective: Cylindrical Perspective: Exploring Visual Perception in Computer VisionFrom EverandCylindrical Perspective: Cylindrical Perspective: Exploring Visual Perception in Computer VisionNo ratings yet
- Reverse Perspective: Reimagining Visual Perception in Computer VisionFrom EverandReverse Perspective: Reimagining Visual Perception in Computer VisionNo ratings yet
- How to Build a Digital Microscope: Construct a Reliable, Inexpensive Microscope for both Regular and Polarized Light MicroscopyFrom EverandHow to Build a Digital Microscope: Construct a Reliable, Inexpensive Microscope for both Regular and Polarized Light MicroscopyNo ratings yet
- Itr3 PreviewDocument61 pagesItr3 PreviewTaranpreet KaurNo ratings yet
- Index NumbersDocument27 pagesIndex NumbersTaranpreet KaurNo ratings yet
- BST HHWDocument5 pagesBST HHWTaranpreet KaurNo ratings yet
- Bumper Production (1 19)Document14 pagesBumper Production (1 19)Taranpreet KaurNo ratings yet
- Accounts ProjectDocument12 pagesAccounts ProjectTaranpreet KaurNo ratings yet
- Taranpreet Kaur 11cDocument2 pagesTaranpreet Kaur 11cTaranpreet KaurNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 QuestionsDocument3 pagesChapter 10 QuestionsTaranpreet KaurNo ratings yet
- Small Business and EnterprisesDocument10 pagesSmall Business and EnterprisesTaranpreet KaurNo ratings yet
- F3CB PreviewDocument21 pagesF3CB PreviewTaranpreet KaurNo ratings yet
- Asm 8579Document2 pagesAsm 8579Taranpreet KaurNo ratings yet
- Worksheet - The Story of Ali CogiaDocument2 pagesWorksheet - The Story of Ali CogiaTaranpreet KaurNo ratings yet
- Asm 7685Document2 pagesAsm 7685Taranpreet KaurNo ratings yet
- CS QuestionsDocument5 pagesCS QuestionsTaranpreet KaurNo ratings yet
- Small Business and EnterprisesDocument11 pagesSmall Business and EnterprisesTaranpreet KaurNo ratings yet
- Asm 8300Document2 pagesAsm 8300Taranpreet KaurNo ratings yet
- Asm 8475Document3 pagesAsm 8475Taranpreet KaurNo ratings yet
- Asm 7993Document2 pagesAsm 7993Taranpreet KaurNo ratings yet
- Asm 8235Document2 pagesAsm 8235Taranpreet KaurNo ratings yet
- Asm 8056Document2 pagesAsm 8056Taranpreet KaurNo ratings yet
- Unconfirmed 82485Document14 pagesUnconfirmed 82485Taranpreet KaurNo ratings yet
- 3ds Max TutorialDocument36 pages3ds Max TutorialScribrestNo ratings yet
- Artificial Passenger Final ApDocument30 pagesArtificial Passenger Final ApKiran KumarNo ratings yet
- Australasian Health Facility Guidelines: BriefingDocument3 pagesAustralasian Health Facility Guidelines: Briefingarief oktavaNo ratings yet
- Marketing Myopia - Learnings From Kodak FailureDocument12 pagesMarketing Myopia - Learnings From Kodak Failuredeepak yadavNo ratings yet
- Cinematic Drone Footage: in 5 StepsDocument8 pagesCinematic Drone Footage: in 5 StepsPrince YoungNo ratings yet
- Nlt20mca108 AI Assignment 2Document2 pagesNlt20mca108 AI Assignment 2Bluebird SolutionNo ratings yet
- Framework of Advanced Driving Assistance System (ADAS) ResearchDocument8 pagesFramework of Advanced Driving Assistance System (ADAS) ResearchherusyahputraNo ratings yet
- My InspirationDocument12 pagesMy InspirationAkinola AnthonyNo ratings yet
- Amateur Photographer - 31 October 2023Document68 pagesAmateur Photographer - 31 October 2023gustavoluizbatoliveiraNo ratings yet
- "Program Reviews" - Late 1970sDocument2 pages"Program Reviews" - Late 1970sCharles AzarNo ratings yet
- The Passionate Photographer - Ten Steps Toward Becoming GreatDocument266 pagesThe Passionate Photographer - Ten Steps Toward Becoming GreatSylvia GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Last Minute CriminalisticDocument895 pagesLast Minute CriminalisticSayon Rasil100% (1)
- Attackpro Vrs Sellsheet FQ PPVX Web1Document4 pagesAttackpro Vrs Sellsheet FQ PPVX Web1Forum PompieriiNo ratings yet
- A Review On The Formation Causes Measurement Implications and Reduction of Neps During Cotton ProcessingDocument104 pagesA Review On The Formation Causes Measurement Implications and Reduction of Neps During Cotton ProcessingMohammad AliNo ratings yet
- High Dynamic RangeDocument13 pagesHigh Dynamic RangeMark ThompsonNo ratings yet
- Dc-x011-2014 e (Cipa Standard)Document56 pagesDc-x011-2014 e (Cipa Standard)zeljavalybiNo ratings yet
- Cat OPMILUMERA300 PDFDocument6 pagesCat OPMILUMERA300 PDFOgut AjaNo ratings yet
- Microscope Parts Word Search: Name: DateDocument2 pagesMicroscope Parts Word Search: Name: DateAnonymous K3WNW5ZopNo ratings yet
- Technical Seminar ON Night Vision TechnologyDocument13 pagesTechnical Seminar ON Night Vision TechnologyWulfy58No ratings yet
- Muscle Movement and Facial Emoji Detection Via Raspberry Pi AuthorsDocument8 pagesMuscle Movement and Facial Emoji Detection Via Raspberry Pi AuthorsGokul KNo ratings yet
- 3.3.5 - 146 - A Device Controlled Using Eye MovementDocument4 pages3.3.5 - 146 - A Device Controlled Using Eye MovementPooja ChendakeNo ratings yet
- Sample 70 - 2Document7 pagesSample 70 - 2Mikhael MangopoNo ratings yet
- Types of Camera MovementDocument3 pagesTypes of Camera Movementabhi100% (2)
- Anafi User Guide v2.6.2Document86 pagesAnafi User Guide v2.6.2Ana VilhenaNo ratings yet
- Spynel Series: Wide Area Surveillance SystemsDocument2 pagesSpynel Series: Wide Area Surveillance SystemsJuan CastañoNo ratings yet
- 13 Great Examples of Slow Sync Flash ImagesDocument11 pages13 Great Examples of Slow Sync Flash Imagesaldy karyadiNo ratings yet
- Video EditingDocument23 pagesVideo EditingEdgetu TakeleNo ratings yet
- Integrated Marketing Communication: Product Information Communication Process Brand Entity SWOT Analysis IMC StrategyDocument10 pagesIntegrated Marketing Communication: Product Information Communication Process Brand Entity SWOT Analysis IMC StrategyDigambar Lohakare0% (1)
- Practice TestDocument8 pagesPractice Testsambhav takkamoreNo ratings yet
- Borescope CatalogDocument9 pagesBorescope CatalogYasmine SalehNo ratings yet