Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nursing Care Plan
Nursing Care Plan
Uploaded by
Jeanette Leigh BravoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Nursing Care Plan
Nursing Care Plan
Uploaded by
Jeanette Leigh BravoCopyright:
Available Formats
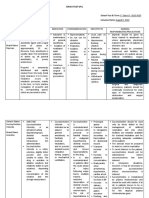
NURSING CARE PLAN
Patient’s Initials: _____________ Chief Complaint: “I feel exhausted and I Name of Student Nurse:
am sweating heavily.”
Age & Gender: 23 years old, female Jeanette Leigh S. Bravo
Birthdate: Admitting Level/Block/Group: AU-FA1-
____________________________________ Diagnosis:_________________________ BSN2-2
Address: __________________________________ Hospital/Area: Emergency
____________________________________ Maternal and Child Health Care
Hospital
____________________________________ Date of Confinement: Clinical Instructor:
______________________________
Anna Lorraine Reyes
Date: _______
ASSESSMENT NURSING PLANNING INTERVENTIONS RATIONALE EVALUATION
ANALYSIS
SUBJECTIVE: ● Risk for ● Patient ● Review the ● Helpful in ● The patient
Maternal will history of identifying accomplished
“I feel exhausted and I
Injury r/t accom labor, possible cervix
am sweating heavily.”
maternal plish onset, and causes, dilation.
As verbalized by the
fatigue and cervix duration. needed ● The patient
patient.
obstruction dilation ● Assess diagnostic improves her
OBJECTIVE: to fetal at least uterine studies, and labor pattern
descent. 1.2 contractile appropriate and the
● Nulliparous ● Risk for cm/hr pattern interventions. identified risk
● Asthmatic Fetal Injury for manually Uterine factors are
● 35th weeks r/t prolonged primipa (palpation) dysfunction reduced.
AOG labor, fetal ra, 1.5 or may be ● The patient
● 7-8 cm dilated malpresentat cm/hr electronical caused by an displays FHR
● Ruptured ion, and for ly via atonic or within normal
membrane cephalopelvi multipa external or hypertonic limits, with
c ra in internal state. Uterine good
disproportion active monitor atony is variability, no
Vital signs: . phase, with classified as late
● Risk for fluid with internal primary when decelerations
BP: 130/90 mmHg volume fetal uterine it occurs noted.
T: 35.9/axilla deficit due to descen pressure before the ● The patient
profuse t at catheter onset of maintains
HR: 110 bpm diaphoresis. least 1 (IUPC). labor (latent fluid balance,
cm/hr ● Investigate phase) or as evidenced
SaO2: 97% on R/a
for reports of secondary by moist
FHR: 156 bpm primipa severe when it mucous
ra, 2 abdominal occurs after membranes,
cm/hr pain. Note well- appropriate
for signs of established urine output,
multipa fetal labor (active and palpable
ra. distress, phase). pulses.
● Patient cessation ● Dysfunctional ● The patient
will of contractions and her baby
particip contraction lengthen are free of
ate in s, presence labor complications
interve of vaginal increasing ..
ntions bleeding. the risk of
to ● Assess maternal/feta
improv FHR l
e labor manually or complication
pattern electronical s.
and/or ly. ● May indicate
reduce ● Note developing
identifi frequency uterine
ed risk of uterine tear/acute
factors. contraction rupture
● Patient s. Notify necessitating
will physician if emergency
display the surgery.
FHR frequency ● Detects
within is 2 min or abnormal
normal less. responses,
limits, ● Monitor such as
with fetal exaggerated
good descent in variability,
variabil birth canal bradycardia,
ity, no in relation and
late to ischial tachycardia,
deceler spines. which may
ations ● Administer be caused by
noted. antibiotic to stress,
● Patient client, as hypoxia,
will indicated. acidosis, or
maintai ● Monitor sepsis.
n fluid vital signs. ● Contractions
balanc Note occurring
e, as reports of every 2 min
eviden dizziness or less do not
ced by with allow for
moist change of adequate
mucou position. oxygenation
s ● Assess lips of intervillous
membr and oral spaces.
anes, mucous ● Descent that
approp membrane is less than 1
riate s and cm/hr for a
urine degree of primipara, or
output, salivation less than 2
and cm/hr for a
palpabl ● Administer multipara,
e fluids may indicate
pulses. intravenous CPD or
● Patient ly.. malposition.
will be ● Prevents/
free of treats
compli ascending
cations infection and
. will protect
fetus as well.
● Increased
pulse rate
and
temperature,
and
orthostatic
BP changes
may indicate
decrease in
circulating
volume.
● Dry oral
mucous
membranes/li
ps and
decreased
salivation are
further
indicators of
dehydration.
● Parenteral
solutions
containing
electrolytes
and glucose
can correct
or prevent
maternal and
fetal
imbalances
and may
reduce
maternal
exhaustion.
You might also like
- RPAH Elimination Diet Handbook With Food Shopping Guide PDFDocument33 pagesRPAH Elimination Diet Handbook With Food Shopping Guide PDFmalamatiyya33% (6)
- NURSING-CARE-PLAN Breech PresentationDocument3 pagesNURSING-CARE-PLAN Breech PresentationGab83% (18)
- CASE STUDY 10 NCPDocument46 pagesCASE STUDY 10 NCPRosemarie R. Reyes100% (8)
- Clinical Management Review 2023-2024: Volume 2: USMLE Step 3 and COMLEX-USA Level 3From EverandClinical Management Review 2023-2024: Volume 2: USMLE Step 3 and COMLEX-USA Level 3No ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Abruptio PlacentaeDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Abruptio Placentaederic93% (29)
- Nursing Care Plan: MDH Ob/GyneDocument10 pagesNursing Care Plan: MDH Ob/GyneTrisha Dianne RaquenioNo ratings yet
- NCP Alterations in Normal LaborDocument9 pagesNCP Alterations in Normal LaborCameron De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Copy of NCP Format)Document4 pagesCopy of NCP Format)shai raNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Rationale Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Rationale Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationMark FernandezNo ratings yet
- Proposed By: Mrs. Sharry Mae G. Awayan, RN, MANDocument7 pagesProposed By: Mrs. Sharry Mae G. Awayan, RN, MANTiffany Joy QuiliopeNo ratings yet
- Now, Try Some Big Leap.: Keep GoingDocument10 pagesNow, Try Some Big Leap.: Keep GoingCameron De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- NCP Term 2Document3 pagesNCP Term 2Cassandra Grace Muerong Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- 3 PRIORITY NURSING CARE PLANS (Intrapartum and Postpartum Periods)Document11 pages3 PRIORITY NURSING CARE PLANS (Intrapartum and Postpartum Periods)Ryan Robert V. VentoleroNo ratings yet
- NCP - 110323Document4 pagesNCP - 110323designericlelynsoronioNo ratings yet
- 3 Priority Nursing Care Plans During DeliveryDocument11 pages3 Priority Nursing Care Plans During DeliveryRyan Robert V. VentoleroNo ratings yet
- Case:: Bleeding Without PainDocument3 pagesCase:: Bleeding Without PainDarwin QuirimitNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan TemplateDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan TemplateKyle Albert EstoestaNo ratings yet
- Abruptio Placenta NCPDocument2 pagesAbruptio Placenta NCPjohncarlo ramos100% (1)
- Nursing-Care-Plans 211112 153011Document57 pagesNursing-Care-Plans 211112 153011Zahraa AlTahanNo ratings yet
- Nursing Diagnosis Planning Rationale Evaluatio N Subjective: Long Term: Independent: - EstablishDocument2 pagesNursing Diagnosis Planning Rationale Evaluatio N Subjective: Long Term: Independent: - EstablishRyann BuayaNo ratings yet
- NCP Estoesta HemorrhageDocument5 pagesNCP Estoesta HemorrhageKyle Albert EstoestaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Cues Nursing Diagnosis Desired Outcome Nursing Intervention Justification EvaluationDocument6 pagesNursing Care Plan: Assessment Cues Nursing Diagnosis Desired Outcome Nursing Intervention Justification EvaluationPaul Gio OebandaNo ratings yet
- NCP On Ectopic PregnancyDocument5 pagesNCP On Ectopic PregnancyDaisy Lui100% (1)
- Defining Characteristic S Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Analysis Plan of Care Nursing Interventions Rationale Subjective: Short Term: IndependentDocument1 pageDefining Characteristic S Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Analysis Plan of Care Nursing Interventions Rationale Subjective: Short Term: Independentboomer SeargeNo ratings yet
- Depolonia NCPDocument6 pagesDepolonia NCPMary AllizaNo ratings yet
- NCP and Fdar.Document4 pagesNCP and Fdar.Ralph Laurent De DiosNo ratings yet
- Case Discussion: Mayan, Mercurio, Murillo BSN 2-ADocument11 pagesCase Discussion: Mayan, Mercurio, Murillo BSN 2-ADhen MarcNo ratings yet
- Silliman University: Nursing Care Plan During DeliveryDocument12 pagesSilliman University: Nursing Care Plan During DeliveryShandle Dynne BaenaNo ratings yet
- MCN Midterm NotesDocument65 pagesMCN Midterm NotesSHIELOU LOMODNo ratings yet
- NCP TemplateDocument3 pagesNCP TemplateJUNNEL JAMES A. CALATRAVANo ratings yet
- OxytocinDocument3 pagesOxytocinjints poterNo ratings yet
- OxytocinDocument3 pagesOxytocinjints poterNo ratings yet
- Maternal Ncps FinalDocument33 pagesMaternal Ncps FinalCarey Jamille YadanNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Placenta PreviaDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan Placenta Previaderic98% (42)
- MCN Midterm NotesDocument33 pagesMCN Midterm NotesSHIELOU LOMODNo ratings yet
- NCP Conception ActivityDocument3 pagesNCP Conception ActivityMarl TanNo ratings yet
- NCP UTI (Artillo)Document3 pagesNCP UTI (Artillo)Al TheóNo ratings yet
- GROUP E2 1M Antenatal ComplicationsDocument25 pagesGROUP E2 1M Antenatal ComplicationsJason Matthew ImpasNo ratings yet
- Ada Bsn-2-10a NCPDocument4 pagesAda Bsn-2-10a NCPABIGAIL ANNE DAPHNE ADANo ratings yet
- Drug Study FORMDocument2 pagesDrug Study FORMLovely heart AñanaNo ratings yet
- Bernas Rhu OpstDocument3 pagesBernas Rhu Opstrbvergz1z5No ratings yet
- Short Term:: As Acetaminophen (Tylenol), Ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin), or Naproxen (Aleve)Document2 pagesShort Term:: As Acetaminophen (Tylenol), Ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin), or Naproxen (Aleve)Aleeyah Krizle EstabilloNo ratings yet
- Fix Resiko CideraDocument7 pagesFix Resiko CideraIndanazulfaaNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Breathing Pattern Related To Obstruction of Airways As Evidenced by Presence of Yellowish Sputum NURSING-CARE-PLANDocument7 pagesIneffective Breathing Pattern Related To Obstruction of Airways As Evidenced by Presence of Yellowish Sputum NURSING-CARE-PLANDenise Joy15No ratings yet
- Oxytocin Drug StudyDocument3 pagesOxytocin Drug StudyKIM NAMJOON'S PEACHES & CREAM100% (2)
- 11 Drug StudyDocument13 pages11 Drug Studykwon nanaNo ratings yet
- Appendix B Nursing Care Plan Clinical Portait Assessment: Received PatientDocument14 pagesAppendix B Nursing Care Plan Clinical Portait Assessment: Received Patientjopearl18No ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Rationale Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationTweenie DalumpinesNo ratings yet
- Mier NCPDocument3 pagesMier NCPMacy MarquezNo ratings yet
- Vi. Nursing Care Plan Cues Analysis Nursing Diagnosis Goal / Plan Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesVi. Nursing Care Plan Cues Analysis Nursing Diagnosis Goal / Plan Intervention Rationale EvaluationRaisa Robelle QuichoNo ratings yet
- NCM 107 (Related Learning Experience) : in Partial Fulfillment of The Requirement inDocument4 pagesNCM 107 (Related Learning Experience) : in Partial Fulfillment of The Requirement inTiffany Joy QuiliopeNo ratings yet
- Giman NCPDocument3 pagesGiman NCPJoedelynne Diane Endaya GarciaNo ratings yet
- Ploya - Multiple Gestation - NCP FinalDocument13 pagesPloya - Multiple Gestation - NCP FinalJullian PloyaNo ratings yet
- Third Trimester Bleeding: Whitney BrantleyDocument17 pagesThird Trimester Bleeding: Whitney BrantleyGeneNo ratings yet
- Uterine AtonyDocument4 pagesUterine Atonykarl de guzmanNo ratings yet
- Abruptio PlacentaDocument6 pagesAbruptio Placenta0320-2300No ratings yet
- Progesterona La Hormona Definitiva del Bienestar FemeninoFrom EverandProgesterona La Hormona Definitiva del Bienestar FemeninoRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Liver Diseases in the Pediatric Intensive Care Unit: A Clinical GuideFrom EverandLiver Diseases in the Pediatric Intensive Care Unit: A Clinical GuidePhilippe JouvetNo ratings yet
- Salvage Therapy for Prostate CancerFrom EverandSalvage Therapy for Prostate CancerSanchia S. GoonewardeneNo ratings yet
- Menstrual Cycle Related Disorders: Volume 7: Frontiers in Gynecological EndocrinologyFrom EverandMenstrual Cycle Related Disorders: Volume 7: Frontiers in Gynecological EndocrinologySarah L. BergaNo ratings yet
- Hiv Aids HistoryDocument23 pagesHiv Aids HistoryJeanette Leigh BravoNo ratings yet
- CHN ReportingDocument7 pagesCHN ReportingJeanette Leigh BravoNo ratings yet
- Rotational PlanDocument3 pagesRotational PlanJeanette Leigh BravoNo ratings yet
- COA RLE ReportingDocument5 pagesCOA RLE ReportingJeanette Leigh BravoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument9 pagesDrug StudyJeanette Leigh BravoNo ratings yet
- DOE Standard - Hoisting and Rigging - 2020 UpdateDocument39 pagesDOE Standard - Hoisting and Rigging - 2020 UpdateLogic TurnipNo ratings yet
- Global Alumni Crisis Support Initiative BrochureDocument11 pagesGlobal Alumni Crisis Support Initiative Brochurepankaj kashyapNo ratings yet
- Hatchery Brochure PDFDocument8 pagesHatchery Brochure PDFUmair ShafiqueNo ratings yet
- 12 White Blood Cell Counting Techniques in BirdsDocument5 pages12 White Blood Cell Counting Techniques in BirdsPablo LópezNo ratings yet
- New HookDocument5 pagesNew Hookhugeellis2No ratings yet
- CAAT AIR CL CER OPM 305 Rev.00 - Checklist For Traning Program Manual TPM Compliance and Approval Airworthiness AspectsDocument9 pagesCAAT AIR CL CER OPM 305 Rev.00 - Checklist For Traning Program Manual TPM Compliance and Approval Airworthiness Aspectsjakara tongchimNo ratings yet
- Cleoshouseofpuppies Infodeck 2Document5 pagesCleoshouseofpuppies Infodeck 2api-558996710No ratings yet
- Part I - 13 Heat Stress 8Document1 pagePart I - 13 Heat Stress 8SKH CultureNo ratings yet
- Assisting Delivery: Mrs. Helen Segundo LubianoDocument34 pagesAssisting Delivery: Mrs. Helen Segundo LubianoJayrelle D. SafranNo ratings yet
- TFN PrelimDocument9 pagesTFN PrelimElla ArnocoNo ratings yet
- Clinical CaseDocument10 pagesClinical CaseNick Benavides LunaNo ratings yet
- ICPR 5 1 WebDocument96 pagesICPR 5 1 WebAndreea-Luciana UrzicăNo ratings yet
- Bisotat For MlsDocument57 pagesBisotat For MlsABAYNo ratings yet
- The Instability Severity Index ScoreDocument8 pagesThe Instability Severity Index ScoreAndré FariasNo ratings yet
- Bibliometric Analysis of Medication Related Osteonecrosis of The Jaw HighDocument17 pagesBibliometric Analysis of Medication Related Osteonecrosis of The Jaw HighJose IgnacioNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia, Is It Bacterial or Viral FINAL EDITINGDocument31 pagesPneumonia, Is It Bacterial or Viral FINAL EDITINGdv prnt1909No ratings yet
- Clean Water For AllDocument8 pagesClean Water For AllArgie Joy Marie AmpolNo ratings yet
- Training Methods: Anuraag AwasthiDocument34 pagesTraining Methods: Anuraag AwasthiStuti Sharma GaurNo ratings yet
- Minimally Invasive Cardiac Surgery in Lucknow - Dr. Gauranga MajumdarDocument3 pagesMinimally Invasive Cardiac Surgery in Lucknow - Dr. Gauranga MajumdarBest Heart Bypass Surgery Dr. Gauranga MajumdarNo ratings yet
- Profile of and Risk Factors For Poststroke CognitiveDocument16 pagesProfile of and Risk Factors For Poststroke CognitiveFera EyFeraNo ratings yet
- Tos TemplateDocument3 pagesTos TemplateJesus LuckyNo ratings yet
- Glycation of HemoglobinDocument3 pagesGlycation of Hemoglobinmadison DeliNo ratings yet
- Important INSTRUCTIONS AND PROCEDURES - TREDocument44 pagesImportant INSTRUCTIONS AND PROCEDURES - TRETariq khosoNo ratings yet
- Social Movement Inclusive Citizenship and Participatory GovernanceDocument7 pagesSocial Movement Inclusive Citizenship and Participatory GovernancePhilippines QatarNo ratings yet
- Family Nursing Care PlanDocument13 pagesFamily Nursing Care PlanThrecia Rota100% (1)
- Use of The Mini International Neuropsychiatric Interview (MINI) As A Screening Tool in Prisons: Results of A Preliminary StudyDocument5 pagesUse of The Mini International Neuropsychiatric Interview (MINI) As A Screening Tool in Prisons: Results of A Preliminary StudyRafael MartinsNo ratings yet
- Corrected Reiteration Re-Strict ImplementationDocument5 pagesCorrected Reiteration Re-Strict ImplementationPRO9 COVID-19No ratings yet
- Haemorrhoid Review-MainDocument9 pagesHaemorrhoid Review-MainWarren SeowNo ratings yet
- Factors Associated With Sleep Quality Among Undergraduate Students at A Malaysian Public UniversityDocument19 pagesFactors Associated With Sleep Quality Among Undergraduate Students at A Malaysian Public UniversityHayati RaisNo ratings yet