Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2021 Technology ATP Grade 8
2021 Technology ATP Grade 8
Uploaded by
siyabonga mpofuOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
2021 Technology ATP Grade 8
2021 Technology ATP Grade 8
Uploaded by
siyabonga mpofuCopyright:
Available Formats
2021 Annual Teaching Plan Template
2021 Annual Teaching Plan – Term 2: TECHNOLOGY: Grade 8
GRADE 8 TERM 1
Week 1 Week 2 Week 3 Week 4 Week 5
Term 1
45 days
27-29 January (3 days) 1-5 February 8-12 February 15-19 February 22-26 February
Revision Structures Communication skills
CAPS Topic
(Learners must not share any resources)
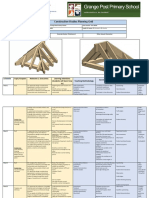
Learners complete the Definition of frame structures. • Purpose of graphics: develop and communicate ideas.
baseline assessment. - Purpose of structural members (components) in wood and steel roof trusses • Conventions: outlines (thick/dark); construction lines (thin/feint);
(king and queen post, strut, tie, rafter, tie beam). hidden detail (dashed); centre lines (chain dash-dot); scaling up
Teachers to discuss the
content of the assessment - Learners identify structural members and type of force (shear, torsion, and scaling down; dimensioning (in mm).
with learners after tension, compression) acting on them in given frame structures. • Working drawing techniques for planning:
completing the activity. • Case study: Electrical pylons – use pictures of a range of pylon designs noting: - Single view flat 2D drawing with dimensions, line types and
- The variety of designs that solve the same problem effectively. scale.
- The use of internal cross-bracing and triangulation to provide stiffness. - Isometric – using underlying isometric grid (term 1) and simple
instruments (term 3).
Core • Structural members under tension/compression (worksheet).
• Artistic drawing: Double vanishing point perspective with
Concepts, Skills and Structural members
colour, texture and shading.
Values • Structures that span over space:
- Sketching – using pencil, ruler and blank paper.
- Beams: steel I-beams (girders), concrete lintels; beam and column bridge.
- Enhancing drawing to promote realism using colour, texture,
- Alternative bridge supports: suspension bridges; cable-stayed bridges. shading and shadows.
- Arches: arches in buildings, bridges, dam walls.
- Cantilevers: simple cantilever, cable stayed cantilever. Structural failure –
the three most likely ways structures fail are:
- Fracture of a member – due to lack of strength.
- Bending (flexing, buckling) – due to lack of stiffness (rigidity).
- Toppling over – due to lack of stability (top heavy, narrow base).
Requisite Pre-
Gr 7 knowledge and skills Types and functions of structures. Basic graphic communication skills
Knowledge
Resources (other than
DBE Sasol Inzalo workbooks/ Textbooks and any applicable resource whether DBE Sasol Inzalo workbooks/ Textbooks and any applicable
textbook) to enhance
“YouTube” videos, etc. resource whether you tube videos, etc.
learning
Informal Assessment Baseline assessment Informal Assessment Informal Assessment
SBA
(Formal Assessment)
Technology Grade 8 Trimmed ATP - TERM 1 - 4 Page 1 of 8
2021 Annual Teaching Plan Template
Week 6 Week 7 Week 8 Week 9 Week 10
/Term 1
45 days
1-5 March 8-12 March 15-19 March 23-26 March (4 days) 29-31 March (3 days)
PAT 1
(Assignment: Investigate and Design)
CAPS Topic Mechanical Systems and Control
• Revision: mechanical advantage. Well-designed machines Learners work individually to design a structure utilising required structural
give “mechanical advantage”. components and mechanisms to suit the context provided.
•All complex machinery consists of combinations of simple mechanisms. • Evaluate: learners examine information on several complex structures and list
advantages and disadvantages in the designs.
- The wedge: e.g. inclined plane or ramp, door wedge, knife blade, etc.
• Design: initial idea sketches.
- The wheel and axle: e.g. from bicycle to shopping trolley.
• Design: design brief with specifications and constraints.
• Gears: (wheels with wedges for teeth)
• Make: a 3D isometric projection of the idea with dimensions and drawn to scale.
- Show how meshing of two spur gears causes counter-rotation.
• Make: a working drawing in 2D showing one view with dimensions and line
- Show how introducing an idler gear between two spur gears types.
synchronises rotation of the driver and driven gears. • Communicate: Individual presentations of plans.
Core • Communicate: a sketch enhanced using two of colour, texture or shading
- Gear ratios:
Concepts, Skills and
Values Show how different sized gears result in a change in the velocity ratio as well as
an ‘opposite’ change in the force ratio – if force increases, speed decreases,
and vice versa.
• Mechanisms that change the direction of movement:
- The Cam: show how a cam converts rotary motion into reciprocating motion.
Compare an eccentric wheel and a snail cam.
- The Crank: an adaptation of a second-class lever. Show how a crank
converts rotary motion into reciprocating motion.
• Graphic skills: Learners draw an artist’s impression of one of each of the
above mechanisms (cam and crank) in their books using colour, shading and
texture.
Mechanical advantage and communication skills Design process skills: I,D, M, E and C
Requisite Pre-Knowledge
Resources (other than
DBE Sasol Inzalo workbooks/ Textbooks and any applicable resource whether you DBE Sasol Inzalo workbooks/ Textbooks and any applicable resource whether you tube
textbook) to enhance
tube videos, etc. videos, etc.
learning
Informal Assessment Informal Assessment
Formal Assessment: Investigate and Design
SBA
(Formal Assessment)
Technology Grade 8 Trimmed ATP - TERM 1 - 4 Page 2 of 8
2021 Annual Teaching Plan Template
GRADE 8 TERM 2
Week 1 Week 2 Week 3 Week 4 Week 5 Week 6
Term 2
51 days
13- 16 April (4 days) 19- 23 April 28 - 30 April (3 days) 3-7 May 10-14 May 17-21 May
Processing Investigation skills Impact of technology
CAPS Topic Investigation skills Designing skills Investigating skills
The positive impact of technology: many Case study 2: technology with a positive impact on society. Case study 3: technological products can have a negative
natural materials have been replaced in modern impact.
times by new or improved materials. Some new • Investigate how waste paper and cardboard are recycled
materials are environmentally friendly by being to produce new products for the packaging industry. • Investigate a technological product that can have a
bio-degradable. negative impact on society.
Core • Development: draw a development of an opened
Concepts, Skills and container. • Class discussion: facilitate a class discussion on possible
• Case study 1: investigate the impact of plastic
Values solutions that can counteract or compensate for the
shopping bags on the environment.
• Practical activity: a product requires packaging. Design negative impact of the technology identified.
Report: learners write a report evaluating the various packaging for different purposes. The nature of
effectiveness of using thicker, bio-degradable plastic the product determines the design and properties of the
shopping bags which shoppers must buy. packaging material.
Pre-knowledge on how to conduct an investigation Pre-knowledge on how to look for and separate information Pre-knowledge on how to look for and separate information
Requisite Pre- and a developed vocabulary on the terminology related to conduct an investigation and basic graphic to conduct an investigation and basic graphic communication
Knowledge to the environment and the effects that some material communication skills. skills.
have on it.
Siyavula workbook/ Textbooks and or any other Siyavula workbook/ Textbooks and or any other relevant Siyavula workbook/ Textbooks and or any other relevant
Resources (other than
relevant resources. resources. resources.
textbook) to enhance
learning
Informal Assessment Informal Assessment Informal Assessment Informal Assessment
SBA
(Formal Assessment)
Technology Grade 8 Trimmed ATP - TERM 1 - 4 Page 3 of 8
2021 Annual Teaching Plan Template
Week 7 Week 8 Week 9 Week 10 WEEK 11
Term 2
51 days
24-28 May 31 May- 4 June 7-11 June 14-18 June (4 days) 21- 25 June
CAPS Topic Structures/ Processing Design & Making skills Consolidation
• Revise: forces that act on material – tension; • Design: learners adapt a material or design a product that Revise challenging topics and or concepts of the
compression; bending; torsion; shear. will solve the problem or reduce the impact or negative term:
effects of the technology identified.
practice more examples on developments
Core • Adapting materials to withstand forces – reinforcing
Concepts, Skills and concrete, plywood. • Design: learners sketch free-hand sketches showing two
Values possible solutions. Types of forces
• Selecting metal sections (I-beam, angle iron, T-bar, etc.)
to withstand forces and to save material. Make (drawing): learners draw their chosen solution in 3D The negative impact that material have on the
using isometric projection. environment.
Requisite Pre- Pre-knowledge of strengthening and reasons why we need Pre-knowledge of basic design skills. Pre-knowledge of content discussed during the
Knowledge to reinforce some materials. term.
Siyavula workbook/ Textbooks and or any other relevant Siyavula workbook/ Textbooks and or any other relevant Siyavula workbook/ Textbooks and or any other
Resources (other than resources. resources. relevant resources.
textbook) to enhance
learning
Informal Assessment Informal Assessment Informal Assessment
SBA
(Formal Assessment) Formal Assessment: Controlled TEST
Technology Grade 8 Trimmed ATP - TERM 1 - 4 Page 4 of 8
2021 Annual Teaching Plan Template
GRADE 8 TERM 3
Week 6
Term 3 Week 1 Week 2 Week 3 Week 4 Week 5
16-20 August
52 days 13-16 July (4 days) 19-23 July 26-30 July 2-6 August 10-13 Aug (4 days)
Mechanical Advantage Mechanical Systems and Control Mechanical Systems and Control
CAPS Topic
Investigation skills Communication skills Design & Investigation skills
Calculate Mechanical advantage (MA) REPRESENT GEAR SYSTEMS GRAPHICALLY: use Sketches (2D) showing gear systems that:
circular templates and/or pair of compasses to draw gear Provide an output force four times greater than the input
Levers: mechanical advantage calculations for levers systems with: force (MA = 4:1).
using ratios. The driven gear rotating in the opposite direction to
the driver (counter rotation). Provide double the rotation rate on a driven axle at 90o to
Calculations using LOAD/EFFORT; load ARM/effort the driver axle.
ARM; etc. The driven gear rotating in the same direction to the
driver (include an idler gear). SYSTEM ANALYSIS – bicycle gear system
Do NOT use the method of “taking moments about a
Core point”. The driven gear rotating faster than the driver (with and Analysis of the gears used on modern bicycles –
Concepts, Skills and without an idler). terminology: master/slave or driver/driven; chain wheel;
Values Gears: mechanical advantage calculations for gears cogs.
using ratios. The driven gear rotating slower than the driver (with
and without an idler). SYSTEMS DIAGRAMS
Calculations using tooth ratios; gear wheel diameters; Analyse a mechanical system by breaking it into input-
velocity ratios. DESIGN BRIEF: learners write a design brief with process-output.
specifications for a device that will use a combination of Draw a Systems Diagram for a gear system with a
gears to achieve: mechanical advantage of 4:1.
A mechanical advantage with force multiplication of Plan a mechanical system to produce a specific output.
three times. Systems diagram for a gear train with the driven gear
An increase in output velocity of four times. rotating faster than the driver.
Requisite Pre- Pre-knowledge on levers, classes of levers. Knowledge on gears and rations as discussed in previous Knowledge on mechanical advantage as covered in weeks 1
Knowledge week. and 2, investigating - and design skills.
Siyavula workbook/ Textbooks and or any other relevant Siyavula workbook/ Textbooks and or any other relevant Siyavula workbook/ Textbooks and or any other relevant
Resources (other than
resources. resources. resources.
textbook) to enhance
learning
Informal Assessment Informal Assessment Informal Assessment Informal Assessment
SBA
(Formal Assessment)
Technology Grade 8 Trimmed ATP - TERM 1 - 4 Page 5 of 8
2021 Annual Teaching Plan Template
Term 3 Week 7 Week 8 Week 9 Week 10 WEEK 11
52 days 23-27 August 30 Aug-3 Sept 6-10 Sept 13-17 Sept 20-23 Sept (4 days)
Impact/ Indigenous and Bias in technology Design &
CAPS Topic Investigation and Design skills
Investigation skills Communication skills
INVESTIGATE and report on one of the following: DRAWINGS for the shaft head-gear – each learner draws a: Revision:
Distribute the investigations so all are covered and reported
in each class. 3D isometric drawing of the selected design giving Mechanical advantage
INVESTIGATE: The impact on the environment as a result dimensions and drawn to scale. Rotation direction of gears
of mining of: Acid mine drainage Elements included in a design brief
2D working drawing showing one or more views with Importance of budgeting
OR dimensions and lines.
INVESTIGATE: The impact on the environment as a result Budget: individual learners prepare a realistic budget
of mining of: detailing expected costs of constructing a real mine shaft
Dust pollution from mine dumps on residential areas. headgear, detailing valid prices of materials and labour
costs of the range of workers who would be involved in
OR designing and building such a device.
Core INVESTIGATE: Iron age technology:
Concepts, Skills and Indigenous mining of iron in South Africa before the modern
Values era
OR
INVESTIGATE: Bias in technology: Gender bias in career
choice / opportunities related to mining.
INVESTIGATE: Lifting mechanisms (wire rope-driven mine
head-gear) in use at South African mines for raising people
and ore.
Sketch: initial idea sketches to meet the requirements given
in the scenario.
Design brief with specifications and constrains.
Knowledge on how to gather information, report on the Knowledge on basic drawing skills.
Requisite Pre-Knowledge
findings verbally and through sketches.
Resources (other than Siyavula workbook/ Textbooks and or any other relevant Siyavula workbook/ Textbooks and or any other relevant Siyavula workbook/ Textbooks and or any other
textbook) to enhance resources. resources. relevant resources.
learning
Informal Assessment Informal Assessment
SBA
Formal Assessment: PAT 2
(Formal Assessment)
Technology Grade 8 Trimmed ATP - TERM 1 - 4 Page 6 of 8
2021 Annual Teaching Plan Template
GRADE 8 TERM 4
Term 4 Week 1 Week 2 Week 3 Week 4 Week 5 Week 6
47 days 5-8 Oct (4 days) 11-15 Oct 18-22 Oct 25-29 Oct 1-5 Nov 8-12 Nov
Electrical Systems and Control Impact of / Biases in technology Electrical Systems and Control
CAPS Topic
Design skills Evaluation skills Impact of technology
REVISE: simple circuit components; input devices Energy for heating, lighting and cooking in rural and GENERATE ELECTRICITY FOR THE NATION -
(electrochemical cell; generator; solar panel), output informal settlements. ADVANTAGES AND DISADVANTAGES of:
devices (resistor; lamp; heater; buzzer; motor); Thermal power stations (steam turbines – sources of
control device (switches). Energy from illegal connections; ethical issues; safety heat: coal, gas, nuclear, sun).
Note: Some devices can serve as input, output, considerations.
process or control device. Hydroelectric power stations (including pumped storage
CORRECT CONNECTIONS, short circuits. CLASS DISCUSSION: equitable sharing of resources – schemes).
Electrical components and their accepted symbols. industry needs reliable power for job creation; schools
DRAWING ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS using need power for lighting and computing. Wind-driven turbines.
Core
accepted symbols (as in Grade 12 see Addendum
Concepts, Skills and
C). WRITTEN REPORT: Learners write a balanced report on ALTERNATING CURRENT; step-up and step-down
Values
TEACHER SET UP CIRCUITS using a range of these issues. transformers; distributing electric power across the
components. Learners draw the circuits using country: the national grid.
symbols. ELECTROCHEMICAL CELLS.
Advantages and disadvantages of series and parallel
batteries.
Photovoltaic cells - advantages and disadvantages of solar
cells.
Requisite Pre- Pre-knowledge of circuit diagrams, components and Pre-knowledge on investigation -, reasoning -and analysing Pre-knowledge on how to identify advantages and
Knowledge their symbols skills disadvantages (tabulate if required)
Siyavula workbook/ Textbooks and or any other Siyavula workbook/ Textbooks and or any other relevant Siyavula workbook/ Textbooks and or any other relevant
Resources (other than
relevant resources. resources. resources.
textbook) to enhance
learning
Informal Assessment Informal Assessment Informal Assessment Informal Assessment
SBA
(Formal Assessment)
Technology Grade 8 Trimmed ATP - TERM 1 - 4 Page 7 of 8
2021 Annual Teaching Plan Template
Week 7 Week 8 Week 9 Week 10
Term 4
47 days
15-19 Nov 22-26 Nov 30 Nov-3 Dec 6-8 Dec (3 days)
Electrical System & Control Electrical Systems & Control
CAPS Topic
Design skills Investigation skills
Practical: learners DRAW CIRCUIT
DIAGRAMS & CONNECT CIRCUITS Revise term 4 Revise term 4 content Consolidation and school closure
showing the effect of circuits with resistors content
connected in series and parallel.
Investigation: AND logic gate and simple
cases where it is used.
Core
Concepts, Skills and Values Investigation: OR logic gate and simple
cases where it is used.
Lesson: truth tables for AND & OR logic
conditions
Requisite Pre-Knowledge Pre-knowledge of circuit diagrams Knowledge on all relevant concepts and content discussed during the term.
Siyavula workbook/ Textbooks and or any Siyavula workbook/ Textbooks and Siyavula workbook/ Textbooks Siyavula workbook/ Textbooks and or any other
Resources (other than other relevant resources. or any other relevant resources. and or any other relevant relevant resources.
textbook) to enhance learning resources.
Informal Assessment Informal Assessment
SBA FORMAL ASSESSMENT: CONTROLLED TEST
(Formal Assessment)
Technology Grade 8 Trimmed ATP - TERM 1 - 4 Page 8 of 8
You might also like
- Mercruiser Service Manual 6 Outdrives R/MR/Alpha One/Alpha SSDocument566 pagesMercruiser Service Manual 6 Outdrives R/MR/Alpha One/Alpha SSTechManuals199788% (41)
- Transmissão Okamura HangchaDocument15 pagesTransmissão Okamura HangchavitrinetecnicaNo ratings yet
- Technology Grade 8 Term 2 Lesson PlansDocument19 pagesTechnology Grade 8 Term 2 Lesson PlansmamkonekNo ratings yet
- Ijvr - GR 8 - Term 3 - Learner - Activities - Ratp 2023-24Document41 pagesIjvr - GR 8 - Term 3 - Learner - Activities - Ratp 2023-24Humphrey MahloNo ratings yet
- NovaDocument29 pagesNovacpoliNo ratings yet
- US Manual EnglishDocument101 pagesUS Manual EnglishFernando ChavezNo ratings yet
- Planning Grid Leaving Cert Construction StudiesDocument4 pagesPlanning Grid Leaving Cert Construction Studiesapi-341109474No ratings yet
- Sepedi Lesson PlanDocument9 pagesSepedi Lesson PlanPretty Selowa100% (1)
- Falco Construction DrawingsDocument395 pagesFalco Construction Drawingsrocketmench100% (1)
- CB 380 Service ManualDocument20 pagesCB 380 Service Manualphantrongthuc100% (2)
- Grade 8.2020 Technology Year End MemoDocument8 pagesGrade 8.2020 Technology Year End MemoHylton EricNo ratings yet
- Technology Grade 8 2017 March Test 1Document8 pagesTechnology Grade 8 2017 March Test 1Nokuthula NdhlovuNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 English HLDocument32 pagesGrade 9 English HLShayneNo ratings yet
- 2021 Creative Arts Dance ATP GR 8 Term 1-4Document4 pages2021 Creative Arts Dance ATP GR 8 Term 1-4siyabonga mpofu100% (1)
- Gr8 Geog Test T1rDocument6 pagesGr8 Geog Test T1rSabelo james BhembeNo ratings yet
- Geography Grade 8 Term 3Document7 pagesGeography Grade 8 Term 3jesmuk7No ratings yet
- The Economy Price Theory Grade 9 Part 1Document10 pagesThe Economy Price Theory Grade 9 Part 1William Sello100% (1)
- Grade 8 Tech Mini PatDocument14 pagesGrade 8 Tech Mini Patboikanomangoale32No ratings yet
- Today Grade 9 Technology Planning PackDocument16 pagesToday Grade 9 Technology Planning Packapi-35935349150% (4)
- 2018 - GCSE - System&Control DNT PaperDocument20 pages2018 - GCSE - System&Control DNT PaperLOL123456787654100% (1)
- Grade 8 Tech 2018Document10 pagesGrade 8 Tech 2018Shirley ManamelaNo ratings yet
- Mathematics P1 Feb-March 2017 Memo Afr & EngDocument18 pagesMathematics P1 Feb-March 2017 Memo Afr & Engaleck mthethwaNo ratings yet
- NWPA GR 9 Tech JUNE Exam Paper 2018Document11 pagesNWPA GR 9 Tech JUNE Exam Paper 2018lungelo.martin556No ratings yet
- 1 School Improvement Guide Life Orientation Career Guidance Pocket Guide Grade 8-12Document34 pages1 School Improvement Guide Life Orientation Career Guidance Pocket Guide Grade 8-12RoxanneNo ratings yet
- Argumentative Essay 2023 Grade 10 Kwadinabakubo SecondayDocument9 pagesArgumentative Essay 2023 Grade 10 Kwadinabakubo SecondaySphesihle Penene100% (2)
- English Fal Grade 10 Catch UpDocument8 pagesEnglish Fal Grade 10 Catch UpNoxolo MotloungNo ratings yet
- TechDocument8 pagesTechMogauNo ratings yet
- Life Sciences P2 Nov 2010 Memo EngDocument14 pagesLife Sciences P2 Nov 2010 Memo Engbellydanceafrica9540100% (1)
- Grade 9 Geography T4 ControlledDocument10 pagesGrade 9 Geography T4 Controllednaledibotshelo14No ratings yet
- Gr8 Nov 2020 Memo & Question PaperDocument17 pagesGr8 Nov 2020 Memo & Question Paperkhuthadzo NdlovuNo ratings yet
- GR 9 Final Exam 2022Document8 pagesGR 9 Final Exam 2022PrettyGent KayyNo ratings yet
- 2022 Creative Art Booklet Form 2 Term 1Document18 pages2022 Creative Art Booklet Form 2 Term 1Tirelo LekomaNo ratings yet
- 2022 LO MEMO GRADE 10 Term 2 Controlled TestDocument7 pages2022 LO MEMO GRADE 10 Term 2 Controlled TestHasani Clever XihlahlaNo ratings yet
- GR 10Document12 pagesGR 10Refilwe Raphalo100% (1)
- Ijvr - GR 9 - Term 2 - Activities - 2023-24 - 230421 - 144143Document64 pagesIjvr - GR 9 - Term 2 - Activities - 2023-24 - 230421 - 144143Oswell NhlangwiniNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Letter 101/3/2021: WavesDocument12 pagesTutorial Letter 101/3/2021: WavesTshepo MolotoNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 EMS Classic Ed GuideDocument41 pagesGrade 8 EMS Classic Ed GuideMartyn Van ZylNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 June Exam Marking Guideline 2023-2Document9 pagesGrade 10 June Exam Marking Guideline 2023-2Masimo SeforaNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Mathematics Whole Numbers Revision Worksheet 1Document3 pagesGrade 9 Mathematics Whole Numbers Revision Worksheet 1shermanNo ratings yet
- 2016 Grade 10 Mid Year Exam June Math Paper 2 MemoDocument8 pages2016 Grade 10 Mid Year Exam June Math Paper 2 MemoAmaza SiswanaNo ratings yet
- Gr9 EMS P2 ENG June 2022 Possible AnswersDocument6 pagesGr9 EMS P2 ENG June 2022 Possible Answers6lackzamokuhleNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 6 Numeric and Geometric Patterns Grade 9 MathsDocument2 pagesWorksheet 6 Numeric and Geometric Patterns Grade 9 MathsneelofahNo ratings yet
- Peruvian North American Abraham Lincoln School: Middle Years Programme - 2020Document2 pagesPeruvian North American Abraham Lincoln School: Middle Years Programme - 2020ErickHenryNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Provincial Examination Mathematics P2 (English) June 2023 Question PaperDocument5 pagesGrade 10 Provincial Examination Mathematics P2 (English) June 2023 Question PaperleokunsunpeiNo ratings yet
- Memo of Grade 8 LO Exam Term 2 - 2017 FinalDocument8 pagesMemo of Grade 8 LO Exam Term 2 - 2017 FinalSmangele ShabalalaNo ratings yet
- English GR 10 HL MEMO Paper 1Document7 pagesEnglish GR 10 HL MEMO Paper 1LathithaNo ratings yet
- Class 8-Revision Worksheet (3) MOY ExamsDocument3 pagesClass 8-Revision Worksheet (3) MOY ExamsKhola Munawar - 79431/TCHR/BFBOYNo ratings yet
- Tech GR 8 Pat 2023 (Memo)Document17 pagesTech GR 8 Pat 2023 (Memo)qayiyanasamkele100% (1)
- GR 8 LO June - July Exam - MEMO 2022Document16 pagesGR 8 LO June - July Exam - MEMO 2022vanderwaltlina100% (1)
- Ems Grade 9 Ed Guide 2021Document224 pagesEms Grade 9 Ed Guide 2021Martyn Van ZylNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 English Home Language Annual Teaching Plan - 2024 - Fs - GdeDocument44 pagesGrade 10 English Home Language Annual Teaching Plan - 2024 - Fs - Gdesamanthajane294No ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Gr. 7 Life Orientation T1 W3-4Document5 pagesLesson Plan Gr. 7 Life Orientation T1 W3-4silantraNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 LO Term 2 Notes and Activities 3 August 2020Document8 pagesGrade 8 LO Term 2 Notes and Activities 3 August 2020Thembile GubevuNo ratings yet
- Exam Study Booklet June GR 9Document8 pagesExam Study Booklet June GR 9RowanChibiNo ratings yet
- Term 3 EMS Learner ActivitiesDocument40 pagesTerm 3 EMS Learner ActivitiesCharmaine Lerato MolefeNo ratings yet
- GR 9 NS (English) June 2023 Question PaperDocument18 pagesGR 9 NS (English) June 2023 Question PaperagangdayimaniNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Tech June 2019 1Document10 pagesGrade 8 Tech June 2019 1Mlanga RamsNo ratings yet
- Durban Girls Secondary School Grade 9 Technology Formal Assessment Term 1 Mini PAT 2021Document2 pagesDurban Girls Secondary School Grade 9 Technology Formal Assessment Term 1 Mini PAT 2021Hayley0% (1)
- Effingham Secondary School Department of Geography Social Studies - Geography Grade 8 Revision Activity 1 Define The Following TermsDocument2 pagesEffingham Secondary School Department of Geography Social Studies - Geography Grade 8 Revision Activity 1 Define The Following TermsStacey Nefdt100% (1)
- Mathematics Grade 9 June Paper (0001) Memo: Time: 2H Total: 100 MarksDocument6 pagesMathematics Grade 9 June Paper (0001) Memo: Time: 2H Total: 100 Marksknhlanhla194No ratings yet
- NS Grade 9 Term 4 Teacher GuideDocument21 pagesNS Grade 9 Term 4 Teacher Guidesinalomanyadu100% (1)
- GR 9 ECO P1 (English) June 2023 Question PaperDocument8 pagesGR 9 ECO P1 (English) June 2023 Question PaperasiyolisengomaNo ratings yet
- Grade 6 PSW Yearend Question PaperDocument8 pagesGrade 6 PSW Yearend Question PaperJerome Buchler100% (1)
- Term-2 - Grade 8 Social Science Mock Test-1Document5 pagesTerm-2 - Grade 8 Social Science Mock Test-1bhagatNo ratings yet
- 2023 Economics GR 10 Exam GuidelinesDocument31 pages2023 Economics GR 10 Exam GuidelinesLinda DladlaNo ratings yet
- Planning Grid Leaving Cert Construction StudiesDocument4 pagesPlanning Grid Leaving Cert Construction Studiesapi-544280724No ratings yet
- Tutu 2Document1 pageTutu 2siyabonga mpofuNo ratings yet
- DesmondDocument16 pagesDesmondsiyabonga mpofuNo ratings yet
- 2021 Mathematics Atp Grade 8Document7 pages2021 Mathematics Atp Grade 8siyabonga mpofuNo ratings yet
- 2022 Life Orientation ATP Grade 8Document6 pages2022 Life Orientation ATP Grade 8siyabonga mpofu100% (1)
- 2021 Revised ATP Creative Arts Visual Art GR 8Document4 pages2021 Revised ATP Creative Arts Visual Art GR 8siyabonga mpofuNo ratings yet
- 2021 Creative Arts Dance ATP GR 8 Term 1-4Document4 pages2021 Creative Arts Dance ATP GR 8 Term 1-4siyabonga mpofu100% (1)
- Grade 8 English HL Term 1-4 AtpDocument22 pagesGrade 8 English HL Term 1-4 Atpsiyabonga mpofuNo ratings yet
- Gr8 Ns Nov District Exam 2017moderated A 2nd TimeDocument16 pagesGr8 Ns Nov District Exam 2017moderated A 2nd Timesiyabonga mpofu100% (3)
- Natural Sciences Grade 8 November 2019Document13 pagesNatural Sciences Grade 8 November 2019siyabonga mpofu100% (2)
- Tech GR 8 November ExamDocument10 pagesTech GR 8 November Examsiyabonga mpofu100% (2)
- S-AAA-ELMS-CRANE (Rev.0-2015)Document7 pagesS-AAA-ELMS-CRANE (Rev.0-2015)Swathish SivaprasadNo ratings yet
- Cycloidal GearboxDocument5 pagesCycloidal GearboxjohnjoviedoNo ratings yet
- Pump Curve ExampleDocument7 pagesPump Curve ExamplesamypalNo ratings yet
- Oriental Motor General Catalogue: 2-Phase Stepping MotorsDocument51 pagesOriental Motor General Catalogue: 2-Phase Stepping MotorsLoth Matheus Barba MazaNo ratings yet
- Acople Nara CatalogDocument48 pagesAcople Nara Catalogmarcelo castillo100% (1)
- Sibre Data Sheet Drum Coupling ABC VDocument18 pagesSibre Data Sheet Drum Coupling ABC VGabriel MoreiraNo ratings yet
- Tooltech AgentDocument32 pagesTooltech AgentIram JavedNo ratings yet
- Study and Design of Automobile Continuously Variable TransmissionDocument43 pagesStudy and Design of Automobile Continuously Variable TransmissionqusayNo ratings yet
- XZM1000 GBDocument32 pagesXZM1000 GBmrivera88No ratings yet
- Multi Angular Gearless DriveDocument4 pagesMulti Angular Gearless Drivemadhanreddy953No ratings yet
- LF 230 Core Drill: Technical Data SheetDocument7 pagesLF 230 Core Drill: Technical Data SheetLuis Aparcana100% (1)
- 5999Document131 pages5999Cao Hao NguyenNo ratings yet
- Drivesystems: Intelligent Drivesystems, Worldwide ServicesDocument36 pagesDrivesystems: Intelligent Drivesystems, Worldwide ServicesAnıl YavuzNo ratings yet
- Basic Mechanical Engineering MCQs PartDocument11 pagesBasic Mechanical Engineering MCQs PartTrbman exaNo ratings yet
- 09e 1Document24 pages09e 1ruslan1580100% (1)
- Lathe Machine 1Document13 pagesLathe Machine 1ronakmeNo ratings yet
- Propeller Shaft & Differential Carrier: Modification NoticeDocument3 pagesPropeller Shaft & Differential Carrier: Modification NoticeAnthonyNo ratings yet
- 500 TransDocument5 pages500 TransRodney WellsNo ratings yet
- GS FunctDocument46 pagesGS FunctCostel Caraman100% (2)
- De Laval Whey SeparatorsDocument36 pagesDe Laval Whey SeparatorsAllen AnyayahanNo ratings yet
- 71 - Design For Hand BrakeDocument13 pages71 - Design For Hand BrakemahendranNo ratings yet
- DSQS-Daewoo Shipbuilding Quality StandardDocument134 pagesDSQS-Daewoo Shipbuilding Quality StandardGoga100% (2)
- Farm MechanizationDocument355 pagesFarm MechanizationJose Carlo Dizon100% (1)
- Paper2911 PDFDocument7 pagesPaper2911 PDFJustin RoxasNo ratings yet