Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pipeline System
Pipeline System
Uploaded by
Rajan Singh PalOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pipeline System
Pipeline System
Uploaded by
Rajan Singh PalCopyright:
Available Formats
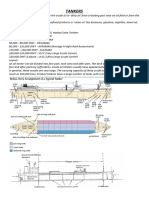
PIPELINE NETWORK
Pipeline networks are composed of several pieces of equipments that operate together to move products from location to location.
Oil, Gas, Water, Chemicals, etc. are generally transferred through a pipeline network stretching across a large geographical area.
Pipelines can be classified in three categories:
1) GATHERING PIPELINES
Group of smaller interconnected pipelines forming complex networks with purpose of bringing crude oil or natural gas from several wells to
a treatment plant or processing facility.
In this group, the pipelines are usually short, a couple of hundred metres and with small diameters.
Also sub-sea pipelines for collecting product from deep water production platforms are considered gathering systems.
2) TRANSPORTATION PIPIELINES
Mainly long pipes with large diameters, moving products (oil, gas, refined products) between cities, countries and even continents.
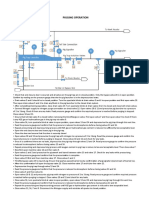
These transportation networks include several stations as Injection Station, Pump/Compressor Station, Block Valve Station, Pigging Facility.
The main elements of a Transportation Pipeline system are:
Injection Station (Supply / Inlet Station)
It is the beginning of the system, where the product (Oil / Gas) is injected into the pipeline.
Storage facilities, pumps, compressors, metering stations are usually located at the injection station.
Metering Stations
Metering stations are placed along gas pipelines. These stations allow pipeline operator to monitor, manage, and account for gas in pipes.
Metering stations employ specialized meters to measure the gas as it flows through the pipeline without impeding its movement.
Pump / Compressor Station (Booster Station)
Pumps for liquid pipelines and compressors for gas pipelines, are located along the line to move the product through the pipeline.
The location of these stations is defined by topography of terrain, type of product being transported, or operational conditions of network.
Booster stations are installed along the pipelines at variable distances to compensate for the pipeline pressure losses and elevation changes
and to ensure a constant flow of liquid.
Block Valve Station
These are the first line of protection for pipelines.
With these valves the operator can isolate any segment of the line for maintenance work or isolate a rupture or leak.
Block valve stations are usually located every 20 to 30 miles (48 km), depending on the type of pipeline.
The location of these stations depends exclusively on the nature of the product being transported, the trajectory of the pipeline and/or the
operational conditions of the line.
Regulator Station
This is a special type of valve station, where the operator can release some of the pressure from the line.
Regulators are usually located at the downhill side of a peak.
Pig Launching / Receiving Facilities
Pigging facilities consist of pig launching or receiving equipment & allow pipeline to accommodate a high-resolution internal inspection tool.
Pigs are devices that are placed into a pipeline to perform certain functions. Some are used to clean the inside of the pipeline or to monitor
its internal and external condition.
Launchers and receivers are facilities that enable pigs to be inserted into or removed from the pipeline.
It may be equipped with an office, workshops, a small permanent camp (in remote locations), power generators, storage areas, and helipad.
It is normally unmanned except during periods of manual pigging and during routing service or repair.
Partial Delivery Station (Intermediate Station)
These facilities allow the pipeline operator to deliver part of the product being transported.
Final Delivery Station (Outlet Station / Terminal)
This is where the product will be delivered by the pipeline operator.
It could be a tank farm for storage or a connection to a distribution network for gas or oil.
3) DISTRIBUTION PIPELINES
Composed of several interconnected pipelines with small diameters, used to take the products to the final consumer.
Feeder lines to distribute gas to homes and businesses downstream.
Pipelines at terminals for distributing products to tanks and storage facilities are included in this group.
You might also like
- Notes On Petroleum Transport and StorageDocument33 pagesNotes On Petroleum Transport and StorageNji Franklin75% (4)
- SP1210 Pipeline Operation and MaintDocument25 pagesSP1210 Pipeline Operation and MaintRoshin99100% (2)
- Coiled Tubing Operations at a Glance: What Do You Know About Coiled Tubing Operations!From EverandCoiled Tubing Operations at a Glance: What Do You Know About Coiled Tubing Operations!Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- SUBSEA1Document16 pagesSUBSEA1alioo44No ratings yet
- Underground Piping PDFDocument40 pagesUnderground Piping PDFAngelita Qtal100% (2)
- STA-C Series - Super Trident Sewage Treatment PlantDocument2 pagesSTA-C Series - Super Trident Sewage Treatment Plantanandsharma123No ratings yet
- Ultrasound Analysis for Condition Monitoring: Applications of Ultrasound Detection for Various Industrial EquipmentFrom EverandUltrasound Analysis for Condition Monitoring: Applications of Ultrasound Detection for Various Industrial EquipmentRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Dense Phase Co2 Transport PDFDocument87 pagesDense Phase Co2 Transport PDFSchöberl ErichNo ratings yet
- Pamphlet 60 - Edition-6 - August-2007 Chlorine PipelinesDocument28 pagesPamphlet 60 - Edition-6 - August-2007 Chlorine PipelinesJacques BlueqNo ratings yet
- Pigging Training Course Mod 7 Rev 1Document26 pagesPigging Training Course Mod 7 Rev 1Suparerk Sirivedin100% (1)
- Pipeline and Riser System Design Course ManualDocument146 pagesPipeline and Riser System Design Course Manualdiepriye100% (5)
- An Introduction About PipelineDocument51 pagesAn Introduction About PipelineAngel NgoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Oil Gas Pipeline and Tankers Week 10Document76 pagesIntroduction To Oil Gas Pipeline and Tankers Week 10Luthfan ArekaNo ratings yet
- Introduction and Chapter 1Document77 pagesIntroduction and Chapter 1Nasir ShafiqNo ratings yet
- Production Engineering TechnologyDocument28 pagesProduction Engineering TechnologyReband AzadNo ratings yet
- Diaphragm Pump CharacteristicsDocument9 pagesDiaphragm Pump CharacteristicslamiaNo ratings yet
- Instrumentation Advance Course Part 2Document69 pagesInstrumentation Advance Course Part 2FACE BOOKNo ratings yet
- Hydrant System For Data CenterDocument3 pagesHydrant System For Data CenterSidik mattganNo ratings yet
- W3 - Basic Upstream Oil - Gas ProcessesDocument63 pagesW3 - Basic Upstream Oil - Gas ProcessesHidayah HumairaNo ratings yet
- Section II Equipment Piping and Assembly ApplicationsDocument47 pagesSection II Equipment Piping and Assembly ApplicationsAndy ChongNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Principles of Pigging TechnologyDocument8 pagesFundamental Principles of Pigging TechnologyQuán Cóc Sài GònNo ratings yet
- Flow LinesDocument1 pageFlow LinesScribdTranslationsNo ratings yet
- Underground Piping and Services SystemsDocument29 pagesUnderground Piping and Services SystemsNabil Al-Khirdaji50% (2)
- Website ContentDocument6 pagesWebsite ContentLakshmi SrujanaNo ratings yet
- Facilities 1Document9 pagesFacilities 1Prem NagappanpillaiNo ratings yet
- Gas Gathering 6Document50 pagesGas Gathering 6THE TERMINATORNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Gas Pipeline Metering StationDocument5 pagesFundamentals of Gas Pipeline Metering Stationsandeepsri9No ratings yet
- Prince Rupert Natural Gas Transmission Compressor Station Basics Factsheet TranscanadaDocument2 pagesPrince Rupert Natural Gas Transmission Compressor Station Basics Factsheet TranscanadaShaho Abdulqader MohamedaliNo ratings yet
- Public Infrastructure ManagementDocument12 pagesPublic Infrastructure ManagementscribdghayasNo ratings yet
- Process Plant Layout and Piping DesignDocument106 pagesProcess Plant Layout and Piping DesignGaurav GuptaNo ratings yet
- FMSP 2Document40 pagesFMSP 2مصطفى عمرNo ratings yet
- OIL and GAS ProcessingDocument35 pagesOIL and GAS ProcessingHlw Dear100% (2)
- Fundamentals of Gas Pipeline Metering Stations - Pipeline & Gas JournalDocument4 pagesFundamentals of Gas Pipeline Metering Stations - Pipeline & Gas JournalMehedi HasanNo ratings yet
- Pump Room SystemsDocument8 pagesPump Room SystemsArdyas Wisnu Baskoro100% (1)
- Function of Piping Component: Steam Trap and Drain TrapDocument23 pagesFunction of Piping Component: Steam Trap and Drain TrapMallela Sampath KumarNo ratings yet
- AMT Module 1 - PartB-1Document12 pagesAMT Module 1 - PartB-1PrathikNo ratings yet
- Components of Tranportation SystemDocument67 pagesComponents of Tranportation SystemGladys BaleñaNo ratings yet
- Pipeline Inspection: Pipe RackDocument4 pagesPipeline Inspection: Pipe RackAnushi DahariaNo ratings yet
- Gas Compressor Station Scope of WorksDocument5 pagesGas Compressor Station Scope of Worksomar mohd zaini100% (1)
- Pipeline TransportDocument9 pagesPipeline TransportSinisaP23No ratings yet
- Design Operation and Maintenance of Lact UnitsDocument12 pagesDesign Operation and Maintenance of Lact UnitsDiana Lucía Padilla0% (1)
- Vapour Management ControlDocument22 pagesVapour Management Controlviktor_gligorovNo ratings yet
- Pressure & Fluid Management SystemDocument6 pagesPressure & Fluid Management SystemLoganBohannonNo ratings yet
- Notes On ControlDocument10 pagesNotes On ControlLINDOHNo ratings yet
- GSR - Topic ChoosingDocument3 pagesGSR - Topic ChoosingSayed YusufNo ratings yet
- Oil Tanker Cargo WorkDocument12 pagesOil Tanker Cargo WorkAshutosh Singh100% (4)
- Marine SystemsDocument44 pagesMarine Systemsvikrantgulhane83% (6)
- New Microsoft Word DocumentDocument26 pagesNew Microsoft Word DocumentThe Progress PortalNo ratings yet
- CV Training InstDocument21 pagesCV Training Instxentrer100% (1)
- 1 - SITES SRL - Company ProfileDocument12 pages1 - SITES SRL - Company ProfileElena VolontèNo ratings yet
- Equipment LayoutDocument25 pagesEquipment LayoutCalNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics and Pneumatics - Components-1Document179 pagesHydraulics and Pneumatics - Components-1edmondkalinde33No ratings yet
- Well CompletionDocument64 pagesWell CompletionNidhal KahouliNo ratings yet
- Compression Stations and Pumping by Erick Martin Ceballos RetanaDocument14 pagesCompression Stations and Pumping by Erick Martin Ceballos RetanaerickNo ratings yet
- Flowlines and ManifoldsDocument5 pagesFlowlines and ManifoldsMSNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Plant Start Up & Shut DownDocument16 pagesChapter 6 - Plant Start Up & Shut DownDharshica MohanNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 10Document28 pagesCHAPTER 10ivorykeyzzNo ratings yet
- PTT System Group-1Document18 pagesPTT System Group-1Shweta SainiNo ratings yet
- Branching PipesDocument53 pagesBranching PipesAhmad HusnainNo ratings yet
- Itmconf Cccar2022 03019Document5 pagesItmconf Cccar2022 03019Sumya Ben mahmoudNo ratings yet
- 3D Model ReviewDocument12 pages3D Model ReviewDana GuerreroNo ratings yet
- Drilling and Production MachineDocument10 pagesDrilling and Production MachineBilly WilsonNo ratings yet
- Inside the Pill Bottle: A Comprehensive Guide to the Pharmaceutical IndustryFrom EverandInside the Pill Bottle: A Comprehensive Guide to the Pharmaceutical IndustryNo ratings yet
- Machines, Tools and Methods of Automobile ManufactureFrom EverandMachines, Tools and Methods of Automobile ManufactureRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Installation and Operation Instructions For Custom Mark III CP Series Oil Fired UnitFrom EverandInstallation and Operation Instructions For Custom Mark III CP Series Oil Fired UnitNo ratings yet
- Cathodic ProtectionDocument2 pagesCathodic ProtectionRajan Singh PalNo ratings yet
- NAMURDocument5 pagesNAMURRajan Singh PalNo ratings yet
- Winterisation InsulationDocument6 pagesWinterisation InsulationRajan Singh PalNo ratings yet
- WHCPDocument8 pagesWHCPRajan Singh Pal100% (1)
- Pipeline PiggingDocument1 pagePipeline PiggingRajan Singh PalNo ratings yet
- Pig SignalerDocument2 pagesPig SignalerRajan Singh PalNo ratings yet
- Centrifugal Compressor SystemsDocument10 pagesCentrifugal Compressor SystemsDaniel YoworldNo ratings yet
- Detalles de Simulador-Pipe-Phase PiggingDocument1 pageDetalles de Simulador-Pipe-Phase PiggingJose Monges100% (1)
- iNPIPE Products Foam Pig Data SheetDocument6 pagesiNPIPE Products Foam Pig Data Sheetichal_zaidanNo ratings yet
- Pipline Cleaning ServicesDocument4 pagesPipline Cleaning Servicesbagus adhitiawarman100% (1)
- EnerMech Process & PipelineDocument4 pagesEnerMech Process & PipelineZulhilmi ZalizanNo ratings yet
- Intelligent PiggingDocument0 pagesIntelligent PiggingSam RajNo ratings yet
- PPSADirectory22 23Document34 pagesPPSADirectory22 23luisgomezrojasNo ratings yet
- SP 1212 Check SheetDocument5 pagesSP 1212 Check SheetDaniel MartinezNo ratings yet
- D BB Pipeline Isolation PaperDocument24 pagesD BB Pipeline Isolation Paperhadi137No ratings yet
- Recommended Practices For Storage and Transport of Edible Oils and FatsDocument13 pagesRecommended Practices For Storage and Transport of Edible Oils and FatsM Alim Ur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Filters For Pipeline Pigging Operations: Engineered Filtration ProductsDocument1 pageFilters For Pipeline Pigging Operations: Engineered Filtration ProductsAkaalj InspeccionNo ratings yet
- Coker Heater Design - The Heart of The Coking ProcessDocument45 pagesCoker Heater Design - The Heart of The Coking ProcessVigneswaran SNo ratings yet
- GgsDocument21 pagesGgsKrishna KumarNo ratings yet
- This Document Was Downloaded From The Penspen Integrity Virtual LibraryDocument52 pagesThis Document Was Downloaded From The Penspen Integrity Virtual LibraryShayan Hasan KhanNo ratings yet
- 2008 Pigging PowerPointDocument59 pages2008 Pigging PowerPointLEO_GONZALEZ100% (1)
- Retrieval of Stuck Pig PDFDocument1 pageRetrieval of Stuck Pig PDFyasir_anjumNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Results of An Intelligent Pig InspectionDocument18 pagesUnderstanding The Results of An Intelligent Pig InspectionLeonardo VazNo ratings yet
- Mitigation Strategy For Sulfur Deposits in Gas PipelinesDocument2 pagesMitigation Strategy For Sulfur Deposits in Gas PipelinesNorfolking100% (1)
- Pigging System IntroductionDocument29 pagesPigging System IntroductionRobert Chai100% (1)
- Design of Onshore Multi-Pipe Slug CatcherDocument28 pagesDesign of Onshore Multi-Pipe Slug Catcherjk.jackycheokNo ratings yet
- Cleaning Pig Designs and ApplicationsDocument24 pagesCleaning Pig Designs and ApplicationsChristopher BrownNo ratings yet
- Multiple Riser Configurations Top-Tensioned Risers Hybrid Riser SystemDocument103 pagesMultiple Riser Configurations Top-Tensioned Risers Hybrid Riser Systemsaeed ghafoori100% (4)
- Spe 192741-MSDocument19 pagesSpe 192741-MSromerobernaNo ratings yet
- ACECO 2020 Product SummaryDocument12 pagesACECO 2020 Product SummaryLynn AlgerNo ratings yet
- Pipeline Pigging: An Innovative Concept in Pipe Cleaning Pipeline Pigging: An Innovative Concept in Pipe CleaningDocument8 pagesPipeline Pigging: An Innovative Concept in Pipe Cleaning Pipeline Pigging: An Innovative Concept in Pipe CleaningdrinkwaterproductsNo ratings yet