Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pressure
Pressure
Uploaded by
DevineCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Ocean's Impact On Climate Activity Worksheet: Name: Mia Popovic Date: 9/22/2020Document4 pagesOcean's Impact On Climate Activity Worksheet: Name: Mia Popovic Date: 9/22/2020Mia Popovic100% (1)
- IC Joshi Aviation Met Total Q.Document59 pagesIC Joshi Aviation Met Total Q.Altivia Aviation Academy100% (7)
- Ther 1 - 111114Document33 pagesTher 1 - 111114So Nny0% (1)
- PSD CEU 194dec12 PDFDocument22 pagesPSD CEU 194dec12 PDFCesar Muñoz OssesNo ratings yet
- EContent 3 2024 03 19 12 18 18 VARIOUSTYPESOFPRESSUREdocx 2024 03 19 12 06 34Document4 pagesEContent 3 2024 03 19 12 18 18 VARIOUSTYPESOFPRESSUREdocx 2024 03 19 12 06 34maanitghodasara.118845No ratings yet
- Industrial Pressure MeasurementDocument49 pagesIndustrial Pressure MeasurementArjay T. EspinoNo ratings yet
- Pressure PresentationDocument30 pagesPressure PresentationalthafscribdNo ratings yet
- 5 Principles of Hydrostatic PressureDocument20 pages5 Principles of Hydrostatic PressureTrixia DuazoNo ratings yet
- Pressure: Introduction To Pressure - Psi and Pa - Online Pressure Units ConverterDocument3 pagesPressure: Introduction To Pressure - Psi and Pa - Online Pressure Units ConverterMauliNo ratings yet
- Gauge and Absolute Pressure (PHYSICS)Document3 pagesGauge and Absolute Pressure (PHYSICS)SherwinNo ratings yet
- PRESSUREDocument2 pagesPRESSUREZoteloNo ratings yet
- 5 - 2 Help For Hydrodistillation Lab ExperimentDocument1 page5 - 2 Help For Hydrodistillation Lab ExperimentAlessandroNo ratings yet
- Static Pressure - DerivationDocument6 pagesStatic Pressure - DerivationNomi WahlaNo ratings yet
- MANOMETERS NotesDocument5 pagesMANOMETERS NotesKawie AñeroNo ratings yet
- Thermatel: Thermal Dispersion Mass FlowDocument34 pagesThermatel: Thermal Dispersion Mass FlowamshahNo ratings yet
- Module 2 & 3Document180 pagesModule 2 & 3Piyush ShahaneNo ratings yet
- Sem218 W1 LECTURE3Document15 pagesSem218 W1 LECTURE3Akashi SilvaNo ratings yet
- Pressure: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument11 pagesPressure: From Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediadarla999No ratings yet
- 48 - 25795 - ME362 - 2020 - 1 - 2 - 1 - Lecture 3 - Fluid 1 - Fluid StaticsDocument29 pages48 - 25795 - ME362 - 2020 - 1 - 2 - 1 - Lecture 3 - Fluid 1 - Fluid StaticsHussien El-masryNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Water FlowDocument4 pagesFundamentals of Water Flowdanijel.borovinsekNo ratings yet
- Understanding Pressure and Pressure MeasurementDocument6 pagesUnderstanding Pressure and Pressure MeasurementAbdul-Wahab Anwar100% (8)
- Pressure: - Pressure Is The Force Exerted by A Gas On A Surface. - Pressure and The Kinetic TheoryDocument60 pagesPressure: - Pressure Is The Force Exerted by A Gas On A Surface. - Pressure and The Kinetic TheoryNenbon NatividadNo ratings yet
- FLUID MECHANICS 03 Pressure.Document19 pagesFLUID MECHANICS 03 Pressure.Shiela SalvillaNo ratings yet
- ME262 Lecture2Document16 pagesME262 Lecture2FawadNo ratings yet
- Temperature and Its Conversions: Temperature Is Usually UsedDocument9 pagesTemperature and Its Conversions: Temperature Is Usually UsedSafeen Y HurmzNo ratings yet
- Details of The BMP180 Barometric Pressure Sensor : Pascals (Pa)Document3 pagesDetails of The BMP180 Barometric Pressure Sensor : Pascals (Pa)chockalingam athilingamNo ratings yet
- F Luid Mec Hanic S: Week 3: Fluid Statics: Pressu ReDocument36 pagesF Luid Mec Hanic S: Week 3: Fluid Statics: Pressu ReAhmad RazaNo ratings yet
- Pressure and It's MeasurementDocument25 pagesPressure and It's Measurementsuyash.2022.awasthiNo ratings yet
- 3 Process Variables Part 2Document22 pages3 Process Variables Part 2Snow DropNo ratings yet
- Pressure Measurements.: TheoryDocument3 pagesPressure Measurements.: Theorymbahbim2No ratings yet
- PSD CEU 194dec12 PDFDocument22 pagesPSD CEU 194dec12 PDFRama RameshNo ratings yet
- Pressure Units ConversionsDocument3 pagesPressure Units ConversionsK S RaoNo ratings yet
- REV - 1 - Module1 - Pneumatic and Electropneumatic TechnologyDocument73 pagesREV - 1 - Module1 - Pneumatic and Electropneumatic TechnologyMuhd IzzatNo ratings yet
- Maintenance Training: Unit Measurement: Pua Wee Ming Tonnage Operation - ReliabilityDocument7 pagesMaintenance Training: Unit Measurement: Pua Wee Ming Tonnage Operation - ReliabilitypuaweemingNo ratings yet
- 1.introduction (Chimtali)Document28 pages1.introduction (Chimtali)lytonchirwa882No ratings yet
- Me Lab 1Document18 pagesMe Lab 1Richmond OlarteNo ratings yet
- Gas Metering PT - 2Document11 pagesGas Metering PT - 2brianNo ratings yet
- Pressure MeasurementDocument24 pagesPressure MeasurementOssy DewintaNo ratings yet
- Atmospheric Pressure - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument9 pagesAtmospheric Pressure - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediaelvi anggiovennyNo ratings yet
- Lecture1 - Introduction GasesDocument31 pagesLecture1 - Introduction Gaseslytonchirwa882No ratings yet
- Ensc26 Lecture02 PressureDocument44 pagesEnsc26 Lecture02 PressureCassandra AyadNo ratings yet
- Absolute and Relative PressureDocument18 pagesAbsolute and Relative PressurewakhalewakhaleNo ratings yet
- FLUIDS - PressureDocument5 pagesFLUIDS - PressureKarl HendrixNo ratings yet
- What's The Difference Between Gauge and Absolute Pressure?Document2 pagesWhat's The Difference Between Gauge and Absolute Pressure?ArindomNo ratings yet
- Process Variables-PressureDocument9 pagesProcess Variables-PressureFarouk BassaNo ratings yet
- Sunu3 2020Document58 pagesSunu3 2020Mir BedirhanNo ratings yet
- 1 Practice Problems (2 - 2)Document3 pages1 Practice Problems (2 - 2)IAN PAOLO BAUTISTA50% (2)
- Dekker Knowledge Database: The Experts in Vacuum SolutionsDocument1 pageDekker Knowledge Database: The Experts in Vacuum Solutionskalyan patilNo ratings yet
- 2023 Lect1 FLUID STATIC Application of Hydro StaticDocument80 pages2023 Lect1 FLUID STATIC Application of Hydro StaticmegatrotronNo ratings yet
- Delivered By:: Rahat SarwarDocument39 pagesDelivered By:: Rahat SarwarinamNo ratings yet
- CHE205 SP22 WK 5 Class TutorialDocument53 pagesCHE205 SP22 WK 5 Class TutorialKW GAMERNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - FluidDocument9 pagesChapter 1 - Fluidfieyza adnNo ratings yet
- Fluids CompletedDocument18 pagesFluids CompletedskystarrepubNo ratings yet
- Facts and Theory of Air: For Industrial PneumaticsDocument74 pagesFacts and Theory of Air: For Industrial PneumaticspfalencarNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Lecture 1Document1 pageThermodynamics Lecture 1Shiela May SantamenaNo ratings yet
- Extract Total MeasurementDocument18 pagesExtract Total MeasurementBien MLNo ratings yet
- Air TheoryDocument74 pagesAir TheoryHASHEMNo ratings yet
- PressureDocument228 pagesPressureDhirajMadanNo ratings yet
- Pressure: This Article Is About Pressure in The Physical Sciences. For Other Uses, SeeDocument7 pagesPressure: This Article Is About Pressure in The Physical Sciences. For Other Uses, SeekopokopoNo ratings yet
- Pressure, Heat and Temperature - Physics for Kids - 5th Grade | Children's Physics BooksFrom EverandPressure, Heat and Temperature - Physics for Kids - 5th Grade | Children's Physics BooksNo ratings yet
- Grup Two PresentiestionDocument23 pagesGrup Two PresentiestionFira tubeNo ratings yet
- Interactive Textbook 2 2 Air Masses and Fronts13Document8 pagesInteractive Textbook 2 2 Air Masses and Fronts13api-240094705No ratings yet
- Year 7 Geography Knowledge BookDocument13 pagesYear 7 Geography Knowledge BooknetoameNo ratings yet
- The Wind and Pressure Over The OceanDocument29 pagesThe Wind and Pressure Over The OceanRonald C. Valdez Jr.No ratings yet
- Continuous Improvement and de Bottlenecking Existing ASU Assets Via Front End RetrofitsDocument7 pagesContinuous Improvement and de Bottlenecking Existing ASU Assets Via Front End RetrofitsVilas AndhaleNo ratings yet
- MET135 Lesson 3 Atmopsheric Moisture and StabilityDocument21 pagesMET135 Lesson 3 Atmopsheric Moisture and StabilityMalik ForbesNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics FormulaDocument2 pagesFluid Mechanics FormulaRiver Run100% (1)
- The Mars Observer MissionDocument66 pagesThe Mars Observer MissionBob AndrepontNo ratings yet
- The Evolutionary Process: Science-Grade 9-Sussex College - WennappuwaDocument8 pagesThe Evolutionary Process: Science-Grade 9-Sussex College - WennappuwaSwarnapaliliyanageNo ratings yet
- Continuous Sintering PDFDocument1 pageContinuous Sintering PDFKrishnanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 Gas LawsDocument14 pagesChapter 13 Gas LawsAlicia WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 NotesProblem SolvingDocument5 pagesGrade 10 NotesProblem Solvingallijah gwyneth dalesNo ratings yet
- Factors That Allow Life To Exist On Earth 2015Document4 pagesFactors That Allow Life To Exist On Earth 2015api-288682437No ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions (MCQS) Class: Iv: Subject: ScienceDocument5 pagesMultiple Choice Questions (MCQS) Class: Iv: Subject: ScienceSudha Pandey100% (1)
- Objective Chemistry Gear UpDocument42 pagesObjective Chemistry Gear UpmohamedNo ratings yet
- Elettrovalvole Pneumatiche: Pneumatic Solenoid ValvesDocument1 pageElettrovalvole Pneumatiche: Pneumatic Solenoid ValvesAdrian MartinNo ratings yet
- LT DPT (LRV & URV) CalcDocument3 pagesLT DPT (LRV & URV) CalcKarthikeyanNo ratings yet
- Human Causes of Global WarmingDocument3 pagesHuman Causes of Global WarmingniaNo ratings yet
- REFRIGERANTSDocument15 pagesREFRIGERANTSedwin barutNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Compressible FlowDocument32 pagesChapter 4 - Compressible FlowNicholas EmildasNo ratings yet
- Elements of Weather and ClimateDocument6 pagesElements of Weather and ClimateFarheen BanoNo ratings yet
- RSM Question Bank - EST 22447 - PVPDBM CompressedDocument23 pagesRSM Question Bank - EST 22447 - PVPDBM Compressed33 .Snehal GhadgeNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning Problem SetDocument3 pagesAir Conditioning Problem SetbacalsojvahronNo ratings yet
- The Earth - A Living Planet: Warming UpDocument6 pagesThe Earth - A Living Planet: Warming UpCristiana PopaNo ratings yet
- 9.5 The Kinetic-Molecular Theory - Chemistry 2e - OpenStaxDocument6 pages9.5 The Kinetic-Molecular Theory - Chemistry 2e - OpenStaxBillyNo ratings yet
- A Year in My Country Weather Reading Comprehension Exercises Tests Warmers Cool - 20163Document1 pageA Year in My Country Weather Reading Comprehension Exercises Tests Warmers Cool - 20163AndresGomezR100% (1)
- Indian Monsoons: Breeze On A Large ScaleDocument7 pagesIndian Monsoons: Breeze On A Large ScaleVikram DasNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Choke PerformanceDocument45 pagesLecture 1 Choke PerformancearvNo ratings yet
Pressure
Pressure
Uploaded by
DevineOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pressure
Pressure
Uploaded by
DevineCopyright:
Available Formats
Pressure – is the force exerted by a fluid per unit area. We speak of pressure when we deal with a gas or a liquid.
uid. The
counter part of pressure in solid is stress
Customary U.S. pressure units are pounds per square inch (lbs/in 2). Standard SI pressure units are kPa or
MPa, although bars are also used in tabulations of thermodynamic data. (1 bar = 10 5 Pa = 100 kPa).
Most pressure gauges read atmospheric pressure, but in general, thermodynamic calculations will be
performed using absolute pressure. The values of a standard atmosphere in various units are given:
Standard Atmospheric Pressure
1.000 atm (atmosphere)
14.696 psia (pounds per square inch absolute)
2116.2 psfa (pounds per square foot absolute)
407.1 in w.g. (Inches of water; inches water gauge)
33.93 ft w.g. (Feet of water; feet water gauge)
29.291 in Hg (inches of mercury)
760.0 mm Hg (millimeter of mercury)
760.0 torr
1.013 bar
101.325 kPa (kilopascals)
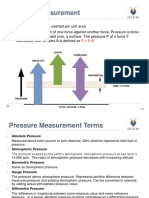
Pressure measurement
Pabs (Absolute pressure that is greater than atmospheric pressure)
Pgage (ordinary pressure gage reads: difference between absolute
absolute and atmospheric pressure)
Standard atmospheric or barometric pressure (29.921 in Hg or 14.7 psia or 101.325 kPa
Gage pressure Zero
Pvac (Pressure Vacuum - negative pressure gage)
Barometric reads (Patm) ordinary vacuum gage reads difference between atmospheric
and absolute pressure
Pabs (absolute pressure – that is less than atmospheric pressure)
absolute pressure zero
(Pabs = 0) absolute zero datum (absolute vacuum)
Pabs = Pgage + Patm (for pressure above Patm)
Pvac = Patm – Pabs (for pressure below Patm)
The word “gage” is generally used in statements of gage pressure, e.g., P = 100 kPa gage. If “gage” is
omitted, the pressure will, in general, be an absolute pressure. Atmospheric pressure is an absolute pressure
and will be taken as 100 kPa (at sea level), unless otherwise stated. It should be noted that atmospheric
pressure is highly dependent on elevation
Positive sign (+) is used when the gauge pressure is greater than atmospheric pressure or surrounding
pressure of the system.
Negative sign (-) is used when the gauge pressure is lower than atmospheric pressure. Negative
gauge pressure is also called as vacuum pressure.
You might also like
- Ocean's Impact On Climate Activity Worksheet: Name: Mia Popovic Date: 9/22/2020Document4 pagesOcean's Impact On Climate Activity Worksheet: Name: Mia Popovic Date: 9/22/2020Mia Popovic100% (1)
- IC Joshi Aviation Met Total Q.Document59 pagesIC Joshi Aviation Met Total Q.Altivia Aviation Academy100% (7)
- Ther 1 - 111114Document33 pagesTher 1 - 111114So Nny0% (1)
- PSD CEU 194dec12 PDFDocument22 pagesPSD CEU 194dec12 PDFCesar Muñoz OssesNo ratings yet
- EContent 3 2024 03 19 12 18 18 VARIOUSTYPESOFPRESSUREdocx 2024 03 19 12 06 34Document4 pagesEContent 3 2024 03 19 12 18 18 VARIOUSTYPESOFPRESSUREdocx 2024 03 19 12 06 34maanitghodasara.118845No ratings yet
- Industrial Pressure MeasurementDocument49 pagesIndustrial Pressure MeasurementArjay T. EspinoNo ratings yet
- Pressure PresentationDocument30 pagesPressure PresentationalthafscribdNo ratings yet
- 5 Principles of Hydrostatic PressureDocument20 pages5 Principles of Hydrostatic PressureTrixia DuazoNo ratings yet
- Pressure: Introduction To Pressure - Psi and Pa - Online Pressure Units ConverterDocument3 pagesPressure: Introduction To Pressure - Psi and Pa - Online Pressure Units ConverterMauliNo ratings yet
- Gauge and Absolute Pressure (PHYSICS)Document3 pagesGauge and Absolute Pressure (PHYSICS)SherwinNo ratings yet
- PRESSUREDocument2 pagesPRESSUREZoteloNo ratings yet
- 5 - 2 Help For Hydrodistillation Lab ExperimentDocument1 page5 - 2 Help For Hydrodistillation Lab ExperimentAlessandroNo ratings yet
- Static Pressure - DerivationDocument6 pagesStatic Pressure - DerivationNomi WahlaNo ratings yet
- MANOMETERS NotesDocument5 pagesMANOMETERS NotesKawie AñeroNo ratings yet
- Thermatel: Thermal Dispersion Mass FlowDocument34 pagesThermatel: Thermal Dispersion Mass FlowamshahNo ratings yet
- Module 2 & 3Document180 pagesModule 2 & 3Piyush ShahaneNo ratings yet
- Sem218 W1 LECTURE3Document15 pagesSem218 W1 LECTURE3Akashi SilvaNo ratings yet
- Pressure: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument11 pagesPressure: From Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediadarla999No ratings yet
- 48 - 25795 - ME362 - 2020 - 1 - 2 - 1 - Lecture 3 - Fluid 1 - Fluid StaticsDocument29 pages48 - 25795 - ME362 - 2020 - 1 - 2 - 1 - Lecture 3 - Fluid 1 - Fluid StaticsHussien El-masryNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Water FlowDocument4 pagesFundamentals of Water Flowdanijel.borovinsekNo ratings yet
- Understanding Pressure and Pressure MeasurementDocument6 pagesUnderstanding Pressure and Pressure MeasurementAbdul-Wahab Anwar100% (8)
- Pressure: - Pressure Is The Force Exerted by A Gas On A Surface. - Pressure and The Kinetic TheoryDocument60 pagesPressure: - Pressure Is The Force Exerted by A Gas On A Surface. - Pressure and The Kinetic TheoryNenbon NatividadNo ratings yet
- FLUID MECHANICS 03 Pressure.Document19 pagesFLUID MECHANICS 03 Pressure.Shiela SalvillaNo ratings yet
- ME262 Lecture2Document16 pagesME262 Lecture2FawadNo ratings yet
- Temperature and Its Conversions: Temperature Is Usually UsedDocument9 pagesTemperature and Its Conversions: Temperature Is Usually UsedSafeen Y HurmzNo ratings yet
- Details of The BMP180 Barometric Pressure Sensor : Pascals (Pa)Document3 pagesDetails of The BMP180 Barometric Pressure Sensor : Pascals (Pa)chockalingam athilingamNo ratings yet
- F Luid Mec Hanic S: Week 3: Fluid Statics: Pressu ReDocument36 pagesF Luid Mec Hanic S: Week 3: Fluid Statics: Pressu ReAhmad RazaNo ratings yet
- Pressure and It's MeasurementDocument25 pagesPressure and It's Measurementsuyash.2022.awasthiNo ratings yet
- 3 Process Variables Part 2Document22 pages3 Process Variables Part 2Snow DropNo ratings yet
- Pressure Measurements.: TheoryDocument3 pagesPressure Measurements.: Theorymbahbim2No ratings yet
- PSD CEU 194dec12 PDFDocument22 pagesPSD CEU 194dec12 PDFRama RameshNo ratings yet
- Pressure Units ConversionsDocument3 pagesPressure Units ConversionsK S RaoNo ratings yet
- REV - 1 - Module1 - Pneumatic and Electropneumatic TechnologyDocument73 pagesREV - 1 - Module1 - Pneumatic and Electropneumatic TechnologyMuhd IzzatNo ratings yet
- Maintenance Training: Unit Measurement: Pua Wee Ming Tonnage Operation - ReliabilityDocument7 pagesMaintenance Training: Unit Measurement: Pua Wee Ming Tonnage Operation - ReliabilitypuaweemingNo ratings yet
- 1.introduction (Chimtali)Document28 pages1.introduction (Chimtali)lytonchirwa882No ratings yet
- Me Lab 1Document18 pagesMe Lab 1Richmond OlarteNo ratings yet
- Gas Metering PT - 2Document11 pagesGas Metering PT - 2brianNo ratings yet
- Pressure MeasurementDocument24 pagesPressure MeasurementOssy DewintaNo ratings yet
- Atmospheric Pressure - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument9 pagesAtmospheric Pressure - Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediaelvi anggiovennyNo ratings yet
- Lecture1 - Introduction GasesDocument31 pagesLecture1 - Introduction Gaseslytonchirwa882No ratings yet
- Ensc26 Lecture02 PressureDocument44 pagesEnsc26 Lecture02 PressureCassandra AyadNo ratings yet
- Absolute and Relative PressureDocument18 pagesAbsolute and Relative PressurewakhalewakhaleNo ratings yet
- FLUIDS - PressureDocument5 pagesFLUIDS - PressureKarl HendrixNo ratings yet
- What's The Difference Between Gauge and Absolute Pressure?Document2 pagesWhat's The Difference Between Gauge and Absolute Pressure?ArindomNo ratings yet
- Process Variables-PressureDocument9 pagesProcess Variables-PressureFarouk BassaNo ratings yet
- Sunu3 2020Document58 pagesSunu3 2020Mir BedirhanNo ratings yet
- 1 Practice Problems (2 - 2)Document3 pages1 Practice Problems (2 - 2)IAN PAOLO BAUTISTA50% (2)
- Dekker Knowledge Database: The Experts in Vacuum SolutionsDocument1 pageDekker Knowledge Database: The Experts in Vacuum Solutionskalyan patilNo ratings yet
- 2023 Lect1 FLUID STATIC Application of Hydro StaticDocument80 pages2023 Lect1 FLUID STATIC Application of Hydro StaticmegatrotronNo ratings yet
- Delivered By:: Rahat SarwarDocument39 pagesDelivered By:: Rahat SarwarinamNo ratings yet
- CHE205 SP22 WK 5 Class TutorialDocument53 pagesCHE205 SP22 WK 5 Class TutorialKW GAMERNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - FluidDocument9 pagesChapter 1 - Fluidfieyza adnNo ratings yet
- Fluids CompletedDocument18 pagesFluids CompletedskystarrepubNo ratings yet
- Facts and Theory of Air: For Industrial PneumaticsDocument74 pagesFacts and Theory of Air: For Industrial PneumaticspfalencarNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Lecture 1Document1 pageThermodynamics Lecture 1Shiela May SantamenaNo ratings yet
- Extract Total MeasurementDocument18 pagesExtract Total MeasurementBien MLNo ratings yet
- Air TheoryDocument74 pagesAir TheoryHASHEMNo ratings yet
- PressureDocument228 pagesPressureDhirajMadanNo ratings yet
- Pressure: This Article Is About Pressure in The Physical Sciences. For Other Uses, SeeDocument7 pagesPressure: This Article Is About Pressure in The Physical Sciences. For Other Uses, SeekopokopoNo ratings yet
- Pressure, Heat and Temperature - Physics for Kids - 5th Grade | Children's Physics BooksFrom EverandPressure, Heat and Temperature - Physics for Kids - 5th Grade | Children's Physics BooksNo ratings yet
- Grup Two PresentiestionDocument23 pagesGrup Two PresentiestionFira tubeNo ratings yet
- Interactive Textbook 2 2 Air Masses and Fronts13Document8 pagesInteractive Textbook 2 2 Air Masses and Fronts13api-240094705No ratings yet
- Year 7 Geography Knowledge BookDocument13 pagesYear 7 Geography Knowledge BooknetoameNo ratings yet
- The Wind and Pressure Over The OceanDocument29 pagesThe Wind and Pressure Over The OceanRonald C. Valdez Jr.No ratings yet
- Continuous Improvement and de Bottlenecking Existing ASU Assets Via Front End RetrofitsDocument7 pagesContinuous Improvement and de Bottlenecking Existing ASU Assets Via Front End RetrofitsVilas AndhaleNo ratings yet
- MET135 Lesson 3 Atmopsheric Moisture and StabilityDocument21 pagesMET135 Lesson 3 Atmopsheric Moisture and StabilityMalik ForbesNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics FormulaDocument2 pagesFluid Mechanics FormulaRiver Run100% (1)
- The Mars Observer MissionDocument66 pagesThe Mars Observer MissionBob AndrepontNo ratings yet
- The Evolutionary Process: Science-Grade 9-Sussex College - WennappuwaDocument8 pagesThe Evolutionary Process: Science-Grade 9-Sussex College - WennappuwaSwarnapaliliyanageNo ratings yet
- Continuous Sintering PDFDocument1 pageContinuous Sintering PDFKrishnanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 Gas LawsDocument14 pagesChapter 13 Gas LawsAlicia WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 NotesProblem SolvingDocument5 pagesGrade 10 NotesProblem Solvingallijah gwyneth dalesNo ratings yet
- Factors That Allow Life To Exist On Earth 2015Document4 pagesFactors That Allow Life To Exist On Earth 2015api-288682437No ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions (MCQS) Class: Iv: Subject: ScienceDocument5 pagesMultiple Choice Questions (MCQS) Class: Iv: Subject: ScienceSudha Pandey100% (1)
- Objective Chemistry Gear UpDocument42 pagesObjective Chemistry Gear UpmohamedNo ratings yet
- Elettrovalvole Pneumatiche: Pneumatic Solenoid ValvesDocument1 pageElettrovalvole Pneumatiche: Pneumatic Solenoid ValvesAdrian MartinNo ratings yet
- LT DPT (LRV & URV) CalcDocument3 pagesLT DPT (LRV & URV) CalcKarthikeyanNo ratings yet
- Human Causes of Global WarmingDocument3 pagesHuman Causes of Global WarmingniaNo ratings yet
- REFRIGERANTSDocument15 pagesREFRIGERANTSedwin barutNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Compressible FlowDocument32 pagesChapter 4 - Compressible FlowNicholas EmildasNo ratings yet
- Elements of Weather and ClimateDocument6 pagesElements of Weather and ClimateFarheen BanoNo ratings yet
- RSM Question Bank - EST 22447 - PVPDBM CompressedDocument23 pagesRSM Question Bank - EST 22447 - PVPDBM Compressed33 .Snehal GhadgeNo ratings yet
- Air Conditioning Problem SetDocument3 pagesAir Conditioning Problem SetbacalsojvahronNo ratings yet
- The Earth - A Living Planet: Warming UpDocument6 pagesThe Earth - A Living Planet: Warming UpCristiana PopaNo ratings yet
- 9.5 The Kinetic-Molecular Theory - Chemistry 2e - OpenStaxDocument6 pages9.5 The Kinetic-Molecular Theory - Chemistry 2e - OpenStaxBillyNo ratings yet
- A Year in My Country Weather Reading Comprehension Exercises Tests Warmers Cool - 20163Document1 pageA Year in My Country Weather Reading Comprehension Exercises Tests Warmers Cool - 20163AndresGomezR100% (1)
- Indian Monsoons: Breeze On A Large ScaleDocument7 pagesIndian Monsoons: Breeze On A Large ScaleVikram DasNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Choke PerformanceDocument45 pagesLecture 1 Choke PerformancearvNo ratings yet