Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Biology Periodic Reviewer
Biology Periodic Reviewer
Uploaded by
Lanz Nicolei0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views6 pages1. The document discusses cell reproduction through both asexual and sexual processes. Asexual reproduction involves a single cell dividing into two identical daughter cells through mitosis or binary fission. Sexual reproduction involves two different cell types, sperm and egg, fusing to form a new cell called a zygote through meiosis.
2. It describes the stages of the cell cycle including interphase (G1, S, G2) and mitosis (prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase). Key cellular structures involved in cell division are also mentioned like chromosomes, centrioles, spindle fibers, and the nuclear envelope.
3. The roles of passive transport (diffusion, facilitated
Original Description:
Gen Bio 1 reviewer
Original Title
BIOLOGY-PERIODIC-REVIEWER
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1. The document discusses cell reproduction through both asexual and sexual processes. Asexual reproduction involves a single cell dividing into two identical daughter cells through mitosis or binary fission. Sexual reproduction involves two different cell types, sperm and egg, fusing to form a new cell called a zygote through meiosis.
2. It describes the stages of the cell cycle including interphase (G1, S, G2) and mitosis (prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase). Key cellular structures involved in cell division are also mentioned like chromosomes, centrioles, spindle fibers, and the nuclear envelope.
3. The roles of passive transport (diffusion, facilitated
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views6 pagesBiology Periodic Reviewer
Biology Periodic Reviewer
Uploaded by
Lanz Nicolei1. The document discusses cell reproduction through both asexual and sexual processes. Asexual reproduction involves a single cell dividing into two identical daughter cells through mitosis or binary fission. Sexual reproduction involves two different cell types, sperm and egg, fusing to form a new cell called a zygote through meiosis.
2. It describes the stages of the cell cycle including interphase (G1, S, G2) and mitosis (prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase). Key cellular structures involved in cell division are also mentioned like chromosomes, centrioles, spindle fibers, and the nuclear envelope.
3. The roles of passive transport (diffusion, facilitated
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 6
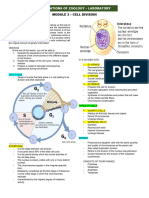
GENBIO REVIEWER Histones Prokaryotes
-It is a DNA tightly coiled around -divide into two
proteins.
-process of binary fission
Chromatids
G1 Stage
-Duplicated chromosomes
-maturing cells
-held together by centromere
S Stage
Chromatic
-DNA Replication
-Chromosomes can’t be seen when G2 Stage
aren’t dividing.
-Preparing for Division
Karyotype
-Proteins are synthesized
-arranged in pairs by sized
Spindle
Autosomes
-poles of the cells
-First 22 pairs
Spindle fiber
XX
-Centrioles in animals
-female
-Microtubules in plants
XY
Cell Division
-male
-Derived from pre-existing cells
Collision of 2 different cell
-divides into two or more daughter cells
-reason why it is not identical
Bio synthesis
CELL REPRODUCTION ASEXUAL
-production of biomolecules
-Single cell dividing 2 new identical
daughter cells Biomolecules are composed of water
and lipids.
-Example Mitosis and Binary fission.
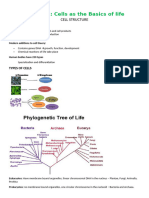
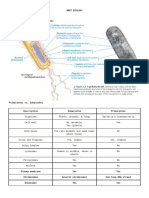
Prokaryotes
Sexual
-bacteria
-Involves two cell
-lack nucleus and other organelles
-sperm and egg cell to make a new cell
called zygote. Eukaryotes
-Not identical to the original cell. - -Have a nucleus
Example Meiosis
Replication
Late Prophase
-is the reason why genetic material has
same copies. -breaks down
DNA -chromosomes fully condensed
- responsible in holding genetic M-Metaphase
materials
-moves to the center
-must be replicated
Center
Complete set of DNA molecules:
-equator of the cell
A-adenine- protein synthesis
A-Anaphase
G-Guanine- make on of the building
-Pulled apart
block of RNA/DNA
T-Telophase -
C-Cytosine- forming the genetic code
disassemble of spindles
T-Thymine-helps stabilize the nucleic
-nuclear envelope forms around.
U-Uracil- Substitute of thymine
Cytokinesis
-division of cytoplasm
Prokaryotic Centrosome
Polar Fiber
-centrosome attracted inside the cell
-Extend to the center of spindle fiber
Eukaryotic Chromosome
Kinetochore Fiber
-Store genetic information
-travel from condensed chromosomes
-Have 10 to 50 chromosomes in their
to the poles.
body cells.
Human body cell:
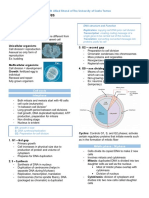
CELL MEMBRANES
-have 46 chromosomes
-Other name Fluid Mosaic Model
-23 identical pairs
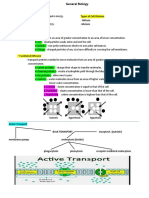
Cell Transport 2 Main Types
DNA
-Passive Transport
-single
-Active Transport
P-Prophase
Early Prophase
-Begin to form
-condensing chromosomes
Passive Transport -higher concentration of solutes
-The Movement of Materials across the Hypotonic
cell membrane without using energy.
-lower concentration of solutes
3 Types of Diffusion:
Osmosis
-Diffusion
-Osmosis is the diffusion of water
-Facilitated Diffusion through a selectivity permeable
membrane down its concentration
-Osmosis
gradient.
Osmotic Pressure
Diffusion
-Prevent the passage of water
-The process by which molecules through a semi permeable membrane
spread from areas of high from a region of low concentration of
concentration, to areas of low solutes to one of high concentration.
concentration. Active Transport
-No energy is required. -Movement against concentration
gradient
Equilibrium
-Requires Energy(ATP)
-Molecules are even throughout a
space. -One direction
Facilitated Diffusion Types:
-Molecules that cannot directly diffuse -Molecular Transport(Protein Pumps)
across the membrane pass through
-Bulk Transport
special protein channels.
-No Additional Energy Needed.
Endocytosis
-Proteins channels (carries)
-Process which cells absorb
Osmotic Solutions
material(molecules such as protein)
Types:
Two types:
Isotonic Hypertonic Hypotonic
-Pinocytosis- Movement of liquid in cell
-Phagocytosis-Movement of solids in
Isotonic cell
-Concentrations of solute and solvent Exocytosis
are equal.
-Eject Waste
Hypertonic
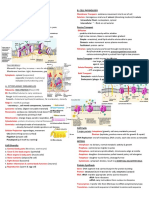
Cell Modification 1. Apical Basal Modification
Modification
-cell modification on the basal surface
-Cell modification found on the apical of the cell.
surface of the cell
Desmosomes/Hemidesmosomes
Cilia and Flagella Cilia
-Anchoring junction on the basal surface
-are usually short, hair like of the cell
structures that move in waves. -Rivet-like links between cytoskeleton
Flagella -are long whiplike and extracellular matrix components
such as the basal lamina that underlie
structures -formed from epithelia
microtubules.
-Primarily composed of keratin, integrins
Villi and Microvilli Villi and cadherins.
- are finger like projections that arise 3. Lateral Modification
from epithelial later in some organs.
Tight Junction
-The help to increase surface area
-Act as barriers that regulate the
allowing for faster and efficient
movement of water and solutes
adsorption.
between epithelial layers
Microvilli
-Prevent leakage of ECF
-are smaller projections that arise from
Adhering Junction
the cell’s surface are allowing faster
and more efficient absorption. -Anchoring junction on the lateral
surface of the cell.
2. Apical Modification Pseudopods
-Very similar to the anchoring junction of
-Temporary, irregular lobes formed by
the basal surface of the cell.
amoebas and some other eukaryotic
cells -fasten cells to one another.
-Bulge outward to move the cell or
engulf prey.
You might also like
- 5.4 SCADA System Functional RequirementsDocument85 pages5.4 SCADA System Functional RequirementsYinwu ZhaoNo ratings yet
- Impulsivity 7Document3 pagesImpulsivity 7Joe Hodge100% (1)
- BBMS1001 NotesDocument41 pagesBBMS1001 NotesHelen WanNo ratings yet
- Management Information System of EDCLDocument47 pagesManagement Information System of EDCLAbir MohammadNo ratings yet
- CELL ORGANELLES-WPS OfficeDocument4 pagesCELL ORGANELLES-WPS OfficePaul TormonNo ratings yet
- 3 Cell Structures FunctionsDocument2 pages3 Cell Structures FunctionsKYLA LORENZ BALUMANo ratings yet
- Lecture/Week 2/ Pre-Recorded Lecture BasedDocument6 pagesLecture/Week 2/ Pre-Recorded Lecture Basedmaria apolonia vergaraNo ratings yet
- HR1Document6 pagesHR1Rose CitcoNo ratings yet
- AnaPhy Chap3 Cell TransesDocument2 pagesAnaPhy Chap3 Cell TransesSophia Margarette CawalingNo ratings yet
- 3 Cell Structures FunctionsDocument2 pages3 Cell Structures FunctionsPia Clarisse Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- CHAP3Document2 pagesCHAP3Caithlyn KirthleyNo ratings yet
- BIODocument7 pagesBIOREYES, Kyla Marie M.No ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Cell Structures & Their Functions: Certain Molecules To Enter/exit The Cell)Document5 pagesChapter 3 Cell Structures & Their Functions: Certain Molecules To Enter/exit The Cell)Gellyace A.No ratings yet
- Transport Across The Cell Membrane Types of Cell Division - Mitosis - MeiosisDocument4 pagesTransport Across The Cell Membrane Types of Cell Division - Mitosis - MeiosisAlex SerdeñaNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle and MitosisDocument3 pagesCell Cycle and MitosisalxndrasenalesNo ratings yet
- Lbybio4 Cell DivisionDocument2 pagesLbybio4 Cell DivisionAlyssaNo ratings yet
- Genetics Lab Dent 1Document6 pagesGenetics Lab Dent 1FRANCHEZKA ANGELICA TANIEGRANo ratings yet
- MitosisDocument8 pagesMitosisMilongy JavierNo ratings yet
- Biology: /duringDocument15 pagesBiology: /duringBianca RimandoNo ratings yet
- The Cell Cycle & Cell Division: Has One Centromere and Two ChromatidsDocument4 pagesThe Cell Cycle & Cell Division: Has One Centromere and Two ChromatidsMnemo SyneNo ratings yet
- Cell BIOLOGYDocument4 pagesCell BIOLOGYAria Moon100% (1)
- GEN. ZOO (Midterms)Document8 pagesGEN. ZOO (Midterms)mimiNo ratings yet
- Basic OrganellesDocument2 pagesBasic OrganellesmaxinejanellaleeNo ratings yet
- Biology Prelim Notes Module 1-4Document54 pagesBiology Prelim Notes Module 1-4kkanaksingh124No ratings yet
- GENETICS LectureDocument27 pagesGENETICS LectureHanna Beth Butiong TandayagNo ratings yet
- Biology (Mitosis Cell Division)Document3 pagesBiology (Mitosis Cell Division)Harry ParconNo ratings yet
- Biology (Mitosis Cell Division)Document3 pagesBiology (Mitosis Cell Division)Harry ParconNo ratings yet
- General BiologyDocument10 pagesGeneral BiologyChelsea NacinoNo ratings yet
- Bio11 Campbell Chapter 12Document4 pagesBio11 Campbell Chapter 12ChristineNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Cellular ReproductionDocument22 pagesChapter 6 Cellular Reproductionnguyenminhhuyen.workNo ratings yet
- Cells: B. Cell PhysiologyDocument29 pagesCells: B. Cell PhysiologyShyenNo ratings yet
- Fact Sheet Bio L2Document7 pagesFact Sheet Bio L2Jodi Kryztel JosolNo ratings yet
- The Cell: Basic Unit of LifeDocument56 pagesThe Cell: Basic Unit of LifeBella VengcoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7 Cell MembraneDocument3 pagesLesson 7 Cell MembraneThea MillanesNo ratings yet
- Cell StructureDocument3 pagesCell StructureKYLA LORENZ BALUMANo ratings yet
- Cell Structure and FunctionDocument18 pagesCell Structure and FunctionBeah Marie AlisosoNo ratings yet
- Scientific Method: Fransisco RediDocument9 pagesScientific Method: Fransisco RediEduardo ZaldivarNo ratings yet
- Genetics - Chapter 2 - Mitosis and Meiosis-Cellular ReproductionDocument37 pagesGenetics - Chapter 2 - Mitosis and Meiosis-Cellular ReproductionDuy AnhNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules and Cells Biol10002Document79 pagesBiomolecules and Cells Biol10002Lily RobinsonNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle - Sequence ofDocument5 pagesCell Cycle - Sequence ofkami gourgaemNo ratings yet
- General Biology 1 Unit 1Document45 pagesGeneral Biology 1 Unit 1lc camposoNo ratings yet
- Topic-4-Bio-1130 Cell DivisionDocument5 pagesTopic-4-Bio-1130 Cell DivisionMohamidin MamalapatNo ratings yet
- Foz Lab M3Document7 pagesFoz Lab M3jsbitsoflyfNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionDocument5 pagesCell Cycle and Cell Division22-50863No ratings yet
- Microana Prelim ReviewerDocument17 pagesMicroana Prelim ReviewerjerlerositaNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Lec (Chapter 3)Document6 pagesAnaphy Lec (Chapter 3)Aya MojicaNo ratings yet
- Gen-Bio-Reviewer-Padua-First GradingDocument4 pagesGen-Bio-Reviewer-Padua-First Gradingmailforprinting101No ratings yet
- General Biology Reviewer 2nd QRTRDocument6 pagesGeneral Biology Reviewer 2nd QRTRAlfer JaoNo ratings yet
- Nmat Biology Cell Biology 1.1 Eukaryotic & Prokaryotic CellsDocument12 pagesNmat Biology Cell Biology 1.1 Eukaryotic & Prokaryotic Cellssavina100% (1)
- General Biology - Cell ReproductionDocument5 pagesGeneral Biology - Cell Reproductionlol okNo ratings yet
- Ana CellsDocument4 pagesAna CellsDCRUZNo ratings yet
- Cell Nutrition: 1 Exchanges Though The Cell MembraneDocument3 pagesCell Nutrition: 1 Exchanges Though The Cell MembraneConikiNo ratings yet
- Bio C6 NotesDocument13 pagesBio C6 NotesTHEN YUE PINGNo ratings yet
- Cell Structure Function Review PresentationDocument8 pagesCell Structure Function Review PresentationCharles IppolitoNo ratings yet
- BiologijaDocument12 pagesBiologijablipNo ratings yet
- L3 - Cellular DivisionDocument33 pagesL3 - Cellular DivisionTiffany LimNo ratings yet
- Cells and Tissues: 2 Types of Cells That Are Found in The BodyDocument6 pagesCells and Tissues: 2 Types of Cells That Are Found in The BodyAngela ReyesNo ratings yet
- Cells: Electron MicroscopeDocument7 pagesCells: Electron MicroscopeGabriela ZahiuNo ratings yet
- Cell StructureDocument10 pagesCell StructureririNo ratings yet
- Cell Exploration: Prokaryotes vs. EukaryotesDocument11 pagesCell Exploration: Prokaryotes vs. EukaryotesMay PaviaNo ratings yet
- Biology ReviewerDocument6 pagesBiology Reviewerleleidy19emanoNo ratings yet
- Gzoo Prelim ReviewerDocument14 pagesGzoo Prelim Reviewermerry joy gadgudeNo ratings yet
- Immigration PowerpointDocument17 pagesImmigration Powerpointapi-296259840No ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines University Town, Northern Samar Website: EmailDocument5 pagesRepublic of The Philippines University Town, Northern Samar Website: EmailCzarina Mae Quinones TadeoNo ratings yet
- KOMAKINO1 - 43643 - 1493201559720 - Kammprofile-TechData-ENKAMMPROFILE GASKETDocument4 pagesKOMAKINO1 - 43643 - 1493201559720 - Kammprofile-TechData-ENKAMMPROFILE GASKETguojun sunNo ratings yet
- NVLAP Scope - Certificate - 2015 09 28Document7 pagesNVLAP Scope - Certificate - 2015 09 28Alex SambagiNo ratings yet
- SOLON Black Blue 230 07 enDocument4 pagesSOLON Black Blue 230 07 enstulemanskiNo ratings yet
- Elnova Pharma: India's Leading Softgel Capsules ManufacturerDocument29 pagesElnova Pharma: India's Leading Softgel Capsules ManufacturerAnkur GulatiNo ratings yet
- Carbon and Its Compounds Revision SheetDocument2 pagesCarbon and Its Compounds Revision Sheetyashvibhatia5No ratings yet
- Mandibulectomy PDFDocument4 pagesMandibulectomy PDFrekabiNo ratings yet
- Theories of Crime CausationDocument7 pagesTheories of Crime CausationNoemi Yabes Domingo MscrimNo ratings yet
- If I Had A Million Dollars EssayDocument4 pagesIf I Had A Million Dollars Essaygejjavbaf100% (2)
- OK - Geagonia v. CADocument2 pagesOK - Geagonia v. CALizzy LiezelNo ratings yet
- 48 Weeks To Total M-Powerment!Document18 pages48 Weeks To Total M-Powerment!sundevil2010usa4605No ratings yet
- Ke-45-Ts Sds JPN EngDocument9 pagesKe-45-Ts Sds JPN Engsouradeepmukherjee20No ratings yet
- Overcome Emotional Eating by Healthy & Psyched PDFDocument74 pagesOvercome Emotional Eating by Healthy & Psyched PDFLarissa Veres100% (1)
- NARRAT1Document8 pagesNARRAT1Incorrect GildaNo ratings yet
- Design Princples For Wood Burning Cook StovesDocument20 pagesDesign Princples For Wood Burning Cook Stoveshana temesegenNo ratings yet
- CP SYSTEM - DESIGN DOCUMENT (Rev.01)Document46 pagesCP SYSTEM - DESIGN DOCUMENT (Rev.01)suman ghosh100% (1)
- Hoch Polatin 2009Document4 pagesHoch Polatin 2009mojepatikeNo ratings yet
- Reading b2 c1Document4 pagesReading b2 c1Karenza ThomasNo ratings yet
- UD150L-40E Ope M501-E053GDocument164 pagesUD150L-40E Ope M501-E053GMahmoud Mady100% (3)
- Modul Science Form 1Document31 pagesModul Science Form 1Norafiza HashimNo ratings yet
- Suzumar Boat Engine PackagesDocument7 pagesSuzumar Boat Engine PackagesmarkoNo ratings yet
- 373 PDFDocument6 pages373 PDFIjdra Journal Jitendra BadjatyaNo ratings yet
- Slope Failure DeterminationDocument7 pagesSlope Failure DeterminationGanjarAsandiPutraPratama100% (1)
- A Heartbreaking Work of Staggering Genius LessonplanDocument229 pagesA Heartbreaking Work of Staggering Genius LessonplanMahmoud El SheikhNo ratings yet
- Yoga 530Document90 pagesYoga 530Juan LatorreNo ratings yet
- Liber eDocument15 pagesLiber eFatimaNo ratings yet