Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Microelectronic Circuits, 8e Sedra, Smith, Carusone, Gaudet
Microelectronic Circuits, 8e Sedra, Smith, Carusone, Gaudet
Uploaded by
BobCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Tutorial Chapter 1 - AnsDocument3 pagesTutorial Chapter 1 - AnsMohd Äwiw Vießar Avondrah100% (1)
- 4.9. Solved ProblemsDocument10 pages4.9. Solved Problems12u88el71% (7)
- Lesson 2 Noise - Gain - Tuned CircuitsDocument64 pagesLesson 2 Noise - Gain - Tuned CircuitsRennel MallariNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document5 pagesAssignment 1Phani SingamaneniNo ratings yet
- Homework #1 (Circuit Basics, Equivalents and Models) : MicroelectronicsDocument7 pagesHomework #1 (Circuit Basics, Equivalents and Models) : MicroelectronicsFuc Fuc LeiNo ratings yet
- ES 104 Problem Set 1Document2 pagesES 104 Problem Set 1Lavdeep Kaur SandhuNo ratings yet
- Sheet 1 هندسة الكترونيهDocument4 pagesSheet 1 هندسة الكترونيهAhmed GamalNo ratings yet
- 電子學 (一) 許恒壽Document12 pages電子學 (一) 許恒壽qw3rtytr3wqNo ratings yet
- ECE3110Fa10 HW1solDocument7 pagesECE3110Fa10 HW1solSaied Aly SalamahNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet 1Document2 pagesTutorial Sheet 1Kanishka MahantyNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4Document7 pagesAssignment 4Niraj Prasad YadavNo ratings yet
- Electronics Mastery 3 Problem SetDocument4 pagesElectronics Mastery 3 Problem SetJonas ParreñoNo ratings yet
- Assignment Unit-3 AEDocument4 pagesAssignment Unit-3 AEDivyanshi UdawatNo ratings yet
- DA1ECE3013Document11 pagesDA1ECE3013Anonymous HA6894aNo ratings yet
- Assignemnt - No - 7a - Operational AmplifierDocument5 pagesAssignemnt - No - 7a - Operational AmplifierSudeep NayakNo ratings yet
- Updated Electronics Module 1 Question BankDocument3 pagesUpdated Electronics Module 1 Question Bankblehbo100% (1)
- The "Operational" Amplifier: Eng - Ahmed HeskolDocument27 pagesThe "Operational" Amplifier: Eng - Ahmed HeskoladilNo ratings yet
- AmplifierDocument2 pagesAmplifierWilliam ZhuangNo ratings yet
- Assignment1-Differential Amplifiers& Operational AmplifierDocument5 pagesAssignment1-Differential Amplifiers& Operational AmplifierAdithya ReddyNo ratings yet
- Ac DC Circuitsset ADocument3 pagesAc DC Circuitsset ALiFamily OnebeeNo ratings yet
- CBSE Test Paper-02 Class - 12 Physics (Alternating Current)Document7 pagesCBSE Test Paper-02 Class - 12 Physics (Alternating Current)anjanaroy35325No ratings yet
- Sheet 2Document4 pagesSheet 2Ahmed GamalNo ratings yet
- Section 3 MineDocument16 pagesSection 3 MineMerna AtefNo ratings yet
- Nama: Herwin Sitanggang NIM: 14S17055 Kelas: 13 TE 2Document4 pagesNama: Herwin Sitanggang NIM: 14S17055 Kelas: 13 TE 2manahanNo ratings yet
- General Amplifier Concepts: Engr. Jomer V. Catipon 0928 6654227Document68 pagesGeneral Amplifier Concepts: Engr. Jomer V. Catipon 0928 6654227Jacklyn Kate Caballero GarduqueNo ratings yet
- EE - Module 2 - APRIL 2012Document4 pagesEE - Module 2 - APRIL 2012Znevba QuintanoNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1Document1 pageTutorial 1Bala DanapalanNo ratings yet
- Sheet 4 - 2022Document2 pagesSheet 4 - 2022Yasmeen MamdouhNo ratings yet
- Practice Problems AC CircuitsDocument2 pagesPractice Problems AC CircuitsJayve BasconNo ratings yet
- EE 315 Module 2Document11 pagesEE 315 Module 2Kevin Cortez100% (1)
- Problems 33Document12 pagesProblems 33Daniyar MuratovNo ratings yet
- DC DC ConverterDocument2 pagesDC DC ConverterMahmoud A. AboulhasanNo ratings yet
- Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur EE 210 Home Assignment #8 Assigned: 24/2/20Document1 pageDepartment of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur EE 210 Home Assignment #8 Assigned: 24/2/20Adarsh BanthNo ratings yet
- False False False False False FalseDocument3 pagesFalse False False False False FalseSuubi brianNo ratings yet
- Ecaquestions (Modified)Document5 pagesEcaquestions (Modified)VivekVickyNo ratings yet
- Problem For Chapter 2Document3 pagesProblem For Chapter 2qasimrazam89No ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet 05Document4 pagesTutorial Sheet 05Debdeep SamajdarNo ratings yet
- AC Circuits Note BookDocument44 pagesAC Circuits Note Bookron Joshua QuirapNo ratings yet
- CLS Aipmt-19-20 XII Phy Study-Package-3 Level-1 Chapter-7 PDFDocument24 pagesCLS Aipmt-19-20 XII Phy Study-Package-3 Level-1 Chapter-7 PDFShubanghiNo ratings yet
- ID Evaluasi 1aDocument2 pagesID Evaluasi 1aTito Bayu ArtomoNo ratings yet
- AE Assignment Unit 2Document3 pagesAE Assignment Unit 2Divyanshi UdawatNo ratings yet
- Untitled 123Document16 pagesUntitled 123Cedric BernardNo ratings yet
- Op-Amp Practical Applications: Design, Simulation and Implementation - 2019 Week 0 Assignment SolutionDocument12 pagesOp-Amp Practical Applications: Design, Simulation and Implementation - 2019 Week 0 Assignment SolutionSalil ChourasiaNo ratings yet
- UNIT-6 Subjective QuestionsDocument4 pagesUNIT-6 Subjective QuestionsRaviNo ratings yet
- March 2009Document10 pagesMarch 2009Myles RangirisNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Circuits Containing Ideal Op AmpDocument12 pagesAnalysis of Circuits Containing Ideal Op Ampbbwx4114No ratings yet
- Ece 9403/9043A - High Frequency Power Electronic Converters Assignment #1Document2 pagesEce 9403/9043A - High Frequency Power Electronic Converters Assignment #1anishthNo ratings yet
- Assignment 01Document6 pagesAssignment 01Z S PlaysNo ratings yet
- Electronics 3 - Final Examination - Set B 1/3Document4 pagesElectronics 3 - Final Examination - Set B 1/3Shir0 NobiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document2 pagesChapter 7Monisha RNo ratings yet
- Circuits 22Document4 pagesCircuits 22Davis Spat TambongNo ratings yet
- Exercises DiodesDocument7 pagesExercises Diodesmurat aydoganNo ratings yet
- Designing A Transistor AmplifierDocument11 pagesDesigning A Transistor Amplifierhemantha dalugamaNo ratings yet
- 15EC303 - Ass I - Aug2017 PDFDocument2 pages15EC303 - Ass I - Aug2017 PDFSlim ShadyNo ratings yet
- Easy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2019-2023)From EverandEasy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2019-2023)No ratings yet
- Easy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2015-2019)From EverandEasy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2015-2019)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- S 15 BE C B E: Microelectronic Circuits, 8e Sedra, Smith, Carusone, GaudetDocument2 pagesS 15 BE C B E: Microelectronic Circuits, 8e Sedra, Smith, Carusone, GaudetBobNo ratings yet
- Microelectronic Circuits, 8e Sedra, Smith, Carusone, GaudetDocument2 pagesMicroelectronic Circuits, 8e Sedra, Smith, Carusone, GaudetBobNo ratings yet
- Microelectronic Circuits, 8e Sedra, Smith, Carusone, GaudetDocument2 pagesMicroelectronic Circuits, 8e Sedra, Smith, Carusone, GaudetBobNo ratings yet
- HW 4 S 22Document3 pagesHW 4 S 22BobNo ratings yet
- HW 5 S 22Document1 pageHW 5 S 22BobNo ratings yet
- ResumeDocument6 pagesResumeAbid AnuarNo ratings yet
- Computer AwarenessDocument64 pagesComputer Awarenessgauravgupta_pusa365No ratings yet
- وصف مواد تخصص هندسة الاتصالاتDocument34 pagesوصف مواد تخصص هندسة الاتصالاتMa'moun Abu MuradNo ratings yet
- Modem Shiron 4gDocument2 pagesModem Shiron 4gdianayjohnNo ratings yet
- LM1117LDocument21 pagesLM1117LfreddyNo ratings yet
- 3 Led Volt MonitorDocument4 pages3 Led Volt MonitorJuan Carlos Regalado AnguianoNo ratings yet
- Beckwith Transformer-Tutorial-2011 PDFDocument96 pagesBeckwith Transformer-Tutorial-2011 PDFaadi_sabujNo ratings yet
- TPS User Manual (Manual - TPS3h-1512-V2)Document14 pagesTPS User Manual (Manual - TPS3h-1512-V2)arifkvt1No ratings yet
- Aspire m3920Document98 pagesAspire m3920euvidalNo ratings yet
- Adaptive Blind Noise Suppression in Some Speech Processing ApplicationsDocument5 pagesAdaptive Blind Noise Suppression in Some Speech Processing ApplicationsSai Swetha GNo ratings yet
- Finite State Machine Implementation: Prith Banerjee Ece C03 Advanced Digital Design Spring 1998Document31 pagesFinite State Machine Implementation: Prith Banerjee Ece C03 Advanced Digital Design Spring 1998Hemant SaraswatNo ratings yet
- Modulating Controlled Actuators: Data SheetDocument8 pagesModulating Controlled Actuators: Data SheetDavid HayesNo ratings yet
- SLAM Manual 2009 - With DigitalDocument34 pagesSLAM Manual 2009 - With DigitalMohammed SairawanNo ratings yet
- Diagrama General DinamometroDocument1 pageDiagrama General DinamometroarthurpumpNo ratings yet
- Circulating CurrentDocument6 pagesCirculating CurrentjogiyajeeNo ratings yet
- Ayra Monitor Manual RevCDocument16 pagesAyra Monitor Manual RevCSphinx DinopolNo ratings yet
- Manualr Revox A 77Document12 pagesManualr Revox A 77TvcrepairNo ratings yet
- DVB-T2: Digital Terrestrial Receiver WD-822T2Document21 pagesDVB-T2: Digital Terrestrial Receiver WD-822T2reza sajatNo ratings yet
- Manual: E300 Series Mini-Type Integrated Universal Inverter ManualDocument68 pagesManual: E300 Series Mini-Type Integrated Universal Inverter ManualDmitryNo ratings yet
- RD 07 Mus 2 BDocument14 pagesRD 07 Mus 2 BRemy MendozaNo ratings yet
- VLSI Design Related Good QuestionsDocument2 pagesVLSI Design Related Good QuestionsGaurav PatelNo ratings yet
- Harmonic Distortion and Variable Frequency Drives: DefinitionsDocument8 pagesHarmonic Distortion and Variable Frequency Drives: DefinitionsAnonymous SOQFPWBNo ratings yet
- Power Your Signal: Antenna SpecificationsDocument3 pagesPower Your Signal: Antenna SpecificationsАлександрNo ratings yet
- Bill Cash CodeDocument36 pagesBill Cash CodeEdicson Rincon RamirezNo ratings yet
- RC3000EDocument5 pagesRC3000EDiego MaldonadoNo ratings yet
- Automatic Door Open and Close AbstractDocument3 pagesAutomatic Door Open and Close AbstractRamachantran Ramachantran100% (1)
- Infinity Beta PDFDocument8 pagesInfinity Beta PDFHuỳnh Lê Hoài BảoNo ratings yet
- 9.2 A 253mW/Channel 4TX/4RX Pulsed Chirping Phased-Array Radar TRX in 65nm CMOS For X-Band Synthetic - Aperture Radar ImagingDocument3 pages9.2 A 253mW/Channel 4TX/4RX Pulsed Chirping Phased-Array Radar TRX in 65nm CMOS For X-Band Synthetic - Aperture Radar ImagingBalaNo ratings yet
- 6AV36271JK000AX0 Datasheet enDocument3 pages6AV36271JK000AX0 Datasheet enPipe CastilloNo ratings yet
Microelectronic Circuits, 8e Sedra, Smith, Carusone, Gaudet
Microelectronic Circuits, 8e Sedra, Smith, Carusone, Gaudet
Uploaded by
BobOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Microelectronic Circuits, 8e Sedra, Smith, Carusone, Gaudet
Microelectronic Circuits, 8e Sedra, Smith, Carusone, Gaudet
Uploaded by
BobCopyright:
Available Formats
EE 315 Homework 1
Due Tuesday, January 25, 2022
Submit your solutions as a pdf file in Canvas.
1. An amplifier operating from ±3 V supplies provides a 2.2 V peak sine wave across a 100 Ω load when
provided with a 0.2 V peak input from which 1.0 mA peak current is drawn. Find the voltage gain,
current gain, and power gain expressed as ratios and in decibels. If the amplifier efficiency is 10%, find
the supply power, supply current, and amplifier power dissipation.
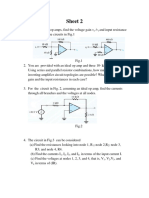
2. Consider the voltage-amplifier circuit model shown below, in which Avo = 100 V/V under the following
conditions:
(a) Ri = 10Rs , RL = 10Ro
(b) Ri = Rs , RL = Ro
(c) Ri = Rs /10, RL = Ro /10
Calculate the overall voltage gain vo /vs in each case, expressed both directly and in decibels.
3. An amplifier with 40 dB of open-circuit voltage gain, an input resistance of 1 MΩ, and an output
resistance of 100 Ω, drives a load of 500 Ω. What voltage and power gains (expressed in dB) would
you expect with the load connected? If the amplifier has a peak output-current limitation of 20 mA,
what is the rms value of the largest sine-wave input for which an undistorted output is possible? What
is the corresponding output power available?
4. A 10 mV signal source having an internal resistance of 5 kΩ is connected to an amplifier for which the
input resistance is 1 kΩ, the open circuit voltage gain is 100 V/V, and the output resistance is 200 Ω.
The amplifier is connected in turn to a 100 Ω load.
(a) What overall voltage gain results as measured from the source internal voltage to the load? What
would the gain be if the source was connected directly to the load?
(b) Now instead, replace the source by its Norton equivalent and the amplifier with the equivalent
current amplifier from Table 1.1 (also in your notes). What is the current gain io /is ?
5. You are given two amplifiers A and B, to connect in cascade between a 10 mV, 100 kΩ source and a
100 Ω load. The amplifiers have the following characteristics:
A B
voltage gain 100 V/V 10 V/V
input resistance 100 kΩ 10 kΩ
output resistance 10 kΩ 1 kΩ
Your problem is to decide how the amplifiers should be connected. To proceed, evaluate the two
possible connections between source S and load L, namely SABL and SBAL. Find the voltage gain
for each both as a ratio and in decibles. Which amplifier arrangement is best?
Sedra, Smith, Carusone, Gaudet Copyright © 2020 Oxford University
1
6. Design an amplifier that provides 0.5W of signal power to a 100 Ω load resistance. The signal source
provides a 30 mV rms signal and has a resistance of 0.5 MΩ. Three types of voltage-amplifier stages
are available:
(a) A high-input resistance type with Ri = 1 MΩ, Avo = 10, and Ro = 10 kΩ
(b) A high-gain type with Ri = 10 kΩ, Avo = 100, and Ro = 1 kΩ
(c) A low-output resistance type with Ri = 10 kΩ, Avo = 1, and Ro = 20 Ω
Design a suitable amplifier using a combination of these stages. Your design should utilize the minimum
number of stages and should ensure that the signal level is not reduced below 10 mV at any point in
the amplifier chain. Find the lad voltage and the power output realized.
You might also like
- Tutorial Chapter 1 - AnsDocument3 pagesTutorial Chapter 1 - AnsMohd Äwiw Vießar Avondrah100% (1)
- 4.9. Solved ProblemsDocument10 pages4.9. Solved Problems12u88el71% (7)
- Lesson 2 Noise - Gain - Tuned CircuitsDocument64 pagesLesson 2 Noise - Gain - Tuned CircuitsRennel MallariNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document5 pagesAssignment 1Phani SingamaneniNo ratings yet
- Homework #1 (Circuit Basics, Equivalents and Models) : MicroelectronicsDocument7 pagesHomework #1 (Circuit Basics, Equivalents and Models) : MicroelectronicsFuc Fuc LeiNo ratings yet
- ES 104 Problem Set 1Document2 pagesES 104 Problem Set 1Lavdeep Kaur SandhuNo ratings yet
- Sheet 1 هندسة الكترونيهDocument4 pagesSheet 1 هندسة الكترونيهAhmed GamalNo ratings yet
- 電子學 (一) 許恒壽Document12 pages電子學 (一) 許恒壽qw3rtytr3wqNo ratings yet
- ECE3110Fa10 HW1solDocument7 pagesECE3110Fa10 HW1solSaied Aly SalamahNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet 1Document2 pagesTutorial Sheet 1Kanishka MahantyNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4Document7 pagesAssignment 4Niraj Prasad YadavNo ratings yet
- Electronics Mastery 3 Problem SetDocument4 pagesElectronics Mastery 3 Problem SetJonas ParreñoNo ratings yet
- Assignment Unit-3 AEDocument4 pagesAssignment Unit-3 AEDivyanshi UdawatNo ratings yet
- DA1ECE3013Document11 pagesDA1ECE3013Anonymous HA6894aNo ratings yet
- Assignemnt - No - 7a - Operational AmplifierDocument5 pagesAssignemnt - No - 7a - Operational AmplifierSudeep NayakNo ratings yet
- Updated Electronics Module 1 Question BankDocument3 pagesUpdated Electronics Module 1 Question Bankblehbo100% (1)
- The "Operational" Amplifier: Eng - Ahmed HeskolDocument27 pagesThe "Operational" Amplifier: Eng - Ahmed HeskoladilNo ratings yet
- AmplifierDocument2 pagesAmplifierWilliam ZhuangNo ratings yet
- Assignment1-Differential Amplifiers& Operational AmplifierDocument5 pagesAssignment1-Differential Amplifiers& Operational AmplifierAdithya ReddyNo ratings yet
- Ac DC Circuitsset ADocument3 pagesAc DC Circuitsset ALiFamily OnebeeNo ratings yet
- CBSE Test Paper-02 Class - 12 Physics (Alternating Current)Document7 pagesCBSE Test Paper-02 Class - 12 Physics (Alternating Current)anjanaroy35325No ratings yet
- Sheet 2Document4 pagesSheet 2Ahmed GamalNo ratings yet
- Section 3 MineDocument16 pagesSection 3 MineMerna AtefNo ratings yet
- Nama: Herwin Sitanggang NIM: 14S17055 Kelas: 13 TE 2Document4 pagesNama: Herwin Sitanggang NIM: 14S17055 Kelas: 13 TE 2manahanNo ratings yet
- General Amplifier Concepts: Engr. Jomer V. Catipon 0928 6654227Document68 pagesGeneral Amplifier Concepts: Engr. Jomer V. Catipon 0928 6654227Jacklyn Kate Caballero GarduqueNo ratings yet
- EE - Module 2 - APRIL 2012Document4 pagesEE - Module 2 - APRIL 2012Znevba QuintanoNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1Document1 pageTutorial 1Bala DanapalanNo ratings yet
- Sheet 4 - 2022Document2 pagesSheet 4 - 2022Yasmeen MamdouhNo ratings yet
- Practice Problems AC CircuitsDocument2 pagesPractice Problems AC CircuitsJayve BasconNo ratings yet
- EE 315 Module 2Document11 pagesEE 315 Module 2Kevin Cortez100% (1)
- Problems 33Document12 pagesProblems 33Daniyar MuratovNo ratings yet
- DC DC ConverterDocument2 pagesDC DC ConverterMahmoud A. AboulhasanNo ratings yet
- Department of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur EE 210 Home Assignment #8 Assigned: 24/2/20Document1 pageDepartment of Electrical Engineering Indian Institute of Technology, Kanpur EE 210 Home Assignment #8 Assigned: 24/2/20Adarsh BanthNo ratings yet
- False False False False False FalseDocument3 pagesFalse False False False False FalseSuubi brianNo ratings yet
- Ecaquestions (Modified)Document5 pagesEcaquestions (Modified)VivekVickyNo ratings yet
- Problem For Chapter 2Document3 pagesProblem For Chapter 2qasimrazam89No ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet 05Document4 pagesTutorial Sheet 05Debdeep SamajdarNo ratings yet
- AC Circuits Note BookDocument44 pagesAC Circuits Note Bookron Joshua QuirapNo ratings yet
- CLS Aipmt-19-20 XII Phy Study-Package-3 Level-1 Chapter-7 PDFDocument24 pagesCLS Aipmt-19-20 XII Phy Study-Package-3 Level-1 Chapter-7 PDFShubanghiNo ratings yet
- ID Evaluasi 1aDocument2 pagesID Evaluasi 1aTito Bayu ArtomoNo ratings yet
- AE Assignment Unit 2Document3 pagesAE Assignment Unit 2Divyanshi UdawatNo ratings yet
- Untitled 123Document16 pagesUntitled 123Cedric BernardNo ratings yet
- Op-Amp Practical Applications: Design, Simulation and Implementation - 2019 Week 0 Assignment SolutionDocument12 pagesOp-Amp Practical Applications: Design, Simulation and Implementation - 2019 Week 0 Assignment SolutionSalil ChourasiaNo ratings yet
- UNIT-6 Subjective QuestionsDocument4 pagesUNIT-6 Subjective QuestionsRaviNo ratings yet
- March 2009Document10 pagesMarch 2009Myles RangirisNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Circuits Containing Ideal Op AmpDocument12 pagesAnalysis of Circuits Containing Ideal Op Ampbbwx4114No ratings yet
- Ece 9403/9043A - High Frequency Power Electronic Converters Assignment #1Document2 pagesEce 9403/9043A - High Frequency Power Electronic Converters Assignment #1anishthNo ratings yet
- Assignment 01Document6 pagesAssignment 01Z S PlaysNo ratings yet
- Electronics 3 - Final Examination - Set B 1/3Document4 pagesElectronics 3 - Final Examination - Set B 1/3Shir0 NobiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document2 pagesChapter 7Monisha RNo ratings yet
- Circuits 22Document4 pagesCircuits 22Davis Spat TambongNo ratings yet
- Exercises DiodesDocument7 pagesExercises Diodesmurat aydoganNo ratings yet
- Designing A Transistor AmplifierDocument11 pagesDesigning A Transistor Amplifierhemantha dalugamaNo ratings yet
- 15EC303 - Ass I - Aug2017 PDFDocument2 pages15EC303 - Ass I - Aug2017 PDFSlim ShadyNo ratings yet
- Easy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2019-2023)From EverandEasy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2019-2023)No ratings yet
- Easy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2015-2019)From EverandEasy(er) Electrical Principles for General Class Ham License (2015-2019)Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- S 15 BE C B E: Microelectronic Circuits, 8e Sedra, Smith, Carusone, GaudetDocument2 pagesS 15 BE C B E: Microelectronic Circuits, 8e Sedra, Smith, Carusone, GaudetBobNo ratings yet
- Microelectronic Circuits, 8e Sedra, Smith, Carusone, GaudetDocument2 pagesMicroelectronic Circuits, 8e Sedra, Smith, Carusone, GaudetBobNo ratings yet
- Microelectronic Circuits, 8e Sedra, Smith, Carusone, GaudetDocument2 pagesMicroelectronic Circuits, 8e Sedra, Smith, Carusone, GaudetBobNo ratings yet
- HW 4 S 22Document3 pagesHW 4 S 22BobNo ratings yet
- HW 5 S 22Document1 pageHW 5 S 22BobNo ratings yet
- ResumeDocument6 pagesResumeAbid AnuarNo ratings yet
- Computer AwarenessDocument64 pagesComputer Awarenessgauravgupta_pusa365No ratings yet
- وصف مواد تخصص هندسة الاتصالاتDocument34 pagesوصف مواد تخصص هندسة الاتصالاتMa'moun Abu MuradNo ratings yet
- Modem Shiron 4gDocument2 pagesModem Shiron 4gdianayjohnNo ratings yet
- LM1117LDocument21 pagesLM1117LfreddyNo ratings yet
- 3 Led Volt MonitorDocument4 pages3 Led Volt MonitorJuan Carlos Regalado AnguianoNo ratings yet
- Beckwith Transformer-Tutorial-2011 PDFDocument96 pagesBeckwith Transformer-Tutorial-2011 PDFaadi_sabujNo ratings yet
- TPS User Manual (Manual - TPS3h-1512-V2)Document14 pagesTPS User Manual (Manual - TPS3h-1512-V2)arifkvt1No ratings yet
- Aspire m3920Document98 pagesAspire m3920euvidalNo ratings yet
- Adaptive Blind Noise Suppression in Some Speech Processing ApplicationsDocument5 pagesAdaptive Blind Noise Suppression in Some Speech Processing ApplicationsSai Swetha GNo ratings yet
- Finite State Machine Implementation: Prith Banerjee Ece C03 Advanced Digital Design Spring 1998Document31 pagesFinite State Machine Implementation: Prith Banerjee Ece C03 Advanced Digital Design Spring 1998Hemant SaraswatNo ratings yet
- Modulating Controlled Actuators: Data SheetDocument8 pagesModulating Controlled Actuators: Data SheetDavid HayesNo ratings yet
- SLAM Manual 2009 - With DigitalDocument34 pagesSLAM Manual 2009 - With DigitalMohammed SairawanNo ratings yet
- Diagrama General DinamometroDocument1 pageDiagrama General DinamometroarthurpumpNo ratings yet
- Circulating CurrentDocument6 pagesCirculating CurrentjogiyajeeNo ratings yet
- Ayra Monitor Manual RevCDocument16 pagesAyra Monitor Manual RevCSphinx DinopolNo ratings yet
- Manualr Revox A 77Document12 pagesManualr Revox A 77TvcrepairNo ratings yet
- DVB-T2: Digital Terrestrial Receiver WD-822T2Document21 pagesDVB-T2: Digital Terrestrial Receiver WD-822T2reza sajatNo ratings yet
- Manual: E300 Series Mini-Type Integrated Universal Inverter ManualDocument68 pagesManual: E300 Series Mini-Type Integrated Universal Inverter ManualDmitryNo ratings yet
- RD 07 Mus 2 BDocument14 pagesRD 07 Mus 2 BRemy MendozaNo ratings yet
- VLSI Design Related Good QuestionsDocument2 pagesVLSI Design Related Good QuestionsGaurav PatelNo ratings yet
- Harmonic Distortion and Variable Frequency Drives: DefinitionsDocument8 pagesHarmonic Distortion and Variable Frequency Drives: DefinitionsAnonymous SOQFPWBNo ratings yet
- Power Your Signal: Antenna SpecificationsDocument3 pagesPower Your Signal: Antenna SpecificationsАлександрNo ratings yet
- Bill Cash CodeDocument36 pagesBill Cash CodeEdicson Rincon RamirezNo ratings yet
- RC3000EDocument5 pagesRC3000EDiego MaldonadoNo ratings yet
- Automatic Door Open and Close AbstractDocument3 pagesAutomatic Door Open and Close AbstractRamachantran Ramachantran100% (1)
- Infinity Beta PDFDocument8 pagesInfinity Beta PDFHuỳnh Lê Hoài BảoNo ratings yet
- 9.2 A 253mW/Channel 4TX/4RX Pulsed Chirping Phased-Array Radar TRX in 65nm CMOS For X-Band Synthetic - Aperture Radar ImagingDocument3 pages9.2 A 253mW/Channel 4TX/4RX Pulsed Chirping Phased-Array Radar TRX in 65nm CMOS For X-Band Synthetic - Aperture Radar ImagingBalaNo ratings yet
- 6AV36271JK000AX0 Datasheet enDocument3 pages6AV36271JK000AX0 Datasheet enPipe CastilloNo ratings yet