Professional Documents
Culture Documents
DFM AllInOne Angles6 ParallelLines
DFM AllInOne Angles6 ParallelLines
Uploaded by
PabloOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
DFM AllInOne Angles6 ParallelLines
DFM AllInOne Angles6 ParallelLines
Uploaded by
PabloCopyright:
Available Formats
KEY SKILLS
139 140
Angles– Part VI – Parallel Lines
www.drfrostmaths.com 141 142
Prerequisites: Angles in a triangle
sum to 180°, angles on a straight Worked Example 1: Worked Example 2:
line sum to 180°, isosceles triangles. Determine 𝑥 and 𝑦. 𝐴
20°
𝐵 𝐶 𝐴𝐵𝐶 and 𝐷𝐸𝐹 are
straight lines and
𝑥 𝑥 the lines 𝐴𝐶 and
𝑥 122° 𝐺 𝑥° 𝐷𝐹 are parallel.
𝑥 70°
𝑦 Determine the
82°
𝑥 𝑥 angle 𝑥.
𝑥 𝐷 𝐸 𝐹
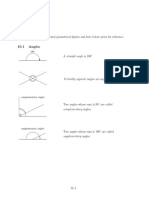
Alternate angles are
equal. Notice that
Cointerior angles
Alternate (“Z”) Corresponding Vertically 𝑥 = 70° add to 180°.
𝐴𝐵𝐸𝐹 forms a ‘Z’
shape.
angles are (“F”) angles are opposite (“X”) ∠𝐴𝐵𝐸 = 82°
equal. equal. angles are equal. 𝑦 = 180° − 122° ∠𝐺𝐵𝐸 = 82° − 20° = 62°
‘Vertically’ here means = 58° 180 − 62
𝑎 Cointerior/allied ‘opposite with respect 𝑥= = 59°
(“C”) angles add to a vertex’. Corresponding angles 2 Triangle 𝐵𝐺𝐸 is
isosceles.
𝑏 to 180°. are equal. Notice that
the angle is in the same
𝑎 + 𝑏 = 180° orientation but just
shifts across.
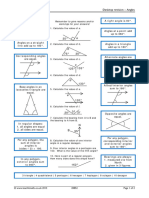
Determine the value of the
Core Questions 3 variable(s) in each diagram.
1 Identify whether each pair a b
𝑦
of angles are alternate, 70° 101°
corresponding, cointerior 𝑥
112° 𝑧
or vertically opposite.
a b
c d 110°
70°
80°
c d
𝑤
𝑥
𝑦
e f
82° 𝑦 𝑥
𝑥 𝑤 65°
43°
Determine the value of the
2 variable(s) in each diagram.
a b
70° Problem Solving
𝑥
Determine the 𝐴𝐵𝐶𝐷 is a rhombus
82°
𝑦 4 value of 𝑥. 5 and 𝐵𝐶 = 𝐸𝐶.
𝑧
40°
Determine ∠𝐴𝐵𝐸.
c d 80° 𝐴 𝐵
𝑥 𝑥
110°
𝑦
62° 55° 𝐸
𝑧
𝐷 𝐶
e f
4. 𝑥 = 95° 5. ∠𝐴𝐵𝐸 = 30°
80°
(e) 16° (f) 𝑥 = 25°, 𝑦 = 72°, 𝑤 = 43°
100° 𝑦
3(a) 110° (b) 𝑦 = 101°, 𝑧 = 68° (c) 𝑦 = 110°, 𝑤 = 30°
𝑥
70° 𝑧 60°
(e) 𝑥 = 70° (f) 𝑦 = 80°, 𝑧 = 120°
2(a) 82° (b) 𝑦 = 70°, 𝑧 = 70° (c) 118° (d) 𝑦 = 80°, 𝑧 = 100°
100° 1(a) Corresponding (b) Alternate (c) Cointerior (d) Opposite
Solutions:
You might also like
- Angle PairsDocument14 pagesAngle PairsDelgado, Ritchel Ann D.No ratings yet
- Br250eefph (2014) (Z250 SL)Document86 pagesBr250eefph (2014) (Z250 SL)Albert DepanoNo ratings yet
- Nozzle CalculationsDocument2 pagesNozzle CalculationsBaher Elsheikh100% (4)
- Parallel Lines, and Pairs of AnglesDocument4 pagesParallel Lines, and Pairs of AngleskrishnaNo ratings yet
- Additional Geometry Notes and Questions For SAT:GRE PDFDocument32 pagesAdditional Geometry Notes and Questions For SAT:GRE PDFAnshul WadhwaNo ratings yet
- Supplementary) Angles: PointDocument9 pagesSupplementary) Angles: PointBianca RimandoNo ratings yet
- Geometry Exercise - 1 (Redo) (Cie Cmabridge Mathematics Answer Guide)Document11 pagesGeometry Exercise - 1 (Redo) (Cie Cmabridge Mathematics Answer Guide)Jenna HanyNo ratings yet
- Year 8 Maths Unit 13 Angles in Parallel Lines and PolygonsDocument1 pageYear 8 Maths Unit 13 Angles in Parallel Lines and Polygonsmukona199No ratings yet
- Mathematics Grade 10 Term 1 Week 7 - 2021Document6 pagesMathematics Grade 10 Term 1 Week 7 - 2021martinajoan1No ratings yet
- Module 2 - Trigonometry Rev 1Document16 pagesModule 2 - Trigonometry Rev 1HERMINIO MENDOZANo ratings yet
- Geometry (Part 1) Lines and AnglesDocument15 pagesGeometry (Part 1) Lines and Anglesunknown :)No ratings yet
- 10 GeometryDocument8 pages10 GeometryrakeshpoddarNo ratings yet
- WO6 Angles in A Triangle Missing Angles 2022Document2 pagesWO6 Angles in A Triangle Missing Angles 2022Reham ElBeheiryNo ratings yet
- 2.9 Angles of TrianglesDocument2 pages2.9 Angles of Triangleswabusb2sNo ratings yet
- Y5 Y6 Properties of Shapes AnglesDocument1 pageY5 Y6 Properties of Shapes AnglesOscar MasindeNo ratings yet
- Types of Triangle: IsoscelesDocument1 pageTypes of Triangle: Isoscelesjessicagong37No ratings yet
- Ángulos 4Document2 pagesÁngulos 4Ana GuardianiNo ratings yet
- Name The Triangle FlapbookDocument1 pageName The Triangle FlapbookHajar Ummi Umairah binti Mohamad NazaliNo ratings yet
- Geometry Cheat SheetDocument7 pagesGeometry Cheat SheetiannybearNo ratings yet
- Math 7-Week 2-Pairs of Angles and LinesDocument132 pagesMath 7-Week 2-Pairs of Angles and LinesAngela Camille PaynanteNo ratings yet
- Angles Cheat SheetDocument3 pagesAngles Cheat SheetAttique IftikharNo ratings yet
- Ac TM SB Year 6 pp37-39 Fillable Saveable-11editedDocument3 pagesAc TM SB Year 6 pp37-39 Fillable Saveable-11editedapi-394727402No ratings yet
- WMCS Geometry Grade 8 Ver 1.0Document53 pagesWMCS Geometry Grade 8 Ver 1.0shishir jhaNo ratings yet
- TrigonometryDocument18 pagesTrigonometryCaitlyn GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Write Up of All Angle RulesDocument6 pagesWrite Up of All Angle RulesNancy RadwanNo ratings yet
- Cheat Sheet g10mt07 FinalDocument2 pagesCheat Sheet g10mt07 FinalLobi RybgNo ratings yet
- Geometry Revision Summary 4: Angle Types Key VocabularyDocument2 pagesGeometry Revision Summary 4: Angle Types Key VocabularyPol PogbaNo ratings yet
- Trig 1Document36 pagesTrig 1Bram PrinceNo ratings yet
- Congruency: Mathematics Grade 9Document12 pagesCongruency: Mathematics Grade 9012 Ni Putu Devi AgustinaNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - TrigonometryDocument15 pagesModule 2 - TrigonometryJake Canlas100% (1)
- Feb 2022 - M1 Chapter 5 (S)Document12 pagesFeb 2022 - M1 Chapter 5 (S)Leen Amer MasoudNo ratings yet
- Useful Facts About Angles: The BasicsDocument2 pagesUseful Facts About Angles: The BasicsAlmira Laney CruzNo ratings yet
- Angles and TrianglesDocument52 pagesAngles and TrianglesadithNo ratings yet
- GR 6-Angles in Parallel Lines PDFDocument5 pagesGR 6-Angles in Parallel Lines PDFFaseeh udeenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Angles and PolygonsDocument23 pagesChapter 5 Angles and PolygonssamNo ratings yet
- Week 19 - AnglesDocument29 pagesWeek 19 - AnglesHau LuNo ratings yet
- Cazoom Maths. Lines and Angles. Angles On Parallel Lines (A) - AnswersDocument2 pagesCazoom Maths. Lines and Angles. Angles On Parallel Lines (A) - AnswersChelsea ChikafuNo ratings yet
- A Sum of 360 Degrees 2Document10 pagesA Sum of 360 Degrees 2lam044980No ratings yet
- 5 Angle RelationshipsDocument42 pages5 Angle Relationshipsaienne peraltaNo ratings yet
- 3-1 Basic GeometryDocument1 page3-1 Basic GeometrygaoNo ratings yet
- Shape and Space Unit 1Document41 pagesShape and Space Unit 1Pavlos StavropoulosNo ratings yet
- Year 6 Maths Worksheet Tues 12th JanDocument2 pagesYear 6 Maths Worksheet Tues 12th JanHannahNo ratings yet
- Angle RelationshipsDocument4 pagesAngle RelationshipsGabriel GangjiNo ratings yet
- Angle Relationships & Parallel Lines: Mrs. WedgwoodDocument41 pagesAngle Relationships & Parallel Lines: Mrs. WedgwoodHuan HuanNo ratings yet
- Angle PropertiesDocument2 pagesAngle PropertiesGEGENo ratings yet
- 5.2 NotesDocument3 pages5.2 NotesAM - 11DA 747745 Turner Fenton SSNo ratings yet
- Angle FactsDocument33 pagesAngle FactsNgọc Hà NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Angle FactsDocument33 pagesAngle FactsJezreel Jezz David BaculnaNo ratings yet
- Angle FactsDocument33 pagesAngle FactsjbzjbisxbisNo ratings yet
- Formulario Sistema Cíclico o Circular ° : Grados Minutos SegundosDocument1 pageFormulario Sistema Cíclico o Circular ° : Grados Minutos SegundosAlan FloresNo ratings yet
- Linear Equations Reference Sheet: Equation of A LineDocument1 pageLinear Equations Reference Sheet: Equation of A LineNoor FarhanNo ratings yet
- 5 Parallel Lines Cut by A TransversalDocument39 pages5 Parallel Lines Cut by A TransversalLOVELY BALBOANo ratings yet
- Kotak KotakDocument2 pagesKotak KotakrasyidNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry Sine Cosine RuleDocument49 pagesTrigonometry Sine Cosine Rulejai bachaniNo ratings yet
- Sine Rule 1Document1 pageSine Rule 1Aditya Kumar ShubhamNo ratings yet
- Math 7 TQDocument7 pagesMath 7 TQAPPLE JOY YONSONNo ratings yet
- Quadratic: ST NDDocument8 pagesQuadratic: ST NDtheturfkitchenNo ratings yet
- Horizontal Format - Calculating Angles On A Straight LineDocument2 pagesHorizontal Format - Calculating Angles On A Straight LineSomala KarthigeshNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 TRIANGLES AND POLYGONSDocument38 pagesChapter 8 TRIANGLES AND POLYGONSBrandon LawyNo ratings yet
- Yr8 ProbabilityDocument40 pagesYr8 ProbabilityPabloNo ratings yet
- GCSE Probability SequencesOfEventsDocument35 pagesGCSE Probability SequencesOfEventsPabloNo ratings yet
- Mark SchemeDocument4 pagesMark SchemePabloNo ratings yet
- Yr7 AnglesDocument70 pagesYr7 AnglesPabloNo ratings yet
- Preliminary Design Report (Group 5)Document10 pagesPreliminary Design Report (Group 5)Shubhankit MohanNo ratings yet
- Nanananda Towards Calm and InsightDocument29 pagesNanananda Towards Calm and Insightanon7535No ratings yet
- 5pmf0508205pmf121a1c41881bbe494c Fpesig0508205ptplkf8xg4u3jsfDocument11 pages5pmf0508205pmf121a1c41881bbe494c Fpesig0508205ptplkf8xg4u3jsfmanoj mannaiNo ratings yet
- Renr5059!14!00 Manuals Service Modules Troubleshooting CeterpilarDocument364 pagesRenr5059!14!00 Manuals Service Modules Troubleshooting CeterpilarRuben100% (1)
- Polyone (Shanghai) Co. LTD PDFDocument14 pagesPolyone (Shanghai) Co. LTD PDFchinmoyd1No ratings yet
- Exploring Strategy, Text and Cases - (Exploring Strategy Features)Document1 pageExploring Strategy, Text and Cases - (Exploring Strategy Features)Mosaab AklNo ratings yet
- анализ "Doctor in the house"Document3 pagesанализ "Doctor in the house"СофьяNo ratings yet
- The Duchess and The Jeweller: by Virginia WoolfDocument4 pagesThe Duchess and The Jeweller: by Virginia WoolfXenoNo ratings yet
- Duolink Probemaker User Manual Proximity Ligation AssayDocument14 pagesDuolink Probemaker User Manual Proximity Ligation AssaylaurakaiohNo ratings yet
- Call Center MetricsDocument16 pagesCall Center MetricsFrancis NyanguwoNo ratings yet
- Weber Impianti Estrusione TubiDocument12 pagesWeber Impianti Estrusione TubiHEMANTKHERANo ratings yet
- Python Interview QuestionsDocument28 pagesPython Interview QuestionsKavya MamillaNo ratings yet
- 16 Prout PrinciplesDocument7 pages16 Prout PrinciplesLuis Miguel DantasNo ratings yet
- Rules:: Final Exam / Network Fundamentals 30 Sept-2013Document6 pagesRules:: Final Exam / Network Fundamentals 30 Sept-2013Lâm QuỳnhNo ratings yet
- Australia As An Egalitarian SocietyDocument6 pagesAustralia As An Egalitarian SocietyJeet Bahadur JotiNo ratings yet
- NASSCOM Annual Report 2009Document42 pagesNASSCOM Annual Report 2009vishu_kirthiNo ratings yet
- Potential Sources of Contamination To Weak Lensing Measurements: Constraints From N-Body SimulationsDocument12 pagesPotential Sources of Contamination To Weak Lensing Measurements: Constraints From N-Body SimulationsRazvan PistoleaNo ratings yet
- An Engineered Alternative Brick Masonry Unit For The Poor Inhabitants at Hawassa Village, EthiopiaDocument19 pagesAn Engineered Alternative Brick Masonry Unit For The Poor Inhabitants at Hawassa Village, EthiopiaDaniel GegziabherNo ratings yet
- HKS Impex Pvt. LTD Completes ISO 9001: 2008 CertificationDocument2 pagesHKS Impex Pvt. LTD Completes ISO 9001: 2008 CertificationKaushal SutariaNo ratings yet
- Tamaya NC 77Document20 pagesTamaya NC 77edtatel73No ratings yet
- Birkosit - MSDS (2017) PDFDocument10 pagesBirkosit - MSDS (2017) PDFSuresh MuruganNo ratings yet
- A Third Latin Translation of Ibn Al AffDocument36 pagesA Third Latin Translation of Ibn Al AffArchimedes_287No ratings yet
- Introduction of IS2062 E250 Grade ADocument2 pagesIntroduction of IS2062 E250 Grade AnareshNo ratings yet
- Convert Web Into AppDocument5 pagesConvert Web Into AppDurgaNo ratings yet
- Specification For Painting and CoatingDocument21 pagesSpecification For Painting and CoatingalkhiatNo ratings yet
- Chandan Kumar SinghDocument1 pageChandan Kumar SinghSuryavanshi ChandanNo ratings yet
- Module 5 - PR 1: Quantitative Research: Definition, Types and GoalsDocument8 pagesModule 5 - PR 1: Quantitative Research: Definition, Types and GoalsJessica AngayenNo ratings yet
- IEMS Module 1Document68 pagesIEMS Module 1VenkatramananNo ratings yet